Influence of Fiber Angle on Steady-State Response of Laminated Composite Rectangular Plates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Formulation
3. Validation
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
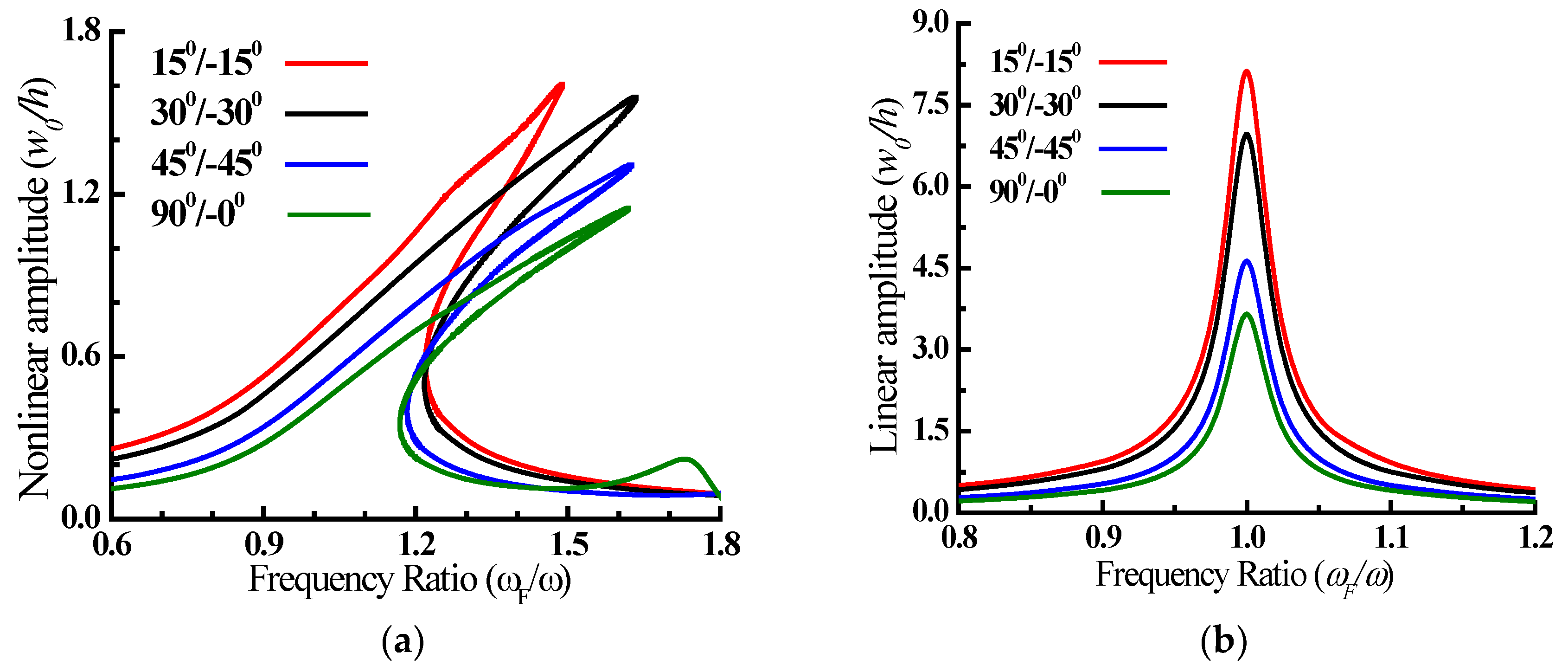
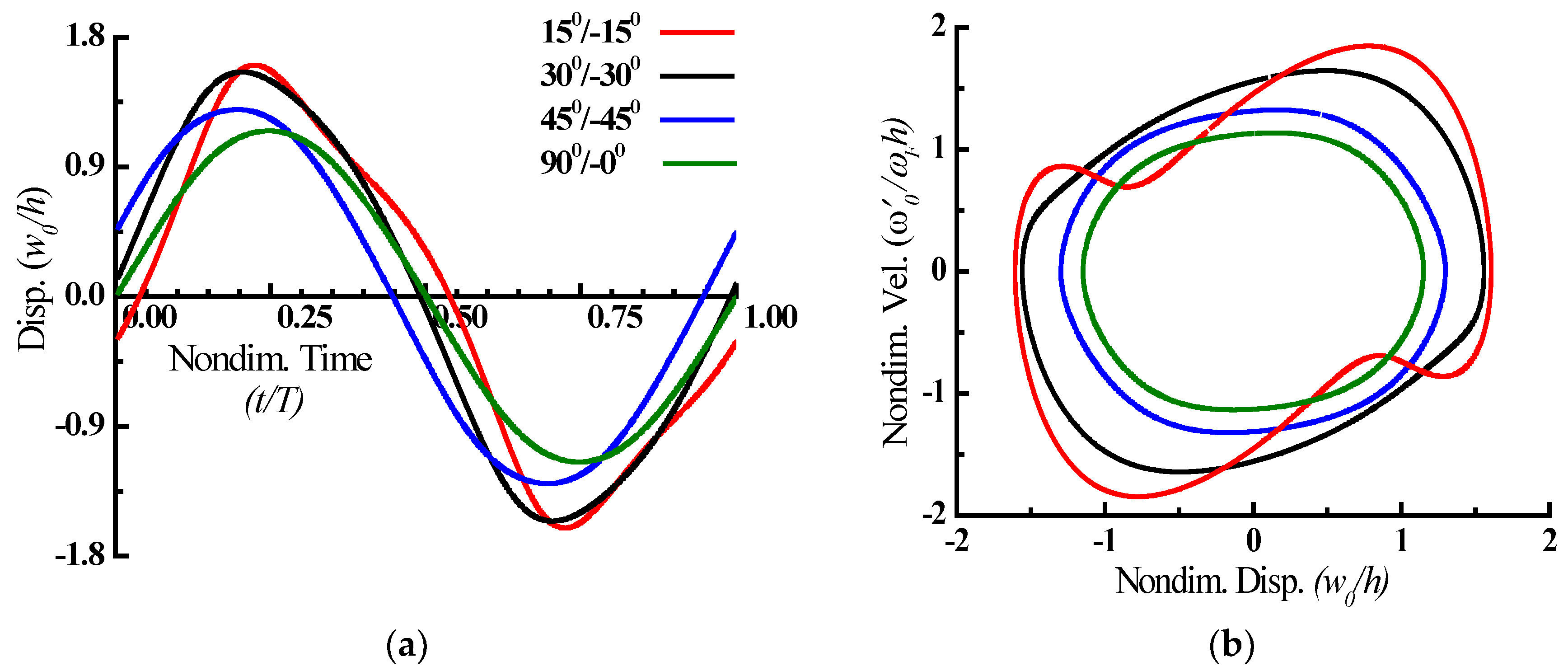
- When compared to the angle-ply plate, the cross-ply plate exhibits more hardening nonlinear behaviour and a lower peak amplitude. As the fiber angle rises, the hardening nonlinearity increases and the peak amplitude drops.
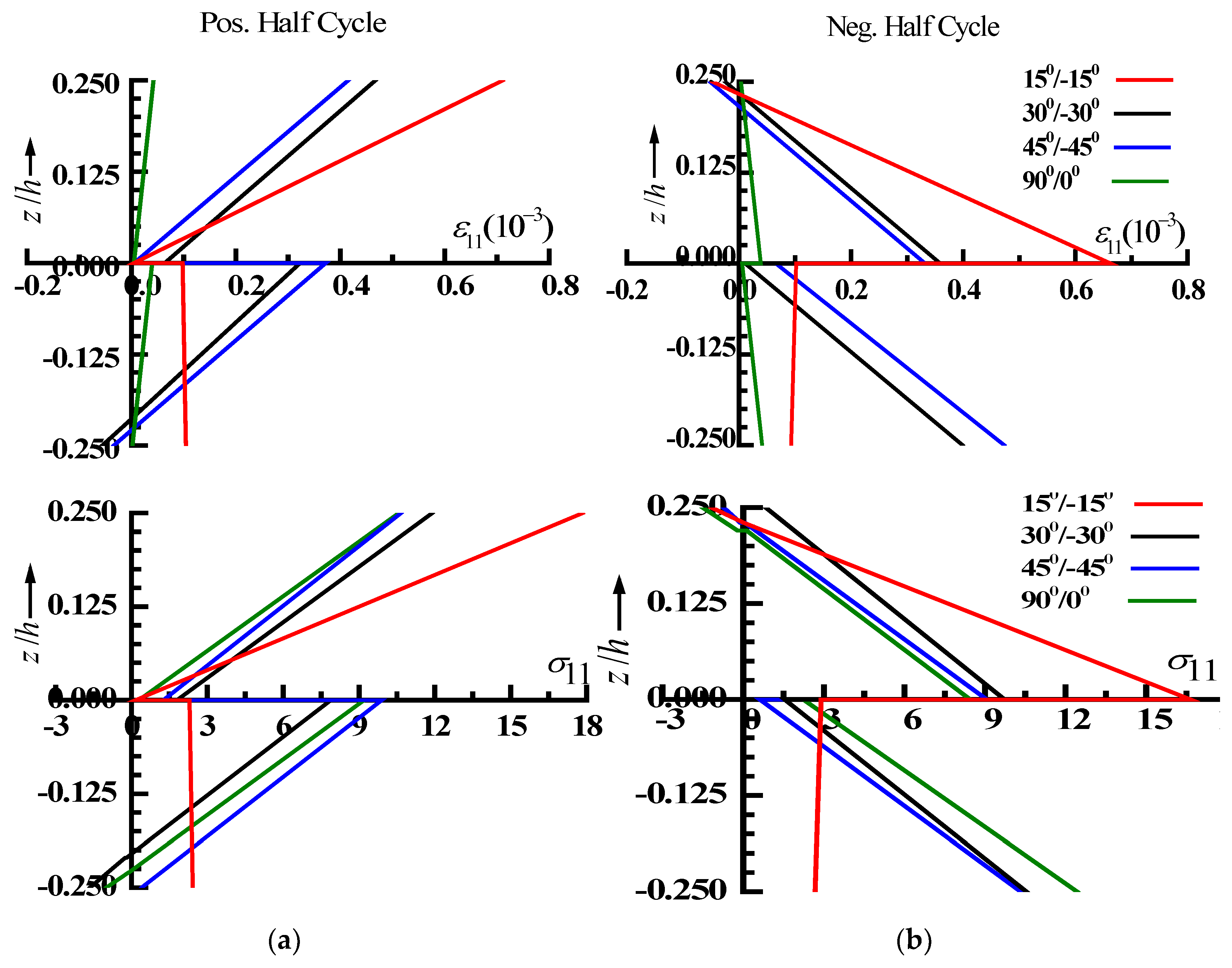
- Variations in nonlinear stresses throughout a loading cycle indicate repeated slope changes and stress reversals, suggesting the presence of fluctuating stresses, which is crucial for fatigue design.
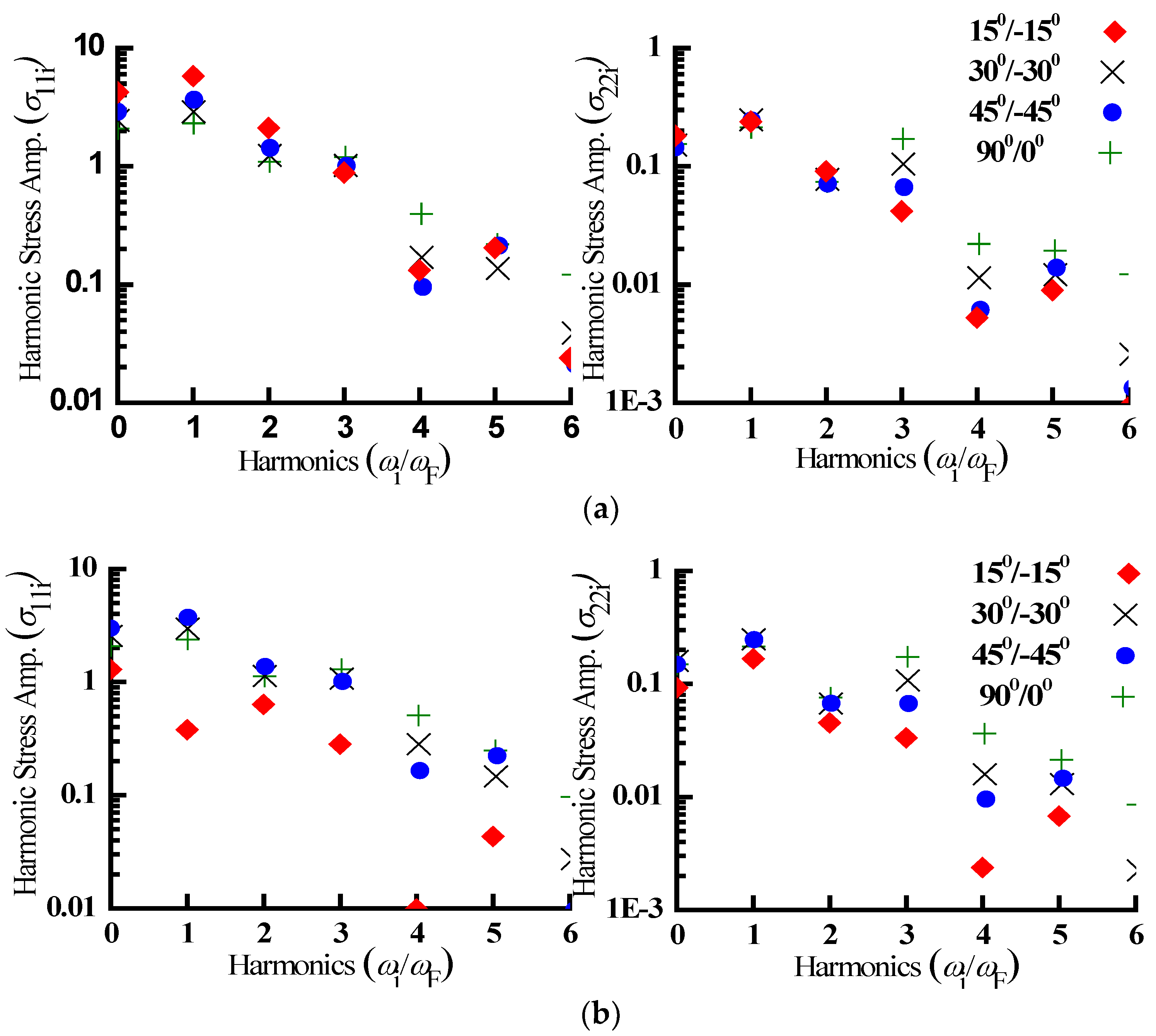
- The frequency spectra of nonlinear steady stress displays significant higher harmonic contributions, and in some circumstances, second/third harmonic contributions are greater/comparable to fundamental harmonic contributions. Greater even-order harmonics result from a higher contribution of quadratic nonlinear restoring forces, whereas higher odd-order harmonics result from a greater participation of cubic nonlinear restoring forces.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mei, C.; Decha-Umphai, K. A finite element method for nonlinear forced vibrations of beams. J. Sound Vib. 1985, 102, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, P.; Noah, S.T. Dynamics of forced nonlinear systems using shooting/are-length continuation method-application to rotor systems. J. Vib. Acoust. Trans. ASME 1997, 119, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yamada, G. Three-Mode Response of Simply Supported Rectangular Laminated Plates. JSME Int. J. 1998, 41, 51–59. Available online: http://www.mendeley.com/research/geology-volcanic-history-eruptive-style-yakedake-volcano-group-central-japan/ (accessed on 24 June 2022). [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.; Petyt, M. Geometrical nonlinear, steady state, forced, periodic vibration of plates, part II: Stability study and analysis of multi-modal response. J. Sound Vib. 1999, 226, 985–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.P.; Ganapathi, M.; Prasad, K.R.; Balamurugan, V. Dynamic instability of layered anisotropic composite plates on elastic foundations. Eng. Struct. 1999, 21, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathi, M.; Patel, B.P.; Touratier, M. Influence of amplitude of vibrations on loss factors of laminated composite beams and plates. J. Sound Vib. 1999, 219, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathi, M.; Patel, B.P.; Boisse, P.; Touratier, M. Nonlinear dynamic stability characteristics of elastic plates subjected to periodic in-plane load. Int. J. Non. Linear. Mech. 2000, 35, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhecha, D.P.; Ganapathi, M.; Patel, B.P. Dynamic analysis of laminated composite plates subjected to thermal/mechanical loads using an accurate theory. Compos. Struct. 2001, 51, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amabili, M. Nonlinear vibrations of rectangular plates with different boundary conditions: Theory and experiments. Comput. Struct. 2004, 82, 2587–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathi, M.; Patel, B.P.; Makhecha, D.P. Nonlinear dynamic analysis of thick composite/sandwich laminates using an accurate higher-order theory. Compos. Part B Eng. 2004, 35, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.; Duarte, R.P. From periodic to chaotic oscillations in composite laminated plates. Comput. Struct. 2006, 84, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.P.; Nath, Y.; Shukla, K.K. Nonlinear thermo-elastic buckling characteristics of cross-ply laminated joined conical-cylindrical shells. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 4810–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayfeh, A.H.; Balachandran, B. Applied Nonlinear Dynamics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, O.; Bilbao, S. Geometrically nonlinear flexural vibrations of plates: In-plane boundary conditions and some symmetry properties. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 315, 569–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.M.; Patel, B.P.; Nath, Y. Modified shooting approach to the nonlinear periodic forced response of isotropic/composite curved beams. Int. J. Non. Linear. Mech. 2009, 44, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P. Nonlinear free periodic vibrations of variable stiffness. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012, 70, 1535–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.K.; Shukla, K.K. Large deformation flexural behavior of laminated composite skew plates: An analytical approach. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 3722–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslavsky, I.D.; Amibili, M.; Legrand, M. Nonlinear vibrations of thin hyperelastic plates. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 4668–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.H.; Patel, B.P. On the nonlinear dynamics of bimodular laminated composite conical panels. Nonlinear Dyn. 2014, 79, 1495–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, H.; Ribeiro, P. Geometrically nonlinear periodic forced vibrations of imperfect laminates with curved fibers by the shooting method. Int. J. Non. Linear. Mech. 2015, 109, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.W.; Xiao, L.N. Mechanical behavior of laminated CNT-reinforced composite skew plates subjected to dynamic loading. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 122, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Cao, S.; Yang, T.; Chen, Y. Geometrically nonlinear analysis of laminated composite quadrilateral plates reinforced with graphene nanoplatelets using the element-free IMLS-Ritz method. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 154, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, B.; Cao, D.; Sun, L. Influence of nonlinear terms on dynamical behavior of graphene reinforced laminated composite plates. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 78, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, B.R.; Verma, S.; Singh, B.N.; Maiti, D.K. Geometrically nonlinear dynamic analysis of laminated composite plate using a nonpolynomial shear deformation theory. Int. J. Non. Linear. Mech. 2020, 128, 103635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saood, A.; Khan, Z.A.; Parvez, M.T.; Khan, A.H. On the Large Amplitude Forced Vibration Analysis of Composite Sectorial Plates. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, S.; Murray, D.W. Incremental Finite Element Matrices. J. Struct. Div. 1973, 99, 2423–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, M.T.; Khan, A.H. Influence of geometric imperfections on the nonlinear forced vibration characteristics and stability of laminated angle-ply composite conical shells. Compos. Struct. 2022, 291, 115555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, K.M. Solving the vibation of thick symmetric laminates by Reissner/Mindlin plate theory and the p-Ritz method. J. Sound Vib. 1996, 198, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.J.M.; Fasshauer, G.E. Analysis of natural frequencies of composite plates by an RBF-pseudospectral method. Compos. Struct. 2007, 79, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo-Cong, D.; Mai-Duy, N.; Karunasena, W.; Tran-Cong, T. Free vibration analysis of laminated composite plates based on FSDT using one-dimensional IRBFN method. Comput. Struct. 2011, 89, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| a/b | t/b | Study | Mode Sequence Number | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 1 | 0.001 | Present | 14.6736 | 17.6454 | 24.6955 | 36.2302 |
| Ngo-Cong et al. [30] | 14.6722 | 17.6383 | 24.5238 | 35.4471 | ||
| Ferreira and Fasshauer [29] | 14.8138 | 17.6138 | 24.5114 | 35.5318 | ||
| Liew et al. [28] | 14.6655 | 17.6138 | 24.5114 | 35.5318 | ||
| 0.2 | Present | 4.4587 | 6.6623 | 7.7246 | 9.2185 | |
| Ngo-Cong et al. [30] | 4.4466 | 6.6419 | 7.6996 | 9.1852 | ||
| Ferreira and Fasshauer [29] | 4.4463 | 6.6419 | 7.6995 | 9.1839 | ||
| Liew et al. [28] | 4.4468 | 6.6419 | 7.6996 | 9.1852 | ||
| 2 | 0.001 | Present | 5.1079 | 10.5547 | 10.6112 | 14.4045 |
| Ngo-Cong et al. [30] | 5.1092 | 10.5447 | 10.6042 | 14.3642 | ||
| Liew et al. [28] | 5.1051 | 10.5265 | 10.5828 | 14.3241 | ||
| 0.2 | Present | 3.0516 | 4.2603 | 5.8075 | 5.9263 | |
| Ngo-Cong et al. [30] | 3.0453 | 4.2484 | 5.7917 | 5.9050 | ||
| Liew et al. [28] | 3.0453 | 4.2484 | 5.7918 | 5.9047 | ||
| Load (Pa) | a/b | Lamination Scheme | Fundamental Frequency (Hz) | Nondimensional Amplitude (w0/h) | % Difference of GNL/GL Amplitudes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNL | GL | |||||
| 100 | 1.0 | 15°/−15° | 31.645 | 1.606 | 9.000 | 460.39 |
| 30°/−30° | 34.012 | 1.558 | 7.715 | 395.19 | ||
| 45°/−45° | 41.584 | 1.308 | 5.129 | 292.13 | ||
| 90°/0° | 47.280 | 1.149 | 4.050 | 252.48 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saood, A.; Khan, A.H.; Equbal, M.I.; Saxena, K.K.; Prakash, C.; Vatin, N.I.; Dixit, S. Influence of Fiber Angle on Steady-State Response of Laminated Composite Rectangular Plates. Materials 2022, 15, 5559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165559
Saood A, Khan AH, Equbal MI, Saxena KK, Prakash C, Vatin NI, Dixit S. Influence of Fiber Angle on Steady-State Response of Laminated Composite Rectangular Plates. Materials. 2022; 15(16):5559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165559
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaood, Ahmad, Arshad Hussain Khan, Md. Israr Equbal, Kuldeep K. Saxena, Chander Prakash, Nikolay Ivanovich Vatin, and Saurav Dixit. 2022. "Influence of Fiber Angle on Steady-State Response of Laminated Composite Rectangular Plates" Materials 15, no. 16: 5559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165559
APA StyleSaood, A., Khan, A. H., Equbal, M. I., Saxena, K. K., Prakash, C., Vatin, N. I., & Dixit, S. (2022). Influence of Fiber Angle on Steady-State Response of Laminated Composite Rectangular Plates. Materials, 15(16), 5559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165559










