Influence Mechanism of Ageing Parameters of Cu-Cr-Zr Alloy on Its Structure and Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
3. Results
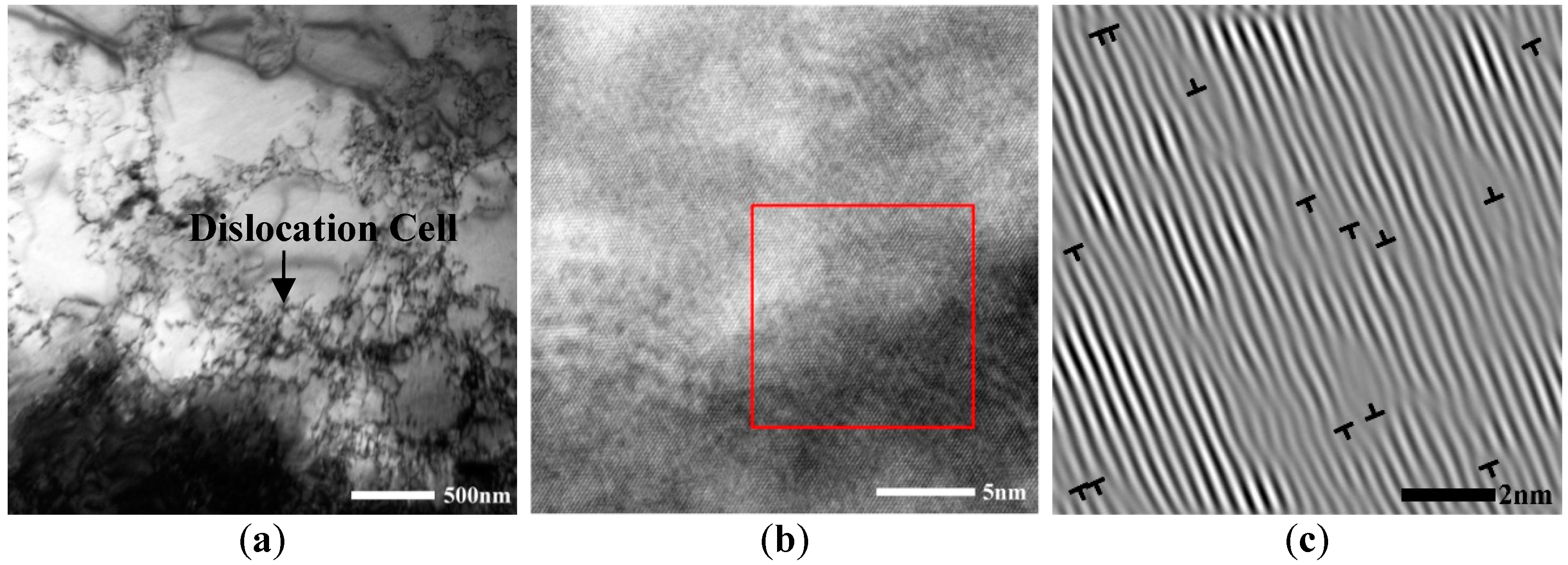
3.1. Influence Laws of Ageing Temperature on Ageing Structures
3.2. Influence Laws of Holding Time on Ageing Structures
4. Discussion
4.1. Nucleation Mechanism of Precipitated Phase in the Cu-Cr-Zr Alloy
4.2. Growth Mechanism of Precipitated Phases in the Cu-Cr-Zr Alloy
4.3. Influence Laws of Cu-Cr-Zr Alloy Structure on Its Properties
5. Conclusions
- With the increase in ageing temperature and holding time, the percentage of Cr precipitated phase in the microstructure increases, and the dislocation content decreases continuously. The tensile strength increases first and then decreases in an inverted V shape. The electrical conductivity shows a rising trend with then a decrease of the increase;
- The tensile strength of the Cu-Cr-Zr alloy reached a peak (359 ± 2 MPa) and the electrical conductivity was 91.9 ± 0.7% IACS after the ageing treatment at 450 °C for 60 min;
- The precipitated Cr phase has two structures, FCC and BCC. The FCC Cr phases are transformed into BCC Cr phases. The FCC Cr precipitated phases nucleate first in regions with high dislocation densities, basically maintaining an N–W orientation relationship with the substrate. The BCC Cr phases basically maintain a K–S orientation relationship with the substrate. The precipitated Zr phase is the Cu3Zr phase, which basically maintains a K–S orientation relationship with the substrate.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, Y.B.; Zhou, Y.J.; Song, K.X.; Huang, T.; Hui, D.; Liu, H.T.; Cheng, C.; Yang, J.Z.; Niu, L.Y.; Guo, H.W. Zr-containing precipitate evolution and its effect on the mechanical properties of Cu-Cr-Zr alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. JMRT 2021, 14, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.C.; Xie, W.B.; Chen, H.M.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. Effect of micro-alloying element Ti on mechanical properties of Cu-Cr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 852, 157004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.D.; Xu, S.; Li, W.; Xie, J.X.; Zhao, H.B.; Pan, Z.J. Effect of rolling and aging processes on microstructure and properties of Cu-Cr-Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2017, 700, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, R.G.; Zou, C.L.; Chen, Z.N.; Wen, W.; Wang, T.M.; Yin, G.M. Effect of direct current pulses on mechanical and electrical properties of aged Cu-Cr-Zr alloys. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobatkin, S.V.; Gubicza, J.; Shangina, D.V.; Bochvar, N.R.; Tabachkova, N.Y. High strength and good electrical conductivity in Cu-Cr alloys processed by severe plastic deformation. Mater. Lett. 2015, 153, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Fu, H.D.; Wang, Y.T.; Xie, J.X. Effect of Ag addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-Cr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2018, 726, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.P.; Zhu, Y.J.; Yang, X.; Tong, W.P. Investigation on the microstructure and properties of Cu-Cr alloy prepared by in-situ synthesis method. Vacuum 2018, 149, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knights, R.W.; Wilkes, P. Precipitation of chromium in copper and copper-nickel base alloys. Metall. Trans. 1973, 4, 2389–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Nakazawa, H.; Kato, M.; Dahmen, U. Crystallography and morphology of nanosized Cr particles in a Cu—0.2% Cr alloy. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.J.; Singh, B.N.; Tähtinen, S. Effect of heat treatments on precipitate microstructure and mechanical properties of a CuCrZr alloy. J. Nucl. Mater. 2007, 367–370, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.D.; Nikolaev, A.K.; Kalinin, G.M.; Rodin, M.E. Effect of heat treatments on the properties of CuCrZr alloys. J. Nucl. Mater. 2002, 307, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.D.; Zhang, W.; Kang, Z.Y.; Jia, Y.L.; Wu, Y.F.; Zhang, R.; Xu, G.Y.; Wang, M.P. High strength and high electrical conductivity Cu-Cr system alloys manufactured by hot rolling-quenching process and thermomechanical treatments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2012, 538, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Volinsky, A.A.; Tran, H.T.; Chai, Z.; Liu, P.; Tian, B.H.; Liu, Y. Aging behavior and precipitates analysis of the Cu-Cr-Zr-Ce alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2016, 650, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Xie, H.; Huang, G.; Xu, G.; Yin, X.; Feng, X.; Mi, X.; Yang, Z. The phase transformation and strengthening of a Cu-0.71 wt% Cr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 708, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, A.; Nie, J.F.; Wei, K.; Kang, H.J.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhao, Y.H. Optimization of strength, ductility and electrical conductivity of a Cu-Cr-Zr alloy by cold rolling and aging treatment. Vacuum 2019, 167, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.P.; Xu, N.; Gong, M.Y.; Li, P.; Zhou, H.B.; Tong, W.P.; Wilde, G. Improved tensile strength and electrical conductivity in Cu-Cr-Zr alloys by controlling the precipitation behavior through severe warm rolling. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 12499–12512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.J.; Hamalainen, M. A Theoretical-Study of the Phase-Equilibria in the Cu-Cr-Zr System. J. Alloys Compd. 1995, 220, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.J.; Haemaelaeinen, M.; Lilius, K. Phase relationships in Cu-rich corner of the Cu-Cr-Zr phase diagram. Scr. Metall. Et Mater. 1995, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, G.M.; Fedorov, V.N.; Rodnyanskaya, A.L. Phase diagram of the Cu−Cr system. Izv. VUZ Tsvetn. Met. 1977, 3, 84–86. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.Y.; Shen, B.; Yu, F.X. Precipitation in a Cu–Cr–Zr–Mg alloy during aging. Mater. Charact. 2013, 81, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherly, G.C.; Humble, P.; Borland, D. Precipitation in a Cu-0.55 wt.% Cr alloy. Acta Metall. 1979, 27, 1815–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovich, A.; Sufiiarov, V.; Polozov, I.; Borisov, E.; Masaylo, D.; Orlov, A. Microstructure and mechanical properties of additive manufactured copper alloy. Mater. Lett. 2016, 179, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Xie, H.; Huang, G.; Li, Y.; Yin, X.; Feng, X.; Mi, X.; Yang, Z. The phase transformation and its effects on properties of a Cu−0.12 wt% Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 633, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chbihi, A.; Sauvage, X.; Blavette, D. Atomic scale investigation of Cr precipitation in copper. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 4575–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shangina, D.V.; Bochvar, N.R.; Gorshenkov, M.V.; Yanar, H.; Purcek, G.; Dobatkin, S.V. Influence of microalloying with zirconium on the structure and properties of Cu-Cr alloy after high pressure torsion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2016, 650, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.X.; Tao, N.R.; Lu, K. A high strength and high electrical conductivity bulk CuCrZr alloy with nanotwins. Scr. Mater. 2015, 99, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.H.; Liu, P.; Li, H.J.; Ren, F.Z.; Dong, Q.M. Phase transformation in Cu-Cr-Zr-Mg alloy. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 4963–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuxiang, H.; Jusheng, M.; Honglong, N.; Zhiting, G.; Chao, L.; Shumei, G.; Xuetao, Y.; Tao, W.; Hong, L.; Huafen, L. Analysis of phases in a Cu–Cr–Zr alloy. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarjuna, S.; Babu, U.C.; Ghosal, P. Effect of cryo-rolling on age hardening of Cu-1.5Ti alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2008, 491, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tao, N.R.; Lu, K. Mechanical properties and rolling behaviors of nano-grained copper with embedded nano-twin bundles. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 2429–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Kang, H.; Chen, Z.; Fan, G.; Zou, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Y.; Jie, J.; Cao, Z.; et al. A promising structure for fabricating high strength and high electrical conductivity copper alloys. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.C.; Karthick, N.K.; Rao, G.S.; Jha, A.K.; Pant, B.; Cherian, R.M. High Strength, Utilizable Ductility and Electrical Conductivity in Cold Rolled Sheets of Cu-Cr-Zr-Ti Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzwarth, U.; Stamm, H. The precipitation behaviour of ITER-grade Cu–Cr–Zr alloy after simulating the thermal cycle of hot isostatic pressing. J. Nucl. Mater. 2000, 279, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Q.; Xie, S.S.; Mi, X.J.; Wu, P.Y. Phase and microstructure analysis of Cu-Cr-Zr alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2007, 23, 795. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.H.; Wang, H.L.; Zheng, D.D.; Shan, J.F.; Chang, Y.Q. Microstructures and mechanical properties of the novel CuCrZrFeTiY alloy for fusion reactor. J. Nucl. Mater. 2020, 532, 152063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Zhou, H.L.; Zhang, T.; Bi, L.M.; Tian, W.; Fu, S.L.; Li, W.; Liu, X.K.; Ma, F.C.; Zhang, K.; et al. Mechanism of interaction between the Cu/Cr interface and its chemical mixing on tensile strength and electrical conductivity of a Cu-Cr-Zr alloy. Mater. Des. 2019, 180, 107976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.B.; Hou, M.L.; Yang, H.Y.; Xie, H.B.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.D.; Feng, Q.; Wang, L.T.; Meng, L.; Wang, H.T. In-situ TEM study of the dynamic interactions between dislocations and precipitates in a Cu-Cr-Zr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 765, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, I.S.; Dey, G.K.; Kulkarni, U.D.; Banerjee, S. Microstructure and properties of a Cu–Cr–Zr alloy. J. Nucl. Mater. 2001, 299, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangina, D.V.; Bochvar, N.R.; Morozova, A.I.; Belyakov, A.N.; Kaibyshev, R.O.; Dobatkin, S.V. Effect of chromium and zirconium content on structure, strength and electrical conductivity of Cu-Cr-Zr alloys after high pressure torsion. Mater. Lett. 2017, 199, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Ageing Temperature/°C | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 |
| Lattice Constant/nm | 0.42338 | 0.41083 | 0.39517 | 0.38714 | 0.37517 |
| Dislocation Density/(1015·m−2) | 2.439 | 2.385 | 2.185 | 2.051 | 1.639 |
| Ageing Time/min | 15 | 30 | 60 | 90 | 120 |
| Lattice Constant/nm | 0.38925 | 0.38714 | 0.37604 | 0.37191 | 0.36204 |
| Dislocation Density/(1015·m−2) | 2.376 | 2.051 | 1.910 | 1.376 | 1.132 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Dang, S. Influence Mechanism of Ageing Parameters of Cu-Cr-Zr Alloy on Its Structure and Properties. Materials 2022, 15, 7605. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217605
Ma Y, Chen H, Li H, Dang S. Influence Mechanism of Ageing Parameters of Cu-Cr-Zr Alloy on Its Structure and Properties. Materials. 2022; 15(21):7605. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217605
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yuxia, Huiqin Chen, Hui Li, and Shue Dang. 2022. "Influence Mechanism of Ageing Parameters of Cu-Cr-Zr Alloy on Its Structure and Properties" Materials 15, no. 21: 7605. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217605
APA StyleMa, Y., Chen, H., Li, H., & Dang, S. (2022). Influence Mechanism of Ageing Parameters of Cu-Cr-Zr Alloy on Its Structure and Properties. Materials, 15(21), 7605. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217605





