Influence of Loading Directions on Dynamic Compressive Properties of Mill-Annealed Ti-6Al-4V Thick Plate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
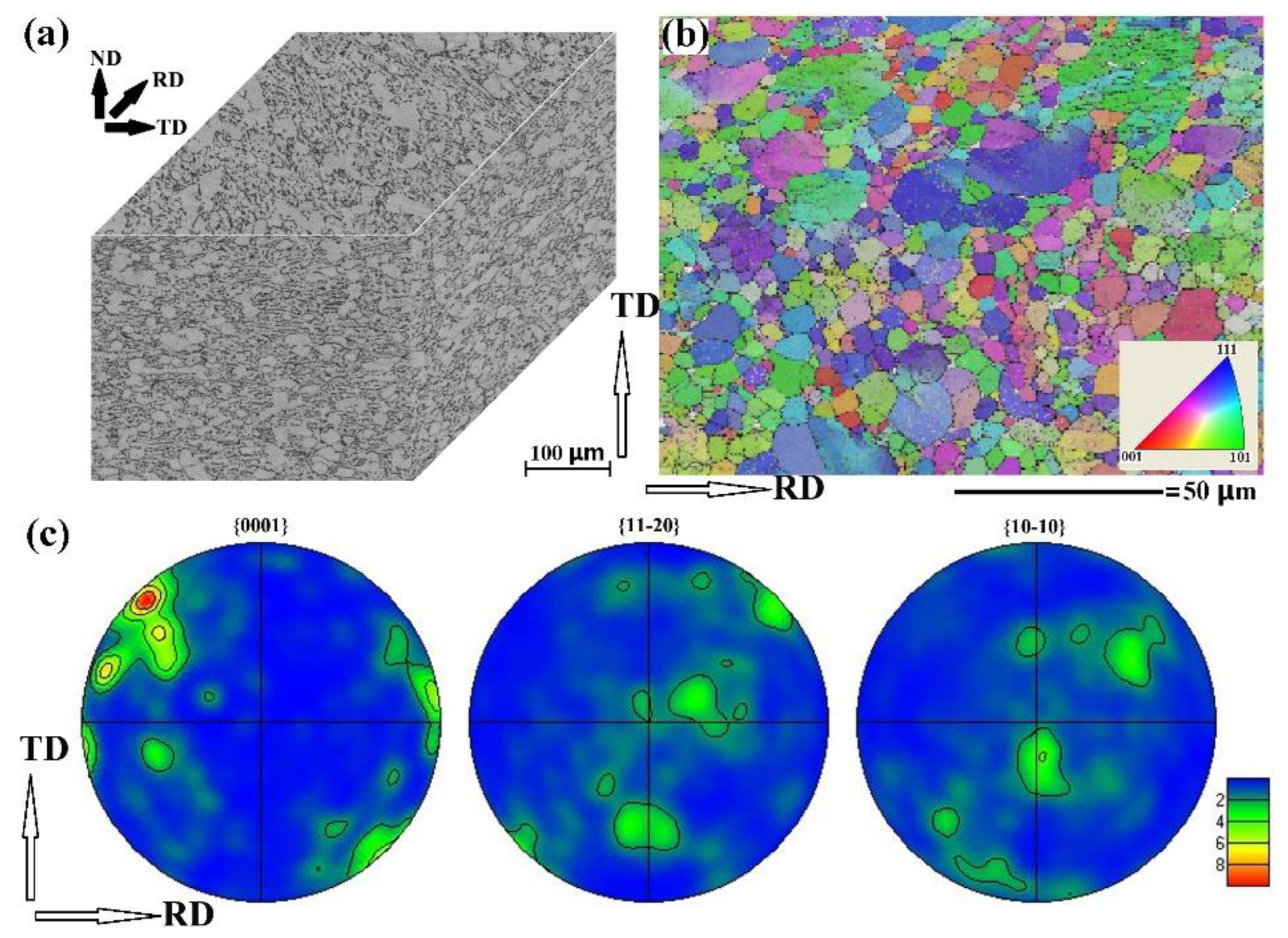
2.1. Initial Microstructure of TC4 Alloy Plate
2.2. Dynamic Compression Test
2.3. Strain-Limited Dynamic Compression Test
2.4. Microstructure Characterization of Strain-Limited Specimen
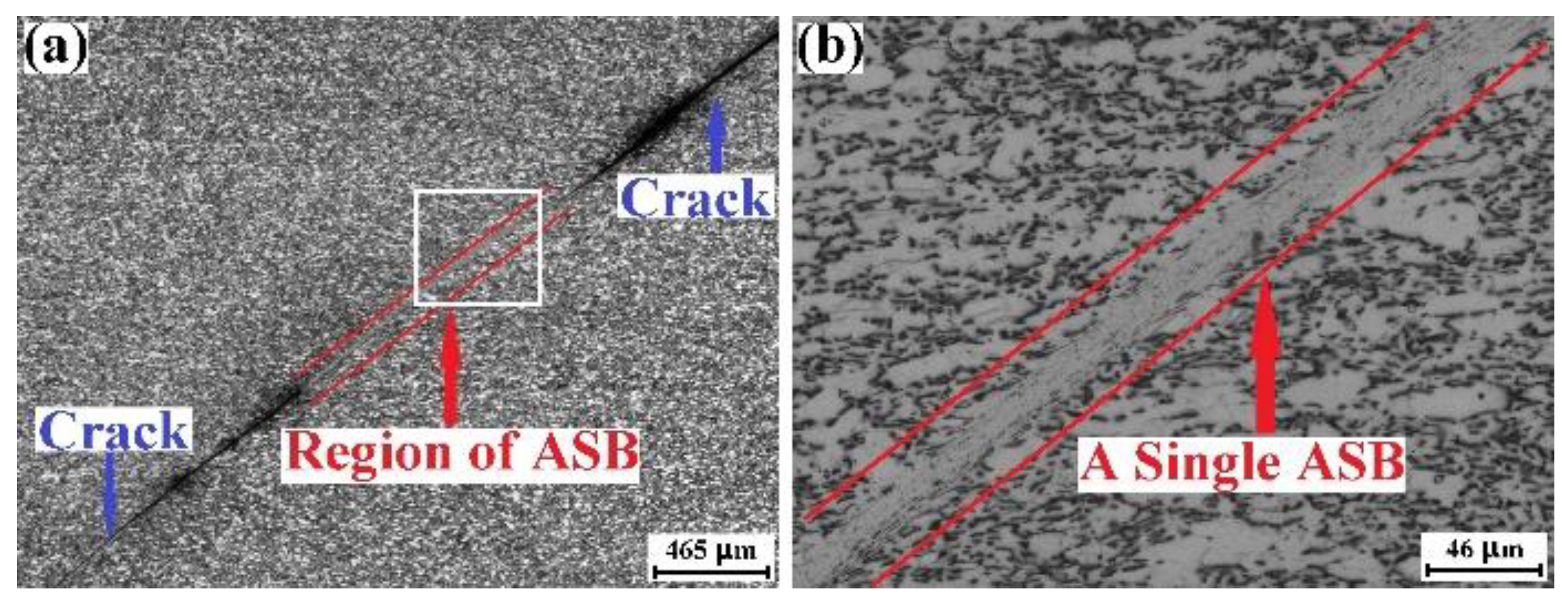
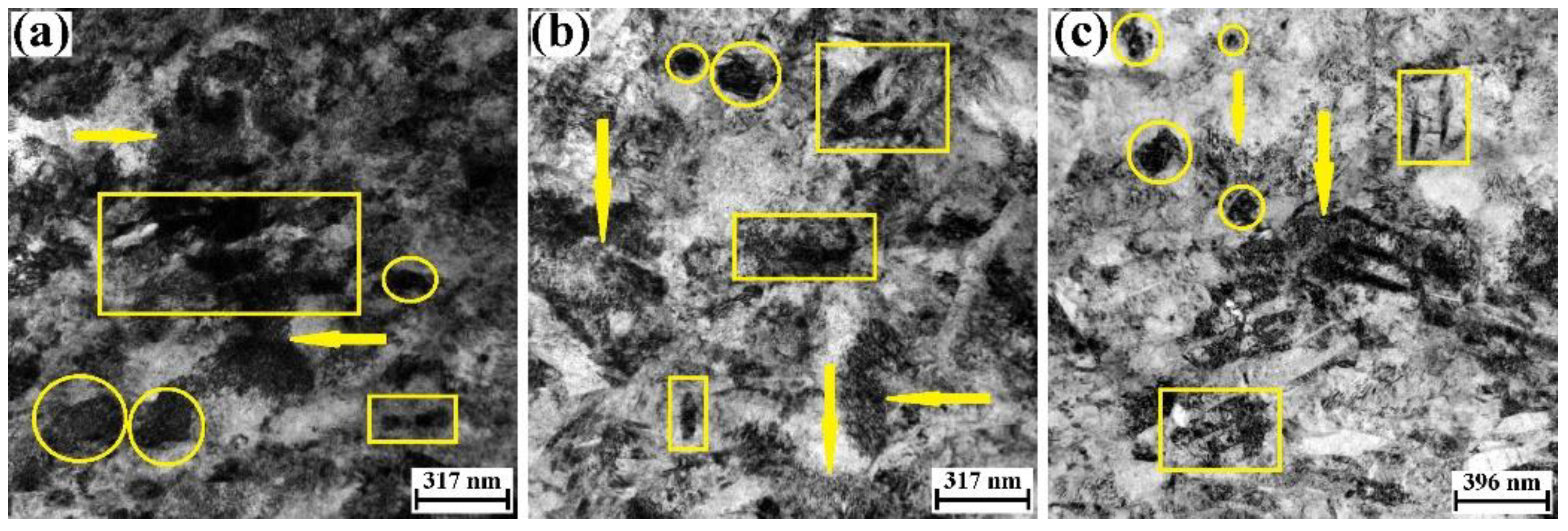
2.5. Microstructure Characterization of ASB
3. Results
3.1. Initial Microstructure of TC4 Plate
3.2. Dynamic Compressive Mechanical Properties of TC4 Plate
3.3. Effects of Loading Direction on Deformation Mechanism of Strain-Limited Specimen
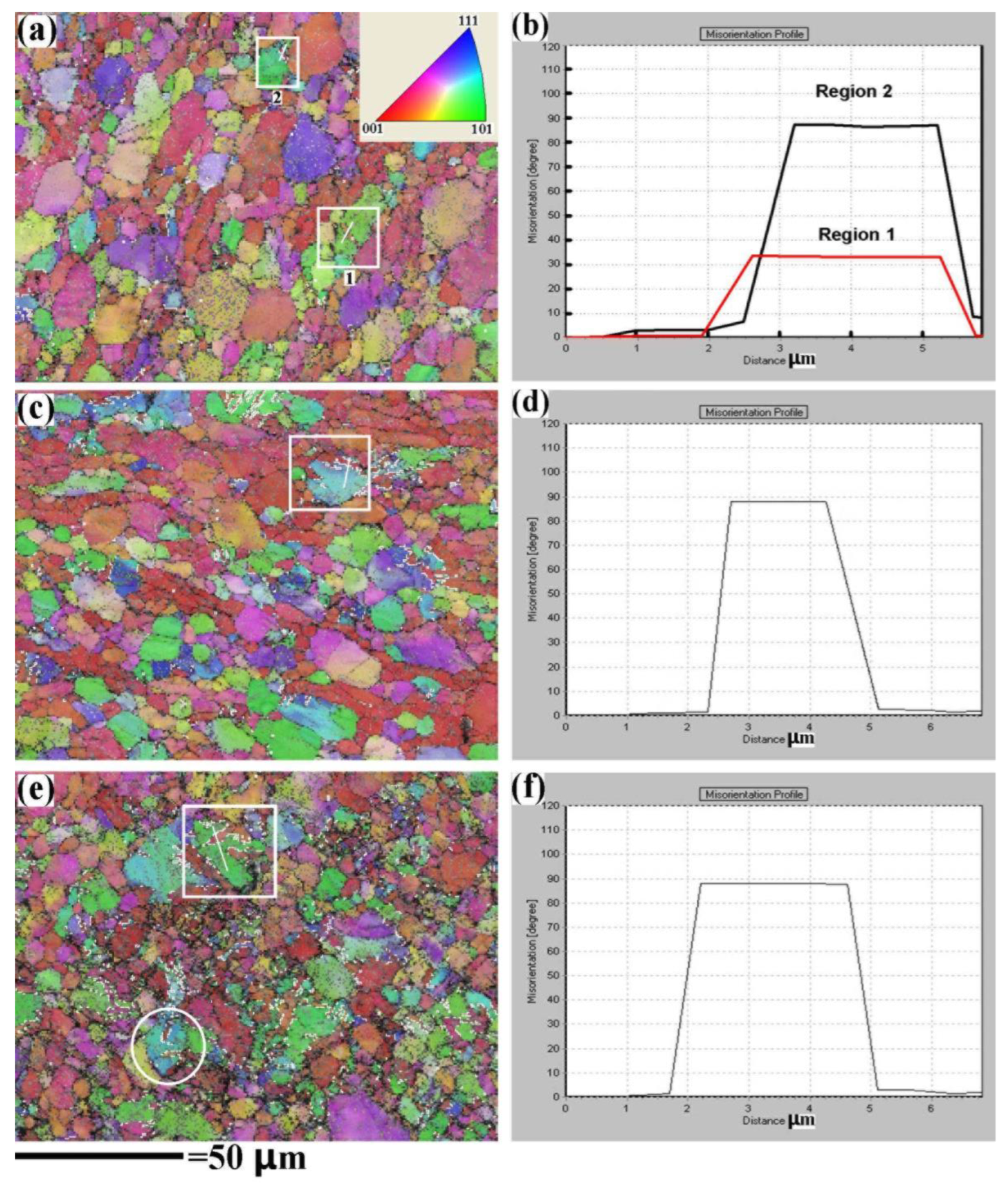
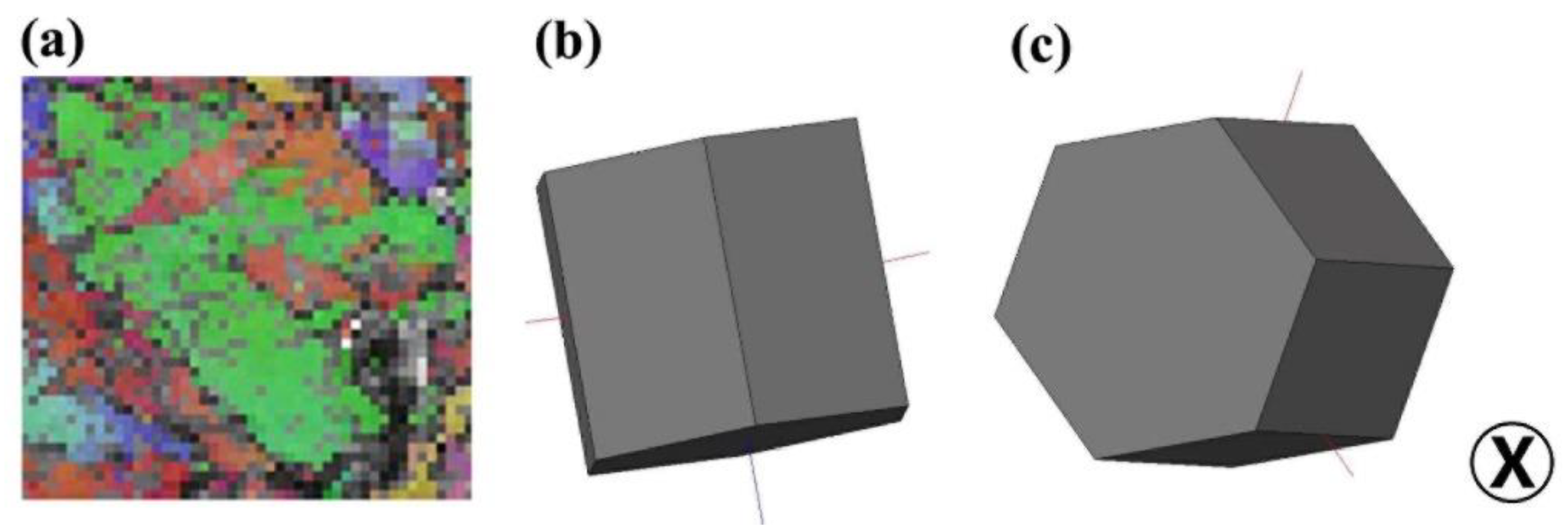
3.3.1. Twinning of Strain-Limited Specimen
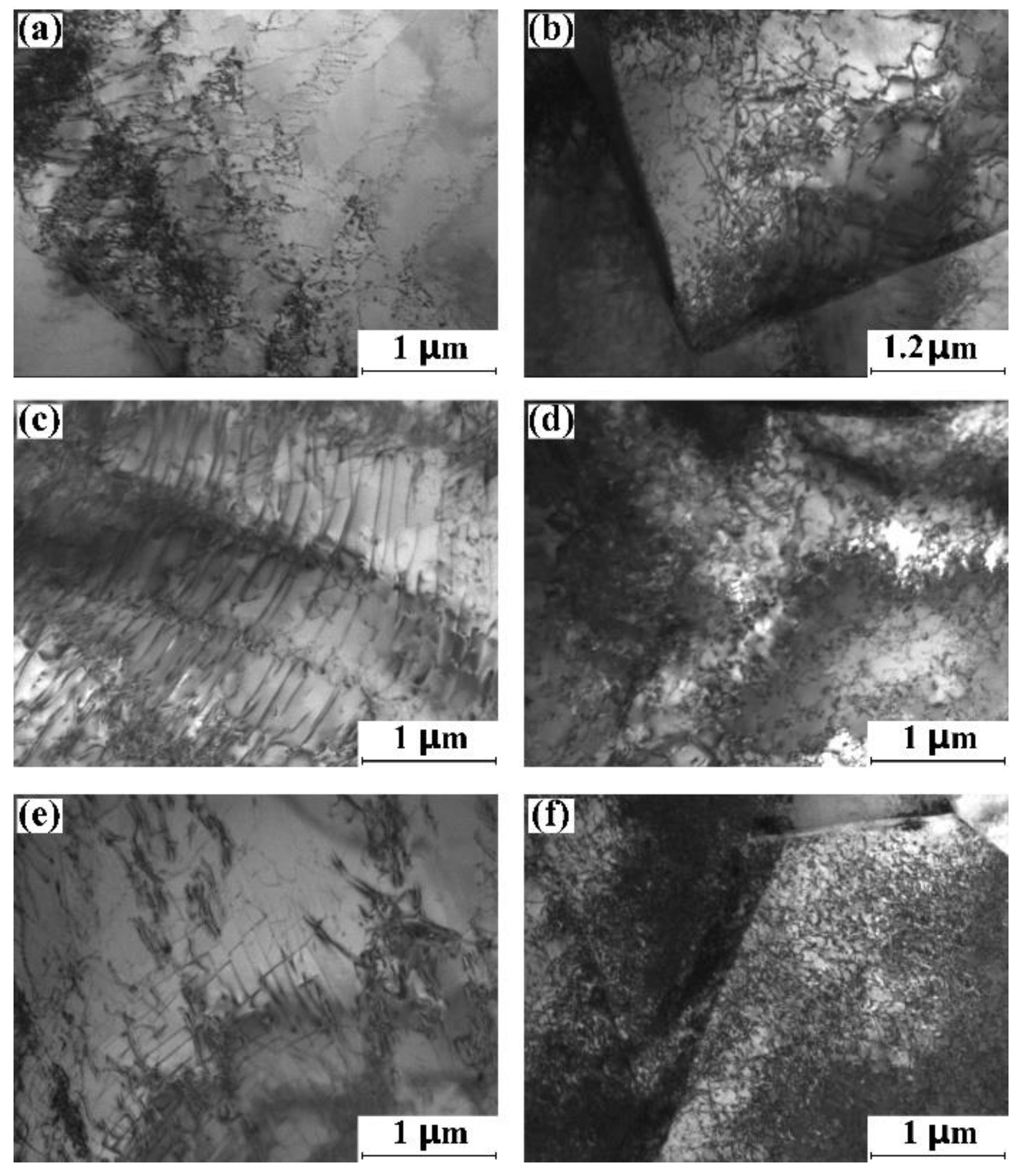
3.3.2. Dislocation Structures of Strain-Limited Specimen
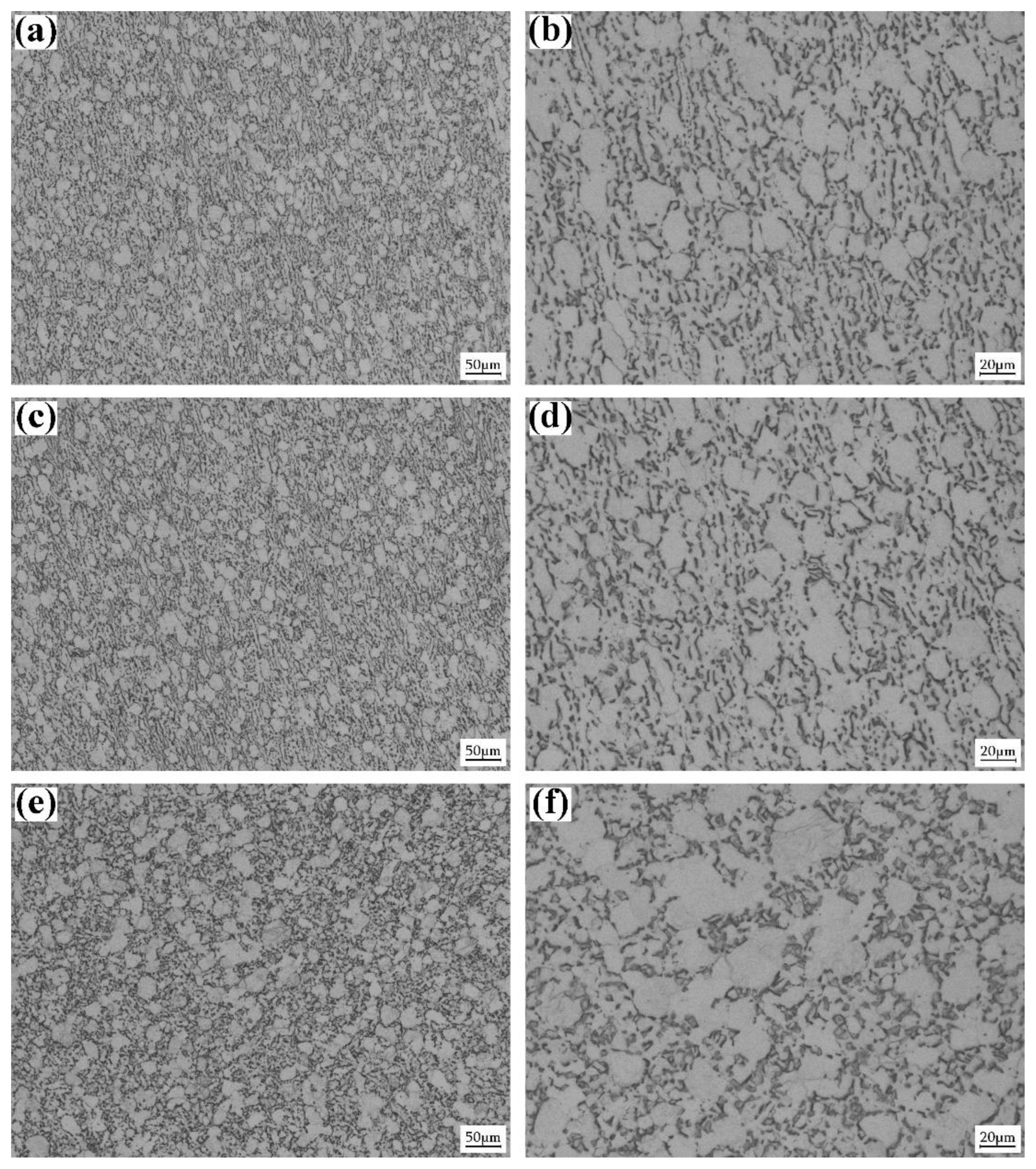
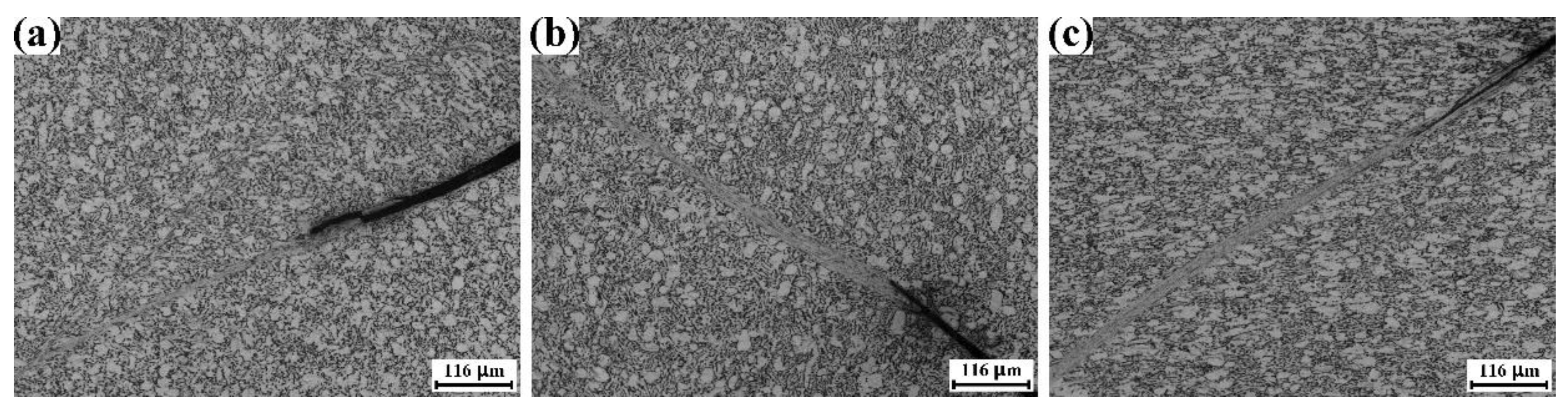
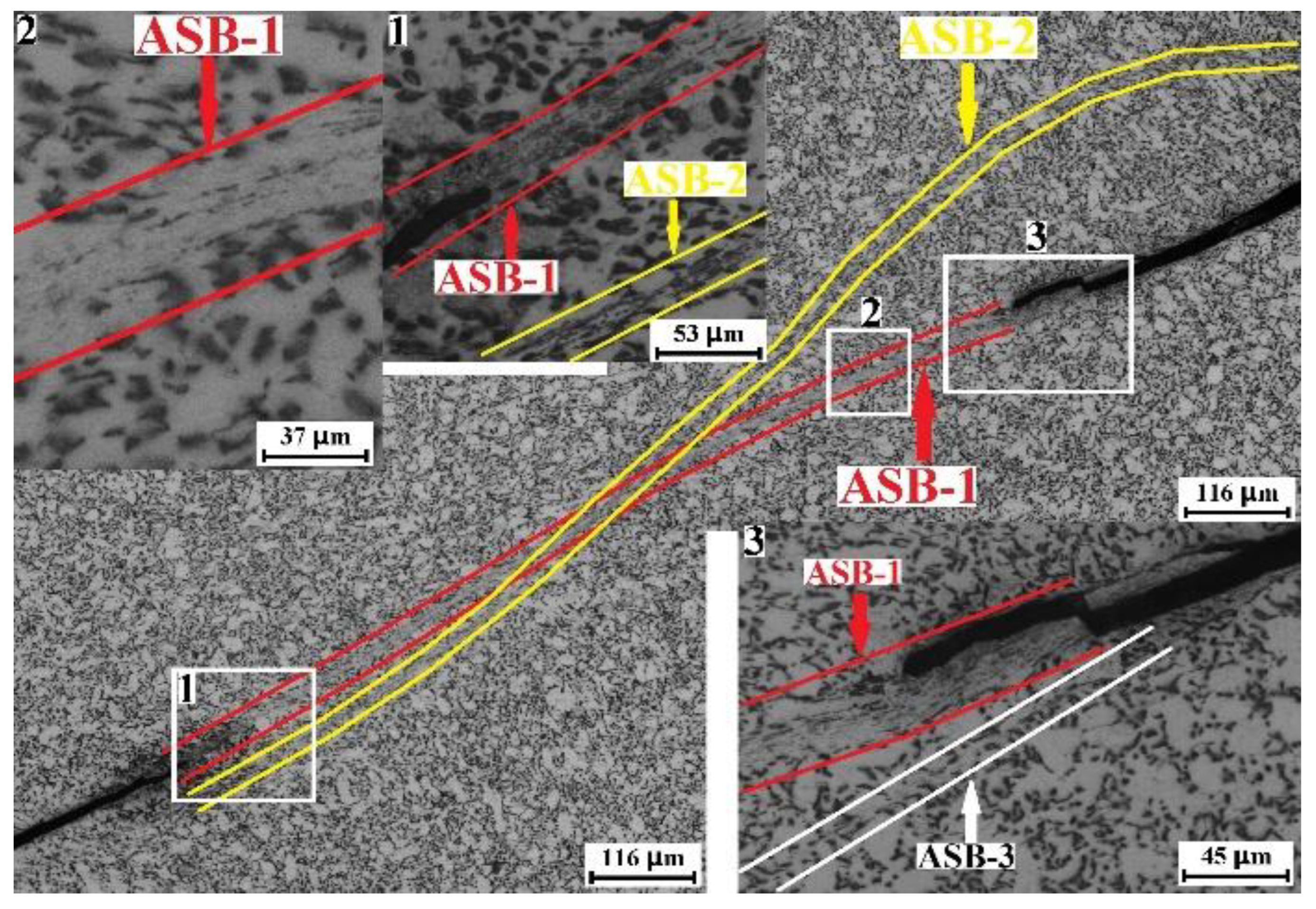
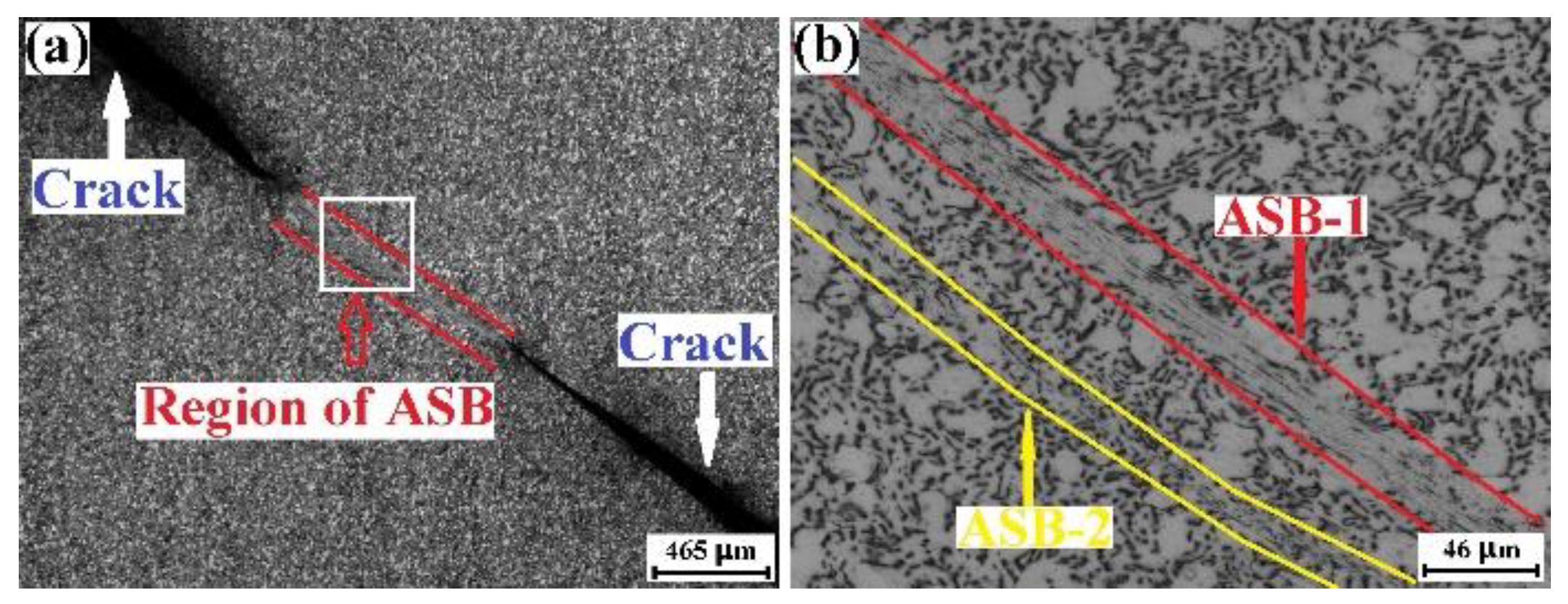
3.4. Influence of Loading Direction on Adiabatic Shearing of TC4 Plate
4. Discussion
4.1. Dynamic Plasticity Anisotropy of TC4 Alloy Thick Plate
4.2. Non-Dynamic Recrystallization for the ASB of Mill-Annealed TC4 Alloy
4.3. Delaying the ASB Formation of TC4 Alloy by Texture Design
5. Conclusions
- The mill-annealed TC4 alloy thick plate consists of globular α grain, fine equiaxial α grain, α laminate and β laminate. The normal of the α laminate is parallel to the normal direction of the plate. The α phase of the plate possesses {11-20} texture.
- The superior dynamic compressive plasticity in the ND of the TC4 plate is caused by {11-20} texture of the globular α grain, the distribution of the α laminate and the highest shear strain of the ASB.
- The {10-12}<10-1-1> twinning within the globular α grain, which is induced by {11-20}α texture, might delay the ASB formation of mill-annealed TC4 alloy.
- Dynamic recrystallization of the α phase does not occur in the adiabatic shearing band of mill-annealed TC4 alloy.
- The strength and plasticity of the mill-annealed Ti-6Al-4V alloy with different dynamic compression strain levels will be investigated in the future.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, B.Q.; Zhou, H.G.; Liu, J.F.; Kang, C. Multiaxial fatigue damage and reliability assessment of aero-engine compressor blades made of TC4 titanium alloy. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 119, 107107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.B.; Hu, D.Y.; Ye, X.B.; Chen, X.; He, Y.H. A simplified Johnson-Cook model of TC4T for aeroengine foreign object damage prediction. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 269, 108523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Yue, W.H.; Li, J.; Bin, G.F.; Li, C. Review of damage mechanism and protection of aero-engine blades based on impact properties. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 140, 106570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutjering, G.; Williams, J.C. Titanium, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Wang, F.C.; Cheng, X.W.; Fu, K.Q.; Liu, J.X.; Wang, Y.F.; Liu, T.T.; Zhu, Z.X. Effect of microstructures on ballistic impact property of Ti–6Al–4V targets. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 608, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Yu, X.D.; Tan, C.W.; Ma, H.L.; Wang, F.C.; Cai, H.N. Effect of microstructure on adiabatic shear band bifurcation in Ti–6Al–4V alloys under ballistic impact. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 595, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Tan, C.W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.C.; Cai, H.N. Correlation of adiabatic shearing behavior with fracture in Ti-6Al-4V alloys with different microstructures. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2009, 36, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, S.N.; Guo, W.G.; Nesterenko, V.F.; Indarkanti, S.S.; Gu, Y.B. Dynamic response of conventional and hot isostatically pressed Ti–6Al–4V alloys: Experiments and modeling. Mech. Mater. 2001, 33, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Lin, C.F. Plastic deformation and fracture behaviour of Ti–6Al–4V alloy loaded with high strain rate under various temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 241, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, N.; Ding, J.L. Numerical study of the deformation and fracture behavior of porous Ti6Al4V alloy under static and dynamic loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 82, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, N.; Ding, J.L.; Balla, V.K.; Field, D.P.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Deformation and fracture behavior of laser processed dense and porous Ti6Al4V alloy under static and dynamic loading. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 549, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.B.; Nesterenko, V.F. Dynamic behavior of HIPed Ti–6Al–4V. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2007, 37, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coghe, F.; Tirry, W.; Rabet, L.; Schryvers, D.; Houtte, P.V. Importance of twinning in static and dynamic compression of a Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy with an equiaxed microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 537, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielewski, E.; Siviour, C.R.; Petrinic, N. On the correlation between macrozones and twinning in Ti–6Al–4V at very high strain rates. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Duan, Y.L.; Xu, G.F.; Peng, X.Y.; Dai, C.; Zhang, L.G.; Li, Z. EBSD characterization of twinning in cold-rolled CP-Ti. Mater. Charact. 2013, 84, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, J.; Phukan, H.; Kenesei, P.; Park, J.S.; Suter, R.M.; Beaudoin, A.J.; Bieler, T.R. Mechanical twinning and detwinning in pure Ti during loading and unloading – An in situ high-energy X-ray diffraction microscopy study. Scr. Mater. 2014, 92, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirry, W.; Nixon, M.; Cazacu, O.; Coghe, F.; Rabet, L. The importance of secondary and ternary twinning in compressed Ti. Scr. Mater. 2011, 64, 840–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirry, W.; Bouvier, S.; Benmhenni, N.; Hammami, W.; Habraken, A.M.; Coghe, F.; Schryvers, D.; Rabet, L. Twinning in pure Ti subjected to monotonic simple shear deformation. Mater. Charact. 2012, 72, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.G.; Hui, S.X.; Ye, W.J.; Song, X.Y. Analysis of twinning behavior of pure Ti compressed at different strain rates by Schmid factor. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 575, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.D.; Schuman, C.; Lecomte, J.S.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L.; Philippe, M.J.; Esling, C. Study of twinning/detwinning behaviors of Ti by interrupted in situ tensile tests. Acta Mater. 2015, 82, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, G.G.; Karaman, I.; Luo, Z.P. Mechanical twinning and texture evolution in severely deformed Ti–6Al–4V at high temperatures. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 3755–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.Y.; Li, Y.L. The role of microstructure and stress state in dynamic mechanical behavior of Ti-5Al-5V-5Mo-3Cr alloy. Mater. Charact. 2019, 147, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paghandeh, M.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Abedi, H.R.; Vahidshad, Y.; Minarik, P. The correlation of c-to-a axial ratio and slip activity of martensite including microstructures during thermomechanical processing of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paghandeh, M.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Abedi, H.R.; Vahidshad, Y.; Kawałko, J.; Dietrich, D.; Lampke, T. Compressive/tensile deformation behavior and the correlated microstructure evolution of Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy at warm temperatures. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Marteleur, M. A new titanium alloy with a combination of high strength, high strain hardening and improved ductility. Scr. Mater. 2015, 94, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaghmandfard, R.; Chalasani, D.; Odeshi, A.; Mohammadi, M. Activated slip and twin systems in electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V subjected to elevated and high strain rate dynamic deformations. Mater. Charact. 2021, 172, 110866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murr, L.E.; Ramirez, A.C.; Gaytan, S.M.; Lopez, M.I.; Martinez, E.Y.; Hernandez, D.H.; Martinez, E. Microstructure evolution associated with adiabatic shear bands and shear band failure in ballistic plug formation in Ti–6Al–4V targets. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 516, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.; Murr, L.E.; Ramirez, A.; Lopez, M.I.; Gaytan, S.M. Dynamic deformation and adiabatic shear microstructures associated with ballistic plug formation and fracture in Ti–6Al–4V targets. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 454–455, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Z.; Zhao, S.T.; Wang, B.F.; Cui, S.; Chen, R.; Valiev, R.Z.; Meyers, M.A. The effects of ultra-fine-grained structure and cryogenic temperature on adiabatic shear localization in titanium. Acta Mater. 2019, 181, 408–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magagnosc, D.J.; Lloyd, J.T.; Meredith, C.S.; Pilchak, A.L.; Schuster, B.E. Incipient dynamic recrystallization and adiabatic shear bands in Ti–7Al studied via in situ X-ray diffraction. Int. J. Plast. 2019, 141, 102992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Wang, F.C.; Cheng, X.W.; Liu, J.X.; Liu, T.T.; Zhu, Z.X.; Yang, K.W.; Peng, M.Q.; Jin, D. Capturing of the propagating processes of adiabatic shear band in Ti–6Al–4V alloys under dynamic compression. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 658, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Loading Directions | Dynamic Yield Strength (MPa) | Dynamic Fracture Strain |
|---|---|---|
| RD | 1427 ± 30 | 0.175 ± 0.017 |
| TD | 1454 ± 18 | 0.183 ± 0.015 |
| ND | 1408 ± 9 | 0.242 ± 0.009 |
| Deformation Systems | Grain 1 |  | Grain 2 |  |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Twinning: {10-12}<10-1-1> | 0.38 | 0.4 | ||
| Slipping: {0001}<11-20> | 0.09 | 0.04 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, D.; Lu, S.; Li, Y. Influence of Loading Directions on Dynamic Compressive Properties of Mill-Annealed Ti-6Al-4V Thick Plate. Materials 2022, 15, 7047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207047
Qin D, Lu S, Li Y. Influence of Loading Directions on Dynamic Compressive Properties of Mill-Annealed Ti-6Al-4V Thick Plate. Materials. 2022; 15(20):7047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207047
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Dongyang, Shenglu Lu, and Yulong Li. 2022. "Influence of Loading Directions on Dynamic Compressive Properties of Mill-Annealed Ti-6Al-4V Thick Plate" Materials 15, no. 20: 7047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207047
APA StyleQin, D., Lu, S., & Li, Y. (2022). Influence of Loading Directions on Dynamic Compressive Properties of Mill-Annealed Ti-6Al-4V Thick Plate. Materials, 15(20), 7047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207047






