Thermal Conductivity of FLiNaK in a Molten State
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Samples
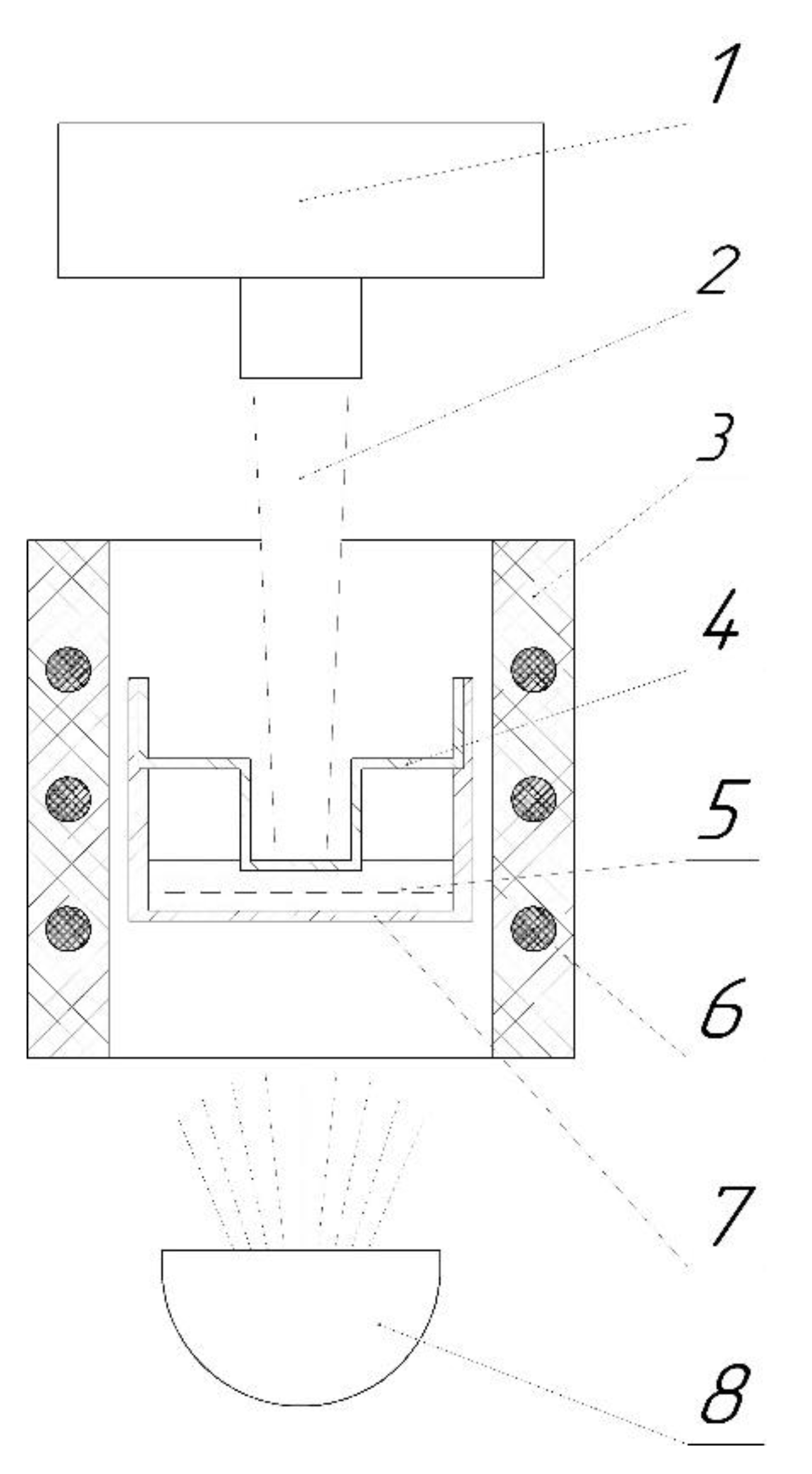
2.2. Laser Flash Method
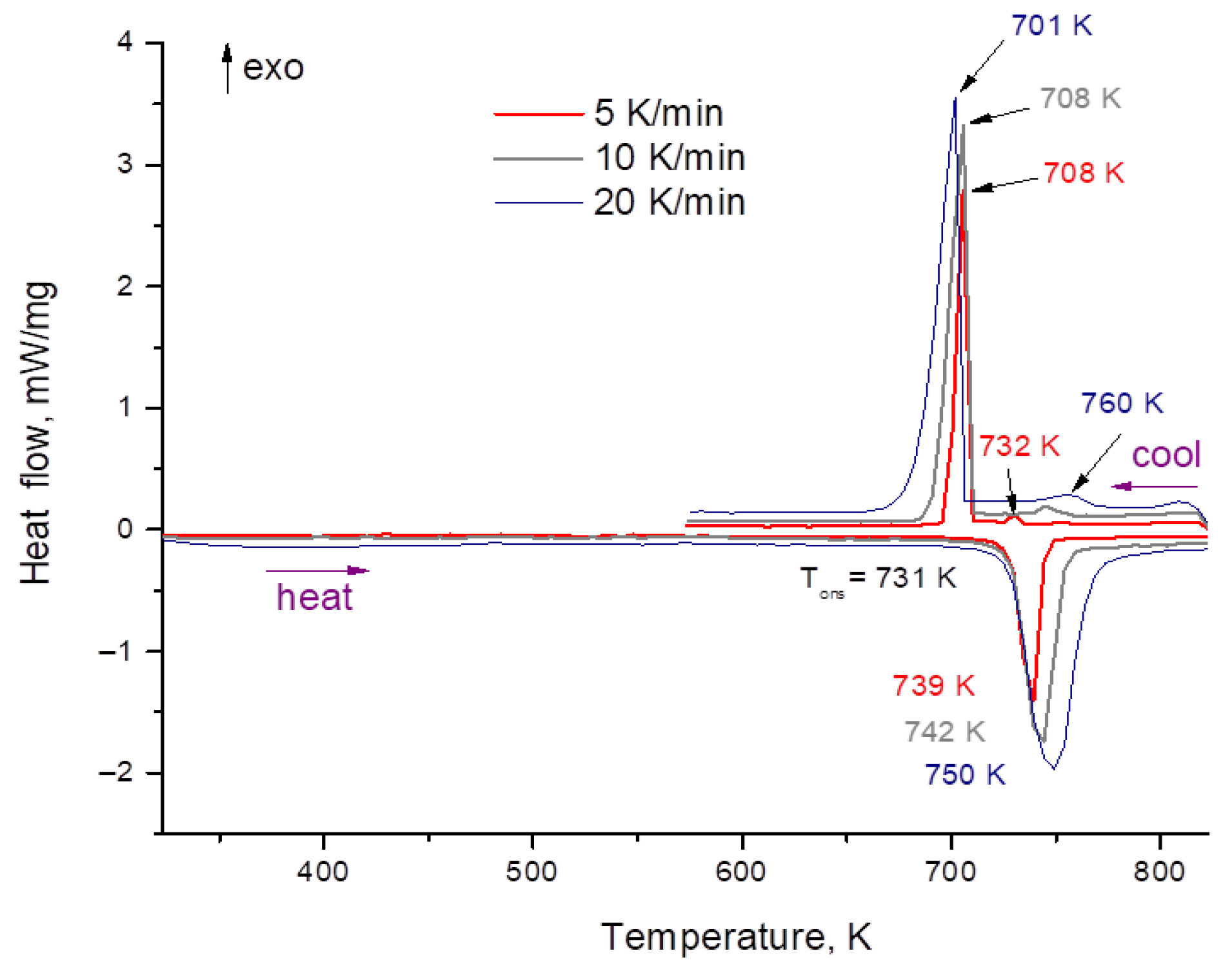
2.3. DSC Method
3. Results
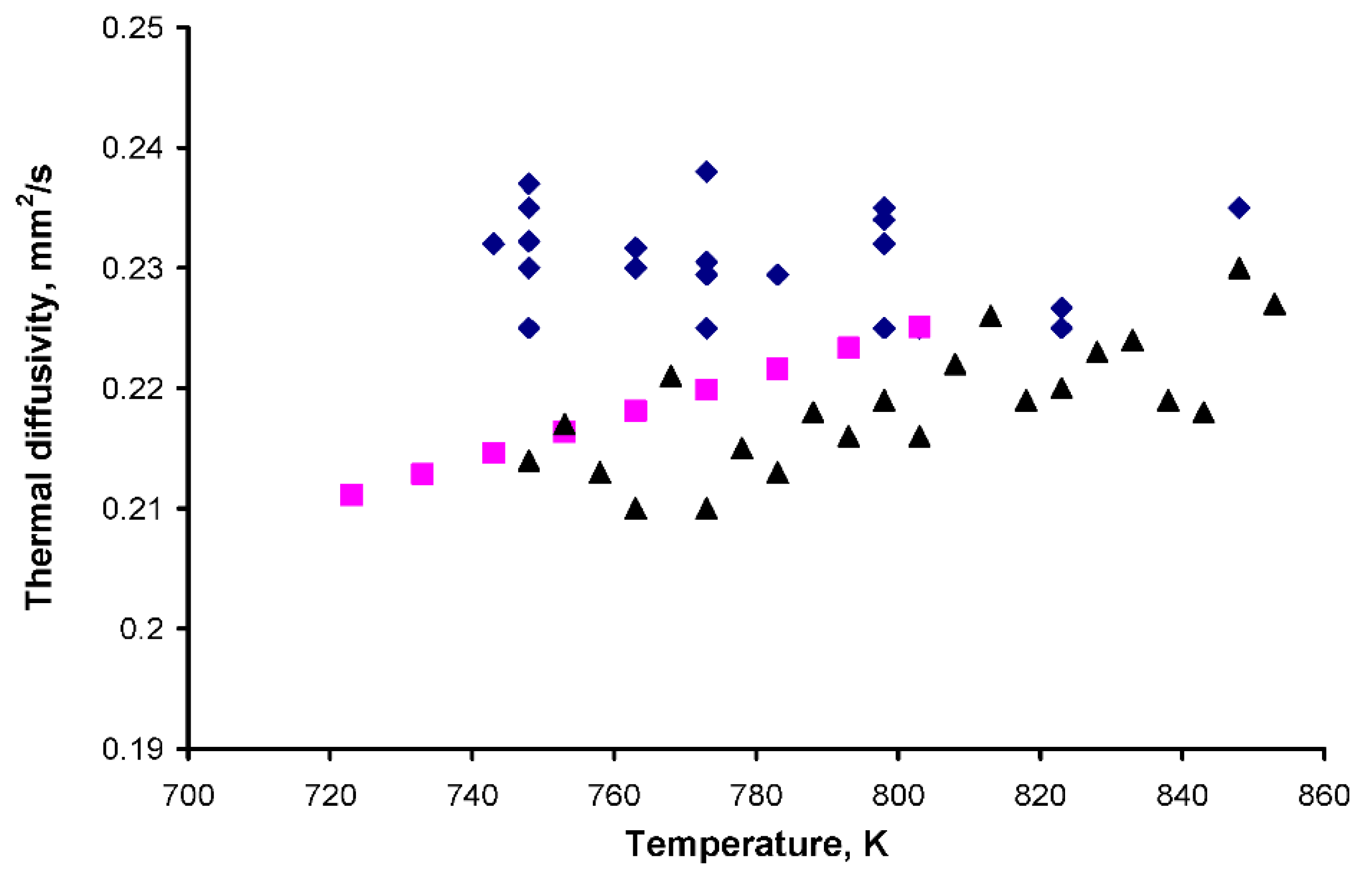
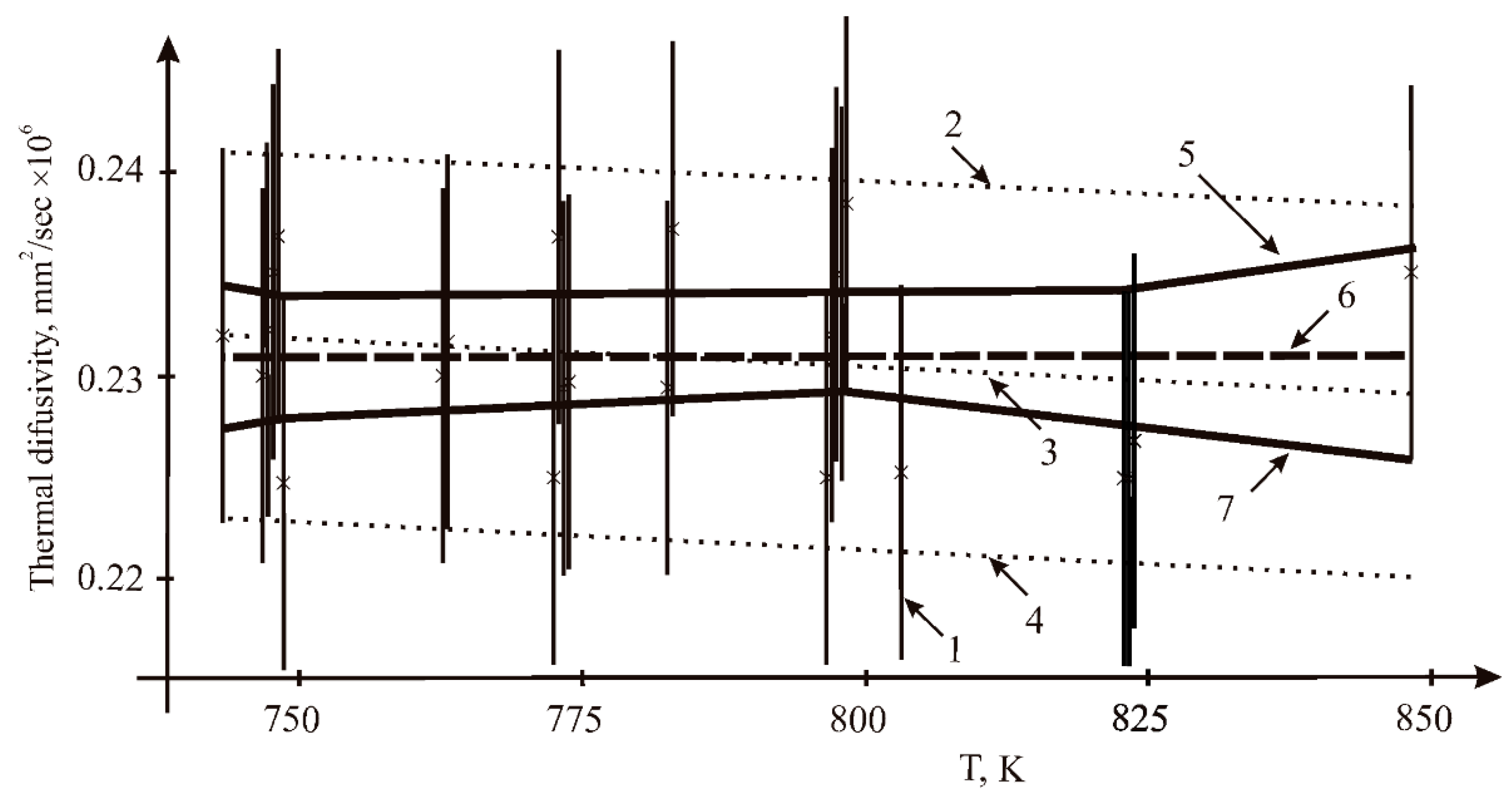
3.1. Thermal Diffusivity
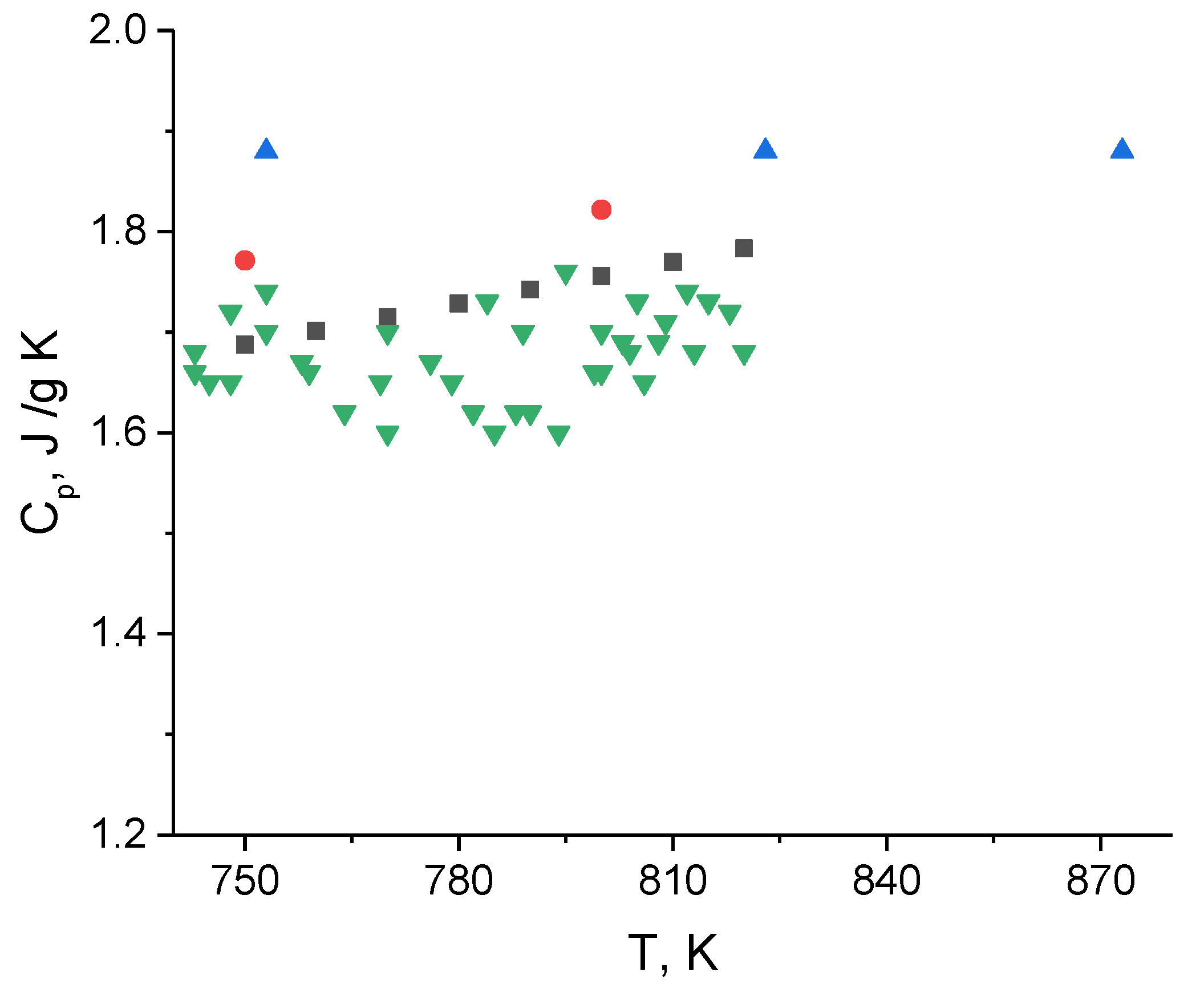
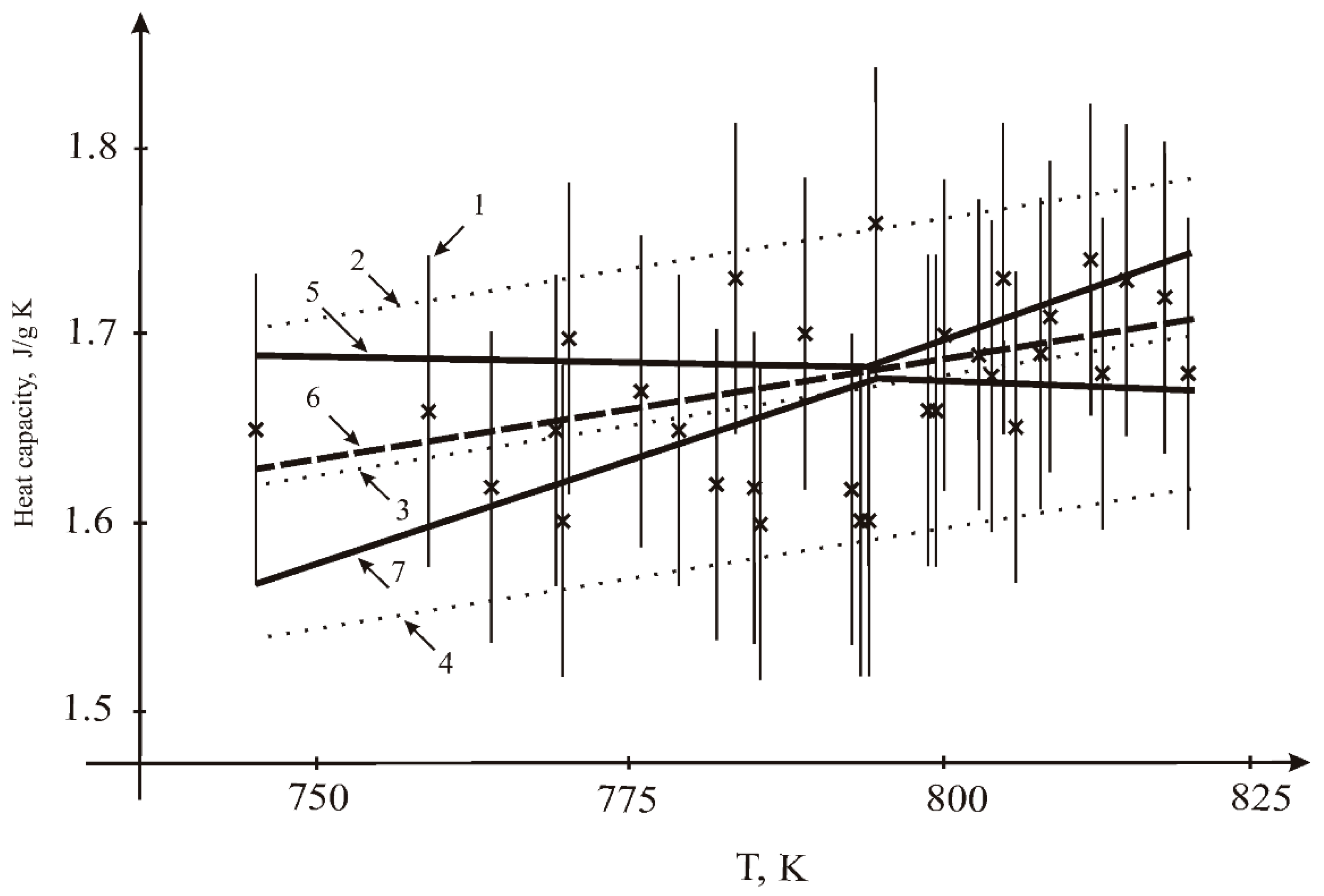
3.2. Heat Capacity
- -
- by LSQM: constant A = 0.80536 J/g K; temperature coefficient B = 1.09202 × 10−3 J/g K2;
- -
- by the interval method: constant A = 0.834 J/g K; temperature coefficient B = 1.096 × 10−3 J/g K2.
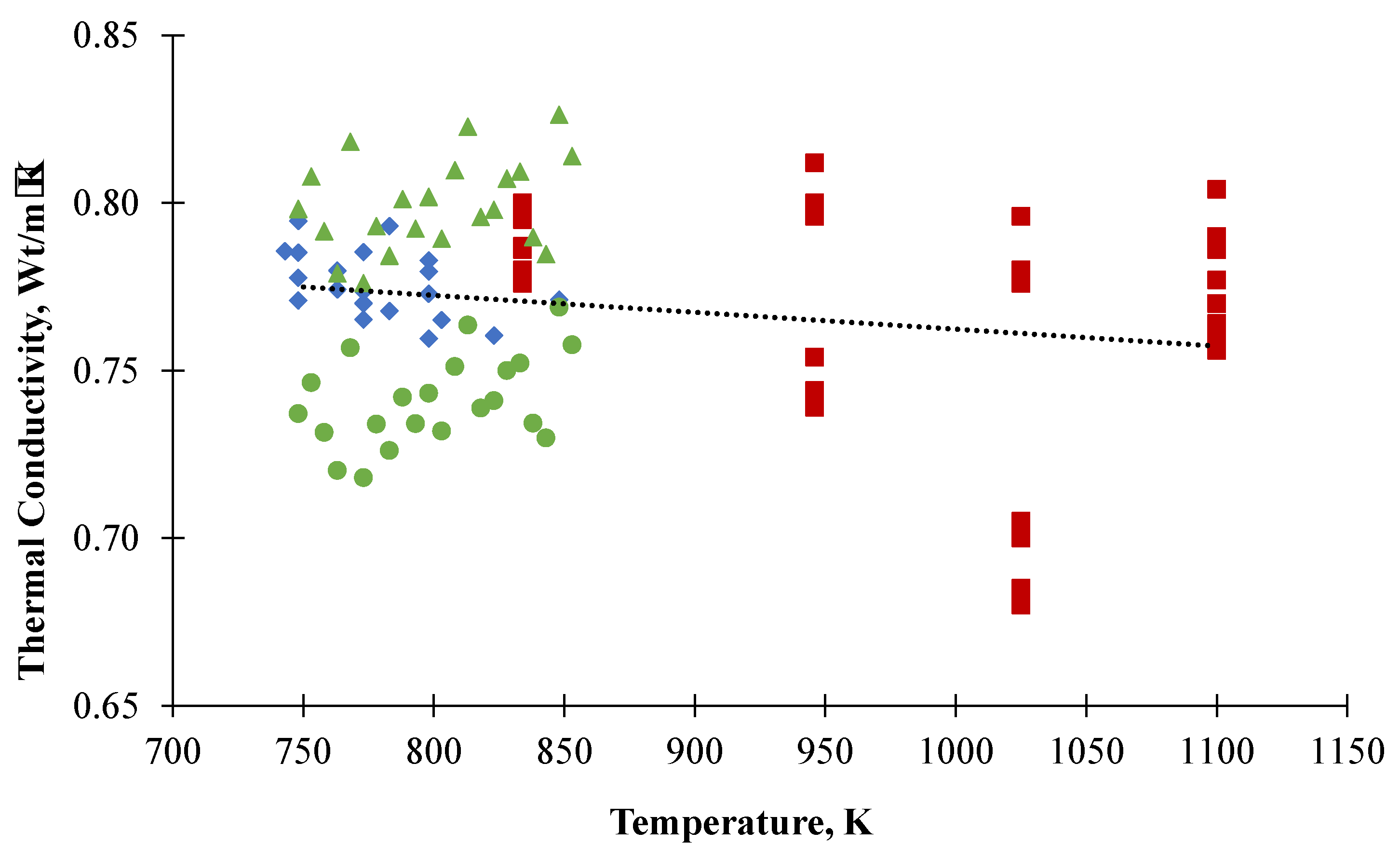
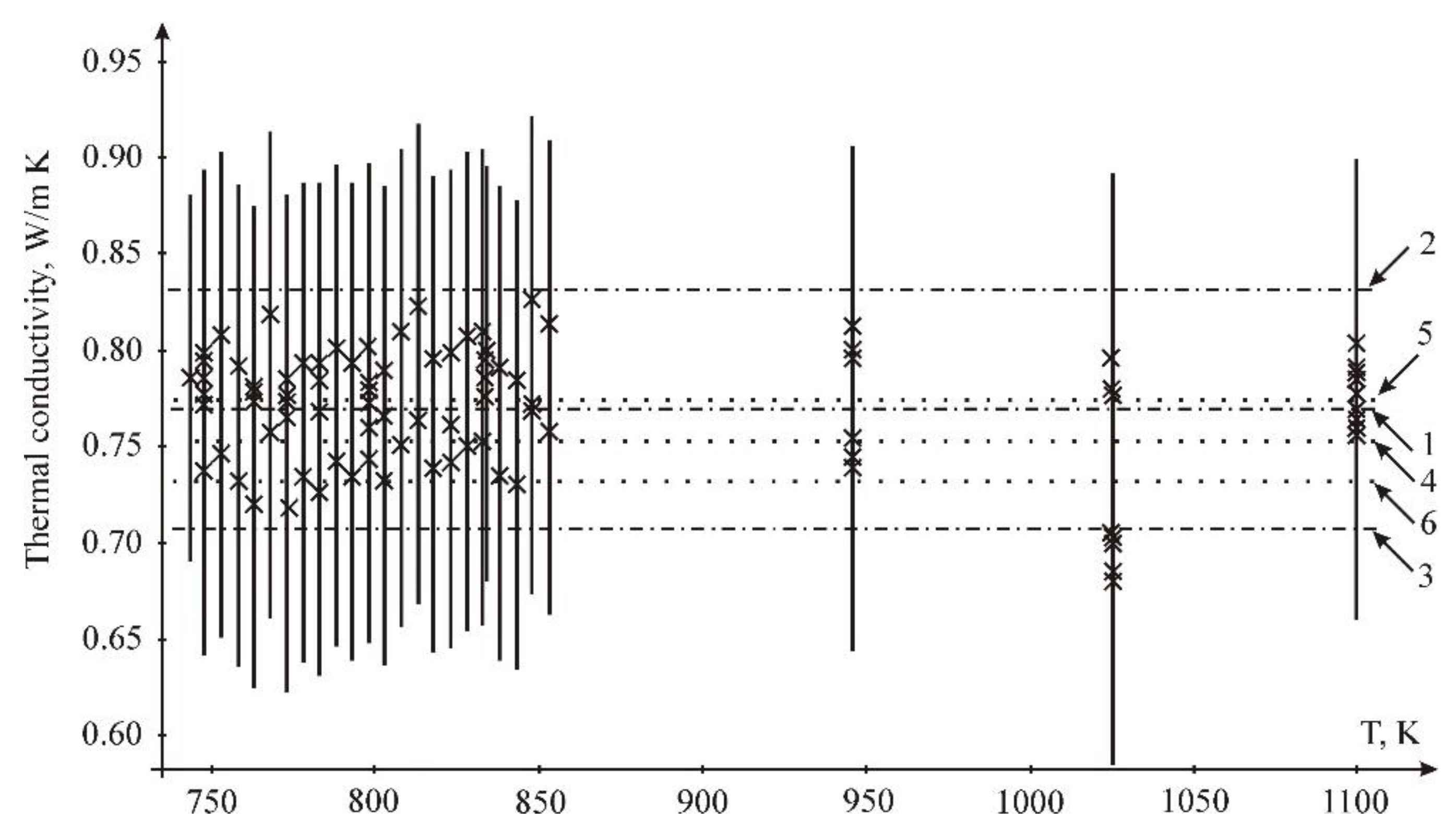
3.3. Thermal Conductivity
- -
- by LSM: constant A = 0.917 Wt/mK; temperature coefficient B = −1.869 × 10−4 Wt/m K2;
- -
- by interval estimation: constant A = 0.901 Wt/mK; temperature coefficient B = −1.584 × 10−4 Wt/m K2.
4. Conclusions
- A new experimental technique based on the laser flash method was developed for thermal diffusivity measurements of molten salts;
- The thermal diffusivity of molten FLiNaK was measured using the laser flash method. It was found to be independent of temperature;
- The heat capacity was measured by the DSC method. A slight positive temperature dependence was explained by the sample shape change;
- The thermal conductivity was calculated using the thermal diffusivity, heat capacity and density data from the literature. It was found to decrease with temperature;
- The results were compared with the latest data from the literature and were found to be in a good agreement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chliatzou, C.C.; Assael, M.J.; Antoniadis, K.D.; Huber, M.L.; Wakeman, W.A. Reference correlations for thermal conductivity of 13 inorganic molten salts. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2018, 47, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redkin, A.A.; Zaikov, Y.P.; Tkacheva, O.Y.; Kumkov, S.I. Molar thermal conductivity of molten salts. Ionics 2016, 22, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, C.T.; Spann, J.R.; Miller, R.R. Radiant transfer of heat in molten inorganic compounds at high temperatures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1962, 7, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, M.V.; Khokhlov, V.A.; Filatov, E.S. Thermal conductivity of molten alkali halides and their mixtures. Electrochim. Acta 1987, 32, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhlov, V.A.; Korzun, I.V.; Dokutovich, V.; Filatov, E.S. Heat capacity and thermal conductivity of molten ternary sodium, potassium, and zirconium fluorides mixtures. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 410, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.-H.; Cheng, J.-H.; Yin, H.-Q.; Xie, L.-D.; Zhang, P. Thermal conductivity of high temperature fluoride molten salt determined by laser flash technique. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 90, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, Y.; Fujita, N.; Yagi, J.; Shibaraha, M.; Sagara, A. Thermal conductivity measurement of fluoride molten salt FLiNaK by transient hot-wire method. High Temp.-High Press. 2017, 46, 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, R.; Birri, A.; Russell, N.; Phan, A.; Gheribi, A. Investigation of the thermal conductivity of molten LiF-NaF-KF with experiments, theory, and equilibrium molecular dynamics. J. Molec. Liq. 2022, 361, 119151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.; Wiser, R.; Yang, W.; Kang, D.; Choi, S.; Baglietto, E.; Short, M. The curious temperature dependence of fluoride molten salt thermal conductivity. J. Appl. Phys. 2022, 131, 225102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, T.D.; Yoko, J.; Janz, G.J. Fusion Properties and Heat Capacities of the Eutectic LiF-NaF-KF Melt. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1982, 27, 366–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janz, G.J.; Tomkins, R.P.T. Physical Properties Data Compilations Relevant to Energy Storage. IV. Molten Salts: Data on Additional Single and Multicomponent Salt Systems; National Bureau of Standards; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 1981; p. 193. [Google Scholar]
- Cibulková, J.; Chrenková, M.; Vasiljev, R.; Kremenetsky, V.; Boča, M. Density and Viscosity of the (LiF + NaF + KF)eut (1) + K2TaF7 (2) + Ta2O5 (3) Melts. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2006, 51, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankus, S.V.; Savchenko, I.V. Laser flash method for measurement of liquid metals heat transfer coefficients. Thermophys. Aeromech. 2009, 16, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agazhanov, A.S.; Khairulin, A.R.; Abdullaev, R.N.; Stankus, S.V. Thermophysical properties of the liquid eutectic K-Pb alloy. Thermophys. Aeromech. 2020, 27, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agazhanov, A.S.; Abdullaev, R.N.; Samoshkin, D.A.; Stankus, S.V. Coefficients of Heat Transfer for Liquid Alloys of the Rb–Bi System. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2021, 95, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agazhanov, A.S.; Khairulin, A.R.; Abdullaev, R.N.; Stankus, S.V. Thermophysical Properties of Liquid K–Pb Alloys. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2021, 30, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janz, G.; Krebs, U.; Siegenthaler, H.; Tomkins, R. Molten salts, Volume 3, Nitrates, nitrites and mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1972, 1, 581–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.; Janz, G. Melting-Crystallysation properties of NaNO3-KNO3, enthalpies and heat capacities. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1982, 27, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGuilio, R.; Teja, A.S. The thermal conductivity of molten NaNO3 KNO3 eutectic between between 525 and 590 K. Int. J. Thermophys. 1992, 13, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotani, T.; Nagasaka, Y.; Nagashima, A. Measurement of the thermal conductivity of molten KNO3 NaNO3 mixtures using transient hot wire method with liquid metal in a capillary probe. Int. J. Thermophys. 1982, 3, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Furukawa, K.; Araki, N.; Kobayasi, K. Thermal diffusivity measurement of molten salts by use of a simple ceramic cell. In Proceedings of the 8th European Thermophysical Properties Conference, Baden-Baden, Germany, 27 September–1 October 1982; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa, N.; Nagasaka, Y.; Nagashima, A. Experimental determination of the thermal diffusivity of molten alkali halides by the forced Rayleigh scattering method. II. Molten NaBr, KBr, RbBr, and CsBr. Int. J. Thermophys. 1992, 13, 753–762. [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa, N.; Nagasaka, Y.; Nagashima, A. Experimental determination of the thermal diffusivity of molten alkali halides by the forced Rayleigh scattering method. III. molten NaI, KI, RbI, and CsI. Int. J. Thermophys. 1992, 13, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, N.; Nagasaka, Y.; Nagashima, A. Experimental determination of the thermal diffusivity of molten alkali halides by the forced Rayleigh scattering method. I Molten LiCl, NaCl, KCl, RbCl, and CsCl. Int. J. Thermophys. 1992, 13, 555–574. [Google Scholar]
- Shary, S.P. Finite Dimensional Interval Analysis; E-book: Novosibirsk, Russia; 617p.
- Kumkov, S.I.; Nikitin, V.S.; Ostanina, T.N.; Rudoy, V.M. Interval processing of electrochemical data. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2020, 380, 112961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheribi, A.; Chartrand, P. Thermal conductivity of molten salt mixtures: Theoretical model supported by equilibrium molecular dynamics simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 084506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiGuilio, R.; Teja, A. A rough hard-sphere model for the thermal conductivity of molten salts. Int. J. Thermophys. 1992, 13, 855–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yang, S.; Pan, G.; Ding, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, W. Thermal and Transport Properties of MoltenChloride Salts with PolarizationEffect on Microstructure. Energies 2021, 14, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakir’yanov, B.; Tkachev, N. Thermal conductivity of alkali metal chlorides: Calculation with molecular dynamics method. TVT 2020, 58, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.; Kassaee, M.; Jeter, S.; Teja, A. New Model for the Thermal Conductivity of Molten Salts. Int. J. Thermophys. 2014, 5, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, P.A.; Sidorov, A.A.; Kul’chenkov, E.A.; Anishchenko, A.M.; Avetissov, I.C.; Sorokin, N.I.; Fedorov, P.P. Thermal conductivity and expansion of PbF2 single crystals. Ionics 2017, 23, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| T, K | α, mm2/s | ρ, g/cm3 [17] | Cp, [18] J/g K | λ, Wt/m K | T, K | λ, Wt/m K [19,20] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593 | 0.150 | 1.893 | 1.530 | 0.435 | 526 | 0.468 |
| 573 | 0.151 | 1.906 | 1.530 | 0.440 | 541 | 0.465 |
| 553 | 0.153 | 1.919 | 1.530 | 0.449 | 558 | 0.458 |
| 533 | 0.159 | 1.933 | 1.530 | 0.471 | 572 | 0.454 |
| 513 | 0.157 | 1.946 | 1.530 | 0.469 | 588 | 0.448 |
| 593 | 0.159 | 1.893 | 1.530 | 0.460 | 497 | 0.462 |
| 573 | 0.153 | 1.906 | 1.530 | 0.446 | 510 | 0.460 |
| 553 | 0.157 | 1.919 | 1.530 | 0.461 | 545 | 0.457 |
| 533 | 0.158 | 1.933 | 1.530 | 0.467 | 573 | 0.446 |
| 513 | 0.156 | 1.946 | 1.530 | 0.465 | 592 | 0.446 |
| T, K | α, mm2/s | T, K | α, mm2/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| 823 | 0.23 | 783 | 0.24 |
| 798 | 0.24 | 743 | 0.23 |
| 773 | 0.21 | 803 | 0.20 |
| 798 | 0.23 | 783 | 0.21 |
| 773 | 0.24 | 763 | 0.22 |
| 748 | 0.24 | 743 | 0.25 |
| 823 | 0.22 | 803 | 0.23 |
| 798 | 0.21 | 783 | 0.23 |
| T, K | Cp, J/g K | T, K | Cp, J/g K | T, K | Cp, J/g K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp 1(20) | Exp 2(10) | Exp 3(5) | |||
| 803 | 1.69 | 759 | 1.66 | 765 | 1.6 |
| 808 | 1.69 | 764 | 1.62 | 770 | 1.6 |
| 813 | 1.68 | 769 | 1.65 | 775 | 1.58 |
| 818 | 1.72 | 774 | 1.65 | 780 | 1.6 |
| 770 | 1.7 | 779 | 1.65 | 785 | 1.62 |
| 776 | 1.67 | 784 | 1.73 | 790 | 1.76 |
| 782 | 1.62 | 789 | 1.7 | 795 | 1.7 |
| 788 | 1.62 | 794 | 1.6 | 800 | 1.73 |
| 794 | 1.6 | 799 | 1.66 | 805 | 1.72 |
| 800 | 1.66 | 804 | 1.68 | 810 | 1.73 |
| 806 | 1.65 | 809 | 1.71 | 815 | 1.68 |
| 812 | 1.74 | 814 | 1.77 | 820 | 1.67 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rudenko, A.; Redkin, A.; Il’ina, E.; Pershina, S.; Mushnikov, P.; Zaikov, Y.; Kumkov, S.; Liu, Y.; Shi, W. Thermal Conductivity of FLiNaK in a Molten State. Materials 2022, 15, 5603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165603
Rudenko A, Redkin A, Il’ina E, Pershina S, Mushnikov P, Zaikov Y, Kumkov S, Liu Y, Shi W. Thermal Conductivity of FLiNaK in a Molten State. Materials. 2022; 15(16):5603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165603
Chicago/Turabian StyleRudenko, Alexey, Alexander Redkin, Evgeniya Il’ina, Svetlana Pershina, Peter Mushnikov, Yuriy Zaikov, Sergey Kumkov, Yalan Liu, and Weiqun Shi. 2022. "Thermal Conductivity of FLiNaK in a Molten State" Materials 15, no. 16: 5603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165603
APA StyleRudenko, A., Redkin, A., Il’ina, E., Pershina, S., Mushnikov, P., Zaikov, Y., Kumkov, S., Liu, Y., & Shi, W. (2022). Thermal Conductivity of FLiNaK in a Molten State. Materials, 15(16), 5603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165603







