Abstract
Significant efforts have been made to improve adsorbents capable of eliminating pollutants from aqueous solutions, making it simple and quick to separate from the treated solution. In the current study, the removal of Crystal Violet Dye (CVD) from an aqueous synthetic solution onto a marine diatom alga, Skeletonema costatum, was investigated. Different experiments were conducted as a function of different pH, contact time, adsorbent dosage, temperature, and initial CVD concentration. The highest adsorption efficiency (98%) was obtained at 0.4 g of S. costatum, pH 3, and a contact time of 120 min, at 25 °C. Furthermore, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) results display that binding of CVD on S. costatum may occur by electrostatic and complexation reactions. Moreover, the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area analysis (BET) obtained was 87.17 m2 g−1, which, in addition to a scanning electron microscope (SEM), reveals large pores that could enhance the uptake of large molecules. However, the equilibrium adsorption models were conducted by Halsey, Langmuir, Freundlich, Henderson, and Tempkin isotherm. In addition, multilayer adsorption isotherm best described the uptake of CVD onto S. costatum. The maximum monolayer adsorption capacity (qmax) was 6.410 mg g−1. Moreover, thermodynamic parameters of the adsorption studies suggested that the uptake of CVD onto S. costatum was endothermic and spontaneous. The pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, and intra-particle diffusion kinetic equations were applied to model the adsorption kinetic data. It was seen that the kinetics of the adsorption may be described using pseudo-second-order kinetic equations. Finally, the present work concluded that the marine diatom alga S. costatum is suitable as a natural material for the adsorption of CVD.
1. Introduction
Water is a necessary component of life and is utilized by almost all living things on the world’s surface [1]. It is also a valuable resource in world economies because agriculture and other commercial uses consume around 70% of freshwater [2,3]. The untreated discharge of synthetic dyes from the industrial sector (textiles, printing, dyeing cosmetics, paints, plastic, rubber, leather, food, etc.) is a major concern for researchers working on wastewater pollution protection [4,5]. Moreover, industrial wastewater mainly contains several organic complicated molecules and dyestuff which are discharged into highly dyed wastewater, which has caused critical environmental concerns globally [6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. Intensive technological and industrial development, along with the increase in other human activities, has led to the overuse of water resources and increased water pollution [7,13]. The textile industry is the main industry that utilizes dyes causing the main source of water pollution, which poses a threat to aquatic life and human life [14,15]. Therefore, dye removal from wastewater poses a challenge to prevent dyes from causing harm to the environment [8], especially to aquatic biological systems [16]. To manage the problems of water pollution, numerous physical, chemical, and biological approaches to decomposing many textile dyes were used over the latest years [8]. For example, advanced oxidation processes, nanofiltration, photocatalytic degradation, adsorption, and biological treatment are among the technologies used to remove organic pollutants [2,17,18,19]. The primary objective of these strategies was to reduce damaging dyes into non-toxic end products, but most of them failed, since the end compounds were more toxic than the primary dyes [20,21]. Among these technologies, adsorption has grown as an effective biological and economical technique for decontamination of organic pollutants from wastewater [22,23,24,25,26]. Sharma et al. [26] reported that adsorption is considered a potential technique because of its ease of operation and relatively low cost of application required for wastewater pollution removal.
There has been a lot of attention recently to converting marine biomass applications into value-added products [27,28,29], especially sorbents, to reduce the impacts of environmental pollutants [23]. Recently, algal cells (microalgae and/or seaweeds) are one of the most important low-cost, eco-friendly, sustainable, and biologically promising technologies for dye and pollutant removal from aqueous solutions [8,30,31]. Algal cells have a long history of bioremediations of toxic dyes and/or water pollutants [32,33,34]. Generally, due to their biomolecules, bioactive compounds, and their functional groups, algae are the richest organisms in our world that can serve and be utilized in several bio-industries, such as human food supplements, animal feeds, bio-pharmaceuticals, bio-cosmetics, bio-fertilizers, fine-biochemicals, bio-energy, and bio-plastic, etc. [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46]. Microalgae have a great prospect of interacting with water pollutants as a major producer in the food chain and a major player in the balance of the marine ecosystem [47,48,49]. Additionally, the use of dead organisms in adsorption is more beneficial for the treatment of water, since dead microorganisms are not affected by harmful wastes, do not necessitate a constant supply of nutrients, and can regenerate and be reused numerous times [50]. Dead cells can be kept or used for a long time at room temperature without putrefaction taking place. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that dead cells acquire contaminants to an equal or greater degree than developing or resting cells [51]. The use of dead biomass in powdered form in the column does, however, present several challenges, including the difficulty of easily separating the biomass after adsorption, mass loss after regeneration, low strength and density, and small particle size, which make it challenging to utilize them in column applications. Dead biomass can be immobilized in supportive material to address these issues [52].
The marine diatom Skeletonema costatum is a chain of microalgal cells extensively used in marine hatcheries as live feed for marine larvae [53,54,55]. In addition, S. costatum species have many bioremediation advantages in adsorbing several pollutants from the aquatic environment, in a process that is simple, easy to observe, and sensitive to toxins [56,57]. The bioremediation process of S. costatum is carried out via passive transport, through the cell wall, and an active transport mechanism [3,58]. The S. costatum cell wall contains numerous functional groups, such as amine, hydroxyl, carboxyl, phosphate, and thiol groups. These functional groups, mainly negatively charged, can react with the positively charged ions of many pollutants [56,59]. The dye removal, especially by using algae, may be attributed to the accumulation of dye ions on the surface of algal biopolymers and further to the diffusion of the dye molecules from the aqueous phase to the solid phase of the biopolymer [60]. Extracellular polymers consist of surface functional groups, which enhance the sorption of the dye molecules onto the surface of the polymer (floc) during the dye removal process [61].
Crystal violet dye (CVD) is mainly used during the manufacturing process to dye cotton, silk, inks, and paints [62]. The protein CVD is used to detect bloody fingerprints. CVD is also applied throughout many kinds of adhesive taps for latent printing. Gram’s stain is frequently employed in the demonstration and basic classification of dyes [22]. CVD is also used to create vibrant dyes [18,63]. It is carcinogenic and has been classified as a recalcitrant molecule, since it is poorly metabolized by microbes, it is non-biodegradable, and it can persist in a variety of environments [64]. Furthermore, biological waste materials, eco-friendly behavior, and the possibility of reusability or regenerating to find low-cost adsorbent materials and reactivity, thus acting as suitable adsorbents, have been considered [65,66].
The objective of the present research was to explore the possibility of using the marine diatom alga Skeletonema costatum as an adsorbent for dye elimination, for example, CVD, a widely used dye in the textile-processing industry. The impact of experimental parameters such as pH, contact times, adsorbent dosages, temperatures, and initial dye concentrations on the adsorptive capacity of the adsorbent was examined. On the other hand, thermodynamic properties, equilibrium adsorption isotherms, and adsorption kinetics were examined by using conventional theoretical methods to investigate the adsorption mechanism. Moreover, the industrial wastewater and seawater applications, regeneration, and reusability have been studied. Therefore, in this study, this material was selected to investigate its ability to remove toxic dyes. However, even though there is literature on the marine diatom alga Skeletonema costatum as an adsorbent for the removal of heavy metal ions, where the previous studies showed the insufficiency of the use of this material in removing toxic dyes from wastewater, this work shows an experimental study on the removal of dyes, especially CVD, by using this novel material. Since it considerably improved the adsorption effectiveness of the specified dyes, it was chosen for the following investigation to cover the gap in the literature. Therefore, the current work aims to create a high-performance, environmentally friendly powder adsorbent from Skeletonema costatum culture for the removal of CVD from an aqueous solution. Furthermore, Skeletonema costatum was considered due to its novelty, which may easily be regenerated and recycled, which makes it applicable for treatment processes. Moreover, the highest suitable model was achieved by using error functions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Skeletonema costatum
The marine diatom alga Skeletonema costatum was identified and isolated previously from the Eastern Harbor of Alexandria Coast (31°13′48″ N; 29°53′12″ E), close to the National Institute of Oceanography and Fisheries (NIOF), Egypt. An isolated diatom strain, S. costatum (cell size from 2 to 5 μm), was cultured at an indoor scale under standard conditions of temperature (22 ± 2 °C), salinity (34 ± 1 ppt), continuous illumination (3500 ± 500 Lux), and continuous aeration. After a batch culture in conical flasks (1 L) filled with F/2 standard Guillard medium [67], the culture cells were harvested by centrifuge (3000× g. 10 min−1) at the late exponential phase on day 5. The harvested biomasses were dried (at 55 °C for 48 h) and preserved at −20 °C for further applications.
2.1.2. Crystal Violet Dye (CVD)
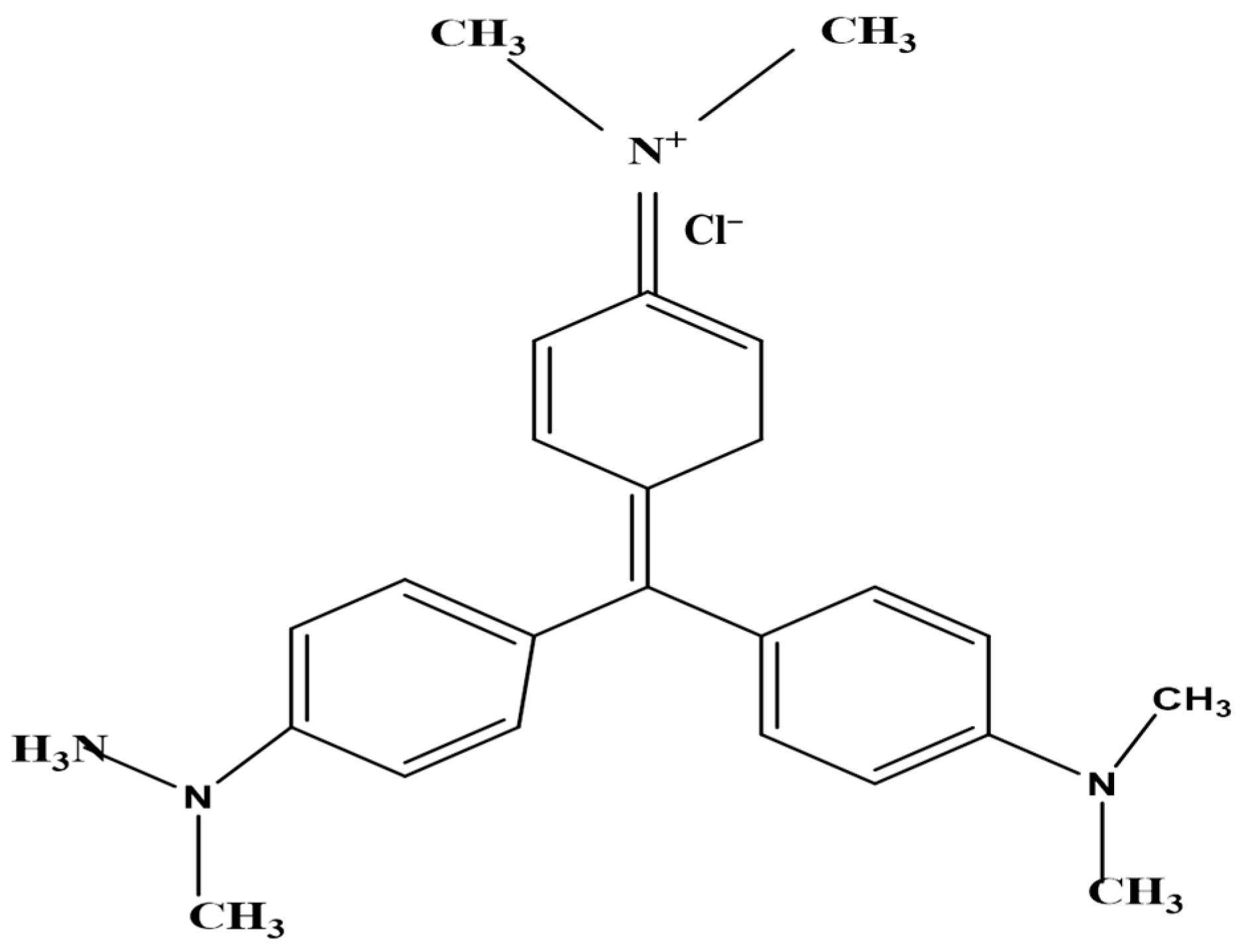
The adsorbate, crystal violet (CV) dye, was a basic, acquired from Daystar, Mumbai, India (basic dye, C.I. 42555, max. abs. = 588 nm, molecular formula C25H30N3Cl and standard purity (97.5% specified)) (Figure 1). Distilled water was used to obtain the desired concentrations. The original pH of the dye solution was 2.0. The maximum absorbance of the dye solutions was monitored using a spectrophotometer to determine their concentrations (Milton Roy, spectronic 2ID).
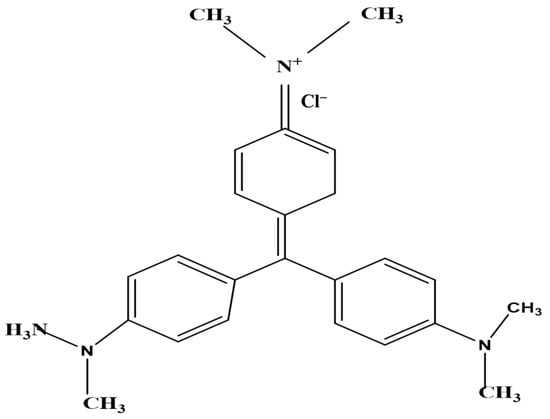
Figure 1.
The chemical structure of the crystal violet dye (CVD).
2.1.3. Chemical and Reagents
The chemicals used in the adsorption study, including sodium hydroxide (NaOH, 98.6%) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4, 98%), were obtained from Fisher Scientific (Fisher Scientific, Montreal, QC, Canada). All the applied chemicals throughout this study were analytical-grade reagents.
2.2. Methods
Batch Adsorption Process
Batch adsorption trials were done in a shaker at various ranges of parametric conditions. Optimization reactions were achieved for pH factors in the range 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11, initial CVD concentration influence in the range 5, 10, 15, 20, and 40 mg L−1, the contact time parameter (15, 30, 60, 120, and 180 min), biomass amount (0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4 g), and temperature influence at 25, 35, 45, and 55 °C. For these aims, the used bottles were shaken at a controlled temperature (25 °C), using an orbital shaker (Orbital incubator model SI50, Stuart Scientific, Redhill, UK) for the minimal contact time necessary to achieve equilibrium, as indicated by the kinetic data, with an agitation rate of 110 rpm.
The efficiency of the treatment was assessed to determine the concentration using the UV–visible spectroscopic method at 588 nm (Milton Roy, Spectronic 21D, Houston, TX, USA). The impact of pH was evaluated by modifying the reaction mixture to various initial values of pH and evaluating the remaining color at the equilibrium contact time. Liquid solutions of NaOH and H2SO4 were utilized to regulate the needed values of pH. The percentages of removal and qe (mg g−1) of CVD onto S. costatum were calculated, as described by Ghoneim, et al. [68], as the following:
where Ci and Cf are the initial and the final CVD (mg L−1), respectively; W is the quantities of S. costatum adsorbent (g); and V is the solution volume (L).
For kinetic observations, 10 mL flasks containing CVD (5 mg L−1) and the adsorbent (0.05 g) were exposed to agitation for numerous contact time intervals. At regular intervals, the flasks were removed from the shakers, and the remaining concentration of CVD solution was calculated.
2.3. Characterizations
Before and after the adsorption process, the surface morphology of the adsorbents was characterized via a Scanning Electron Microscope, SEM (JSM-IT200 with an accelerating voltage of 20.0 kV at a magnification ×2000). The samples were coated with platinum to prevent charging. On the other hand, the functional groups of the adsorbents, as well as a binding mechanism (s), were conducted using a Fourier-transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) (Thermo Nicolet 6700). Furthermore, in this study, quantachrome instruments (cyl. pore) (NLDFT Ads. model) were used to examine the surface area of the raw adsorbent at 77.35 K.
2.4. Data Analysis
The normality and homogeneity assumptions were performed before the statistical analysis of the data. The experiments were applied in triplicates and the obtained data were presented in the form of means ± standard deviation (SD, n = 3). Before analysis, all results in percentages were arcsine transformed [69].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. S. costatum (Adsorbent) Characterization
3.1.1. SEM
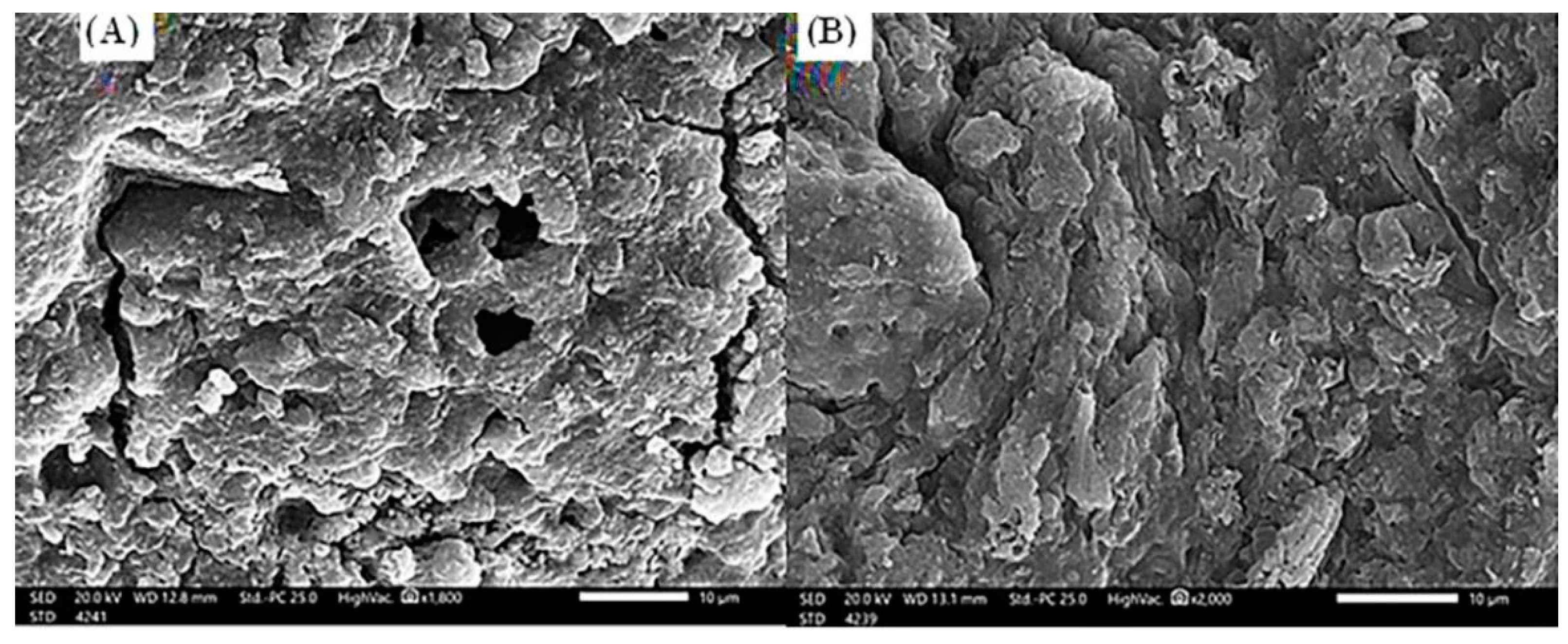
The scanning electron microscope investigations of S. costatum, before and after the adsorption process (Figure 2), concluded that the adsorbent (Figure 2A) has an irregular and heterogeneous surface morphology with a well-developed porous structure. Moreover, pores of several sizes and shapes were determined. The presence of these fine particles leads to an increase in the surface area and the porosity of S. costatum [70]. After adsorption of CVD (Figure 2B), the remarkable changes were investigated in the morphological structure of CVD-loaded S. costatum, revealing an irregular surface with a molecular cloud of the CVD, where the CVD may be adsorbed and trapped. The higher the porosity, the higher the adsorption capacity [17].
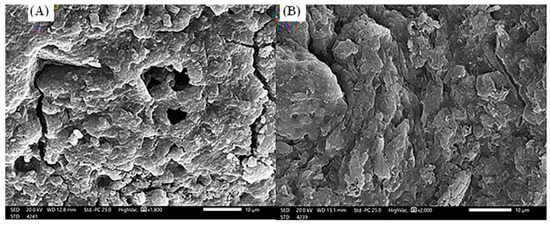
Figure 2.
Scanning electron microscope (20.0 kv, ×2000) of S. costatum adsorbent before (A) and after (B) adsorption of CVD.
3.1.2. FTIR
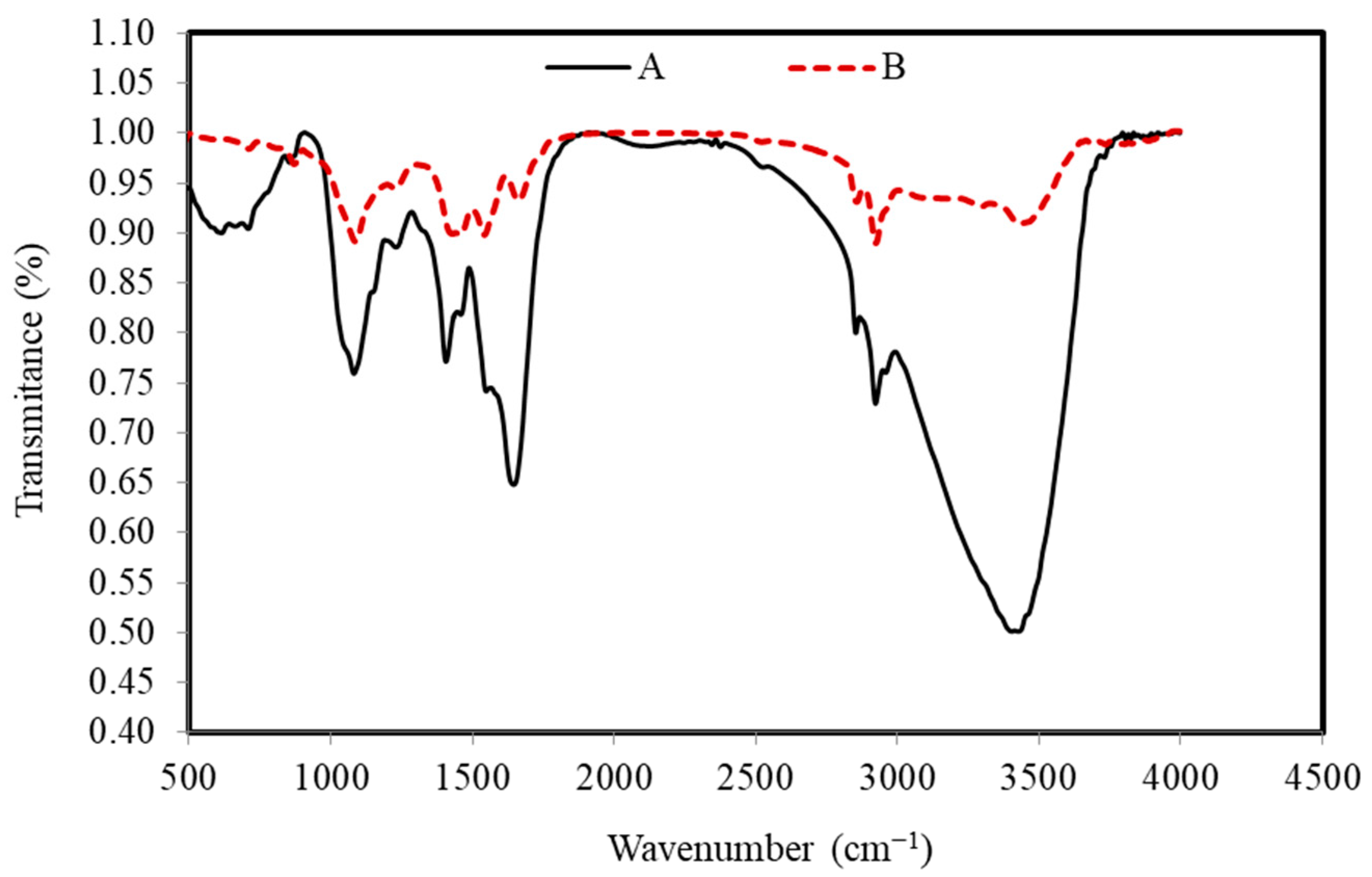
FTIR spectra of the S. costatum before and after the adsorption process confirmed that there are several functional groups, as shown in Figure 3.
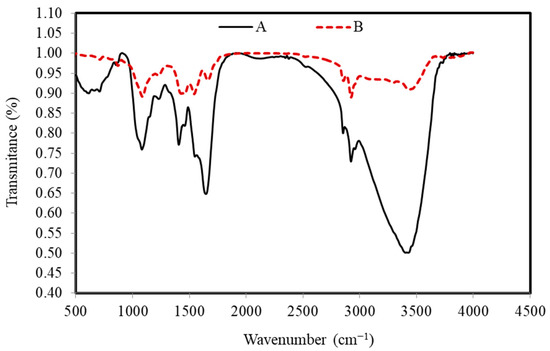
Figure 3.
FTIR peaks of the S. costatum adsorbent before (A) and after (B) adsorption of CVD.
The wide peaks, which are located at around 3403, 3295, and 3495 cm−1, are typically due to adsorbed water and/or the groups of hydroxyl [64]. The bands that existed around 2922 and 2856 cm−1 correspond to C–H vibrations of methyl and methylene groups. However, the band around 1645 and 1662 cm−1 generally happened by the stretching vibration of C=O carboxyl groups, while the bands around 1548 and 1542 cm−1 are ascribed to the aromatic ring or C=C stretching vibration [71]. In addition, the bands at around 1406 and 1458 cm−1 correspond to the C–H in-plane bending vibrations in methylene and methyl groups. The band at 1227–1230 cm−1 corresponds to C–C stretching in alkanes and a comparatively intense band at about 1081 and 1081 cm−1 can be assigned to C–O stretching vibrations in alcohols. The C–H out-of-plane bending vibrations cause the bands at 853 and 871 cm−1. Disappearance and band shifting from 1406 to 1457 cm−1 are determined in the CVD-adsorbed S. costatum attributed to the stretching of C=C modes of the benzene ring of lignin. Transmittance at wave number 3429 cm−1 is found to be shifted to 3403 cm−1 on adsorption and this perhaps assumes the responsibility for the chemical reaction of the CVD with O–H groups on the adsorbent. Several bands were found in the region of 1000–500 cm−1, which is perhaps attributed to the C–H stretching. From FTIR observations, CV dye ions may interact with the active surface of S. costatum adsorbents, resulting in the creation of new absorption bands, changes in absorption strength, and a movement in the wavenumber of functional groups. CVD ions bound to the active sites of the S. costatum adsorbents through complexation mechanism and electrostatic attraction. In addition, the electrostatic attraction was between carbonate groups and CVD ions. Furthermore, the complexation mechanism engaged in sharing the electron pair between electron donor atoms (N and O). The current work determined that carbonate, carbonyl, hydroxyl, and amine are the primary adsorption sites in S. costatum adsorbents. Another study found that Cu adsorption by S. costatum has a high percentage of removal due to the same functional groups being responsible for the adsorption process, which were mainly carboxyl, hydroxyl, and amine, as well as, thiol and phosphate groups, as reported by Pratama et al. [56,57,59].
3.1.3. BET
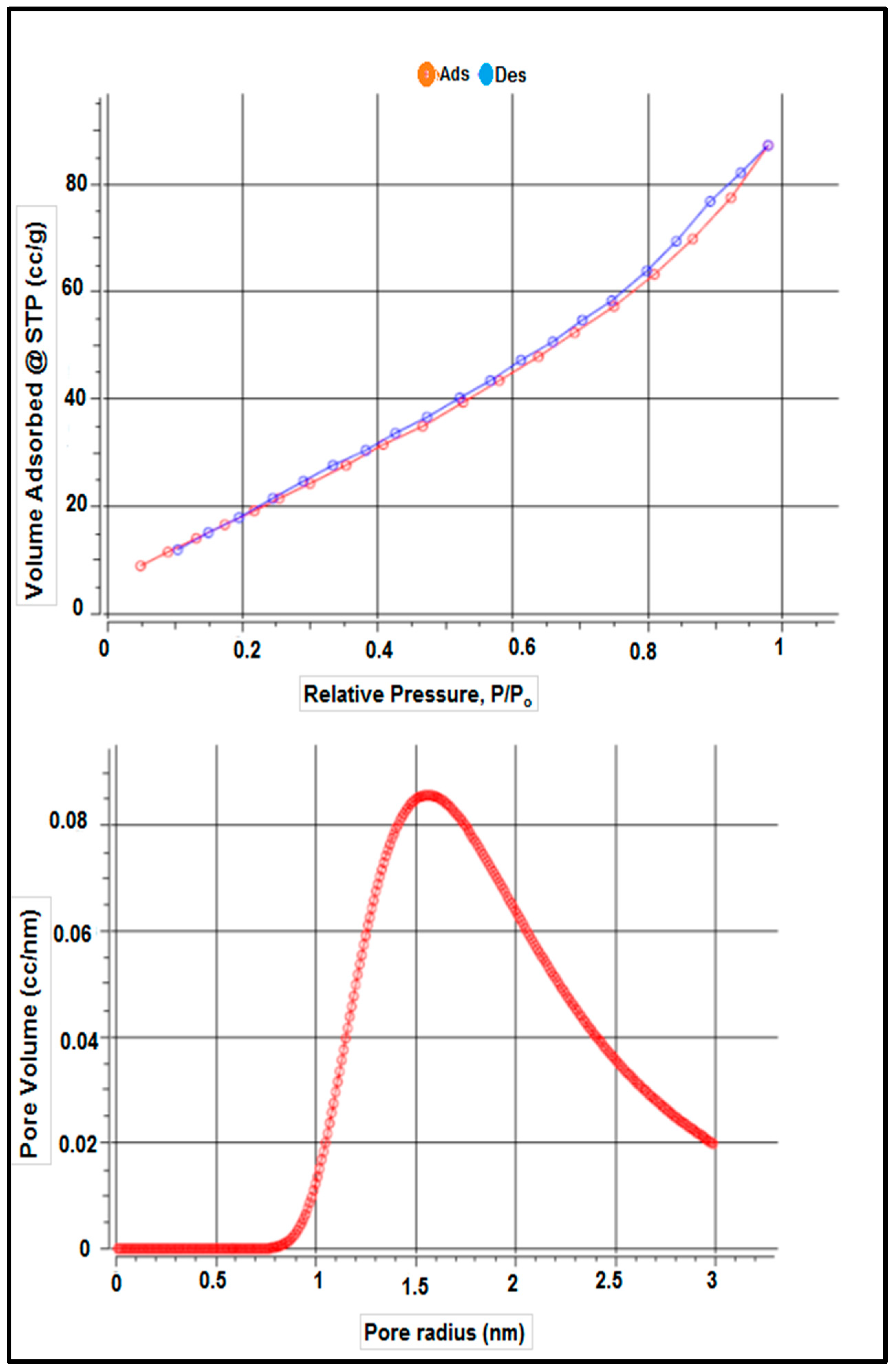
Table 1 shows the surface characteristics of the dry adsorbent employed in this investigation based on adsorbent-specific surface area characterization using the BET technique, according to nitrogen adsorption and desorption isotherms. Table 1 and Figure 4 show the adsorbent’s surface area was 87.172 m2 g−1, as determined by the results. The total pore volume and average pore size of S. costatum were also evaluated and found to be 0.103 CC g−1 and 3.131 nm, respectively.

Table 1.
Physical properties of S. costatum.
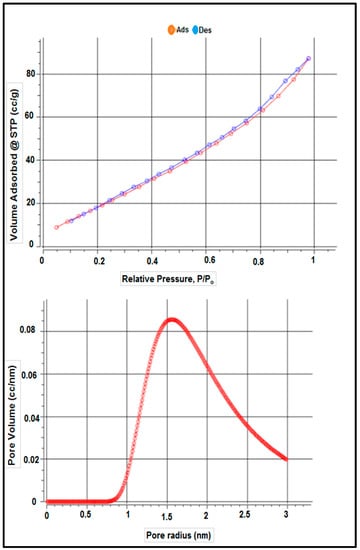
Figure 4.
Isotherm–Isotherm isotherms and the pore size distribution.
3.2. Adsorption Studies
3.2.1. pH
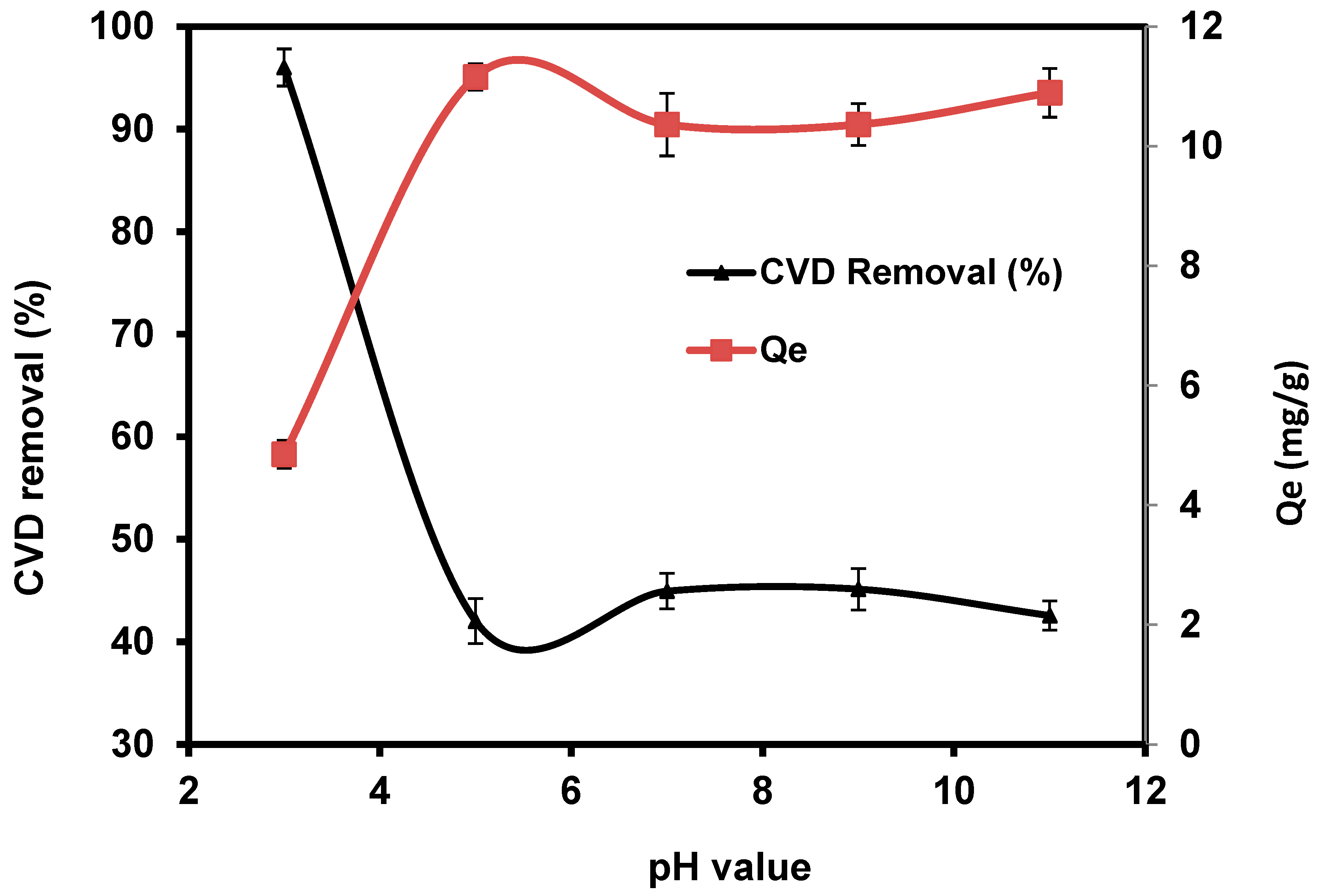
The pH value is an important parameter affecting the removal uptake of toxic pollutants from wastewater due to the variation of H+ and OH− in the treatment medium [72]. The effect of solution pH on adsorption of CVD on S. costatum was studied by varying the pH of the dye solution for an initial concentration of 5 mg L−1, while the adsorbent dosage, contact time, agitation speed, and temperature were fixed at 0.4 g/50 mL, 180 min, 110 rpm, and 25 °C, respectively. The obtained results indicate that the adsorption process of CVD was favorable in an acidic medium, as shown in Figure 5.
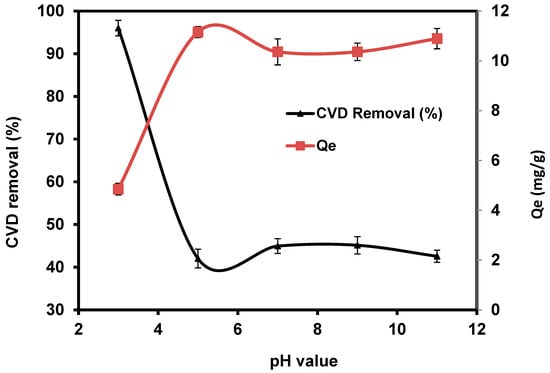
Figure 5.
Impact of pH values on the adsorption of CVD onto S. costatum.
Dye removal efficiency decreased when the pH increased from 5 to 11, indicating that pH did not significantly affect the percentage of CVD removal, particularly under alkaline conditions. The highest percentage of CVD uptake was obtained at pH 3, with a percentage removal of 96%. CVD is based on chromophores combined with several kinds of reactive groups that react with the active functional groups of S. costatum, such as chitin, carboxyl, hydroxyl, acidic polysaccharides, amine, and the other functional groups [57,59]. Higher removal observed at low pH values is perhaps attributed to the electrostatic appeal between negatively charged CVD anions and positively charged S. costatum cell surface [73]. Furthermore, as the pH value increases, the adsorption of CVD decreases because of competition between the anionic dye and excess OH− ions in the solution [74]. According to Wu et al. [75], the amount of adsorption decreased because the negatively charged adsorbent gave fewer effective sites for adsorption as repulsive forces increased. Following that, adsorption experiments were carried out at the optimal pH.
3.2.2. Adsorbent Dose of S. costatum
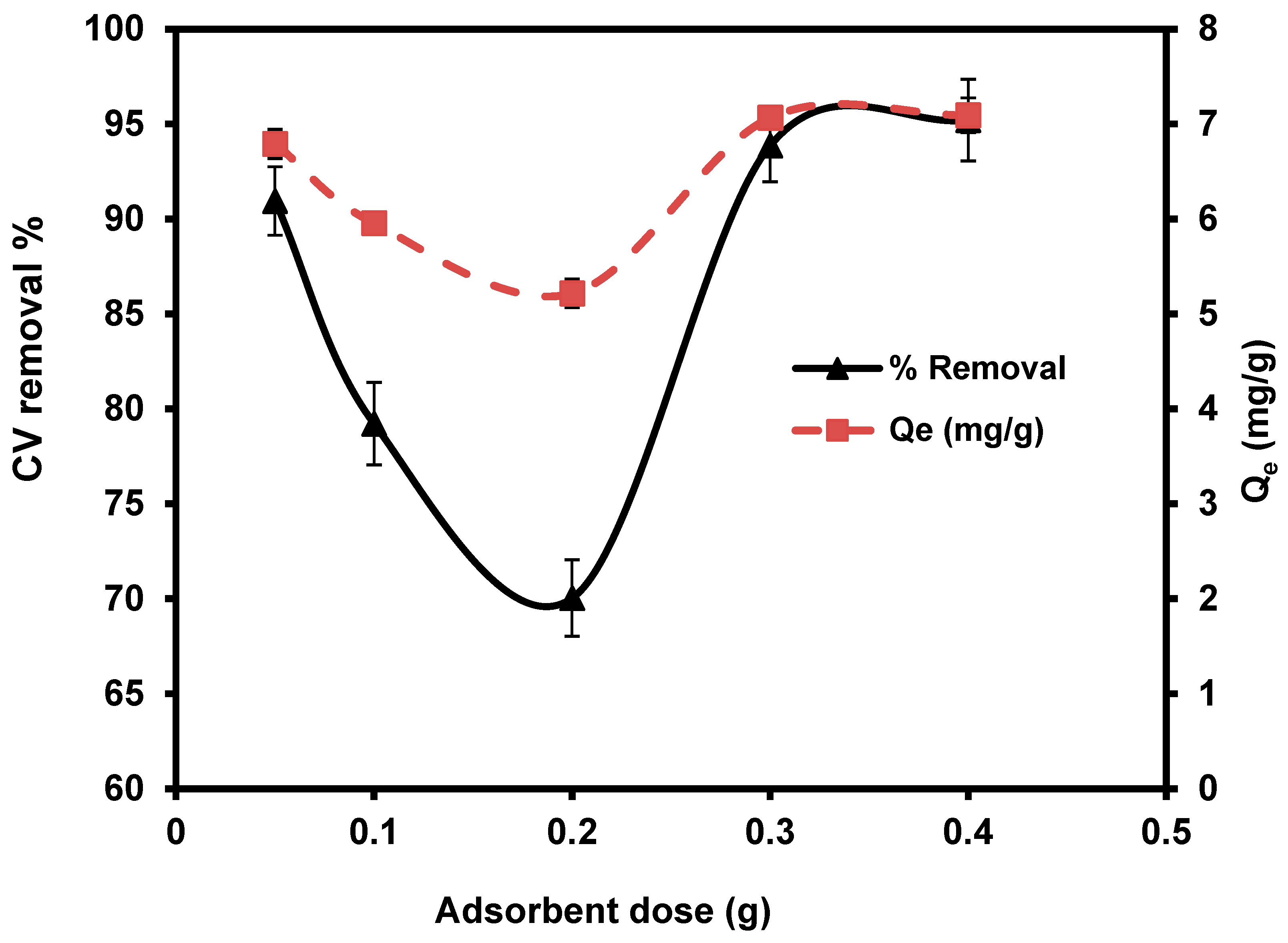
The effect of different S. costatum levels (0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4 g/50 mL) were studied at 25 °C, for 180 min. With the increasing doses of S. costatum, the quantities of CVD adsorption and the percentage of removal increased from 90.90% to 95.20% and from 0.05 to 0.4g (Figure 6). This phenomenon can be attributed to an increase in the adsorbent-specific surface area and the availability of more adsorption sites [76]. Furthermore, this pattern might be described as a result of partial biomass agglomeration at increasing biomass concentrations, resulting in a reduction in the specific surface area of adsorption [77]. Only about a 3% increase was observed as the adsorbent dose was increased from 0.05 to 0.03 g; overlap of adsorption sites may describe the small increase in percentage adsorption. The decrease in the amount of CVD adsorbed qe (mg g−1) with increased adsorbent mass is attributed to a division of the flow or a concentration gradient between the solution and the absorbing surface. When S. costatum sorbent mass increases, the level of CVD that is adsorbed onto the unit weight of S. costatum decreases, resulting in a drop in the qe value as the adsorbent mass concentration rises [78]. In the present study, the adsorbent dose of 0.4 g/50 mL is the optimal value for the removal of CVD.
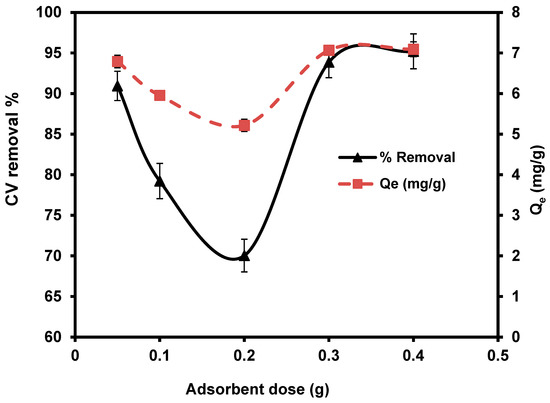
Figure 6.
Impact of S. costatum concentrations on the adsorption of CVD.
3.2.3. CVD Concentrations
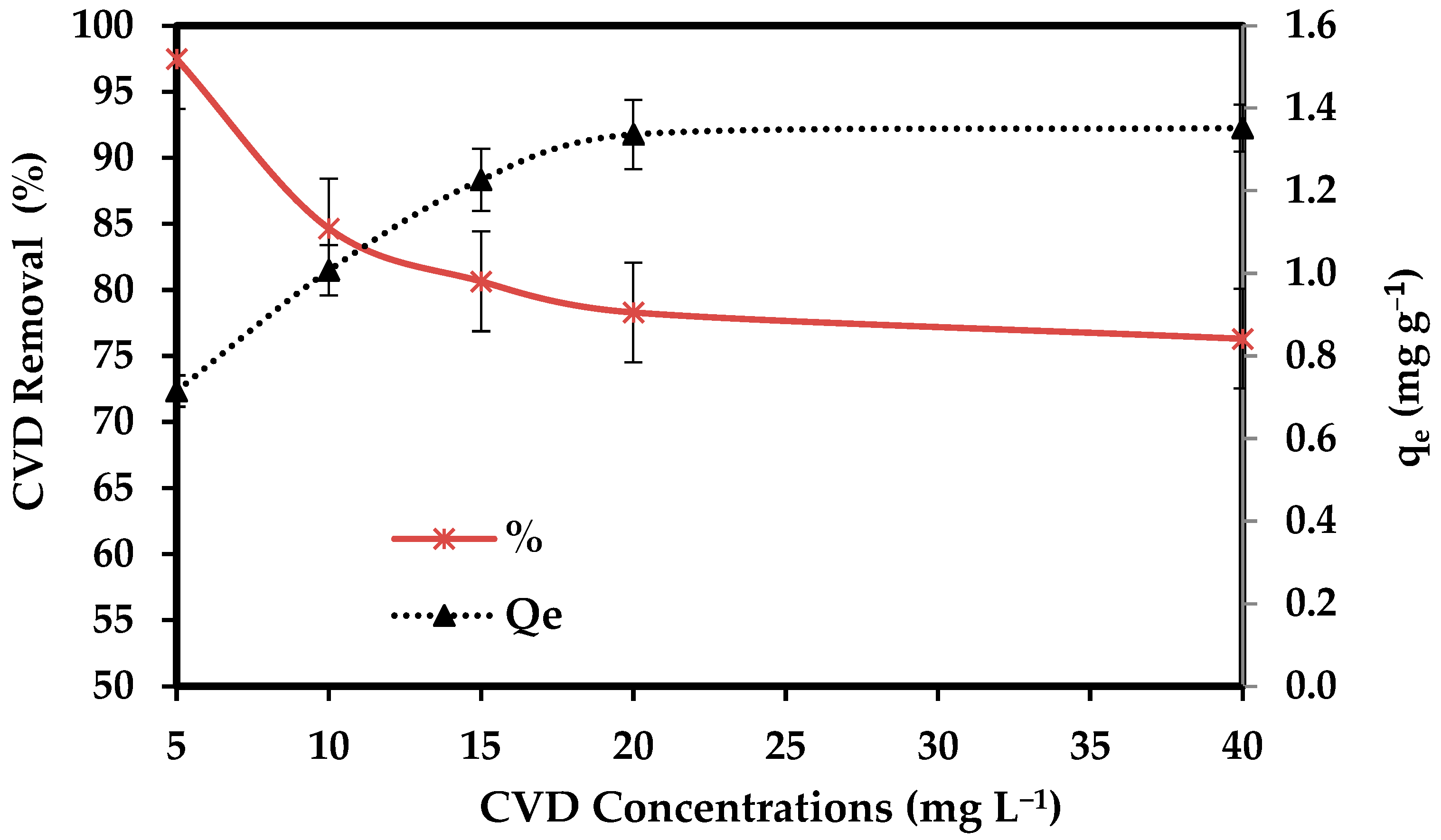
The effect of initial CVD levels (5, 10, 15, 20, and 40 mg L−1) on adsorption onto 0.1 g/ 50 mL of the dried S. costatum for a contact time of 3 h at 25 °C was investigated. Figure 7 shows that the uptake capacity and adsorption capacity of CVD by S. costatum increased with the increasing initial level of CVD. This increase in the amount of adsorption with increased initial CVD concentration may be due to the increased driving force that dominates the resistance of mass transfer of the CVD between the solid phase and bulk liquid phase [79].
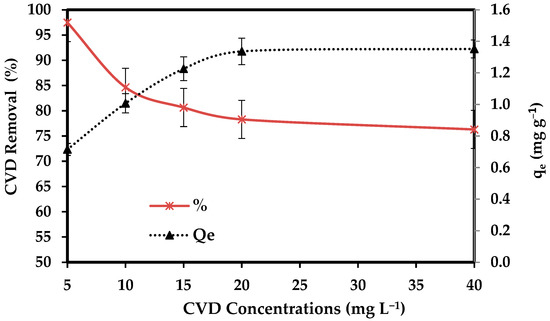
Figure 7.
Impact of CVD concentrations on the adsorption process.
Furthermore, the surface of the sorbent is bare in the initial stage; sorption happens quickly and is usually regulated by the diffusion process from the bulk to the surface. Since there are fewer sorption sites accessible at this stage, the sorption is most likely an attachment-controlled process. Increasing the initial concentration results in increased diffusion of more CVD molecules in the bulk solution towards the external surface of the S. costatum and enhanced interaction between crystal violet anions and the S. costatum surface leading to increased adsorption uptake of CVD. The adsorption typically starts rapidly and then gradually slows because when a significant number of vacant surface sites seem to have been able to adsorb at first, then it is always difficult to occupy the residual vacant surface sites due to repulsive forces between the CVD molecules on the S. costatum and the bulk phase [74]. The obtained data indicate that the efficiency of S. costatum in the removal of CVD was highly related to the initial concentration of CVD. Similar suggestions were reported by Alprol et al. [80], who indicated that the efficiency of A. platensis in the removal of IV2R was highly related to the initial concentration of IV2R. Inventor et al. [81] confirmed that initial quick adsorption is due to dye molecules contacting available surface adsorption sites, while the following gradual adsorption is due to dye molecules’ absorption into the pores of the adsorbents.
3.2.4. Contact Times
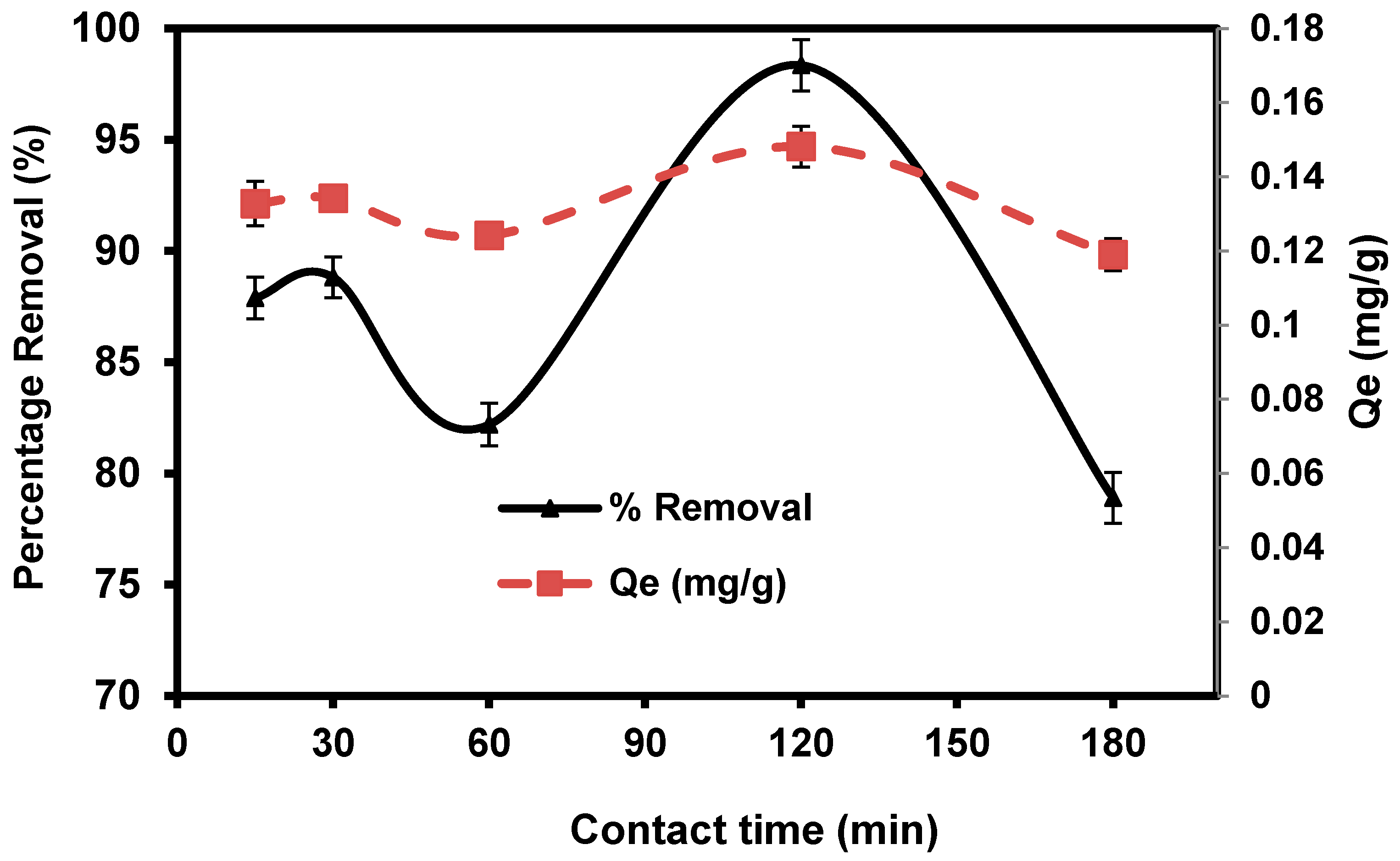
The practical efficiency of the adsorption technique in solution is largely based on the immersion time in the medium (i.e., contact time). Figure 8 illustrates the amount of CVD adsorbed onto S. costatum as a time function at 0.1 g/50 mL. CVD adsorptions were fast initially and gradually reduced over time until equilibrium was attained. Fast adsorption was observed within the first 15 min (87.88%) and then the adsorption rate of dye is high, which may be attributed to abundant adsorption sites, which attracted the dye particles from the bulk solution at the initial stages. The adsorption process becomes less efficient due to the gradual occupancy of these sites. In the figure, it is shown that the adsorption reaction nearly attained equilibrium within 120 min, after which no substantial amount of crystal violet was adsorbed with increasing contact time after equilibrium was achieved, indicating that all available sorption sites had been occupied [68]. Due to increased repulsive forces between dye molecules and the bulk solution, the occupation of the remaining unoccupied spots becomes increasingly difficult as time passes.
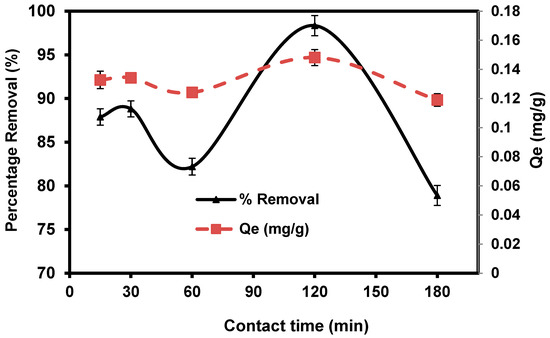
Figure 8.
Impact of agitating time in the percentage removal of crystal violet dye.
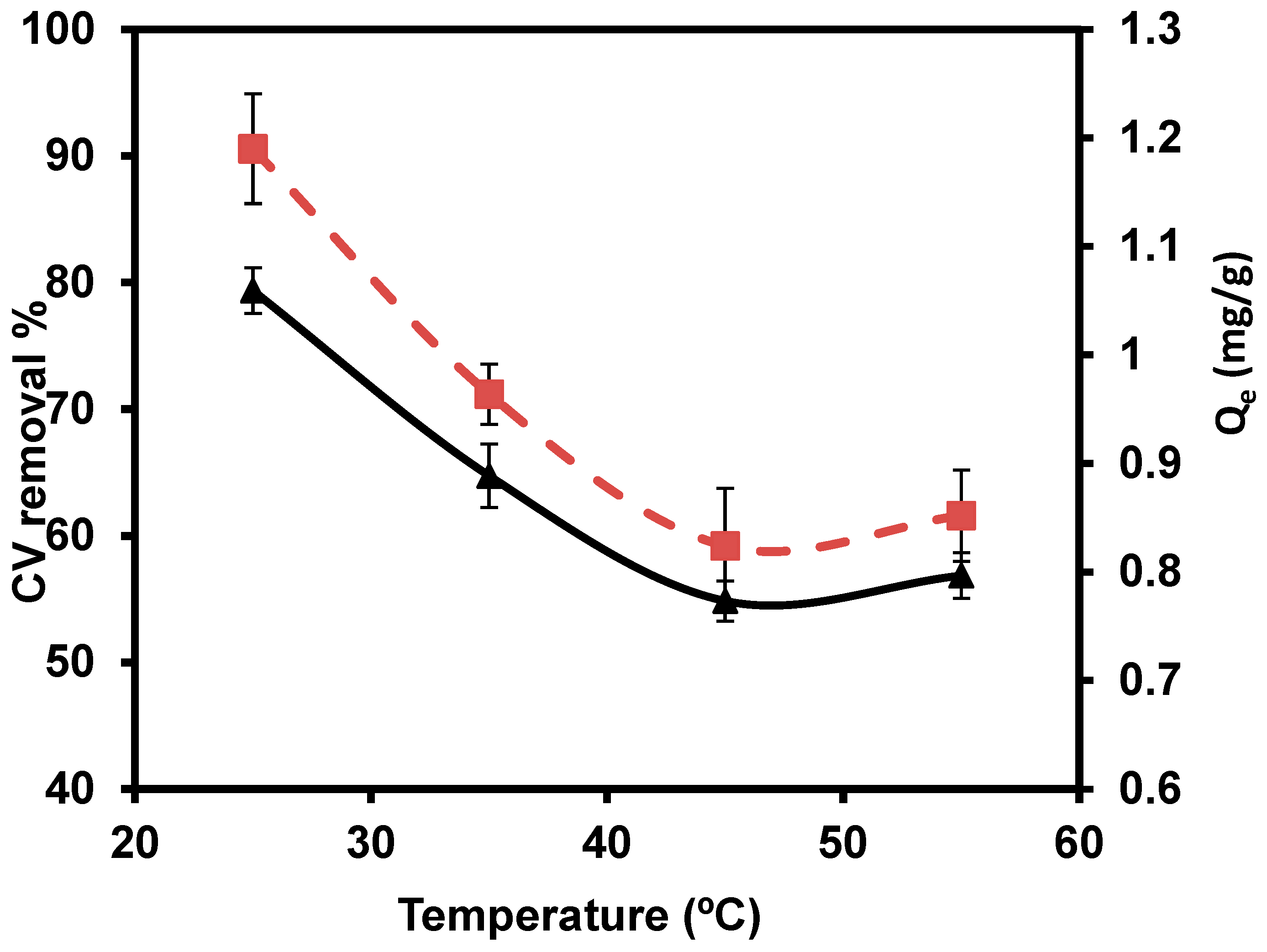
3.2.5. Temperature
The temperatures of 25, 35, 45, and 55 °C were studied with 0.1/ 50 mL (Figure 9). The maximum percentage removal (79.30%) of CVD was observed at 25 °C. Based on the relation between removal efficiency and temperature, the results reported that the CVD sorption takes place through the aggregation of the dimers and/or monomers of CVD. The dimeric or monomeric dispersed from the cellular membrane are perhaps trapped as an outcome of accumulation, even at a low equilibrium CVD level. The relative increase in dye level in the cell probably leads to aggregation. Aggregation is most likely caused by a relative rise in CVD concentration in the cell. Hence, the reduction of sorbed quantities at higher temperatures, perhaps due to deaggregation, is based on the relative increase in thermal motions of CVD aggregates [82].
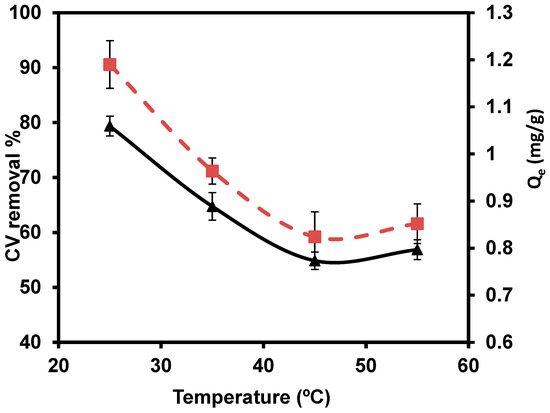
Figure 9.
Impact of several temperatures on the removal percentage of CVD.
3.3. Thermodynamics Properties
To investigate the thermodynamic properties and thermal impact on the adsorption process, several temperatures (25, 35, 45, and 55 °C) were conducted with 0.05 g/50 mL of S. costatum. Different parameters of thermodynamics such as entropy change (ΔS), enthalpy change (ΔH), and Gibbs free energy (ΔG) were calculated to determine the natural process of the adsorption, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
The calculated values of thermodynamic parameters of the adsorption of CVD onto S. costatum.
The magnitude of ΔG (kJ mol−1) was conducted using the following equation:
where R is the universal gas constant (0.008314 kJ mol−1 K); T is the absolute temperature (°K); and Ka is the adsorption equilibrium constant. ΔH (kJ mol−1) was calculated by the following equation:
A plot of ∆G against T was found to be linear and the value of ∆H and ∆S was calculated from the slope and intercept of the plots. The negative values of ∆G for S. costatum have confirmed the feasibility of the process and the spontaneous nature of adsorption. However, the values of ∆G were increased from −5.050 to −2.636 kJ mol−1 as the temperature increased from 25 to 55 °C. The values of ∆H and ∆S were calculated and are given as 8.636 kJ mol−1 and −0.036 kJ mol−1 K, respectively. Hossain et al. [83] and Subbareddy et al. [84] reported that the positive value of ∆H indicates that the adsorption reaction was endothermic, and the strong affinity of the S. costatum diatom for CVD ions suggests some structural changes in CVD ions and the S. costatum [85]. In addition, the negative value of ∆S also suggests that the adsorption was enthalpy-driven and spontaneous [86]. Furthermore, the negative ∆S reflected the affinity of the S. costatum for the CVD and the decrease of randomness at the solid/liquid interface occurring in the internal structure during the adsorption process [75,86]. The negative value of ∆S shows a decline in the degree of freedom of the adsorbed CVD ions [87].
3.4. Equilibrium Adsorption Isotherm
Adsorption isotherms are essential in calculating the maximum capacity and the kind of adsorption front that is produced. To characterize the equilibrium nature of S. costatum, various adsorption isotherms have been examined [82]. The data were fitted to the Freundlich and Halsey isotherm equations and the fixed parameters of the isotherm equations were calculated.
3.4.1. Langmuir Isotherm
The Langmuir model [88] assumes monolayer adsorption (the adsorbed layer is one molecule in thickness), with adsorption only occurring at a finite (fixed) number of definite localized sites that are identical and equivalent, with no lateral interaction and steric hindrance between the adsorbed molecules, even on adjacent sites. In its derivation, the Langmuir isotherm refers to homogeneous adsorption, in which each molecule possesses constant enthalpies and sorption activation energy (all sites possess an equal affinity for the adsorbate) [89]. The nonlinear form of the Langmuir equation was calculated by the following non-linear form (Lineweaver–Burk linearization of the Langmuir model—Type 2) [90]:
where qmax (mg g−1) is the maximum sorption capacity corresponding to the saturation capacity (representing the total binding sites of an adsorbent) and KL (L mg−1) is a coefficient related to the affinity among the adsorbent and dye ions.
qe = qmax KL Ce/(1 + KLCe)
The relationship was calculated from plotting curve (1/qe) vs. (1/Ce):
where KL and qmax are determined from the slope and intercept, respectively.
1/qe = 1/(KL qmax Ce) + 1/qmax
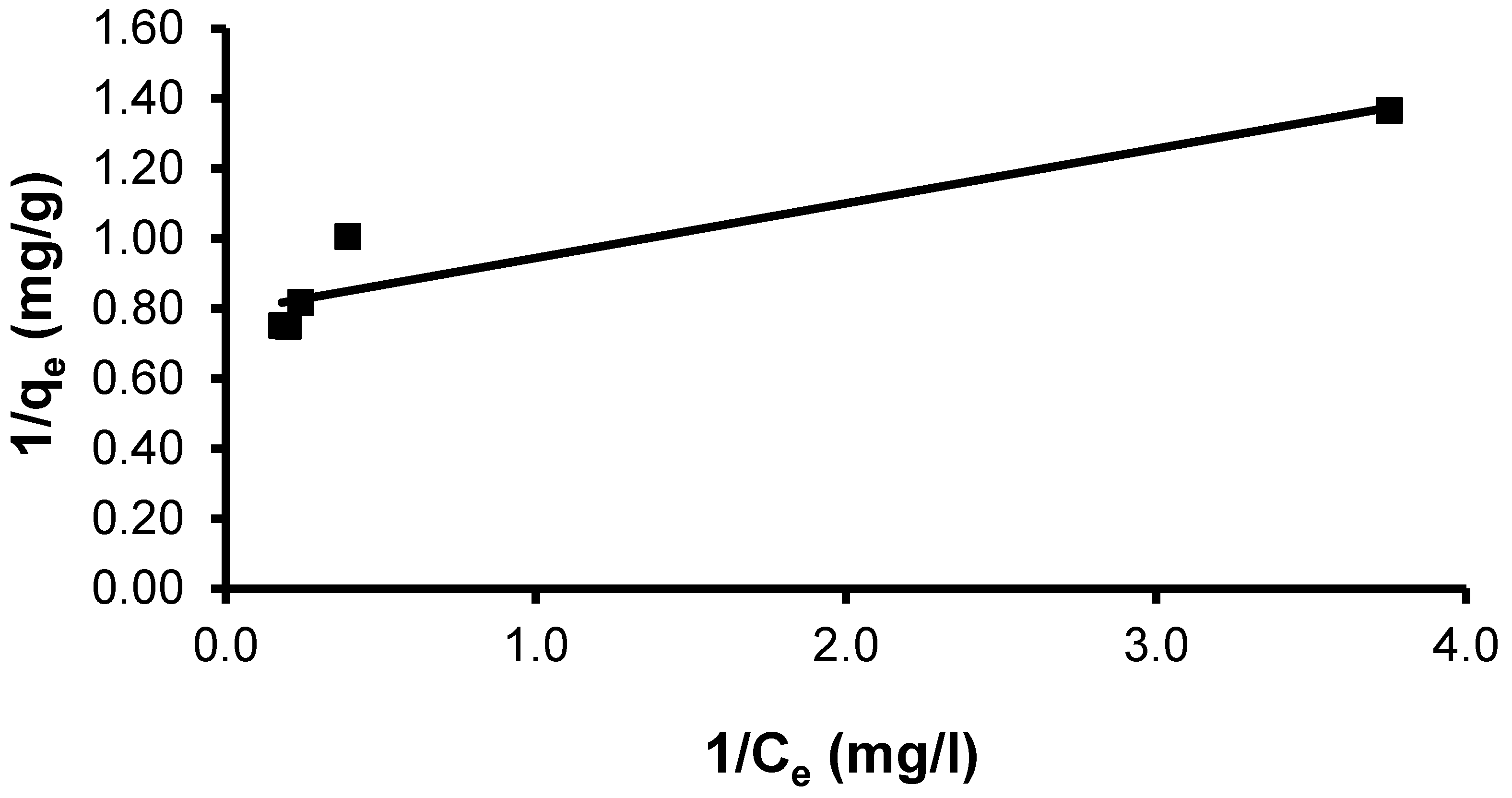
The CVD dye showed a maximal uptake capacity (qmax) of 17.76 mg g−1 by the S. costatum. The observed linear correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.876) indicates this model does not give a good fit to the adsorption process (Figure 10). The Langmuir constant (KL), which is related to the heat of adsorption, was found to be 5.06. The Langmuir constant KL can serve as an indicator of the strength or affinity of the sorbent for the solute [87].
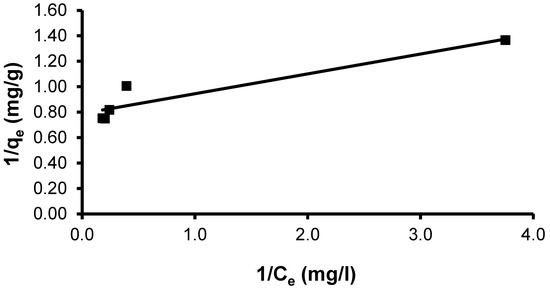
Figure 10.
Plot of the Langmuir isotherm model for CVD adsorbed onto S. costatum.
The essential characteristics of the Langmuir isotherms can be expressed in terms of a dimensionless constant separation factor or equilibrium parameter, RL, which is defined by Hall et al. [91]:
where Ci is the initial adsorbate concentration (mg L−1). The RL value indicates the shape of the isotherm, as shown in Table 3. RL values lie between 0 and 1, which indicates a favorable sorption isotherm for CVD. The RL was found to be 0.011.
RL = 1/(1+ KL Ci)

Table 3.
Relationship between RL and the type of isotherm [92].
3.4.2. Freundlich Isotherm
The Freundlich model can be applied to multilayer adsorption, with non-uniform distribution of adsorption heat and affinities over the heterogeneous surface [93]. Using the observed data of the S. costatum experiment, the feasibility of the empirical Freundlich isotherm was determined depending on sorption on heterogeneous surfaces, by plotting log (qe) versus log (Ce). The Freundlich adsorption isotherm was expressed in the equation as the following [94]:
Log qe = Log KF + 1/n LogCe
Freundlich constants KF and 1/n were determined from the isotherm equation according to Equation (9). Freundlich adsorption isotherm constants and correlation coefficients are shown in Table 4. As its value is closer to zero, the constant 1/n, which represents the intensity of dye adsorption onto the sorbent or surface heterogeneity, becomes more heterogeneous. The nF value reflects the degree of nonlinearity between solution concentration and adsorption in the following ways: if nF = 1, adsorption is linear; if nF < 1, the adsorption process is chemical; if nF > 1, the adsorption is a beneficial physical process [95]. The value of n was calculated to be 5.102, showing that the adsorption process is chemical. In addition, the value of 1/n (0.196) was found to lie between 0 and 1, indicating that CVD is confidently adsorbed by the S. costatum diatom adsorbent. Correspondingly, the obtained results fit with the data of the experiment of the Freundlich isotherm model, which was confirmed by a high correlation coefficient of R2 = 0.936 for the adsorbent (Figure 11). Therefore, the Freundlich isotherm can be employed to describe heterogeneous systems.

Table 4.
Factors of the isotherm models from linear solvation.
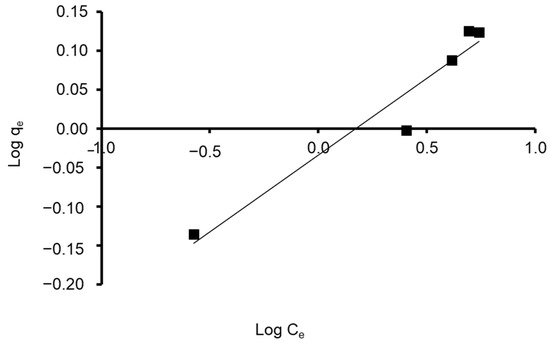
Figure 11.
Plot of the Freundlich isotherm model for CVD adsorbed onto S. costatum.
3.4.3. Tempkin Isotherm
According to the Tempkin isotherm model, the heat of adsorption for every molecule in the layer falls linearly with coverage as a result of adsorbent–adsorbate interactions. Additionally, the model assumes that adsorption is characterized by a uniform distribution of binding energies up to maximum binding energy [96].
The Tempkin isotherm was calculated from the following form [97]:
where A is the constant of equilibrium binding (L g−1) associated with higher binding energy, B = (RT/b) (J mol−1) is the Tempkin constant and is related to the heat of adsorption and the gas constant (R = 8.314 J mol−1 K−1), and b (J mol−1) is a constant corresponding to the heat of sorption.
qe = B Ln A + B Ln Ce
qe = B Ln (AT Ce)
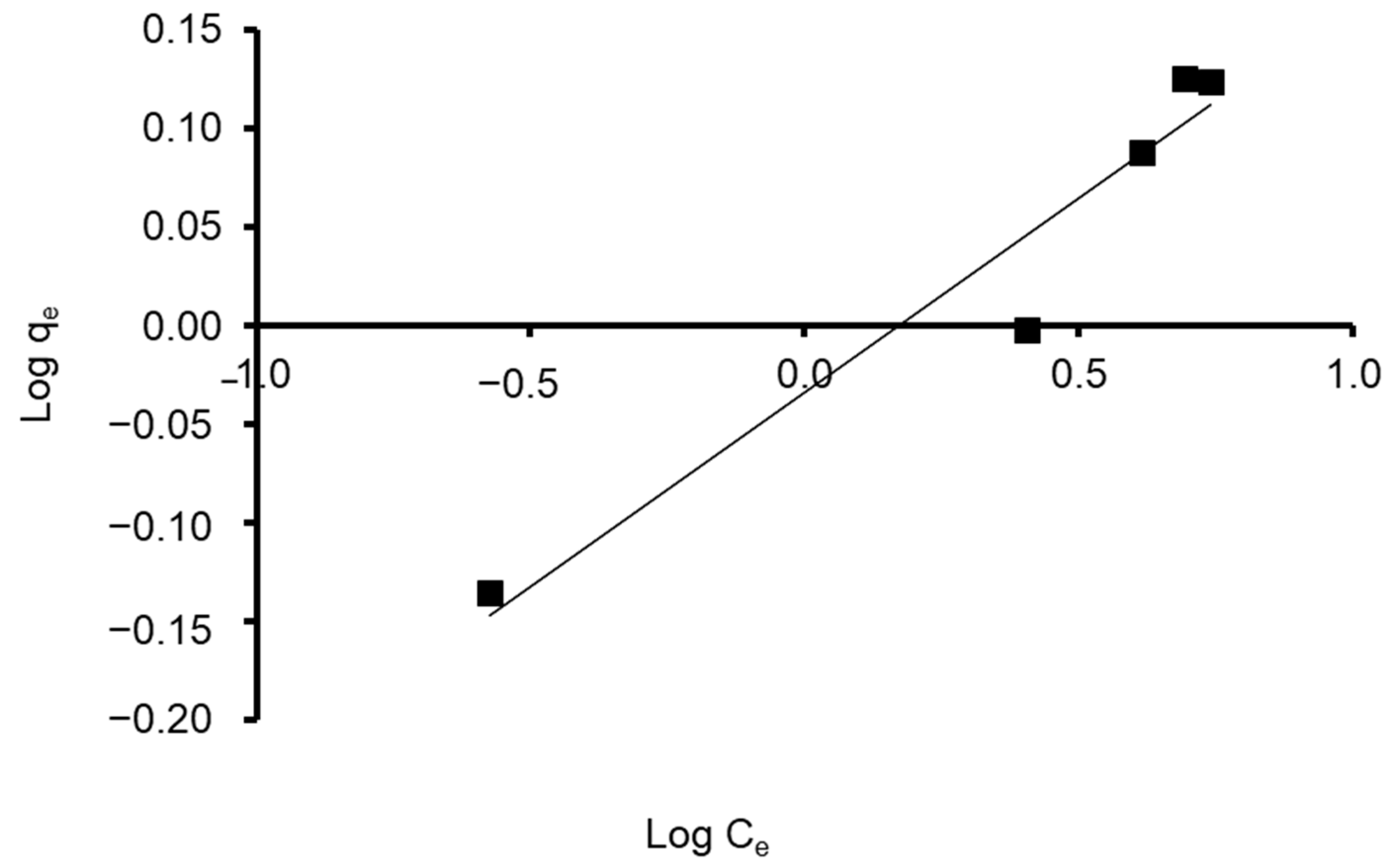
A plot of qe vs. Ln Ce enables the determination of isotherm constants A and bT. Table 4 shows the values of the parameters. The data revealed that the Tempkin isotherm model applies to the CVD adsorption onto S. costatum adsorbent, as shown by the low regression correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.895). This can be obvious when the estimated qe values differ from those derived from the experimental study, as in Figure 12.
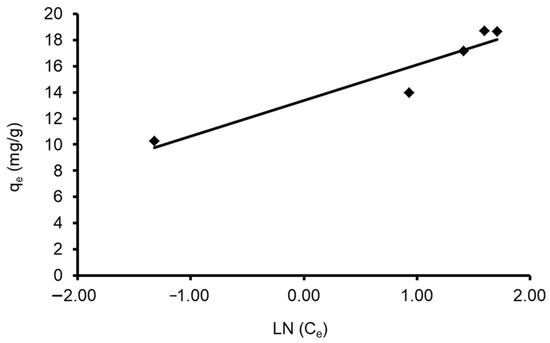
Figure 12.
Plot of the Tempkin isotherm models for CVD adsorbed onto S. costatum.
3.4.4. Halsey and Henderson Isotherm
These models are suitable for heterosporous solids and the multilayer sorption technique [98]. The Halsey model was calculated using the following equation [99]:
Meanwhile, the Henderson model was obtained from the following equation [97]:
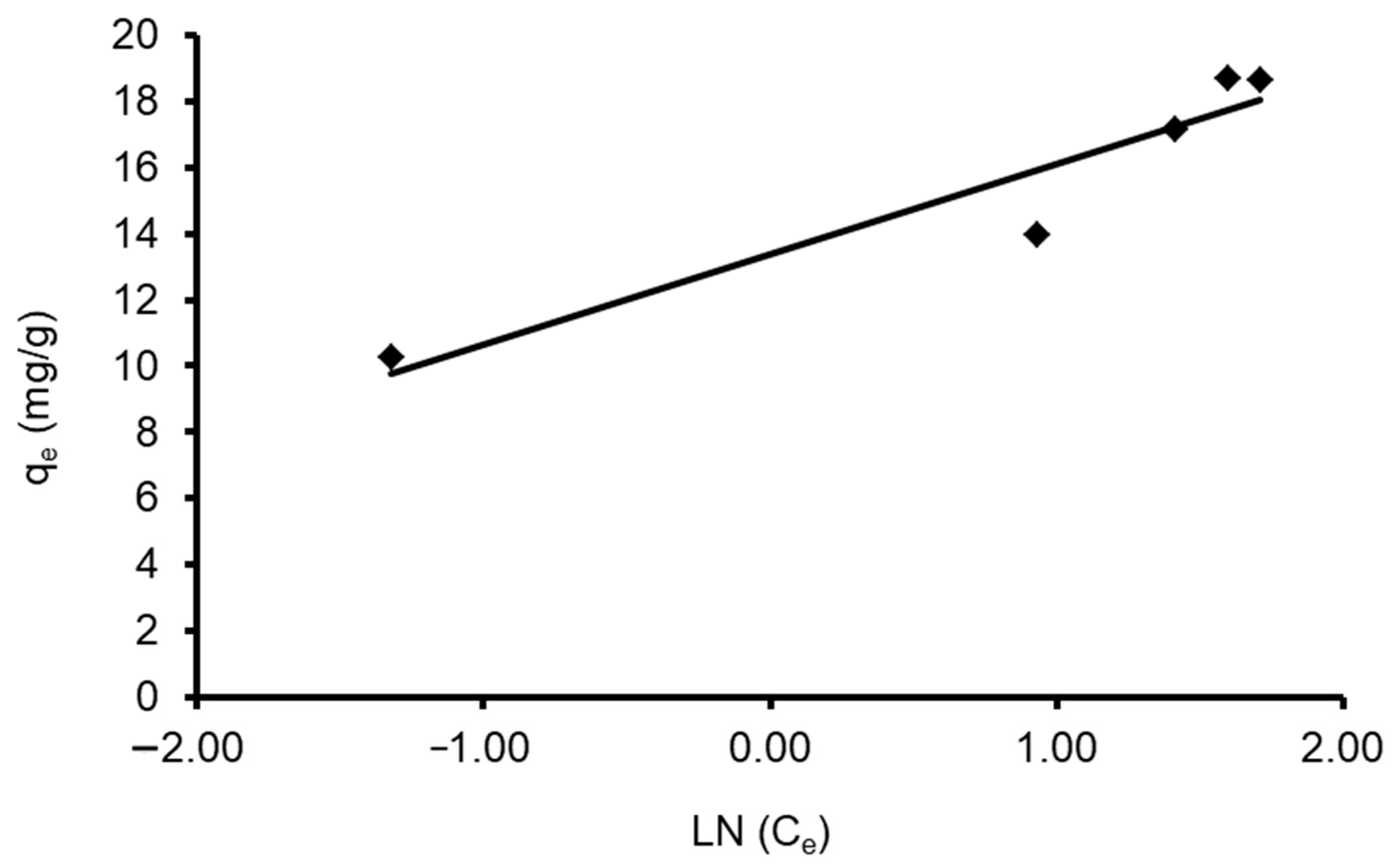
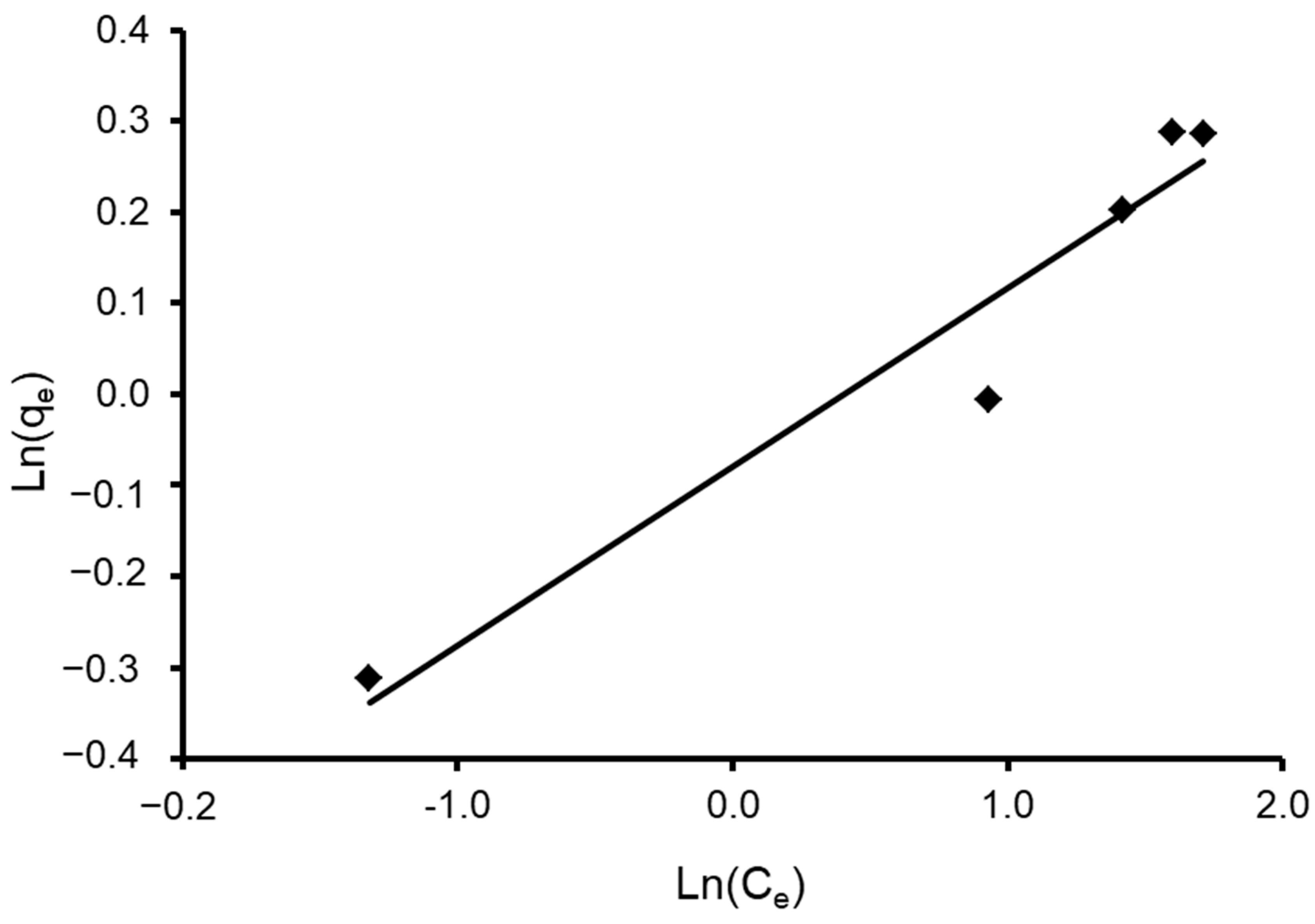
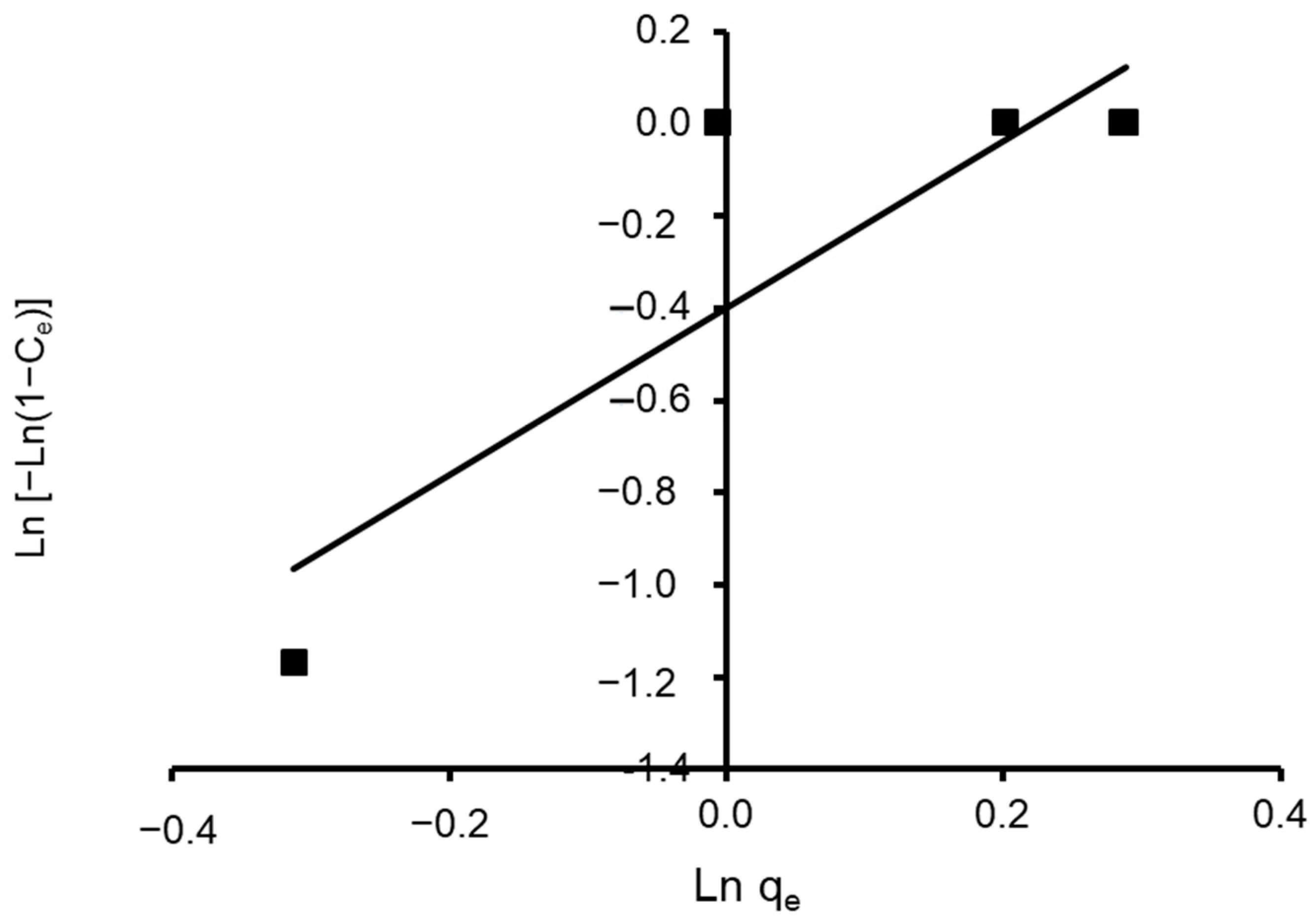
where n and K are Halsey constants for both Halsey and Henderson isotherms. A plot of ln qe versus ln Ce for Halsey and ln [−ln(1−Ce)] versus ln qe for Henderson. The isotherm constants and correlation coefficients are summarized in Table 4. Halsey showed a correlation coefficient of R2 = 0.936 (Figure 13), while Henderson showed an R2 of 0.780 (Figure 14). The results obtained display that the Halsey model is applicable for the adsorption of CVD onto the adsorbent.
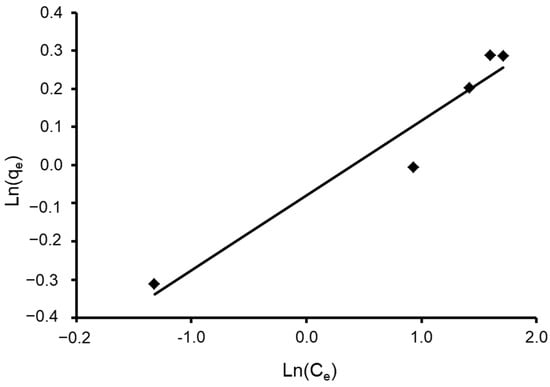
Figure 13.
Plot of the Halsey isotherm model for CVD adsorbed onto S. costatum.
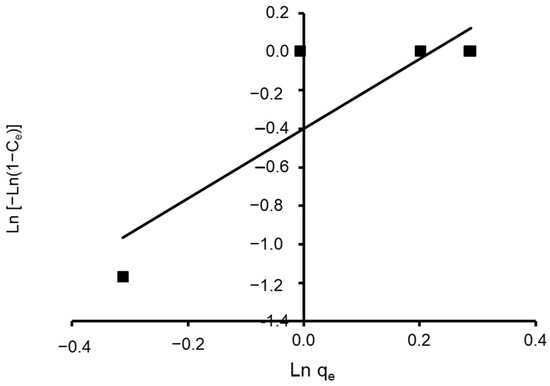
Figure 14.
Plot of the Henderson isotherm model for CVD adsorbed onto S. costatum.
3.4.5. Error Analyses
This study used isotherm models to evaluate the materials’ removal effectiveness, and the linear correlation coefficient was used to determine the relationship between the experimental data and the model under study (R2). The Chi-square (X2) test was additionally used as a standard to ensure the fitting quality was the non-linear regression. This statistical analysis is based on the sum of the squares of the differences between experimentally determined data and model-calculated data, where each squared difference was divided by the corresponding data produced by modeling, as calculated by the following Equation (14).
Based on the coefficient of determination (R2) value and the smallest Chi-square test (X2) result, the best fit model for the adsorption isotherm was selected. Halsey and Freundlich isotherm equations were found to best match the equilibrium data acquired for CVD onto S. costatum after analysis of R2 values and the data were fitted. When compared to the other isotherm forms, the Langmuir, Henderson, and Tempkin forms provided the worst fit to the experimental data. Additionally, the Chi-square test of both the Halsey and Freundlich isotherm yielded the lowest value, indicating that the qe, cal of the Halsey and Freundlich isotherms and the qe, exp, as summarized in Table 4, are the isotherms that are most similar to one another. Therefore, with consideration of the R2 and the error functions, it is concluded that the Halsey and Freundlich isotherm best fitted the experimental data. The RL and nF values from the experiment indicate that the adsorption process is favorable and chemical.
3.5. Adsorption Kinetic
To examine the regulatory mechanism of the adsorption technique, for example, mass transfer and chemical reaction, Lagergren pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kineticss in addition to the intraparticle diffusions were applied to the investigation of the experimental data of CVD adsorption by S. costatum in the batch examinations (Figure 11, Figure 12 and Figure 13).
3.5.1. Pseudo-First–Order Kinetic
The pseudo-first-order rate expression of Lagergren depends on the sorption capacity of the adsorbent and is generally expressed as follows:
where qe is the quantity of CVD adsorbed at equilibrium (mg g−1), qt is the quantity of CVD adsorbed at time t (mg g−1), and K1 is expressed as a pseudo-first-order rate constant (min−1). The integrating equation was assessed [100] as follows:
Dq/dt = K1 (qe − qt)
Log (qe/qe − qt) = K1t/2.303
The pseudo-first-order equation is given by the following formula in an equation:
Log (qe − qt) = Log qe − K1t/2.303
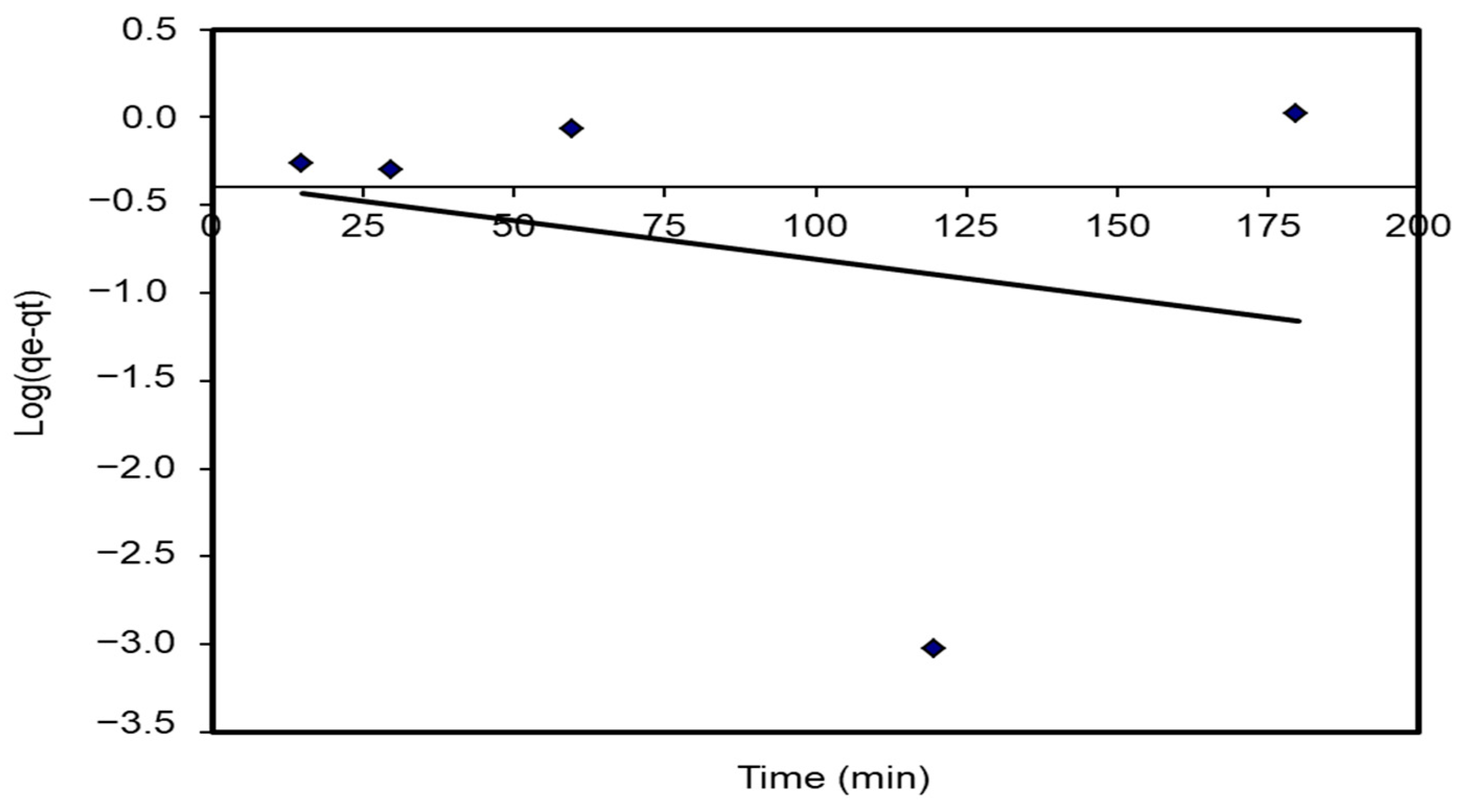
The plot of log (qe – qt) agents t provides a straight line for the first-order adsorption kinetics. The value of the first-order rate constant k1 was given from the slope of the straight line. The K1 correlation coefficients, R2 values, and predicted and experimental qe values for different S. costatum/CVD combinations are presented in Table 5. Figure 15 shows a plot of the form of the pseudo-first-order model at 25 °C. However, the correlation coefficients for the first-order kinetic model were low. In addition, the theoretical qe values found from the first-order kinetic model did not give reasonable values (R2 = 0.752). This suggests that this adsorption process does not follow a first-order reaction.

Table 5.
The calculated values of kinetic parameters of the adsorption of CVD onto S. costatum.
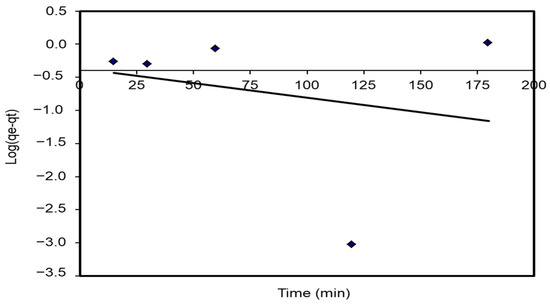
Figure 15.
Pseudo-first-order plots for the adsorption of CVD onto S. costatum.
3.5.2. Pseudo-Second–Order Kinetic
The pseudo-second-order equations depend on the sorption efficiency of the solid phase, which, contrary to the other model, predicts the behavior over the whole range of concentrations. The pseudo-second-order kinetic rate equation is expressed as:
where K2 is the constant of the second-order rate (g m−1 min−1). The integrated equation is presented as follows:
dqt /dt = K2 (qe − qt)2
1/(qe − qt) = 1/qe+ K2
A form of the pseudo-second-order equation was obtained as described by Yang, et al. [101] as follows:
t/qt = 1/K2 qe2 + t/qe
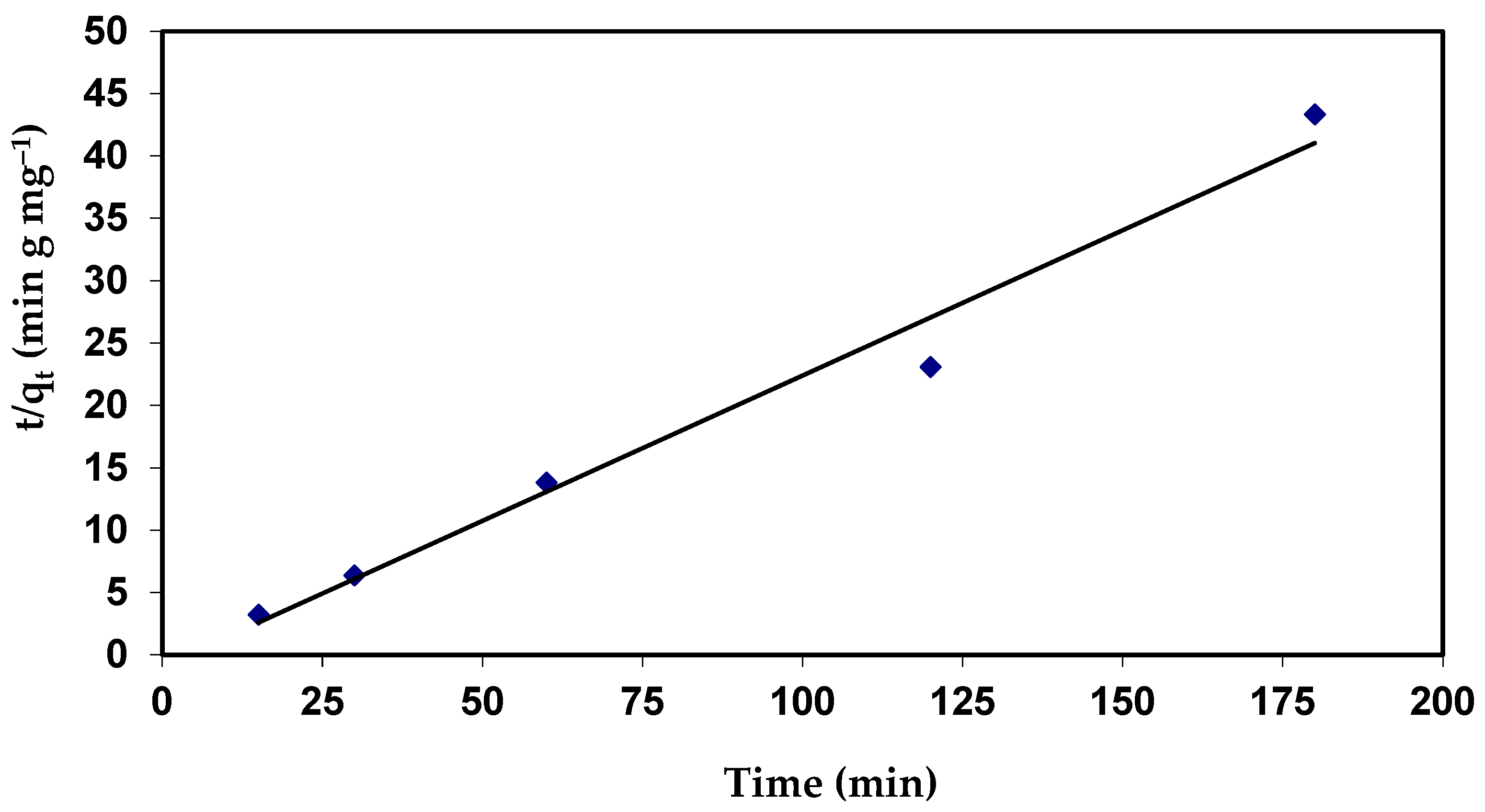
Plots of (t/qt) against (t) would provide a relationship (Figure 10), and the values of the qe and K2 parameters can be calculated from the slope and intercept, respectively.
Meanwhile, the initial adsorption rate ho (mg g−1 min−1) at the time was calculated by the following [102]:
ho = K2qe2
The results indicate that the values of qe for second-order kinetics are closer to the estimated values (Table 5). The correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.978) value for the pseudo-second order is also closer to unity when compared to the first order (Figure 16 and Table 5). The near values between the predicted values of qe from the pseudo-second-order model and the experimental qe, in contrast to the pseudo-first-order, predicted qe values, which significantly differed from experimental qe, serve as more evidence for this. This shows that the adsorption process follows a pseudo-second-order model and that it appears to be governed by chemical adsorption, including valency forces, by sharing or exchange of electrons among dye anions and the adsorbent, which provides the best correlation of the data for the dye [73].
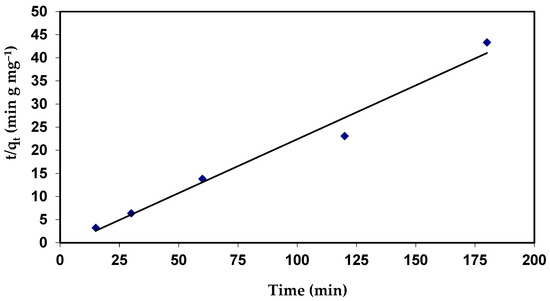
Figure 16.
Pseudo-second-order plots for the adsorption of CVD onto S. costatum.
3.5.3. Intra-Particle Diffusion Equation
Intra-particle diffusion is a key rate-controlling phase in the first phase of adsorption, and outside mass transfer or boundary layer diffusion could be defined by the initial rate of solute sorption. The acquired data were examined using mass transfer and kinetic models [103]. Adsorption kinetics are obtained by the following stages. The intra-particle diffusion model was calculated as follows [73,104]:
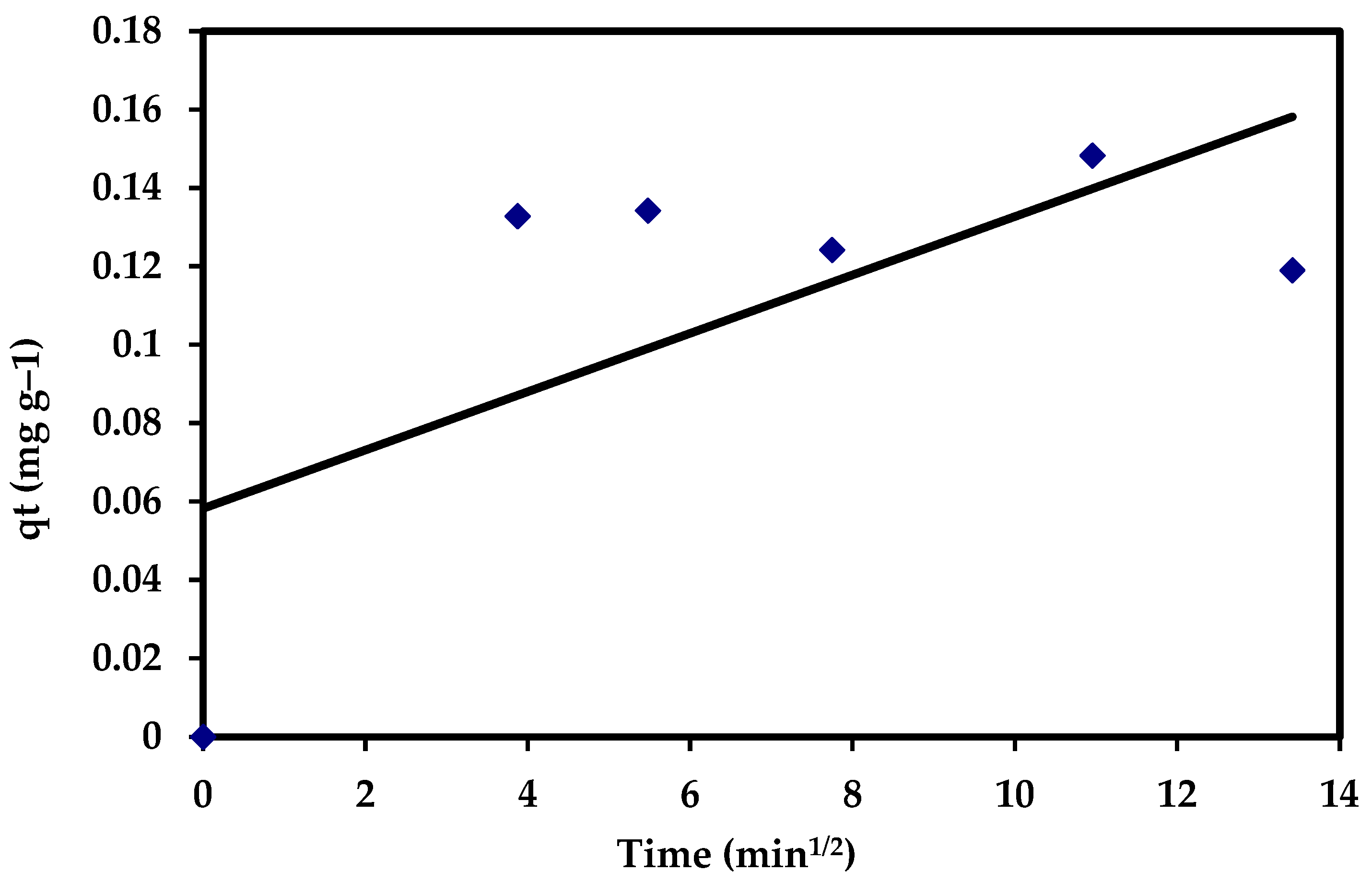
where C is the intercept and Kdif (mg g−1 min−0.5) reflects the intra-particle diffusion rate constant, which is estimated through the slope of the regression line. The intra-particle diffusion model showed no fit with the experimental data (R2 = 0.438). Moreover, the data assigned that, in the intra-particle diffusion plots for adsorption of CVD, it appeared that none of the regions has C values equal to zero, which did not pass throughout the origin (Figure 17), suggesting that the pore diffusion is not the rate-controlling step of the investigated adsorption process (Table 5).
qt = Kdif t1/2 + C
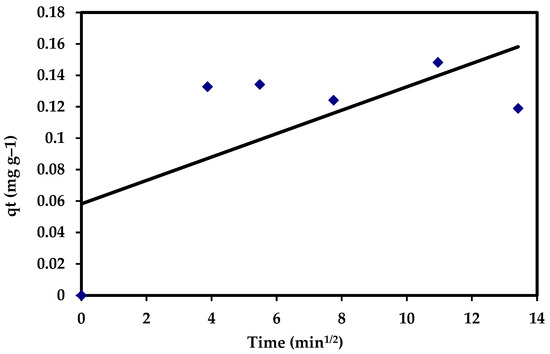
Figure 17.
The intra-particle diffusion plots for the adsorption of CVD onto S. costatum.
3.6. Industrial Wastewater and Seawater Applications
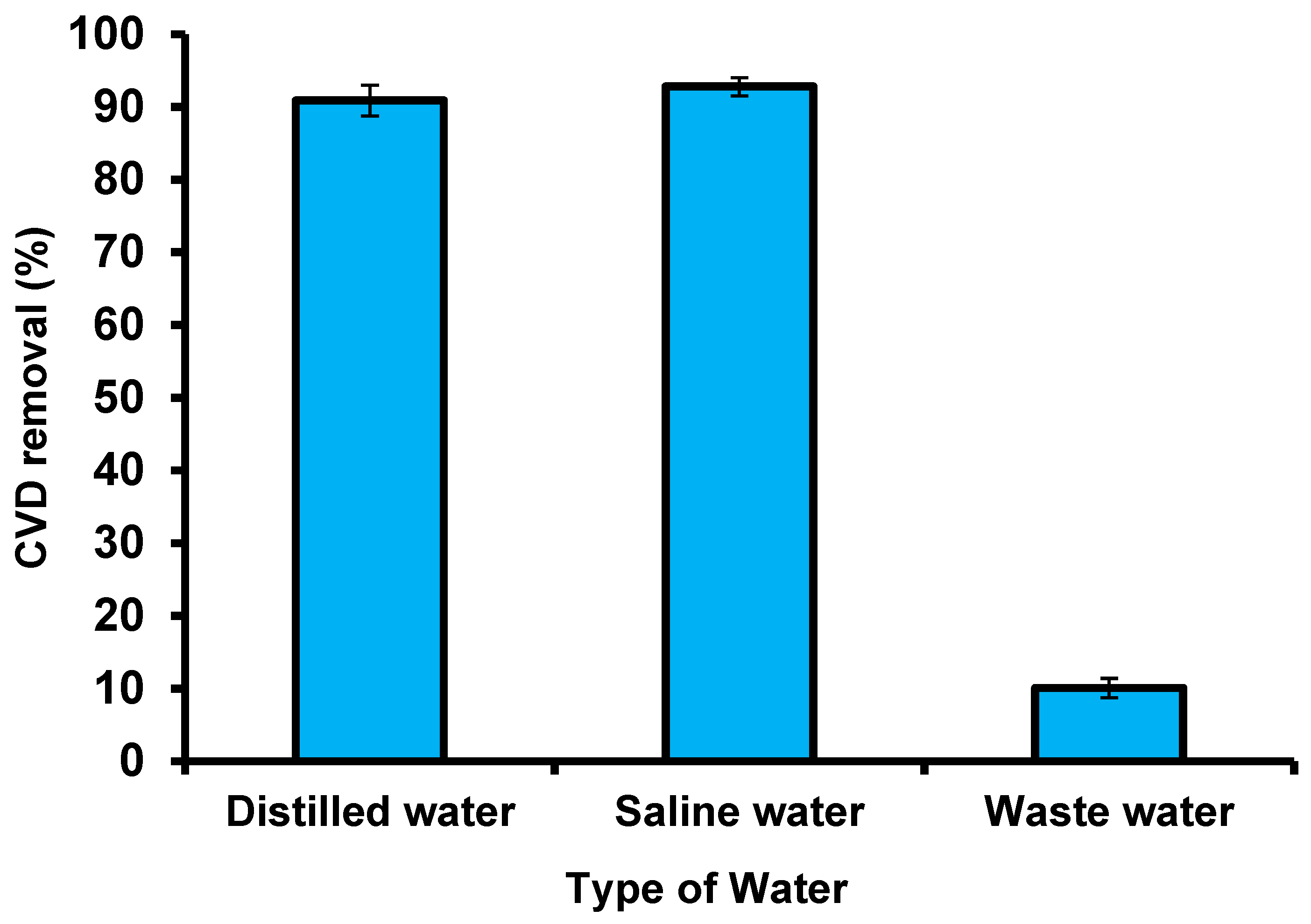
A wastewater sample was collected from the El-Naboria drain, which belongs to Alexandria, Egypt, and comprises numerous industrial sewage and agricultural wastes. To assess the adsorbent validity of S. costatum, real wastewater mixed with simulated dye samples was collected to examine the removal of CVD by the adsorbent under optimal conditions (Figure 18). Owing to the low CVD concentrations, an amount of CVD was added to obtain 5 mg L−1 of this dye. The characteristics of the wastewater used are as follows: values of salinity (PPT) are 186.5 and pH is 8.44; the dissolved oxygen (mg L−1) value was 11.01, nitrite (135.45 μg L−1), nitrate (622.7 μg L−1), ammonia (468.5 μg L−1), and phosphate (52.37 μg L−1). The CVD solution was filtered to remove precipitates and suspended the matter. The presence of salt did not affect the removal of CVD by S. costatum, which leads us to deduce that there was no interaction between the salt and the S. costatum, nor between the salt and the CVD. Moreover, the high concentration of CVD ions may make them more preferably adsorbed by S. costatum, since the effect of salt cannot influence the active groups of the adsorbent. The results show that adding saltwater to the dye solution increases the adsorption capacity of the CVD, and the reason for this is that the interactions between solvent molecules and NaCl ions are fewer than that of dyes, which leads to an increase in the solubility of dyes in the aqueous solution, and thus leads to a desire in the ability to adsorb it on the surface. Furthermore, it is possible to explain this flow based on the process of imbibition. This is because this process leads to swelling of the adsorbent material and the removal of the osmotic pressure of the saline solution, which leads to a change in the geometry of the pores of the adsorbent material, and thus leads to a decrease or increase in adsorption according to changes of the shape of the surface [105]. The application of S. costatum to remove the CVD from wastewater was carried out under optimized conditions (pH 3 for 180 min at 25 °C and 0.05 g of adsorbents in the solution). Deionized water comprising a similar concentration of CVD was applied as a control to estimate the effect of S. costatum on CVD. The obtained results reveal that changing the type of wastewater had a substantial impact on the greatest removal, with deionized water having the least impact on the adsorption method, with a color removal of 90.9% at pH 3 after 180 min.
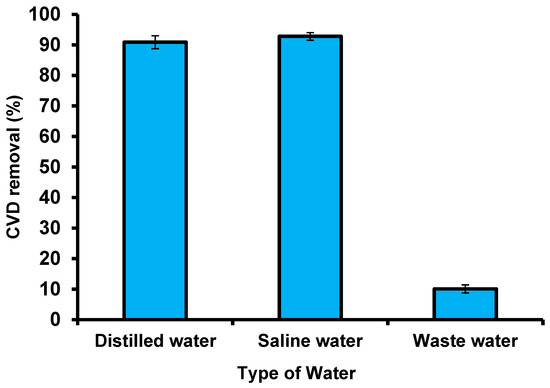
Figure 18.
Removal of CVD from different solutions using S. costatum.
By contrast, real wastewater comprises very high concentrations of interfering ions from numerous pollutants, which had a significant influence on the elimination efficiency of CVD, with a color removal of 10.08 % after 180 min at pH 3. Regardless, the results reveal that S. costatum adsorbents can be successfully used as a low-cost adsorbent to remove CVD from aqueous mixtures and wastewater. Furthermore, changing the same kind of CVD solution did not affect the maximal adsorption capabilities.
3.7. Regeneration and Reusability Study
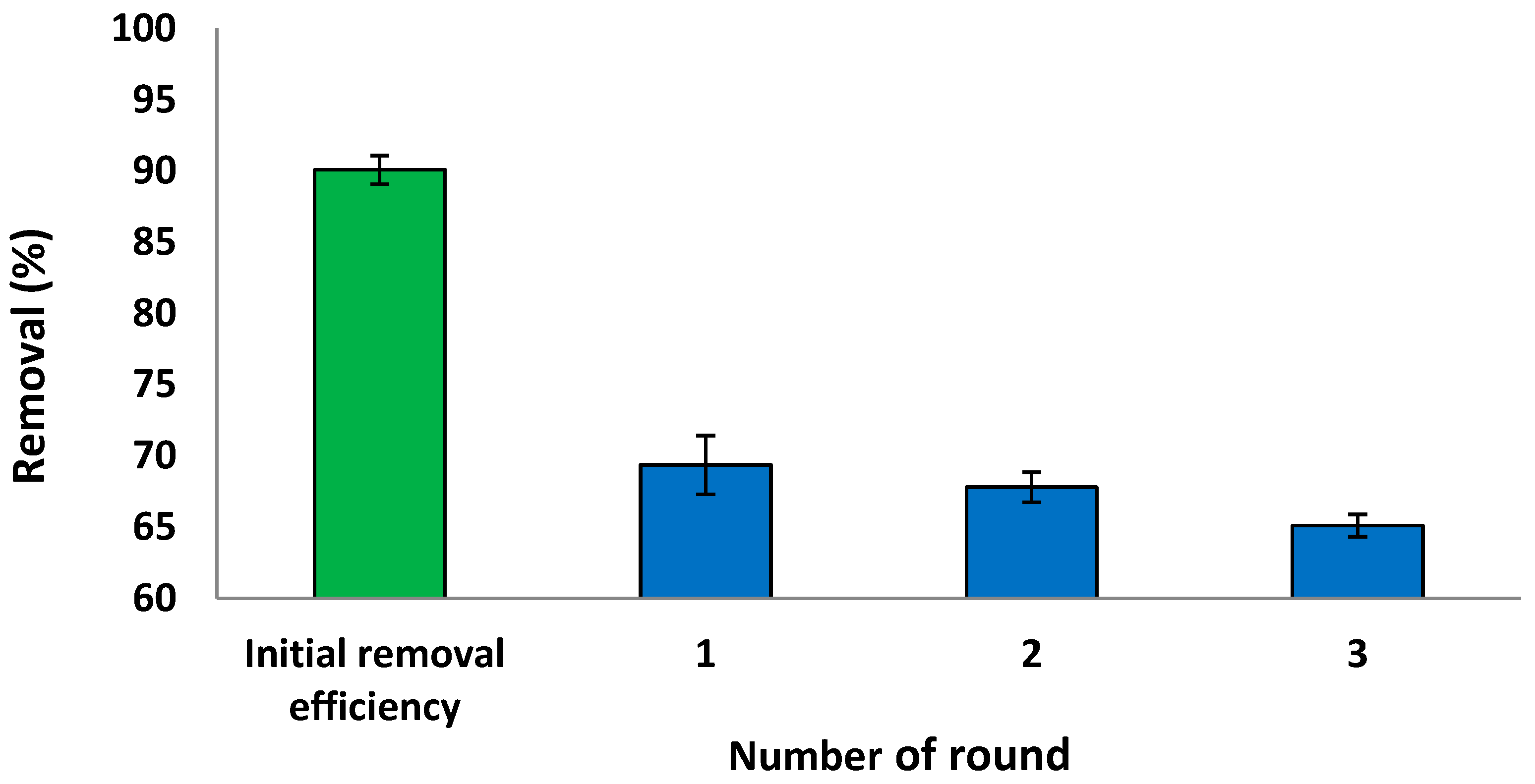
The regeneration and reuse of the sorbent material are essential for its economic viability [8]. To evaluate the reusability of S. costatum, adsorption–desorption experiments were conducted using 5 mg L−1 of CVD solution, shaken at 110 rpm for 3 h, as presented in Figure 19. The current results reveal that the removal efficiency of the S. costatum for CVD uptake remained nearly unchanged for the three consecutive series. The initial removal efficiency was 90.10% in 180 min, which was reduced to 69.30% after the first round. Hence, it could be concluded that the sorption capacity of the adsorbent remains unaffected with extended regeneration rounds. This decrease shows that the adsorbent represents a good material that can be used in industrial operations. It can be easily known that desorption efficiency decreases with increasing cycle numbers due to the decrease of adsorption capacity. This indicates that, while biomass-adsorbing sites were still available, they became more difficult to locate. Changes in the chemistry and structure of the adsorbent, as well as changes in the mass transport conditions, may have an influence on adsorption performance after the third cycle of use [106].
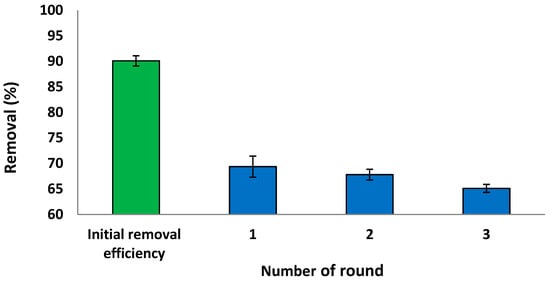
Figure 19.
Reusability study of the S. costatum after adsorption of CVD.
3.8. Comparison with Other Studies
Table 6 presents the comparison amongst the maximum values of CVD adsorption capacities of the prepared adsorbent, and some adsorbents, comprising some activated carbons, modified biomasses, nanoparticles, and zeolite. In the present work, the amount of maximum monolayer uptake capacity of CVD by S. costatum was obtained at 6.41 mg g−1; this amount has been compared with qm achieved from other studies on the removal of CVD. Table 6 shows the maximum uptake capacity from the Langmuir model by various sorbents.

Table 6.
The comparisons of the maximum uptake capacity of CVD by different adsorbents.
3.9. Suggested Mechanism
The adsorption mechanism could be affected by a wide variety of factors. Adsorption is the outcome of the interaction between ions, molecules, and the surface of the adsorbent. The surface of the adsorbent carries different kinds of functional groups, such as amino, carbonyl, phosphate, carboxylate, carboxyl, and hydroxyl, as reported by FTIR analysis, which are responsible for the confiscation of harmful materials from industrial wastewater [119]. However, the dye remediation process is mainly comprised of two mechanisms: active uptake and passive uptake [65]. The active uptake is the exchange of monovalent and divalent ions such as Na, Mg, and Ca in the cell walls, which are replaced by ions of dyes. Passive uptake is the formation of a complex between the ions of dyes with functional groups located on the cell wall; this process is alternating and fast, while active uptake is a process that occurs when dye ions bind to the cell [65]. This mechanism occurs in combination with the usage of dye ions by microorganisms and intracellular accumulation of dye ions; dyes can also be deposited in the metabolism and excretion process on a second level. pH and the presence of other ions are factors that influence the uptake passive process. pH and the presence of other ions influence the passive uptake process, whereas pH and temperature influence the active uptake process [120].
On the other hand, Soedarti et al. [66] found that Skeletonema sp., including microalgae, are aquatic organisms containing molecular mechanisms that may discriminate non-essential toxic metals from metal ions that are required for growth. Skeletonema costatum can absorb CVD ions in two ways: absorption and adsorption, according to this study. S. costatum has cell walls, which allow for adsorption. S. costatum has cellulose-based cell walls. The functional groups in the cellulose inside cell walls, such as hydroxyl, can bond with ions in dye [66]. S. costatum also absorbs nutrients because it produces phytochelatins [59]. S. costatum is like other microalgae that also produces phytochelatins, namely, peptides metallothionein class III (Mt-III), to detoxify heavy metals, which can be induced by the existence of heavy metal ions, as reported by Perales-Vela et al. [121] and Shaw [122].
4. Conclusions
The diatom Skeletonema costatum was found to be effective in the uptake of Crystal Violet Dye (CVD). Maximum dye adsorption was achieved by a batch technique at pH 3, adsorbent dose 0.4 g, contact time 120 min, and 5 mg L−1 initial dye concentration at 25 °C. The percentage removal of the S. costatum diatom rose to 95.2% for an adsorbent dosage of 0.4 g. Freundlich and Halsey’s isotherm models describe the adsorption of CVD onto S. costatum, suggesting that adsorption was onto a non-uniform site and that the CVD adsorption data followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. Thermodynamic data indicate the endothermic nature of adsorption systems. The calculated RL value was less than 1, while the value of n was greater than 1, hence the adsorption process was favorable. Values of qe agreed with the values of the current experiment. However, initial rapid adsorption was onto a uniform site, thus maximum monolayer adsorption capacity was obtained to be 6.410 mg g−1. The S. costatum displayed significant regeneration possibility and application on real wastewater. Finally, the current work concluded that the marine diatom S. costatum is significantly used to eliminate the textile toxic dye from wastewater, since it is an effective, eco-friendly, and locally available adsorbent.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.E.A. and M.A.; methodology, A.E.A., M.A. and M.K.; software, A.E.A., A.T.M. and M.A.; validation, A.E.A., M.A., M.K. and A.T.M.; formal analysis, A.E.A. and M.A.; investigation, A.E.A., M.A. and M.K.; resources, A.E.A., M.A., K.M.A. and A.T.M.; data curation, A.E.A., M.A., M.K. and A.T.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.E.A., M.A. and A.T.M.; writing—review and editing, A.E.A., M.A. and A.T.M.; visualization, A.E.A., M.A. and A.T.M.; supervision, A.E.A., M.A. and A.T.M.; project administration, A.E.A., M.A. and A.T.M.; funding acquisition, A.E.A., M.A., K.M.A. and A.T.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number TURSP-2020/267, Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully appreciate Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number TURSP-2020/267, Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia for support publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sharma, A.; Choudhry, A.; Rathi, G.; Tara, N.; Abdulla, N.K.; Sajid, M.; Chaudhry, S.A. Ferrite based magnetic nanocomposites for wastewater treatment through adsorption. In Contamination of Water; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 449–460. [Google Scholar]
- Mangla, D.; Sharma, A.; Ikram, S. Critical review on adsorptive removal of antibiotics: Present situation, challenges and future perspective. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhry, A.; Sharma, A.; Khan, T.A.; Chaudhry, S.A. Flax seeds based magnetic hybrid nanocomposite: An advance and sustainable material for water cleansing. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, A.; Bhatti, H.N. Adsorptive removal of reactive green 5 (RG-5) and direct yellow 50 (DY-50) from simulated wastewater by Mangifera indica seed shell and its magnetic composite: Batch and Column study. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, C.; Karaman, O.; Show, P.-L.; Orooji, Y.; Karimi-Maleh, H. Utilization of a double-cross-linked amino-functionalized three-dimensional graphene networks as a monolithic adsorbent for methyl orange removal: Equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamics and artificial neural network modeling. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Bindary, A.A.; Hussien, M.A.; Diab, M.A.; Eessa, A.M. Adsorption of Acid Yellow 99 by polyacrylonitrile/activated carbon composite: Kinetics, thermodynamics and isotherm studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 197, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualnaja, K.M.; Alprol, A.E.; Abu-Saied, M.A.; Ashour, M.; Mansour, A.T. Removing of Anionic Dye from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption Using of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes and Poly (Acrylonitrile-styrene) Impregnated with Activated Carbon. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualnaja, K.M.; Alprol, A.E.; Abu-Saied, M.A.; Mansour, A.T.; Ashour, M. Studying the Adsorptive Behavior of Poly(Acrylonitrile-co-Styrene) and Carbon Nanotubes (Nanocomposites) Impregnated with Adsorbent Materials towards Methyl Orange Dye. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualnaja, K.M.; Alprol, A.E.; Ashour, M.; Mansour, A.T. Influencing Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for the Removal of Ismate Violet 2R Dye from Wastewater: Isotherm, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Studies. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunge, Y.M.; Uchida, A.; Tominaga, Y.; Fujii, Y.; Yadav, A.A.; Kang, S.-W.; Suzuki, N.; Shitanda, I.; Kondo, T.; Itagaki, M. Visible light-assisted photocatalysis using spherical-shaped bivo4 photocatalyst. Catalysts 2021, 11, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Li, J.; Xi, B. Photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B using Bi4O5Br2-doped ZSM-5. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 278, 125697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Kang, S.-W.; Hunge, Y. Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B using graphitic carbon nitride photocatalyst. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 15577–15585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Agarwal, A.; Singh, M.; Singh, N. Removal of Red RB dye from aqueous solution by belpatra bark charcoal (BBC) adsorbent. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 3654–3665. [Google Scholar]
- Alprol, A.E. Study of environmental concerns of dyes and recent textile effluents treatment technology: A Review. Asian J. Fish. Aquat. Res. 2019, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Darabi, R.; Shabani-Nooshabadi, M.; Baghayeri, M.; Karimi, F.; Rouhi, J.; Alizadeh, M.; Karaman, O.; Vasseghian, Y.; Karaman, C. Determination of D&C Red 33 and Patent Blue V Azo dyes using an impressive electrochemical sensor based on carbon paste electrode modified with ZIF-8/g-C3N4/Co and ionic liquid in mouthwash and toothpaste as real samples. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 162, 112907. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alprol, A.E.; Heneash, A.M.M.; Soliman, A.M.; Ashour, M.; Alsanie, W.F.; Gaber, A.; Mansour, A.T. Assessment of Water Quality, Eutrophication, and Zooplankton Community in Lake Burullus, Egypt. Diversity 2021, 13, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Khan, A.; Bhatti, H.N.; Zahid, M.; Alissa, S.; El-Badry, Y.A.; Hussein, E.E.; Iqbal, M. Composite of polypyrrole with sugarcane bagasse cellulosic biomass and adsorption efficiency for 2,4-dicholrophonxy acetic acid in column mode. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 2016–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreen, S.; Tahira, M.; Ghamkhar, M.; Hafiz, I.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nadeem, R.; Murtaza, M.A.; Yaseen, M.; Sheikh, A.A.; Naseem, Z. Treatment of textile wastewater containing acid dye using novel polymeric graphene oxide nanocomposites (GO/PAN, GO/PPy, GO/PSty). J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Hunge, Y.; Kang, S.-W. Porous nanoplate-like tungsten trioxide/reduced graphene oxide catalyst for sonocatalytic degradation and photocatalytic hydrogen production. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 24, 101075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.N.; Siddique, M.; Wahid, F.; Khan, R. Removal of reactive blue 19 dye by sono, photo and sonophotocatalytic oxidation using visible light. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 26, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, N.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M.; Noreen, S. Biopolymers composites with peanut hull waste biomass and application for Crystal Violet adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Sharif, M.; Iqbal, M. Application potential of grapefruit peel as dye sorbent: Kinetics, equilibrium and mechanism of crystal violet adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, B.C.S.; Teodoro, F.S.; Mageste, A.B.; Gil, L.F.; de Freitas, R.P.; Gurgel, L.V.A. Application of a new carboxylate-functionalized sugarcane bagasse for adsorptive removal of crystal violet from aqueous solution: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 65, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, S.; Pius, A.; Thomas, S. Enhanced adsorption of crystal violet by synthesized and characterized chitin nano whiskers from shrimp shell. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alprol, A.E.; Abd El Azzem, M.; Amer, A.; El-Metwally, M.E.; Abd El-Hamid, H.T.; El-Moselhy, K.M. Adsorption of cadmium (II) ions from aqueous solution onto mango leaves. Asian J. Phys. Chem. Sci. 2017, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Chaudhry, S.A. Adsorption of Pharmaceutical Pollutants Using Lignocellulosic Materials. In Green Materials for Wastewater Treatment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 277–289. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, E.M.; Ali, F.S.; Desouky, M.G.; Ashour, M.; El-Shafei, A.; Maaty, M.M.; Sharawy, Z.Z. Novel Comprehensive Molecular and Ecological Study Introducing Coastal Mud Shrimp (Solenocera Crassicornis) Recorded at the Gulf of Suez, Egypt. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, A.S.; El-Naggar, H.A.; El-Damhougy, K.A.; Bashar, M.A.E.; Ashour, M.; Abo-Taleb, H.A.H. GC-MS analysis of bioactive components in six different crude extracts from the Soft Coral (Sinularia maxim) collected from Ras Mohamed, Aqaba Gulf, Red Sea, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2020, 24, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.; Mabrouk, M.M.; Abo-Taleb, H.A.; Sharawy, Z.Z.; Ayoub, H.F.; Van Doan, H.; Davies, S.J.; El-Haroun, E.; Goda, A.M.S.A. A liquid seaweed extract (TAM®) improves aqueous rearing environment, diversity of zooplankton community, whilst enhancing growth and immune response of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, challenged by Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 736915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, S.; Shang, H.; Barati, B.; Gong, X.; Hu, X.; Abomohra, A.E.-F. Study on the co-operative effect of kitchen wastewater for harvest and enhanced pyrolysis of microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 317, 123983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, R.; Jin, W.; Xi, T.; Yang, Q.; Han, S.-F.; Abomohra, A.E.-F. Effect of static magnetic field on the oxygen production of Scenedesmus obliquus cultivated in municipal wastewater. Water Res. 2015, 86, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Jin, W.; Chen, Y.; Tu, R.; Abomohra, A.E.-F. Enhancement of lipid production of Chlorella pyrenoidosa cultivated in municipal wastewater by magnetic treatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 180, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadda, M.A.; Li, C.; Gouda, M.; Abomohra, A.E.-F.; Shitu, A.; Ahsan, A.; Zhu, S.; Liu, D. Enhancement of nitrite/ammonia removal from saline recirculating aquaculture wastewater system using moving bed bioreactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, D.; Abo-Shady, A.; Khairy, H.; Abomohra, A.E.-F.; Elshobary, M. Potential cultivation of halophilic oleaginous microalgae on industrial wastewater. Egypt. J. Bot. 2018, 58, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.; Hassan, S.M.; Elshobary, M.E.; Ammar, G.A.G.; Gaber, A.; Alsanie, W.F.; Mansour, A.T.; El-Shenody, R. Impact of Commercial Seaweed Liquid Extract (TAM®) Biostimulant and Its Bioactive Molecules on Growth and Antioxidant Activities of Hot Pepper (Capsicum annuum). Plants 2021, 10, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battah, M.; El-Ayoty, Y.; Abomohra, A.E.-F.; El-Ghany, S.A.; Esmael, A. Optimization of growth and lipid production of the Chlorophyte Microalga Chlorella vulgaris as a feedstock for biodiesel production. World Appl. Sci. J. 2013, 28, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.; Sun, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, S.; Yuan, J.; Esakkimuthu, S.; Bernard Uzoejinwa, B.; Yuan, C.; Abomohra, A.E.F.; Qian, L.; et al. Synergistic effects of co-pyrolysis of macroalgae and polyvinyl chloride on bio-oil/bio-char properties and transferring regularity of chlorine. Fuel 2019, 246, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebaid, R.; Elhussainy, E.; El-Shourbagy, S.; Ali, S.; Abomohra, A.E.-F. Protective effect of Arthrospira platensis against liver injury induced by copper nanoparticles. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2017, 17, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mesery, H.S.; Mao, H.; Abomohra, A.E.F. Applications of non-destructive technologies for agricultural and food products quality inspection. Sensors 2019, 19, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shouny, W.; Sharaf, M.; Abomohra, A.; Abo-Eleneen, M. Production enhancement of some valuable compounds of Arthrospira platensis. J. Basic Environ. Sci. 2015, 2, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, W.; Ebaid, R.; El-Sheekh, M.; Abomohra, A.; Eladel, H. Pharmaceutical applications and consequent environmental impacts of Spirulina (Arthrospira): An overview. Grasas Y Aceites 2019, 70, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Basheer, S.; Liu, F.; Elshobary, M.; Zhang, C.; Qian, J.; Xu, L.; Arslan, M.; Cui, F.; Zan, X.; et al. Bacterial intervention on the growth, nutrient removal and lipid production of filamentous oleaginous microalgae Tribonema sp. Algal Res. 2020, 52, 102088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.E.; Abo-shady, A.M.; Elshobary, M.E. Production and characterization of antimicrobial active substance from some macroalgae collected from Abu-Qir bay (Alexandria) Egypt. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 6847–6858. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, M.E.H.; Abo-shady, A.M.; Elshobary, M.E. In vitro screening of antimicrobial activity of extracts of some macroalgae collected from Abu-Qir bay Alexandria, Egypt. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 7203–7208. [Google Scholar]
- Madkour, F.F.; Kamil, A.E.-W.; Nasr, H.S. Production and nutritive value of Spirulina platensis in reduced cost media. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2012, 38, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kassas, H.Y.; Mohamed, L.A. Bioremediation of the textile waste effluent by Chlorella vulgaris. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Chai, J.; Xu, F.; Ding, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, Z.; Khoo, K.S.; Bian, X.; Wang, S. Development of environmentally friendly biological algicide and biochemical analysis of inhibitory effect of diatom Skeletonema costatum. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 33, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, T.; Ma, J.; Li, F.; Xu, J. Physiological responses of Skeletonema costatum to the interactions of seawater acidification and the combination of photoperiod and temperature. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabaka, S.H. Checklist of seaweeds and seagrasses of Egypt (Mediterranean Sea): A review. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2018, 44, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Viraraghavan, T. Removal of Congo Red from an aqueous solution by fungus Aspergillus niger. Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 7, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaymon, A.H.; Ebrahim, S.E.; Abdullah, S.M.; Al-Musawi, T.J. Removal of lead, cadmium, and mercury ions using biosorption. Desalination Water Treat. 2010, 24, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z. Application of biosorption for the removal of organic pollutants: A review. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 997–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, A.C.; Malcata, F.X. Nutritional value and uses of microalgae in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2012, 10, 59–78. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeswari, M.V.; Balasubramanian, T. Comparative study on growth of Skeletonema costatum: A microalga as live feed for aquaculture importance. Int. J. Res. Fish. Aquac. 2014, 4, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Azmi, K.; Arsad, S.; Sari, L. The effect of commercial nutrients to increase the population of Skeletonema costatum on laboratory and mass scales. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Surabaya, Indonesia, 26 September 2019; p. 12039. [Google Scholar]
- Pratama, N.; Rahardja, B.; Sari, L. The effect of density as Skeletonema costatum bioremediation agent of copper (Cu) heavy metal concentration. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Surabaya, Indonesia, 26 September 2019; p. 12039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Tan, L. Toxic effects of microplastic on marine microalgae Skeletonema costatum: Interactions between microplastic and algae. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangla, D.; Sharma, A.; Ikram, S. Synthesis of ecological chitosan/PVP magnetic composite: Remediation of amoxicillin trihydrate from its aqueous solution, isotherm modelling, thermodynamic, and kinetic studies. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 175, 105261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassiri, Y.; Mansot, J.; Wéry, J.; Ginsburger-Vogel, T.; Amiard, J. Ultrastructural and electron energy loss spectroscopy studies of sequestration mechanisms of Cd and Cu in the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1997, 33, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, A.; Akkaya, G.; Turabik, M. The removal of Acid Red 274 from wastewater: Combined biosorption and biocoagulation with Spirogyra rhizopus. Dye. Pigment. 2006, 71, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.V.; Rao, N.C.; Prasad, K.K.; Karthikeyan, J. Treatment of simulated Reactive Yellow 22 (Azo) dye effluents using Spirogyra species. Waste Manag. 2002, 22, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Ramalingam, S.; Senthamarai, C.; Niranjanaa, M.; Vijayalakshmi, P.; Sivanesan, S. Adsorption of dye from aqueous solution by cashew nut shell: Studies on equilibrium isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics of interactions. Desalination 2010, 261, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumaar, S.; Kalaamani, P.; Subburaam, C. Liquid phase adsorption of crystal violet onto activated carbons derived from male flowers of coconut tree. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, R.S.; El-Bahy, S.M.; Mannaa, M.A. Sulfamic acid supported on mesoporous MCM-41 as a novel, efficient and reusable heterogenous solid acid catalyst for synthesis of xanthene, dihydropyrimidinone and coumarin derivatives. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 628, 127261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soedarti, T.; Tini, S.; Sucipto, H.; Kuncoro, E.P. Bioremediation of mercury (II) contaminated seawater using the diatom Skeletonema costatum. KnE Life Sci. 2017, 3, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soedarti, T.; Surtiningsih, T.; Hariyanto, S.; Kuncoro, E.P. Remediation of Pb (II) and Cd (II) in seawater by Skeletonema costatum. Sustinere J. Environ. Sustain. 2017, 1, 63–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guillard, R.R. Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1975; pp. 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, M.M.; El-Desoky, H.S.; El-Moselhy, K.M.; Amer, A.; Abou El-Naga, E.H.; Mohamedein, L.I.; Al-Prol, A.E. Removal of cadmium from aqueous solution using marine green algae, Ulva lactuca. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J. Biostatistical Analysis, 2nd ed.; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Hashem, F. Removal of methylene blue by magnetitecovered bentonite nano-composite. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2013, 2, 524–529. [Google Scholar]
- Eddebbagh, M.; Abourriche, A.; Berrada, M.; Zina, M.B.; Bennamara, A. Adsorbent material from pomegranate (Punica granatum) leaves: Optimization on removal of methylene blue using response surface methodology. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 2021–2033. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Zhang, W.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. Adsorption of methyl orange dye onto multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 18, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z.; Tezer, S. Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of biosorption of Remazol Black B by Rhizopus arrhizus in a batch system: Effect of temperature. Process Biochem. 2000, 36, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Bing, H.; Feifei, X.; Xiaofeng, C. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of methyl orange adsorption on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Yu, J.; Jiang, X. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified by polyaniline for the removal of alizarin yellow R from aqueous solutions. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirmardi, M.; Mahvi, A.H.; Hashemzadeh, B.; Naeimabadi, A.; Hassani, G.; Niri, M.V. The adsorption of malachite green (MG) as a cationic dye onto functionalized multi walled carbon nanotubes. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Das, A.; Majumder, K.; Arora, N.; Mayo, H.G.; Singh, P.P.; Beg, M.S.; Singh, S. Obesity is independently associated with increased risk of hepatocellular cancer-related mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 41, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğar, Ç.; Gürses, A.; Açıkyıldız, M.; Özkan, E. Thermodynamics and kinetic studies of biosorption of a basic dye from aqueous solution using green algae Ulothrix sp. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuda, O.S.; Olayiwola, A.O.; Alade, A.O.; Farombi, A.G.; Adebisi, S.A. Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution using steam-activated carbon produced from Lantana camara Stem. J. Environ. Prot. 2014, 5, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alprol, A.E.; Heneash, A.M.M.; Ashour, M.; Abualnaja, K.M.; Alhashmialameer, D.; Mansour, A.T.; Sharawy, Z.Z.; Abu-Saied, M.A.; Abomohra, A.E. Potential Applications of Arthrospira platensis Lipid-Free Biomass in Bioremediation of Organic Dye from Industrial Textile Effluents and Its Influence on Marine Rotifer (Brachionus plicatilis). Materials 2021, 14, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyinbor, A.; Adekola, F.; Olatunji, G.A. Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic modeling of liquid phase adsorption of Rhodamine B dye onto Raphia hookerie fruit epicarp. Water Resour. Ind. 2016, 15, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufik, A.; Saleh, R. Synthesis of iron (II, III) oxide/zinc oxide/copper (II) oxide (Fe3O4/ZnO/CuO) nanocomposites and their photosonocatalytic property for organic dye removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 491, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Nguyen, T. Removal of copper from water by adsorption onto banana peel as bioadsorbent. GEOMATE J. 2012, 2, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbareddy, Y.; Jeseentharani, V.; Jayakumar, C.; Nagaraja, K.; Jeyaraj, B. Adsorptive removal of Malachite Green (oxalate) by low cost adsorbent. J. Environ. Res. Dev. 2012, 7, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Achak, M.; Hafidi, A.; Ouazzani, N.; Sayadi, S.; Mandi, L. Low cost biosorbent “banana peel” for the removal of phenolic compounds from olive mill wastewater: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, J.R.; Memon, S.Q.; Bhanger, M.; Memon, G.Z.; El-Turki, A.; Allen, G.C. Characterization of banana peel by scanning electron microscopy and FT-IR spectroscopy and its use for cadmium removal. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 66, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, O.; Amin, N. Adsorption of phenol from aqueous solutions by Luffa cylindrica fibers: Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2013, 39, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. II. Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1917, 39, 1848–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; You, S.-J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.P. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, K.R.; Eagleton, L.C.; Acrivos, A.; Vermeulen, T. Pore-and solid-diffusion kinetics in fixed-bed adsorption under constant-pattern conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1966, 5, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahalya, N.; Kanamadi, R.; Ramachandra, T. Biosorption of iron (III) from aqueous solutions using the husk of Cicer arientinum. CSIR 2006, 13, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Adamson, A.W.; Gast, A.P. Physical Chemistry of Surfaces; Interscience publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1967; Volume 150. [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich, H. Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Habilitationsschrift Durch Welche… zu Haltenden Probevorlesung” Kapillarchemie und Physiologie” Einladet Dr. Herbert Freundlich; W. Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1906. [Google Scholar]
- Kargi, F.; Cikla, S. Biosorption of zinc (II) ions onto powdered waste sludge (PWS): Kinetics and isotherms. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2006, 38, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, D.; Namasivayam, C. Experimental and kinetic studies on methylene blue adsorption by coir pith carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Yang, L.; Han, M.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, X. Nanomaterials as sorbents to remove heavy metal ions in wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2012, 2, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volesky, B. Detoxification of metal-bearing effluents: Biosorption for the next century. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 59, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsey, G. Physical adsorption on non-uniform surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.P.; King, P.; Prasad, V. Removal of copper from aqueous solution using Ulva fasciata sp.—A marine green algae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.I.; Seth, J.; Strachan, J.P.; Gentemann, S.; Kim, D.; Holten, D.; Lindsey, J.S.; Bocian, D.F. Ground and excited state electronic properties of halogenated tetraarylporphyrins. Tuning the building blocks for porphyrin-based photonic devices. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 1999, 3, 117–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menkiti, M.; Aniagor, C.; Agu, C.; Ugonabo, V. Effective adsorption of crystal violet dye from an aqueous solution using lignin-rich isolate from elephant grass. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2018, 3, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nemr, A.; Abdelwahab, O.; El-Sikaily, A.; Khaled, A. Removal of direct blue-86 from aqueous solution by new activated carbon developed from orange peel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, N.; Meenakshisundaram, M. Adsorption of Congo Red on various activated carbons. A comparative study. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2002, 138, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.; Partt, N. Current chemical Papars. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1961, 70, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volesky, B.; Weber, J.; Park, J. Continuous-flow metal biosorption in a regenerable Sargassum column. Water Res. 2003, 37, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Deng, W.; Tang, S.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E.; Luo, J.; Wang, X. Pod-inspired MXene/porous carbon microspheres with ultrahigh adsorption capacity towards crystal violet. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, H.; Al Alili, A.; Morajkar, P.P.; Alhassan, S.M. Graphene oxide crosslinked hydrogel nanocomposites of xanthan gum for the adsorption of crystal violet dye. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 323, 115034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satapathy, M.K.; Das, P. Optimization of crystal violet dye removal using novel soil-silver nanocomposite as nanoadsorbent using response surface methodology. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabi, A.S.; Shirani, M.; Semnani, A. Apple stem as a high performance cellulose based biosorbent for low cost and eco-friendly adsorption of crystal violet from aqueous solutions using experimental design: Mechanism, kinetic and thermodynamics. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, K.N.A.; Keereerak, A.; Chinpa, W. Novel cellulose-based biosorbent from lemongrass leaf combined with cellulose acetate for adsorption of crystal violet. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falaki, Z.; Bashiri, H. Preparing an adsorbent from the unused solid waste of Rosewater extraction for high efficient removal of Crystal Violet. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2021, 18, 2689–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Li, H. High surface area activated carbon derived from chitin for efficient adsorption of Crystal Violet. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2021, 118, 108516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, T.C.R.; Izidoro, J.C.; Magdalena, C.P.; Fungaro, D.A. Adsorption of crystal violet dye from aqueous solution onto zeolites from coal fly and bottom ashes. Orbital Electron. J. Chem. 2013, 5, 179–191. [Google Scholar]
- Sarabadan, M.; Bashiri, H.; Mousavi, S.M. Removal of crystal violet dye by an efficient and low cost adsorbent: Modeling, kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodu, O.S.; Ojumu, T.V.; Ntwampe, S.K.; Ayanda, O.S. Rapid adsorption of crystal violet onto magnetic zeolite synthesized from fly ash and magnetite nanoparticles. J. Encapsulation Adsorpt. Sci. 2015, 5, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Muhammad, S.K. Biosorption of crystal violet from water on leaf biomass of Calotropis procera. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 1, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, U.A.; Ersan, M.; Tuncel, E.; Dügenci, F. Mono and simultaneous removal of crystal violet and safranin dyes from aqueous solutions by HDTMA-modified Spirulina sp. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 99, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S. Methods of dye removal from dye house effluent—An overview. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2008, 25, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauer, K.; Behra, R.; Sigg, L. Adsorption and uptake of copper by the green alga scenedesmus subspicatus (chlorophyta) 1. J. Phycol. 1997, 33, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales-Vela, H.V.; Pena-Castro, J.M.; Canizares-Villanueva, R.O. Heavy metal detoxification in eukaryotic microalgae. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J. Heavy Metal Tolerance in Plants: Evolutionary Aspects; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).