An Experimental Study on the Solidification Treatment of Debris Flow Siltation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
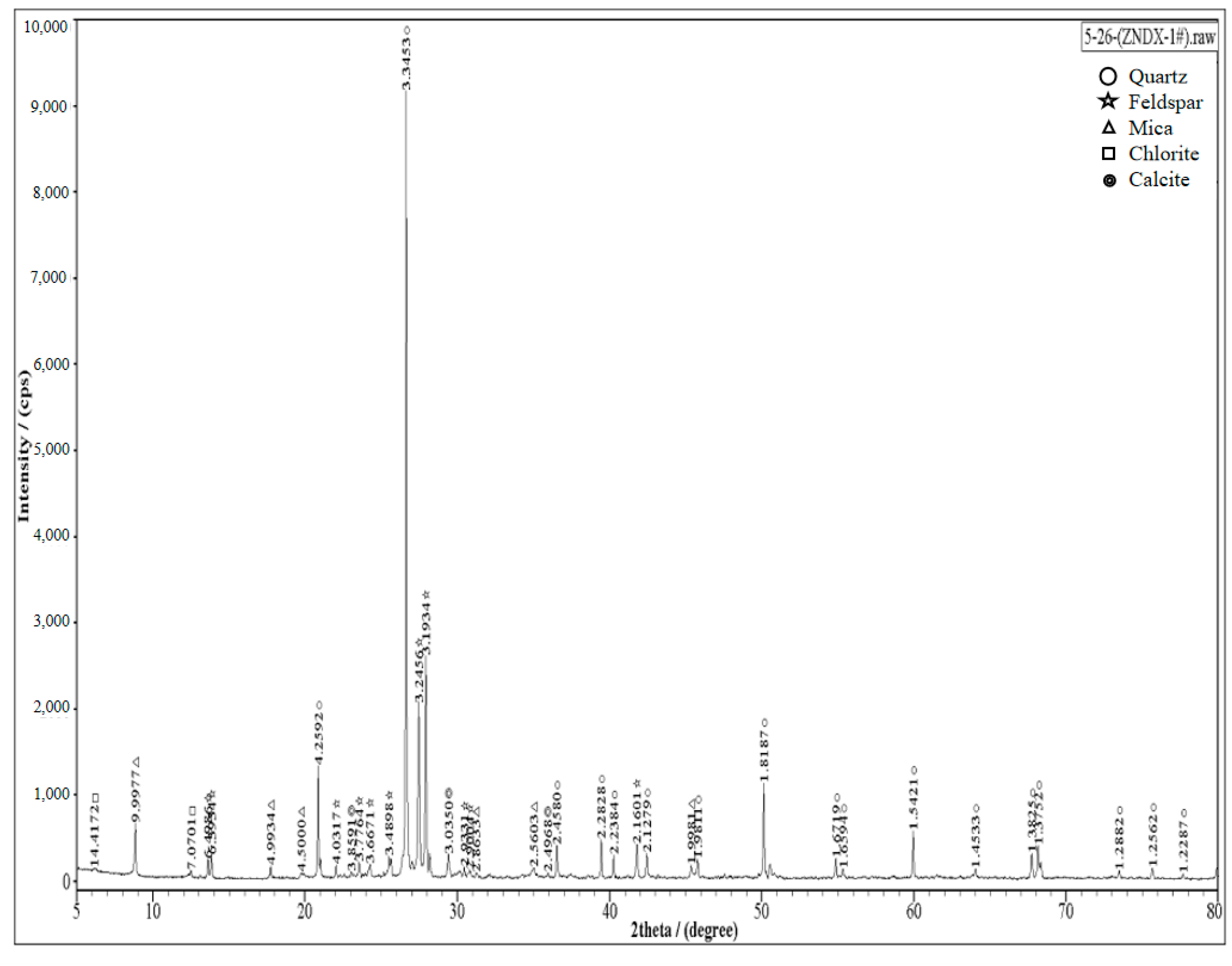
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Experimental Design
2.2.2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Orthogonal Test Results
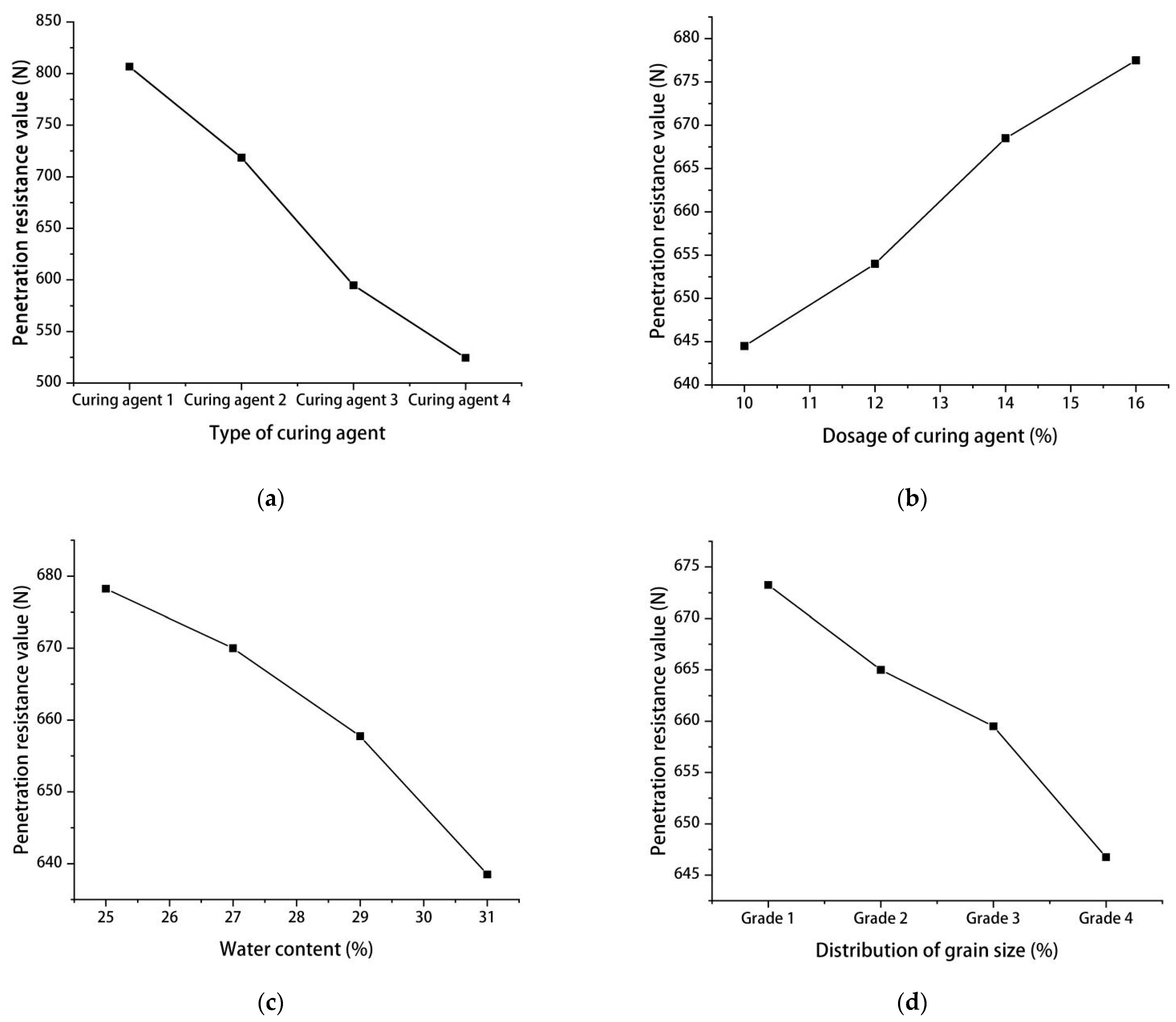
3.1.1. Intuition and Range Analysis of Orthogonal Test
3.1.2. ANOVA for the Orthogonal Experiments
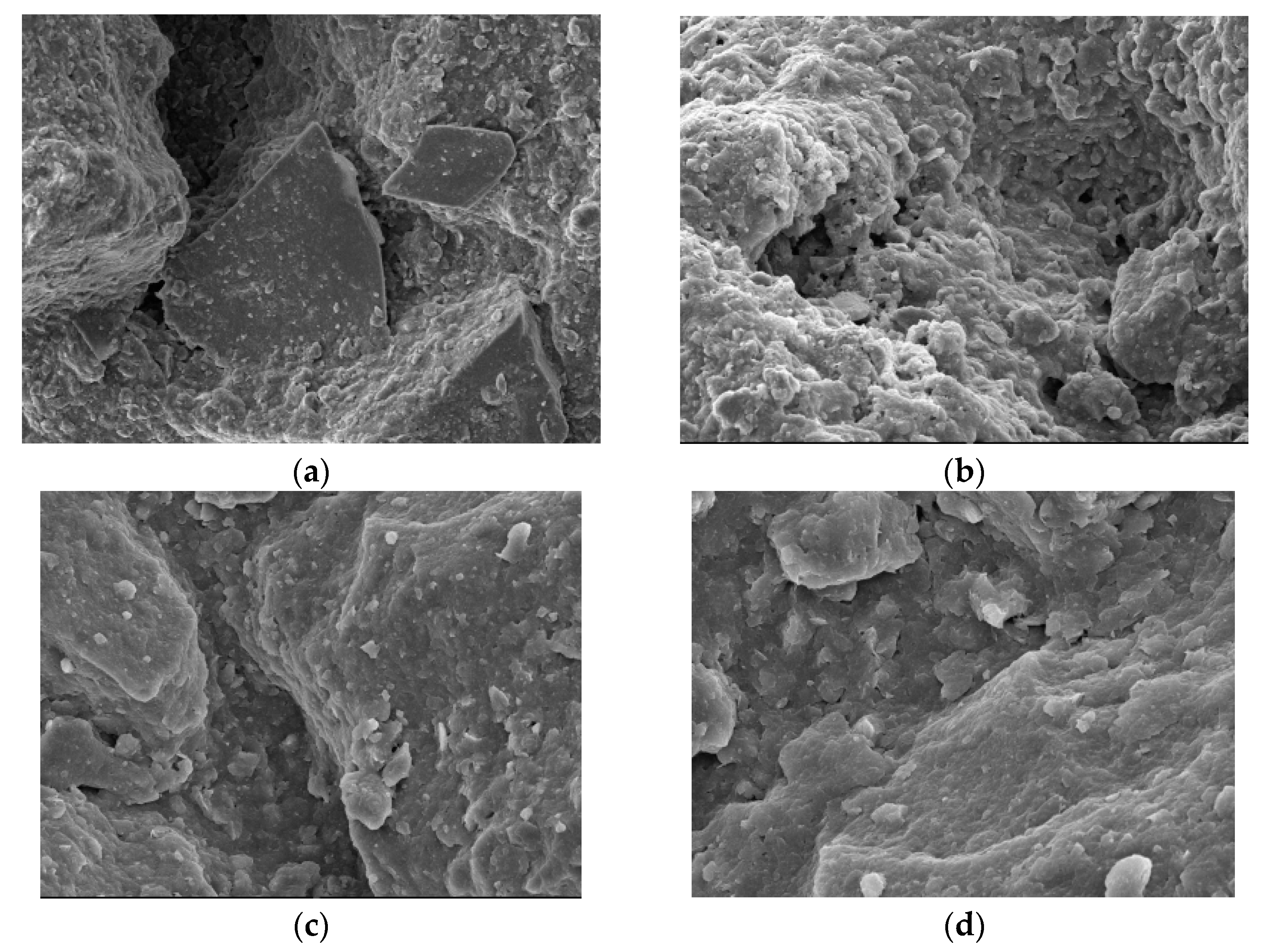
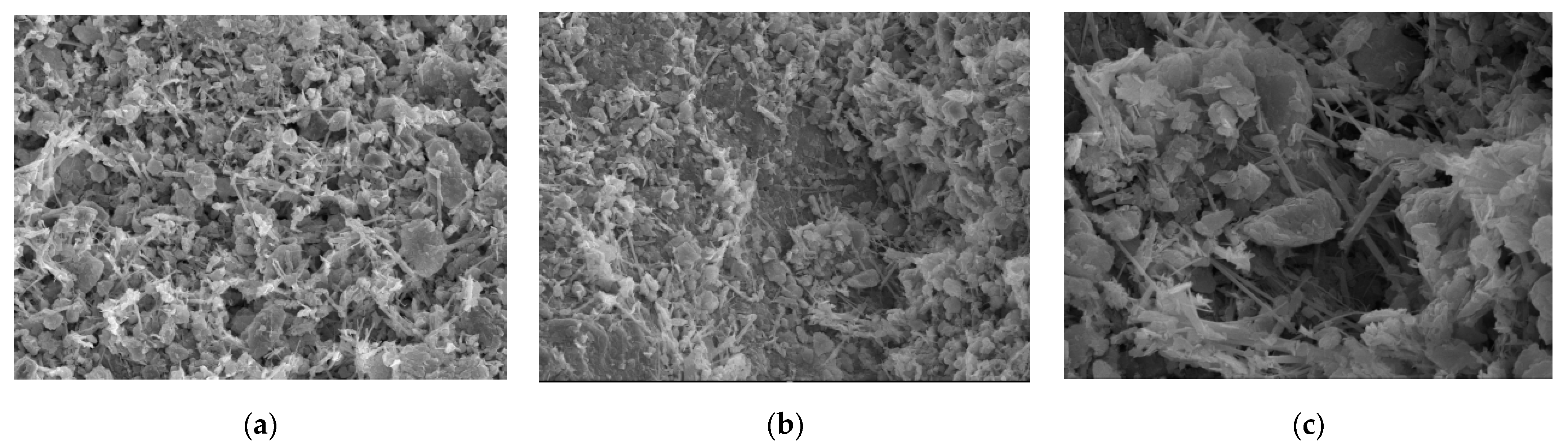
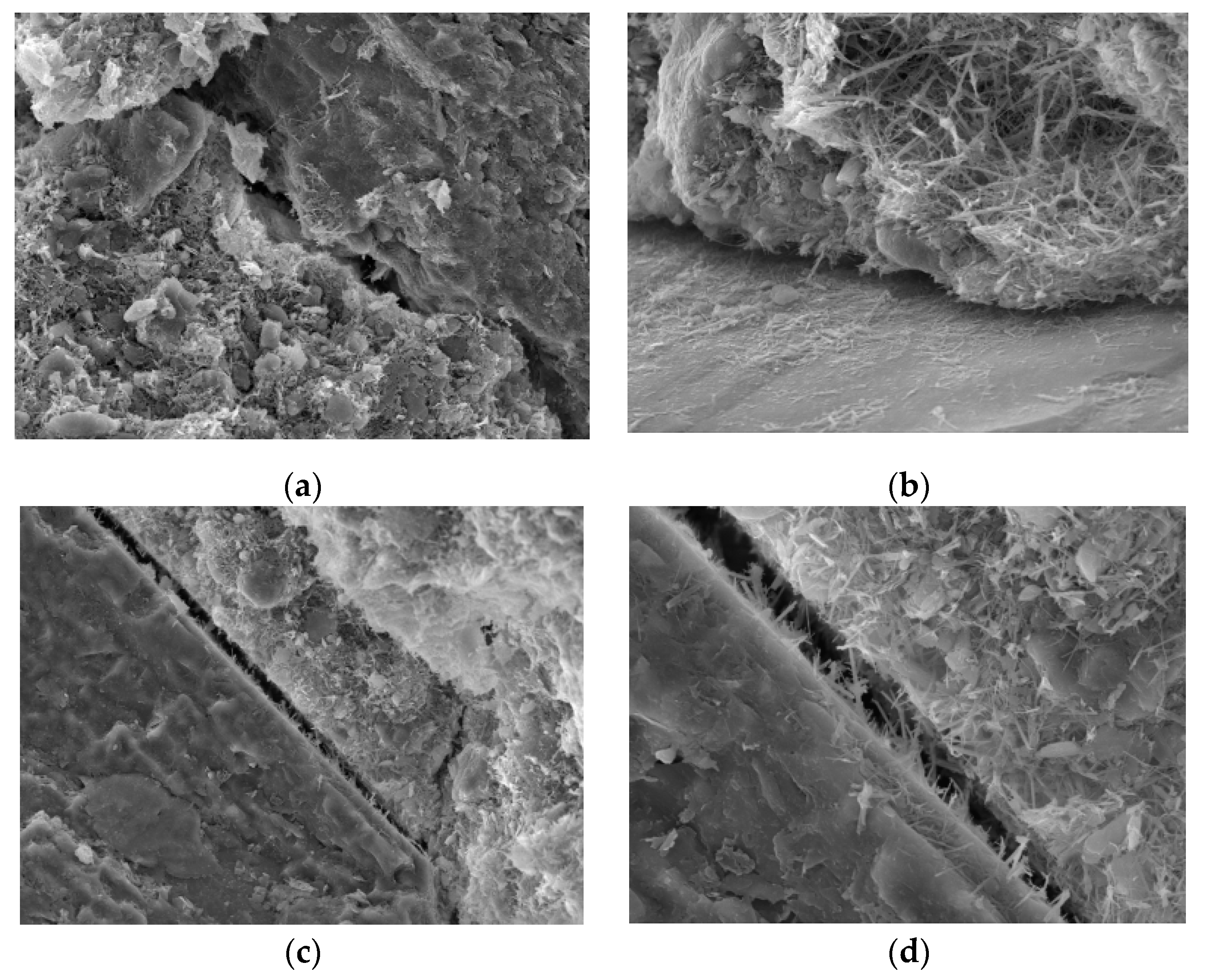
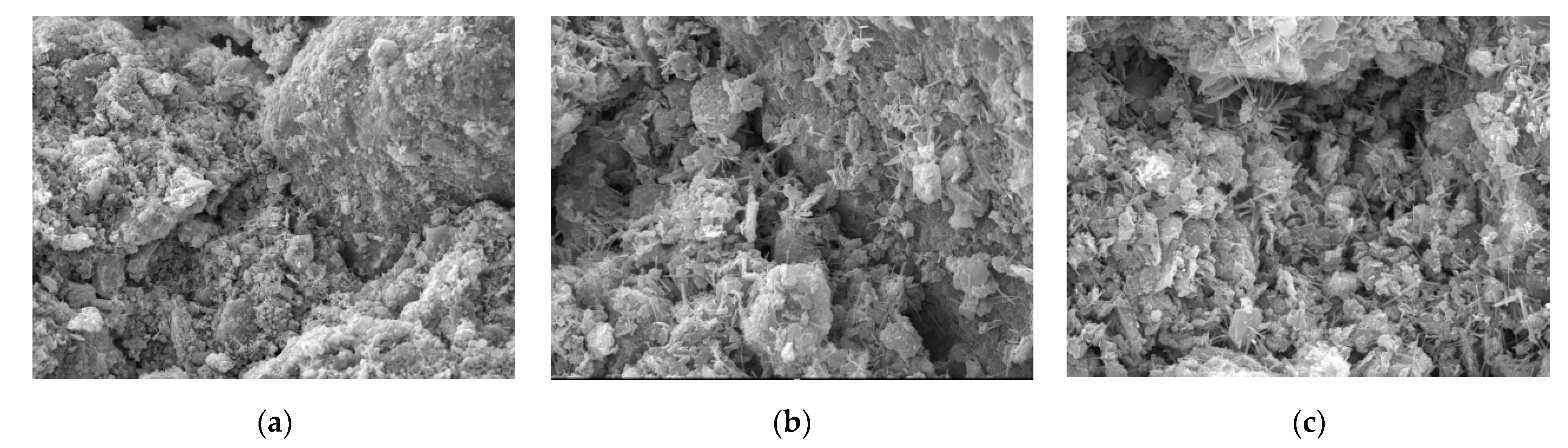
3.2. Microscopic Mechanism Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Che, H. Hazard assessment of a catastrophic mine waste debris flow of Hou Gully, Shimian, China. Eng. Geol. 2020, 275, 105733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikoš, M.; Bezak, N. Debris Flow Modelling Using RAMMS Model in the Alpine Environment with Focus on the Model Parameters and Main Characteristics. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 8, 605061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, C.; An, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, Q. Viscous Elastoplastic SPH Model for Long-Distance High-Speed Landslide. Int. J. Comput. Methods 2019, 16, 1846011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Hu, X.; Liu, B.; Zhou, R.C.; Xi, C.J.; Han, M.; Zhang, X.Y. Development characteristics of debris flow group in a station of sichuan-tibet railway and its influence on the line. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2021, 48, 137–149. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hu, G.; Chen, N.; Yang, Z.; Han, Z. Study on the formation movement characteristics and engineering hazards of valley-type debris flow on the Sichuan-Tibet Railway. J. Disaster Prev. Mitig. Eng. 2021, 41, 432–440+462. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Kim, M.; Lee, G.; Kim, Y.; Lim, H. Estimation of the area of sediment deposition by debris flow using a physical-based modeling approach. Quat. Int. 2018, 503 (Pt A), 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Wu, F.; Zhang, B.; Liu, M. The deformation analysis of Wenjiagou giant landslide by the distributed scatterer interferometry technique. Landslides 2018, 15, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, O.T.; Germain, D.; Meseşan, F.; Gavrilă, I.-G.; Alexe, M.; Buzilă, L.; Holobâcă, I.; Irimuş, I.-A. Dendrogeomorphic assessment and sediment transfer of natural vs. mining-induced debris-flow activity in Călimani Mountains, Eastern Carpathians, Romania. Geomorphology 2019, 327, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chai, S.; Li, M. Rain erosion resistance of debris flow accumulation soil sprayed with sh soil-fixing agent. J. Eng. Geol. 2018, 26, 334–339. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Shi, Z.; Hanley, K.J.; Peng, M.; Guan, S.; Feng, S.; Chen, K. Deposition characteristics of debris flows in a lateral flume considering upstream entrainment. Geomorphology 2021, 394, 107960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Paik, J. Depositional characteristics of debris flows in a rectangular channel with an abrupt change in slope. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staley, D.M.; Wasklewicz, T.A.; Blaszczynski, J.S. Surficial patterns of debris flow deposition on alluvial fans in Death Valley, CA using airborne laser swath mapping data. Geomorphology 2006, 74, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, M.; Sass, O. Combining airborne and terrestrial laser scanning for quantifying erosion and deposition by a debris flow event. Geomorphology 2012, 138, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, C.L.; E Gresswell, R. Spatial and temporal patterns of debris-flow deposition in the Oregon Coast Range, USA. Geomorphology 2004, 57, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, M. Spatio-temporal analysis of erosion and deposition in an ephemeral debris-flow torrent in the Patagonian Andes. Quat. Int. 2012, 279–280, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banihabib, M.E.; Nazarieh, F. A model for simulation of debris flow sedimentation in slit detention-dam reservoirs. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2019, 27, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselt, I.; de Oliveira, G.Q.; Fischer, J.-T.; Pudasaini, S.P. Deposition morphology in large-scale laboratory stony debris flows. Geomorphology 2022, 396, 107992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Fang, J.; Tang, C.; Yang, G. Empirical relationships for the estimation of debris flow runout distances on depositional fans in the Wenchuan earthquake zone. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghilardi, P.; Natale, L.; Savi, F. Modeling debris flow propagation and deposition. Phys. Chem. Earth Part C Solar Terr. Planet. Sci. 2001, 26, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, D.; Trousil, E.; Santi, P. Estimation of inundation areas of post-wildfire debris flows in Southern California USA. Eng. Geol. 2021, 285, 105991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, M.L.; Prestininzi, P.; Elango, L.; Hinkelmann, R.; Montessori, A. Depth averaged modelling of loose rectangular granular piles collapsing in water. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 143, 103663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhang, J.; Shi, B.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of the benefits of facility for disaster mitigation based on the risk of debris flow. Landslides 2022, 19, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosoughi, F.; Nikoo, M.R.; Rakhshandehroo, G.; Adamowski, J.F.; Gandomi, A.H. Downstream semi-circular obstacles’ influence on floods arising from the failure of dams with different levels of reservoir silting. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 013312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.G.D.; Li, S.; Song, D.; Choi, C.E.; Chen, X. Depositional mechanisms and morphology of debris flow: Physical modelling. Landslides 2018, 16, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cui, P.; Wang, F.; Dong, Y.G. Research on the initiation mechanism of engineering spoilage and debris flow under different particle size gradation conditions. Chin. J. Eng. Geol. 2018, 26, 1593–1599. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Tang, H.; Chen, H. Model test on impact characteristics of debris flow under the combined conditions of slurry viscosity and graded particles. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2014, 36, 977–982. (In Chinese). Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1124.TU.20140210.1551.001.html (accessed on 4 November 2021).
- Wang, T.; Weng, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, P.C.; Zhang, S. Experimental study on compressive strength of composite solidified sandy soil under dry-wet cycle conditions. Chin. J. Railw. Sci. Eng. 2017, 14, 721–729. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Serial Numbers | A | B (%) | C (%) | D | Penetration Resistance Value (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 (Sulfoaluminate Cement) | 1 (10) | 1 (25) | 1 (Grade 1) | 828 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 (12) | 2 (27) | 2 (Grade 2) | 816 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 (14) | 3 (29) | 3 (Grade 3) | 805 |
| 4 | 1 | 4 (16) | 4 (31) | 4 (Grade 4) | 778 |
| 5 | 2 (Sulfoaluminate Cement and Lime (3%)) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 701 |
| 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 710 |
| 7 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 719 |
| 8 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 744 |
| 9 | 3 (Portland Cement) | 1 | 3 | 4 | 564 |
| 10 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 572 |
| 11 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 615 |
| 12 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 628 |
| 13 | 4 (Portland cement and lime (0.3%)) | 1 | 4 | 2 | 485 |
| 14 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 518 |
| 15 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 535 |
| 16 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 560 |
| k1j | 3227 | 2578 | 2713 | 2693 | - |
| k2j | 2874 | 2616 | 2680 | 2660 | - |
| k3j | 2379 | 2674 | 2631 | 2638 | - |
| k4j | 2098 | 2710 | 2554 | 2587 | - |
| 806.75 | 644.5 | 678.25 | 673.25 | - | |
| 718.5 | 654 | 670 | 665 | - | |
| 594.75 | 668.5 | 657.75 | 659.5 | - | |
| 524.5 | 677.5 | 638.5 | 646.75 | - | |
| R | 282.25 | 33 | 39.75 | 26.5 | - |
| Source of Variance | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | F Value | Significant Results | Critical Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 186,669.75 | 3 | 62,223.25 | 485.17 | particularly notable | F0.05 (3, 3) = 9.23 |
| B | 1774.25 | 3 | 591.42 | 4.61 | have a certain influence | F0.01 (3, 3) = 29.5 |
| C | 5319.10 | 3 | 1773.03 | 13.83 | significant | |
| D | 1510.75 | 3 | 503.58 | 3.93 | have a certain influence | |
| Error | 384.75 | 3 | 128.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, F.; Xu, L.; Su, N. An Experimental Study on the Solidification Treatment of Debris Flow Siltation. Materials 2022, 15, 6860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196860
Gu F, Xu L, Su N. An Experimental Study on the Solidification Treatment of Debris Flow Siltation. Materials. 2022; 15(19):6860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196860
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Fengyu, Linrong Xu, and Na Su. 2022. "An Experimental Study on the Solidification Treatment of Debris Flow Siltation" Materials 15, no. 19: 6860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196860
APA StyleGu, F., Xu, L., & Su, N. (2022). An Experimental Study on the Solidification Treatment of Debris Flow Siltation. Materials, 15(19), 6860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196860





