Study on the Effects of the Composite Addition of Al–5Ti–0.8C and La on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Mechanical Properties of ZL205A Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure
3.1.1. Grain Size Analysis
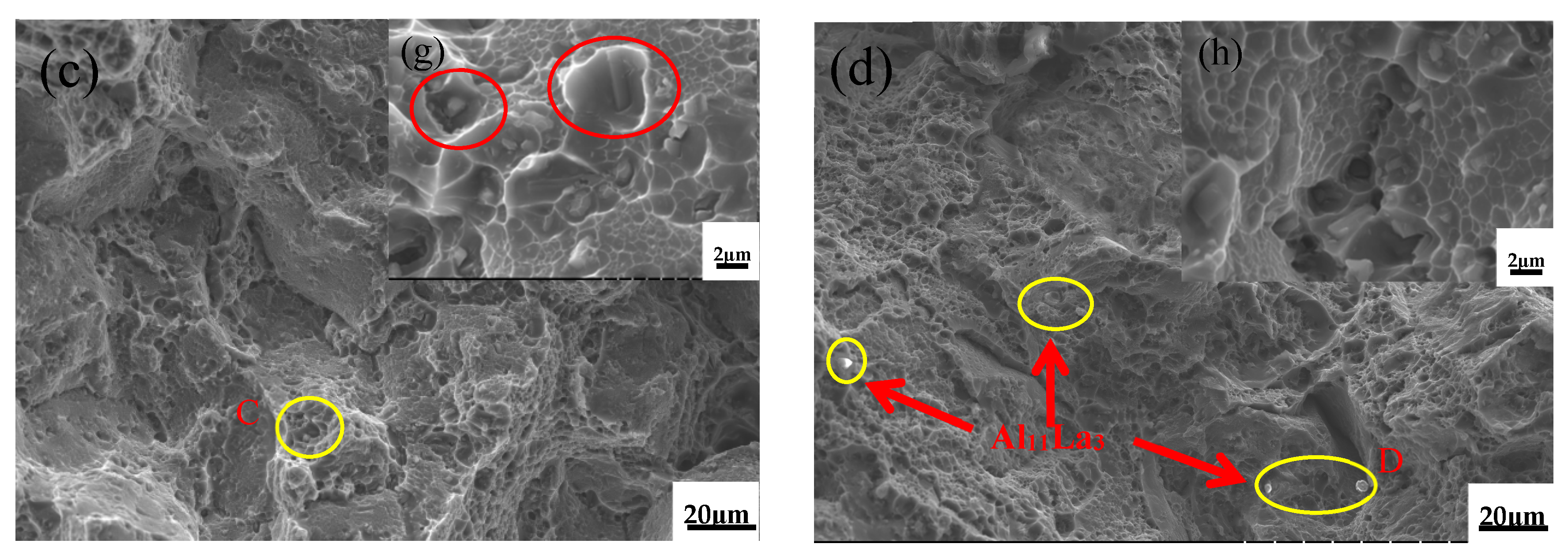
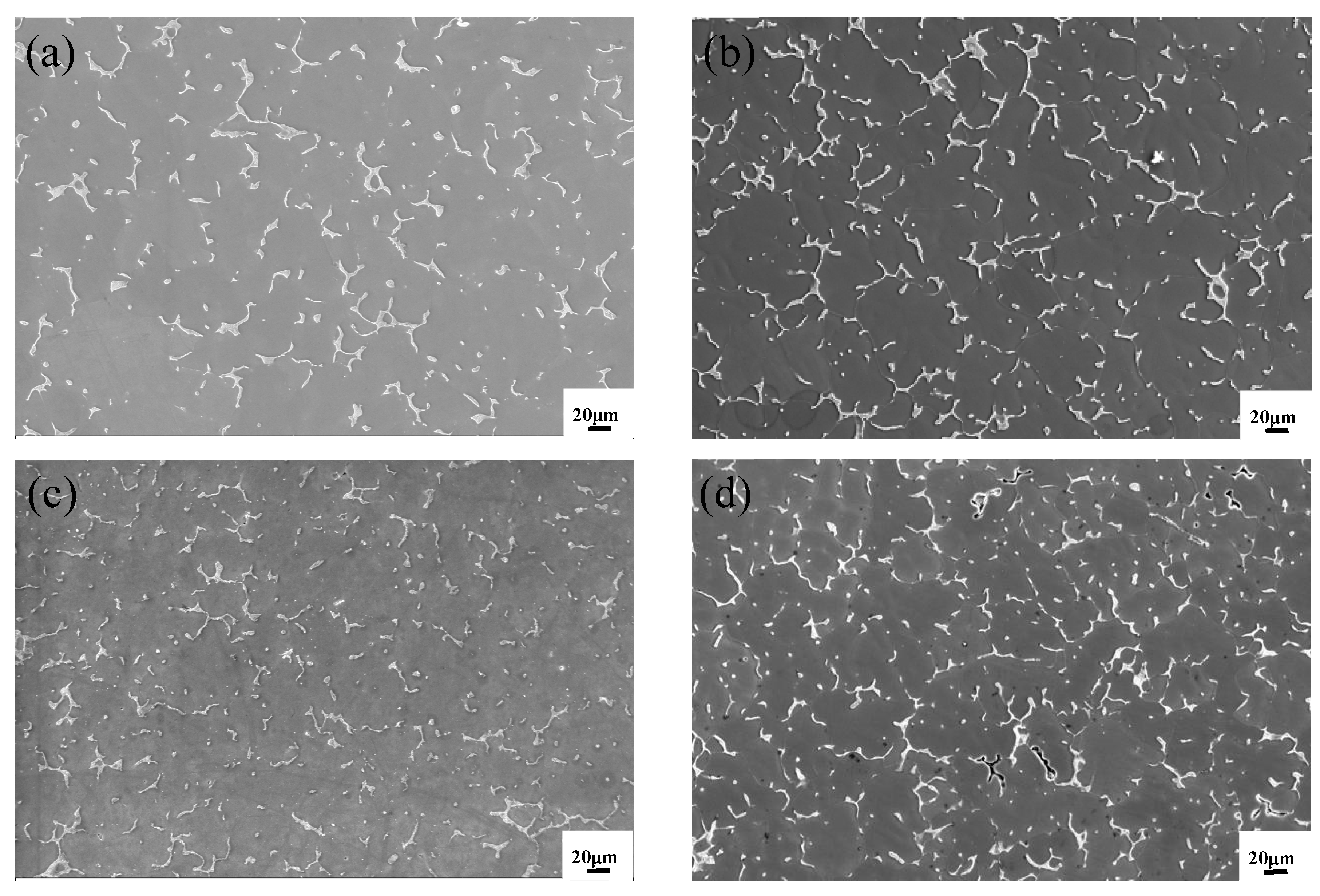
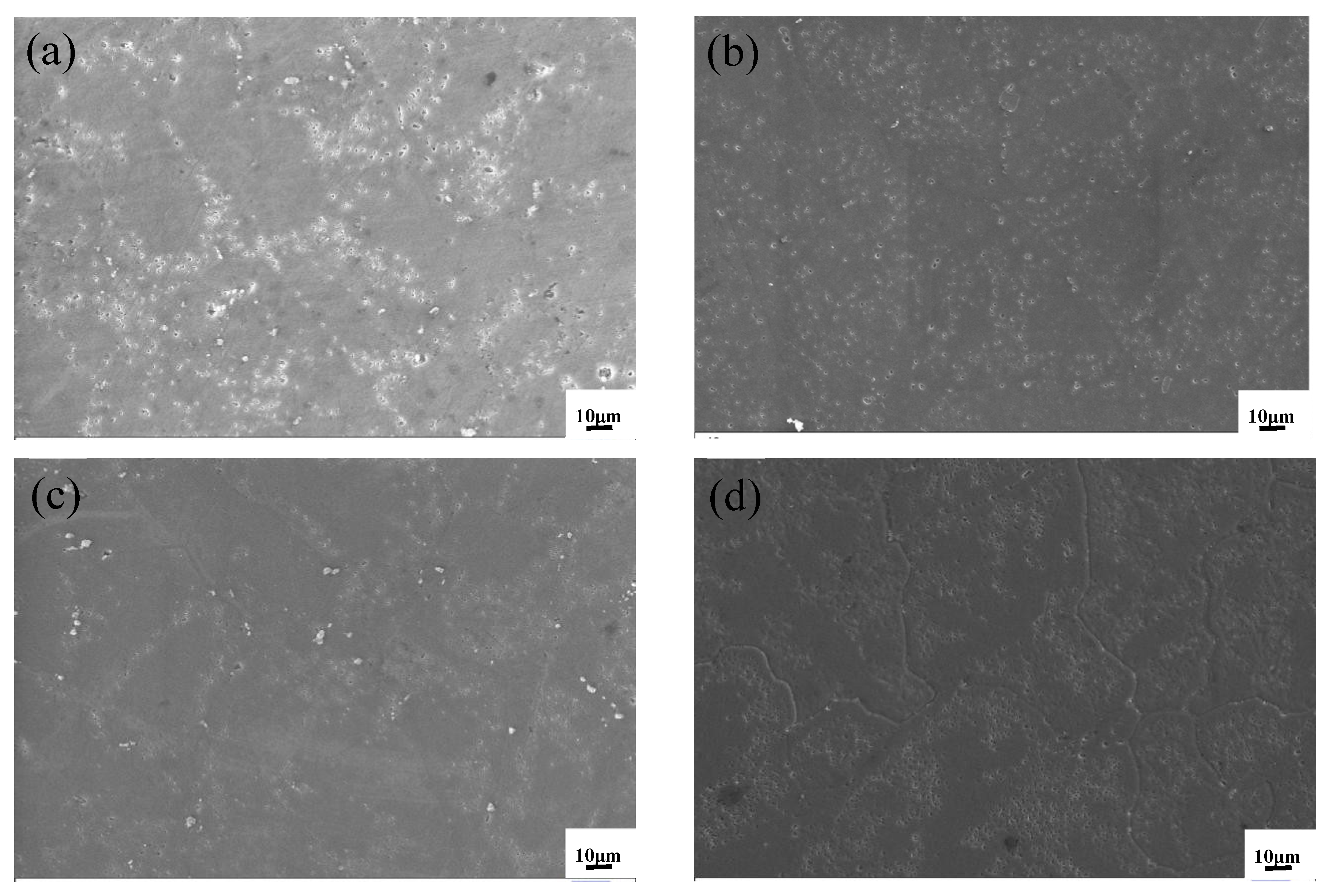
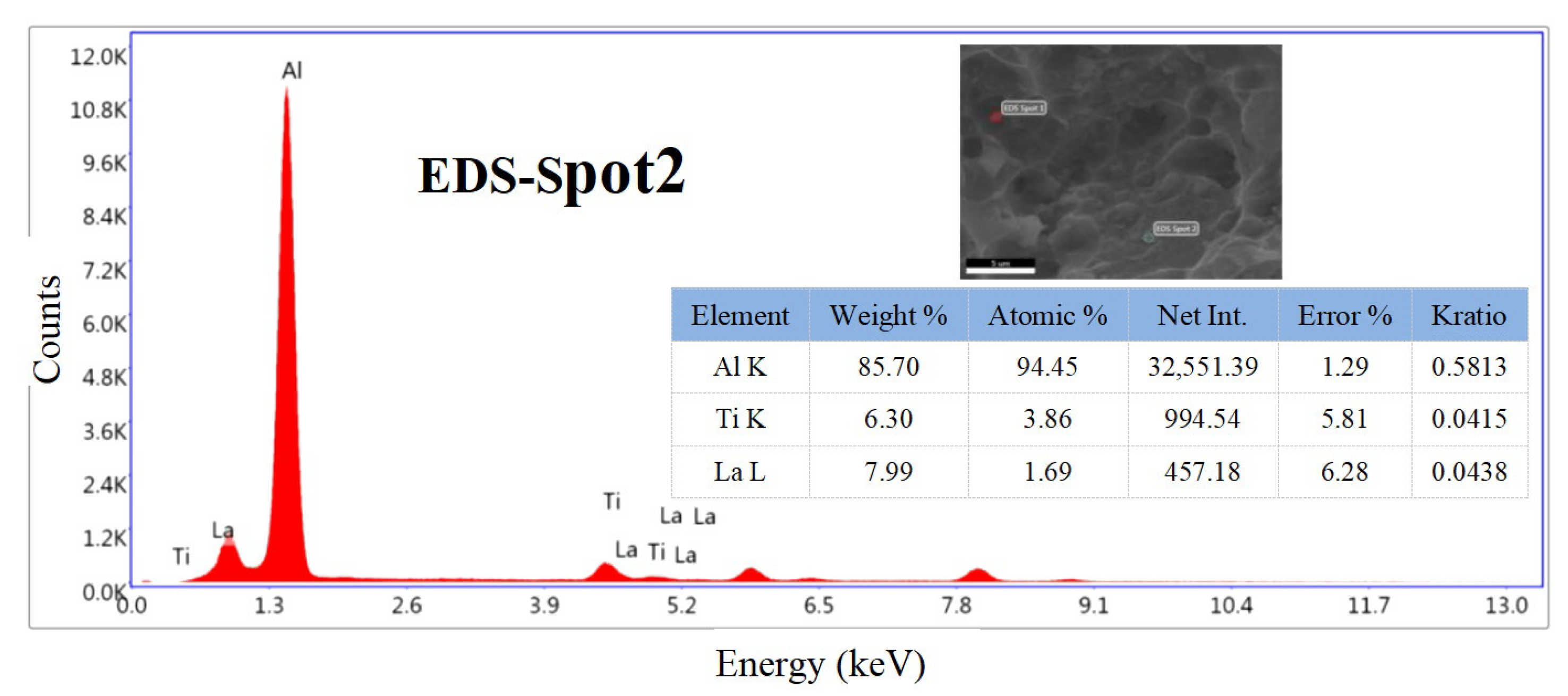
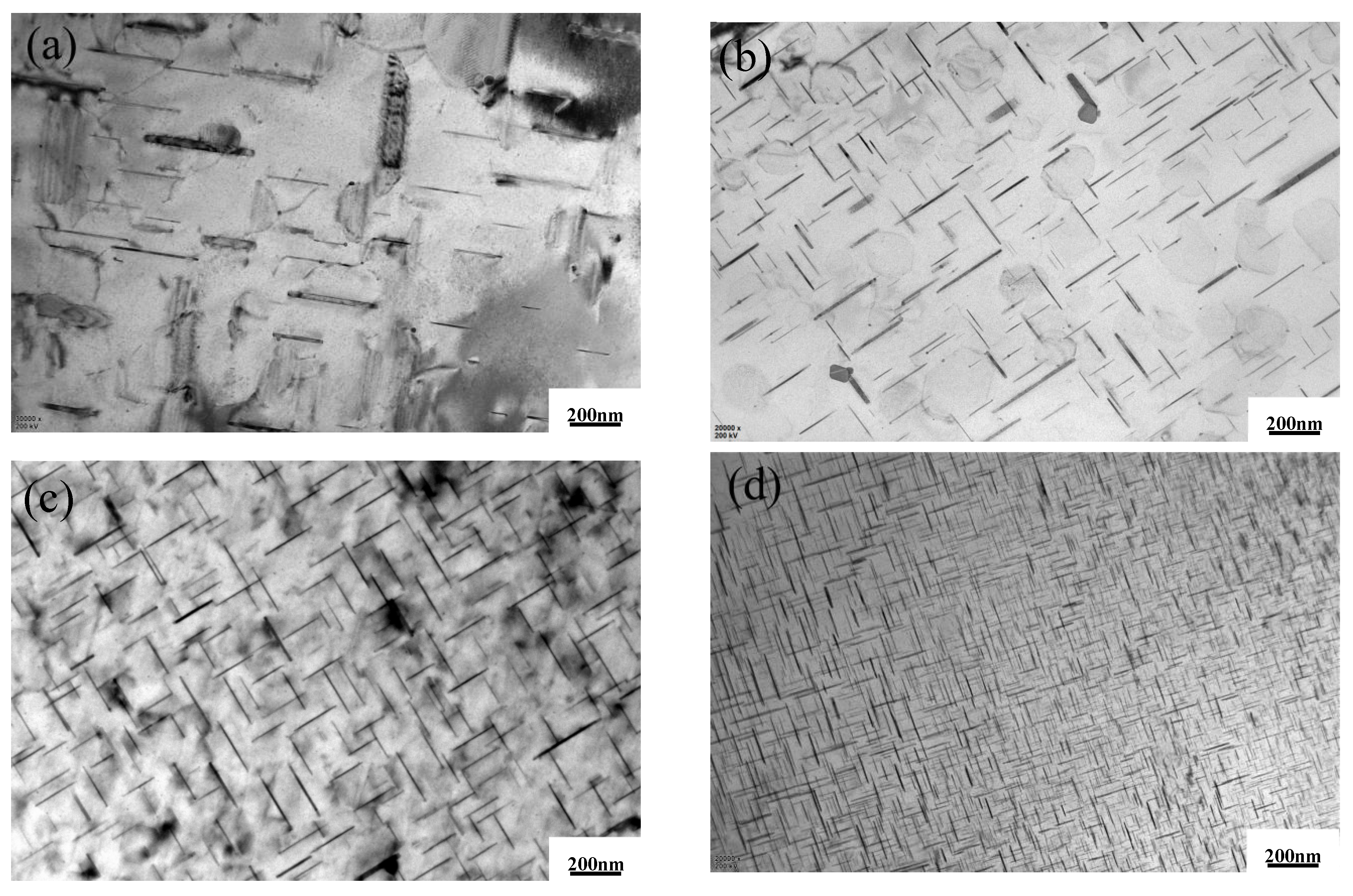
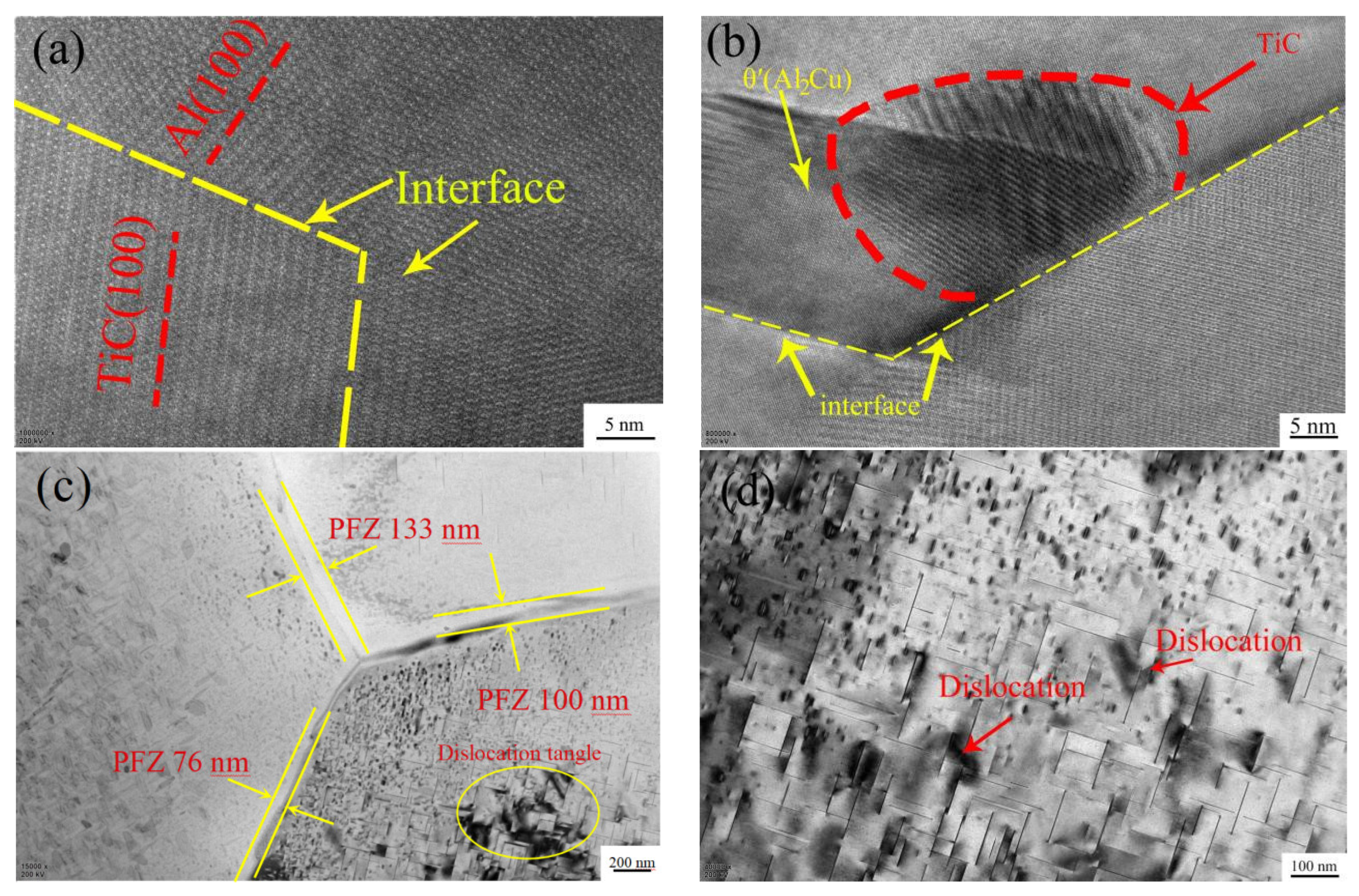
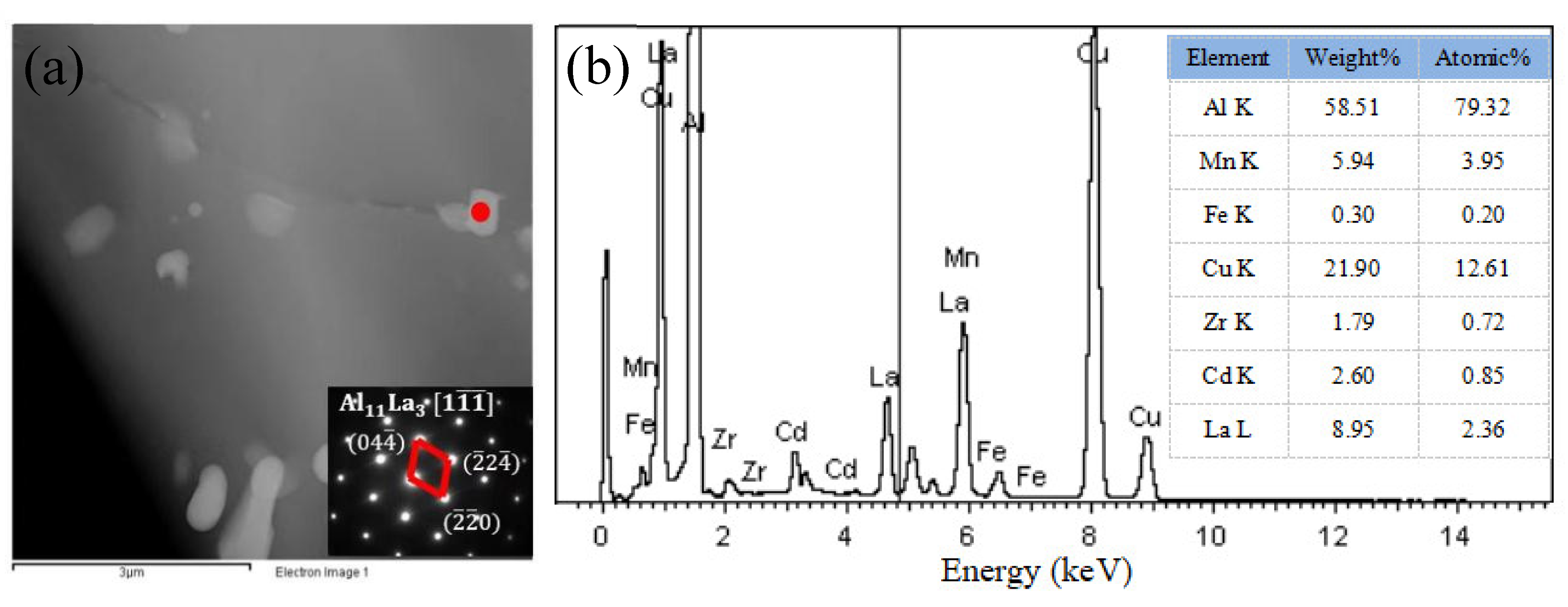
3.1.2. Microstructure Analysis
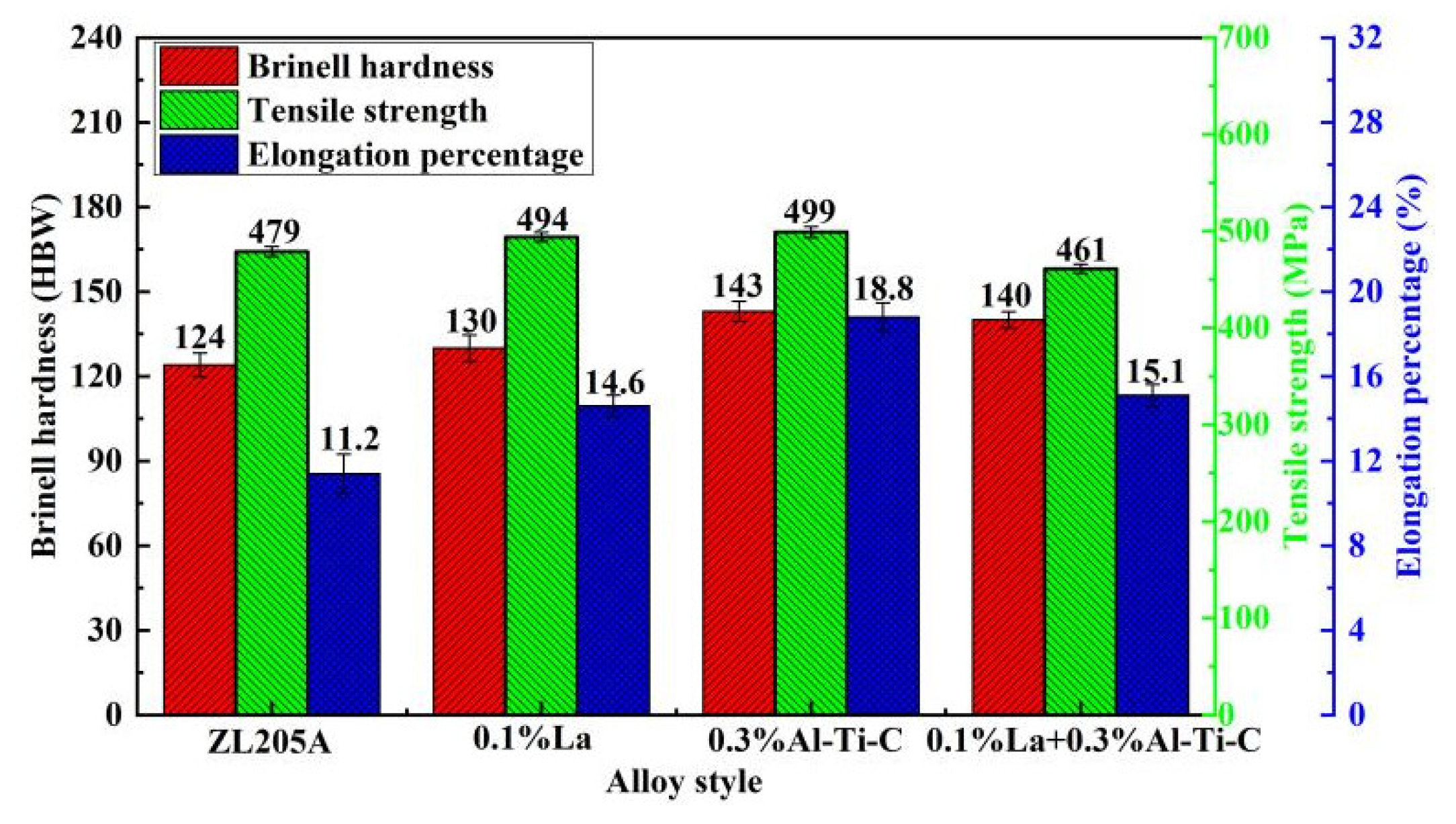
3.2. Room-Temperature Mechanical Properties
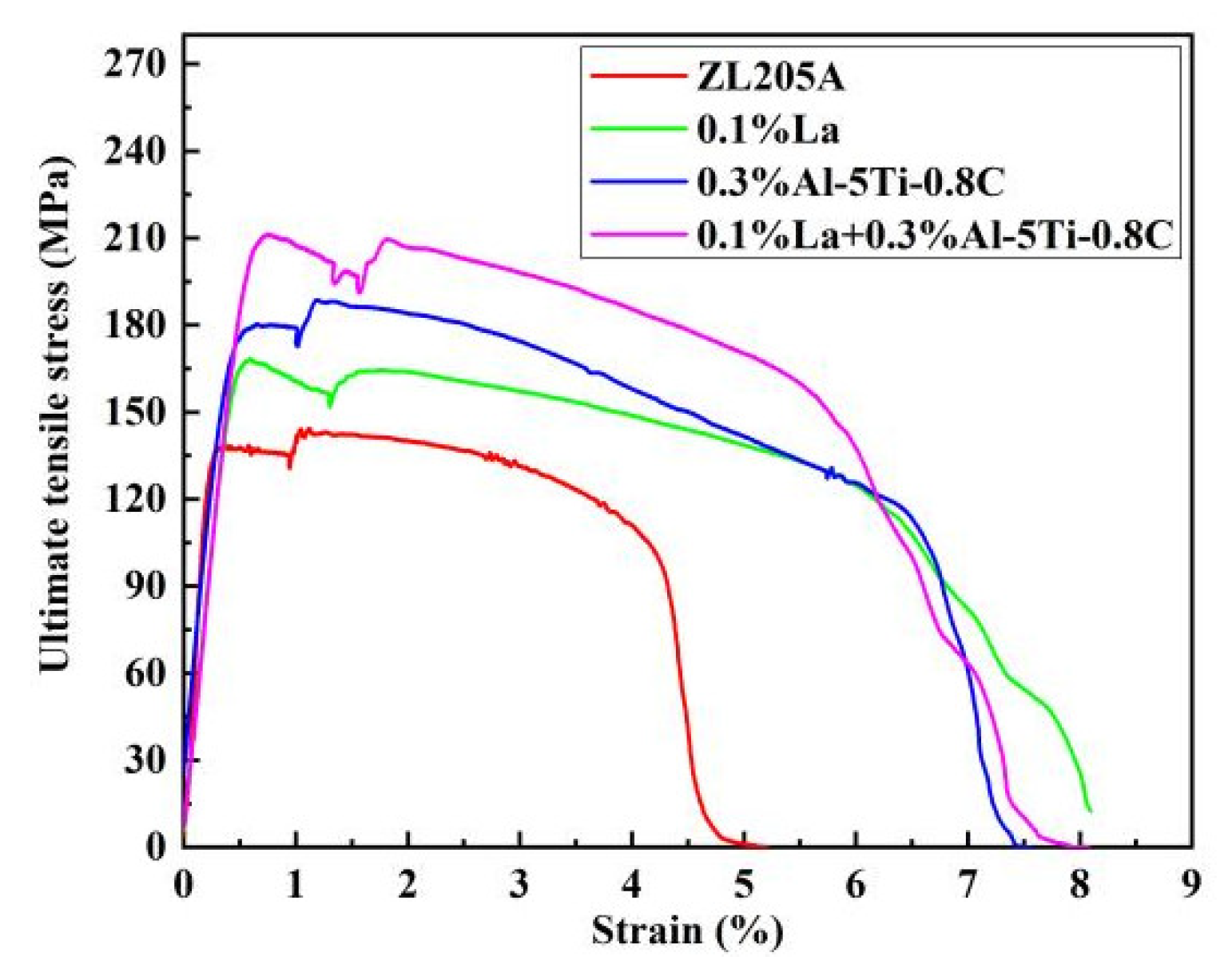
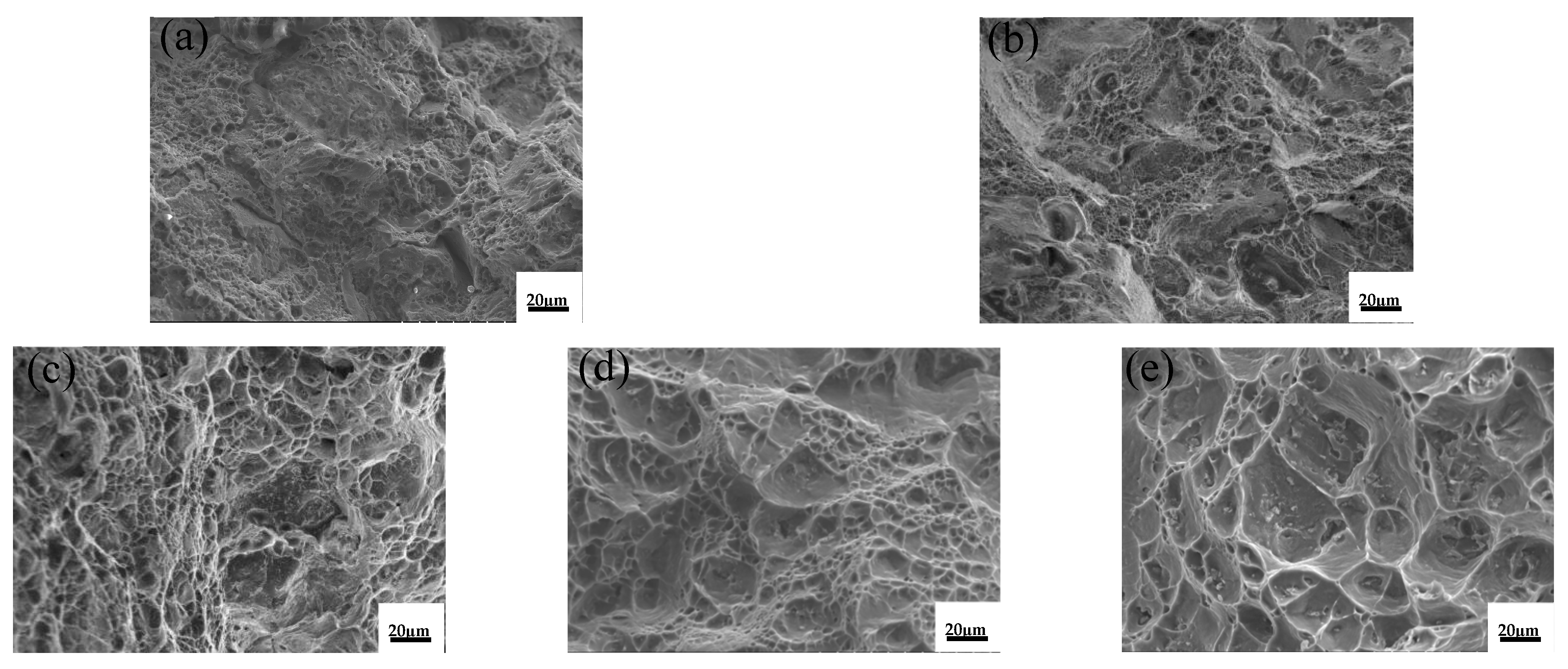
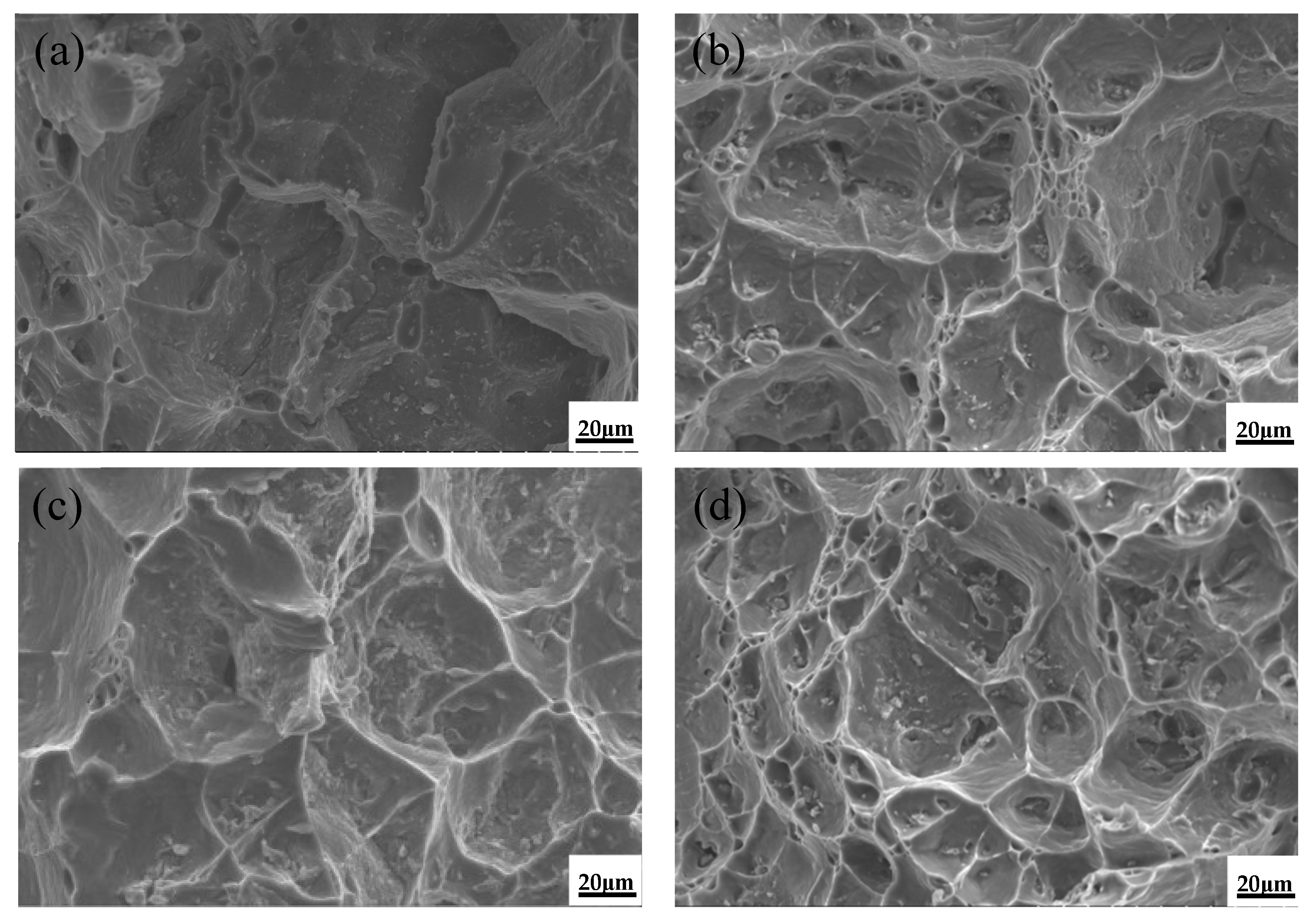
3.3. High-Temperature Mechanical Properties
3.4. High-Temperature Strengthening Mechanism
4. Conclusions
- The grains of the 0.1%La + 0.3%Al–5Ti–0.8C alloy are fine, the morphology of the as-cast Al2Cu phase is fragmented, and the precipitated phase is fine after T5 treatment. The high-temperature strength of the 0.1%La + 0.3%Al–5Ti–0.8C alloy increases significantly without decreasing the elongation above 250 °C. After T5 heat treatment, the tensile strength and elongation at 300 °C can be as high as 190 MPa and 8.8%, respectively. Compared with unmodified alloy and single additions, the maximum increase in tensile strength is 31.9%, and the elongation is slightly increased.
- Compound addition of 0.1%La + 0.3%Al–5Ti–0.8C increases the high-temperature plasticity of ZL205A due to the Al–La phase and the TiC particles, which refine the grains and reduce the tendency for intergranular fracture at high temperatures.
- The TiC introduced by the Al–5Ti–0.8C alloy and the Al11La3 formed by the addition of La refine the grains in the matrix, promote the precipitation of the needle-like θ’(Al2Cu) phase, reduce the size of the θ’(Al2Cu) phase, decrease the PFZ, and increase the θ’(Al2Cu) phase number, hindering dislocation and grain boundary motion.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, B.W. Study on the sealing performance of engine cylinder gasket. South. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Girgis, A.; Samuel, A.M.; Doty, H.W.; Valtierra, S.; Samuel, F.H. On the Elevated Temperature, Tensile Properties of Al-Cu Cast Alloys: Role of Heat Treatment. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MeCartney, D.G. Grain refining of aluminum and its alloys using inoculants. Int. Mater. Rev. 1989, 34, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Nie, J.; Gao, T.; Wang, T.; Liu, X. Influence of nitrogen on the synthesis and nucleation ability of TiCx in Al-Ti-C master alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 601, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, A.; Reif, W. Development of Al-Ti-C grain refiners containing TiC. Met. Mater Trans. A 1986, 17, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod Kumar, G.S.; Murty, B.S.; Chakraborty, M. Development of Al-Ti-C grain refiners and study of their grain refining efficiency on Al and Al-7Si alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 396, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Gao, T.; Zhang, P.; Nie, J.; Liu, X. Influence of a new kind of Al-Ti-C master alloy on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-5Cu alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 589, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Bichler, L. Effect of TiC Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of B319 Alloy. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2015, 68, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Tian, S.; Gao, T.; Nie, J.; You, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Liu, X. High-temperature mechanical properties of 2024 Al matrix nanocomposite reinforced by TiC network architecture. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 763, 38121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gao, T.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Nie, J.; Liu, X. Microstructure and mechanical properties at both room and high temperature of in-situ TiC reinforced Al-4.5Cu matrix nanocomposite. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 767, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.S.; Zhao, Q.L.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Qiu, F.; Jiang, Q.C. Simultaneously increasing the high-temperature tensile strength and ductility of nano-sized TiCp reinforced Al-Cu matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 71, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, A.K.; Doherty, R. Grain boundary ductile fracture in precipitation hardened aluminum alloys. Acta Met. 1987, 35, 1193–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantzsche, K.; Bohlen, J.; Wendt, J.; Kainer, K.U.; Yi, S.B.; Letzig, D. Effect of rare earth additions on microstructure and texture development of magnesium alloy sheets. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, L.; Wu, G.; Zhang, X.; Chen, A.; Tao, J. Effects of Sc addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of cast Al-3Li-1.5Cu-0.15Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 680, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xia, Q.; Liu, Y. Grain Refinement of the Al-Cu-Mg-Ag Alloy with Er and Sc Additions. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38, 2853–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Xia, Y.; Qiu, F.; Jiang, Q. Effects of La addition on the elevated temperature properties of the casting Al–Cu alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng.: A 2011, 528, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, F.; Mao, J.; Niu, G. The difference of La and Ce as additives of electrical conductivity aluminum alloys. Mater. Charact. 2019, 158, 109963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; He, J.; Zheng, Q.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J. The influence of rare earth element lanthanum on the microstructures and properties of as-cast 8176 (Al-0.5Fe) aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 859, 157804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.G.; Samuel, A.M.; Doty, H.W.; Samuel, F.H. Effect of the Addition of La and Ce on the Solidification Behavior of Al-Cu and Al-Si-Cu Cast Alloys. Int. J. Met. 2019, 14, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Jiang, H.; He, J.; Zhao, J. Effect of La addition on microstructure evolution of hypoeutectic Al–6Si alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 7546–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Niu, J.; Xu, H.; Ren, X. Enhanced Fluidity of ZL205A Alloy with the Combined Addition of Al-Ti-C and La. Materials 2021, 14, 6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Liang., L.; Lu, B.; Zhang, J.; Liang, W. Effect of La on Microstructure and Grain-Refining Performance of Al-Ti-C Grain Refiner. J. Rare Earths 2006, 24, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.R.; Karantzalis, A.E.; Wyatt, S.M. The microstructure and mechanical properties of TiC and TiB2-reinforced cast metal matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezer, B.T.; Toptan, F.; Daglilar, S.; Kerti, I. Production of Al-Ti-C grain refiners with the addition of elemental carbon. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, S30–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, Z.; Xia, L.; Xia, P.; Zeng, S. Severe plastic deformation-induced dissolution of θ” particles in Al–Cu binary alloy and subsequent nature aging behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassner, M.E. The effect of grain size on the elevated temperature yield strength of polycrystalline aluminum. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1991, 25, 2833–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraju, S.; Heilmaier, M.; Murty, B.S.; Vadlamani, S.S. On the Estimation of True Hall-Petch Constants and Their Role on the Superposition Law Exponent in Al Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2012, 14, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidman, D.N.; Marquis, E.A.; Dunand, D.C. Precipitation strengthening at ambient and elevated temperatures of heat-treatable Al(Sc) alloys. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 4021–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Aging Temperature (°C) | Aging Time (min) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 250 | - | 10 | - | 30 | 60 | - | 180 | - | 300 | 480 |
| 300 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 60 | 120 | 180 | 210 | 300 | - |
| Specimen | Unmodified Alloy | 0.3%Al–5Ti–0.8C Alloy | 0.1%La Alloy | 0.1%La + 0.3%Al–5Ti–0.8C Alloy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average grain size/μm | 82 | 62 | 68 | 61 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Niu, J.; Xu, H. Study on the Effects of the Composite Addition of Al–5Ti–0.8C and La on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Mechanical Properties of ZL205A Alloy. Materials 2022, 15, 7087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207087
Li Y, Zhang G, Niu J, Xu H. Study on the Effects of the Composite Addition of Al–5Ti–0.8C and La on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Mechanical Properties of ZL205A Alloy. Materials. 2022; 15(20):7087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207087
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yu, Guowei Zhang, Jingwei Niu, and Hong Xu. 2022. "Study on the Effects of the Composite Addition of Al–5Ti–0.8C and La on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Mechanical Properties of ZL205A Alloy" Materials 15, no. 20: 7087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207087
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhang, G., Niu, J., & Xu, H. (2022). Study on the Effects of the Composite Addition of Al–5Ti–0.8C and La on the Microstructure and High-Temperature Mechanical Properties of ZL205A Alloy. Materials, 15(20), 7087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207087





