The Impact of Plastic Deformation on the Microstructure and Tensile Strength of Haynes 282 Nickel Superalloy Produced by DMLS and Casting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- -
- Based on the results of the 3D scanning, it can be concluded that the surface quality of DMLS and as-cast samples in the base state are at a similar level.
- -
- The quality of the surfaces of 3D printed materials depends on factors such as the parameters of the raw material (the metallic powder), the design process, the 3D printing parameters, and the post-processing.
- -
- During the microscopic examinations of the DMLS samples, no cracks were found. There was slight porosity in the structure. In the structure of the cast samples, precipitations of MX-type carbides were observed.
- -
- Haynes 282 nickel superalloy with a dendritic microstructure can be produced by the DMLS method. The fine crystalline dendritic microstructure and low porosity showed very good tensile strength compared with the cast material.
- -
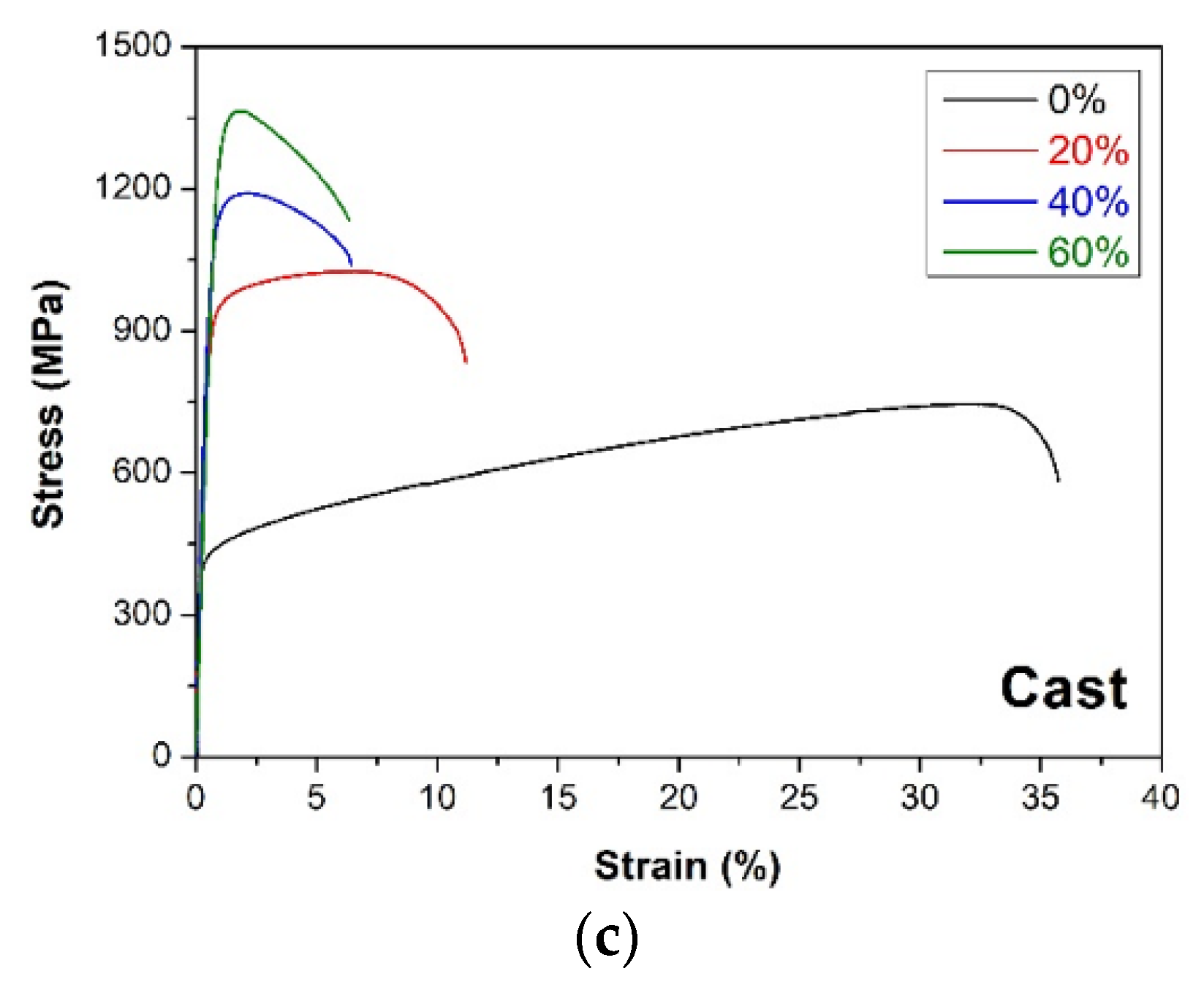
- An increase in the degree of plastic deformation of the Haynes 282 materials produced by DMLS and by casting resulted in an increase in the tensile strength of the tested samples, along with a reduction in ductility. The results of the microhardness tests were consistent with the results of the mechanical properties tests.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kruger, K.L. HAYNES 282 alloy. In Materials for Ultra-Supercritical and Advanced Ultra-Supercritical Power Plants, 1st ed.; Di Gianfrancesco, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 511–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, J.; Jones, J.; Barnard, N.; Clark, D.; Whittaker, M.; Lancaster, R. The effects of energy density and heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of laser additive manufactured Haynes 282. Mater. Des. 2021, 205, 109725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigirisetty, M. Role of Additive Manufacturing in Investment Casting Process. IJRASET 2022, 10, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, S.; Smith, P.; Xu, Z.; Gaspard, G.; Hyde, C.J.; Wits, W.W.; Ashcroft, I.A.; Chen, H.; Clare, A.T. Powder Bed Fusion of nickel-based superalloys: A review. Int. J. Mach. 2021, 165, 103729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, M.; Salem, A.; Beuth, J.; Harrysson, O.; Lewandowski, J.J. Overview of Materials Qualification Needs for Metal Additive Manufacturing. JOM 2016, 68, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DebRoy, T.; Wei, H.L.; Zuback, J.S.; Mukherjee, T.; Elmer, J.W.; Milewski, J.O.; Beese, A.M.; Wilson-Heid, A.; De, A.; Zhang, W. Additive manufacturing of metallic components—Process, structure and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 92, 112–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetharaman, S.; Krishnan, M.; Wen, F.; Niaz, K.; Lai, G. Research updates on the additive manufacturing of nickel based alloys. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, USA, 8–10 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, R.; Brøtan, V.; Carvalho, P.A.; Reiersen, M.; Graff, J.S.; Sunding, M.F.; Åsebø Berg, O.; Diplas, S.; Azar, A.S. Roadmap for additive manufacturing of HAYNES® 282® superalloy by laser beam powder bed fusion (PBF-LB) technology. Mater. Des. 2021, 204, 109656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, A.; Dinda, G.P. Microstructure and mechanical properties of direct laser metal deposited Haynes 282 superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 748, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unocic, K.A.; Kirka, M.M.; Cakmak, E.; Greeley, D.; Okello, A.O.; Dryepondt, S. Evaluation of additive electron beam melting of haynes 282 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiaasiaan, R.; Ahmad, N.; Gradl, P.R.; Shao, S.; Shamsaei, N. Additively manufactured Haynes 282: Effect of unimodal vs. bimodal γʹ- microstructure on mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 831, 142234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaafi Shaikh, A.; Schulz, F.; Minet-Lallemand, K.; Hryha, E. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Haynes 282 superalloy produced by laser powder bed fusion. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 26, 102038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, O.; Vegard, B.; Amin, A.; Olav Åsebø, B. Processing of Haynes® 282® Alloy by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Technology. In Proceedings of the TMS 2019 148th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings, San Antonio, TX, USA, 10–14 March 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Fernandez-Zelaia, P.; Hu, X.; Kirka, M.M. Effect of microstructure on fatigue crack propagation in additive manufactured nickel-based superalloy Haynes 282: An experiment and crystal plasticity study. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 9741–9768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Zelaia, P.; Rojas, J.O.; Ferguson, J.; Dryepondt, S.; Kirka, M.M. Fatigue crack growth resistance of a mesoscale composite microstructure Haynes 282 fabricated via electron beam melting additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 9866–9884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, Z.; Agrawal, A.K.; Rankouhi, B.; Magnin, C.; Anderson, M.H.; Pfefferkorn, F.E.; Thoma, D.J. A High-Throughput Method to Define Additive Manufacturing Process Parameters: Application to Haynes 282. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2022, 53, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagh, D.; Subrata, N.; Sundar, A.; Keng, H. Effect of Post Processing Heat Treatment Routes on Microstructure and Mechanical Property Evolution of Haynes 282 Ni-Based Superalloy Fabricated with Selective Laser Melting (SLM). Metals 2020, 10, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirka, M.M.; Unocic, K.A.; Kruger, K.L.; Forsythe, A.K. Process Development for Haynes® 282® Using Additive Manufacturing; Technical Report; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem, A.S.; Patel, F.; Minhas, N.; Malkawi, A.; Aleid, Z.; Ali Ehsan, M.; Sharrofna, H.; Al Ghanim, A. Comparative evaluation of thermal and mechanical properties of nickel alloy 718 prepared using selective laser melting, spark plasma sintering, and casting methods. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snopiński, P.; Woźniak, A.; Pagáč, M. Microstructural Evolution, Hardness, and Strengthening Mechanisms in SLM AlSi10Mg Alloy Subjected to Equal-Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP). Materials 2021, 14, 7598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ulbrich.com/alloys/haynes-282-alloy-282-wire-uns-n07208/ (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Majchrowicz, K.; Pakieła, Z.; Brynk, T.; Romelczyk-Baishya, B.; Płocińska, M.; Kurzynowski, T.; Chlebus, E. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-Re manufactured by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 765, 138290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brynk, T.; Pakieła, Z.; Ludwichowska, K.; Romelczyk, B.; Molak, R.M.; Płocińska, M.; Kurzac, J.; Kurzynowski, T.; Chlebus, E. Fatigue crack growth rate and tensile strength of Re modified Inconel 718 produced by means of selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 698, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehoff, R.; Duty, C.; Peter, W.; Yamamoto, Y.; Chen, W.; Blue, C.; Tallman, C. Case study: Additive manufacturing of aerospace brackets. Adv. Mater. Process. 2013, 171, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mumtaz, K.; Hopkinson, N. Top surface and side roughness of Inconel 625 parts processed using selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2009, 15, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strano, G.; Hao, L.; Everson, R.M.; Evans, K.E. Surface roughness analysis, modelling and prediction in selective laser melting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majchrowicz, K.; Pakieła, Z.; Kamiński, J.; Płocińska, M.; Kurzynowski, T.; Chlebus, E. The effect of rhenium addition on microstructure and corrosion resistance of Inconel 718 processed by selective laser melting. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 6479–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y. Microstructural Evolution of Large As-cast Haynes 282 at Elevated Temperature. Crystals 2021, 11, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Ni | Cr | Co | Mo | Ti | Al | Fe | Mg | Si | C | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <57 | 20 | 10 | 8.5 | 1.2 | 1.5 | <1.5 | 0.3 | <0.15 | 0.06 | 0.005 |
| No | Manufacturing Method | Orientation | Deformation [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DMLS | X-Y | 0 |
| 2 | DMLS | X-Y | 20 |
| 3 | DMLS | X-Y | 40 |
| 4 | DMLS | X-Y | 60 |
| 5 | DMLS | Y-Z | 0 |
| 6 | DMLS | Y-Z | 20 |
| 7 | DMLS | Y-Z | 40 |
| 8 | DMLS | Y-Z | 60 |
| 9 | Cast | - | 0 |
| 10 | Cast | - | 20 |
| 11 | Cast | - | 40 |
| 12 | Cast | - | 60 |
| Manufacturing Method | Building Orientation | Deformation Degree (%) | YS (MPa) | UTS (MPa) | A (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMLS | X-Y | 0 | 594 ± 8 | 835 ± 7 | 36.9 ± 3.4 |
| 20 | 863 ± 16 | 1019 ± 24 | 13.0 ± 2.4 | ||
| 40 | 1036 ± 29 | 1141 ± 18 | 8.6 ± 1.4 | ||
| 60 | 1223 ± 18 | 1345 ± 9 | 7.7 ± 0.2 | ||
| Y-Z | 0 | 656 ± 18 | 879 ± 26 | 31.7 ± 3.1 | |
| 20 | 968 ± 22 | 1094 ± 12 | 11.5 ± 1.1 | ||
| 40 | 1074 ± 18 | 1235 ± 13 | 5.7 ± 0.9 | ||
| 60 | 1265 ± 42 | 1418 ± 48 | 6.7 ± 1.4 | ||
| Casting | - | 0 | 421 ± 8 | 742 ± 28 | 35.0 ± 1.7 |
| 20 | 902 ± 21 | 1022 ± 19 | 10.7 ± 0.3 | ||
| 40 | 1043 ± 9 | 1164 ± 19 | 7.1 ± 1.1 | ||
| 60 | 1261 ± 42 | 1412 ± 53 | 6.2 ± 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sitek, R.; Puchlerska, S.; Nejman, I.; Majchrowicz, K.; Pakieła, Z.; Żaba, K.; Mizera, J. The Impact of Plastic Deformation on the Microstructure and Tensile Strength of Haynes 282 Nickel Superalloy Produced by DMLS and Casting. Materials 2022, 15, 7545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217545
Sitek R, Puchlerska S, Nejman I, Majchrowicz K, Pakieła Z, Żaba K, Mizera J. The Impact of Plastic Deformation on the Microstructure and Tensile Strength of Haynes 282 Nickel Superalloy Produced by DMLS and Casting. Materials. 2022; 15(21):7545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217545
Chicago/Turabian StyleSitek, Ryszard, Sandra Puchlerska, Ilona Nejman, Kamil Majchrowicz, Zbigniew Pakieła, Krzysztof Żaba, and Jarosław Mizera. 2022. "The Impact of Plastic Deformation on the Microstructure and Tensile Strength of Haynes 282 Nickel Superalloy Produced by DMLS and Casting" Materials 15, no. 21: 7545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217545
APA StyleSitek, R., Puchlerska, S., Nejman, I., Majchrowicz, K., Pakieła, Z., Żaba, K., & Mizera, J. (2022). The Impact of Plastic Deformation on the Microstructure and Tensile Strength of Haynes 282 Nickel Superalloy Produced by DMLS and Casting. Materials, 15(21), 7545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217545







