Comparative Study between Two Simple Synthesis Methods for Obtaining Green Gold Nanoparticles Decorating Silica Particles with Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extract Preparation
2.3. Synthesis-1 of Silica-Gold Nanoparticles
2.4. Synthesis-2 of Silica-Gold Nanoparticles
2.5. Characterization
2.5.1. Size and Morphology
2.5.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.5.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
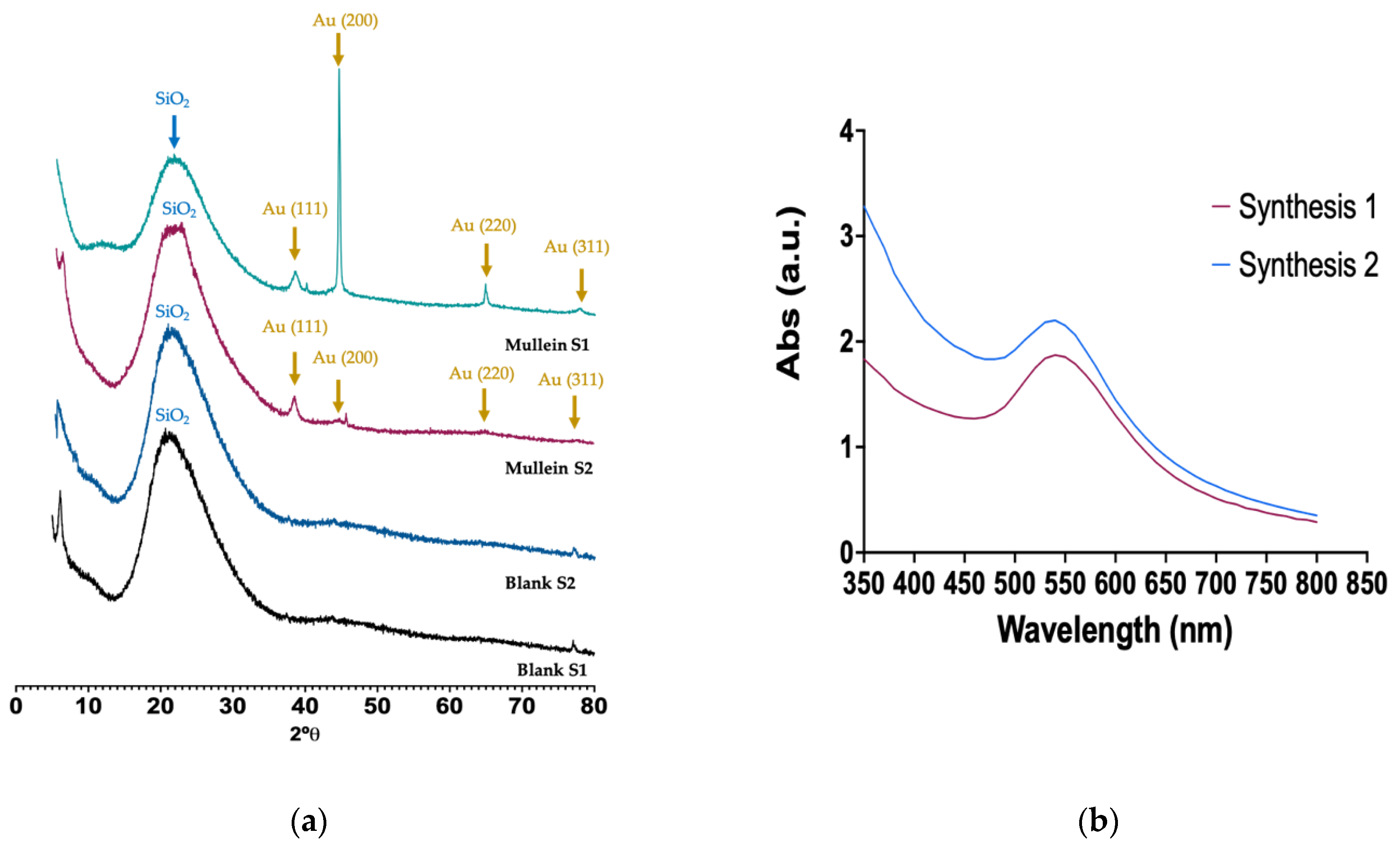
2.5.4. UV-Vis Analysis
2.5.5. Stability
2.5.6. Antibacterial Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Size and Morphology
3.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
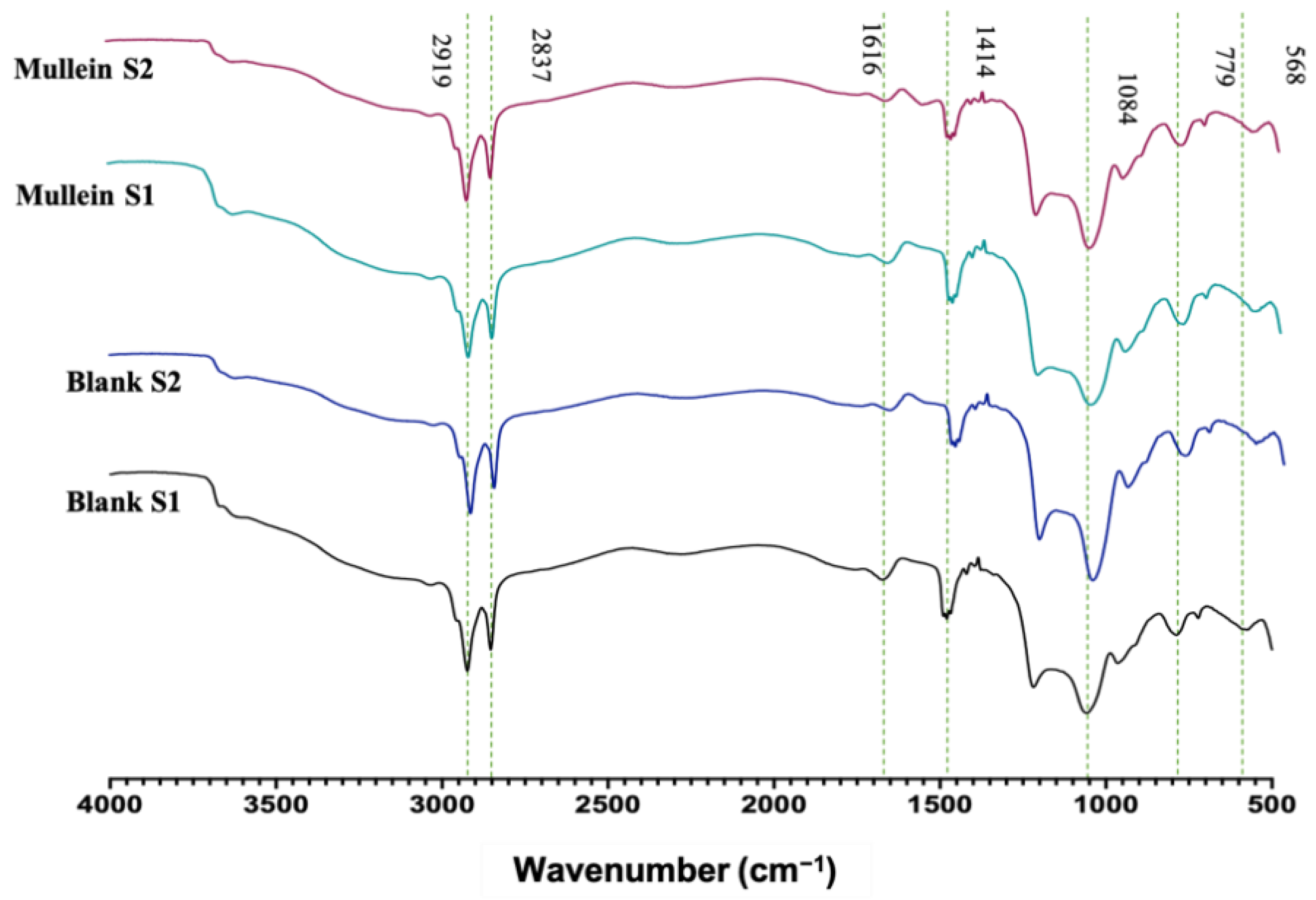
3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
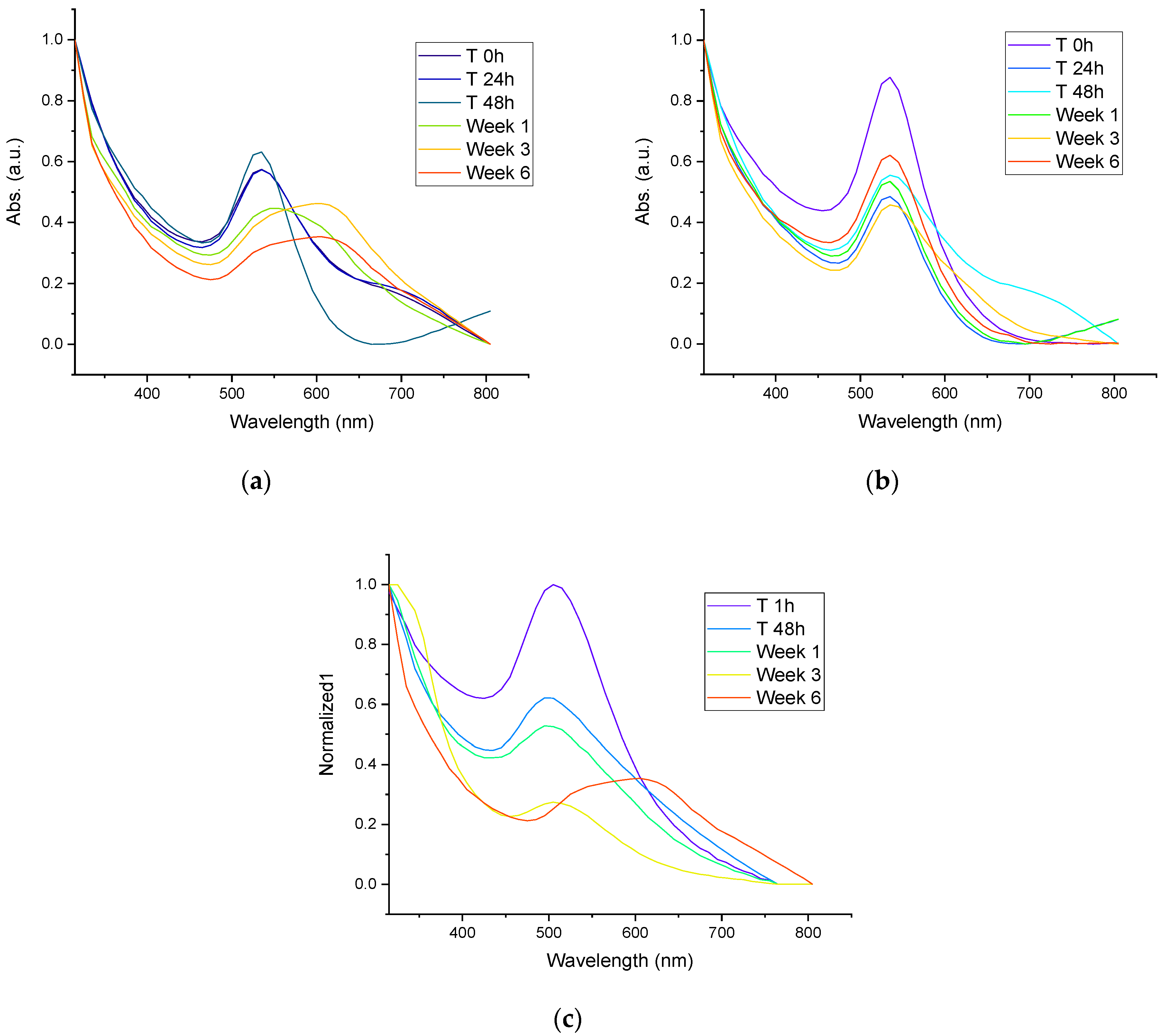
3.4. Stability of AuNPs
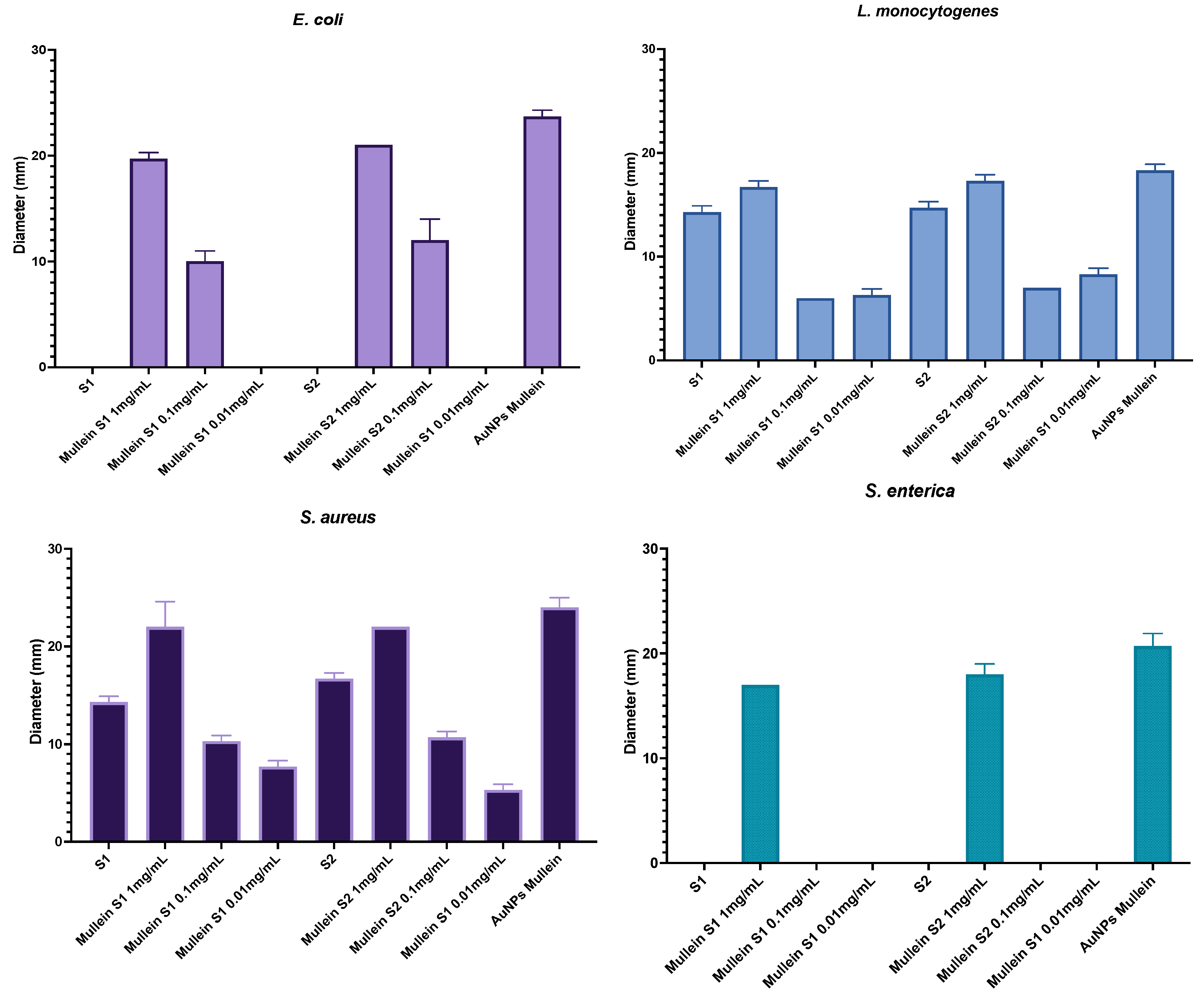
3.5. Antibacterial Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thangamani, N.; Bhuvaneshwari, N. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Simarouba glauca leaf extract and their biological activity of micro-organism. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 732, 136587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, Y.; Kaur, G.; Kumar, R.; Singh, S.K.; Gulati, M.; Khursheed, R.; Clarisse, A.; Gowthamarajan, K.; Karri, V.N.R.; Mahalingam, R.; et al. Gold nanoparticles: New routes across old boundaries. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 274, 102037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Ballesteros, N.; Prado-López, S.; Rodríguez-González, J.; Lastra, M.; Rodríguez-Argüelles, M. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using brown algae Cystoseira baccata: Its activity in colon cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 153, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, K.M.; Quezada-Cervantes, C.T.; Hernández-Iturriaga, M.; Luna-Bárcenas, G.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Mendoza, S. Fruit peels waste for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial activity against foodborne pathogens. LWT 2019, 103, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Jin, X.; Tang, J.; Tian, X.; Tan, H.; Zhang, X. Factors Influencing Aggregation of Gold Nanoparticles in Whole Blood. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 3762–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-L.; Lee, F.-C.; Tang, T.-Y.; Zhou, C.; Tsai, D.-H. Assembly of functional gold nanoparticle on silica microsphere. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 469, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbaghian, M.; Babalou, A.; Hadi, P.; Jannatdoust, E. A Parametric Study of the Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticles via Sol-Gel Precipitation Method. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 6, 104–113. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.D.; Kim, H.T. Formation of Silica Nanoparticles by Hydrolysis of TEOS Using a Mixed Semi-Batch/Batch Method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2002, 25, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Lee, J.-H.; Cho, E.-B. Recent Trends in Morphology-Controlled Synthesis and Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Barnes, J.C.; Bosoy, A.; Stoddart, J.F.; Zink, J.I. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2590–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Crucho, C.I.C.; Alves, S.P.C.; Baleizão, C.; Farinha, J.P.S. Hybrid Mesoporous Nanoparticles for pH-Actuated Controlled Release. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ab Rahman, I.; Padavettan, V. Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticles by Sol-Gel: Size-Dependent Properties, Surface Modification, and Applications in Silica-Polymer Nanocomposites—A Review. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cong, V.T.; Ganbold, E.-O.; Saha, J.K.; Jang, J.; Min, J.; Choo, J.; Kim, S.; Song, N.W.; Son, S.J.; Lee, S.B.; et al. Gold Nanoparticle Silica Nanopeapods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3833–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, L.L.; Porcel, J.M.; Aragón, F.F.H.; Pacheco-Salazar, D.G.; Sousa, M.H. Simple synthesis of gold-decorated silica nanoparticles by in situ precipitation method with new plasmonic properties. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, M.J.; Guzmán, L.; Corvalán, A.H.; Kogan, M.J. Gold@Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Oligonucleotides: A Prominent Tool for the Detection of the Methylated Reprimo Gene in Gastric Cancer by Dynamic Light Scattering. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soto, K.M.; Luzardo-Ocampo, I.; López-Romero, J.M.; Mendoza, S.; Loarca-Piña, G.; Rivera-Muñoz, E.M.; Manzano-Ramírez, A. Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized with Common Mullein (Verbascum thapsus) and Castor Bean (Ricinus communis) Ethanolic Extracts Displayed Antiproliferative Effects and Induced Caspase 3 Activity in Human HT29 and SW480 Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, M.S.; Martínez, A.G.; Cucinotta, F. Facile Strategy for the Synthesis of Gold@Silica Hybrid Nanoparticles with Controlled Porosity and Janus Morphology. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, J.B.; Cockerill, F.R.; Bradford, P.A.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 27th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standars Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Satpathy, S.; Patra, A.; Ahirwar, B.; Hussain, M.D. Process optimization for green synthesis of gold nanoparticles mediated by extract of Hygrophila spinosa T. Anders and their biological applications. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostructures 2020, 121, 113830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajdari, N.; Vyas, C.; Bogan, S.L.; Lwaleed, B.A.; Cousins, B.G. Gold nanoparticle interactions in human blood: A model evaluation. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirthalingam, T.; Kalirajan, J. Use of Silica-Gold Core Shell Structured Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery System. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pajerski, W.; Ochonska, D.; Brzychczy-Wloch, M.; Indyka, P.; Jarosz, M.; Golda-Cepa, M.; Sojka, Z.; Kotarba, A. Attachment efficiency of gold nanoparticles by Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains governed by surface charges. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2019, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, G.; Agrawal, R. Janus Nanoparticles: Recent Advances in Their Interfacial and Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1738–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, A.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, C.; Yu, B.; Zhao, N.; Xu, F.-J. Silica-Coated Gold–Silver Nanocages as Photothermal Antibacterial Agents for Combined Anti-Infective Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17177–17183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobed, A.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Seidi, F. Anti-bacterial activity of gold nanocomposites as a new nanomaterial weapon to combat photogenic agents: Recent advances and challenges. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 34688–34698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turker, A.U.; Camper, N. Biological activity of common mullein, a medicinal plant. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 82, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.; Ullah, R.; Wahab, Z.; Uddin, M.N. Antimicrobial effects of Verbascum thapsus L. leaf extracts. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2020, 49, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


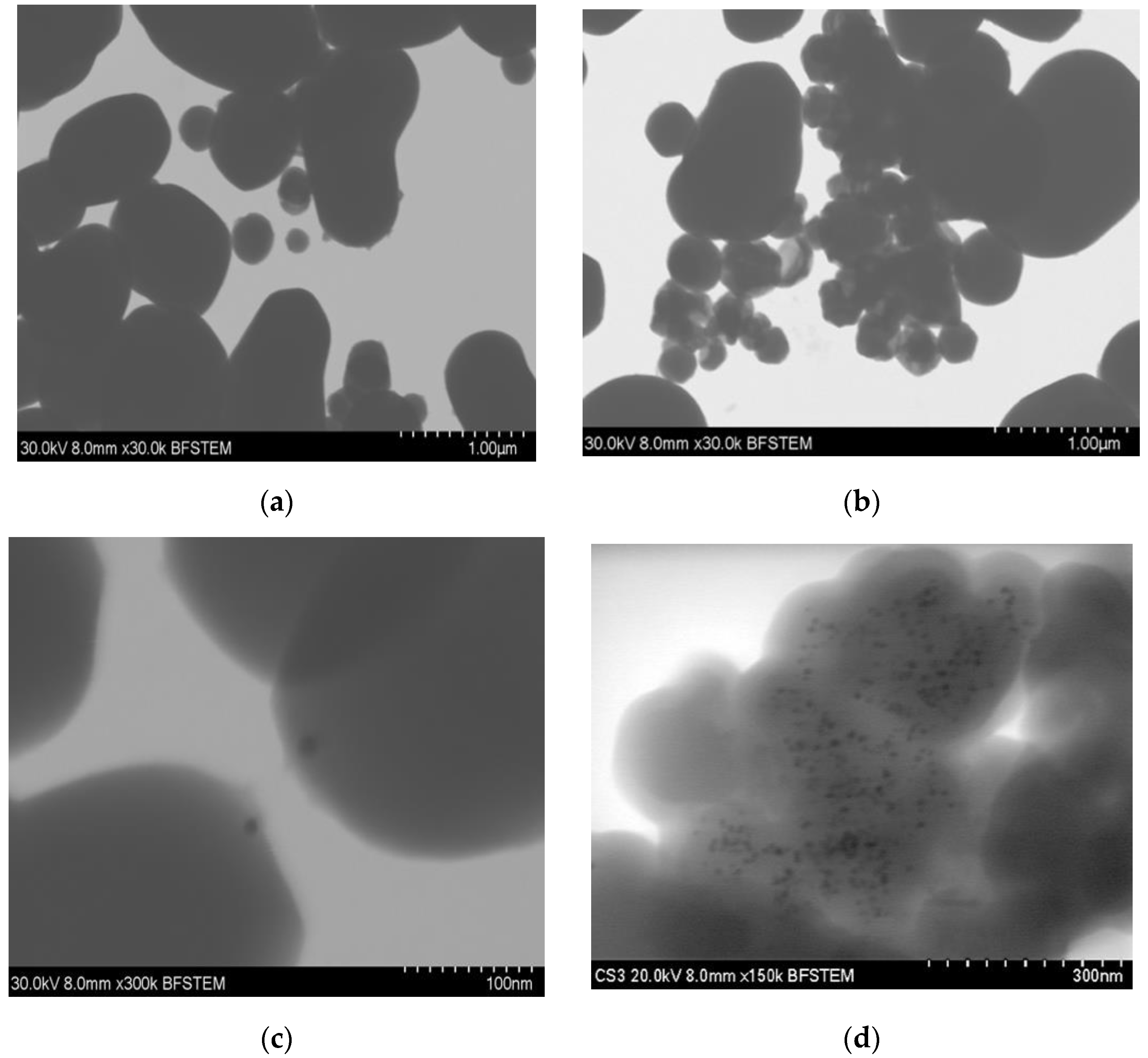
| Sample | Diameter (nm) | Si (%) | O (%) | Au (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank S1 | 196.96 ± 9.19 | 90.83 ± 0.62 a | 9.16 ± 0.60 a | nd |
| Mullein S1-AuNPs | 116.22 ± 2.04 * | 89.16 ± 2.34 a | 8.53 ± 1.96 a | 2.33 ± 0.43 c |
| Blank S2 | 560.32 ± 32.82 | 80.33 ± 0.88 a | 19.66 ± 0.88 a | nd |
| Mullein S2-AuNPs | 263.99 ± 18.65 * | 70 ± 7.08 a | 20.16 ± 4.1 a | 7.73 ± 1.86 a |
| Sample | E. coli | L. monocytogenes | S. aureus | S. enterica |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank S1 | 0.0 ± 0.0 *d | 14.3 ± 0.6 b | 14.3 ± 0.6 b | 0.0 ± 0.0 *b |
| Mullein S1-AuNPs | 19.7 ± 0.6 b | 16.7 ± 0.6 a | 22.0 ± 2.6 a | 17.0 ± 0.0 a |
| Blank S2 | 0.0 ± 0.0 *d | 14.7 ± 0.6 b | 16.7 ± 0.6 b | 0.0 ± 0.0 *b |
| Mullein S2-AuNPs | 21.0 ± 0.0 a | 17.3 ± 0.6 a | 22.0 ± 0.0 a | 18.0 ± 1.0 a |
| Mullein AuNPs | 23.7 ± 0.6 a | 18.3 ± 0.6 a | 24.0 ± 1.0 a | 20.7 ± 1.2 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soto, K.M.; Gódinez-Oviedo, A.; López-Romero, J.M.; Rivera-Muñoz, E.M.; López-Naranjo, E.J.; Mendoza-Díaz, S.; Manzano-Ramírez, A. Comparative Study between Two Simple Synthesis Methods for Obtaining Green Gold Nanoparticles Decorating Silica Particles with Antibacterial Activity. Materials 2022, 15, 7635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217635
Soto KM, Gódinez-Oviedo A, López-Romero JM, Rivera-Muñoz EM, López-Naranjo EJ, Mendoza-Díaz S, Manzano-Ramírez A. Comparative Study between Two Simple Synthesis Methods for Obtaining Green Gold Nanoparticles Decorating Silica Particles with Antibacterial Activity. Materials. 2022; 15(21):7635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217635
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoto, Karen M., Angelica Gódinez-Oviedo, José. M. López-Romero, Eric. M. Rivera-Muñoz, Edgar Jose López-Naranjo, Sandra Mendoza-Díaz, and Alejandro Manzano-Ramírez. 2022. "Comparative Study between Two Simple Synthesis Methods for Obtaining Green Gold Nanoparticles Decorating Silica Particles with Antibacterial Activity" Materials 15, no. 21: 7635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217635
APA StyleSoto, K. M., Gódinez-Oviedo, A., López-Romero, J. M., Rivera-Muñoz, E. M., López-Naranjo, E. J., Mendoza-Díaz, S., & Manzano-Ramírez, A. (2022). Comparative Study between Two Simple Synthesis Methods for Obtaining Green Gold Nanoparticles Decorating Silica Particles with Antibacterial Activity. Materials, 15(21), 7635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217635








