The Microstructure Evolution and Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of 7A46 Aluminum Alloy in Different Quenching Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Heat Treatment
2.2. Isothermal Quenching Treatment
2.3. Performance Tests and Microstructure Observations
2.4. Electrochemical Tests
3. Results
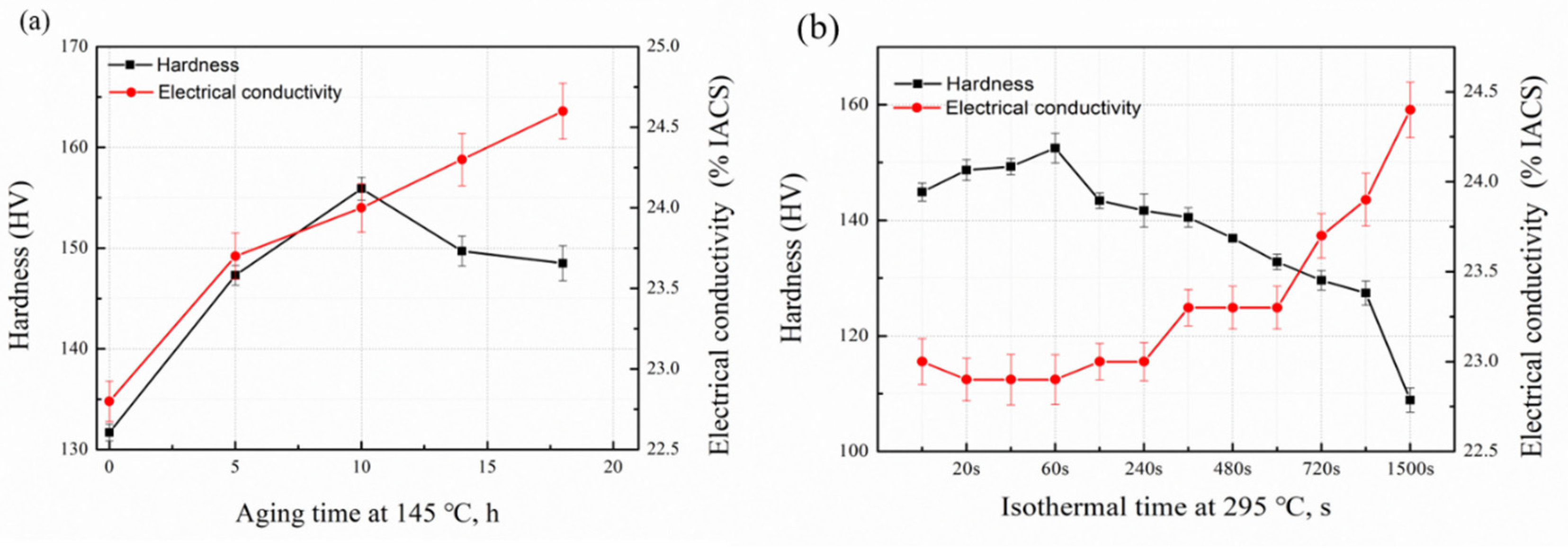
3.1. Hardness and Electrical Conductivity Tests
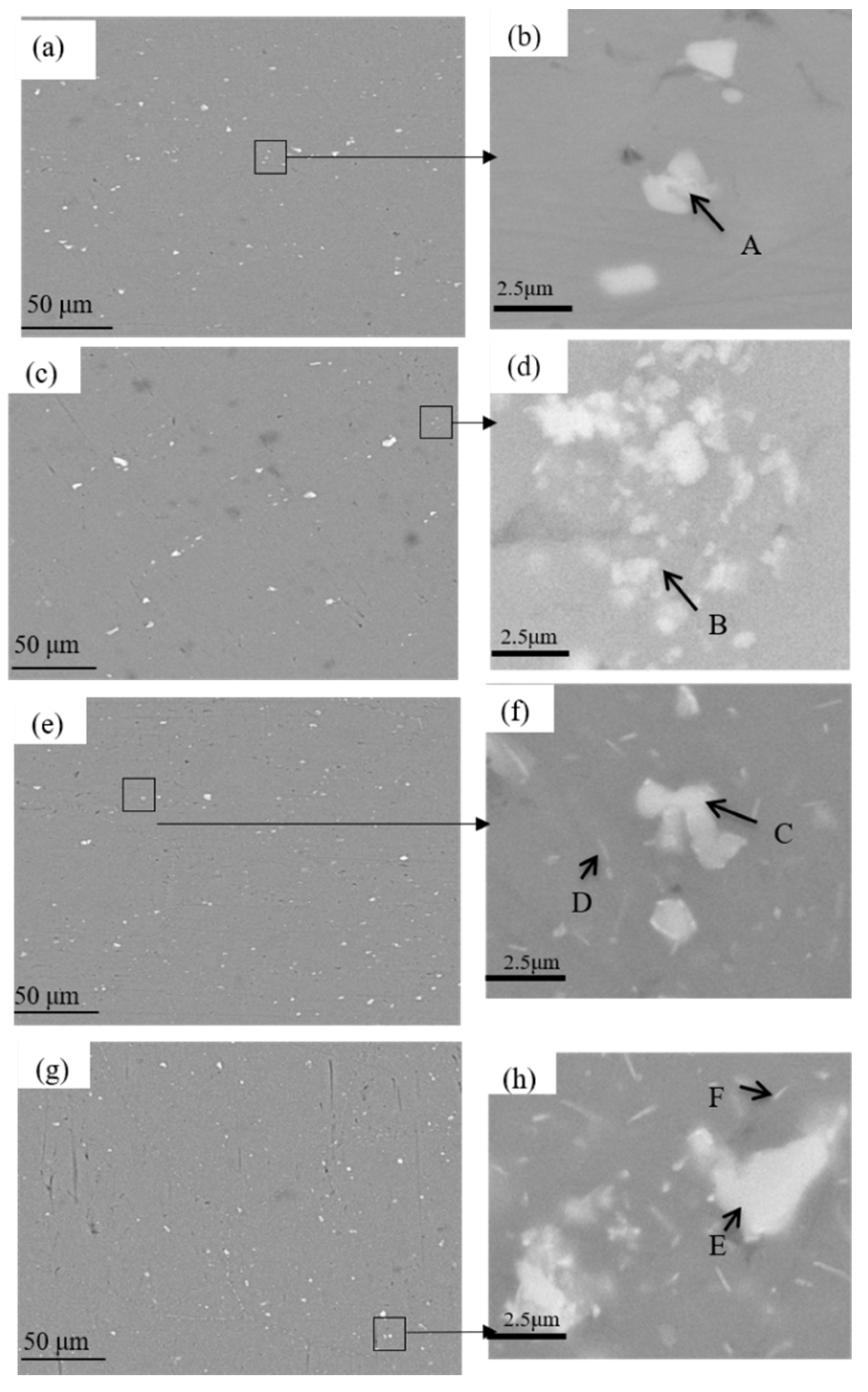
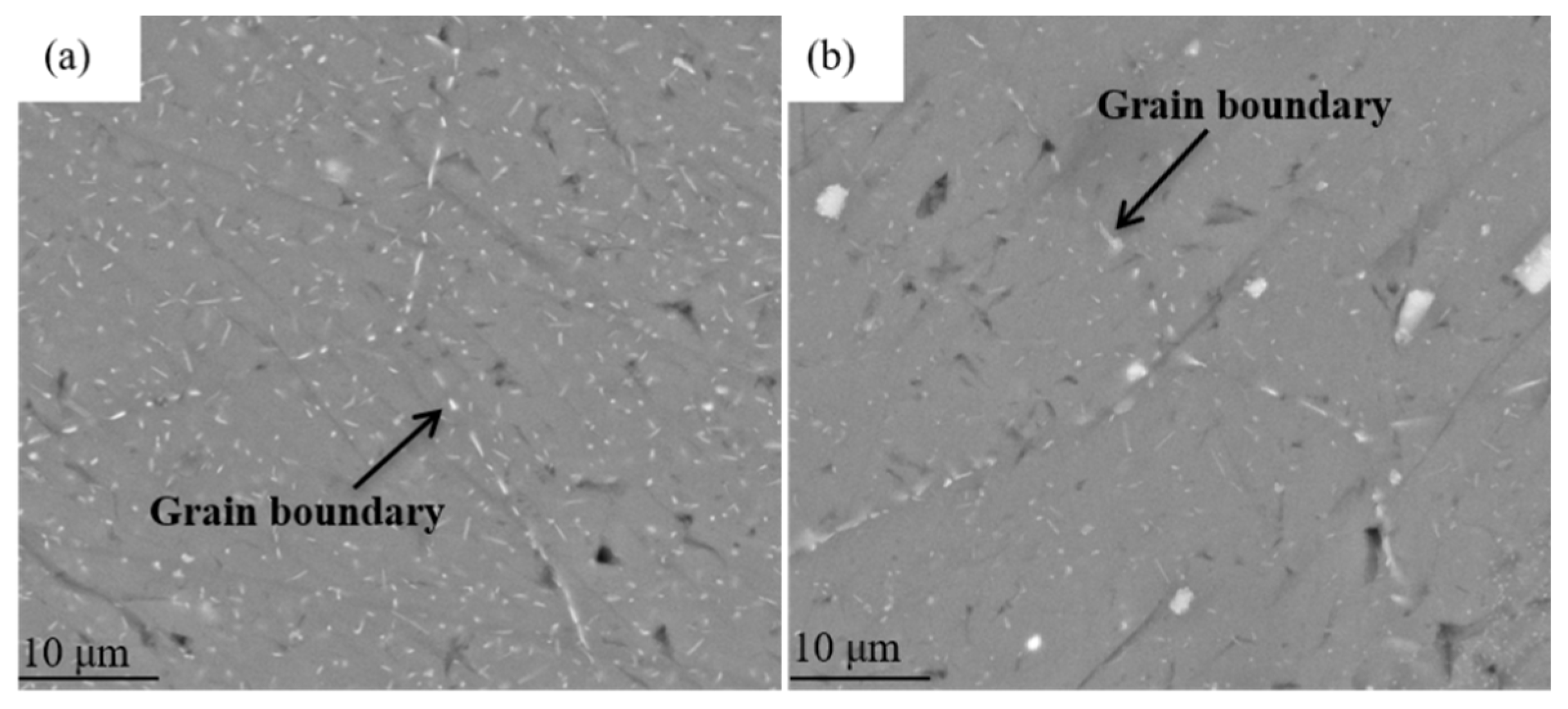
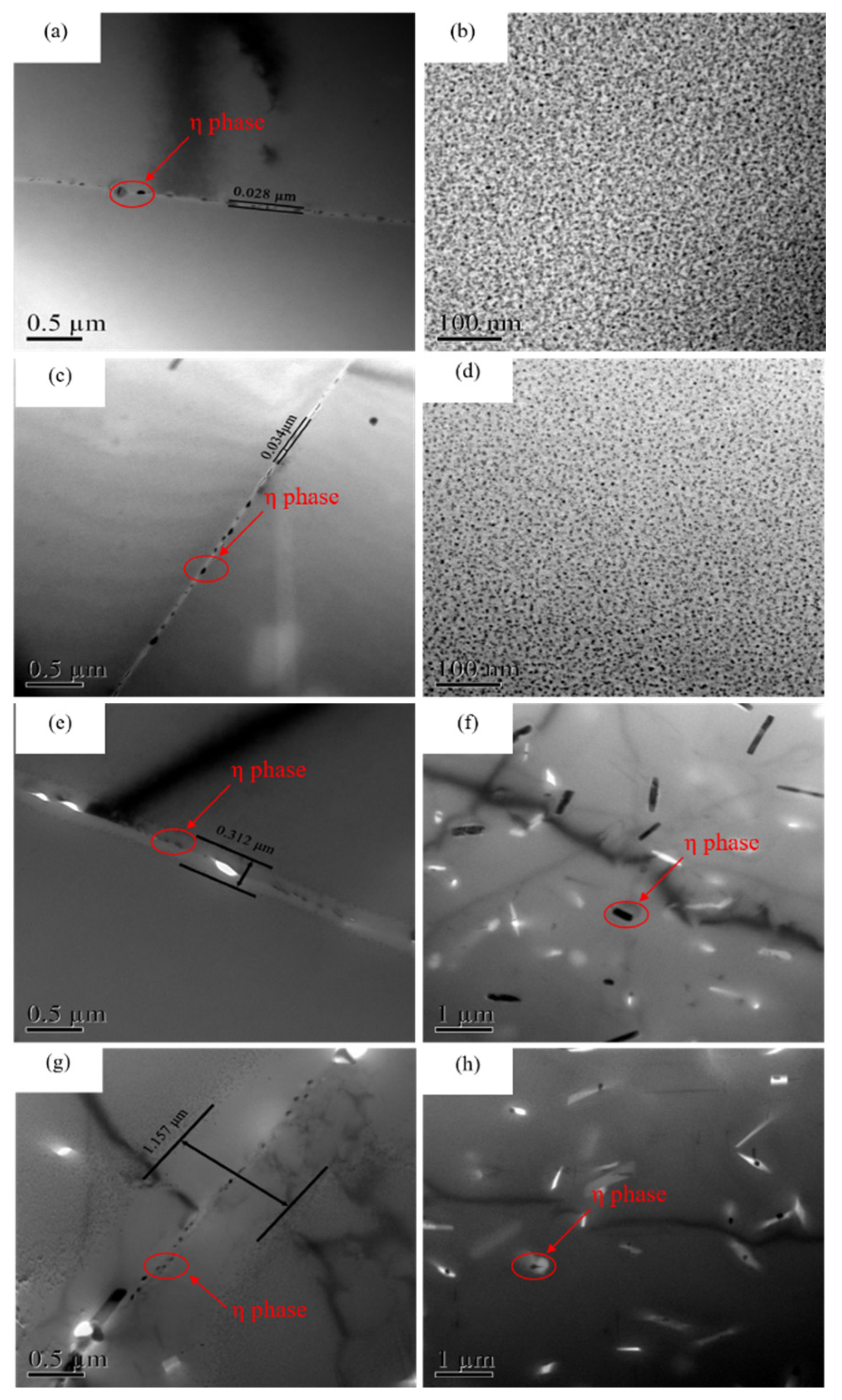
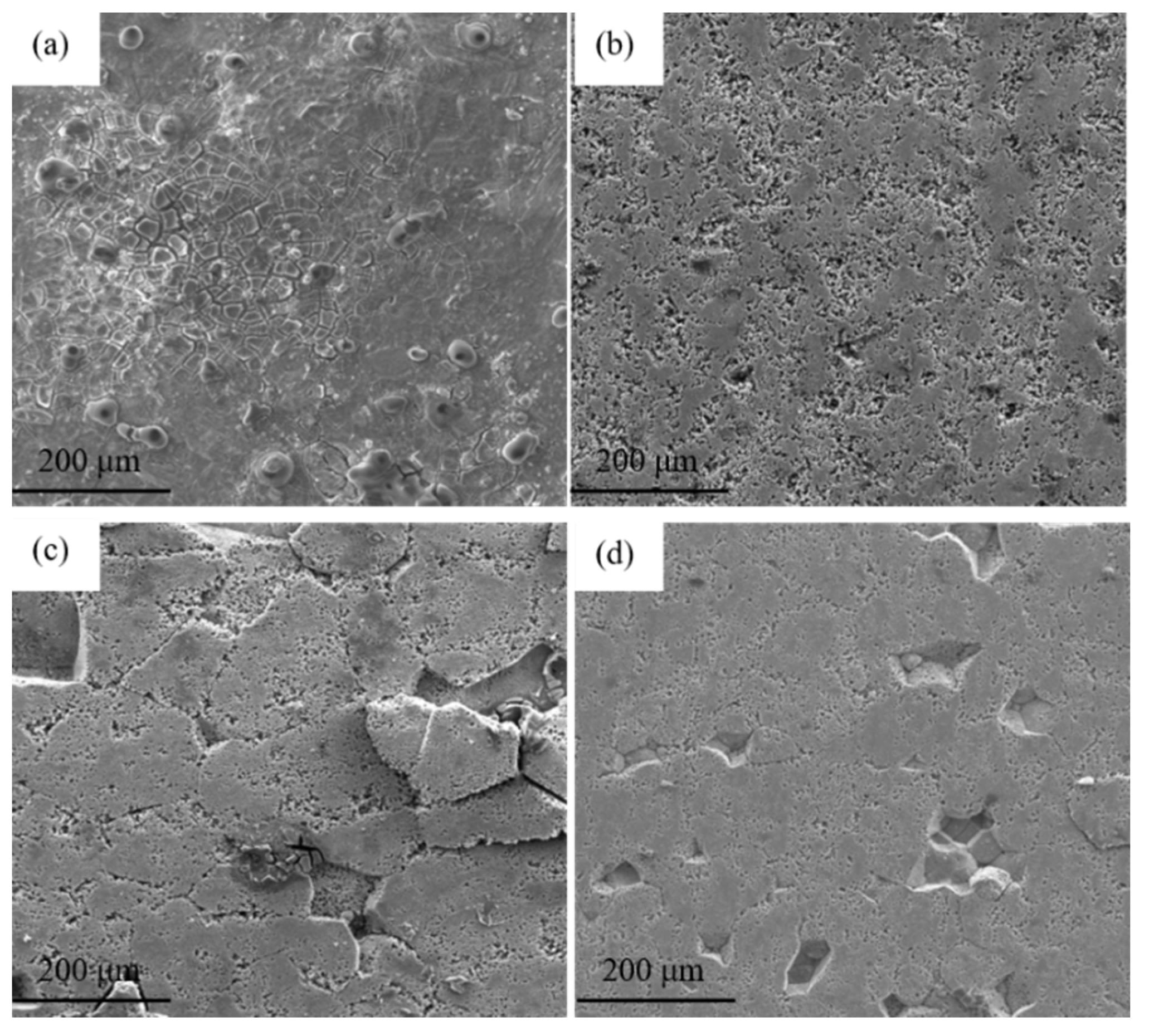
3.2. Microstructure Evolution
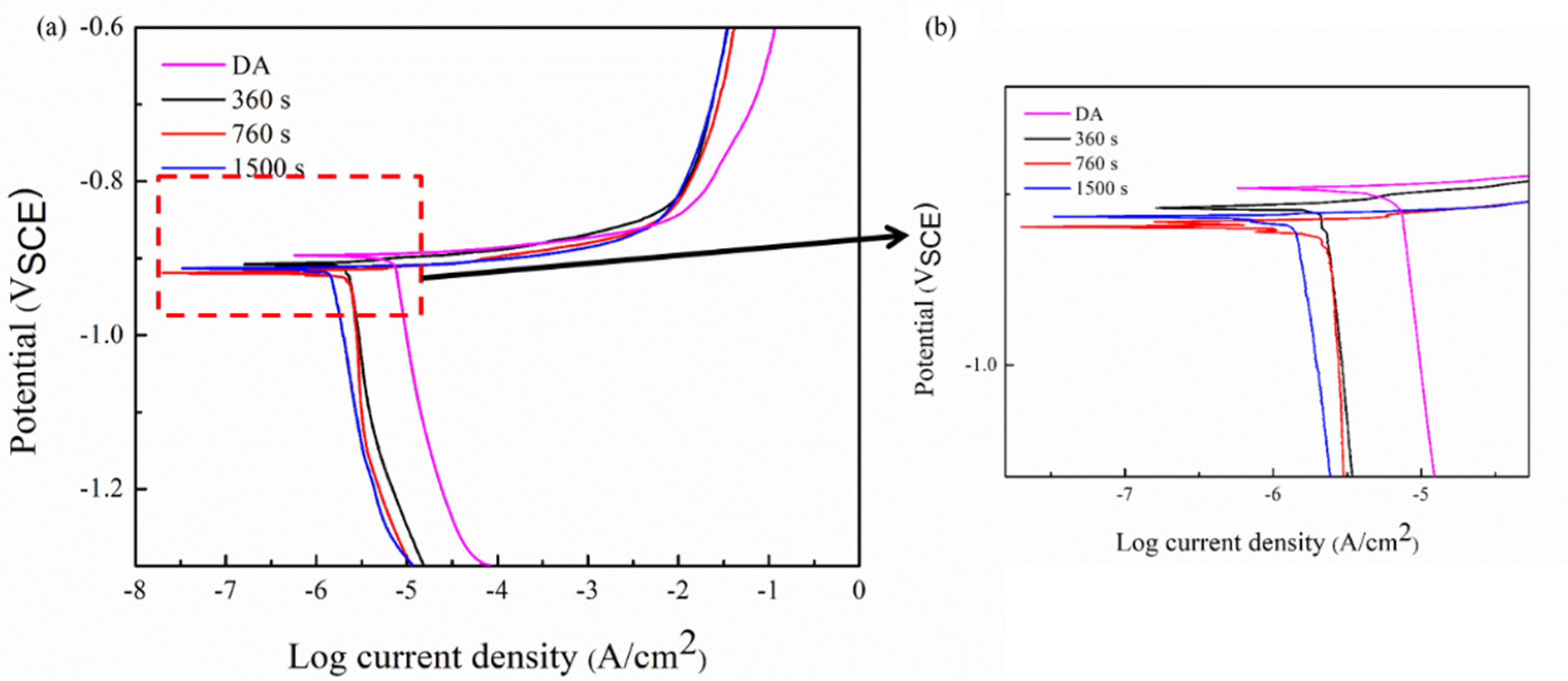
3.3. Polarization Curves
3.4. EIS Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- During the isothermal treatment, the quenched precipitates consume a large number of solute atoms, which decreases the precipitation of age-strengthening phases and results in a decline of the final mechanical properties of the studied alloy.
- With the extension of isothermal holding time, the size of grain boundary precipitates increases significantly, and the PFZ is widened from 0.034 μm at 100 s to 1.157 μm at 1500 s.
- The degree of electrochemical corrosion of the quenched alloy increases, showing a quench sensitivity.
- The corrosion resistance of the quenched alloy increases at first and then decreases with the prolonging of the isothermal holding time. The DA sample has the highest self-corrosion potential (−0.896V) and lowest self-current density (1.017μA/cm2), and the 800 s isothermal treatment sample has the lowest corrosion resistance among all the tested samples, at −0.919 V self-corrosion potential and 2.371 μA/cm2 self-current density 2.371 μA/cm2.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kremmer, T.M.; Dumitraschkewitz, P.; Poschmann, D.; Ebner, T.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Kolb, G.K.H.; Pogatscher, S. Microstructural Change during the Interrupted Quenching of the AlZnMg(Cu) Alloy AA7050. Materials 2020, 13, 2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-Z.; Li, G.-A.; Cai, X.; Jiang, J.-T.; Shao, W.-Z.; Yang, L.; Zhen, L. Microstructure evolution and the resulted influence on localized corrosion in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy during non-isothermal ageing. Materials 2018, 11, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Dong, H.G.; Wang, X.X.; Liu, Z.Y. Quenching Sensitivity of Al-Zn-Mg Alloy after Non-Isothermal Heat Treatment. Materials 2019, 12, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, X.F.; Lei, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, M.P. Precipitation Behavior and Quenching Sensitivity of a Spray Deposited Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr Alloy. Materials 2017, 10, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Luo, B.H.; Bai, Z.H.; He, C.; Tan, S.Z.; Jiang, G. Effect of Zn/Mg ratios on microstructure and stress corrosion cracking of 7005 alloy. Materials 2019, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robson, J.D.; Prangnell, P.B. Dispersoid precipitation and process modelling in zirconium containing commercial aluminum alloys. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, B.H.; Liu, P.Y.; Zhou, T.T. Effect of compositions on the quenching sensitivity of 7050 and 7085 alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 667, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, D. Investigation on the Quench Sensitivity of 7085 Aluminum Alloy with Different Contents of Main Alloying Elements. Metals 2019, 9, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.B.; Liu, S.D.; Zhang, X.M. Effect of Zener-Hollomon parameter on quench sensitivity of 7085 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starink, M.J.; Milkereit, B.; Zhang, Y.; Rometsch, P.A. Predicting the quench sensitivity of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys: A model for linear cooling and strengthening. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.L.; Wan, L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.M. Influence of Mg content on quench sensitivity of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu aluminum alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 4636–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, Q.; Ortega Vega, M.R.; De Fraga Malfatti, C.; Duluard, S.; Ansart, F. Correlation between morphology and electrochemical behavior of chromium-free conversion coatings for aluminum alloys corrosion protection. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 351, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Chen, K.; Peng, G.; Jia, L.; Dong, P. Effect of heat treatment on strength, exfoliation corrosion and electrochemical behavior of 7085 aluminum alloy. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhao, R.; Qin, Z.B.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.Q.; Liu, L.; Lu, W.J. Evolution of the Corrosion Product Film on Nickel-Aluminum Bronze and Its Corrosion Behavior in 3.5 wt % NaCl Solution. Materials 2019, 12, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, P.; Chen, S.; Chen, K.; Jiao, H.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z. Enhancing the stress corrosion cracking resistance of a low-Cu containing Al-Zn-Mg-Cu aluminum alloy by step-quench and aging heat treatment. Corros. Sci. 2019, 161, 108–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbilis, N.; Cavanaugh, M.K.; Buchheit, R.G. Electrochemical behavior and localized corrosion associated with Al7Cu2Fe particles in aluminum alloy 7075-T651. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 4202–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejun, K.; Jinchun, W. Salt spray corrosion and electrochemical corrosion properties of anodic oxide film on 7475 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 632, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Wang, J.H.; Fu, C.W. Characterization of pitting corrosion of 7A60 aluminum alloy by EN and EIS techniques. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 3907–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Pan, Q.L.; Li, H.; Huang, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.R.; Wang, X.D.; Li, M.J. Quench Sensitivity of a 7A46 Aluminum Alloy. JOM 2019, 71, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.R.; Pan, Q.; Li, H.; Huang, Z.; Ye, J.; Li, M. Revealing the evolution of microstructure, mechanical property and corrosion behavior of 7A46 aluminum alloy with different ageing treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 792, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ni, D.R.; Ma, Z.Y. Effect of pre-strain and two-step aging on microstructure and stress corrosion cracking of 7050 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 494, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Pan, Q.; Li, M.; Huang, X.; Li, B. Influence of alloyed Sc and Zr, and heat treatment on microstructures and stress corrosion cracking of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 621, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Ul-Hamid, A.; Abdul-Aleem, B.J. The corrosion behavior of scandium alloyed Al 5052 in neutral sodium chloride solution. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 1227–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.K.; Ghosh, M.M.; Ghosh, K.S. Effect of solution pH on electrochemical and stress corrosion cracking behaviour of a 7150 Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 604, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Pan, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Ye, J.; Lin, G.; Liu, S.; Huang, Z.; Xiang, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Non-isothermal aging: A heat treatment method that simultaneously improves the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of ultra-high strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 845, 156286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, A.; De Damborenea, J. Evaluation of exfoliation susceptibility by means of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 1363–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keddam, M.; Kuntz, C.; Takenouti, H.; Schustert, D.; Zuili, D. Exfoliation corrosion of aluminium alloys examined by electrode impedance. Electrochim. Acta 1997, 42, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Han, X.; Du, Z.; Wang, G.; Lu, L.; Lei, J.; Zhou, T. Effect of microstructure on exfoliation corrosion resistance in an Al-Zn-Mg alloy. Mater. Charact. 2018, 135, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Ardell, A.J. Microchemical analysis of precipitate free zones in 7075-A1 in the T6, T7 and RRA tempers. Acta Metall. Mater. 1991, 39, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wloka, J.; Hack, T.; Virtanen, S. Influence of temper and surface condition on the exfoliation behaviour of high strength Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.J.; Robinson, M.J. Influence of Heat Treatment and Grain Shape on Exfoliation Corrosion of Al-Li Alloy 8090. J. Corros. Sci. Eng. 1993, 49, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Hashimoto, T.; Liu, B. Localized corrosion in AA2024-T351 aluminium alloy: Transition from intergranular corrosion to crystallographic pitting. Mater. Charact. 2017, 130, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Tan, Q.; Li, D. The effect of quench rate and overageing temper on the corrosion behaviour of AA7050. Corros. Sci. 2014, 78, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Element | Zn | Mg | Cu | Fe | Si | Mn | Ti | Zr | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition (wt.%) | 6.69 | 1.32 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.01 | Bal. |
| Phase | Al | Zn | Mg | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 93.03 | 2.79 | 1.47 | 2.71 |
| B | 90.62 | 2.18 | 1.31 | 5.90 |
| C | 84.56 | 2.49 | 0.81 | 12.14 |
| D | 92.64 | 4.61 | 2.59 | 0.16 |
| E | 89.95 | 2.98 | 1.35 | 5.72 |
| F | 93.99 | 4.08 | 1.93 | 0 |
| Condition | Ecorr (V) | Icorr (μA/cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| DA | −0.896 ± 0.006 | 1.017 |
| 100 s | −0.908 ± 0.012 | 1.429 |
| 800 s | −0.919 ± 0.002 | 2.371 |
| 1500 s | −0.914 ± 0.018 | 1.633 |
| Sample State | Time (h) | Rt (Ω·cm−2) | Rs (Ω·cm−2) | Rf (Ω·cm−2) | Cf (/F·cm−2) | nl | L (H) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DA | 0 | 1.097 × 104 | 12.27 | 1.021 × 104 | 3.000 × 10−5 | 8.829 × 10−1 | 3.588 × 104 |
| 100 s | 0 | 9.659 × 103 | 12.04 | 2.919 × 103 | 2.158 × 10−5 | 8.490 × 10−1 | 5.735 × 104 |
| 800 s | 0 | 4.837 × 103 | 5.472 | 8.122 × 102 | 1.278 × 10−5 | 8.662 × 10−1 | 9.001 × 103 |
| 1500 s | 0 | 5.956 × 103 | 6.277 | 3.107 × 103 | 2.685 × 10−5 | 8.831 × 10−1 | 3.229 × 105 |
| DA | 48 h | 8.554 × 103 | 7.345 | 5.601 × 103 | 1.207 × 10−5 | 8.818 × 10−1 | 1.648 × 105 |
| 100 s | 48 h | 6.740× 103 | 6.608 | 1.130 × 103 | 3.517 × 10−5 | 8.519 × 10−1 | 3.584 × 102 |
| 800 s | 48 h | 4.084 × 103 | 6.594 | 5.632 × 102 | 1.503 × 10−5 | 8.314 × 10−1 | 1.114 × 104 |
| 1500 s | 48 h | 4.431 × 103 | 9.196 | 4.911 × 103 | 3.777 × 10−5 | 8.348 × 10−1 | 1.324 × 105 |
| DA | 96 h | 6.44 × 103 | 4.895 | 4.847 × 103 | 3.082 × 10−5 | 8.637 × 10−1 | 2.072 × 104 |
| 100 s | 96 h | 3.582 × 103 | 10.39 | 2.307 × 103 | 2.359 × 10−5 | 8.414 × 10−1 | 2.43 × 104 |
| 800 s | 96 h | 3.041 × 103 | 6.268 | 1.225 × 102 | 2.783 × 10−5 | 8.329 × 10−1 | 6.652 × 102 |
| 1500 s | 96 h | 3.293 × 103 | 7.108 | 3.536 × 103 | 3.870 × 10−5 | 8.492 × 10−1 | 3.739 × 103 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Xing, L.; Zeng, Q.; Pan, Q.; Li, S.; Liang, J.; Yang, H. The Microstructure Evolution and Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of 7A46 Aluminum Alloy in Different Quenching Conditions. Materials 2022, 15, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020477
Liu Y, Xing L, Zeng Q, Pan Q, Li S, Liang J, Yang H. The Microstructure Evolution and Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of 7A46 Aluminum Alloy in Different Quenching Conditions. Materials. 2022; 15(2):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020477
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yaru, Lu Xing, Qing Zeng, Qinglin Pan, Sheng Li, Jun Liang, and Haoru Yang. 2022. "The Microstructure Evolution and Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of 7A46 Aluminum Alloy in Different Quenching Conditions" Materials 15, no. 2: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020477
APA StyleLiu, Y., Xing, L., Zeng, Q., Pan, Q., Li, S., Liang, J., & Yang, H. (2022). The Microstructure Evolution and Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of 7A46 Aluminum Alloy in Different Quenching Conditions. Materials, 15(2), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020477




