Influence of Adaptive Gap Control Mechanism and Tool Electrodes on Machining Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) Alloy in EDM Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- To implement an adaptive gap control mechanism to reduce the arcing effect while machining a titanium alloy;
- To investigate the influence of the adaptive gap control mechanism on the enhancement of the surface quality;
- To conduct an analysis of the tool electrode’s impacts on the surface roughness and morphology in the die sinking EDM process.
2. Materials and Methods
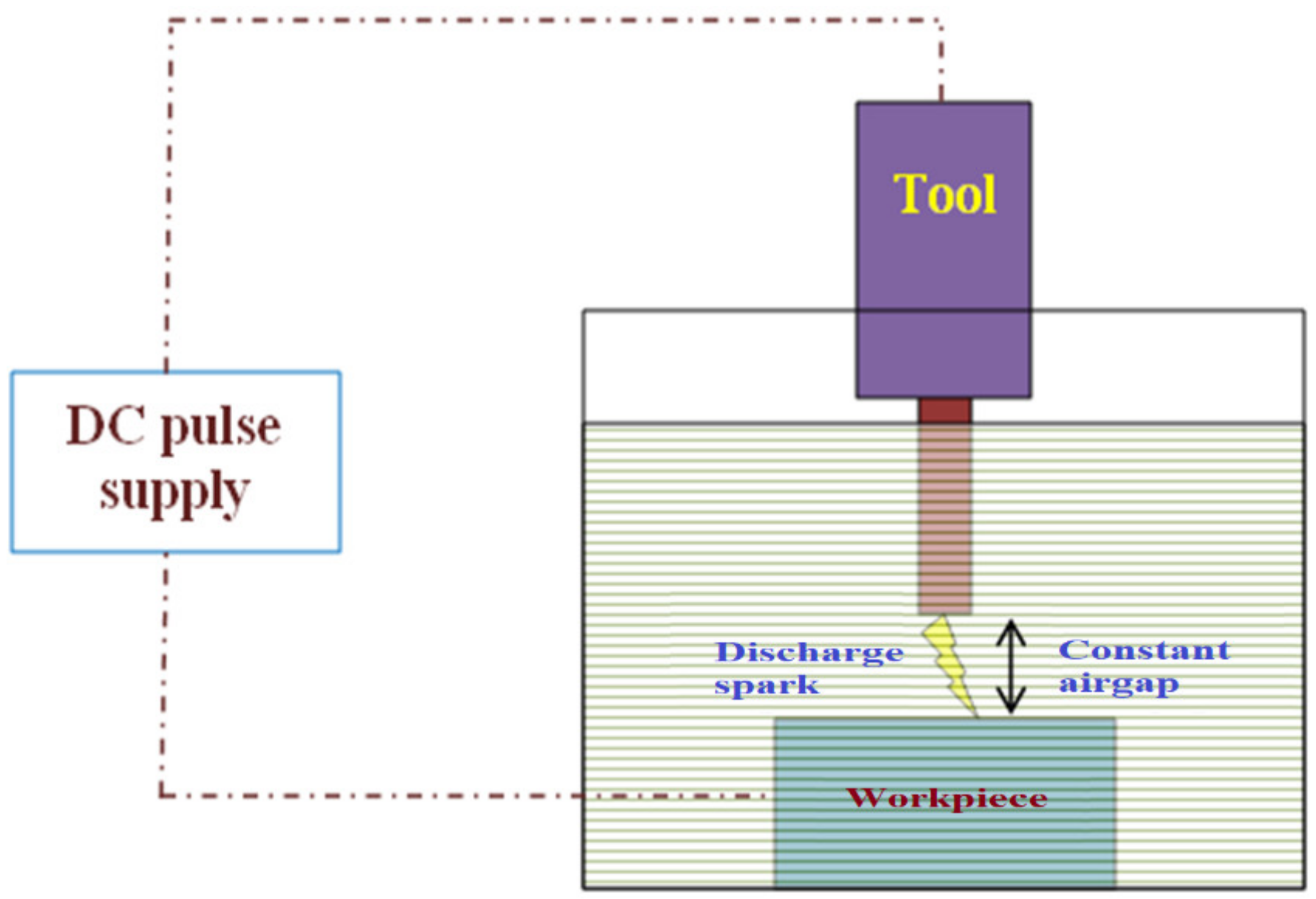
2.1. Design of EDM Process Arrangement
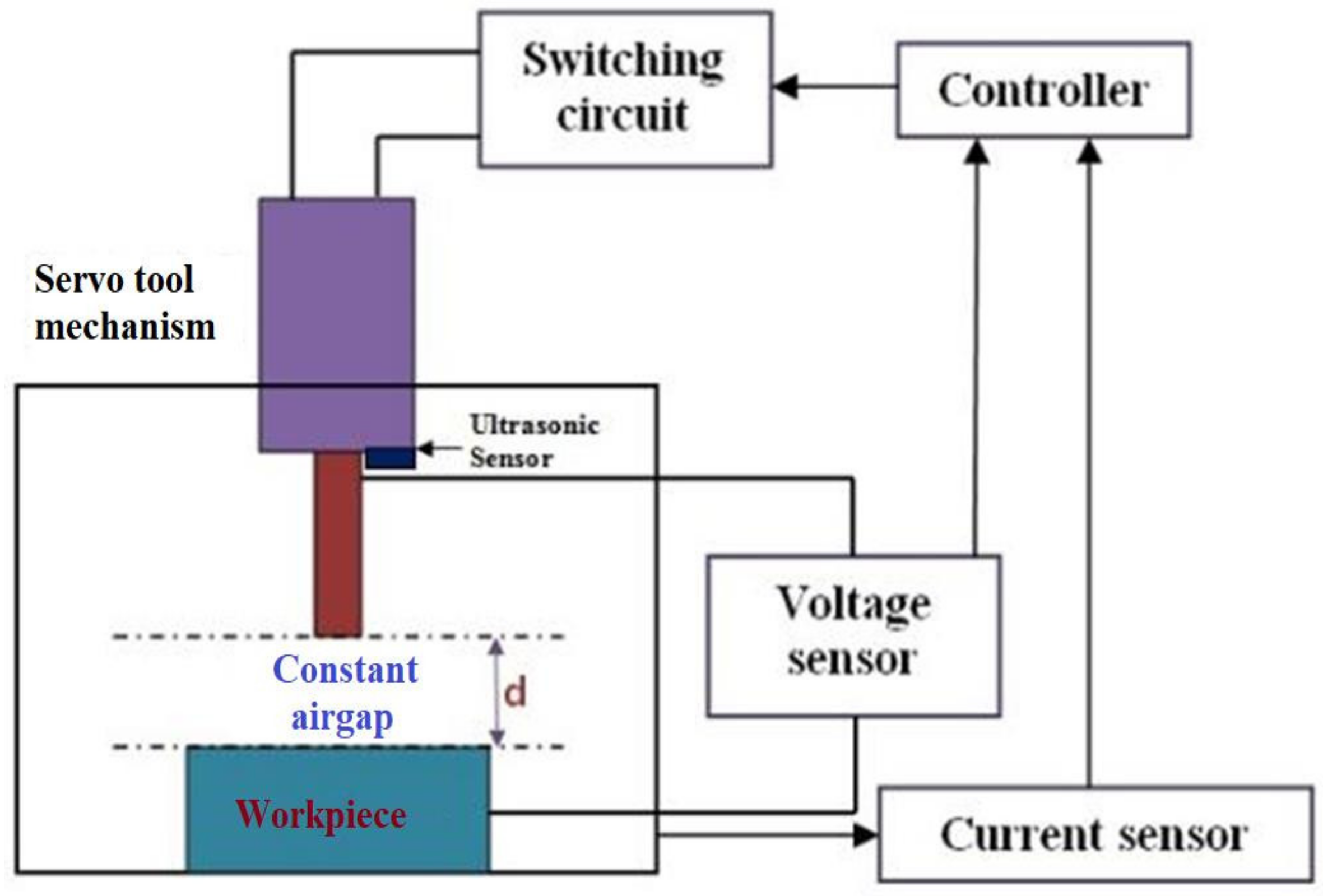
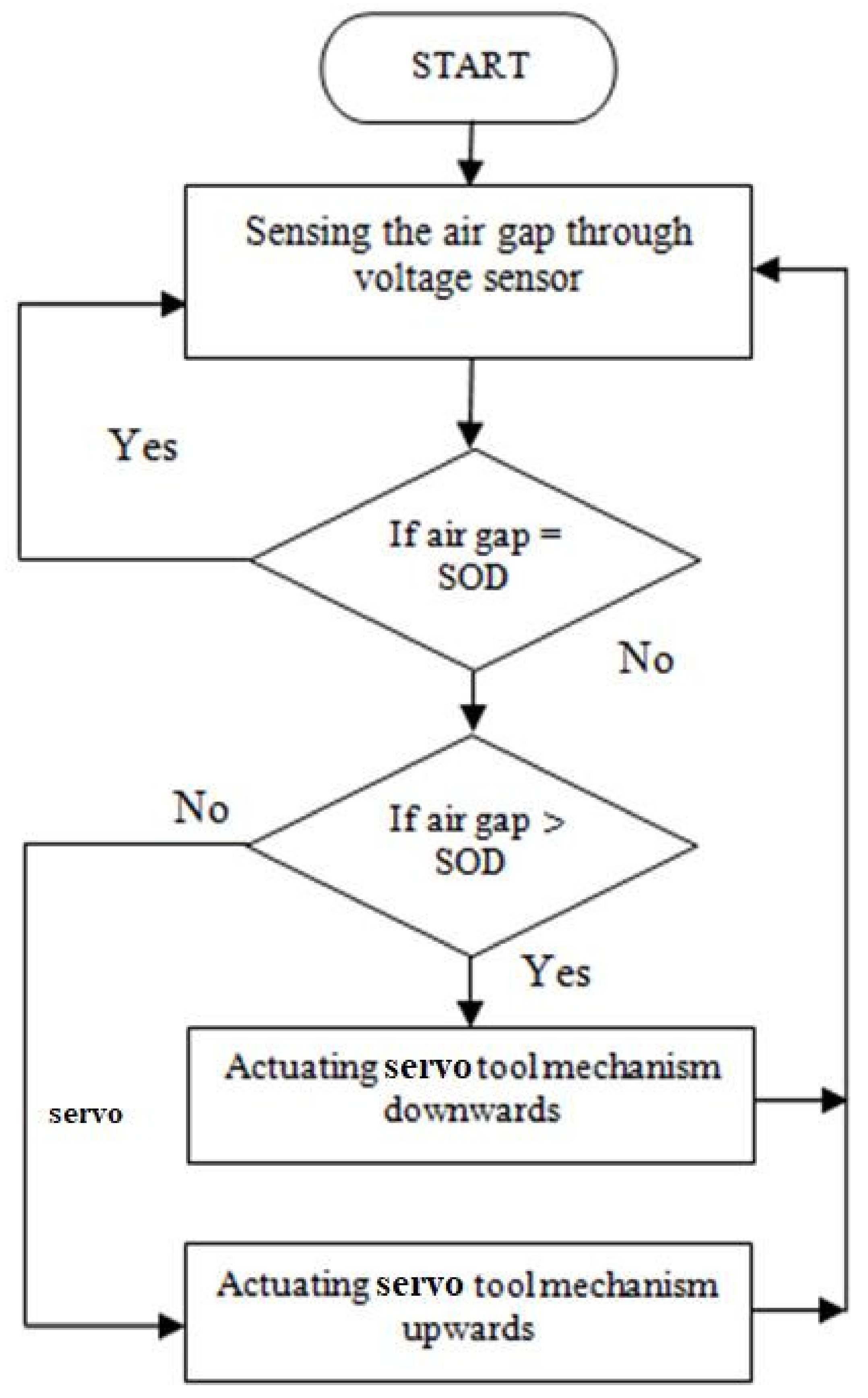
2.2. Design of the Servo Tool Feed Control
2.3. Design of Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
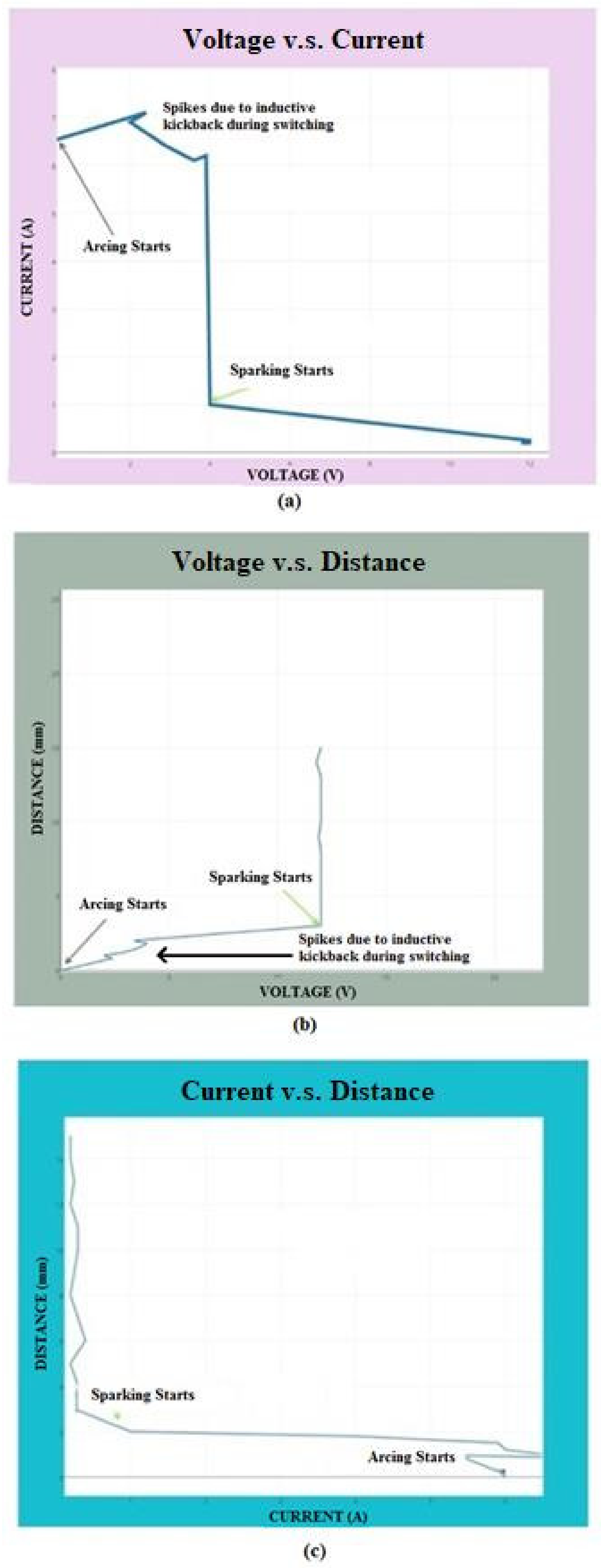
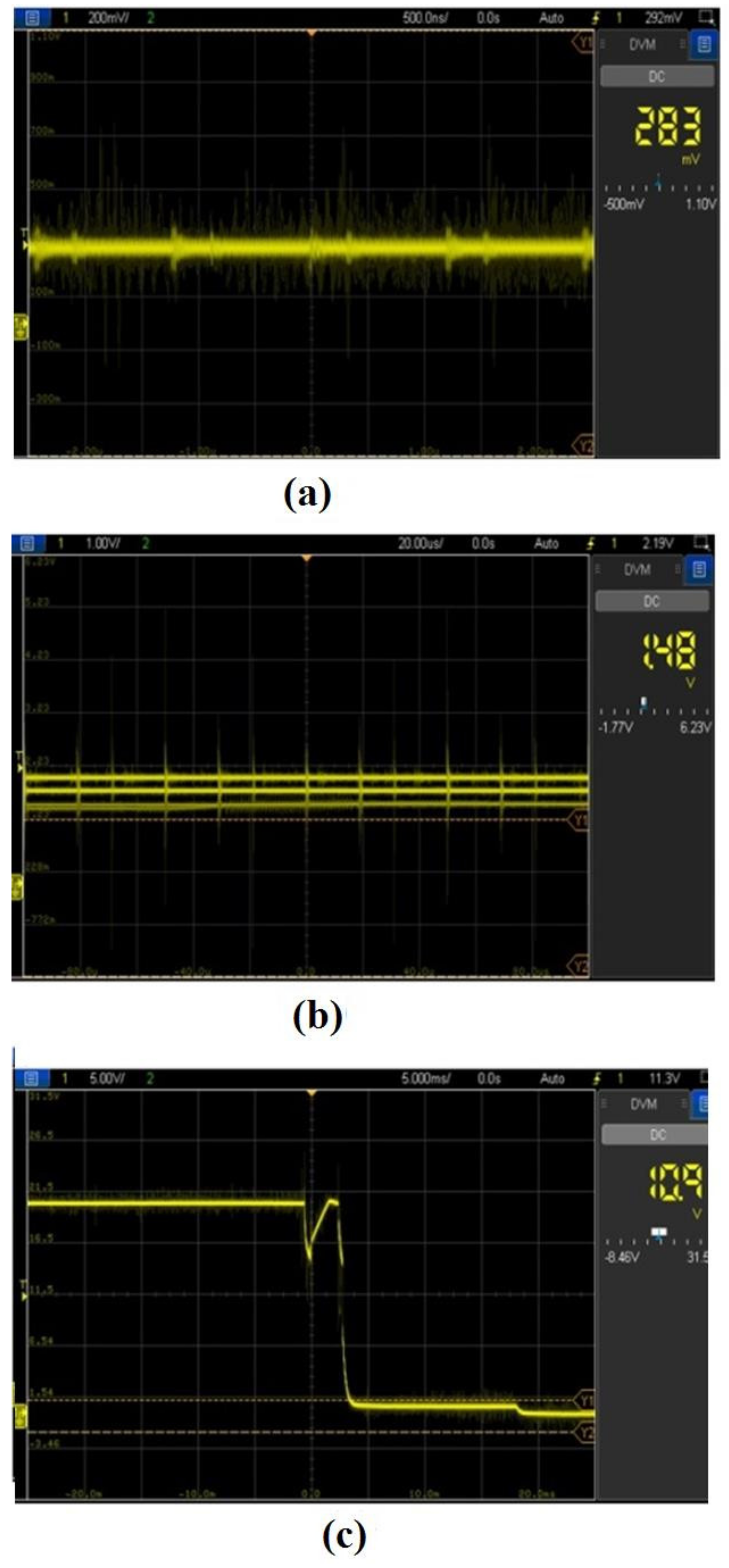
3.1. Waveform Analysis
3.2. Pulse Form Analysis
3.3. Pulse Form Analysis
3.4. Significance of Electrodes on Ra while Machining Titanium Specimens
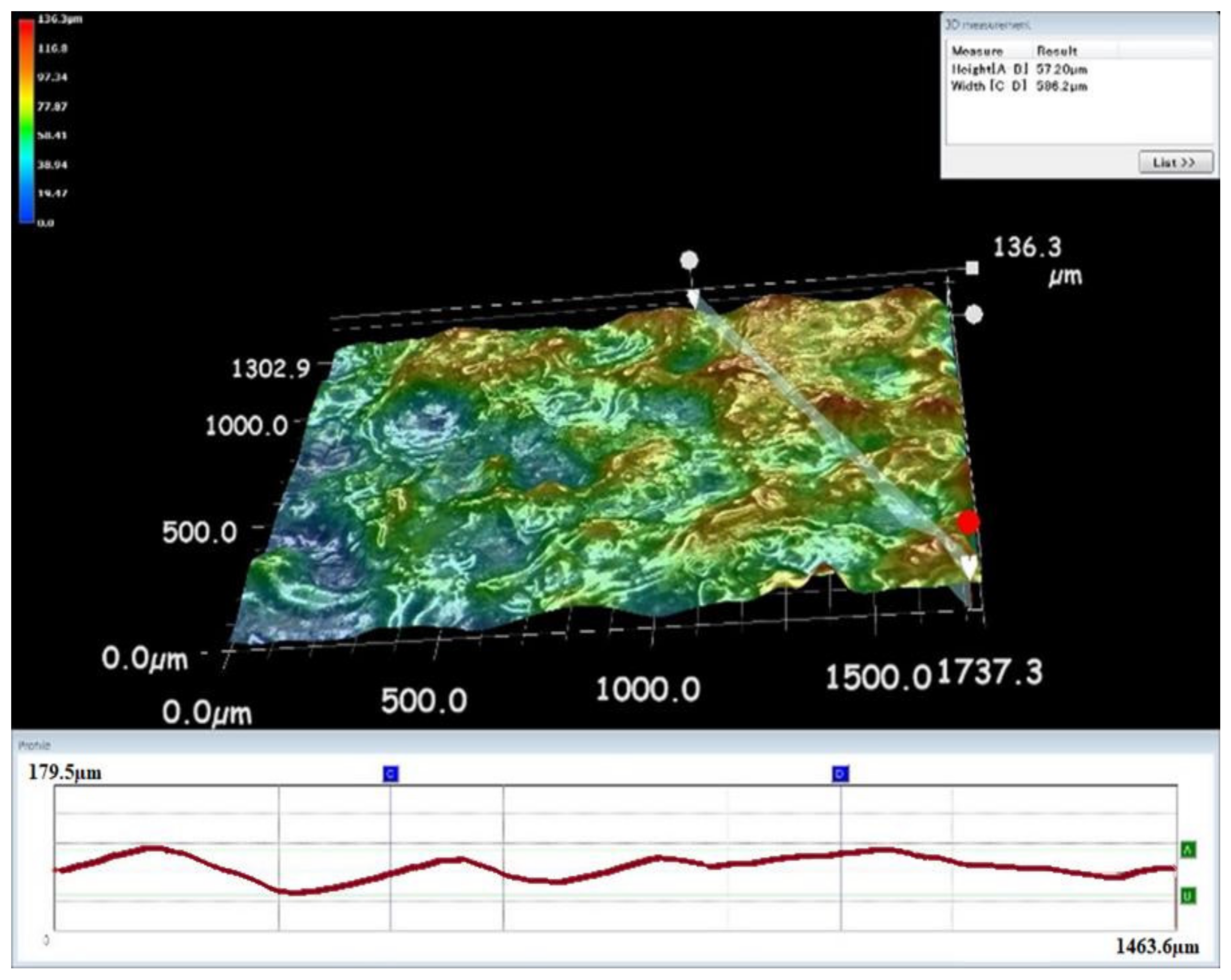
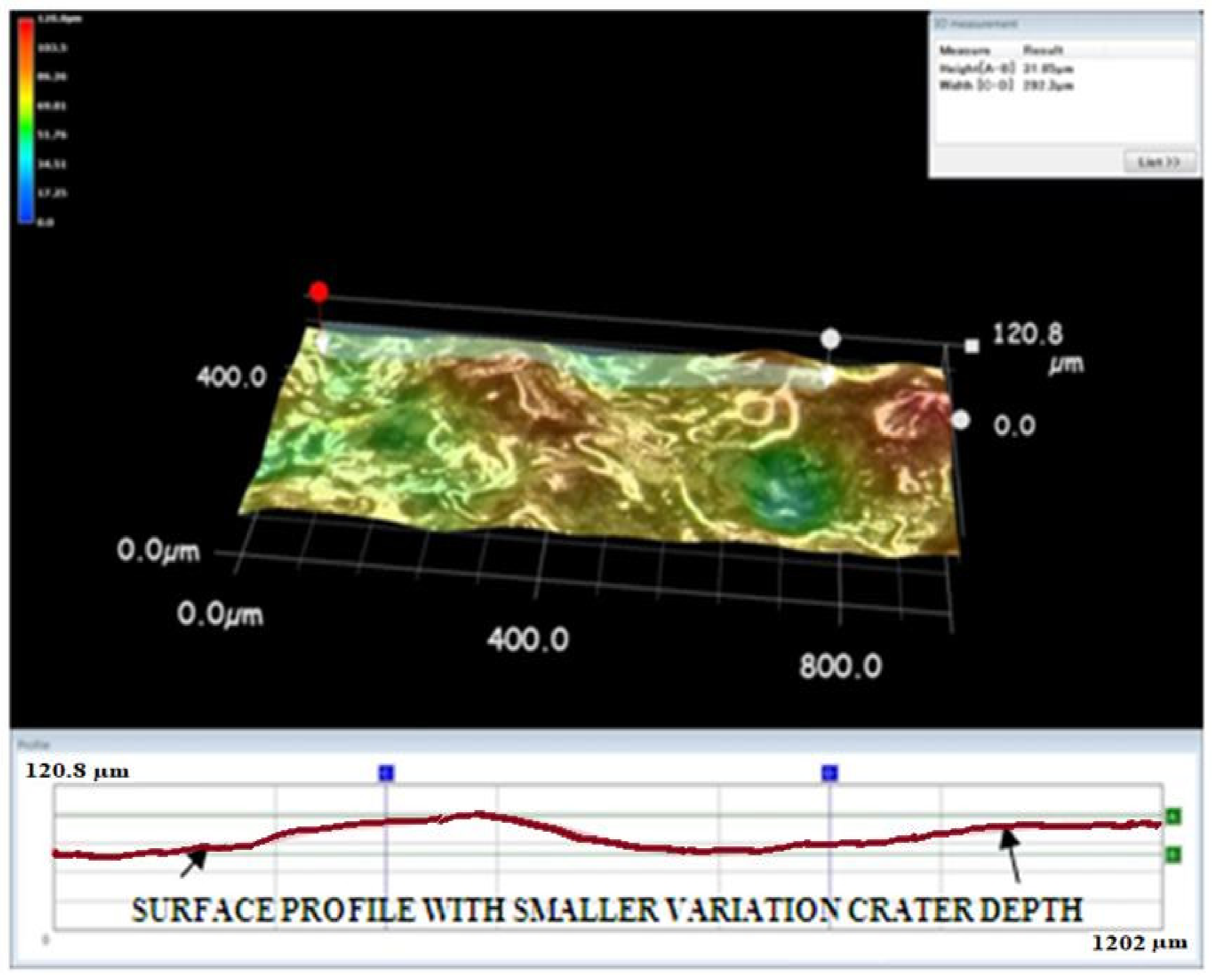
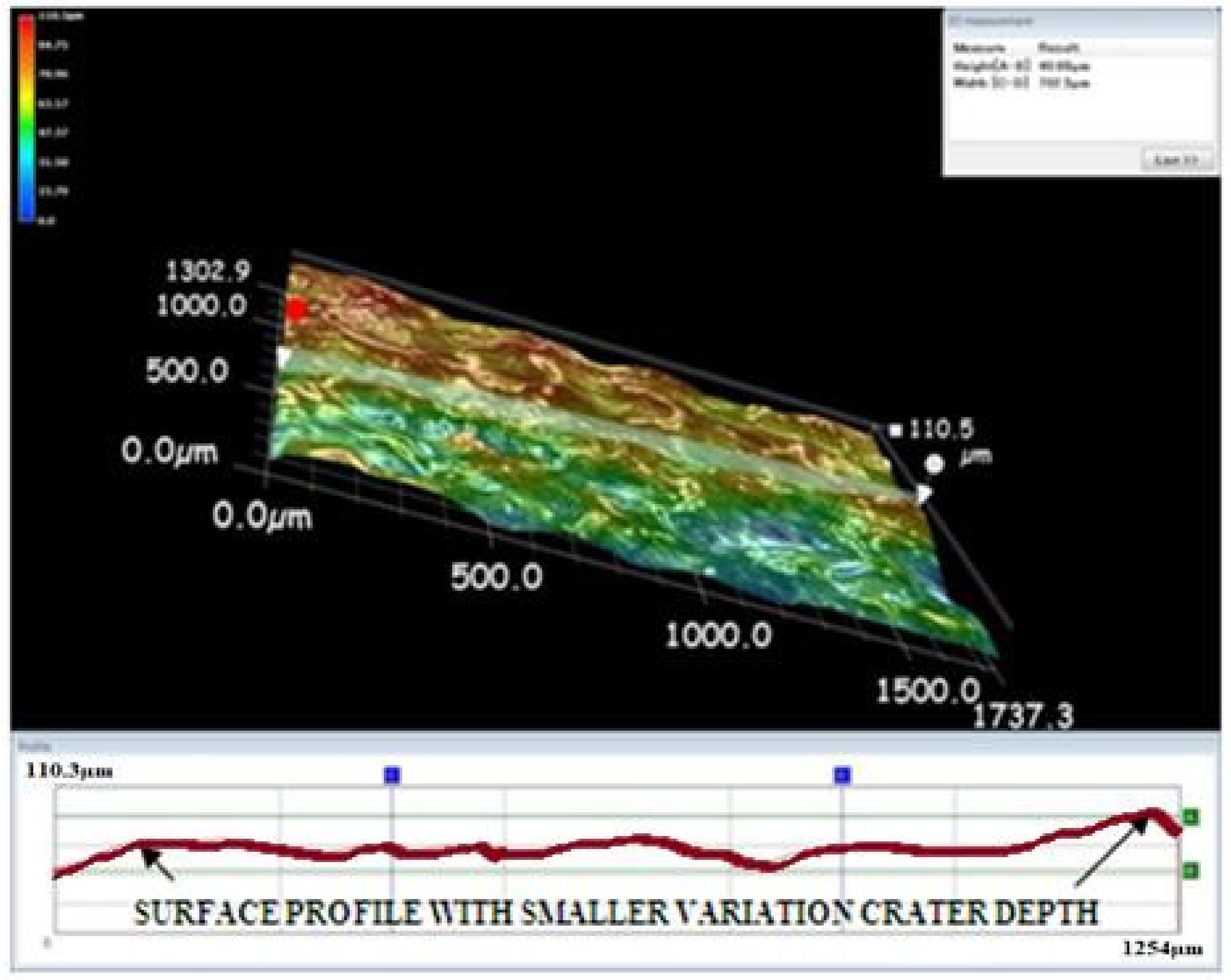
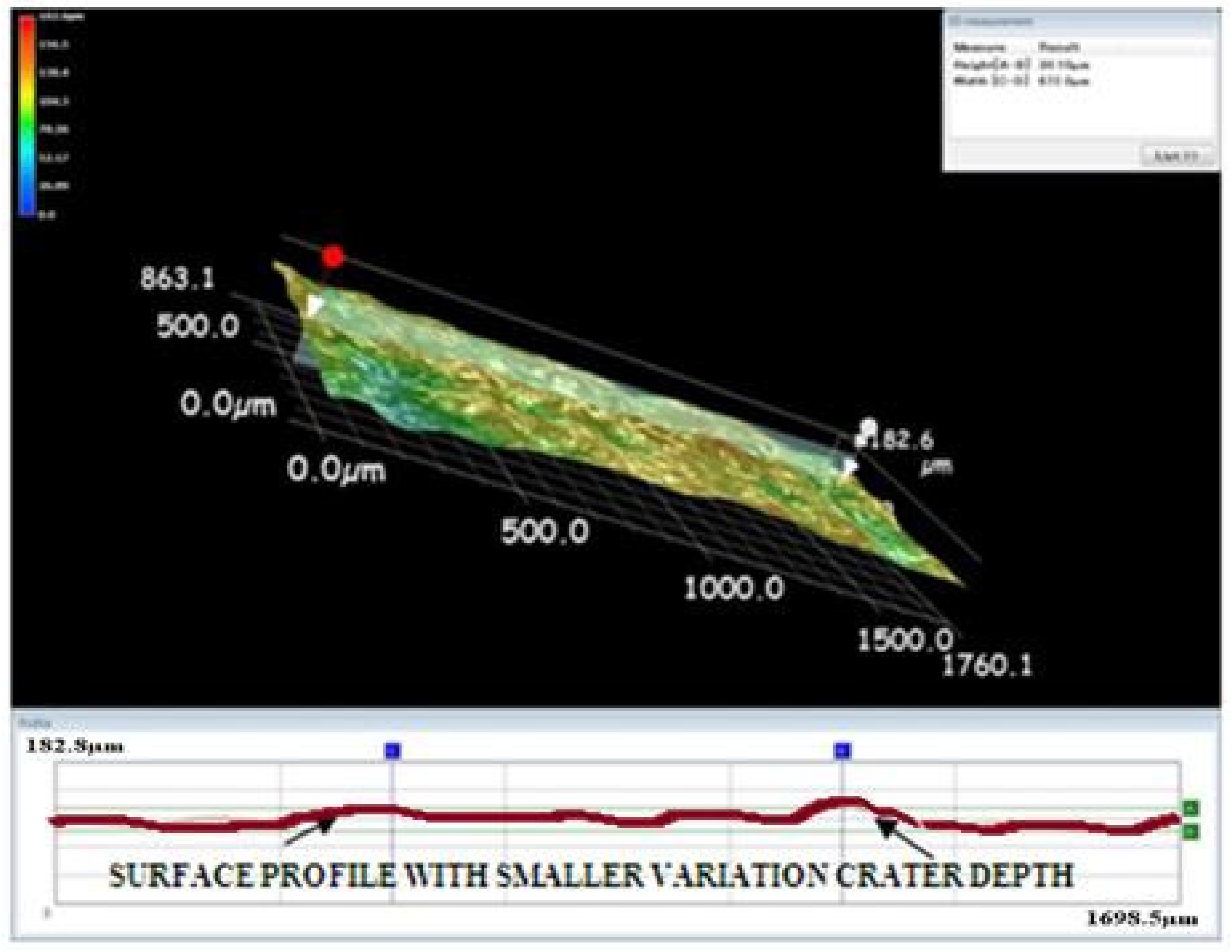
3.5. Surface Morphology Analysis with Different Tool Electrodes
4. Conclusions
- The proposed scheme enhances the servo feed mechanism to enhance the machinability as compared with the existing approach due to efficient switching between sparking and arcing.
- The proposed approach on an air gap can produce better surface morphology of the machined specimens.
- The tungsten carbide electrode creates tiny and uniform craters for making a better smooth surface in the EDM process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muthuramalingam, T.; Akash, R.; Krishnan, S.; Phan, N.H.; Pi, V.N.; Elsheikh, A.H. Surface quality measures analysis and optimization on machining titanium alloy using CO2 based Laser beam drilling process. J. Manuf. Process 2021, 62, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethapriyan, T.; Thangaraj, M.; Moiduddin, K.; Mian, S.M.; Alkhalefah, H.; Umer, U. Performance Analysis of Electrochemical Micro Machining of Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) Alloy under Different Electrolytes Concentrations. Metals 2021, 11, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, R.; Ramoni, M.O.; Geethapriyan, T.; Thangaraj, M. Influence of additive manufactured stainless steel tool electrode on machinability of beta titanium alloy. Metals 2021, 11, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.H.; Newman, S.T. State of the art electrical discharge machining. Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manuf. 2003, 43, 1287–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuramalingam, T.; Mohan, B. Performance analysis of iso current pulse generator on machining characteristics in EDM process. Arch. Civil Mech. Eng. 2014, 14, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, A.; Sivaramakrishnan, R.; Muthuramalingam, T.; Venugopal, S. Performance analysis of wire electrodes on machining Ti-6Al-4V alloy using electrical discharge machining process. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2015, 19, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuramalingam, T.; Mohan, B.; Rajadurai, A.; Prakash, M.D.A.A. Experimental Investigation of iso Energy Pulse Generator on Performance Measures in EDM. Mater. Manuf. Process 2013, 28, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Marimuthu, K.; Sakthivel, M. Study of crack formation and resolidified layer in EDM Process on T90Mn2W50Cr45 tool steel. Mater. Manuf. Process 2012, 28, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuramalingam, T.; Mohan, B. Design and fabrication of control system based iso current pulse generator for electrical discharge machining. Int. J. Mechatron. Manuf. Syst. 2013, 6, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuramalingam, T.; Rabik, M.M.; Saravanakumar, D.; Jaswanth, K. Sensor integration based approach for automatic fork lift trucks. IEEE Sens. 2018, 18, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabik, M.M.; Thangaraj, M. Tracking and locking system for shooter with sensory noise cancellation. IEEE Sens. 2018, 18, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y. A plate capacitor model of the EDM process based on the field emission theory. Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manuf. 2011, 51, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraj, M.; Ramamurthy, A.; Moiduddin, K.; Alkindi, M.; Ramalingam, S.; Alghamdi, O. Enhancing the Surface Quality of Micro Titanium Alloy Specimen in WEDM Process by Adopting TGRA-Based Optimization. Materials 2020, 13, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thangaraj, M.; Ramamurthy, A.; Sridharan, K.; Ashwin, S. Analysis of surface performance measures on WEDM processed titanium alloy with coated electrodes. Mater. Res. Exp. 2018, 5, 126503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuramalingam, T.; Mohan, B. Influence of tool electrode properties on machinability in electrical discharge machining. Mater. Manuf. Process 2013, 28, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Maheswari, S.; Sharma, C.; Beri, N. Machining efficiency evaluation of cryogenically treated copper electrode in additive mixed EDM. Mater. Manuf. Process 2012, 27, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, I.; Sarhan, A.A.D.; Marashi, H.; Barzani, M.M.; Hamdi, M. White layer thickness prediction in wire-EDM using CuZn-coated wire electrode—ANFIS modeling. Trans. IMF 2016, 94, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saodaen, R.; Janmanee, P.; Rodchanarowan, A. Characteristics of Ternary Metal (Cu-Ni-TiN) Electrodes Used in an Electrical Discharge Machining Process. Metals 2021, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamkamon, K.; Janmanee, P. Improving machining performance for deep hole drilling in the electrical discharge machining process using a step cylindrical electrode. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowiak, T.; Mendak, M.; Mrozek, K.; Wieczorowski, M. Analysis of Surface Microgeometry Created by Electric Discharge Machining. Materials 2020, 13, 3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarto, M.; Bissacco, G.; D’Urso, G. Machinability and energy efficiency in micro-EDM milling of zirconium boride reinforced with silicon carbide fibers. Materials 2019, 12, 3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Świercz, R.; Oniszczuk-Świercz, D. Experimental investigation of surface layer properties of high thermal conductivity tool steel after electrical discharge machining. Metals 2017, 7, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattia, B.; Wu, M.; Jun, Q.; Dominiek, R. Tool wear and material removal predictions in micro- EDM drilling: Advantages of data-driven approaches. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Patowari, P.K. Electrode wear phenomenon and its compensation in micro electrical discharge milling: A review. Mater. Manuf. Process 2018, 33, 1491–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Mu, X.; He, L.; Ye, Q. Improving EDM performance by adapting gap servo-voltage to machining state. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 37, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmelpfennig, T.M.; Rübeling, G.; Lorenz, M. Development of novel gap control method for the Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) of implant-supported dentures. Procedia CIRP 2020, 95, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuramalingam, T.; Mohan, B.; Rajadurai, A.; Saravanakumar, D. Monitoring and fuzzy control approach for efficient electrical discharge machining process. Mater. Manuf. Process 2014, 29, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, J.A.; Jahanzaib, M.; Azam, M.; Hussain, S.; Wasim, A.; Abbas, M. Effects of wire Cut EDM process parameters on surface roughness of HSLA steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Wu, H.; Qiu, F. Experimental study on high-speed WEDM finishing in steam water mist. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 3285–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, N.H.; Thangaraj, M.; Vu, N.N.; Tuan, N.Q. Influence of micro size titanium powders mixed dielectric medium on surface quality measures in EDM process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 109, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Tool Electrode | Electrical Conductivity (S/m) | Melting Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Copper | 5.96 × 107 | 1085 |
| Brass | 1.67 × 107 | 930 |
| Tungsten carbide | 6.37 × 106 | 2870 |
| Trial | V(v) | I(A) | DF |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 9 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 40 | 9 | 0.6 |
| 3 | 40 | 9 | 0.8 |
| 4 | 40 | 12 | 0.4 |
| 5 | 40 | 12 | 0.6 |
| 6 | 40 | 12 | 0.8 |
| 7 | 40 | 15 | 0.4 |
| 8 | 40 | 15 | 0.6 |
| 9 | 40 | 15 | 0.8 |
| 10 | 60 | 9 | 0.4 |
| 11 | 60 | 9 | 0.6 |
| 12 | 60 | 9 | 0.8 |
| 13 | 60 | 12 | 0.4 |
| 14 | 60 | 12 | 0.6 |
| 15 | 60 | 12 | 0.8 |
| 16 | 60 | 15 | 0.4 |
| 17 | 60 | 15 | 0.6 |
| 18 | 60 | 15 | 0.8 |
| 19 | 80 | 9 | 0.4 |
| 20 | 80 | 9 | 0.6 |
| 21 | 80 | 9 | 0.8 |
| 22 | 80 | 12 | 0.4 |
| 23 | 80 | 12 | 0.6 |
| 24 | 80 | 12 | 0.8 |
| 25 | 80 | 15 | 0.4 |
| 26 | 80 | 15 | 0.6 |
| 27 | 80 | 15 | 0.8 |
| No | Cu | Brass | WC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 2.378 | 3.564 | 0.384 |
| 2. | 3.732 | 4.127 | 0.474 |
| 3. | 5.502 | 7.931 | 0.612 |
| 4. | 3.958 | 5.781 | 0.482 |
| 5. | 5.881 | 6.623 | 0.627 |
| 6. | 7.706 | 9.978 | 0.742 |
| 7. | 5.234 | 7.524 | 0.591 |
| 8. | 7.659 | 10.127 | 0.733 |
| 9. | 10.505 | 14.374 | 0.878 |
| 10. | 3.123 | 3.993 | 0.408 |
| 11. | 4.509 | 5.235 | 0.579 |
| 12. | 6.006 | 8.743 | 0.654 |
| 13. | 4.355 | 6.075 | 0.545 |
| 14. | 6.302 | 7.793 | 0.689 |
| 15. | 8.502 | 10.489 | 0.804 |
| 16. | 5.569 | 7.823 | 0.607 |
| 17. | 8.103 | 10.742 | 0.779 |
| 18. | 11.25 | 15.670 | 0.912 |
| 19. | 3.345 | 4.778 | 0.415 |
| 20. | 5.016 | 5.939 | 0.601 |
| 21. | 6.184 | 9.232 | 0.685 |
| 22. | 4.635 | 6.217 | 0.588 |
| 23. | 7.054 | 9.384 | 0.707 |
| 24. | 8.805 | 12.697 | 0.838 |
| 25. | 6.145 | 8.124 | 0.678 |
| 26. | 8.453 | 10.987 | 0.807 |
| 27. | 12.105 | 17.788 | 0.925 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Thangaraj, M.; Moiduddin, K.; Al-Ahmari, A.M. Influence of Adaptive Gap Control Mechanism and Tool Electrodes on Machining Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) Alloy in EDM Process. Materials 2022, 15, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020513
Liu S, Thangaraj M, Moiduddin K, Al-Ahmari AM. Influence of Adaptive Gap Control Mechanism and Tool Electrodes on Machining Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) Alloy in EDM Process. Materials. 2022; 15(2):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020513
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shoufa, Muthuramalingam Thangaraj, Khaja Moiduddin, and Abdulrahman M. Al-Ahmari. 2022. "Influence of Adaptive Gap Control Mechanism and Tool Electrodes on Machining Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) Alloy in EDM Process" Materials 15, no. 2: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020513
APA StyleLiu, S., Thangaraj, M., Moiduddin, K., & Al-Ahmari, A. M. (2022). Influence of Adaptive Gap Control Mechanism and Tool Electrodes on Machining Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) Alloy in EDM Process. Materials, 15(2), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020513








