Effect of Magnetorheological Grease’s Viscosity to the Torque Performance in Magnetorheological Brake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication of MRG
2.2. Characterization
2.3. The Evaluation of the Diluted MRG in MR Brake
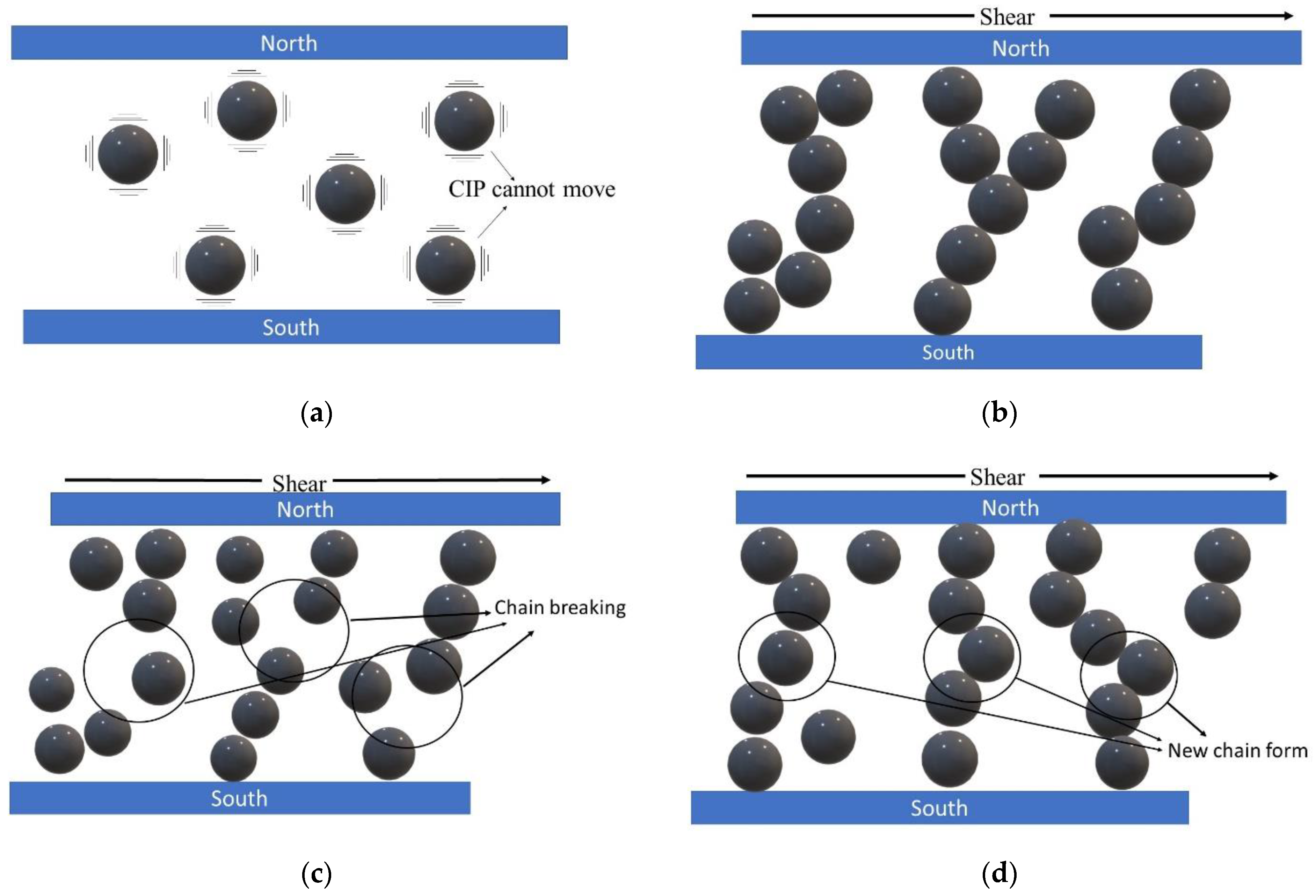
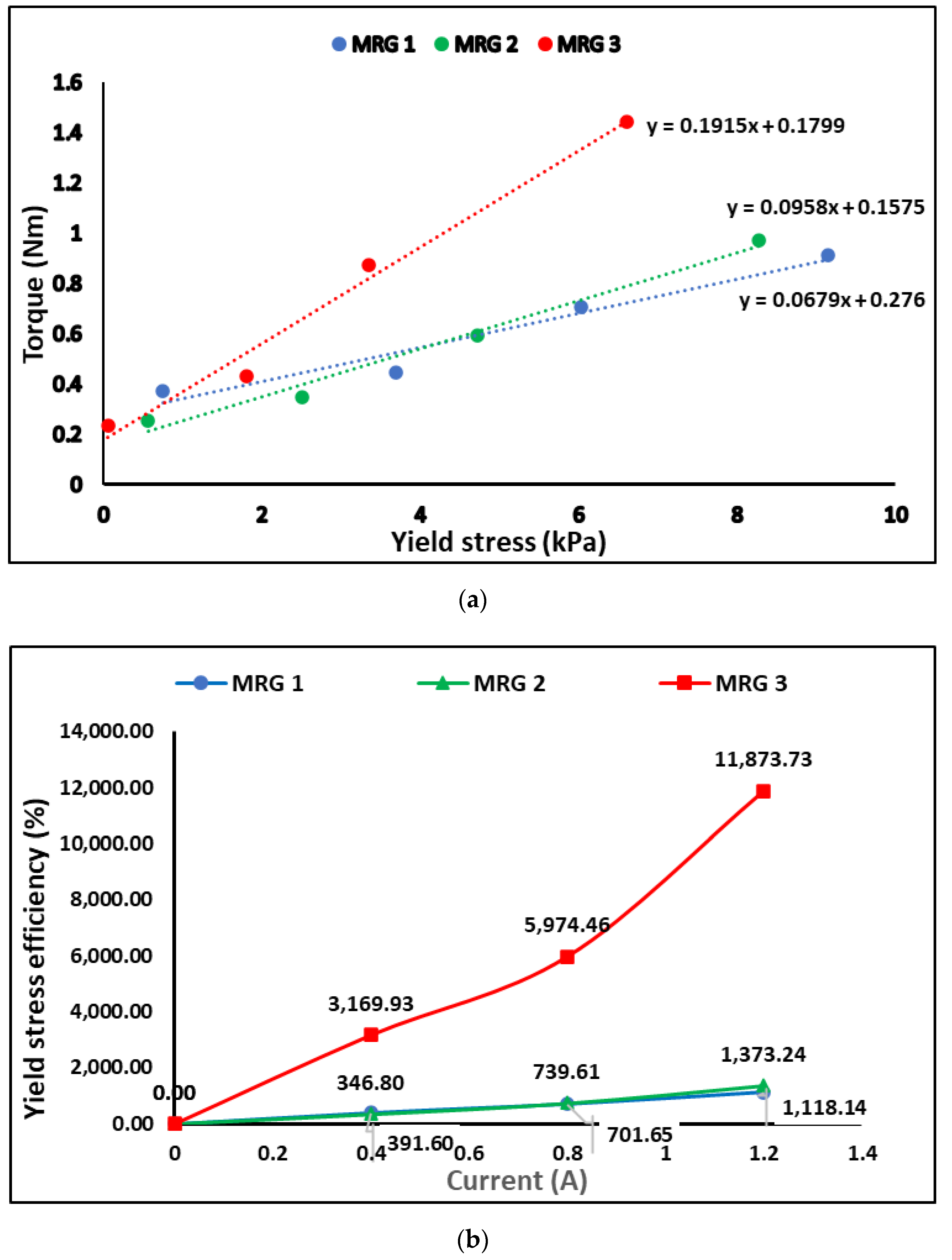
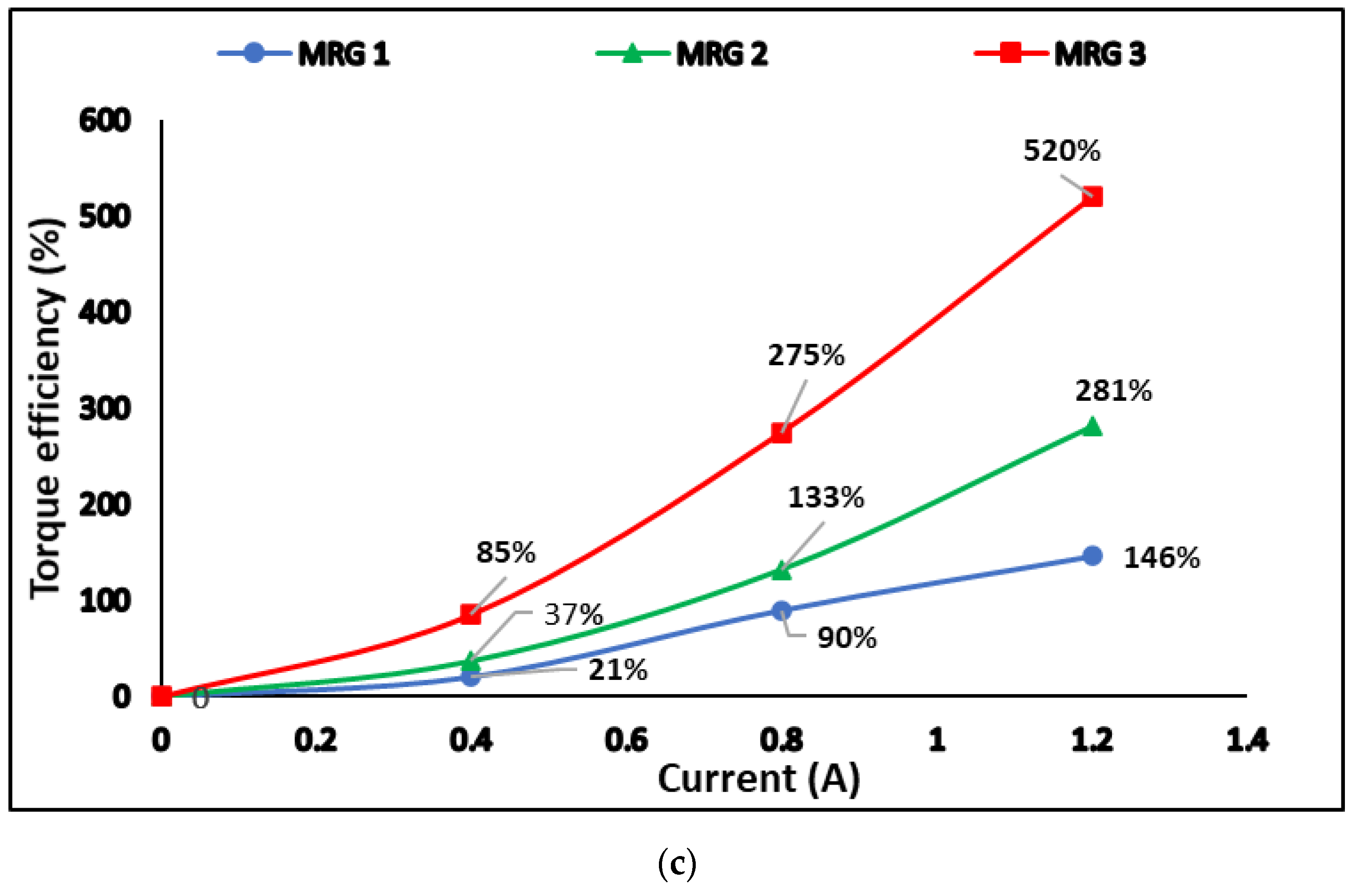
3. Results
3.1. Magnetic Properties of MRG
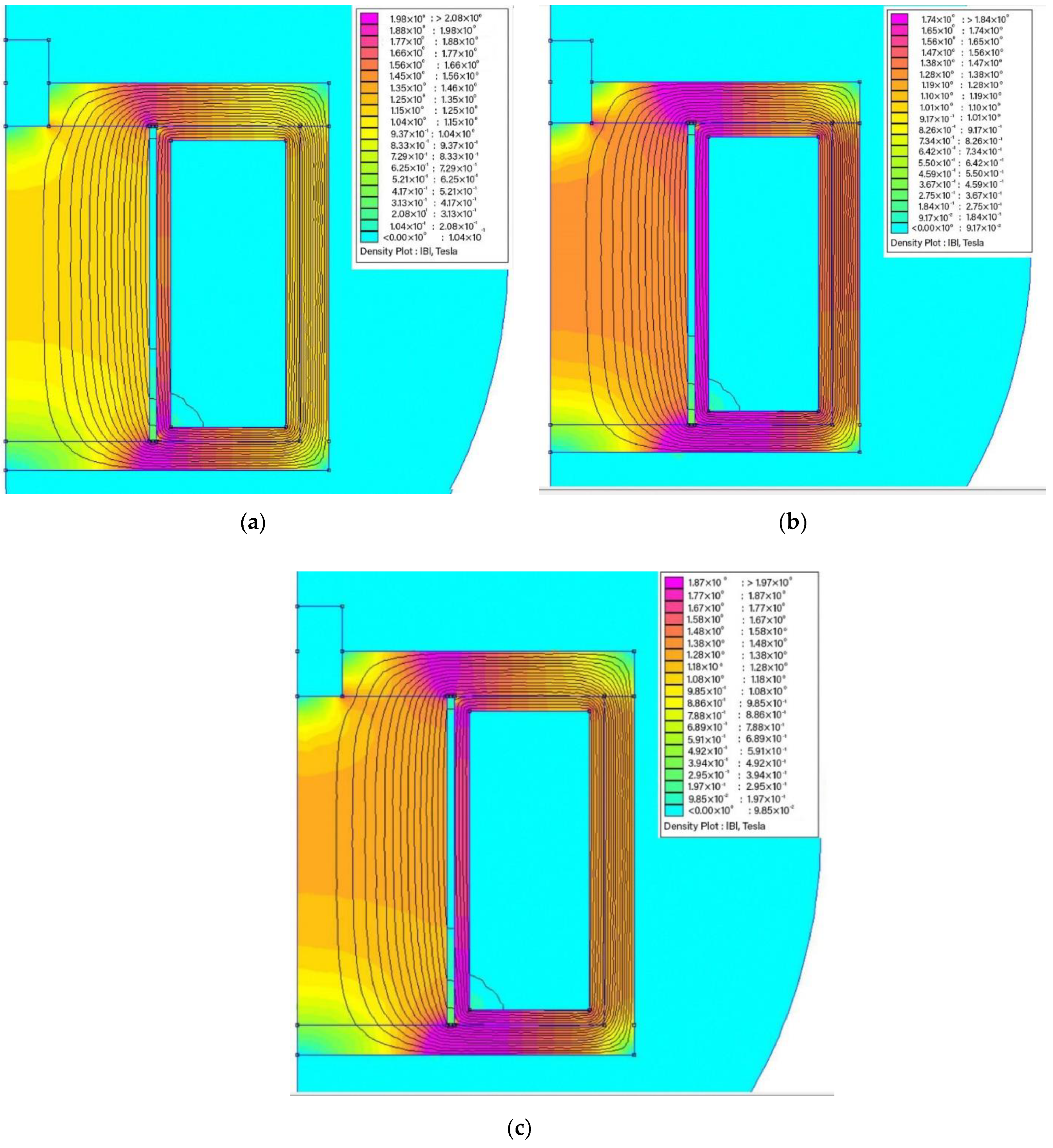
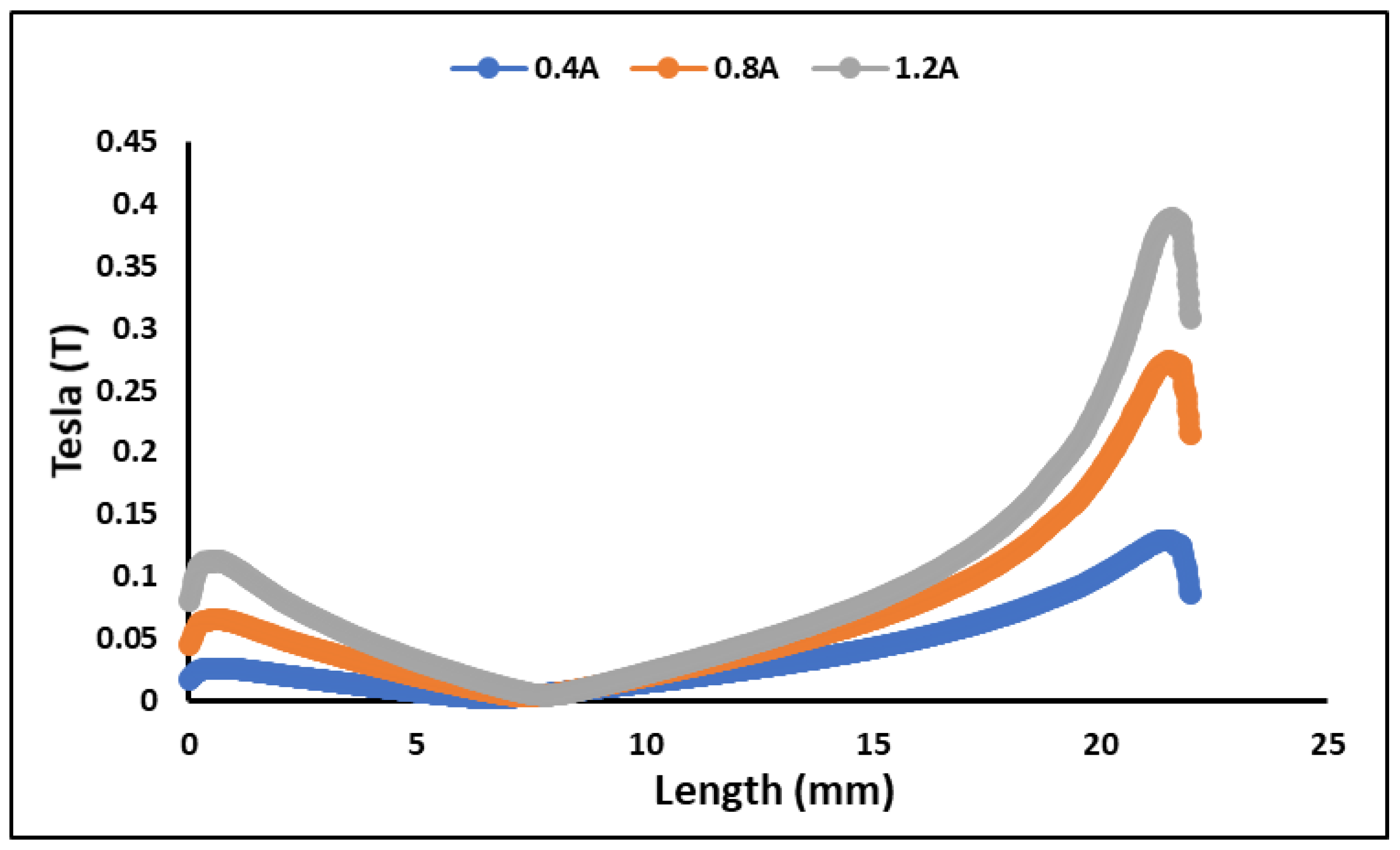
3.2. Finite Element Method Magnetic (FEMM)
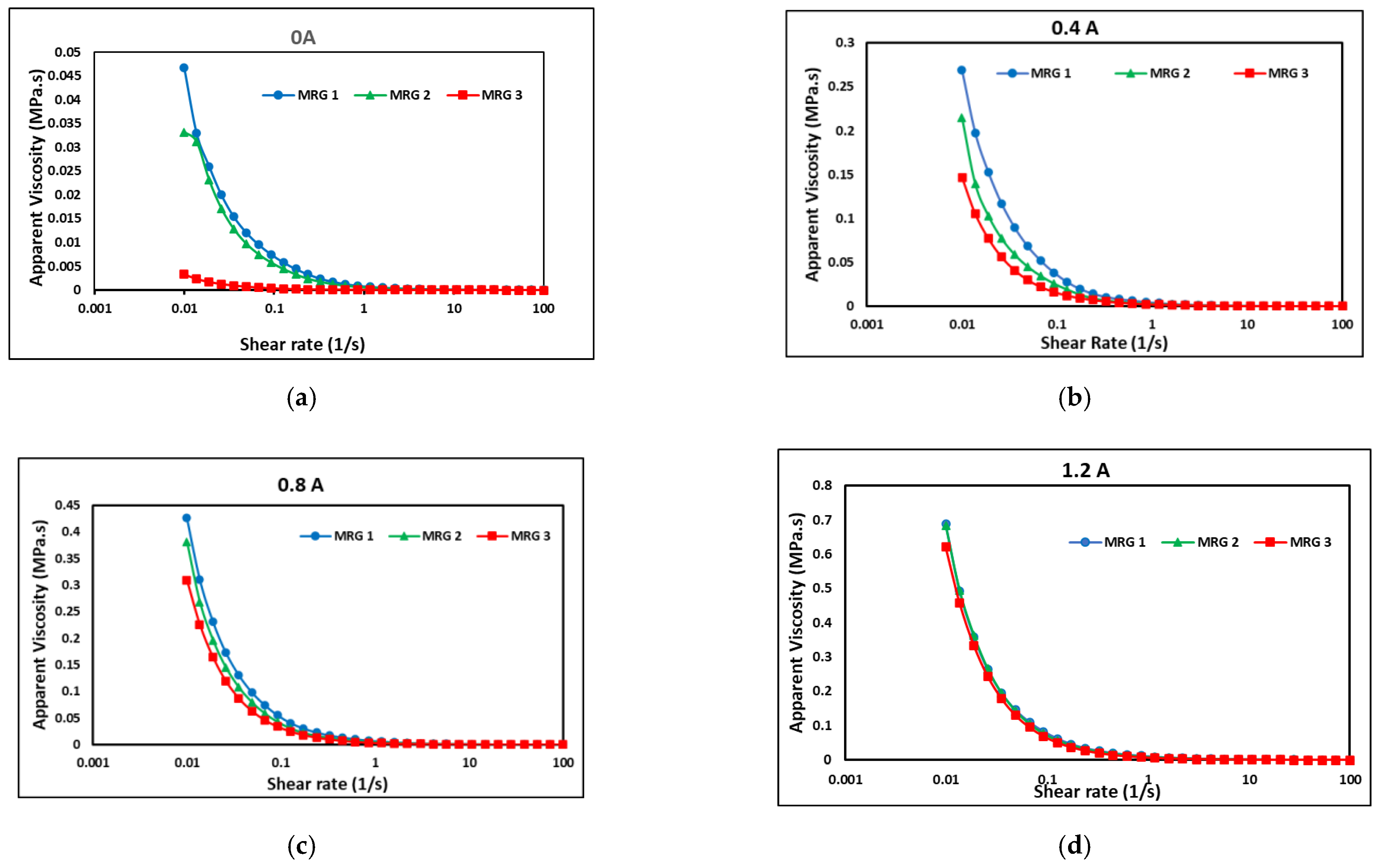
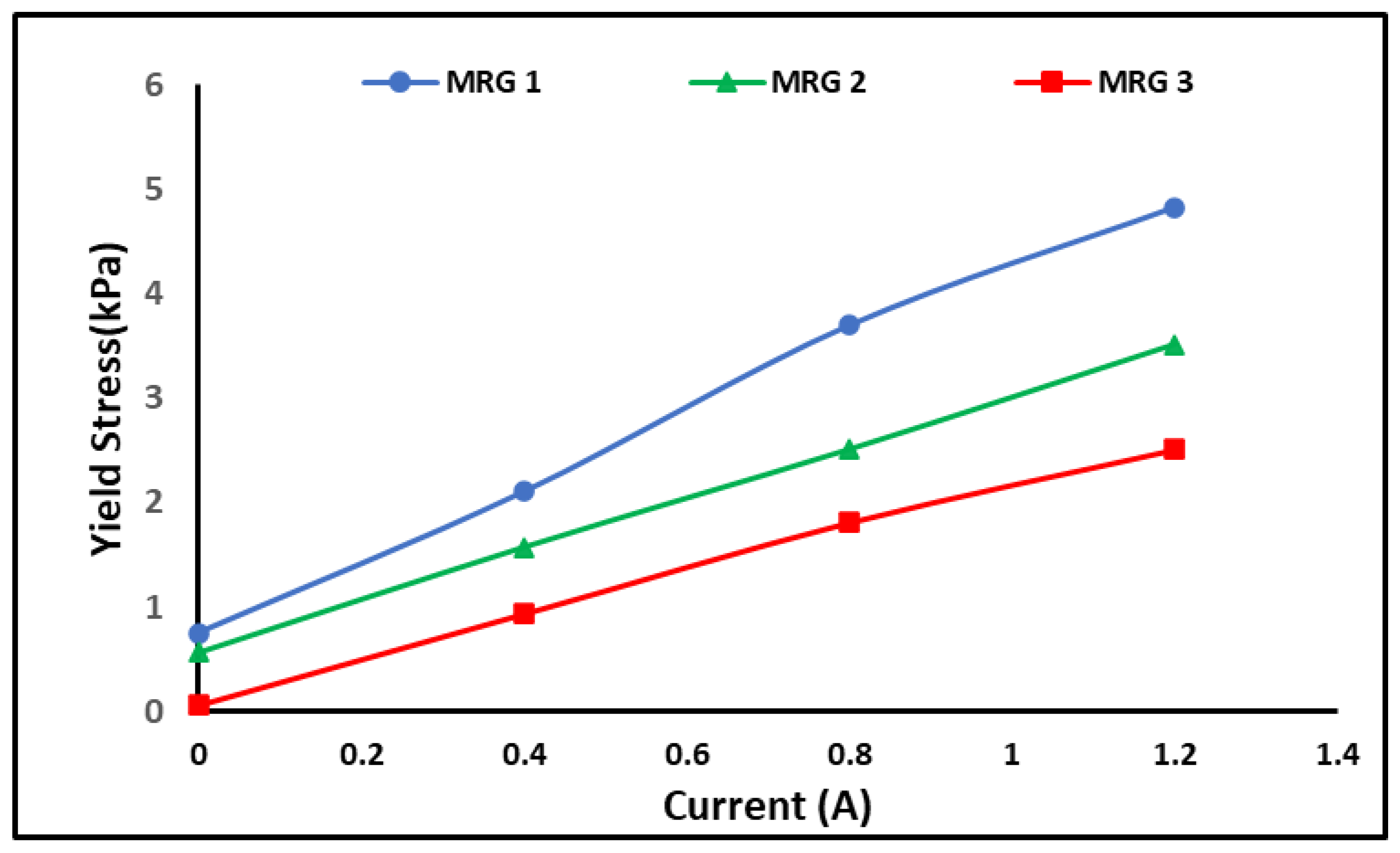
3.3. Rheological Properties of MRG
3.4. Evaluation of Diluted MRG Performance in MR Brake
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, D.M.; Hou, Y.F.; Tian, Z.Z. A novel high-torque magnetorheological brake with a water cooling method for heat dissipation. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.D.; LeRoy, D.F.; Holzheimer, J.C.; Prindle, D.R.; Marjoram, R.H. Controllable Brake. U.S. Patent No. 5,842,547, 1 December 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Adiputra, D.; Ubaidillah, U.; Mazlan, S.A.; Zamzuri, H.; Rahman, M.A.A. Fuzzy logic control for ankle foot orthoses equipped with magnetorheological brake. J. Teknol. 2016, 78, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Phu, D.X.; Choi, S.B. Rheological properties of bi-dispersed magnetorheological fluids based on plate-like iron particles with application to a small-sized damper. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 203907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Phu, D.X.; Seong, M.S.; Upadhyay, R.V.; Choi, S.B. A low sedimentation magnetorheological fluid based on plate-like iron particles, and verification using a damper test. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 027001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.B.; Do, X.P.; Jeon, J.; Choi, S.B.; Liu, Y.D.; Choi, H.J. Brake performance of core-shell structured carbonyl iron/silica based magnetorheological suspension. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 367, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Wu, L.; Li, L.; Yu, L. Performance analysis of rotary magnetorheological brake with multiple fluid flow channels. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 173323–173335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Meng, W.; Wang, Y. Numerical and experimental studies on a novel magneto-rheological fluid brake based on fluid–solid coupling. Sci. Prog. 2020, 103, 36850419879000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalikate, S.M.; Patil, S.R.; Sawant, S.M. Design and simulation of magneto-rheological (MR) brake for automotive application. SAE Technol. Pap. 2014, 28, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhau, S.R.P.; Kumbhar, K.; Khalkar, V.R.; Jadhav, P.N. Design of Magneto-Rheological Brake for Automotive. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 238–249. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Królczyk, G.; Li, Z.; Li, W. Effect of Temperature on the Transmission Characteristics of High-Torque Magnetorheological Brakes. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 057002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Kobayashi, K. Development of cylindrical magnetorheological fluid brake for virtual cycling system. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Karon Beach, Thailand, 7–11 December 2011; pp. 2547–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiputra, D.; Rahman, M.A.A.; Ubaidillah; Mazlan, S.A. Improving Passive Ankle Foot Orthosis System Using Estimated Ankle Velocity Reference. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 194780–194794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Wu, L.; Li, L. Torque Characteristics Analysis of a Magnetorheological Brake with Double Brake Disc. Actuators 2021, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avraam, M.; Horodinca, M.; Romanescu, I.; Preumont, A. Computer controlled rotational MR-brake for wrist rehabilitation device. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2010, 21, 1543–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Tak, R.S.S.; Singh, S.B.; Kumar, H. Characterization of magnetorheological brake utilizing synthesized and commercial fluids. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 46, 9419–9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijesh, H.H.; Kumar, K.P.D. Synthesis and field dependent shear stress evaluation of stable MR fluid for brake application. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2017, 69, 655–665. [Google Scholar]
- Quoc, N.V.; Tuan, L.D.; Hiep, L.D.; Quoc, H.N.; Choi, S.B. Material characterization of MR fluid on performance of MRF based brake. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Chang, H.; Zhao, R.; Huang, J.; Li, K.; Xie, S. Investigation of the relationship among the microstructure, rheological properties of MR grease and the speed reduction performance of a rotary micro-brake. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 116, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarmizi, S.M.A.; Nordin, N.A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Mohamad, N.; Rahman, H.A.; Aziz, S.A.A.; Nazmi, N.; Azmi, M.A. Incorporation of Cobalt Ferrite on the Field Dependent Performances of Magnetorheological Grease. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 9, 15566–15574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.; Mazlan, S.A.; Ubaidillah; Choi, S.B.; Imaduddin, F.; Aziz, S.A.A. The field-dependent viscoelastic and transient responses of plate-like carbonyl iron particle based magnetorheological greases. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2019, 30, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.; Mazlan, S.A.; Ubaidillah; Choi, S.B.; Nordin, M.F.M. The Field-Dependent Rheological Properties of Magnetorheological Grease Based on Carbonyl-Iron-Particles. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 095043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J. Effect of temperature on rheological properties of lithium-based magnetorheological grease. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordaninejad, F.; Kavlicoglu, B.M.; Wang, X. Study of a magneto-rheological grease (MRG) clutch. In Active and Passive Smart Structures and Integrated Systems 2007; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2007; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhwani, V.K.; Hirani, H. A Comparative Study of Magnetorheological-Fluid-Brake and Magnetorheological-Grease-Brake. Tribol. Online 2008, 3, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Thakur, M.K.; Sarkar, C. Design and development of a wedge shaped magnetorheological clutch. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2020, 234, 1252–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.R.; Sawant, S.M. Experimental studies on magnetorheological brake for automotive application. Int. J. Automot. Mech. Eng. 2018, 15, 4893–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbhar, B.K.; Patil, S.R.; Sawant, S.M. Synthesis and characterization of magneto-rheological (MR) fluids for MR brake application. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2015, 18, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Choi, S.B. Optimal design of an automotive magnetorheological brake considering geometric dimensions and zero-field friction heat. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 115024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Ko, J.D.; Liu, Y.D.; Kim, I.G.; Choi, H.J. Effect of medium oil on magnetorheology of soft carbonyl iron particles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3442–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.; Rosli, M.A.; Ubaidillah; Aziz, S.A.A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Nordin, N.A.; Yahaya, H.; Fatah, A.Y.A. Intrinsic Apparent Viscosity and Rheological Properties of Magnetorheological Grease with Dilution Oils. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference and Exhibition on Sustainable Energy and Advanced Materials, Surakarta, Indonesia, 16–17 October 2019; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamad, N.; Yasser, A.; Fatah, A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Nordin, N.A.; Nabil, M. Dilution dependent of different types of redispersing oils on magnetorheological greases. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2019, 8, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.O.; Park, B.J.; Hato, M.J.; Choi, H.J. Soft magnetic carbonyl iron microsphere dispersed in grease and its rheological characteristics under magnetic field. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2011, 289, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippa, L.; Doghieri, F.; Pellegrino, A.M.; Pavesi, E. Thixotropic behavior of reconstituted debris-flow mixture. Water 2021, 13, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, H.; Wang, X.; Gordaninejad, F. Temperature dependence of magneto-rheological materials. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2009, 20, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.B.; Kim, H.B.; Lee, J.Y.; You, J.L.; Choi, H.J.; Jhon, M.S. Role of organic coating on carbonyl iron suspended particles in magnetorheological fluids. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisuwala, M.; Upadhyay, R.V.; Parekh, K. Evaluation of Static and Dynamic Yield Stress for Isotropic and Anisotropic Particle–Based MR Fluids: Modeling and Analysis. Braz. J. Phys. 2020, 50, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.W.; Gang, H.G.; Choi, S.B. An experimental study on torque characteristics of magnetorheological brake with modified magnetic core shape. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10, 168781401775222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Wang, S.; Choi, S.B.; Wang, N.; Xiu, S. Thermal and tribological characteristics of a disc-type magnetorheological brake operated by the shear mode. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2019, 30, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezasoltani, A.; Khonsari, M.M. Mechanical degradation of lubricating grease in an EHL line contact. Tribol. Int. 2017, 109, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cann, P.M.; Doner, J.P.; Webster, M.N.; Wikstrom, V. Grease degradation in rolling element bearings. Tribol. Trans. 2001, 44, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Bosman, R.; Lugt, P.M. A Master Curve for the Shear Degradation of Lubricating Greases with a Fibrous Structure. Tribol. Trans. 2019, 62, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.D. Scientific Opinion on Mineral Oil Hydrocarbons in Food. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Li, W.; Zhao, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X. A Study on Microstructure, Friction and Rheology of Four Lithium Greases Formulated with Four Different Base Oils. Tribol. Lett. 2021, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoc, K.; Park, E.J.; Suleman, A. Design considerations for an automotive magnetorheological brake. Mechatronics 2008, 18, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Song, A.; Zeng, X.; Hu, S. Design and evaluation of a small-scale multi-drum magnetorheological brake. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 29, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
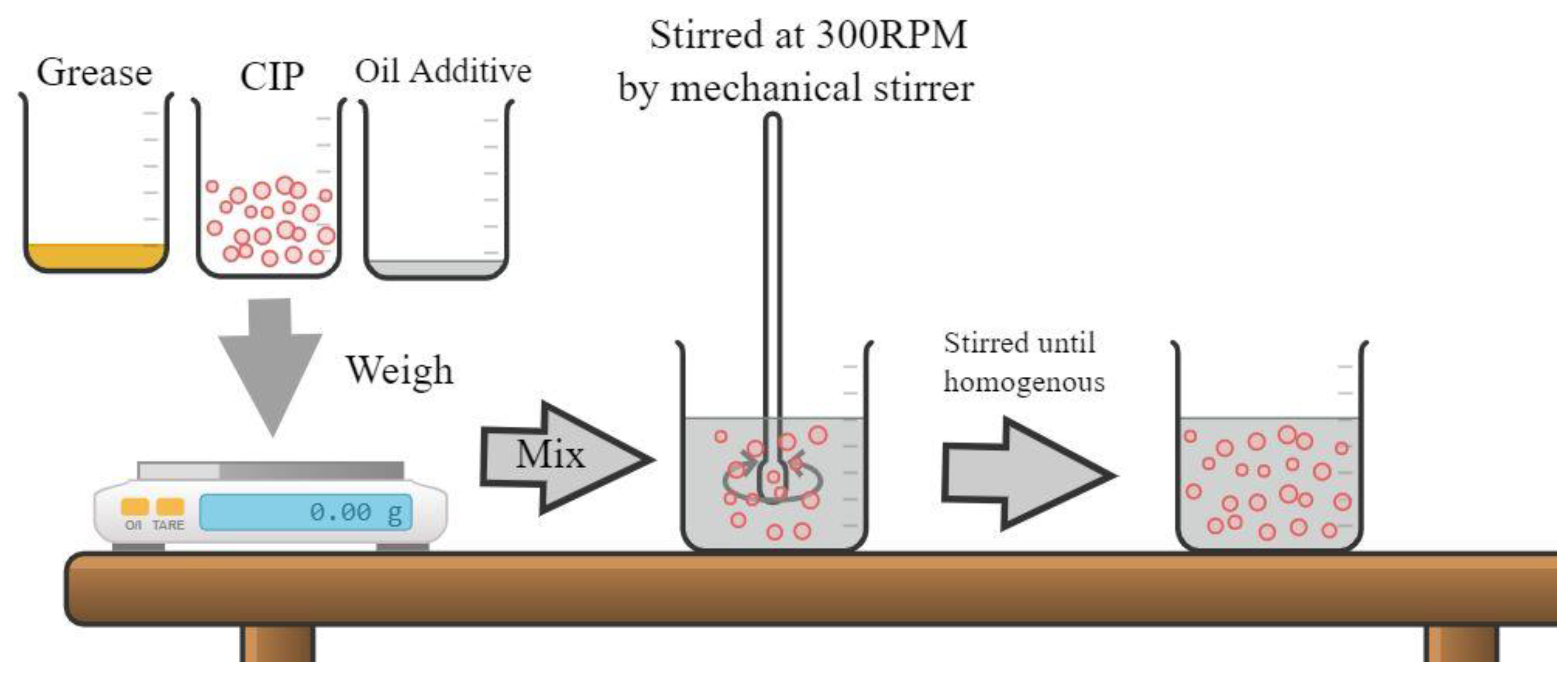
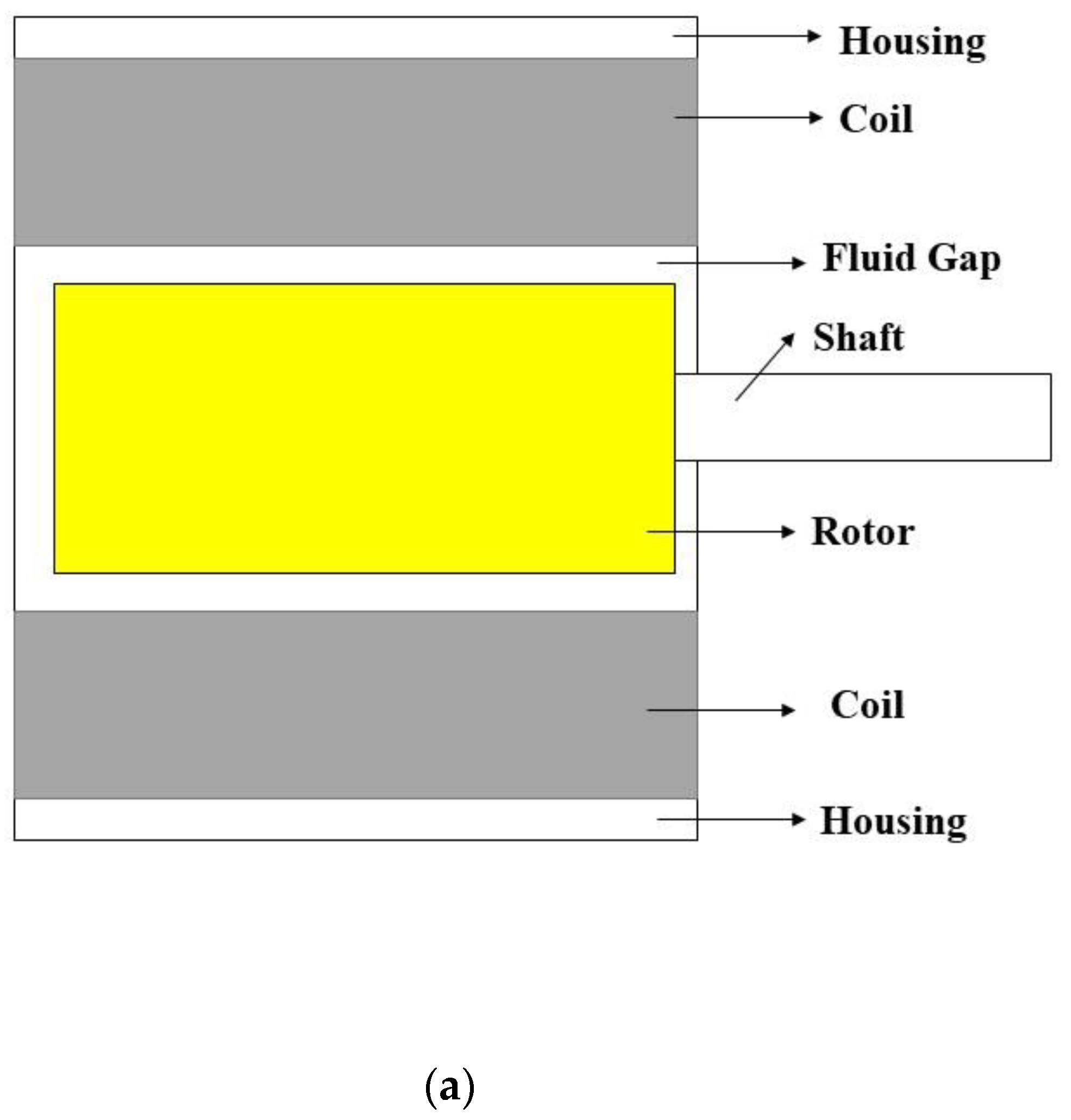
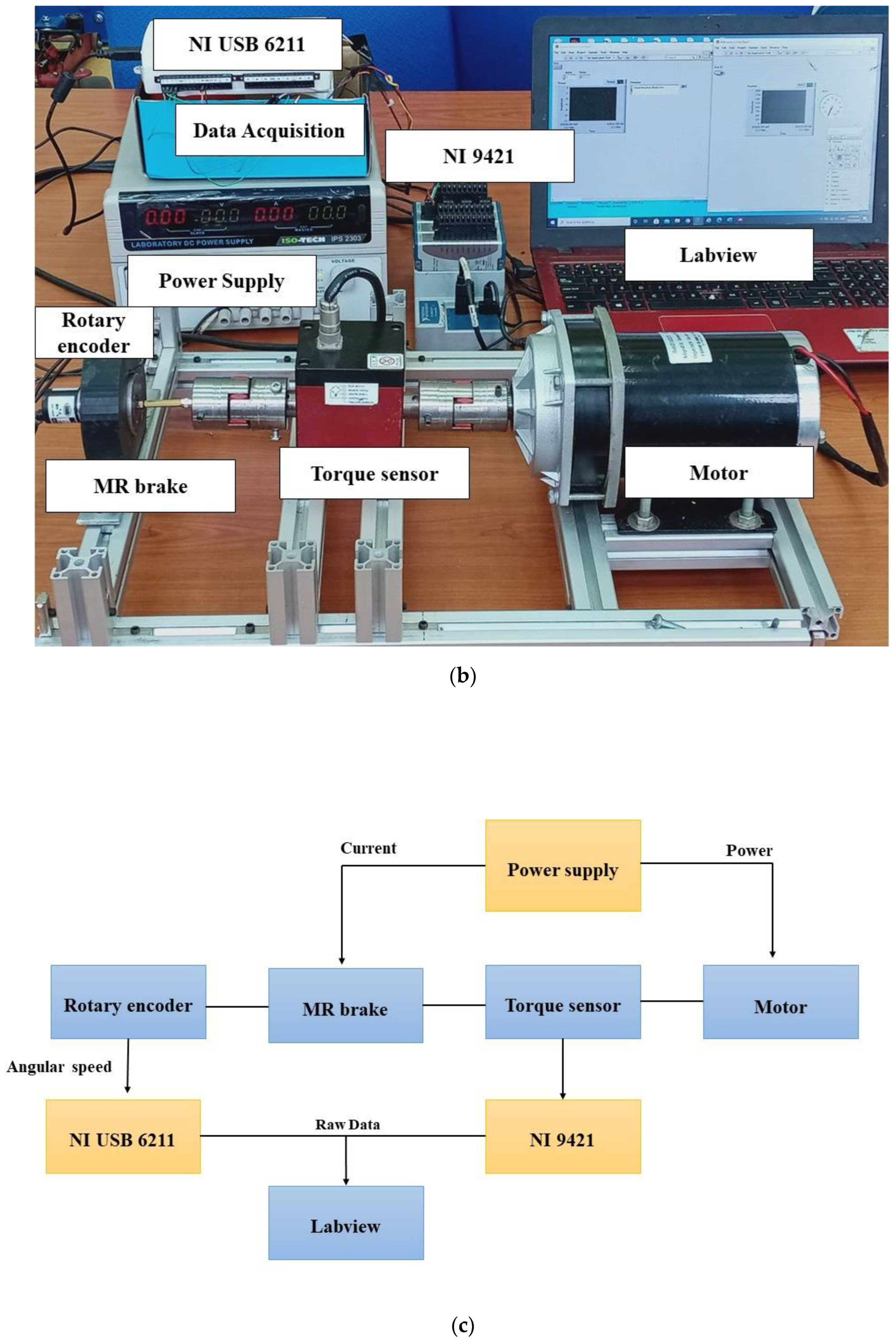
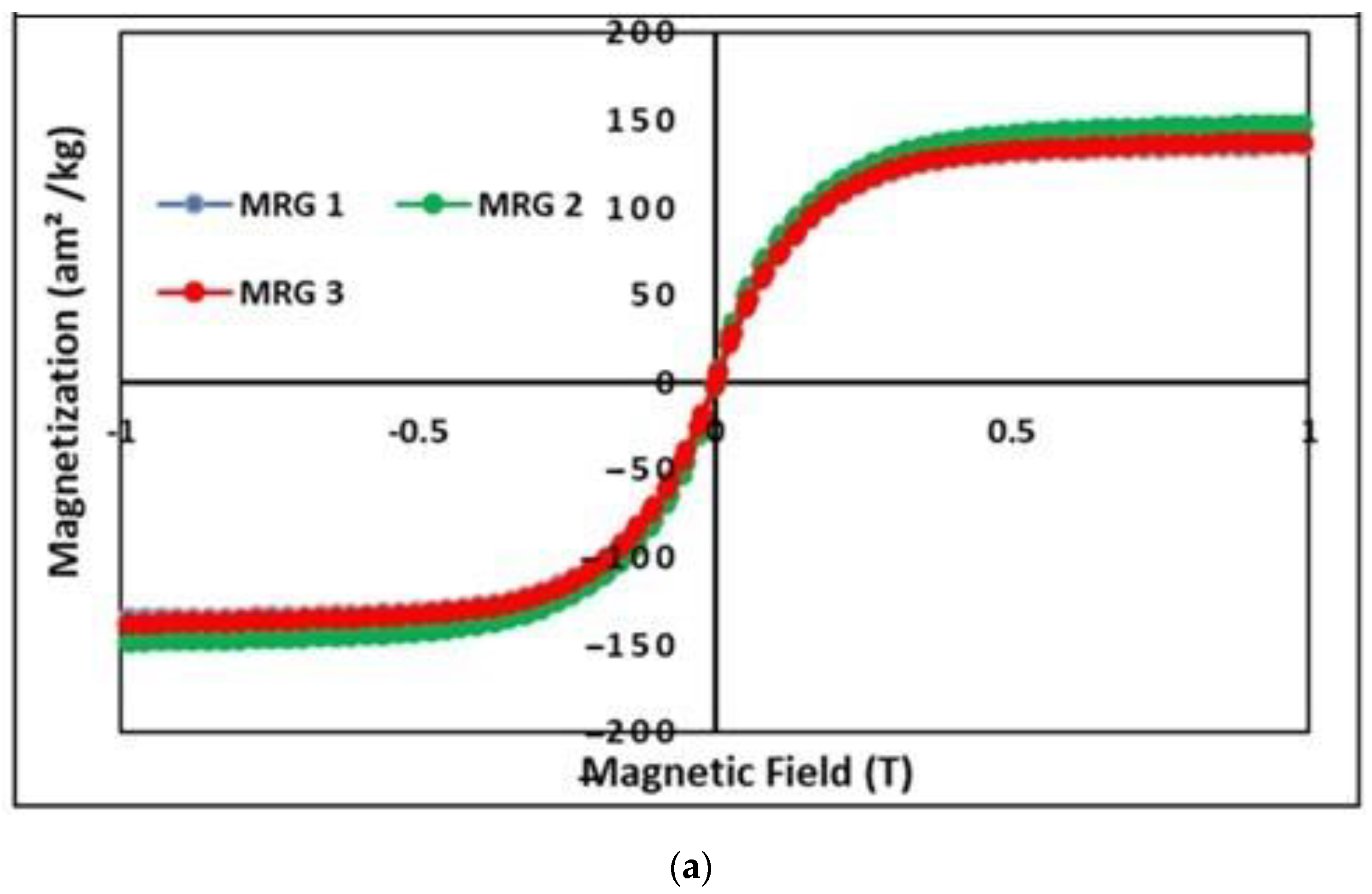



| Sample | Grease (wt%) | CIP (wt%) | Hydraulic Oil (wt%) | Kerosene Oil (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRG 1 | 30 | 70 | - | - |
| MRG 2 | 20 | 70 | 10 | - |
| MRG 3 | 20 | 70 | - | 10 |
| Samples | Magnetic Flux Density (T) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current (A) | ||||
| 0 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 1.2 | |
| MRG 1 | 0 | 0.082 | 0.168 | 0.253 |
| MRG 2 | 0 | 0.081 | 0.167 | 0.251 |
| MRG 3 | 0 | 0.074 | 0.153 | 0.231 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdul Kadir, K.A.; Nazmi, N.; Mohamad, N.; Shabdin, M.K.; Adiputra, D.; Mazlan, S.A.; Nordin, N.A.; Mohd Yusuf, S.; Ubaidillah. Effect of Magnetorheological Grease’s Viscosity to the Torque Performance in Magnetorheological Brake. Materials 2022, 15, 5717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165717
Abdul Kadir KA, Nazmi N, Mohamad N, Shabdin MK, Adiputra D, Mazlan SA, Nordin NA, Mohd Yusuf S, Ubaidillah. Effect of Magnetorheological Grease’s Viscosity to the Torque Performance in Magnetorheological Brake. Materials. 2022; 15(16):5717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165717
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdul Kadir, Khairul Anwar, Nurhazimah Nazmi, Norzilawati Mohamad, Muhammad Kashfi Shabdin, Dimas Adiputra, Saiful Amri Mazlan, Nur Azmah Nordin, Shahir Mohd Yusuf, and Ubaidillah. 2022. "Effect of Magnetorheological Grease’s Viscosity to the Torque Performance in Magnetorheological Brake" Materials 15, no. 16: 5717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165717
APA StyleAbdul Kadir, K. A., Nazmi, N., Mohamad, N., Shabdin, M. K., Adiputra, D., Mazlan, S. A., Nordin, N. A., Mohd Yusuf, S., & Ubaidillah. (2022). Effect of Magnetorheological Grease’s Viscosity to the Torque Performance in Magnetorheological Brake. Materials, 15(16), 5717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165717








