Optically Transparent Tri-Wideband Mosaic Frequency Selective Surface with Low Cross-Polarisation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. MFSS
- (1)
- An opaque MFSS as a reference, fabricated on an FR4 substrate with a permittivity ( of 4.3, loss tangent of 0.02, lossy substrate thickness of 1.6 mm and copper layer thickness of 0.035 mm with a conductivity () of S/m.
- (2)
- A transparent MFSS using a polycarbonate substrate with a of 2.9, of 0.005, substrate thickness of 1.5 mm and a silver layer thickness of 0.006 mm with a conductivity of S/m.
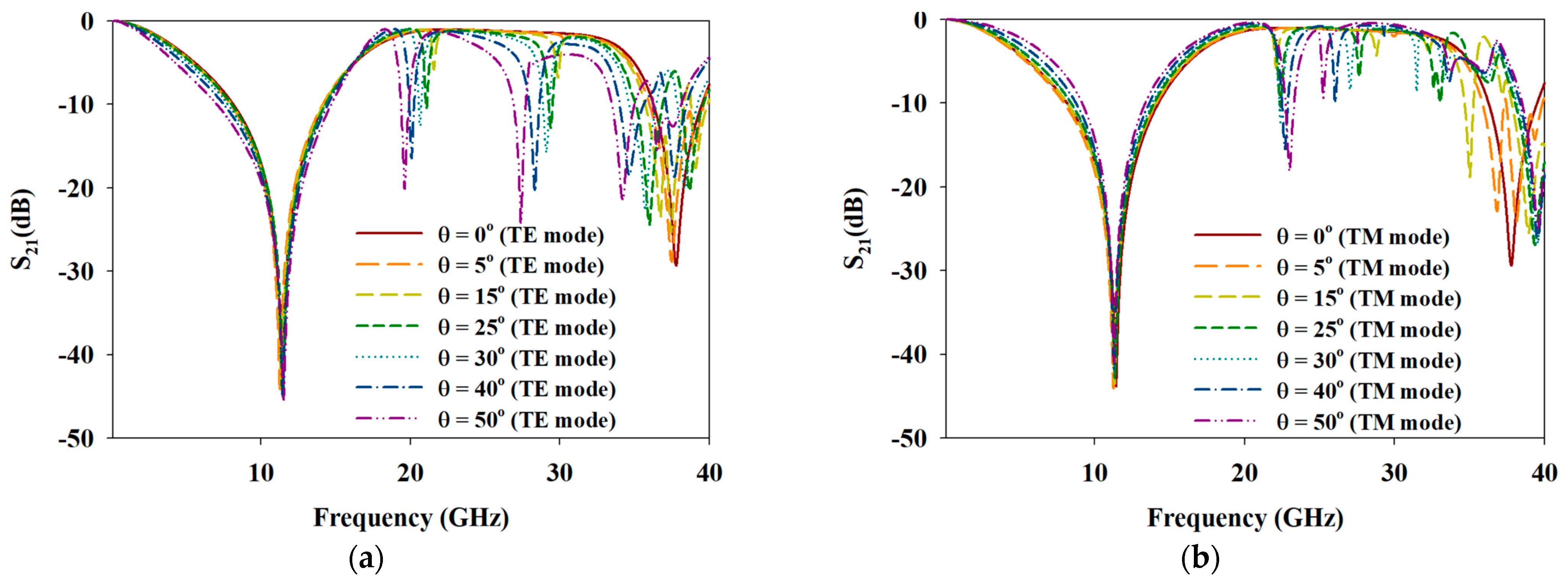
3. Simulation Results
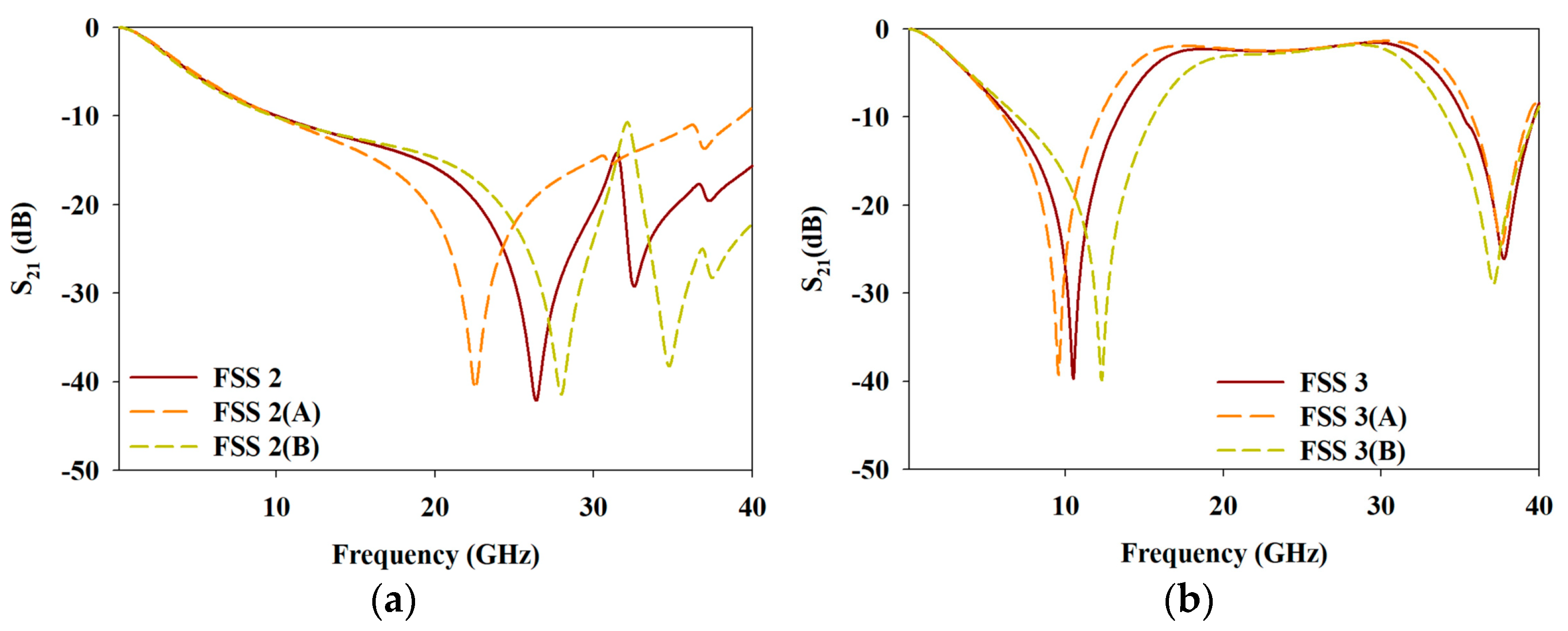
3.1. Wideband MFSS—Evolution of Unit Cell (Opaque)
- (1)
- The propagation constant equals a surface wave propagation constant .
- (2)
- The grid spacings , are such that the equality of propagation constants in (1) occurs for values of , in real space.
- (3)
- The TM (TE) surface wave pole of (1) is not cancelled by a zero value of ().
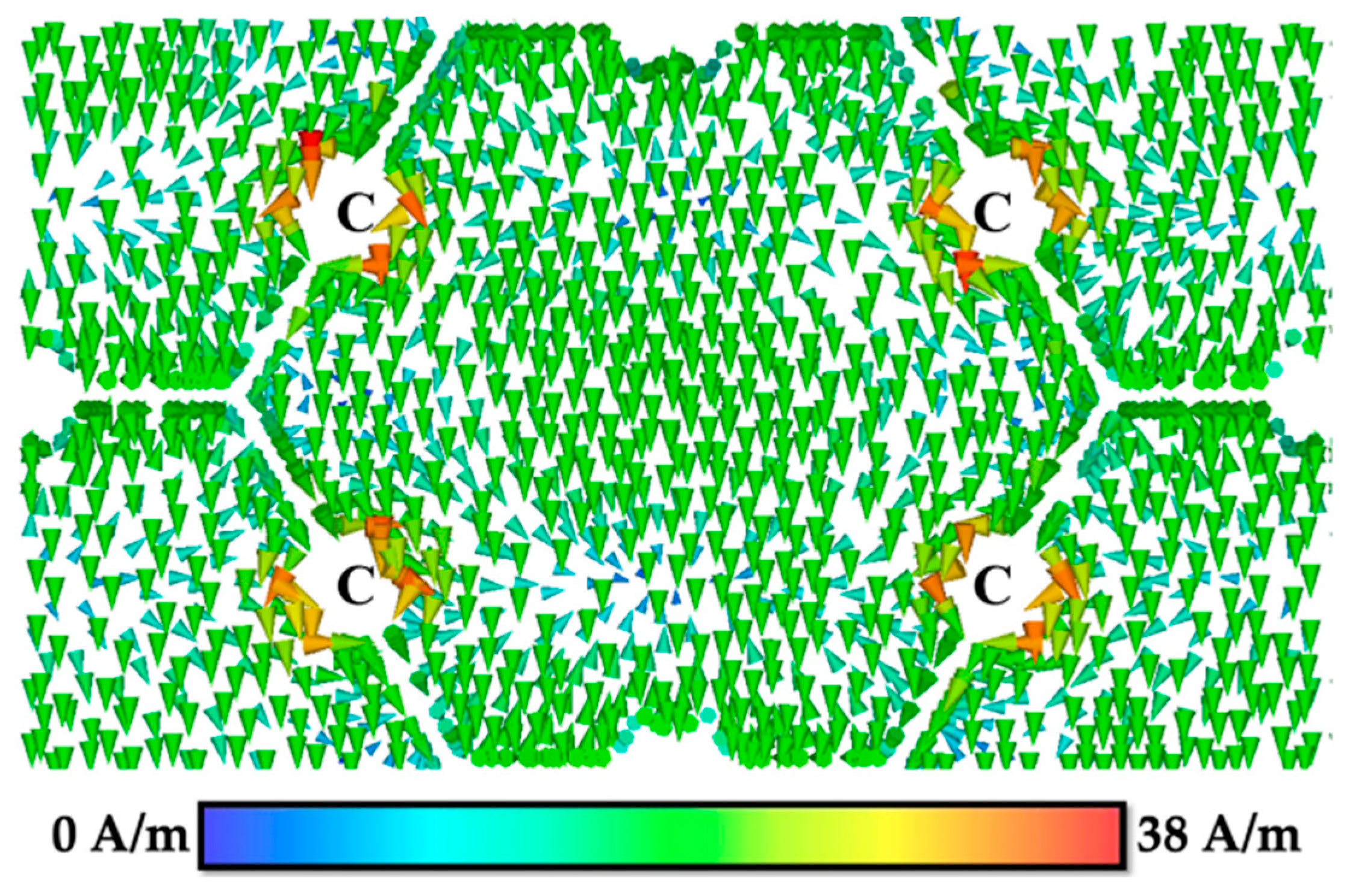
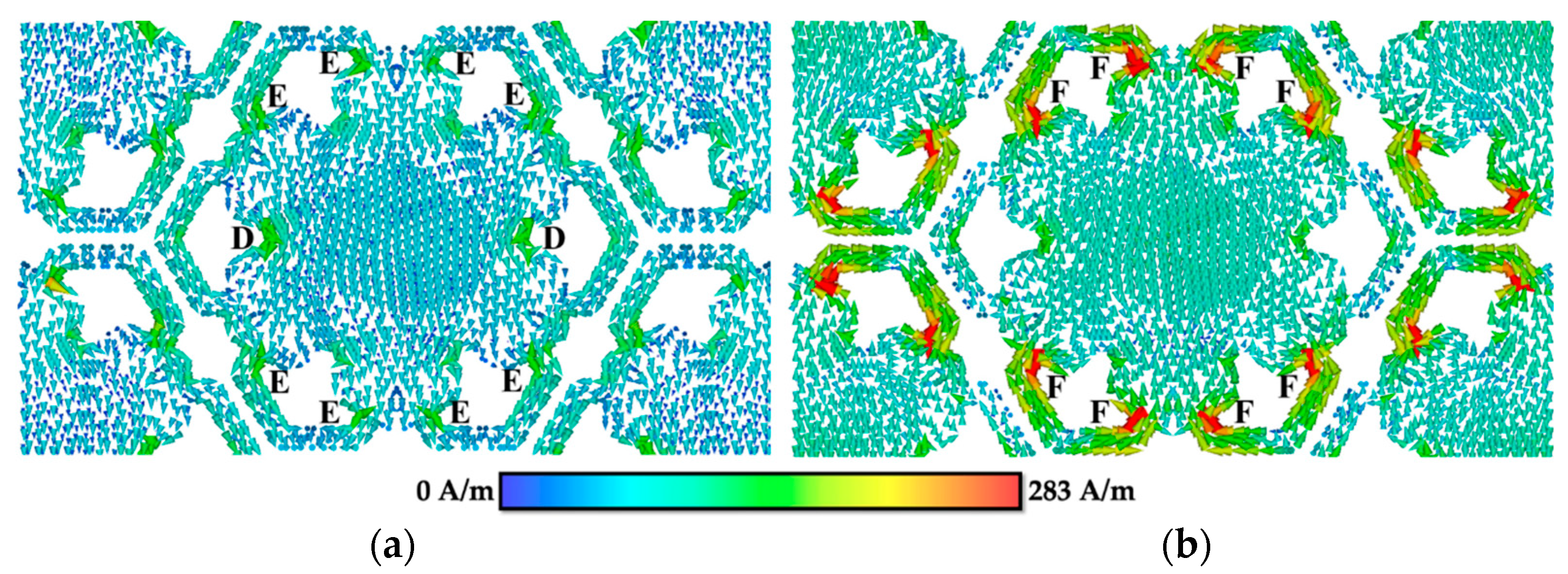
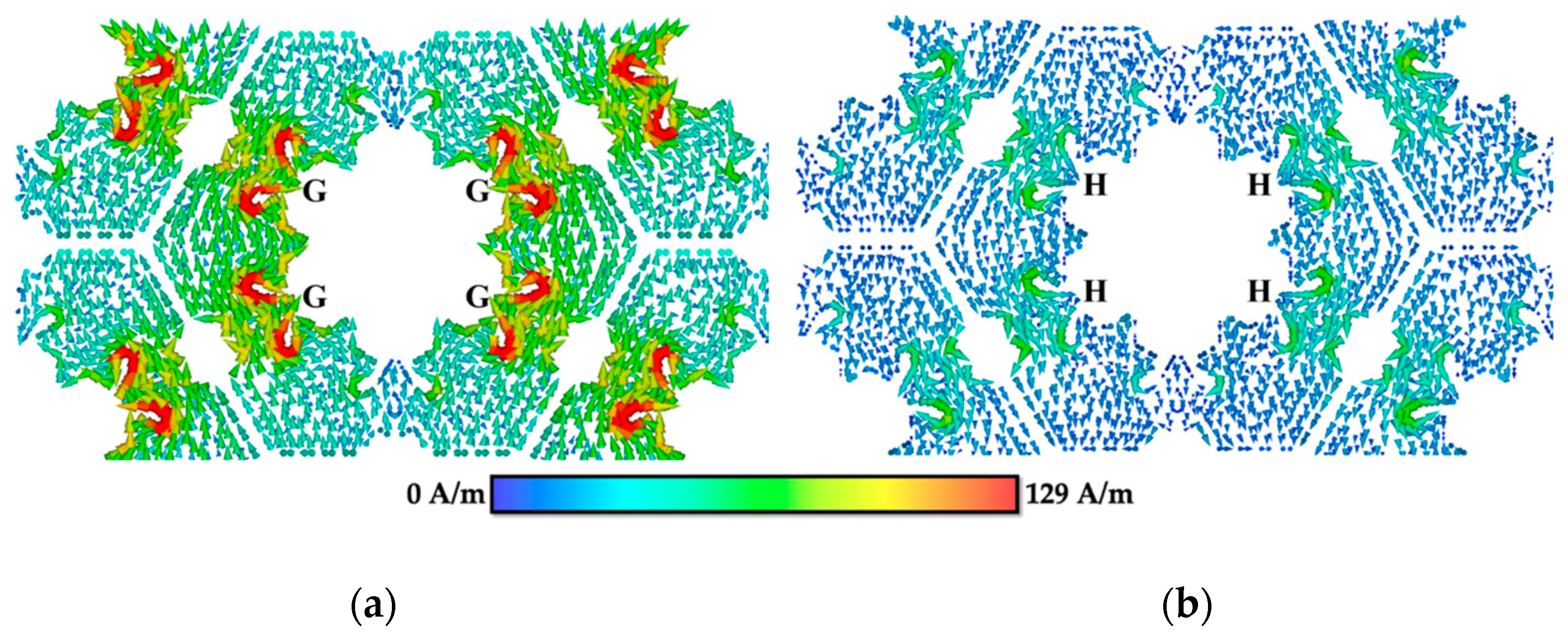
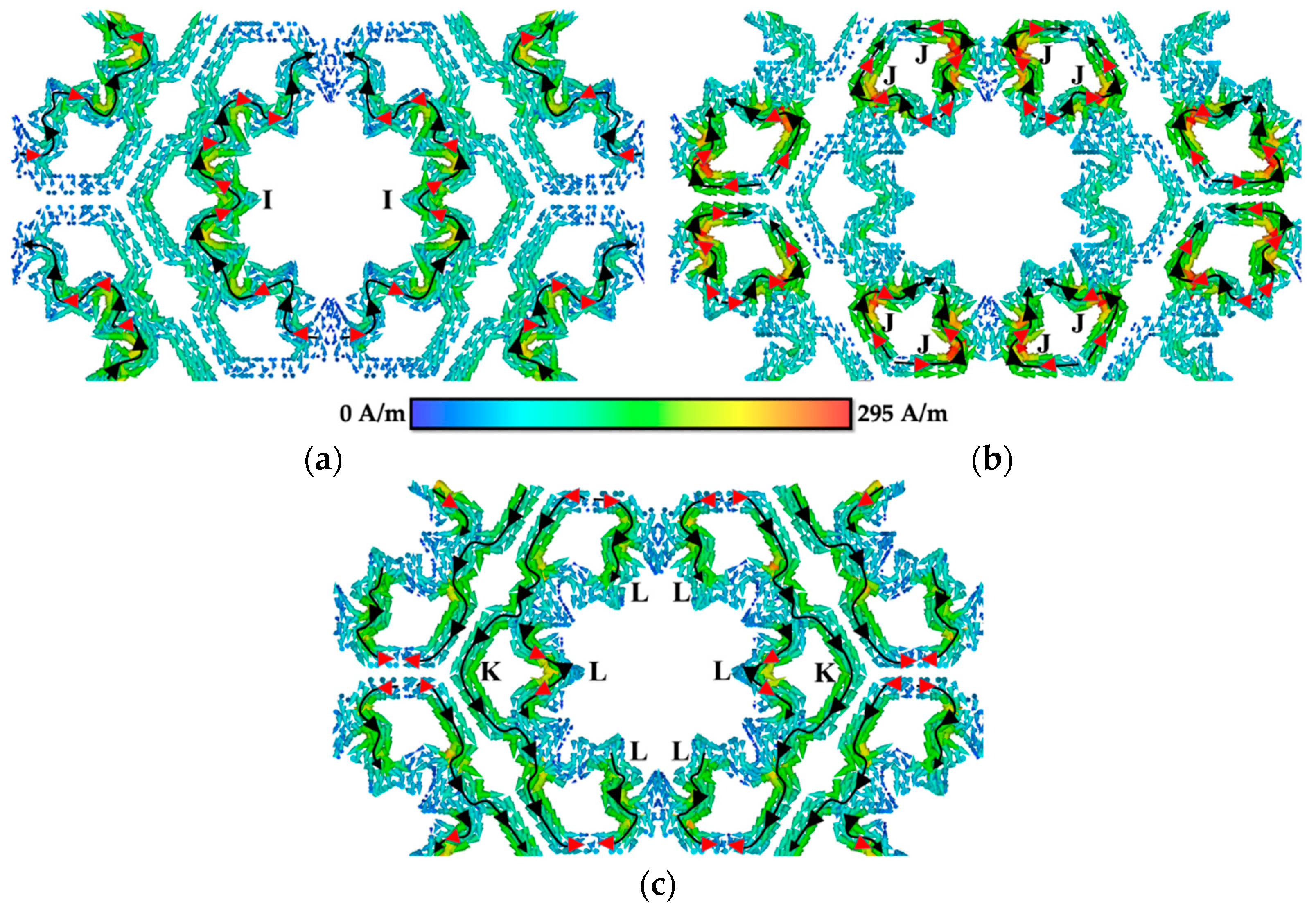
3.2. Surface Current Distribution
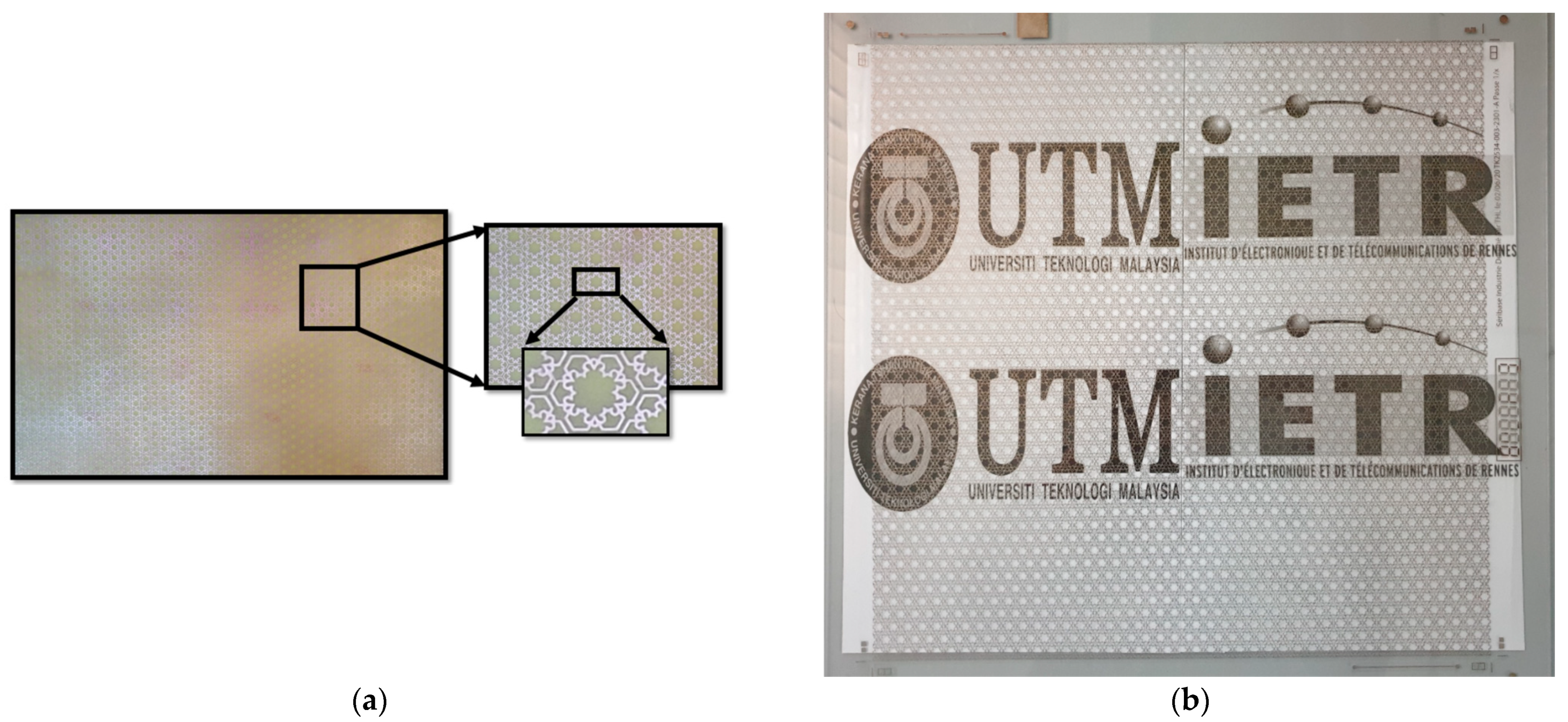
3.3. Optical Transparency of MFSS
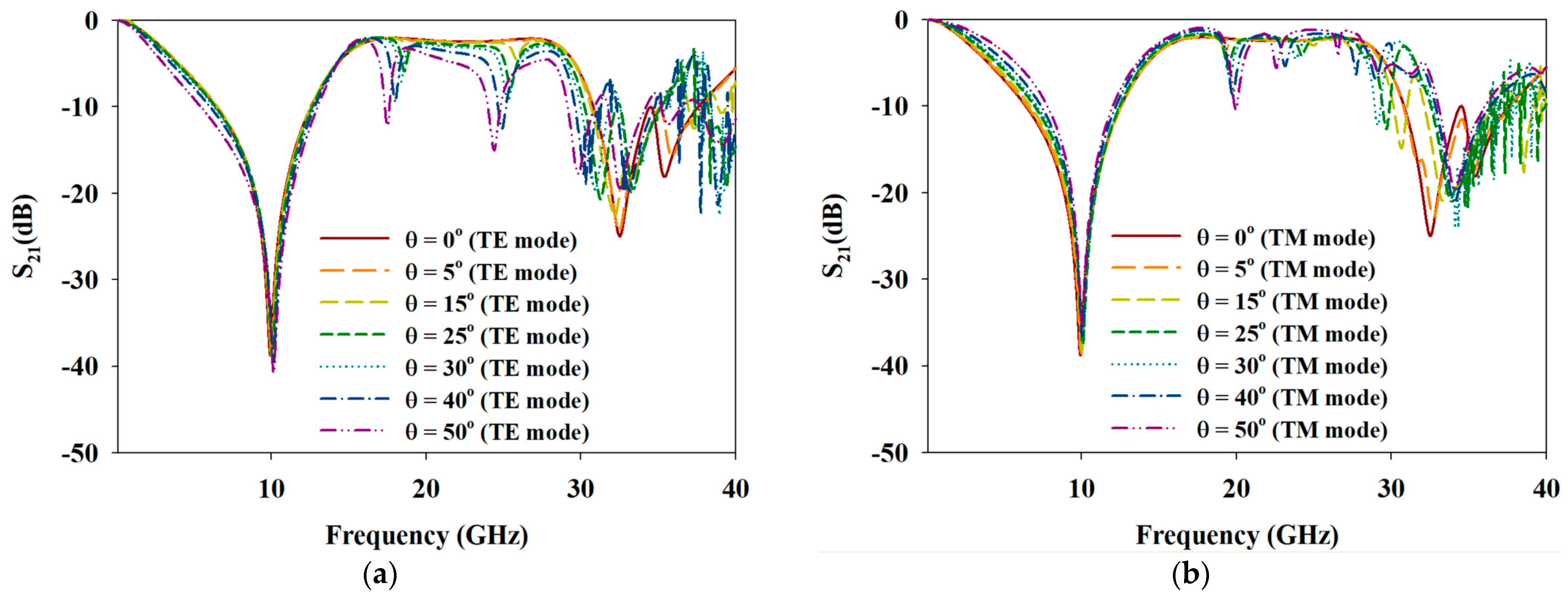
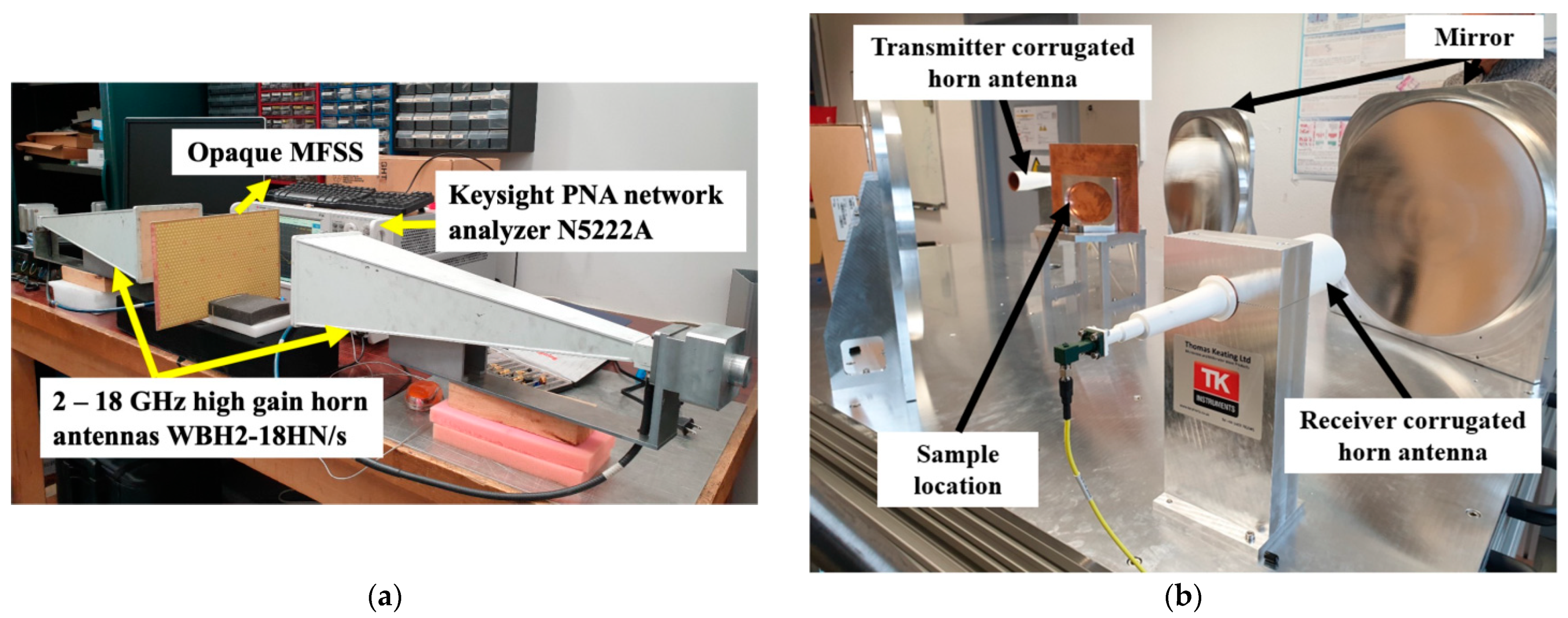
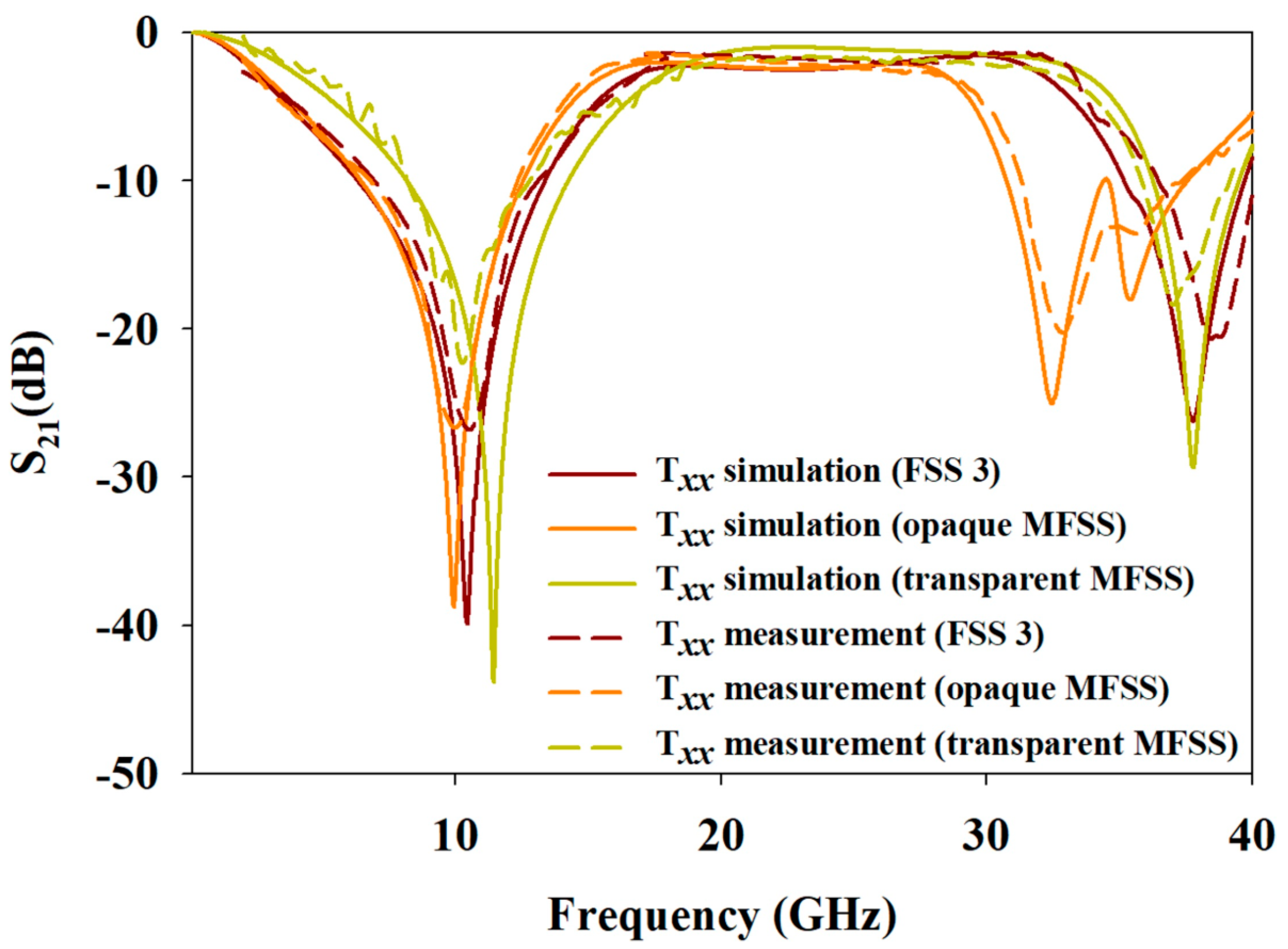
4. Experiment
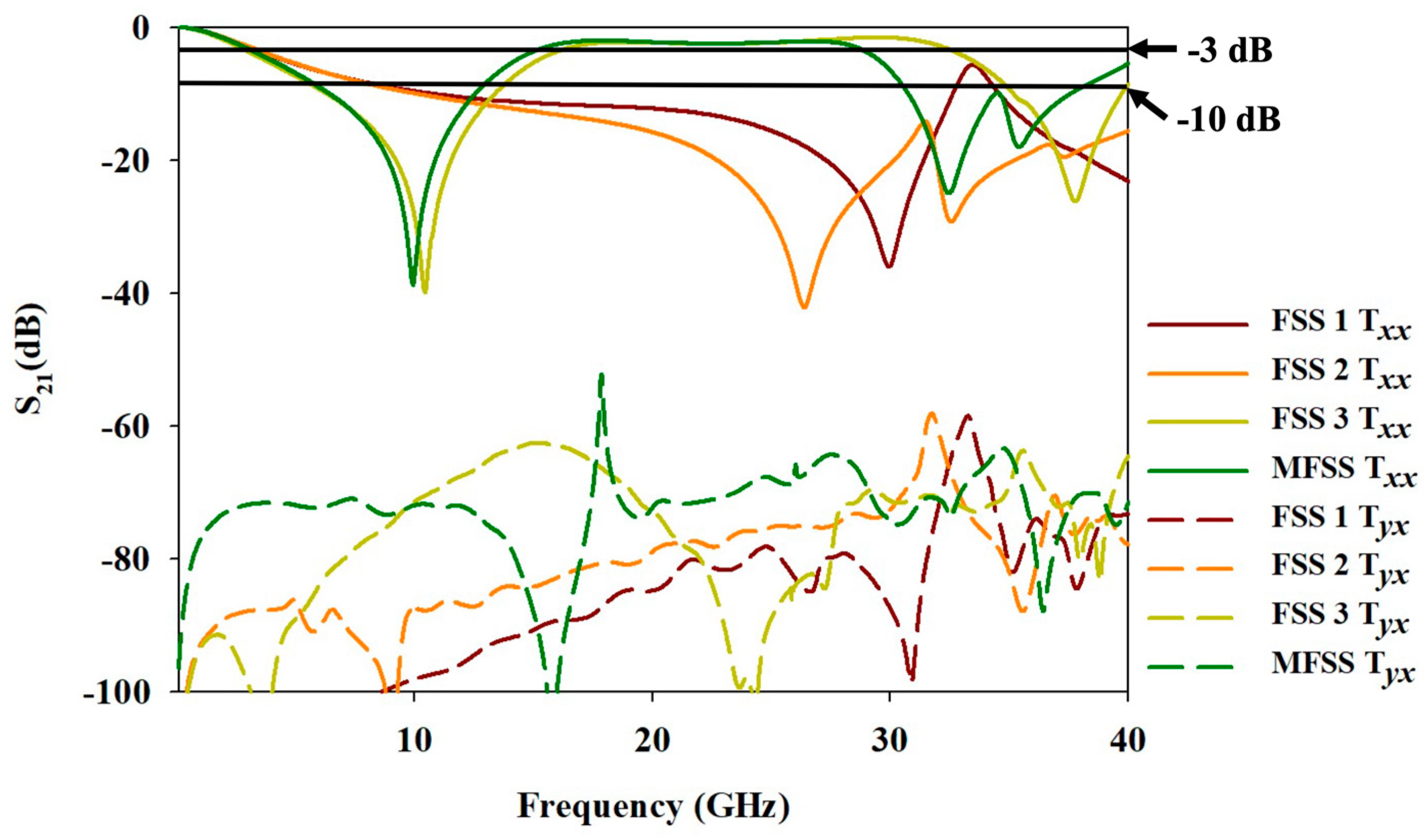
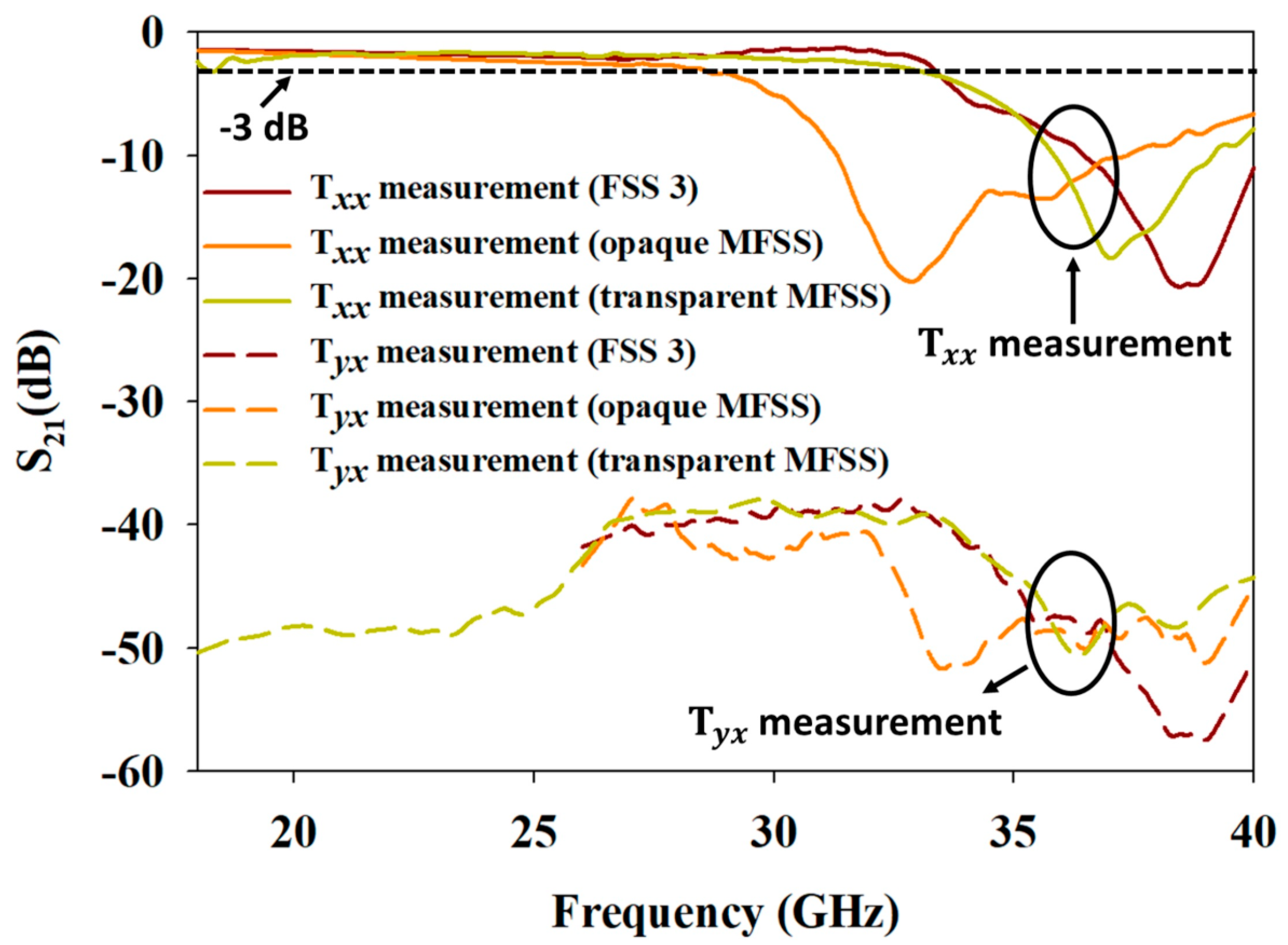
5. Comparative Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elmobarak Elobaid, H.A.; Abdul Rahim, S.K.; Himdi, M.; Castel, X.; Abedian Kasgari, M. A Transparent and Flexible Polymer-Fabric Tissue UWB Antenna for Future Wireless Networks. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 1333–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, M.S.A.; Rahim, S.K.A.; Kamarudin, M.R.; Peter, T.; Cheung, S.W.; Saad, B.M. Electromagnetic Behaviors of Thin Film CPW-Fed CSRR Loaded on UWB Transparent Antenna. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2014, 13, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, T.; Rahman, T.A.; Cheung, S.W.; Nilavalan, R.; Abutarboush, H.F.; Vilches, A. A Novel Transparent UWB Antenna for Photovoltaic Solar Panel Integration and RF Energy Harvesting. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, R.B.; Guzman, M.; Izyumskaya, N.; Ullah, B.; Hia, S.; Pitchford, J.; Timsina, R.; Avrutin, V.; Ozgur, U.; Morkoc, H.; et al. Optically Transparent Antennas and Filters: A Smart City Concept to Alleviate Infrastructure and Network Capacity Challenges. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2019, 61, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, B.A. Frequency Selective Surfaces: Theory and Design; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Panwar, R.; Lee, J.R. Progress in Frequency Selective Surface-Based Smart Electromagnetic Structures: A Critical Review. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 66, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, I.S.; Ranga, Y.; Matekovits, L.; Esselle, K.P.; Hay, S.G. A Single-Layer Frequency-Selective Surface for Ultrawideband Electromagnetic Shielding. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2014, 56, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.-H.; Mi, Y. Low-Pass Frequency Selective Surface with Wideband High-Stop Response for Shipboard Radar. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2013, 27, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.A.; Shen, Z. Thin 3-D Bandpass Frequency-Selective Structure Based on Folded Substrate for Conformal Radome Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, R.J.; Parker, E.A. Equivalent Circuit Model for Arrays of Square Loops. Electron. Lett. 1982, 18, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.; Caldeirinha, R.F.S.; Cuinas, I.; Fernandes, T.R. Square Loop and Slot Frequency Selective Surfaces Study for Equivalent Circuit Model Optimization. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 3947–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, K.R.; Singh, G.; Jyoti, R. A Simple Synthesis Technique of Single- Square-Loop Frequency Selective Surface. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 2012, 45, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trindade, J.I.; Silva, P.H.; Campos, A.L.; D’Assuncao, A.G. Analysis of Stop-Band Frequency Selective Surfaces With Dürer’s Pentagon Pre-Fractals Patch Elements. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 1518–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.H.; dos Santos, A.F.; Cruz, R.M.S.; D’Assunção, A.G. Dual-Band Bandstop Frequency Selective Surfaces with Gosper Prefractal Elements. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2012, 54, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Zhang, H.; Wu, R.; Min, X. Novel Dual-Band Miniaturized Frequency Selective Surface Based on Fractal Structures. Frequenz 2017, 71, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Neto, V.P.; D’Assuncao, A.G.; Baudrand, H. Analysis of Finite Size Nonuniform Stable and Multiband FSS Using a Generalization of the WCIP Method. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2018, 60, 1802–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manicoba, R.H.C.; Campos, A.L.P.S.; de Lima Silva, T.; D’Assuncao, A.G. Experimental Investigation of FSS Cascading with Fractal Elements. In Proceedings of the 2011 SBMO/IEEE MTT-S International Microwave and Optoelectronics Conference (IMOC 2011), Natal, Brazil, 29 October–1 November 2011; pp. 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manicoba, R.H.C.; D’Assuncao, A.G.; Campos, A.L.P.S. Improving Stop-Band Properties of Frequency Selective Surfaces with Koch Fractal Elements. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Workshop on Antenna Technology (iWAT), Lisbon, Portugal, 1–3 March 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira de Siqueira Campos, A.L.; Maniçoba, R.H.C.; D’Assunção, A.G. Investigation of Enhancement Band Using Double Screen Frequency Selective Surfaces with Koch Fractal Geometry at Millimeter Wave Range. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2010, 31, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohyuddin, W.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, H.C.; Kim, K.W. Comparative Study of Square and Circular Loop Frequency Selective Surfaces for Millimeter-Wave Imaging Diagnostics Systems. Sensors 2018, 18, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohyuddin, W.; Woo, D.S.; Choi, H.C.; Kim, K.W. A Practical Double-Sided Frequency Selective Surface for Millimeter-Wave Applications. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 024703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, K.; Li, B.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Q. Multi-layer Tri-band Frequency Selective Surface Using Stepped- and Uniform-impedance Resonators. Electron. Lett. 2016, 52, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidzadeh, M.; Ghobadi, C.; Nourinia, J. Novel Single Layer Reconfigurable Frequency Selective Surface with UWB and Multi-Band Modes of Operation. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2016, 70, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, G.S.; Mandal, K. Polarization-Insensitive and Angularly Stable Compact Ultrawide Stop-Band Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchana, D.; Radha, S.; Sreeja, B.S.; Manikandan, E. A Single Layer UWB Frequency Selective Surface for Shielding Application. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 4794–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocakaya, A.; Çimen, S.; Çakır, G. Novel Angular and Polarization Independent Band-Stop Frequency Selective Surface for Ultra-Wide Band Applications. Radioengineering 2019, 27, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoch, K.; Jaglan, N.; Gupta, S.D. Design and Analysis of Single Sided Modified Square Loop UWB Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2021, 63, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.Y.; Abdul Rahim, S.K.; Himdi, M.; Seman, F.C.; Suong, D.L.; Ramli, M.R.; Elmobarak, H.A. Flexible Convoluted Ring Shaped FSS for X-Band Screening Application. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 11657–11665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewani, A.A.; O’Keefe, S.G.; Thiel, D.V.; Galehdar, A. Window RF Shielding Film Using Printed FSS. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewani, A.A.; O’Keefe, S.G.; Thiel, D.V.; Galehdar, A. Optically Transparent Frequency Selective Surfaces on Flexible Thin Plastic Substrates. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 027107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Tan, W.; Shen, Z.; Jin, C. Integrated Frequency-Selective Surface and Antenna Printed on a Transparent Substrate. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2020, 19, 2062–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Zhou, D.; Luttgen, A.; Sarris, C.D. A Micro Copper Mesh-Based Optically Transparent Triple-Band Frequency Selective Surface. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantash, M.; Kesavan, A.; Denidni, T.A. Highly Transparent Frequency Selective Surface Based on Electrotextiles for On-Chip Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 2351–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-K.; Lee, S.; Hee Lee, D.; Hee Park, I.; Seong Bae, J.; Woo Lee, T.; Kim, J.-Y.; Hun Park, J.; Chan Cho, Y.; Ryong Cho, C.; et al. Cu Mesh for Flexible Transparent Conductive Electrodes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parker, E.A.; Antonopoulos, C.; Simpson, N.E. Microwave Band FSS in Optically Transparent Conducting Layers: Performance of Ring Element Arrays. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 1997, 16, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azini, A.S.; Kamarudin, M.R.; Rahman, T.A.; Iddi, H.U.; Abdulrahman, A.Y.; Bin Jamlos, M.F. Transparent Antenna Design for WiMAX Application. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2013, 138, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hautcoeur, J.; Castel, X.; Colombel, F.; Benzerga, R.; Himdi, M.; Legeay, G.; Motta-Cruz, E. Transparency and Electrical Properties of Meshed Metal Films. Thin Solid Film. 2011, 519, 3851–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Lafond, O.; Himdi, M.; Castel, X. Improvement of 60 GHz Transparent Patch Antenna Array Performance Through Specific Double-Sided Micrometric Mesh Metal Technology. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 2256–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Castel, X.; Himdi, M.; Lafond, O. Mesh Parameters Influence on Transparent and Active Antennas Performance at Microwaves. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 085120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Jin, P.; Liu, B.; Ma, J.; Tan, J.B. Optical-transparent Wi-Fi Bandpass Mesh-coated Frequency Selective Surface. Electron. Lett. 2014, 50, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettak, K.; Shaker, J. Screen-Printed Dual-Band Flexible Frequency Selective Surface for 5G Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 49th European Microwave Conference (EuMC), Paris, France, 1–3 October 2019; pp. 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewani, A.A.; O’Keefe, S.G.; Thiel, D.V.; Galehdar, A. Miniaturised Meandered Square Frequency Selective Surface on a Thin Flexible Dielectric with Selective Transmission. Flex. Print. Electron. 2016, 1, 025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.-K.; Hong, I.-P. Design of Security Paper with Selective Frequency Reflection Characteristics. Sensors 2018, 18, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.-K.; Lim, J.-I.; Hong, I.-P. Security Paper Design with Frequency-Selective Structure for X-Band Electromagnetic Detection System. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Kim, S.-S. Ultrawide Bandwidth Electromagnetic Wave Absorbers Using a High-Capacitive Folded Spiral Frequency Selective Surface in a Multilayer Structure. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-S.; Kim, S.-S. Design and Fabrication of 77-GHz Radar Absorbing Materials Using Frequency-Selective Surfaces for Autonomous Vehicles Application. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Components Lett. 2019, 29, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, T.-K.; Lee, S.-W. Tri-Band Frequency Selective Surface with Circular Ring Elements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1994, 42, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-K. Frequency Selective Surfaces. In Encyclopedia of RF and Microwave Engineering; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crépin, T.; Martel, C.; Gabard, B.; Boust, F.; Martinaud, J.P.; Dousset, T.; Rodriguez-Ulibarri, P.; Beruete, M.; Loecker, C.; Bertuch, T.; et al. Blind Spot Mitigation in Phased Array Antenna Using Metamaterials. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Radar Conference, Lille, France, 13–17 October 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pozar, D.; Schaubert, D. Scan Blindness in Infinite Phased Arrays of Printed Dipoles. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1984, 32, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaw, C.; Yahiaoui, R.; Burrow, J.A.; Tran, V.; Keelen, K.; Sims, W.; Red, E.C.; Rockward, W.S.; Thomas, M.A.; Sarangan, A.; et al. Polarization-Selective Modulation of Supercavity Resonances Originating from Bound States in the Continuum. Commun. Phys. 2020, 3, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautcoeur, J.; Colombel, F.; Himdi, M.; Castel, X.; Cruz, E.M. Large and Optically Transparent Multilayer for Broadband H-Shaped Slot Antenna. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2013, 12, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickie, R.; Cahill, R.; Gamble, H.S.; Fusco, V.F.; Huggard, P.G.; Moyna, B.P.; Oldfield, M.L.; Grant, N.; de Maagt, P. Polarisation Independent Bandpass FSS. Electron. Lett. 2007, 43, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickie, R.; Cahill, R.; Gamble, H.; Fusco, V.; Henry, M.; Oldfield, M.; Huggard, P.; Howard, P.; Grant, N.; Munro, Y.; et al. Submillimeter Wave Frequency Selective Surface With Polarization Independent Spectral Responses. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2009, 57, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, R.; Goussetis, G.; Fusco, V.; Cahill, R.; Zelenchuk, D.; Pal, A.; Saenz, E.; Simeoni, M.; Drioli, L.S. Circular Polarization Frequency Selective Surface Operating in Ku and Ka Band. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP 2014), The Hague, The Netherlands, 6–11 April 2014; pp. 1969–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Shi, H.; Guo, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, A. Stopband Frequency Selective Surface With Ultra-Large Angle of Incidence. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Xing, W.; Zhao, Q.; Gu, Y.; Gong, S. Single-Layer Frequency Selective Surface With Angular Stability Property. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahzaani, M.; Dadashzadeh, G.; Khorshidi, M. New Technique for Designing Wideband One Layer Frequency Selective Surface in X-Band with Stable Angular Response. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2018, 60, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

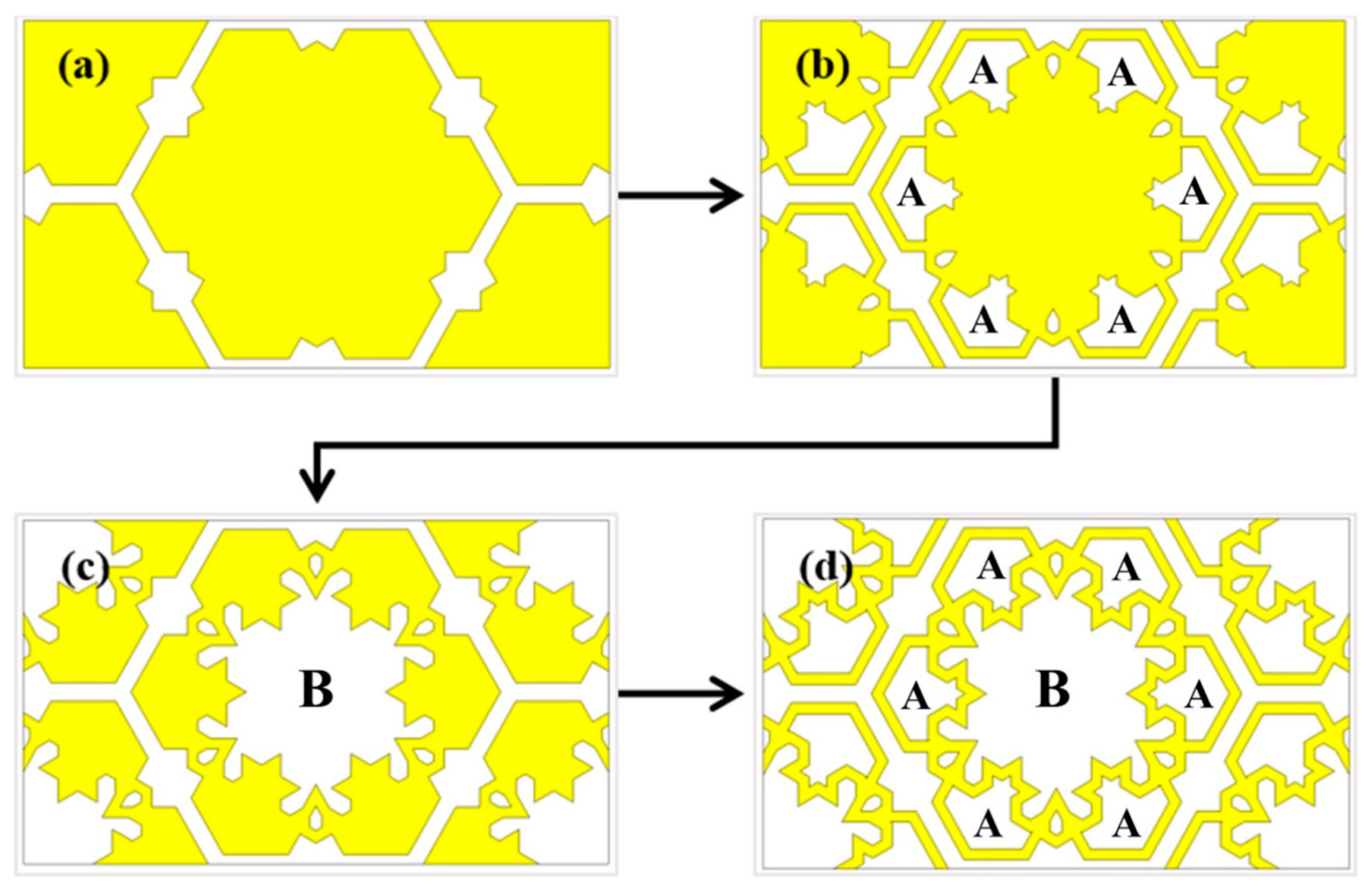



| Type of Elements | Total Area of the Unit Cell (mm2) | Area of the Metal Element (mm2) | Optical Transparency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FSS 1 | 42.55 | 36.27 | 5.09 |
| FSS 2 | 26.19 | 38.4 | |
| FSS 3 | 22.15 | 42.0 | |
| MFSS | 12.62 | 70.3 |
| Ref. | Layers | Total Thickness | Size Dimension | Angle Stability | T (%) | Operating Frequency (GHz) | FBW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [8] | 1S 1C | 0.03 | - | 30° | - | 8.02–18.20 | 80.28% (−10 dB Bandstop) |
| [58] | 1S 1C | 0.02 | 0.25 | 45° | - | 8.00–13.00 | 50.00% (−3 dB Bandpass) |
| [24] | 1S 1C | 0.04 | 0.20 | 80° | - | 2.5–13.23 | 136.00% (−10 dB Bandstop) |
| [25] | 1S 1C | 0.03 | 0.30 | 30° | - | 4.85–17.23 | 112.14% (−10 dB Bandstop) |
| [26] | 1S 1C | 0.01 | 0.11 | 60° | - | 3.05–10.73 | 111.47% (−3 dB Bandstop) |
| [27] | 1S 1C | 0.04 | 0.13 | 80° | - | 3.10–10.80 | 110.79% (−10 dB Bandstop) |
| [56] | 1S 1C | 0.05 | 0.12 | 80° | - | ~5.75–7.75 | ~29.60% (−10 dB Bandstop) |
| [57] | 1S 1C | 0.02 | 0.16 | 85° | - | ~5.00–6.75 | ~29.79% (−10 dB Bandstop) |
| [28] | 1S 1C | 0.004 | 0.25 | 45° | Semi–transparent | ~9.00–11.30 | ~22.78% (−10 dB Bandstop) |
| [29] | 1S 1C | 0.0002 | 0.11 | 60° | Semi–transparent | 1.50–2.50 | 50.00% (−10 dB Bandstop) |
| [30] | 1S 1C | 0.009 | 0.31 | 90° | transparent | ~11.00–14.50 | 27.00% (−10 dB Bandstop) |
| [31] | 1S 1C | 0.032 | 0.32 | 60° | 95% | fr = 2.40 | 1.00% (−20 dB Bandstop) |
| [32] | 1S 1C | 0.007 | 0.15 | 30° | 76.2% | fr = 1.80, 3.00 and 4.90 | Very narrow BW (−10 dB Bandstop) |
| [33] | 1S 1C | 0.2 | 0.68 | - | Radioscreen + acrylic = 50%VeilSheild + acrylic = 70% | 27.00–35.00 | 25.81% (−10 dB Bandstop) |
| This work (Opaque MFSS) | 1S 1C | 0.05 | 0.23 | 25° | - | 6.43–12.53 | 64.35% (−10 dB Bandstop) |
| 15.49–28.53 | 59.25% (−3 dB Bandpass) | ||||||
| 30.74–37.55 | 19.94% (−10 dB Bandstop) | ||||||
| This work (Transparent MFSS) | 1S 1C | 0.06 | 0.27 | 25° | 70.3% | 8.16–14.23 | 54.22% (−10 dB Bandstop) |
| 17.67–33.84 | 62.78% (−3 dB Bandpass) | ||||||
| 36.27–39.50 | 8.53% (−10 dB Bandstop) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed Nafis, N.B.; Himdi, M.; A Rahim, M.K.; Ayop, O.; Dewan, R. Optically Transparent Tri-Wideband Mosaic Frequency Selective Surface with Low Cross-Polarisation. Materials 2022, 15, 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020622
Mohamed Nafis NB, Himdi M, A Rahim MK, Ayop O, Dewan R. Optically Transparent Tri-Wideband Mosaic Frequency Selective Surface with Low Cross-Polarisation. Materials. 2022; 15(2):622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020622
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed Nafis, Nur Biha, Mohamed Himdi, Mohamad Kamal A Rahim, Osman Ayop, and Raimi Dewan. 2022. "Optically Transparent Tri-Wideband Mosaic Frequency Selective Surface with Low Cross-Polarisation" Materials 15, no. 2: 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020622
APA StyleMohamed Nafis, N. B., Himdi, M., A Rahim, M. K., Ayop, O., & Dewan, R. (2022). Optically Transparent Tri-Wideband Mosaic Frequency Selective Surface with Low Cross-Polarisation. Materials, 15(2), 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020622







