Preparation and Application of Foaming Agent Based on the Compound System of Short-Chain Fluorocarbon and Soybean Residue Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of SRP Foaming Agent
2.2.2. Single-factor Test
2.2.3. Response Surface Test
2.2.4. Analysis Methods
2.3. Preparation of Foam and Foam Concrete
2.4. Characteristics of Foam
2.4.1. Viscosity Test
2.4.2. Surface Tension Test
2.4.3. Foam Stability
2.4.4. Optical Microscopy
2.5. Properties of Foam Concrete
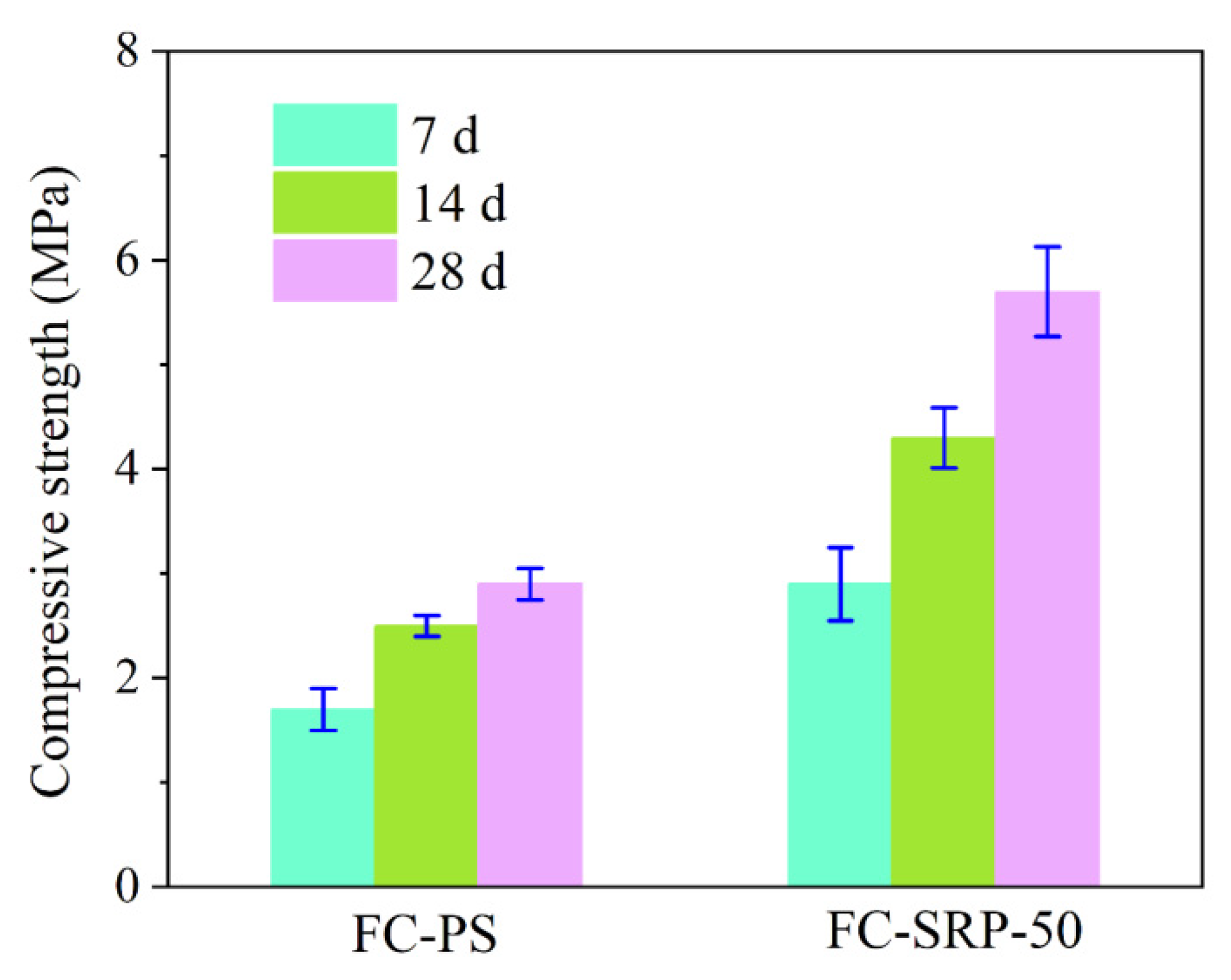
2.5.1. Compressive Strength
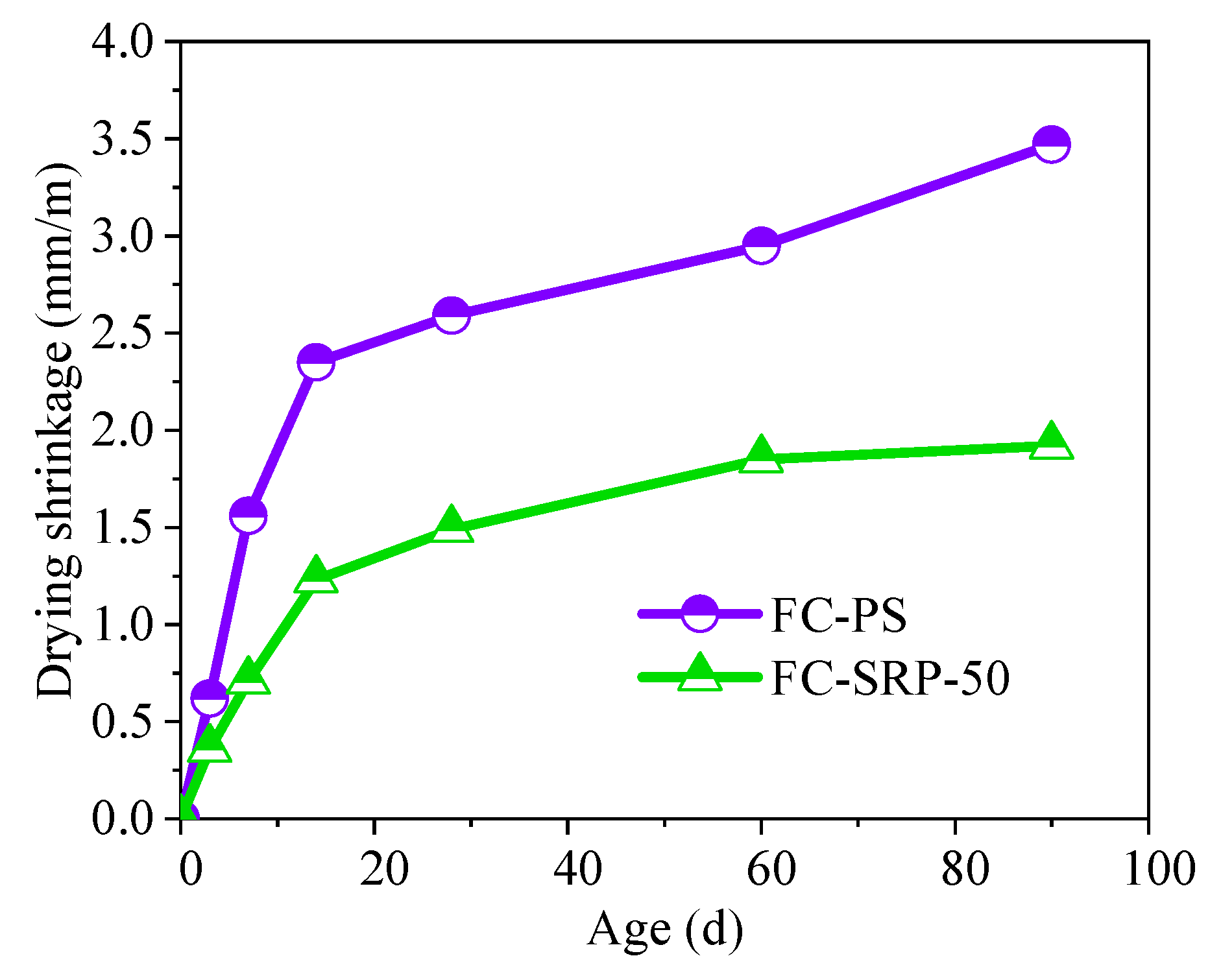
2.5.2. Drying Shrinkage
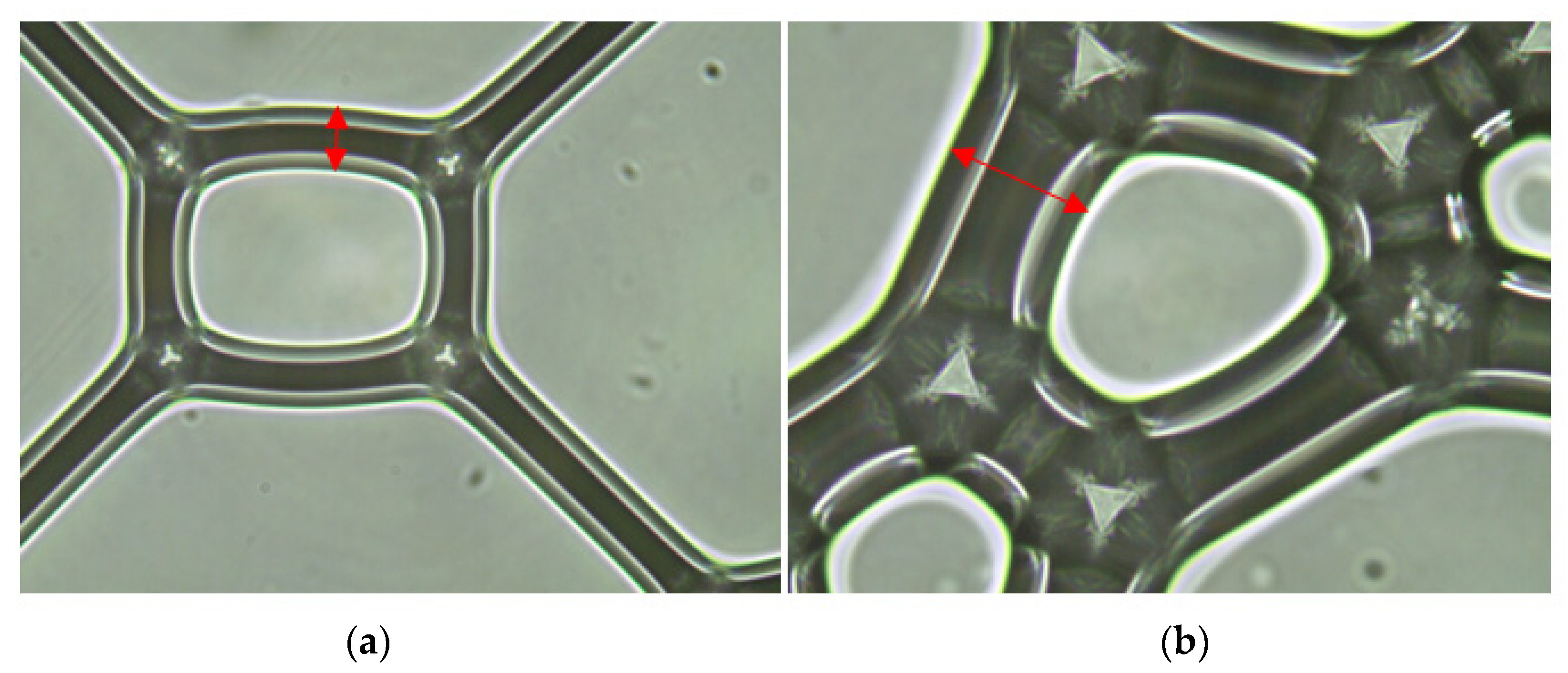
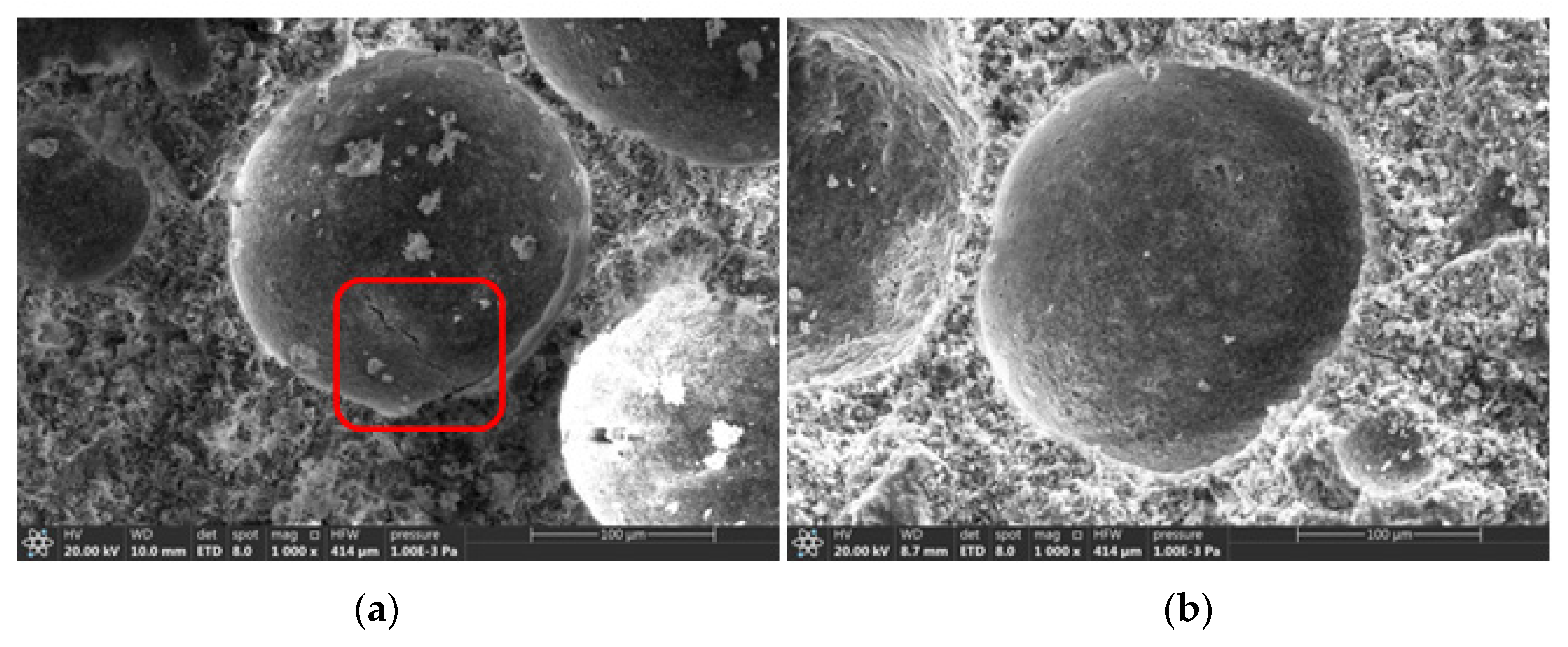
2.5.3. Microstructure and Pore Structure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Single-Factor Test Results
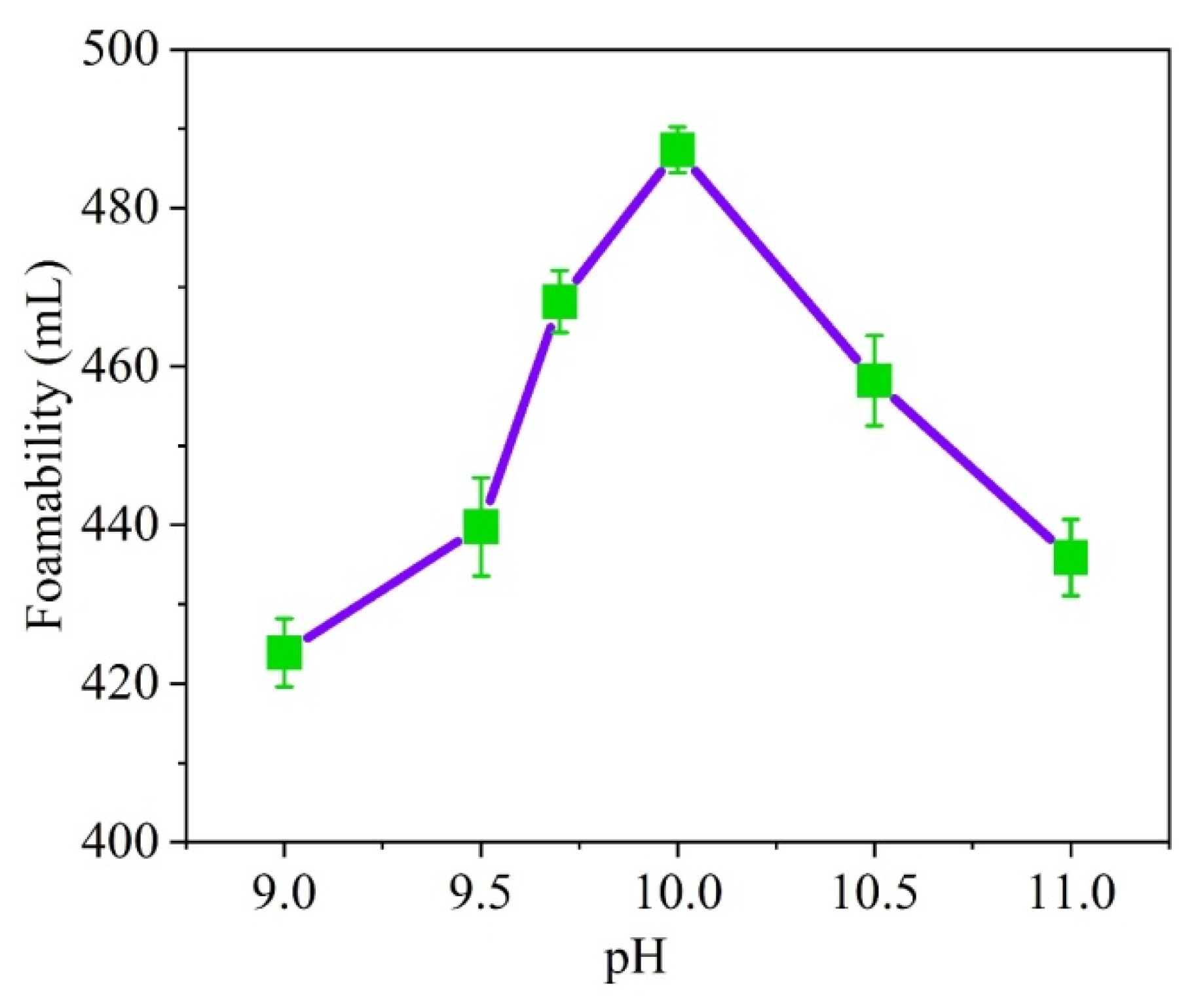
3.1.1. Effect of PH Value on Foaming Ability
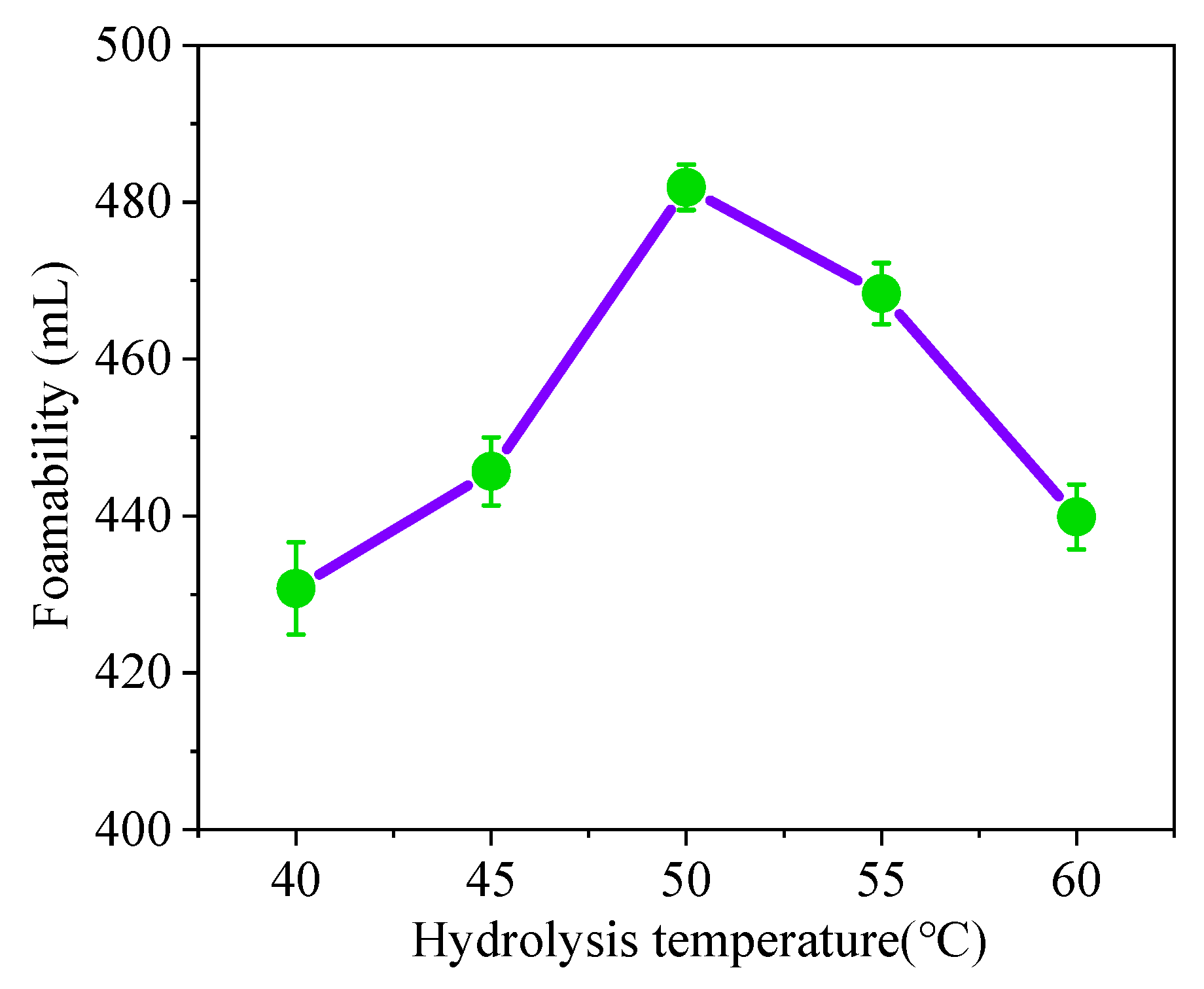
3.1.2. Effect of Temperature on Foaming Hydrolysis Ability
3.1.3. Effect of Hydrolysis Time on Foaming Ability
3.2. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
3.2.1. Property Fitting and Data Analysis
−16.42X22 − 18.62X32
3.2.2. Response Surface Experimental Analysis
3.2.3. Model Verification and Adjustment
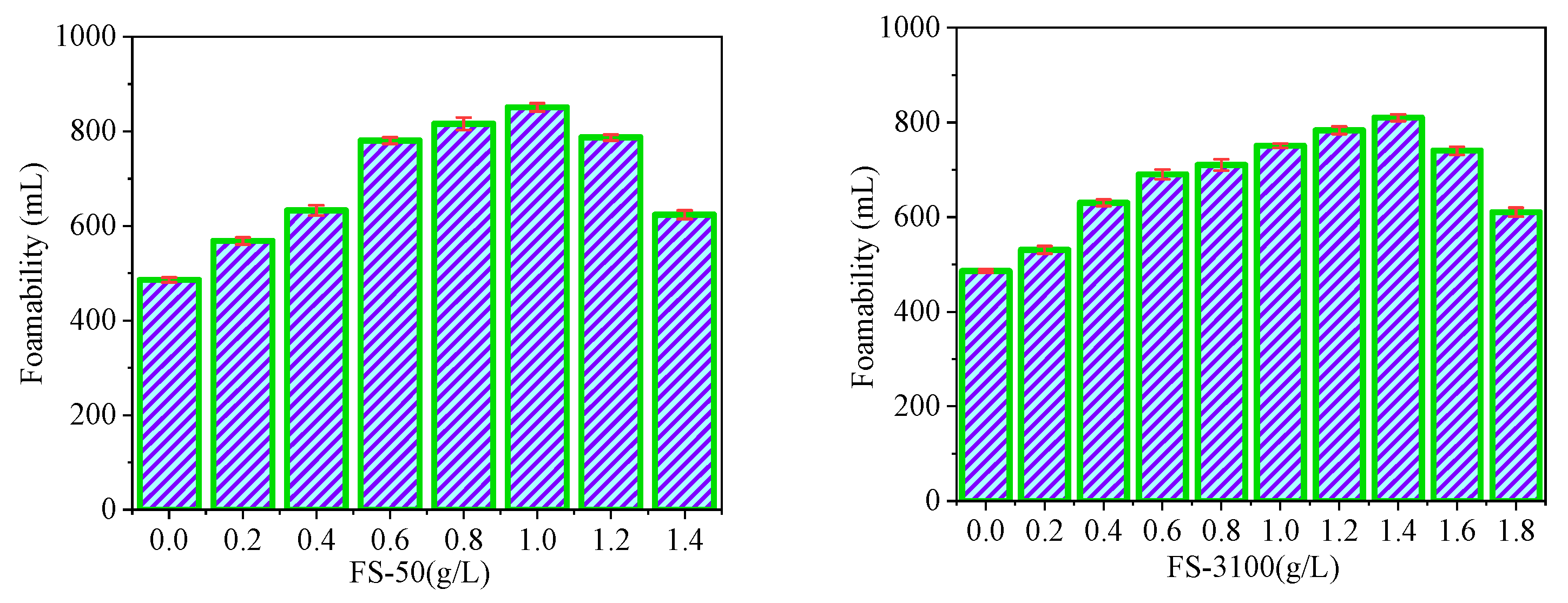
3.3. Performance Evaluation of Additives
3.4. Properties of Foams
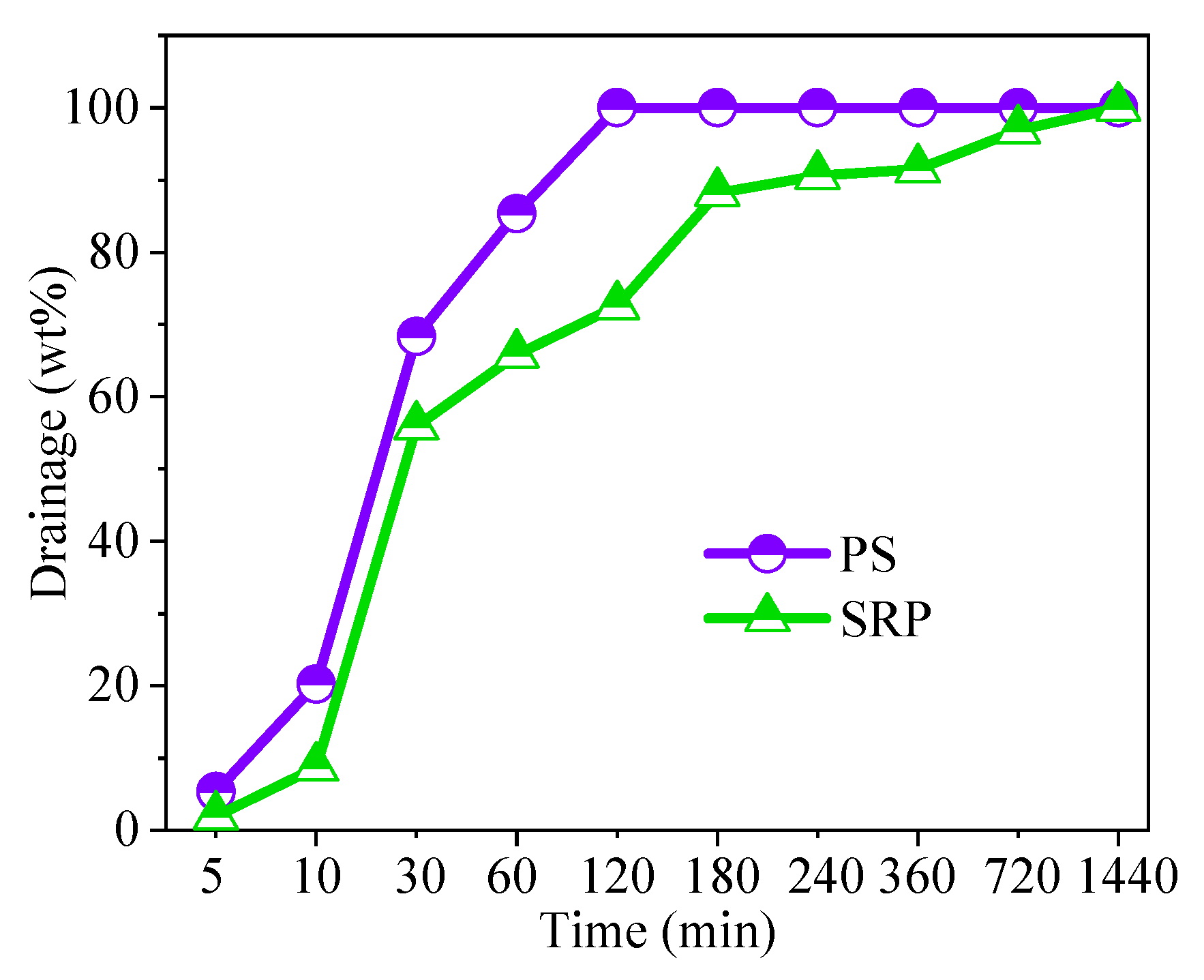
3.4.1. Density, Viscosity, and Stability of Foams
3.4.2. Morphology of Foams
3.5. Influence of SRP on Foam Concrete
3.5.1. Compressive strength and shrinkage
3.5.2. Microstructure of the Foam Concrete
3.5.3. Pore Characteristics
3.6. Overall Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koksal, F.; Sahin, Y.; Gencel, O. Influence of expanded vermiculite powder and silica fume on properties of foam concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Qu, N.; Li, J. Development and functional characteristics of novel foam concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 324, 126666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falliano, D.; Parmigiani, S.; Suarez-Riera, D.; Ferro, G.A.; Restuccia, L. Stability, flexural behavior and compressive strength of ultra-lightweight fiber-reinforced foamed concrete with dry density lower than 100 kg/m3. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 51, 104329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, Y.M.; Farzadnia, N.; Ali, A.A. Properties and applications of foamed concrete; a review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 990–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Qian, K.; Ding, J.; Zhao, Y. Experimental study on seismic performance of new foam concrete composite wall panel based on nanomaterials. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2022, 7, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, A.J. Materials, Production, Properties and Application of Aerated Lightweight Concrete: Review. Int. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falliano, D.; Restuccia, L.; Gugliandolo, E. A simple optimized foam generator and a study on peculiar aspects concerning foams and foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 268, 121101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panesar, D. Cellular concrete properties and the effect of synthetic and protein foaming agents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, J.K. Hydraulic Fracturing Chemicals and Fluids Technology; Gulf Professional Publishing: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, J. Insight into binding behavior, structure, and foam properties of α-lactalbumin/glycyrrhizic acid complex in an acidic environment. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 125, 107411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.-Y.; Zhou, X.-G.; Yu, J.-S.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z. Protein foaming method to prepare Si3N4 foams by using a mixture of egg white protein and whey protein isolate. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 11503–11509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.S. Stabilization of bubbles and foams. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 12, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdolotti, L.; Liguori, B.; Capasso, I.; Errico, A.; Caputo, D.; Lavorgna, M.; Iannace, S. Synergistic effect of vegetable protein and silicon addition on geopolymeric foams properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 50, 2459–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Chen, T.; Li, Y. Research on foaming characteristics and application of foaming agent of high stability sludge protein. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 3, 2254–2260. [Google Scholar]
- Haberl-Meglic, S.; Janez, N.; Peterka, M.; Miklavcic, D. Selective extraction of proteins from bacterial cells by electroporation, sonoporation or glass bead homogenization. New Biotechnol. 2018, 44, S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhou, H. Preparation of protein foaming agent by Baijiu vinasse. China Brew. 2017, 36, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, G.; Peng, M. Biomass and pigments production in photosynthetic bacteria wastewater treatment: Effects of photoperiod. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 190, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoping, L.I.; Yumei, J.I. Grain, Oil and Food Processing Technology; Chongqing University Press: Chongqing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Peng, G.; Luo, D.; Zhou, X. Preparation and Adsorption Properties of Soybean Dreg/Hydrocalumite Composites. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 27491–27500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuhuan, X.U.; Yuefang, W.U. Research report on key soybean food processiong enterprises in 2019. Soybean Sci. Technol. 2019, 6, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Qiao, M.; Lu, F. Composition, Nutrition, and Utilization of Okara (Soybean Residue). Food Rev. Int. 2012, 28, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiyan, I.; Ligen, Z.; Liping, W. Nutritional components analyzation and protein nutrition evaluation of soybean residue. Food Ind. 2020, 41, 325–328. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J. Studies on tea protein extraction using alkaline and enzyme methods. Food Chem. 2007, 107, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong-Ly, K.C.; Gabelli, S.B. Salting out of Proteins Using Ammonium Sulfate Precipitation. Methods Enzymol. 2014, 541, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, G.; Xie, Z.; Zhu, Y. Preparation of foaming agent from photosynthetic bacteria liquid by direct thermal alkaline treatment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 238, 117715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyens, E.; Baeyens, J.; Creemers, C. Alkaline thermal sludge hydrolysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, S. Protein Stabilization of Emulsions and Foams. J. Food Sci. 2006, 70, R54–R66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, G.; Wan, T.; Lu, Y. Influences of light and oxygen conditions on photosynthetic bacteria macromolecule degradation: Different metabolic pathways. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9503–9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falliano, D.; De Domenico, D.; Ricciardi, G.; Gugliandolo, E. Compressive and flexural strength of fiber-reinforced foamed concrete: Effect of fiber content, curing conditions and dry density. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 198, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, W.; Du, Y.; Miao, C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y. Application of organic- and nanoparticle-modified foams in foamed concrete: Reinforcement and stabilization mechanisms. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 106, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Z.; Shi, T.; Rongrong, L. Physicochemical and processing properties of tartary buckwheat protein extracted by enzymatic method. Food Sci. 2010, 31, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, C.; Eastoe, J. Foams: From nature to industry. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 247, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek-Krowiak, A.; Chojnacka, K.; Podstawczyk, D.; Dawiec, A.; Pokomeda, K. Application of response surface methodology and artificial neural network methods in modelling and optimization of biosorption process. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manyala, D.L.; Rajput, G.; Pandya, N.; Varade, D. Enhanced foamability and foam stability of polyoxyethylene cholesteryl ether in occurrence of ionic surfactants. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 551, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.; Starrenburg, D.; Tait, S.; Barr, K.; Batstone, D.; Lant, P. Decreasing activated sludge thermal hydrolysis temperature reduces product colour, without decreasing degradability. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4699–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Tian, Z.; Chen, L.; Temelli, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y. Functionality of Barley Proteins Extracted and Fractionated by Alkaline and Alcohol Methods. Cereal Chem. 2010, 87, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foegeding, E.A.; Luck, P.; Davis, J. Factors determining the physical properties of protein foams. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, D.; Kaur, D.M. Extraction, purification and characterization of enzyme amylase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2013, 3, 158–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Huo, M.; Li, Y.; Guo, R.; Li, Y. Research on the influence of different stabilizers on foaming characreristics of sludge protein. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2010, 4, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Nguyen, A.V.; Farrokhpay, S. A critical review of the growth, drainage and collapse of foams. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 228, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Chen, J.J.J. Effect of SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) foam on polarized light characteristics. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 104, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.J.; Kunjappu, J.T. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Li, J.; Lu, Z.; Niu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Li, T. Effect of nanoparticles on foaming agent and the foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearsely, E.P.; Visagie, M. Micro-properties of foamed concrete, proceedings creating with concrete. In Proceedings of the Specialist Techniques and Materials for Concrete Construction, University of, Dundee, Dundee, UK, 8–10 September 1999; pp. 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- She, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jones, M. Three-dimensional numerical modeling and simulation of the thermal properties of foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y. Effect of nano-alumina modified foaming agents on properties of foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 267, 121045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Deng, K.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Xin, X.; Liu, Y.; Khan, I.A.; Yang, S.; Wang, T.; Xu, Q. New Triterpenoid Saponins from Green Vegetable Soya Beans and Their Anti-Inflammatory Activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 11065–11072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Oxide | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | MgO | SO3 | K2O | Na2O | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 64.65 | 21.32 | 5.04 | 3.12 | 0.97 | 0.49 | 2.96 | 0.39 | 0.23 | 3.21 |
| Variables | Symbol | Range and Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| pH | X1 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| Hydrolysis temperature (°C) | X2 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| Hydrolysis time (h) | X3 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Mix | Target Density (kg/m3) | Foaming Agent | Cement (kg) | Water (kg) | Foam (m3) | Actual Average Dry Density (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC-PS | 600 | PS | 600 | 300 | 0.9 | 607 ± 4 |
| FC-SRP-50 | 600 | SRP | 600 | 300 | 0.9 | 613 ± 5 |
| Run | pH | Hydrolysis Temperature (°C) | Hydrolysis Time (h) | Foamability (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 50 | 3 | 489.5 |
| 2 | 11 | 60 | 4 | 420 |
| 3 | 10 | 50 | 2 | 430 |
| 4 | 9 | 40 | 2 | 425 |
| 5 | 9 | 50 | 3 | 435 |
| 6 | 10 | 50 | 3 | 480.5 |
| 7 | 10 | 50 | 3 | 485 |
| 8 | 11 | 40 | 2 | 430.5 |
| 9 | 11 | 40 | 4 | 428 |
| 10 | 10 | 50 | 3 | 485.5 |
| 11 | 10 | 60 | 3 | 440 |
| 12 | 9 | 60 | 2 | 435.5 |
| 13 | 10 | 50 | 3 | 483.5 |
| 14 | 10 | 50 | 4 | 438.5 |
| 15 | 11 | 50 | 3 | 440 |
| 16 | 10 | 40 | 3 | 441.5 |
| 17 | 10 | 50 | 3 | 485 |
| 18 | 9 | 60 | 4 | 433.5 |
| 19 | 11 | 60 | 2 | 439 |
| 20 | 9 | 40 | 4 | 435.5 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | Significant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 11,245.23 | 9 | 1249.47 | 71.55 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X1 (pH) | 0.81 | 1 | 0.81 | 0.05 | 0.8336 | |
| X2 (Hydrolysis temperature) | 3.30 | 1 | 3.30 | 0.19 | 0.6730 | |
| X3 (Hydrolysis time) | 0.29 | 1 | 0.29 | 0.02 | 0.8990 | |
| X1X2 | 6.46 | 1 | 6.46 | 0.37 | 0.5566 | |
| X1X3 | 103.32 | 1 | 103.32 | 5.92 | 0.0353 | |
| X2X3 | 104.18 | 1 | 104.18 | 5.97 | 0.0347 | |
| X12 | 4318.46 | 1 | 4318.46 | 247.28 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X22 | 3887.88 | 1 | 3887.88 | 222.62 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X32 | 4998.65 | 1 | 4998.65 | 286.23 | <0.0001 | ** |
| Residual | 174.64 | 10 | 17.46 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 136.08 | 5 | 27.22 | 3.53 | 0.0963 | |
| Pure Error | 38.56 | 5 | 7.71 | |||
| Cor Total | 11,419.87 | 19 | ||||
| R2 | 0.9847 | |||||
| Radj2 | 0.9709 |
| Additive | Price (USD/kg) | Dosage (kg/L) | Cost (USD/L) | Economy | Safety | Foaming Ability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FS-50 | 258 | 1.0 × 10−3 | 0.258 | *** | ** | *** |
| FS-3100 | 258 | 1.4 × 10−3 | 0.362 | * | ** | ** |
| Type | Density (kg/m3) | Viscosity (Pa∙S) | Surface Tension (mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PS | 17 | 0.113 | 35.1 |
| SRP | 22 | 0.142 | 31.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, N.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Xiong, Y. Preparation and Application of Foaming Agent Based on the Compound System of Short-Chain Fluorocarbon and Soybean Residue Protein. Materials 2022, 15, 7384. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207384
Song N, Li Z, Wang S, Xiong Y. Preparation and Application of Foaming Agent Based on the Compound System of Short-Chain Fluorocarbon and Soybean Residue Protein. Materials. 2022; 15(20):7384. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207384
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Ning, Zhihe Li, Shaoqing Wang, and Yuanliang Xiong. 2022. "Preparation and Application of Foaming Agent Based on the Compound System of Short-Chain Fluorocarbon and Soybean Residue Protein" Materials 15, no. 20: 7384. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207384
APA StyleSong, N., Li, Z., Wang, S., & Xiong, Y. (2022). Preparation and Application of Foaming Agent Based on the Compound System of Short-Chain Fluorocarbon and Soybean Residue Protein. Materials, 15(20), 7384. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207384






