Electric Arc Furnace Dust Recycled in 7075 Aluminum Alloy Composites Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Powders
2.2. Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)
2.3. Characterization
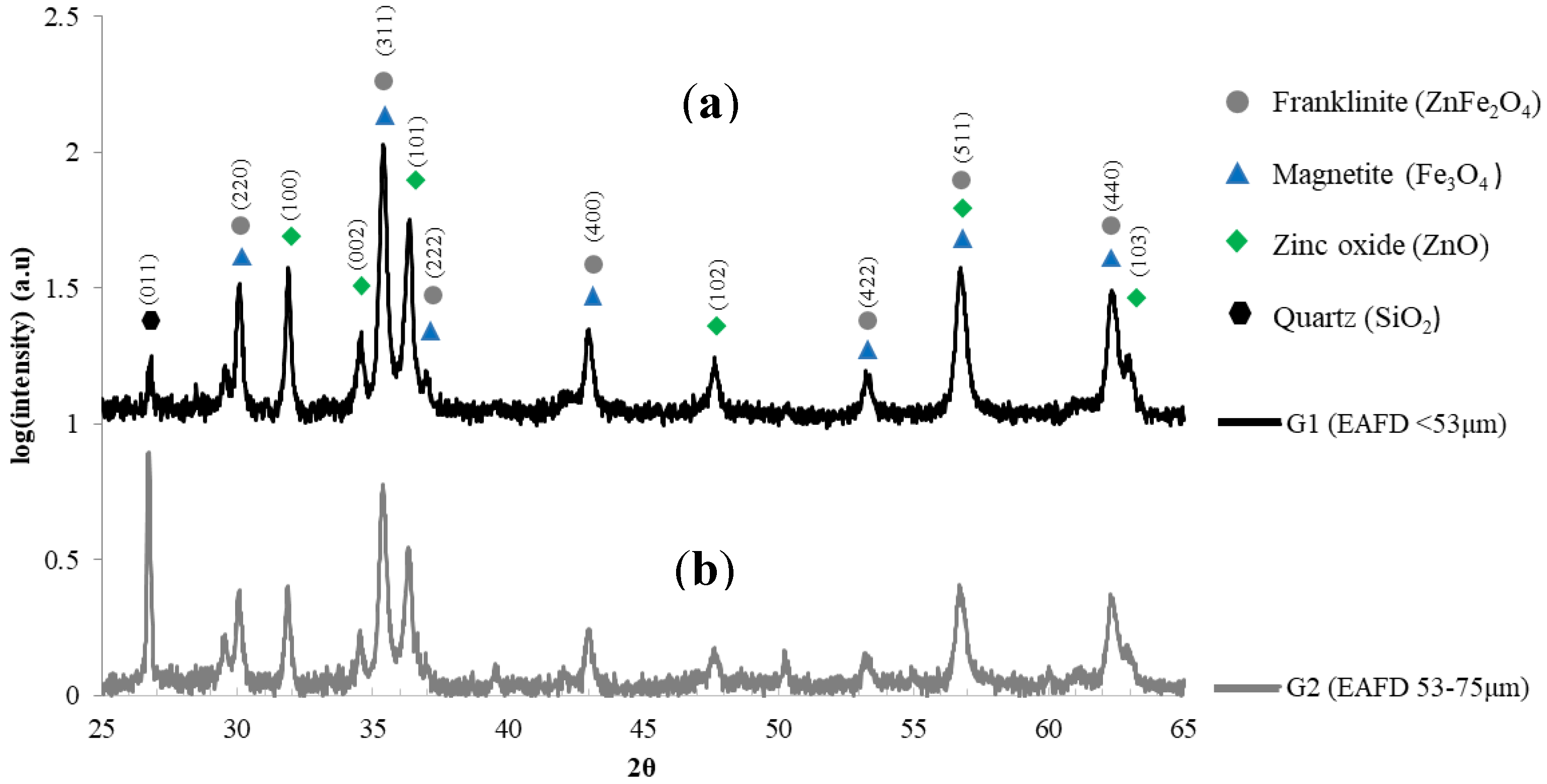
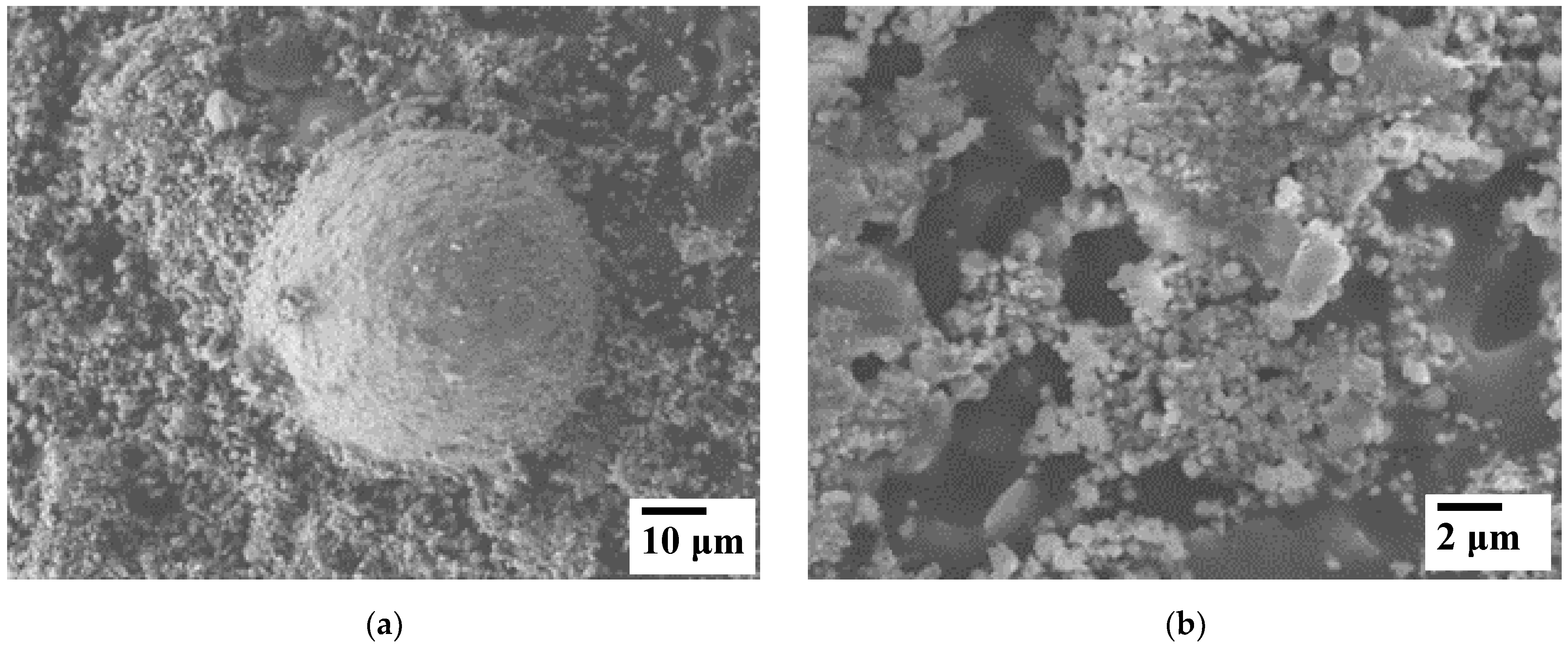
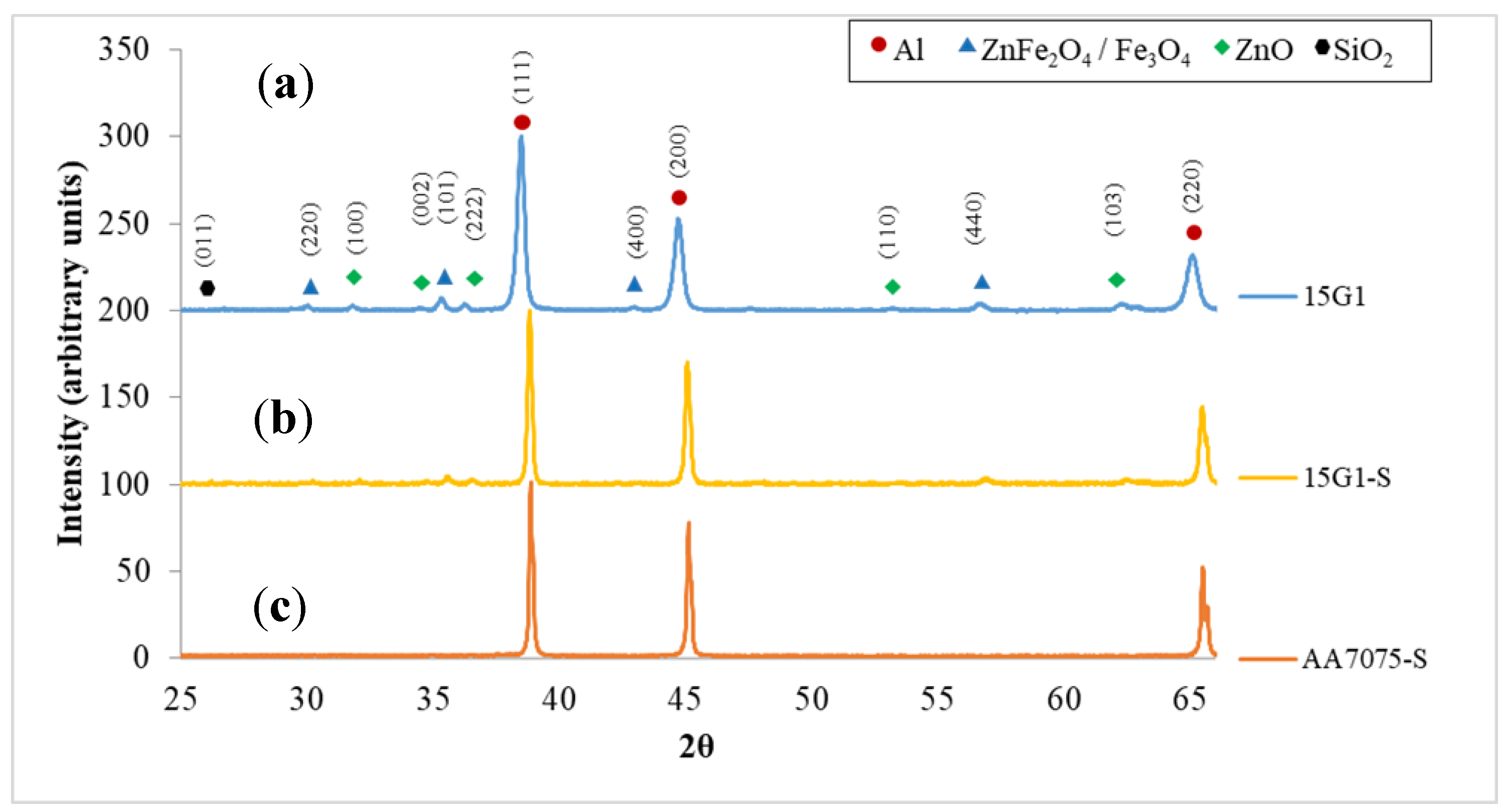
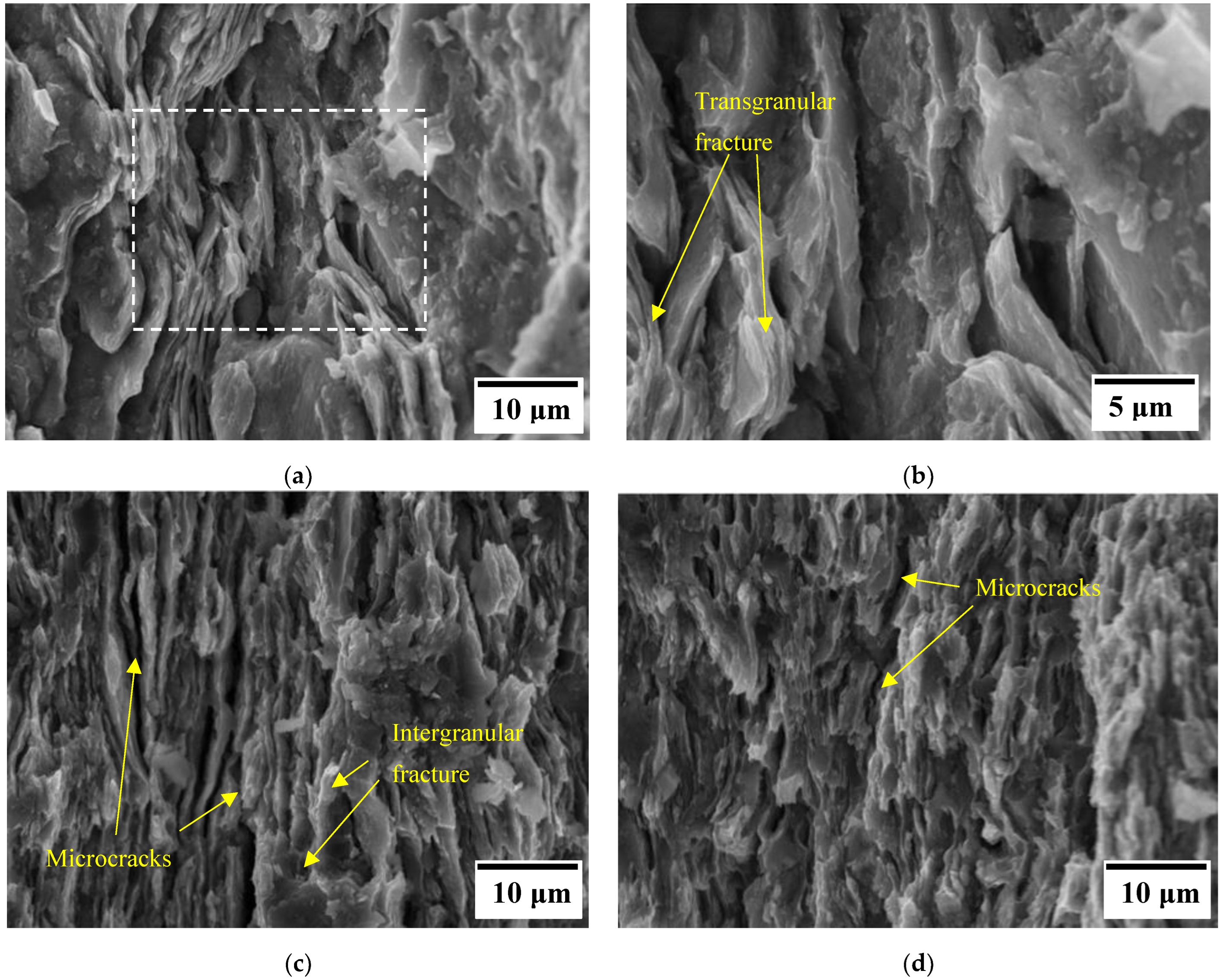
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Araújo, J.A.; Schalch, V. Recycling of electric arc furnace (EAF) dust for use in steel making process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2014, 3, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guézennec, A.-G.; Huber, J.-C.; Patisson, F.; Sessiecq, P.; Birat, J.-P.; Ablitzer, D. Dust formation in Electric Arc Furnace: Birth of the particles. Powder Technol. 2005, 157, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Buzin, P.J.W.K.; Heck, N.C.; Vilela, A.C.F. EAF dust: An overview on the influences of physical, chemical and mineral features in its recycling and waste incorporation routes. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2017, 6, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas (ABNT). NBR 10004: Resíduos Sólidos—Classificação; ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bakkar, A. Recycling of electric arc furnace dust through dissolution in deep eutectic ionic liquids and electrowinning. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency. European Waste Catalogue and Hazardous Waste List; EPA: Wexford, Ireland, 2002. Available online: https://www.epa.ie/publications/monitoring--assessment/waste/2019--FULL-template.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Nuruddin, M.F.; Fauzi, A.; Wahab, M.M.A.; Shafiq, N.; Malkawi, A.B. Utilization of EAFD in Concrete Composite. Mater. Sci. Forum 2017, 894, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamuyuni, J.; Halli, P.; Tesfaye, F.; Leikola, M.; Lundström, M. A Sustainable Methodology for Recycling Electric Arc Furnace Dust; Minerals, Metals and Materials Series; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niubó, M.; Fernandez, A.I.; Chimenos, J.M.; Haurie, L. A possible recycling method for high grade steels EAFD in polymer composites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreneche, C.; Navarro, M.E.; Niubó, M.; Cabeza, L.F.; Fernandez, A.I. Use of PCM–polymer composite dense sheet including EAFD in constructive systems. Energy Build. 2014, 68, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathopoulos, V.; Papandreou, A.; Kanellopoulou, D.; Stournaras, C. Structural ceramics containing electric arc furnace dust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsheyab, M.A.; Khedaywi, T.S. Effect of electric arc furnace dust (EAFD) on properties of asphalt cement mixture. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2013, 70, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Vélez, L.M.; Chavez, J.; Hernández, L.; Domínguez, O. Characterization and properties of aluminum composite materials prepared by powder metallurgy techniques using ceramic solid wastes. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2001, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeosun, S.O.; Akpan, E.I.; Sekunowo, O.I.; Ayoola, W.A.; Balogun, S.A. Mechanical Characteristics of 6063 Aluminum-Steel Dust Composite. ISRN Mech. Eng. 2012, 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.; Amaro, D.R.A.; Silva, E.C.D.O.; Filho, O.O.D.A.; Alves, K.G.B. Study on Effect of EAFD Particulate Reinforcement in AA7075 Aluminum Matrix Composites. Mater. Res. 2018, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, V.; Sateesh, N.; Hussain, M.M. Manufacture of Aluminium Metal Matrix Composite (Al7075-SiC) by Stir Casting Technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 3403–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaneyan, S.P.; Ganesh, R.; Senthilvelan, T. On the Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Aluminium 7075 Matrix Composite Material Reinforced with SiC and TiC Produced by Powder Metallurgy Method. Indian J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 2017, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.B. An Experimental Investigation on Mechanical and Wear Properties of Al7075/SiCp Composites: Effect of SiC Content and Particle Size. J. Tribol. 2017, 140, 031601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakci, A.; Varol, T. Microstructure and properties of AA7075/Al–SiC composites fabricated using powder metallurgy and hot pressing. Powder Technol. 2014, 268, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeravalli, R.R.; Nallu, R.; Sarcar, M.M.M. Mechanical and tribological properties of AA7075–TiC metal matrix composites under heat treated (T6) and cast conditions. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2016, 5, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Wu, C.; Luo, G.; Fang, P.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-7075/B4C composites fabricated by plasma activated sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 588, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, H.; Badheka, V.; Kumar, A. Fabrication of Al7075 / B4C Surface Composite by Novel Friction Stir Processing (FSP) and Investigation on Wear Properties. Procedia Technol. 2016, 23, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molnárová, O.; Málek, P.; Veselý, J.; Šlapáková, M.; Minárik, P.; Lukáč, F.; Chráska, T.; Novák, P.; Průša, F. Nanocrystalline Al7075 + 1 wt% Zr Alloy Prepared Using Mechanical Milling and Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials 2017, 10, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Ruiz, R.; Flores-Campos, R.; Treviño-Rodríguez, G.; Herrera-Ramirez, J.; Sánchez, R.M. Wear resistance analysis of the aluminum 7075 alloy and the nanostructured aluminum 7075—Silver nanoparticles composites. J. Min. Met. Sect. B Met. 2016, 52, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanithi, R.; Ghosh, K.S.; Bera, S. Effect of Dispersoid Size and Volume Fraction on Aging Behavior and Mechanical Properties of TiO2-Dispersed AA7075 Alloy Composites. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 4062–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, K.; Ramanujam, R.; Shanbhag, V.; Yalamoori, N.; Reddy, D. Preparation, Characterization and Machinability of Al7075-Al2O3 Matrix Composite Using Multi Layer Coated Carbide Insert. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaneme, K.K.; Sanusi, K.O. Microstructural characteristics, mechanical and wear behaviour of aluminium matrix hybrid composites reinforced with alumina, rice husk ash and graphite. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2015, 18, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, B.; Meng, Q.; Ma, S.; Dai, W. Reduced Graphene Oxide Reinforced 7075 Al Matrix Composites: Powder Synthesis and Mechanical Properties. Metals 2017, 7, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.K.; Sinha, O.P. New-Generation Aluminum Composite with Bottom Ash Industrial Waste. JOM 2018, 70, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Khan, A.A.; Megeri, S.; Sadik, S. Study of hardness and tensile strength of Aluminium-7075 percentage varying reinforced with graphite and bagasse-ash composites. Resour. Technol. 2016, 2, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Soltani, N.; Pech-Canul, M.; Gutiérrez, C.A. Development of metal-matrix composites from industrial/agricultural waste materials and their derivatives. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 143–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladston, J.A.K.; Dinaharan, I.; Sheriff, N.M.; Selvam, J.D.R. Dry sliding wear behavior of AA6061 aluminum alloy composites reinforced rice husk ash particulates produced using compocasting. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2017, 5, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.S.; Shoba, C.; Ramanaiah, N. Investigations on mechanical properties of aluminum hybrid composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2014, 3, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.D.; Senthilkumar, M.; Shankar, S. Effect of Particle Size on Tribological Behavior of Rice Husk Ash–Reinforced Aluminum Alloy (AlSi10Mg) Matrix Composites. Tribol. Trans. 2013, 56, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, L.F.; Suresh, P. Wear Behavior of Aluminium Metal Matrix Composite Prepared from Industrial Waste. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokita, M. Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) Method, Systems, and Applications, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, E.; Bouchonneau, N.; Alves, E.; Alves, K.; Filho, O.A.; Mesguich, D.; Chevallier, G.; Laurent, C.; Estournès, C. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AA7075 Aluminum Alloy Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS). Materials 2021, 14, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Aluminium Association. International Alloy Designations and Chemical Composition Limits for Wrought Aluminum and Wrought Aluminum Alloys with Support for On-Line Access from: Aluminum Extruders Council Use of the Information; The Aluminum Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2015; 31p. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, J.G.; Brehm, F.A.; Moraes, C.A.M.; dos Santos, C.A.; Vilela, A.; da Cunha, J.B.M. Chemical, physical, structural and morphological characterization of the electric arc furnace dust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocabois, P.; Huber, J.C.; Lectard, E.; Patisson, F. Thermodynamic assessment of the oxide phase in the Fe–Zn–O system: Application to the dust formation in EAF. In Proceedings of the 10th International IUPAC Conference on High Temperature Materials Chemistry, Julich, Germany; 2000; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.S.; Girisha, H.N.; Keshavamurthy, R. Impact of Hot Rolling on Mechanical Characteristics of AA7075/TiB2/Graphite Hybrid Composites. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. D 2022, 103, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Liu, Z.-F.; Lu, J.-F.; Shen, X.-B.; Wang, F.-C.; Wang, Y.-D. The sintering mechanism in spark plasma sintering—Proof of the occurrence of spark discharge. Scr. Mater. 2014, 81, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | Content (wt.%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | G2 | AA7075 | |
| AA7075 | - | - | 100 |
| 05G1 | 5 | - | 95 |
| 10G1 | 10 | - | 90 |
| 15G1 | 15 | - | 85 |
| 05G2 | - | 5 | 95 |
| 10G2 | - | 10 | 90 |
| 15G2 | - | 15 | 85 |
| Fe | Zn | Ca | Mn | Si | Mg | Al | Pb | Gd | La | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 39.89 | 36.93 | 7.00 | 4.13 | 2.74 | 2.69 | 1.48 | 1.22 | 0.66 | 0.65 |
| G2 | 45.33 | 28.80 | 7.66 | 2.99 | 4.98 | 2.90 | 2.02 | 1.22 | 0.40 | - |
| Cr | K | Cu | Cl | Ti | Ba | S | P | Others | ||
| G1 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.44 | |
| G2 | 0.40 | 0.52 | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.69 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.73 | |
| Sample | G1 (wt.%) | G2 (wt.%) | AA7075 (wt.%) | ρc (g∙cm−3) | ρ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA7075-S | - | - | 100 | 2.81 | 99.3 ± 0.1 |
| 05G1-S | 5 | - | 95 | 2.85 | 96.5 ± 0.2 |
| 10G1-S | 10 | - | 90 | 2.88 | 97.5 ± 0.1 |
| 15G1-S | 15 | - | 85 | 2.92 | 98.2 ± 0.1 |
| 05G2-S | - | 5 | 95 | 2.83 | 99.1 ± 0.1 |
| 10G2-S | - | 10 | 90 | 2.86 | 97.2 ± 0.1 |
| 15G2-S | - | 15 | 85 | 2.89 | 100.0 ± 0.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soares, E.; Bouchonneau, N.; Alves, E.; Alves, K.; Filho, O.A.; Mesguich, D.; Chevallier, G.; Khalile, N.; Laurent, C.; Estournès, C. Electric Arc Furnace Dust Recycled in 7075 Aluminum Alloy Composites Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS). Materials 2022, 15, 6587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196587
Soares E, Bouchonneau N, Alves E, Alves K, Filho OA, Mesguich D, Chevallier G, Khalile N, Laurent C, Estournès C. Electric Arc Furnace Dust Recycled in 7075 Aluminum Alloy Composites Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS). Materials. 2022; 15(19):6587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196587
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoares, Elder, Nadège Bouchonneau, Elizeth Alves, Kleber Alves, Oscar Araújo Filho, David Mesguich, Geoffroy Chevallier, Nouhaila Khalile, Christophe Laurent, and Claude Estournès. 2022. "Electric Arc Furnace Dust Recycled in 7075 Aluminum Alloy Composites Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)" Materials 15, no. 19: 6587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196587
APA StyleSoares, E., Bouchonneau, N., Alves, E., Alves, K., Filho, O. A., Mesguich, D., Chevallier, G., Khalile, N., Laurent, C., & Estournès, C. (2022). Electric Arc Furnace Dust Recycled in 7075 Aluminum Alloy Composites Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS). Materials, 15(19), 6587. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196587








