The Effect of Mixture Proportion on the Performance of Alkali-Activated Slag Concrete Subjected to Sulfuric Acid Attack
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Test Procedure
2.1. Material Properties
2.2. Mix Proportions and Casting
2.3. Curing Methods and Test Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
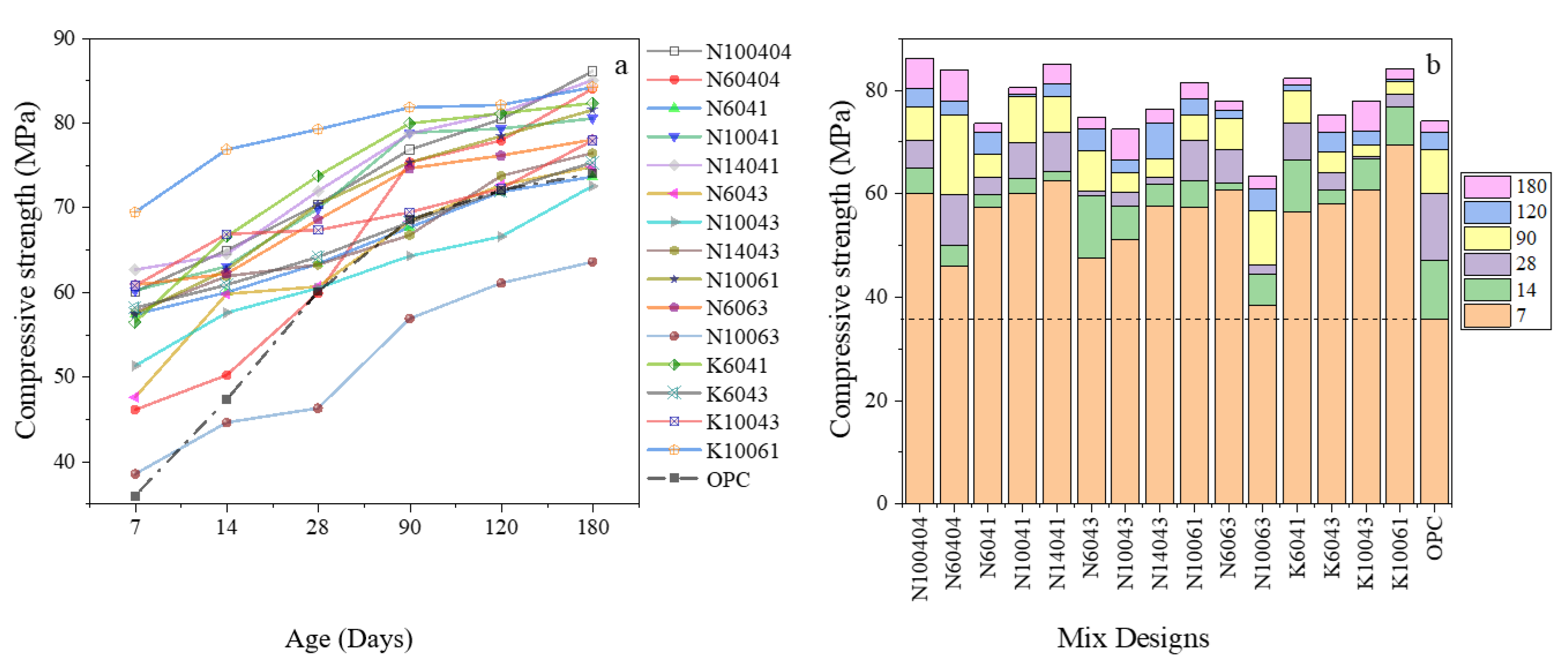
3.1. Mix Design Effects on Compressive Strength of AASC
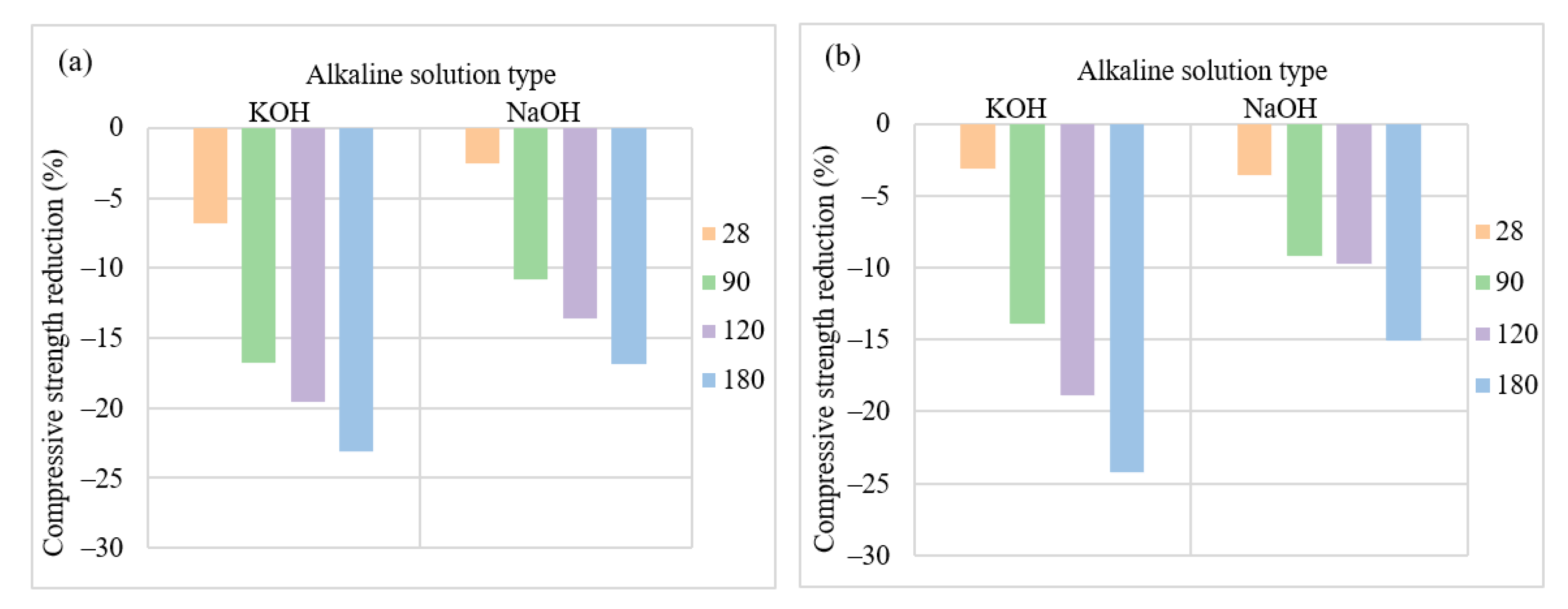
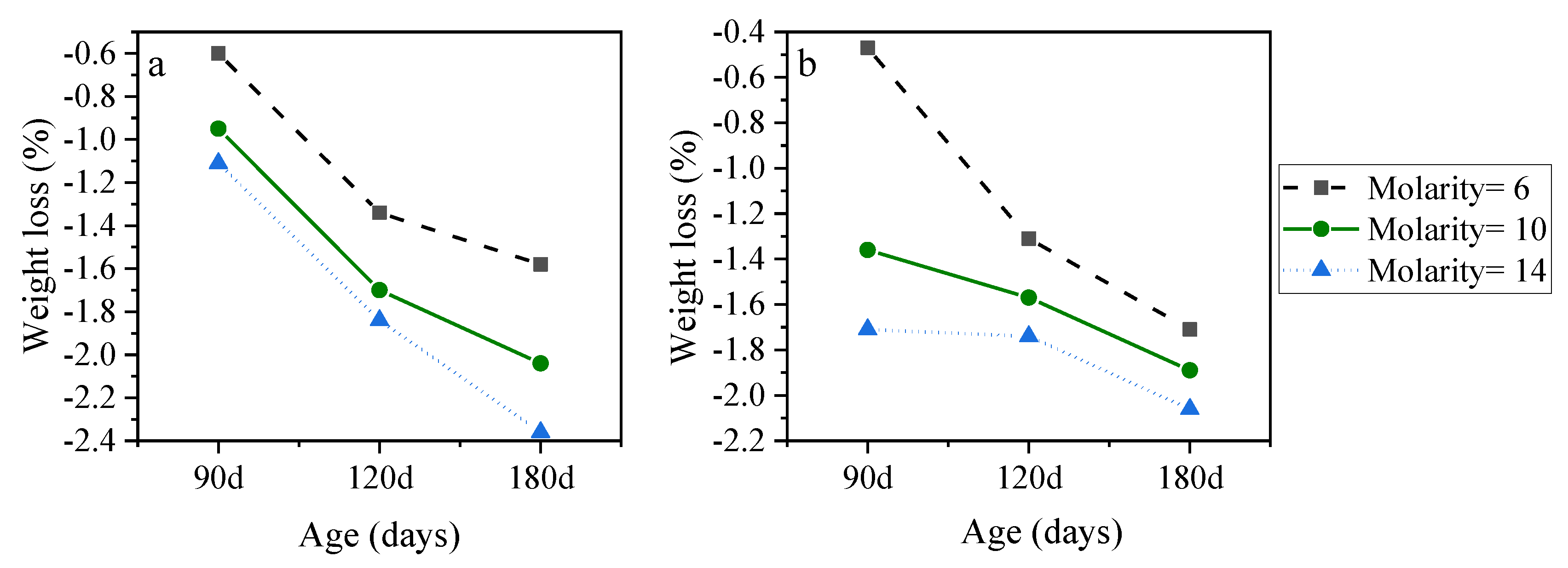
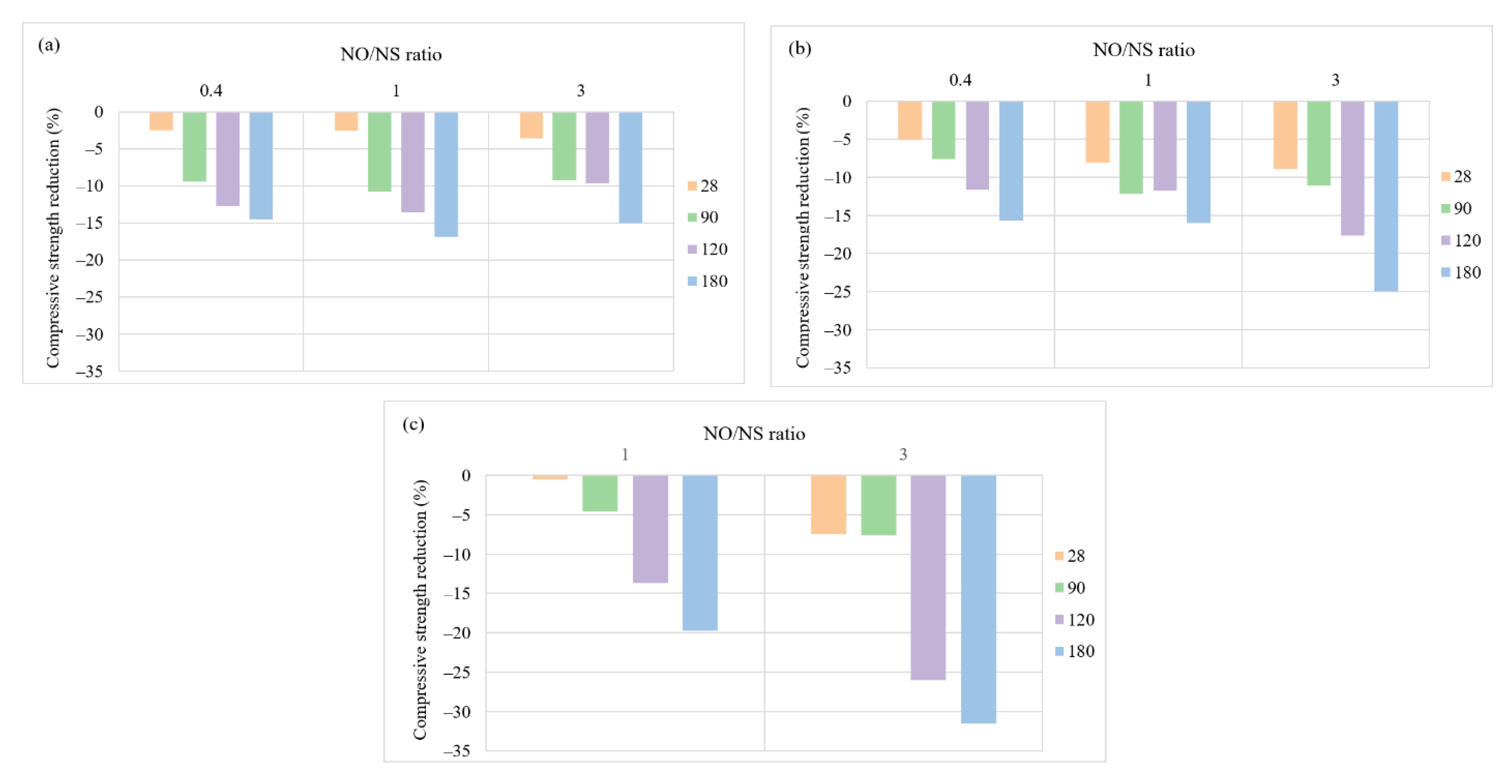
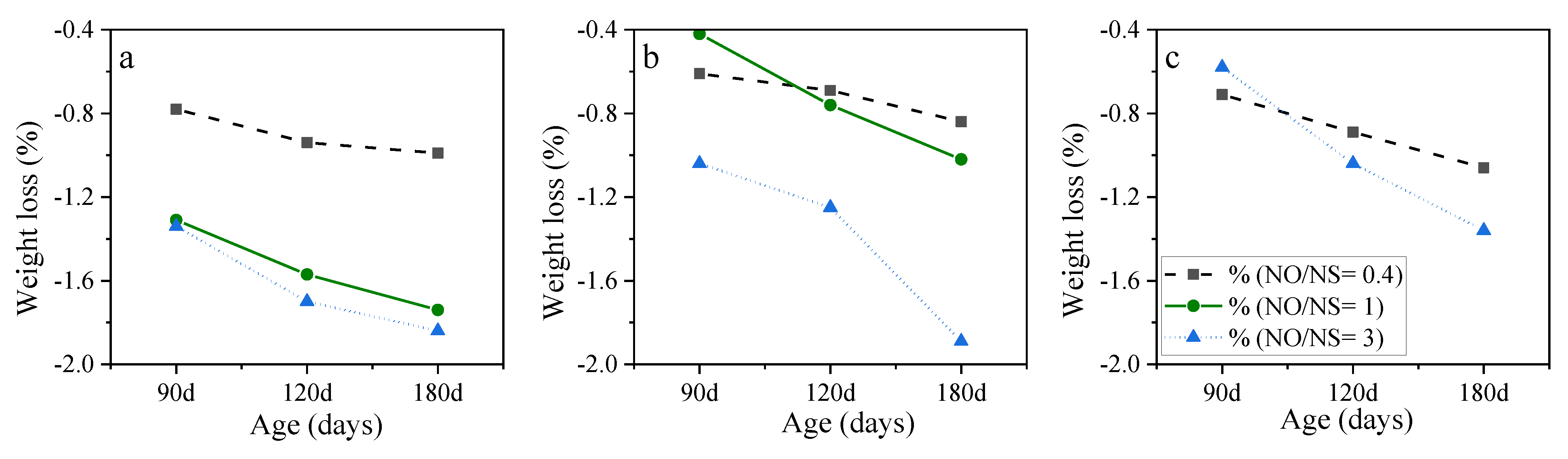
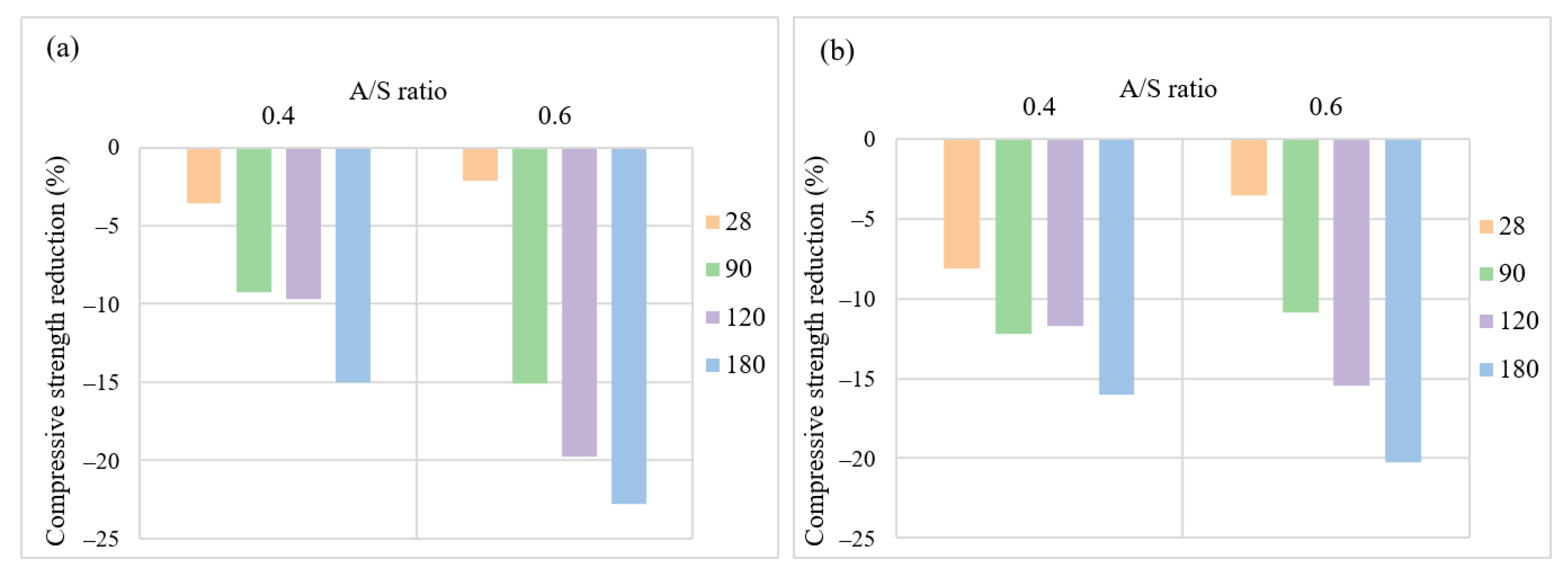
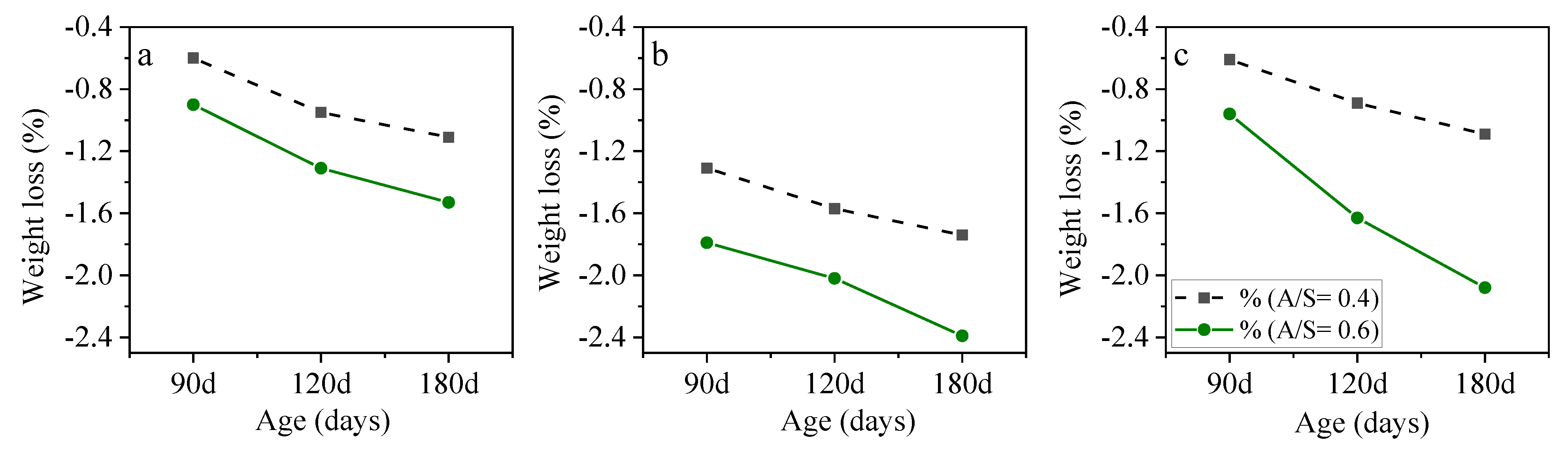
3.2. Mix Design Effects on the Performance of AASC in the Acidic Environment
3.2.1. Type of Alkaline Activator
3.2.2. NaOH Molarity
3.2.3. NaOH to Na2SiO3 Ratio
3.2.4. Alkali Solution Content to Slag Ratio
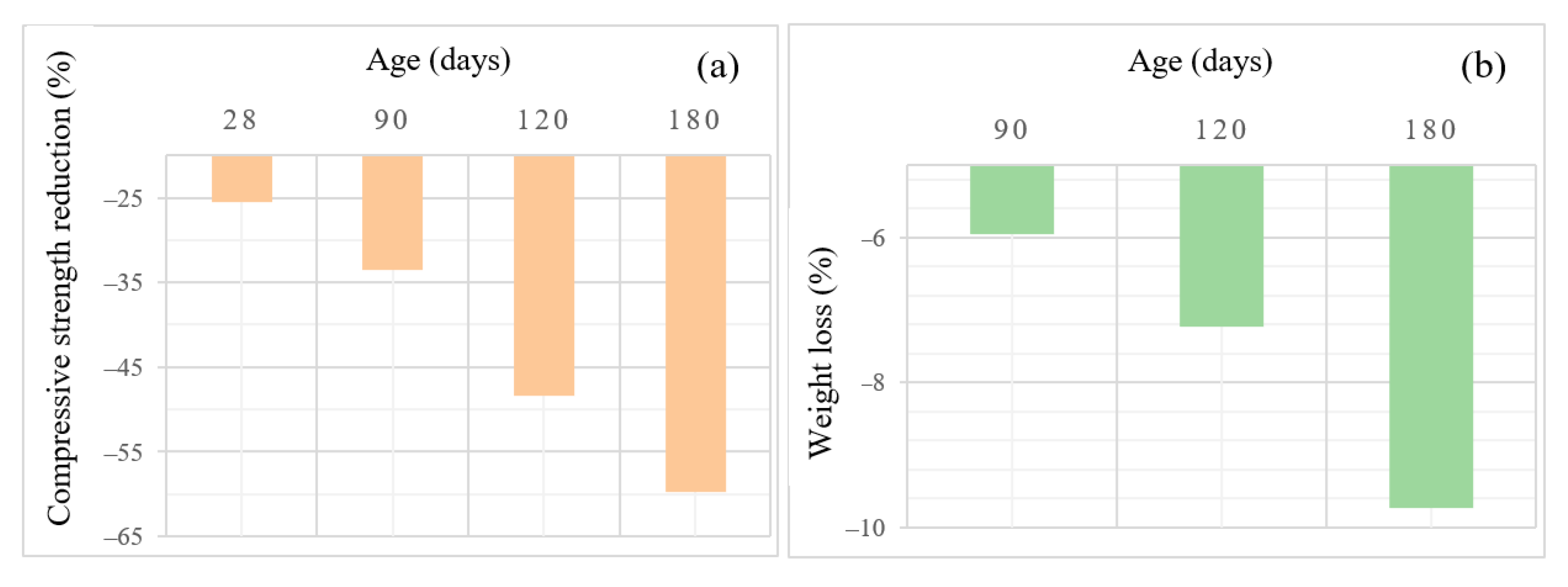
3.3. Comparative Study on the Performance of AASC and OPC in Sulfuric Acid Attack
4. XRF Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Youn, M.H.; Park, K.T.; Lee, Y.H.; Kang, S.-P.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, Y.E.; Ko, Y.N.; Jeong, S.K.; Lee, W. Carbon dioxide sequestration process for the cement industry. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 34, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivica, V.; Bajza, A. Acidic attack of cement based materials—A review. Part 1. Principle of acidic attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2001, 15, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, P.S.N.; Dayaratnam, P. Durability of concrete exposed to dilute sulphuric acid. Build. Environ. 1984, 19, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, T.; Melchers, R.E. Modelling concrete deterioration in sewers using theory and field observations. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 77, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdi, A.; Škvára, F. Acidic corrosion of hydrated cement based materials. Part 1. Mechanism of the phenomenon. Ceram. Silik. 2000, 44, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Teymouri, M.; Shakouri, M.; Vaddey, N.P. pH-dependent chloride desorption isotherms of Portland cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 312, 125415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Guerrero, A.M.; Robayo-Salazar, R.A.; de Gutiérrez, R.M. Corrosion resistance of alkali-activated binary reinforced concrete based on natural volcanic pozzolan exposed to chlorides. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 33, 101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, S.; Baradan, B. Sulfate resistance of alkali-activated slag and Portland cement based reactive powder concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 103205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunath, R.; Narasimhan, M.C. An experimental investigation on self-compacting alkali activated slag concrete mixes. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, B.C.; Pedroti, L.G.; Vieira, C.M.F.; Marvila, M.; Azevedo, A.R.G.; de Carvalho, J.M.F.; Ribeiro, J.C.L. Application of eco-friendly alternative activators in alkali-activated materials: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 35, 102010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmegam, A.; Avudaiappan, S.; Amran, M.; Guindos, P.; Vatin, N.I.; Fediuk, R. Retrofitting RC beams using high-early strength alkali-activated concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian, G.; Behfarnia, K.; Teymouri, M. Drying shrinkage of one-part alkali-activated slag concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 51, 104263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Bu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, W.; Yuan, Q.; Niu, D. Hydration Characteristics and Microstructure of Alkali-Activated Slag Concrete: A Review. Engineering 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, I.; Kohail, M.; El-Feky, M.S.; Rashad, A.; Khalaf, M.A. A review on alkali-activated slag concrete. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 1475–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, M.M.A.; Hossain, M.M.; Karim, M.R.; Zain, M.F.M.; Shearer, C. A review on alkali-activated binders: Materials composition and fresh properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo Júnior, N.T.; Lima, V.M.E.; Torres, S.M.; Basto, P.E.A.; Melo Neto, A.A. Experimental investigation of mix design for high-strength alkali-activated slag concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 291, 123387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliques-Granero, J.; Tognonvi, T.M.; Tagnit-Hamou, A. Durability test methods and their application to AAMs: Case of sulfuric-acid resistance. Mater. Struct./Mater. Constr. 2017, 50, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakharev, T.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Cheng, Y.B. Resistance of alkali-activated slag concrete to acid attack. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1607–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, C.; Faleschini, F.; Meyer, C. 2—Recycled materials in concrete. In Developments in the Formulation and Reinforcement of Concrete, 2nd ed.; Mindess, S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 19–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Torgal, F.; Labrincha, J.; Leonelli, C.; Palomo, Á.; Chindaprasirt, P. Handbook of Alkali-Activated Cements, Mortars and Concretes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bakharev, T. Resistance of geopolymer materials to acid attack. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.S.; Sarker, P.K.; Barbhuiya, S. Sorptivity and acid resistance of ambient-cured geopolymer mortars containing nano-silica. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 72, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, P.; Gluth, G.J.G.; Jäger, C.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Kühne, H.C. Sulfuric acid resistance of one-part alkali-activated mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 109, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, F.N.; Prakash, S.; Singh, N.B. Durability of fly ash based geopolymer concrete in the presence of silica fume. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakharev, T.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Cheng, Y.B. Effect of admixtures on properties of alkali-activated slag concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-D.; Pu, X.-C.; Scrivener, K.L.; Pratt, P.L. Alkali-activated slag cement and concrete: A review of properties and problems. Adv. Cem. Res. 1995, 7, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.A.M.; Cincotto, M.A.; Repette, W. Drying and autogenous shrinkage of pastes and mortars with activated slag cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Roy, D.; Krivenko, P. Alkali-Activated Cements and Concretes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Teymouri, M.; Behfarnia, K.; Shabani, A. Mix Design Effects on the Durability of Alkali-Activated Slag Concrete in a Hydrochloric Acid Environment. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habert, G.; Ouellet-Plamondon, C. Recent update on the environmental impact of geopolymers. RILEM Tech. Lett. 2016, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Aydın, S.; Yardımcı, M.Y.; Lesage, K.; De Schutter, G. Rheology and microstructure of alkali-activated slag cements produced with silica fume activator. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 125, 104303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passuello, A.; Rodríguez, E.D.; Hirt, E.; Longhi, M.; Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L.; Kirchheim, A.P. Evaluation of the potential improvement in the environmental footprint of geopolymers using waste-derived activators. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, S.; Kızıltepe Cavit, Ç. Valorization of Boron Mine Tailings in Alkali-Activated Mortars. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, V.K.; Babu, D.L.V. Assessing the performance of molarity and alkaline activator ratio on engineering properties of self-compacting alkaline activated concrete at ambient temperature. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 20, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakharev, T.; Sanjayan, J.G.; Cheng, Y.B. Sulfate attack on alkali-activated slag concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunuguntla, C.S.; Gunneswara Rao, T.D. Effect of mix design parameters on mechanical and durability properties of alkali activated slag concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 193, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, R.M.; Butt, F.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, T.; Tufail, R.F. A Comprehensive Study on the Factors Affecting the Workability and Mechanical Properties of Ambient Cured Fly Ash and Slag Based Geopolymer Concrete. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behfarnia, K.; Yazeli, H.T.; Khasraghi, M.B.K. The Effect of Alkaline Activator on Workability and Compressive Strength of Alkali-Activated Slag Concrete. AUT J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 1, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Runci, A.; Serdar, M. Effect of curing time on the chloride diffusion of alkali-activated slag. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Gawwad, H.A.; Sikora, P.; Mohammed, A.H.; Arif, M.A.; Al-kroom, H.; Elrahman, M.A. Resistance of alkali-activated slag mixed with wastewater towards biogenic sulfuric acid attack. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.J. A study on the setting characteristics of sodium silicate-activated slag pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, M.; Behfarnia, K.; Mohebi, R. Application of alkali-activated slag concrete in railway sleepers. Mater. Des. 2015, 69, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komljenović, M.; Baščarević, Z.; Marjanović, N.; Nikolić, V. External sulfate attack on alkali-activated slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebregziabiher, B.S.; Thomas, R.; Peethamparan, S. Very early-age reaction kinetics and microstructural development in alkali-activated slag. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 55, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brough, A.R.; Atkinson, A. Sodium silicate-based, alkali-activated slag mortars: Part I. Strength, hydration and microstructure. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodi, F.; Norouzi, S.; Dashti, P. Mechanical properties and durability of alkali-activated slag repair mortars containing silica fume against freeze-thaw cycles and salt scaling attack. Adv. Concr. Constr. 2021, 11, 493–505. [Google Scholar]
- Puertas, F.; González-Fonteboa, B.; González-Taboada, I.; Alonso, M.M.; Torres-Carrasco, M.; Rojo, G.; Martínez-Abella, F. Alkali-activated slag concrete: Fresh and hardened behaviour. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 85, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.K.; Lee, H.K. Setting and mechanical properties of alkali-activated fly ash/slag concrete manufactured at room temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, T.A.; Kwasny, J.; Sha, W.; Tong, K.T. Mechanical and durability properties of alkali-activated fly ash concrete with increasing slag content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Radlińska, A. Carbonation-induced volume change in alkali-activated slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Ann, K.Y.; Cho, C.-G. Resistance of Alkali-Activated Slag Concrete to Chloride-Induced Corrosion. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 273101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awoyera, P.; Adesina, A. A critical review on application of alkali activated slag as a sustainable composite binder. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2019, 11, e00268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoodloorad, H.; Allahverdi, A. Developing Low-Cost Activators for Alkali-Activated Phosphorus Slag-Based Binders. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04017006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Materials | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | TiO2 | MnO | S | K2O | Fe2O3 | NaO2 | SO3 | LOI * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPC | 63.50 | 21.50 | 5.10 | 2.30 | - | - | - | 0.93 | 3.80 | - | 2.00 | 0.70 |
| GGBFS | 36.52 | 38.35 | 10.88 | 8.77 | 1.48 | 1.25 | 1.21 | 0.93 | 0.52 | 0.49 | - | 0.26 |
| Aggregate Type | Fineness Module | Sand Equality | Specific Gravity (SSD) (gr/cm3) | Water Absorption (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine | 2.99 | 77 | 2.47 | 2.06 |
| Course | - | - | 2.59 | 0.76 |
| Mix Code | Alkaline Solution | Molarity | A/S | NO/NS (KO/NS) | Alkaline Solution (Kg/m3) | Slag (Kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N6041 | NaOH | 6 | 0.4 | 1 | 158 | 394 |
| N6043 | NaOH | 6 | 0.4 | 3 | 158 | 394 |
| N10041 | NaOH | 10 | 0.4 | 1 | 158 | 394 |
| N10043 | NaOH | 10 | 0.4 | 3 | 158 | 394 |
| N14041 | NaOH | 14 | 0.4 | 1 | 158 | 394 |
| N14043 | NaOH | 14 | 0.4 | 3 | 158 | 394 |
| N60404 | NaOH | 6 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 158 | 394 |
| N100404 | NaOH | 10 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 158 | 394 |
| N10061 | NaOH | 10 | 0.6 | 1 | 207 | 345 |
| N6063 | NaOH | 6 | 0.6 | 3 | 207 | 345 |
| N10063 | NaOH | 10 | 0.6 | 3 | 207 | 345 |
| K6041 | KOH | 6 | 0.4 | 1 | 158 | 394 |
| K6043 | KOH | 6 | 0.4 | 3 | 158 | 394 |
| K10043 | KOH | 10 | 0.4 | 3 | 158 | 394 |
| K10061 | KOH | 10 | 0.6 | 1 | 207 | 345 |
| CaO | SiO2 | SO3 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | K2O | NaO2 | TiO2 | P2O5 | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20.43 | 29.88 | 27.55 | 3.89 | 0.8 | 0.36 | 1.03 | 0.59 | 0.45 | 0.09 | 14.86 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teymouri, M.; Behfarnia, K.; Shabani, A.; Saadatian, A. The Effect of Mixture Proportion on the Performance of Alkali-Activated Slag Concrete Subjected to Sulfuric Acid Attack. Materials 2022, 15, 6754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196754
Teymouri M, Behfarnia K, Shabani A, Saadatian A. The Effect of Mixture Proportion on the Performance of Alkali-Activated Slag Concrete Subjected to Sulfuric Acid Attack. Materials. 2022; 15(19):6754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196754
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeymouri, Mohammad, Kiachehr Behfarnia, Amirhosein Shabani, and Armin Saadatian. 2022. "The Effect of Mixture Proportion on the Performance of Alkali-Activated Slag Concrete Subjected to Sulfuric Acid Attack" Materials 15, no. 19: 6754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196754
APA StyleTeymouri, M., Behfarnia, K., Shabani, A., & Saadatian, A. (2022). The Effect of Mixture Proportion on the Performance of Alkali-Activated Slag Concrete Subjected to Sulfuric Acid Attack. Materials, 15(19), 6754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196754








