High-Quality Natural Fibers from Cotton Stalk Bark via Limited Alkali Penetration and Simultaneous Accelerated Temperature Rise
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Coarse Fiber Bundles
2.2.2. Extraction of Cotton Stalk Fibers
2.2.3. Determination of the Viscosity and Temperature of Alkali/Glycerin Mixtures
2.2.4. Determination of the Fiber Dimension
2.2.5. Determination of the Mechanical Properties of Cotton Stalk Fibers
2.2.6. Characterization of Alkali Penetration in the Cotton Stalk Fibers
2.2.7. Determination of Fiber Composition
2.2.8. Crystalline Structure of Cotton Stalk Fibers
2.2.9. Thermogravimetric Analysis of Cotton Stalk Fibers
2.2.10. Wettability of the Cotton Stalk Fibers
2.2.11. Morphological Analysis of the Cotton Stalk Fibers
2.2.12. FTIR-ATR Spectrum of Cotton Stalk Fibers
3. Results
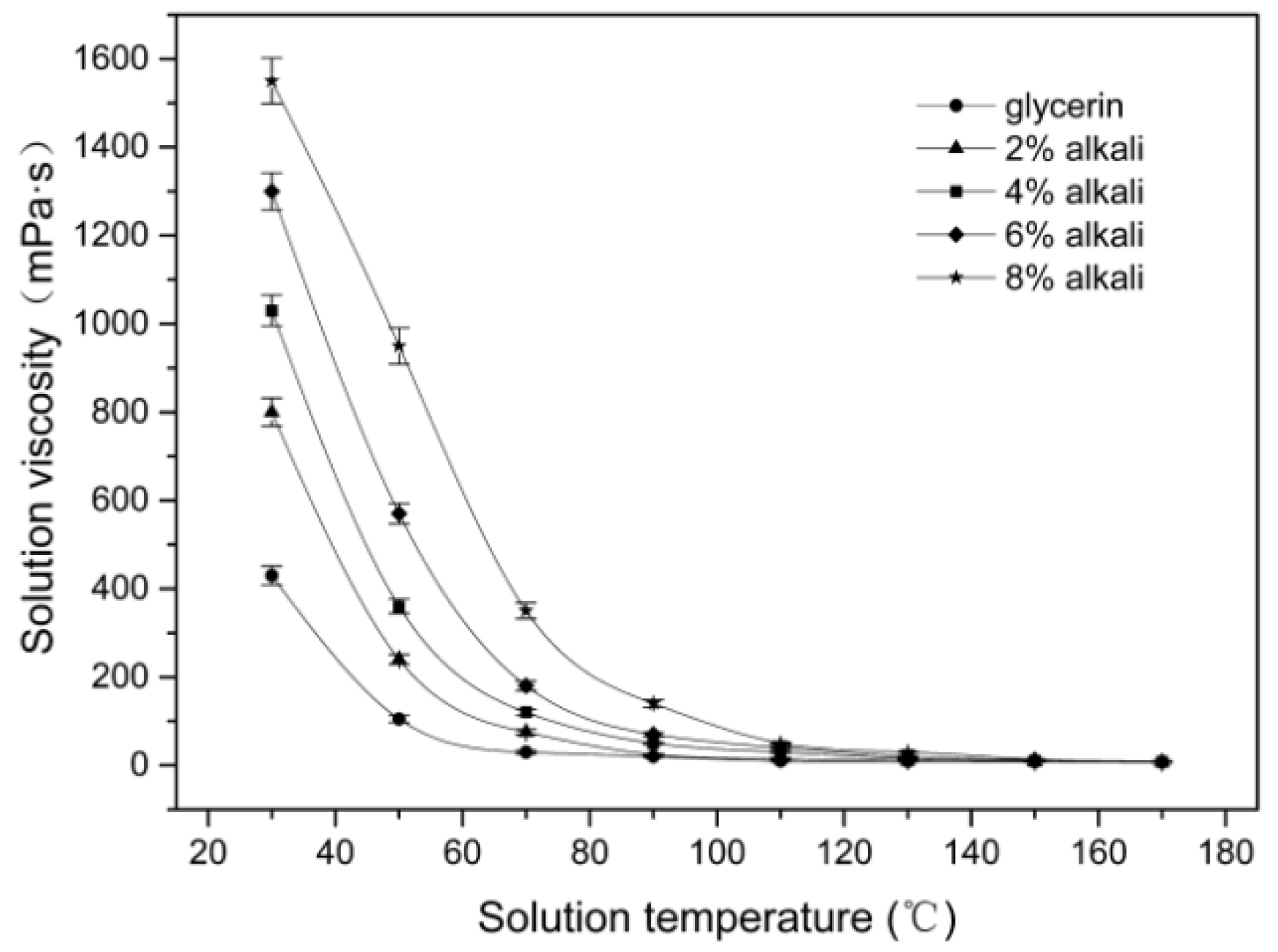
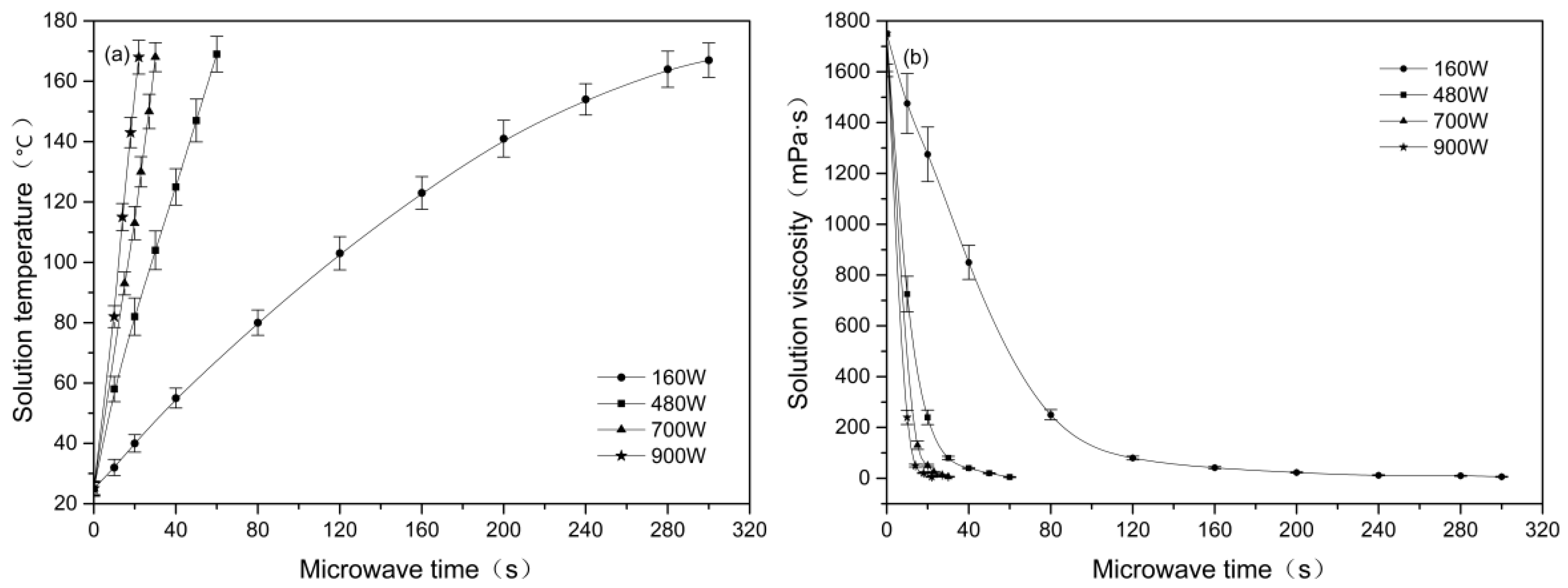
3.1. Effect of Microwave Parameters on the Solution Viscosity
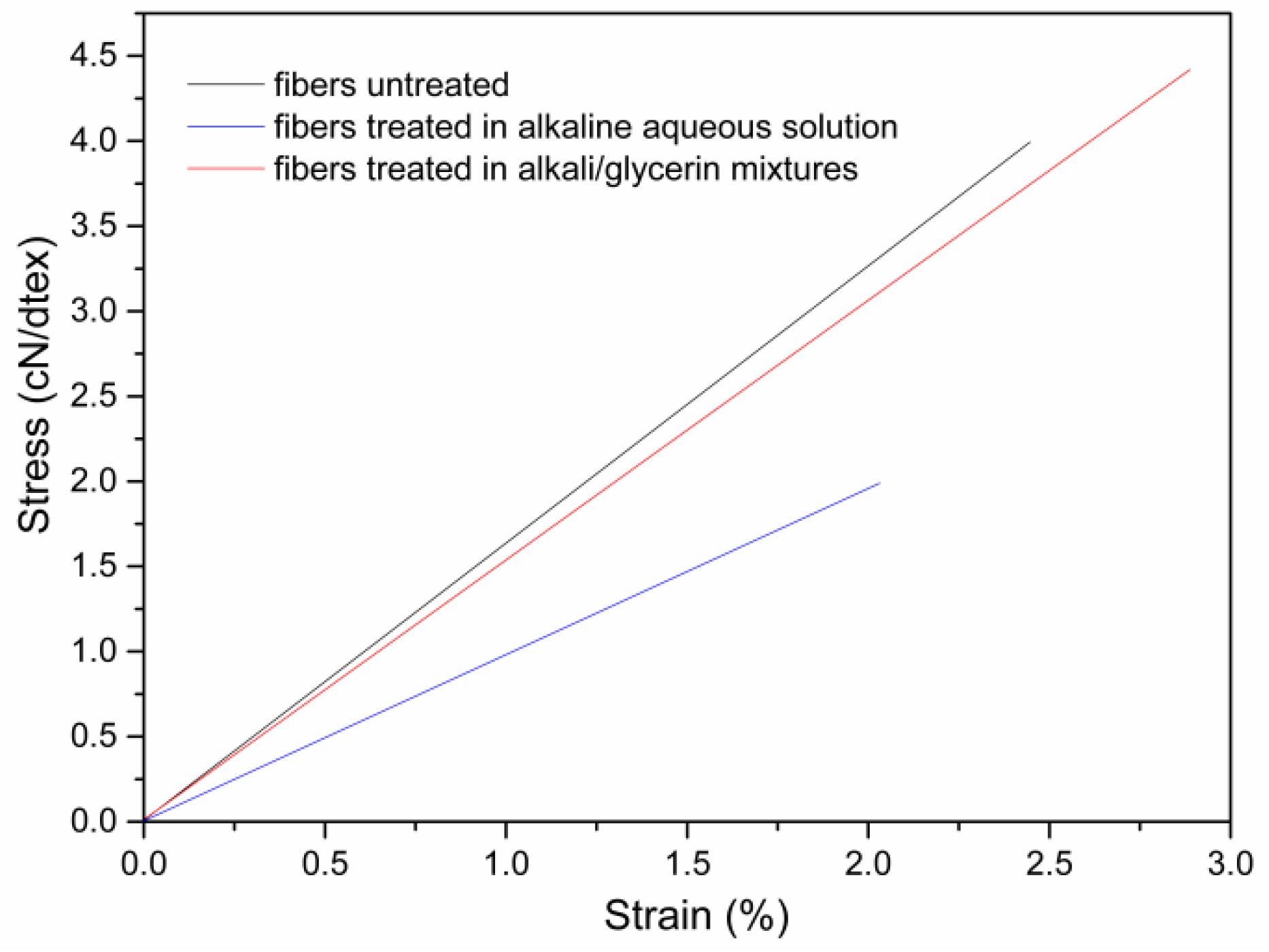
3.2. Effect of Microwave Parameters on the Dimension and Tensile Properties of Cotton Stalk Fibers
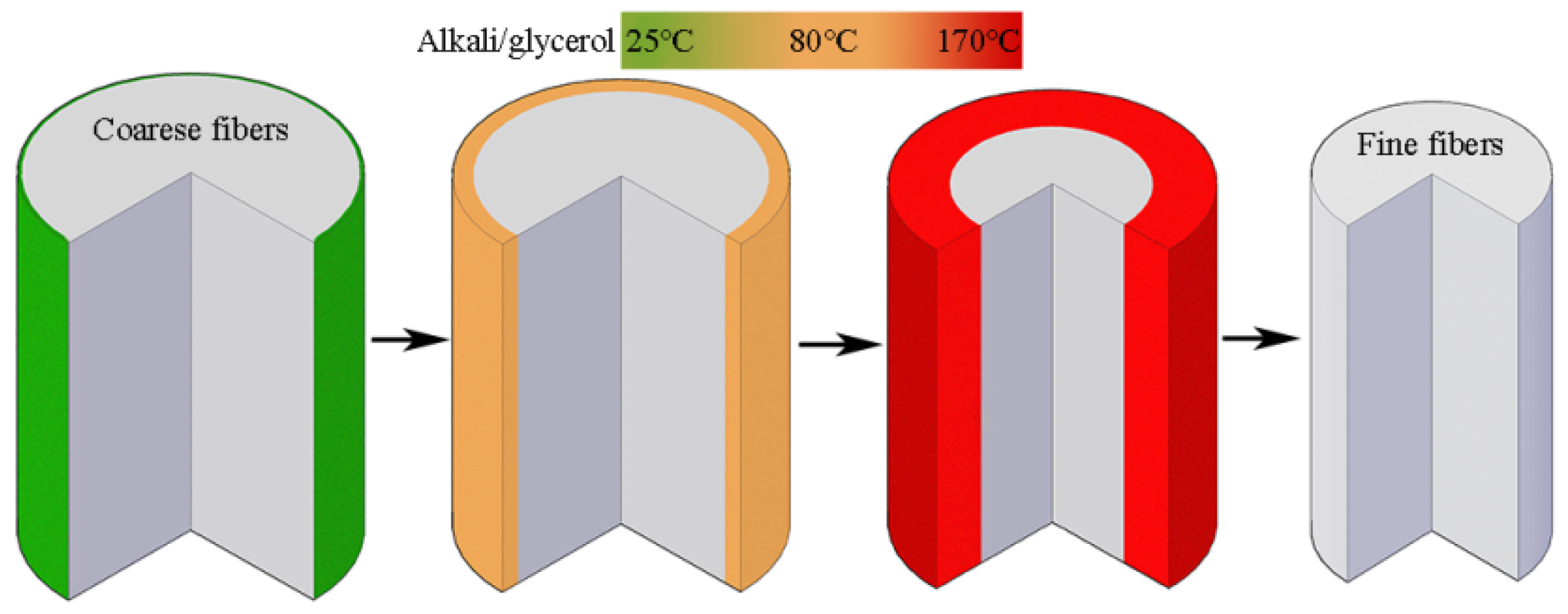
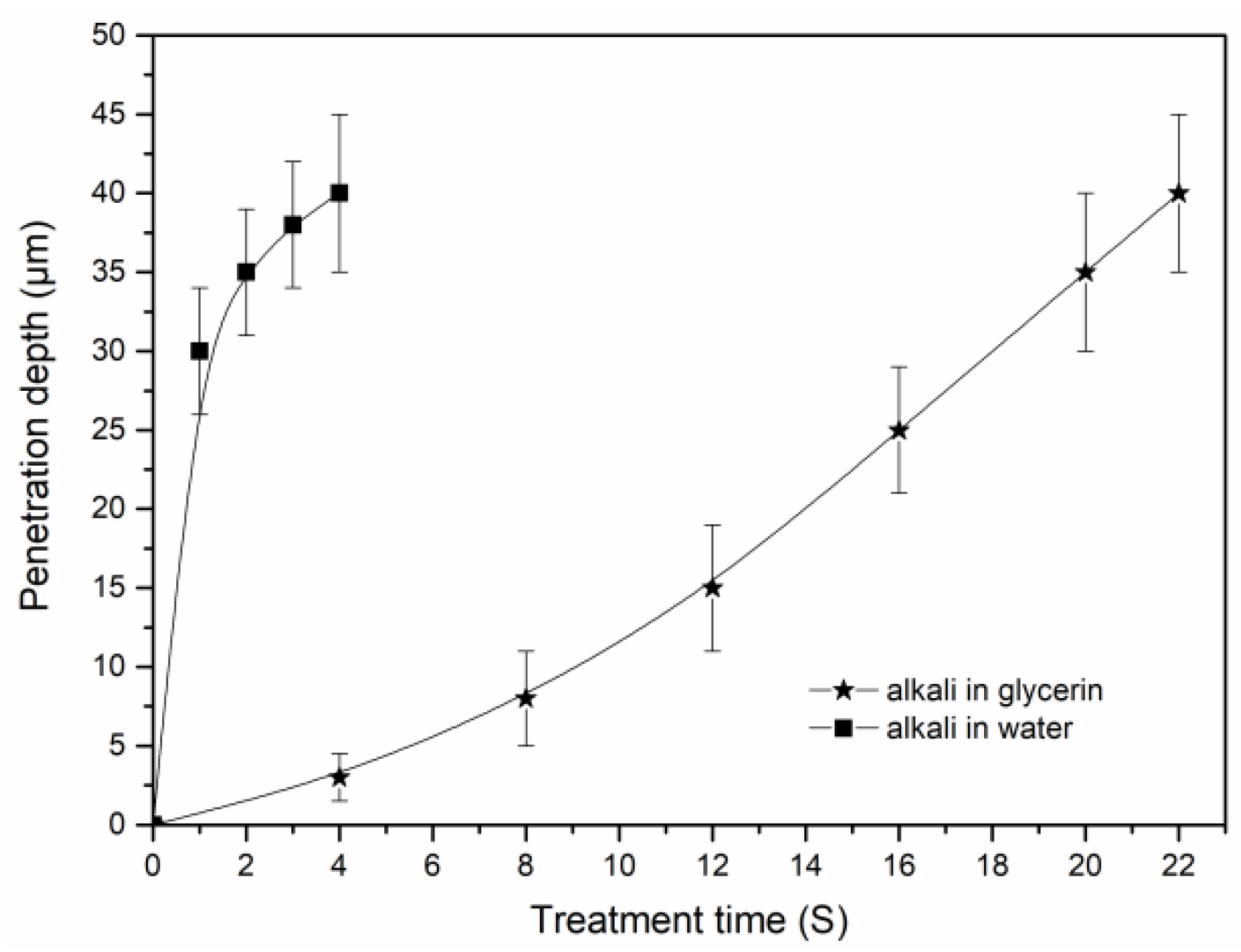
3.3. Penetration of Alkali in the Cotton Stalk Fibers
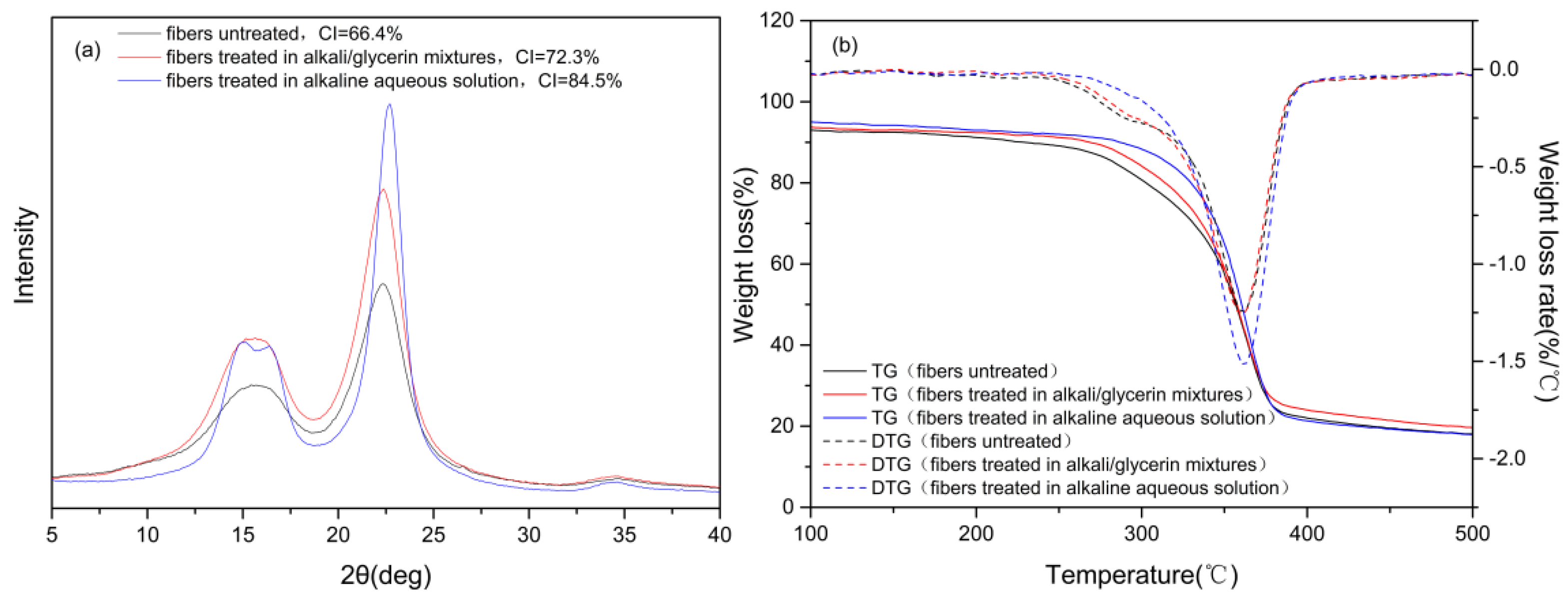
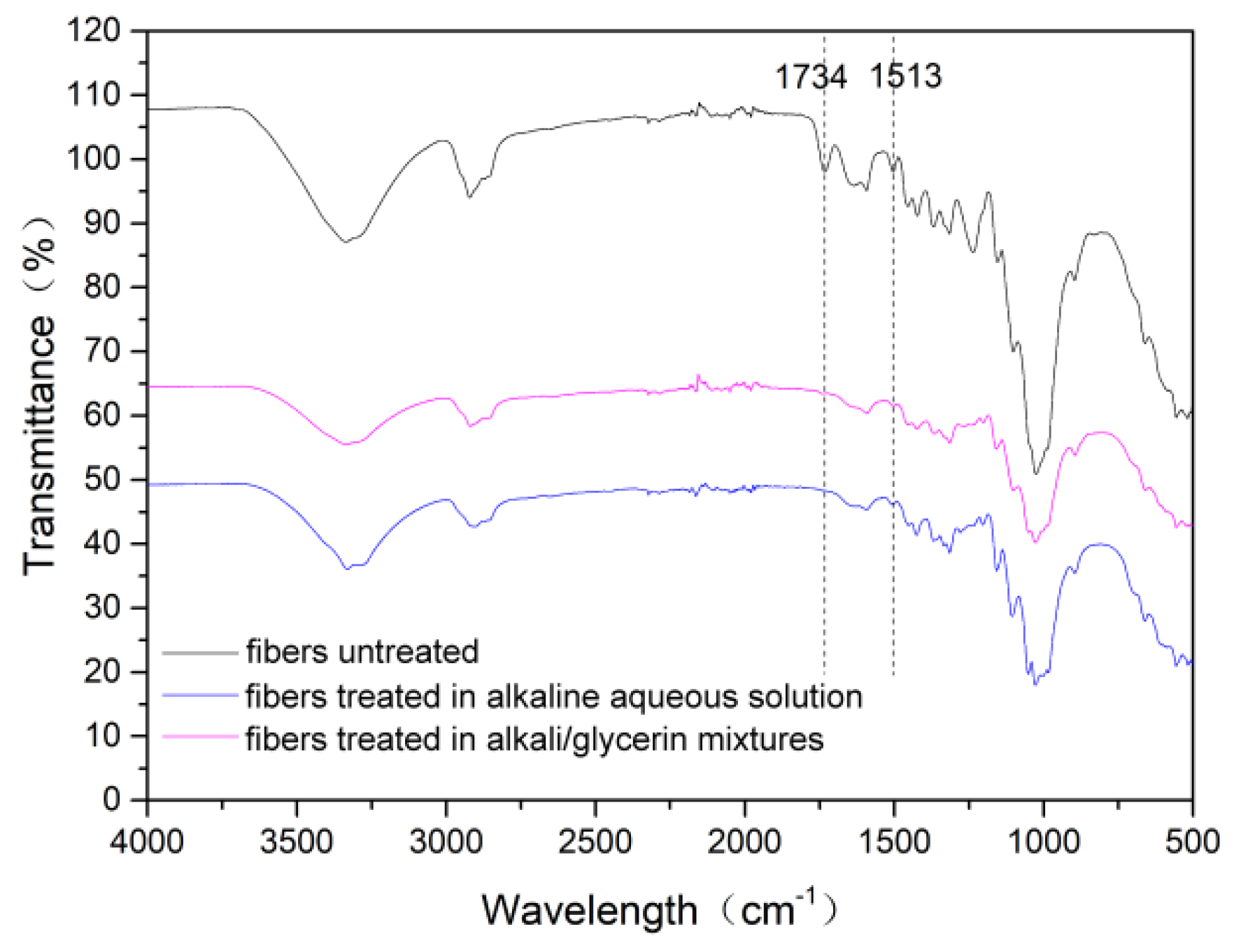
3.4. Composition, Crystalline Structure and Thermal Stability of the Cotton Stalk Fibers
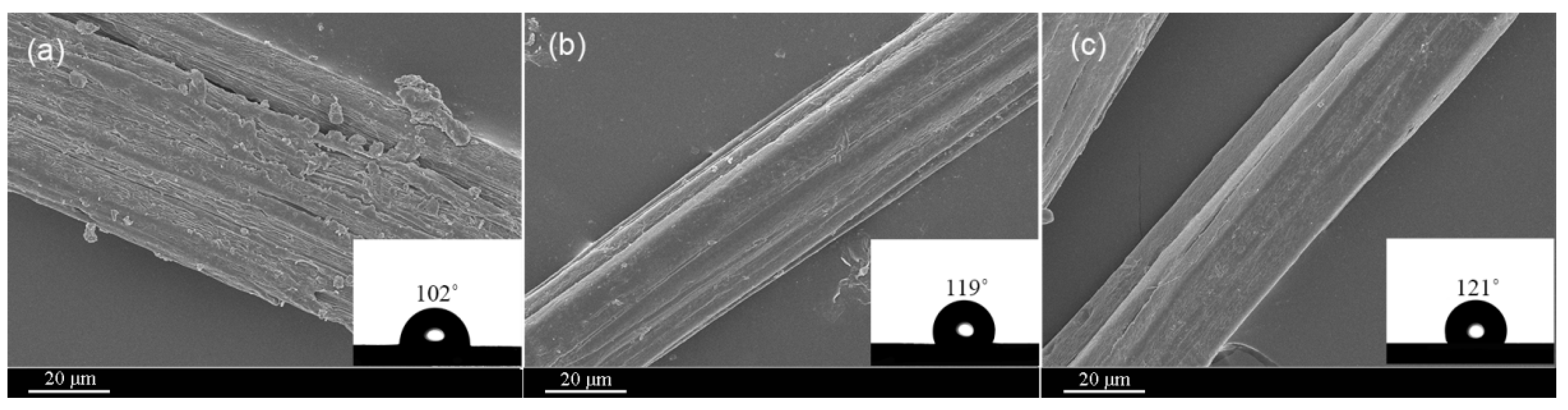
3.5. Surface Morphology and Wettability of the Cotton Stalk Fibers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, B.; Wang, L.; Ma, G.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, X. Preparation and properties of bio-geopolymer composites with waste cotton stalk materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Lin, J.; Tian, F.; Li, X.; Bian, F.; Wang, J. Cellulose nanofibrils extracted from the byproduct of cotton plant. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Hou, X.; Sun, F.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y. Textile grade long natural cellulose fibers from bark of cotton stalks using steam explosion as a pretreatment. Cellulose 2014, 21, 3851–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliaei, E.; Berthold, F.; Berglund, L.A.; Lindström, T. Eco-Friendly High-Strength Composites Based on Hot-Pressed Lignocellulose Microfibrils or Fibers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, B.; Hassan, E.B.; Mahmoud, B. Chemical isolation and characterization of different cellulose nanofibers from cotton stalks. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, C.-M.; Jones, D.; Schalnat, J.; Segerholm, K.; Henriksson, M.; Westin, M. Structural characterization and mechanical properties of wet-processed fibreboard based on chemo-thermomechanical pulp, furanic resin and cellulose nanocrystals. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathirselvam, M.; Kumaravel, A.; Arthanarieswaran, V.; Saravanakumar, S. Characterization of cellulose fibers in Thespesia populnea barks: Influence of alkali treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 217, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, B.F.A.; Kamke, F.A. Comparison of alkali treatments on selected chemical, physical and mechanical properties of grape cane fibers. Cellulose 2020, 27, 7371–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W. Morphologies and properties of Juncus effusus fiber after alkali treatment. Cellulose 2020, 27, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Sun, F.; Yan, D.; Xu, H.; Dong, Z.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y. Preparation of lightweight polypropylene composites reinforced by cotton stalk fibers from combined steam flash-explosion and alkaline treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 83, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.; Yang, Y. Properties and potential applications of natural cellulose fibers from the bark of cotton stalks. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3563–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Hou, X.; Haigler, I.; Yang, Y. Preparation and properties of cotton stalk bark fibers and their cotton blended yarns and fabrics. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 139, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, N.; Ren, L.; Wu, H.; Wu, Q.; Xie, Y. New insights on structure of lignin-carbohydrate complex from hot water pretreatment liquor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 224, 115130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Kang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Sun, R. Comparative Characterization of Lignins Extracted from Cotton Stalk Based on Complete Dissolution in Different Systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 9858–9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, N.; Lin, X.; Pan, X.; Zhou, Y. Selective Cleavage of the Aryl Ether Bonds in Lignin for Depolymerization by Acidic Lithium Bromide Molten Salt Hydrate under Mild Conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8379–8387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Li, N.; Dong, A.; Ma, B.; Yu, C.; Chu, T.; Liu, Q. Enhancement of Interface between Lignocellulosic Fibers and Polypropylene Matrix via the Structure Alteration of Lignin at Elevated Temperatures. Materials 2020, 13, 5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, H.; Yang, Y. Natural Fibres From the Bark of Mulberry Branches for Textile Application. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2017, 25, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.; Fan, X.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Wang, P.; Yuan, J.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Changes on Content, Structure and Surface Distribution of Lignin in Jute Fibers After Laccase Treatment. J. Nat. Fibers 2017, 15, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, A.D.; Cintron, M.S. Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the Segal Crystallinity Index. Cellulose 2013, 20, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Drzal, L.T. Surface modifications of natural fibers and performance of the resulting biocomposites: An overview. Compos. Interfaces 2001, 8, 313–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, N.; Yoshida, M.; Hafrén, J.; Fukushima, K.; Westermark, U. Proposed supramolecular structure of lignin in softwood tracheid compound middle lamella regions. Holzforschung 2012, 66, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-J.; Li, H.-Y.; Cao, X.-F.; Sun, S.-N.; Sun, R.-C. Understanding the Distribution and Structural Feature of Eucalyptus Lignin Isolated by γ-Valerolactone/Water/Acid System. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 12124–12131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, A.D. Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 2013, 21, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandekar, H.; Chaudhari, V.; Waigaonkar, S. A review of jute fiber reinforced polymer composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 2079–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilangovan, M.; Guna, V.; Prajwal, B.; Jiang, Q.; Reddy, N. Extraction and characterisation of natural cellulose fibers from Kigelia africana. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 115996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Experimental Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| NaOH Concentration (wt %) | Microwave Power (W) | Microwave Time (S) | |
| Range of values | 2, 4, 6, 8 | 160, 480, 700, 900 | 0–300 |
| Cotton Stalk Fibers | Hemicellulose Content (%) | Lignin Content (%) | Cellulose Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 17.0 ± 2.1 | 24.6 ± 2.0 | 48.5 ± 3.2 |
| In alkali/glycerol solution | 16.8 ± 1.2 | 24.2 ± 1.7 | 50.8 ± 4.5 |
| In alkaline water solution | 4.6 ± 0.2 | 13.4 ± 0.7 | 78.4 ± 4.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Z.; Li, N.; Chu, T.; Ding, J.; Zhang, J.; Dong, A. High-Quality Natural Fibers from Cotton Stalk Bark via Limited Alkali Penetration and Simultaneous Accelerated Temperature Rise. Materials 2022, 15, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020422
Dong Z, Li N, Chu T, Ding J, Zhang J, Dong A. High-Quality Natural Fibers from Cotton Stalk Bark via Limited Alkali Penetration and Simultaneous Accelerated Temperature Rise. Materials. 2022; 15(2):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020422
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Zhen, Na Li, Teye Chu, Jiangxin Ding, Junxiong Zhang, and Aixue Dong. 2022. "High-Quality Natural Fibers from Cotton Stalk Bark via Limited Alkali Penetration and Simultaneous Accelerated Temperature Rise" Materials 15, no. 2: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020422
APA StyleDong, Z., Li, N., Chu, T., Ding, J., Zhang, J., & Dong, A. (2022). High-Quality Natural Fibers from Cotton Stalk Bark via Limited Alkali Penetration and Simultaneous Accelerated Temperature Rise. Materials, 15(2), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020422








