Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite Application in Wastewater Treatment: Methylene Blue, Zinc and Cadmium Abatement Tests and Kinetic Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Adsorbent Materials
2.2. Structural and Textural Characterizations
2.3. Abatement Tests
2.3.1. Methylene Blue Abatement with Clinoptilolite
2.3.2. Methylene Blue Abatement with Activated Charcoal
2.3.3. Abatement Tests with Methylene Blue and Metal Cations
3. Results
3.1. Structural and Textural Properties
3.2. Abatement Tests
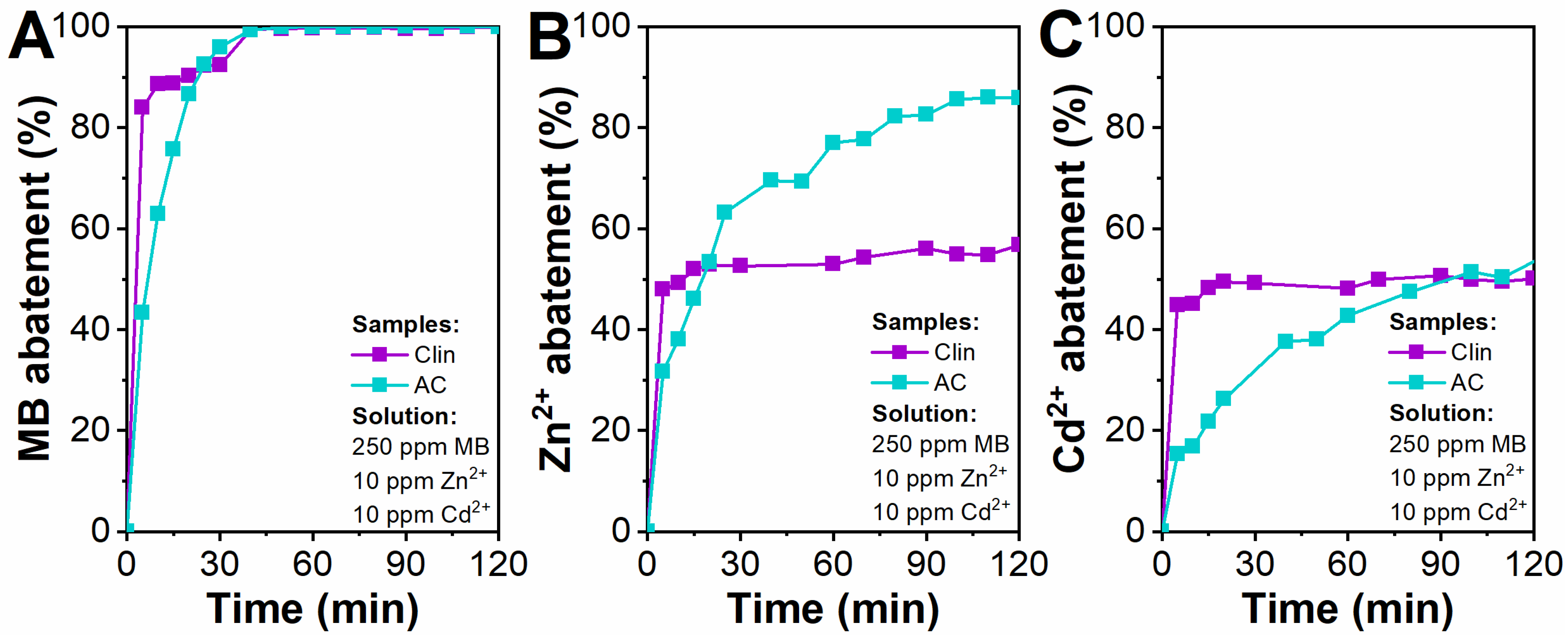
3.2.1. Methylene Blue Abatement with Clinoptilolite and Activated Charcoal
3.2.2. Methylene Blue, Zn2+ and Cd2+ Abatement with Clinoptilolite and Activated Charcoal
3.3. Abatement Kinetics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adhikari, B.; Palui, G.; Banerjee, A. Self-Assembling Tripeptide Based Hydrogels and Their Use in Removal of Dyes from Waste-Water. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 3452–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, G.; Meehan, C.; Conneely, A.; Kirby, N.; Robinson, T.; Nigam, P.; Banat, I.M.; Marchant, R.; Smyth, W.F. Microbial Decolourisation and Degradation of Textile Dyes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 56, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, C.I.; Lloyd, J.R.; Guthrie, J.T. The Removal of Colour from Textile Wastewater Using Whole Bacterial Cells: A Review. Dye. Pigment. 2003, 58, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosa, M.; Piumetti, M.; Galletti, C.; Russo, N.; Fino, D.; Bensaid, S.; Mancini, G.; Freyria, F.S.; Saracco, G. A Novel Fe-Containing Clinoptilolite for Wastewater Remediation: Degradation of Azo-Dyes Acid Orange 7 by H2O2 and Ascorbic Acid. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 159, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Madan, S.; Madan, R. Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater by Adsorption. In Heavy Metals; Nazal, M.K., Zhao, H., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021; pp. 169–178. ISBN 978-1-83968-122-6. [Google Scholar]
- Łach, M.; Grela, A.; Pławecka, K.; Guigou, M.D.; Mikuła, J.; Komar, N.; Bajda, T.; Korniejenko, K. Surface Modification of Synthetic Zeolites with Ca and HDTMA Compounds with Determination of Their Phytoavailability and Comparison of CEC and AEC Parameters. Materials 2022, 15, 4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piumetti, M.; Freyria, F.S.; Armandi, M.; Geobaldo, F.; Garrone, E.; Bonelli, B. Fe- and V-Doped Mesoporous Titania Prepared by Direct Synthesis: Characterization and Role in the Oxidation of AO7 by H2O2 in the Dark. Catal. Today 2014, 227, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyria, F.S.; Compagnoni, M.; Ditaranto, N.; Rossetti, I.; Piumetti, M.; Ramis, G.; Bonelli, B. Pure and Fe-Doped Mesoporous Titania Catalyse the Oxidation of Acid Orange 7 by H2O2 under Different Illumination Conditions: Fe Doping Improves Photocatalytic Activity under Simulated Solar Light. Catalysts 2017, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banat, I.M.; Nigam, P.; Singh, D.; Marchant, R. Microbial decolorization of textile-dye-containing effluents: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 1996, 58, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xue, M.; Huang, K.; Liu, Z. Textile Dyeing Wastewater Treatment. Adv. Treat. Text. Effl. 2011, 5, 91–116. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.N.V.R.; Sridhari, T.R.; Bhavani, K.D.; Dutta, P.K. Trends in Color Removal from Textile Mill Effluents. Colourage 1998, 45, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Yang, L. The Adsorption of Basic Dyes from Aqueous Solution on Modified Peat-Resin Particle. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosa, M.; Piumetti, M.; Davarpanah, E.; Moncaglieri, G.; Bensaid, S.; Fino, D. Natural Zeolites as Sustainable Materials for Environmental Processes. In Nanostructured Catalysts for Environmental Applications; Piumetti, M., Bensaid, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 367–381. ISBN 978-3-030-58934-9. [Google Scholar]
- Dosa, M.; Piumetti, M.; Bensaid, S.; Russo, N.; Baglieri, O.; Miglietta, F.; Fino, D. Properties of the Clinoptilolite: Characterization and Adsorption Tests with Methylene Blue. J. Adv. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.K.; Amita, M.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, R. Basic Dye (Methylene Blue) Removal from Simulated Wastewater by Adsorption Using Indian Rosewood Sawdust: A Timber Industry Waste. Dye. Pigment. 2004, 63, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, N.; Rubab, N.; Sadiq, N.; Manzoor, S.; Khan, M.I.; Garcia, J.F.; Aragao, I.B.; Tariq, M.; Akhtar, Z.; Yasmin, G. Aluminum-Doped Cobalt Ferrite as an Efficient Photocatalyst for the Abatement of Methylene Blue. Water 2020, 12, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, J.I.I.; Leikin, J.B. Methylene Blue. Am. J. Ther. 2003, 10, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekambaram, S.P.; Perumal, S.S.; Rajendran, D.; Samivel, D.; Khan, M.N. New Approach of Dye Removal in Textile Effluent: A Cost-Effective Management for Cleanup of Toxic Dyes in Textile Effluent by Water Hyacinth. In Toxicity and Biodegradation Testing; Bidoia, E.D., Montagnolli, R.N., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 241–267. ISBN 978-1-4939-7425-2. [Google Scholar]
- EL-Mekkawi, D.M.; Ibrahim, F.A.; Selim, M.M. Removal of Methylene Blue from Water Using Zeolites Prepared from Egyptian Kaolins Collected from Different Sources. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulushewa, Z.; Dinbore, W.T.; Ayele, Y. Removal of Methylene Blue from Textile Waste Water Using Kaolin and Zeolite-x Synthesized from Ethiopian Kaolin. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2021, 36, e2021007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galletti, C.; Dosa, M.; Russo, N.; Fino, D. Zn2+ and Cd2+ Removal from Wastewater Using Clinoptilolite as Adsorbent. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 24355–24361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.A.; Shahbazi, D.; Mahmoudi, A.; Darvishi, P. Methylene Blue Removal Using Prepared Activated Carbon from Grape Wood Wastes: Adsorption Process Analysis and Modeling. Water Qual. Res. J. 2021, 57, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, R.; Muntean, S.-G.; Nistor, M.-A.; Putz, A.-M.; Almásy, L.; Săcărescu, L. Highly Efficient and Fast Removal of Colored Pollutants from Single and Binary Systems, Using Magnetic Mesoporous Silica. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oves, M.; Saghir Khan, M.; Huda Qari, A.; Nadeen Felemban, M.; Almeelbi, T. Heavy Metals: Biological Importance and Detoxification Strategies. J. Bioremediat. Biodegrad. 2016, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Xi, S. The Effects of Heavy Metals on Human Metabolism. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2020, 30, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, N.K.; Majumder, C.B. Novel Biofiltration Methods for the Treatment of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Us Epa National Primary Drinking Water Regulations. Drink. Water Contam. 2013, 141–142.
- Bedrin, A.G.; Bubnov, I.A.; Dashuk, S.P.; Mironov, I.S. Compact Spectral Analyzer of Heavy-Metal Impurities in Air. J. Opt. Technol. 2003, 70, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- EPA. Technical Support Document for the 2004 Effluent Guidelines Program Plan; National Service Center for Environmental Publications (NSCEP): Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana, D.Lgs. 152/2006—Norme in Materia Ambientale. Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/dettaglio/codici/materiaAmbientale (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- O’Connell, D.W.; Birkinshaw, C.; O’Dwyer, T.F. Heavy Metal Adsorbents Prepared from the Modification of Cellulose: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6709–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunsom, M.; Pruksathorn, K.; Damronglerd, S.; Vergnes, H.; Duverneuil, P. Electrochemical Treatment of Heavy Metals (Cu2+, Cr6+, Ni2+) from Industrial Effluent and Modeling of Copper Reduction. Water Res. 2005, 39, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and Disadvantages of Techniques Used for Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Qu, X.; Li, Z.; Ni, J. Mechanism of Combination Membrane and Electro-Winning Process on Treatment and Remediation of Cu2+ Polluted Water Body. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobade, V.; Eshtiaghi, N. Heavy Metals Removal from Wastewater by Adsorption Process: A Review; Barton, A.C.T. Engineers Australia: Melbourne, Australia, 2015; pp. 312–317. [Google Scholar]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Zorpas, A.A. Handbook of Natural Zeolites; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, UAE, 2012; ISBN 9781608054466. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, D.; Tezel, F.H. Cation Exchange Modification of Clinoptilolite—Screening Analysis for Potential Equilibrium and Kinetic Adsorption Separations Involving Methane, Nitrogen, and Carbon Dioxide. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 262, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumpton, F.A. Clinoptilolite Redefined. Am. Mineral. 1960, 45, 351–369. [Google Scholar]
- Mumpton, F.A. La Roca Magica: Uses of Natural Zeolites in Agriculture and Industry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3463–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsitsishvili, G.; Andronikashvili, T.; Kirov, G.; Filizova, L. Natural Zeolites; Ellis Horwood: Chichester, UK, 1992; ISBN 1581152833. [Google Scholar]
- Osmanlioglu, A.E. Treatment of Radioactive Liquid Waste by Sorption on Natural Zeolite in Turkey. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooney, E.L.; Booker, N.A.; Shallcross, D.C.; Stevens, G.W. Ammonia Removal from Wastewaters Using Natural Australian Zeolite. I. Characterization of the Zeolite. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1999, 34, 2307–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, G.; Maunaye, M.; Martin, G. Removal of Heavy Metals from Waters by Means of Natural Zeolites. Water Res. 1984, 18, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moirou, A.; Xenidis, A.; Paspaliaris, I. Stabilization Pb, Zn, and Cd-Contaminated Soil By Means of Natural Zeolite. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2001, 10, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, T. Clinoptilotite-Heulandite: Applications and Basic Research. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Galarneau, A., Fajula, F., di Renzo, F., Vedrine, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 135, pp. 13–27. ISBN 0167-2991. [Google Scholar]
- Davarpanah, E.; Armandi, M.; Hernández, S.; Fino, D.; Arletti, R.; Bensaid, S.; Piumetti, M. CO2 Capture on Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite: Effect of Temperature and Role of the Adsorption Sites. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 275, 111229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, A.; Hernandez-Maldonado, A.J.; Yang, R.T.; Chinn, D.; Munson, C.L.; Mohr, D.H. Clinoptilolites for Nitrogen/Methane Separation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 2407–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, M.; Tahmasebpoor, M.; Foroutan, R. Enhanced Adsorption Capacity of Low-Cost Magnetic Clinoptilolite Powders/Beads for the Effective Removal of Methylene Blue: Adsorption and Desorption Studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 278, 125655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aysan, H.; Edebali, S.; Ozdemir, C.; Celiїk Karakaya, M.; Karakaya, N. Use of Chabazite, a Naturally, Abundant Zeolite, for the Investigation of the Adsorption Kinetics and Mechanism of Methylene Blue Dye. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 235, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largitte, L.; Pasquier, R. A Review of the Kinetics Adsorption Models and Their Application to the Adsorption of Lead by an Activated Carbon. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 109, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varank, G.; Demir, A.; Yetilmezsoy, K.; Top, S.; Sekman, E.; Bilgili, S. Removal of 4-Nitrophenol from Aqueous Solution by Natural Low-Cost Adsorbents. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2012, 19, 7–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, N.F.; Pinto, R.B.; Lima, E.C.; Calvete, T.; Amavisca, C.V.; Royer, B.; Cunha, M.L.; Fernandes, T.H.M.; Pinto, I.S. Removal of Remazol Black B Textile Dye from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption. Desalination 2011, 269, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladoja, N.A. A Critical Review of the Applicability of Avrami Fractional Kinetic Equation in Adsorption-Based Water Treatment Studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 15813–15825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Sorption of Dyes and Copper Ions onto Biosorbents. Process Biochem. 2003, 38, 1047–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.; Nazar, M.F.; Zafar, M.N.; Zubair, M.; Ashfaq, M.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Khan, S.U.D.; Ahmad, A. Effective Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue from Water by Didodecyldimethylammonium Bromide-Modified Brown Clay. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 16711–16721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayomie, O.S.; Kandeel, H.; Shoeib, T.; Yang, H.; Youssef, N.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Novel Approach for Effective Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Water Using Fava Bean Peel Waste. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaamary, E.A.S.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Rahim, R.A.A.; Idris, M. Rawatan Metilena Biru Dalam Air Sisa Menggunakan Scirpus Grossus. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2017, 21, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Noor, W.; Faruk, O.; Bhoumick, M.C.; Uddin, M.T. Removal of Methylene Blue (MB) from Waste Water by Adsorption on Jackfruit Leaf Powder (JLP) in Continuously Stirred Tank Reactor. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; Institute of Physics Publishing: Bristol, UK, 13 September 2018; Volume 1086. [Google Scholar]
- Ustinov, E.A.; Do, D.D. Invited Contribution Adsorption in Slit Pores and Pore-Size Distribution: A Molecular Layer Structure Theory. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2006, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcoya, A.; González, J.A.; Travieso, N.; Seoane, X.L. Physicochemical and Catalytic Properties of a Modified Natural Clinoptilolite. Clay Min. 1994, 29, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Huang, M.; Ma, H.L.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Gao, J.M.; Zhu, Y.L.; Han, X.J.; Guo, X.Y. Preparation of a Carbon-Based Solid Acid Catalyst by Sulfonating Activated Carbon in a Chemical Reduction Process. Molecules 2010, 15, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khalil, H.P.S.; Jawaid, M.; Firoozian, P.; Rashid, U.; Islam, A.; Akil, H.M. Activated Carbon from Various Agricultural Wastes by Chemical Activation with KOH: Preparation and Characterization. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2013, 7, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumpton, F.A.; Ormsby, W.C. Morphology of Zeolites in Sedimentary Rocks by Scanning Electron Microscopy. Clays Clay Min. 1976, 24, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramoff, M.; Magalhães, P.; Ram, S.J. Image Processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2003, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, N.; Sundaram, M.M. Kinetics and Mechanism of Removal of Methylene Blue by Adsorption on Various Carbons—A Comparative Study. Dye. Pigment. 2001, 51, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badeenezhad, A.; Azhdarpoor, A.; Bahrami, S.; Yousefinejad, S. Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Solutions by Natural Clinoptilolite and Clinoptilolite Modified by Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Mol. Simul. 2019, 45, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćurković, L.; Cerjan-Stefanović, Š.; Filipan, T. Metal Ion Exchange by Natural and Modified Zeolites. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppert, D. Heavy Metal Sorption with Clinoptilolite Zeolite. Alternatives for Treating Contaminated Soil and Water. Min. Eng. 1990, 42, 604–608. [Google Scholar]
- Kesraoui-Ouki, S.; Cheeseman, C.R.; Perry, R. Natural Zeolite Utilisation in Pollution Control: A Review of Applications to Metals’ Effluents. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Int. Res. Process Environ. Clean Technol. 1994, 59, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Low-Cost Adsorbents: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, M.; Silva, J.; Carrasco, S.; Barrientos, N. Design, Cost Estimation and Sensitivity Analysis for a Production Process of Activated Carbon from Waste Nutshells by Physical Activation. Processes 2020, 8, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.; Marshall, W.E.; Rao, R.M.; Bansode, R.R.; Losso, J.N. Activated Carbon from Pecan Shell: Process Description and Economic Analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2003, 17, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, I.M.; McAloon, A.; Boateng, A.A. Activated Carbon from Broiler Litter: Process Description and Cost of Production. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos, G.G.; Zabaniotou, A.A. Minimizing Activated Carbons Production Cost. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.L.; Pereira, M.F.R. The Role of Surface Chemistry in Catalysis with Carbons. Catal. Today 2010, 150, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colella, C. Environmental Applications of Natural Zeolitic Materials Based on Their Ion Exchange Properties. In Natural Microporous Materials in Environmental Technology; Misaelides, P., Macášek, F., Pinnavaia, T.J., Colella, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 207–224. ISBN 978-94-011-4499-5. [Google Scholar]
- Pauling, L. The Nature of the Chemical Bond—1992. J. Chem. Educ. 1992, 69, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.H. The Use of Ionization Potentials Part 1. Ionic Radii of the Elements. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1952, 2, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpat, S.K.; Özbayrak, Ö.; Alpat, Ş.; Akçay, H. The Adsorption Kinetics and Removal of Cationic Dye, Toluidine Blue O, from Aqueous Solution with Turkish Zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.L.; Hameed, B.H. Insight into the Adsorption Kinetics Models for the Removal of Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 74, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edet, U.A.; Ifelebuegu, A.O. Kinetics, Isotherms, and Thermodynamic Modeling of the Adsorption of Phosphates from Model Wastewater Using Recycled Brick Waste. Processes 2020, 8, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songolzadeh, M.; Soleimani, M.; Takht Ravanchi, M. Using Modified Avrami Kinetic and Two Component Isotherm Equation for Modeling of CO2/N2 Adsorption over a 13X Zeolite Bed. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 27, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


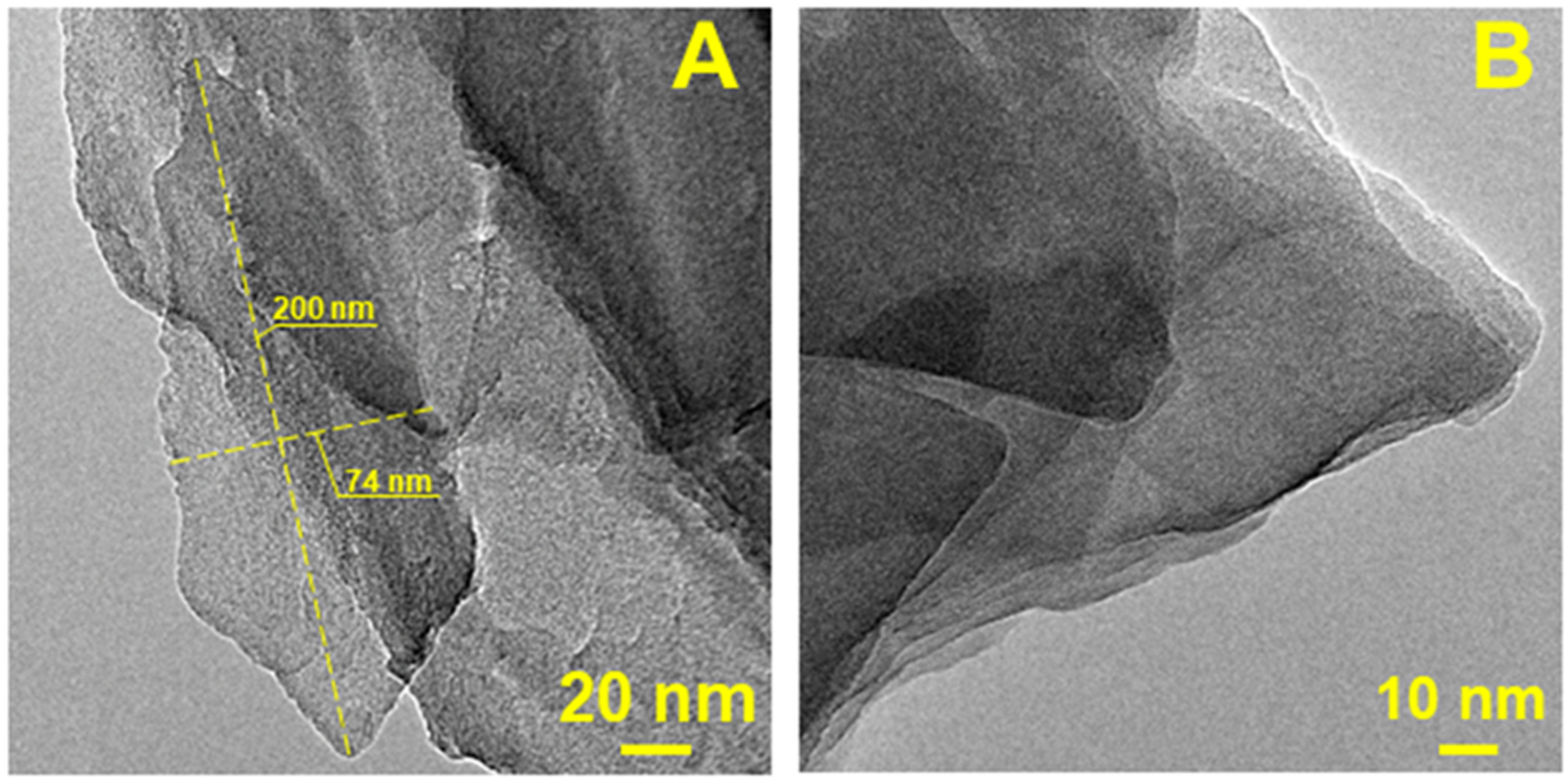




| Adsorbent Material | SSA (m2 g−1) a | VTP (cm3 g−1) b | Dp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clin | 32 | 0.12 | A channel 3.0 × 7.6 Å c |
| B channel 3.3 × 4.6 Å c | |||
| C channel 2.6 × 4.7 Å c | |||
| AC | 891 | 0.56 | 3.3 nm d |
| Adsorbent Material | EDX | XRF | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | Al | K | Ca | Fe | Si | Al | K | Ca | Fe | |
| Clin | 72.5 | 14.9 | 7.3 | 3.7 | 1.6 | 79.1 | 11.1 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 2.1 |
| Adsorbent Material | MB Concentration (ppm) | pH|time=0 min | pH|time=210 min |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clin | 100 | 8.36 | 7.11 |
| 200 | 8.01 | 5.65 | |
| 250 | 6.18 | 6.09 |
| MB Concentration (ppm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clin | AC | |||||
| Model | Equation | Parameters | 100 | 200 | 250 | 250 |
| Pseudo-First-Order | (7) | 0.2496 | 0.7594 | 0.9159 | 0.9188 | |
| 0.0116 | 0.0133 | 0.0111 | 0.0134 | |||
| 0.7371 | 6.3630 | 19.8459 | 51.4803 | |||
| 19.5897 | 41.4197 | 56.2159 | 53.5020 | |||
| Pseudo-Second-Order | (8) | 1 | 1 | 0.9985 | 0.9786 | |
| 0.4460 | 0.0127 | 0.0033 | 0.0005 | |||
| 19.4932 | 41.4938 | 55.5556 | 56.8182 | |||
| 19.5897 | 41.4197 | 56.2159 | 53.5020 | |||
| Intraparticle Diffusion | (4) | 0.3017 | 0.4887 | 0.6499 | 0.9707 | |
| 0.5235 | 1.1673 | 1.9014 | 3.1658 | |||
| 13.7420 | 25.6400 | 28.5310 | 3.9967 | |||
| Elovich | (9) | 0.4478 | 0.7116 | 0.8158 | 0.9613 | |
| 1693.8155 | 360.2312 | 175.6284 | 6.4746 | |||
| 0.5850 | 0.2275 | 0.1559 | 0.1067 | |||
| Bangham | (5) | 0.3179 | 0.3889 | 0.4279 | 0.9158 | |
| 0.2147 | 0.2704 | 0.3063 | 0.5562 | |||
| 7.4536 | 11.2211 | 12.1399 | 2.8460 | |||
| Avrami | (10) | 0.3992 | 0.7133 | 0.7088 | 0.6826 | |
| 0.2150 | 0.2959 | 0.2404 | 0.4954 | |||
| 1.7049 | 0.8992 | 0.7728 | 0.1353 | |||
| Clin | AC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Equation | Parameters | MB | Zn | Cd | MB | Zn | Cd |
| Pseudo-First-Order | (7) | 0.5591 | 0.2499 | 0.0434 | 0.7044 | 0.6648 | 0.1891 | |
| 0.0286 | 0.0167 | 0.0067 | 0.0650 | 0.0183 | 0.0086 | |||
| 2.0530 | 0.3422 | 0.0576 | 7.7145 | 1.7296 | 0.3836 | |||
| 22.2054 | 1.9820 | 0.643 | 24.4256 | 2.968 | 0.6300 | |||
| Pseudo-Second-Order | (8) | 0.9999 | 0.9990 | 0.9995 | 0.9979 | 0.9902 | 0.9631 | |
| 0.0609 | 0.3228 | 1.8599 | 0.0108 | 0.0253 | 0.0699 | |||
| 22.2717 | 1.9716 | 0.6370 | 25.3807 | 3.1279 | 0.6797 | |||
| 22.2054 | 1.9820 | 0.6430 | 24.4256 | 2.968 | 0.6300 | |||
| Intraparticle Diffusion | (4) | 0.3409 | 0.4493 | 0.3961 | 0.6889 | 0.9267 | 0.9844 | |
| 0.6897 | 0.0938 | 0.0289 | 1.7666 | 0.2322 | 0.0537 | |||
| 15.1210 | 1.0874 | 0.3732 | 9.2597 | 0.5441 | 0.0353 | |||
| Elovich | (9) | 0.4426 | 0.6557 | 0.6077 | 0.8979 | 0.9920 | 0.9616 | |
| 1645.0404 | 3.6169 | 1.4994 | 10.1944 | 0.5882 | 0.0832 | |||
| 0.5040 | 3.4758 | 11.0011 | 0.2013 | 1.6420 | 7.6746 | |||
| Bangham | (5) | 0.3064 | 0.7467 | 0.2486 | 0.7299 | 0.9356 | 0.0402 | |
| 0.2317 | 0.1050 | −0.0474 | 0.5263 | 0.2646 | 0.0721 | |||
| 2.0936 | 1.2354 | 0.7519 | 2.9032 | 0.8139 | 0.3194 | |||
| Avrami | (10) | 0.4655 | 0.3438 | 0.2837 | 0.5768 | 0.5305 | 0.3941 | |
| 0.2664 | 0.2064 | 0.1804 | 0.5516 | 0.3342 | 0.2883 | |||
| 1.4421 | 1.2376 | 1.4599 | 0.4703 | 0.4316 | 0.3639 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dosa, M.; Grifasi, N.; Galletti, C.; Fino, D.; Piumetti, M. Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite Application in Wastewater Treatment: Methylene Blue, Zinc and Cadmium Abatement Tests and Kinetic Studies. Materials 2022, 15, 8191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15228191
Dosa M, Grifasi N, Galletti C, Fino D, Piumetti M. Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite Application in Wastewater Treatment: Methylene Blue, Zinc and Cadmium Abatement Tests and Kinetic Studies. Materials. 2022; 15(22):8191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15228191
Chicago/Turabian StyleDosa, Melodj, Nadia Grifasi, Camilla Galletti, Debora Fino, and Marco Piumetti. 2022. "Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite Application in Wastewater Treatment: Methylene Blue, Zinc and Cadmium Abatement Tests and Kinetic Studies" Materials 15, no. 22: 8191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15228191
APA StyleDosa, M., Grifasi, N., Galletti, C., Fino, D., & Piumetti, M. (2022). Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite Application in Wastewater Treatment: Methylene Blue, Zinc and Cadmium Abatement Tests and Kinetic Studies. Materials, 15(22), 8191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15228191







