Enhanced Design of Gold Catalysts for Bioorthogonal Polyzymes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
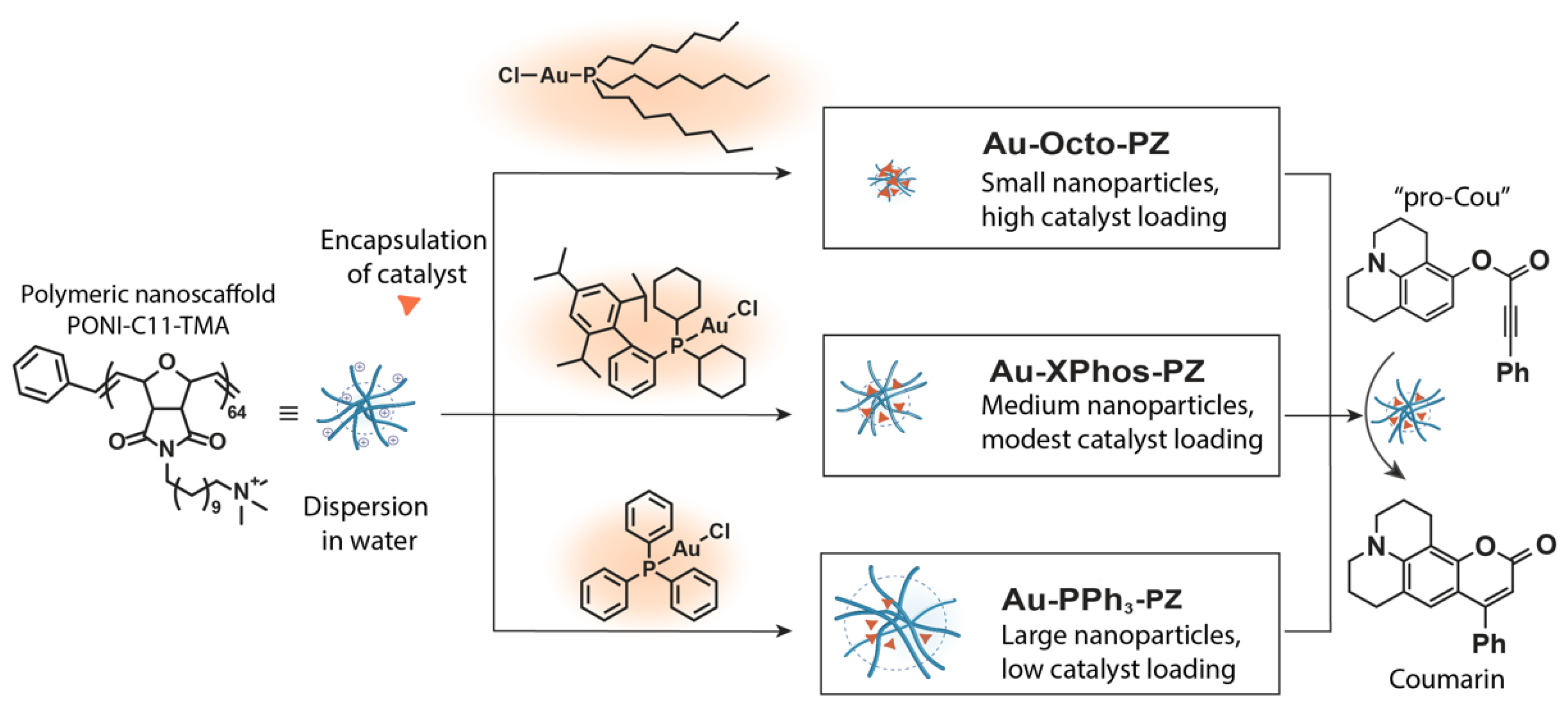
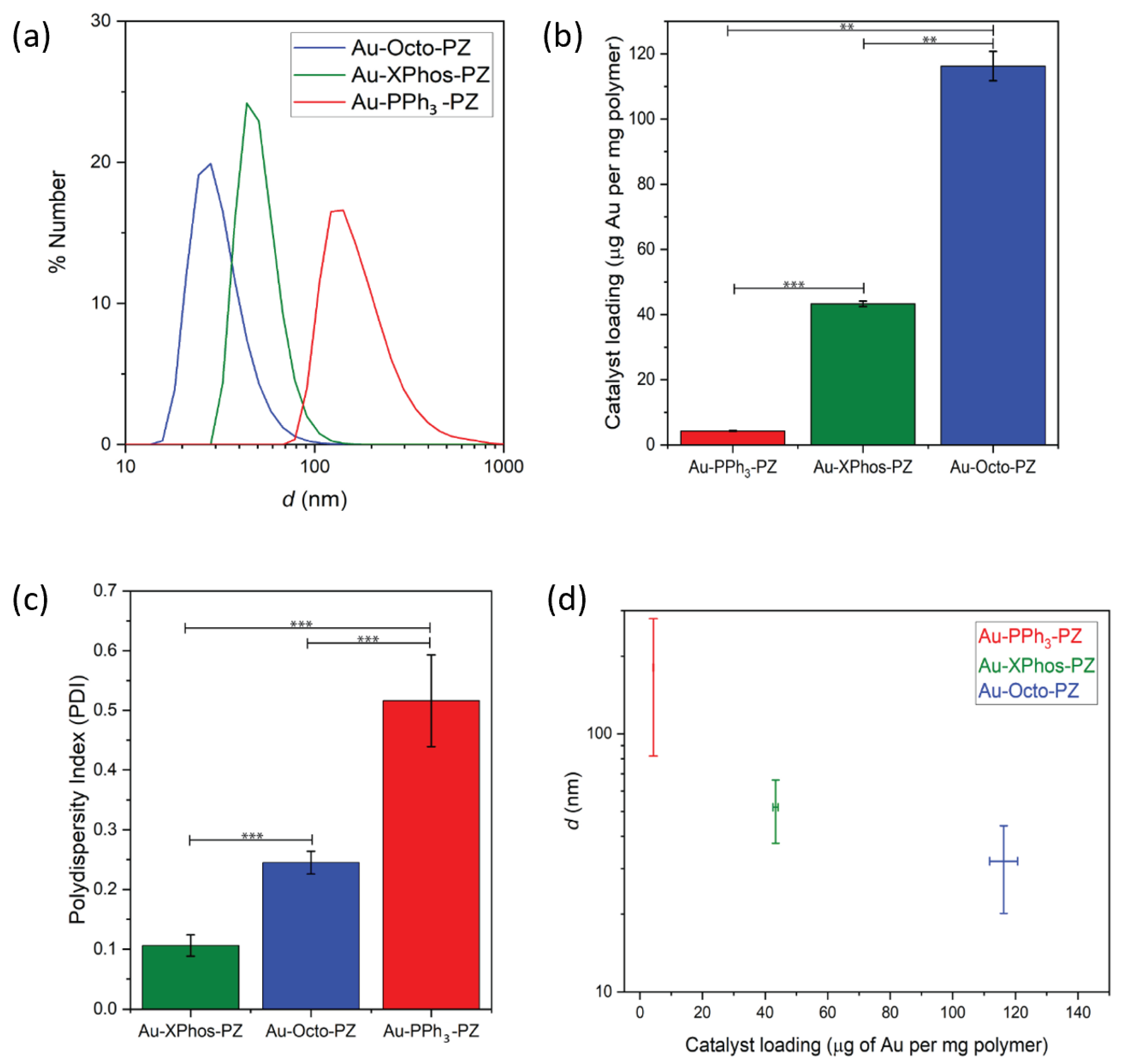
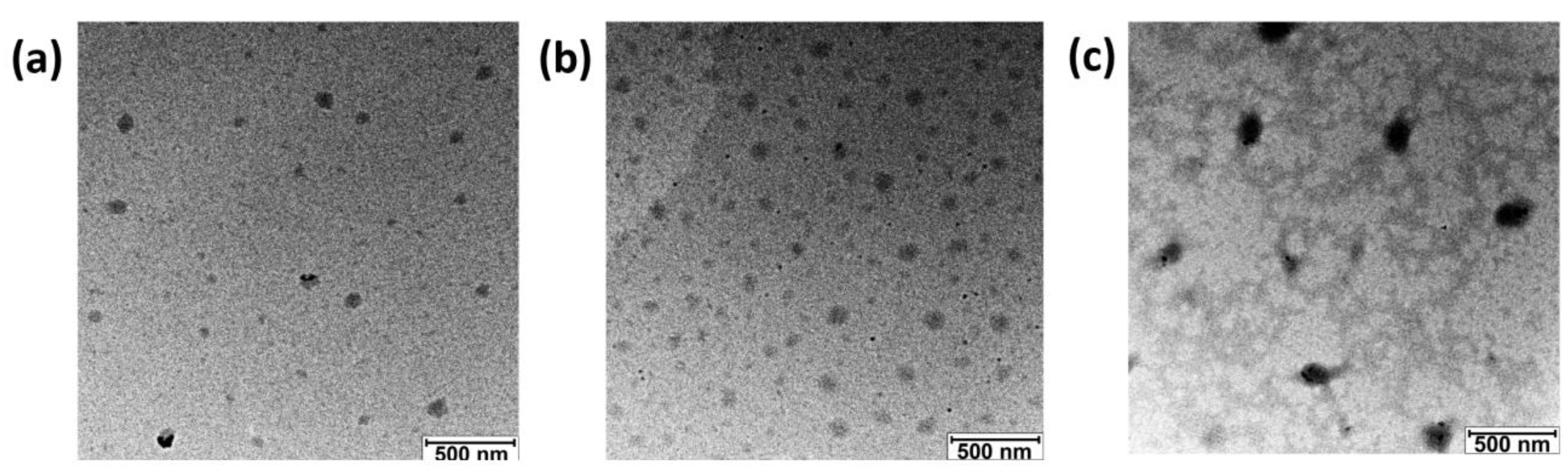
3.1. Physical Properties of Polyzymes
3.2. Catalytic Performance of the Free TMCs and Polyzymes
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Bai, Y. Design and Engineering of Metal Catalysts for Bio-orthogonal Catalysis in Living Systems. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 4717–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Huang, R.; Hirschbiegel, C.M.; Wang, H.; Ding, Y.; Rotello, V.M. In situ activation of therapeutics through bioorthogonal catalysis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chankeshwara, S.V.; Indrigo, E.; Bradley, M. Palladium-mediated chemistry in living cells. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fedeli, S.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Huang, R.; Gupta, A.; Luther, D.C.; Rotello, V.M. Protection and Isolation of Bioorthogonal Metal Catalysts by Using Monolayer-Coated Nanozymes. ChemBioChem 2020, 21, 2759–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Völker, T.; Meggers, E. Transition-metal-mediated uncaging in living human cells—An emerging alternative to photolabile protecting groups. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 25, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Landis, R.F.; Keshri, P.; Cao-Milán, R.; Luther, D.C.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, R.; Li, G.; Malassiné, M.; et al. Intracellular Activation of Anticancer Therapeutics Using Polymeric Bioorthogonal Nanocatalysts. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Chen, J.; Zimmerman, S.C. Designed transition metal catalysts for intracellular organic synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W.; Hysell, D.; Hall, L.; Campbell, K.; Stara, J. Preliminary studies on the toxicity and metabolism of palladium and platinum. Environ. Health Perspect. 1975, 10, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathla, S.; Jain, T. Heavy Metals Toxicity. Int. J. Health Sci. Res. 2016, 5, 361–368. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, J.T.; Kollmannsberg, C.; Kanz, L.; Bokemeyer, C. Platinum organ toxicity and possible prevention in patients with testicular cancer. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 6, 866–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabec, V.; Nováková, O. DNA binding mode of ruthenium complexes and relationship to tumor cell toxicity. Drug Resist. Updates 2006, 9, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, S.; Du, M.; Tang, S.; Chen, M.; Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J. Toxic effect of palladium on embryonic development of zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 159, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sava, G.; Bergamo, A. Ruthenium-based compounds and tumour growth control (review). Int. J. Oncol. 2000, 17, 353–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Sivaram, H.; Huynh, H.V. Gold(I) bis(N-heterocyclic carbene) complexes: Metabolic stability, in vitro inhibition, and genotoxicity. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysouli, M.P.; Banti, C.N.; Kourkoumelis, N.; Panayiotou, N.; Markopoulos, G.S.; Tasiopoulos, A.J.; Hadjikakou, S.K. Chloro(triphenylphosphine)gold(I) a forefront reagent in gold chemistry as apoptotic agent for cancer cells. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2018, 179, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.R.; Casini, A. Gold compounds for catalysis and metal-mediated transformations in biological systems. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2020, 55, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, C.; Tomás-Gamasa, M.; Destito, P.; López, F.; Mascareñas, J.L. Concurrent and orthogonal gold(I) and ruthenium(II) catalysis inside living cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, F.; Sanz, S.; Vergara, E.; Cerrada, E.; Laguna, M. Water-soluble and water-stable gold(I), gold(II) and gold(III) phosphine complexes: The early years. Gold Bull. 2006, 39, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.; Stenton, B.J.; Bernardes, G.J.L. Bioorthogonal Decaging Reactions for Targeted Drug Activation. CHIMIA Int. J. Chem. 2018, 72, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeli, S.; Im, J.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Elia, J.L.; Gupta, A.; Kim, D.; Rotello, V.M. Nanomaterial-based bioorthogonal nanozymes for biological applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 13467–13480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Li, C.-H.; Cao-Milán, R.; He, L.D.; Makabenta, J.M.; Zhang, X.; Yu, E.; Rotello, V.M. Polymer-Based Bioorthogonal Nanocatalysts for the Treatment of Bacterial Biofilms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 10723–10729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, N.D.; Toste, F.D. Synthesis and structural characterization of isolable phosphine coinage metal π-complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2779–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, V.W.-W.; Choi, S.W.-K. Synthesis, photophysics and photochemistry of alkynylgold(I) phosphine complexes. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1996, 4227–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mézailles, N.; Ricard, L.; Gagosz, F. Phosphine Gold(I) Bis-(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imidate Complexes as New Highly Efficient and Air-Stable Catalysts for the Cycloisomerization of Enynes. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 4133–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, W.S.; Prud’homme, R.K. Principles of nanoparticle formation by flash nanoprecipitation. Nano Today 2016, 11, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Chow, S.F.; Zheng, Y. Application of flash nanoprecipitation to fabricate poorly water-soluble drug nanoparticles. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Das, R.; Makabenta, J.M.; Gupta, A.; Zhang, X.; Jeon, T.; Huang, R.; Liu, Y.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Milán, R.-C.; et al. Erythrocyte-mediated delivery of bioorthogonal nanozymes for selective targeting of bacterial infections. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 3424–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, B.; Escofet, I.; Echavarren, A.M. Anatomy of gold catalysts: Facts and myths. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 7103–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cai, R.; Sharma, S.; Jirak, J.; Thummanapelli, S.K.; Akhmedov, N.G.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Petersen, J.L.; Shi, X. “Silver Effect” in Gold(I) Catalysis: An Overlooked Important Factor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9012–9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hammond, G.B.; Xu, B. Ligand Effects and Ligand Design in Homogeneous Gold(I) Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5697–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, A.S.K. Homogeneous gold catalysts and alkynes: A successful liaison. Gold Bull. 2003, 36, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wile, B.M.; McDonald, R.; Ferguson, M.J.; Stradiotto, M. Au(I) Complexes Supported by Donor-Functionalized Indene Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization, and Catalytic Behavior in Aldehyde Hydrosilylation. Organometallics 2007, 26, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Landis, R.F.; Li, C.-H.; Schnurr, M.; Das, R.; Lee, Y.-W.; Yazdani, M.; Liu, Y.; Kozlova, A.; Rotello, V.M. Engineered Polymer Nanoparticles with Unprecedented Antimicrobial Efficacy and Therapeutic Indices against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Biofilms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 38, 12137–12143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Catalyst Species | Au-PPh3 | Au-XPhos | Au-Octo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yield a | 73% | 77% | 29% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hirschbiegel, C.-M.; Fedeli, S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, R.; Park, J.; Xu, Y.; Rotello, V.M. Enhanced Design of Gold Catalysts for Bioorthogonal Polyzymes. Materials 2022, 15, 6487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186487
Hirschbiegel C-M, Fedeli S, Zhang X, Huang R, Park J, Xu Y, Rotello VM. Enhanced Design of Gold Catalysts for Bioorthogonal Polyzymes. Materials. 2022; 15(18):6487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186487
Chicago/Turabian StyleHirschbiegel, Cristina-Maria, Stefano Fedeli, Xianzhi Zhang, Rui Huang, Jungmi Park, Yisheng Xu, and Vincent M. Rotello. 2022. "Enhanced Design of Gold Catalysts for Bioorthogonal Polyzymes" Materials 15, no. 18: 6487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186487
APA StyleHirschbiegel, C.-M., Fedeli, S., Zhang, X., Huang, R., Park, J., Xu, Y., & Rotello, V. M. (2022). Enhanced Design of Gold Catalysts for Bioorthogonal Polyzymes. Materials, 15(18), 6487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186487









