On the Use of NaOH Solution to Simulate the Crevice Conditions of a Nuclear Steam Generator
Abstract
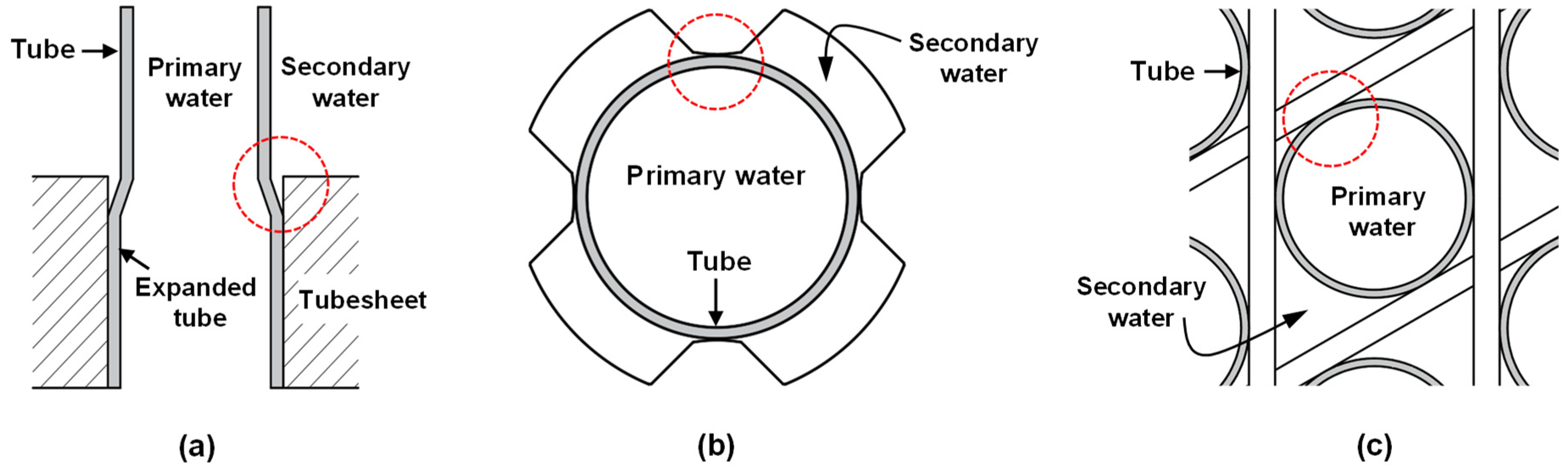
1. Introduction
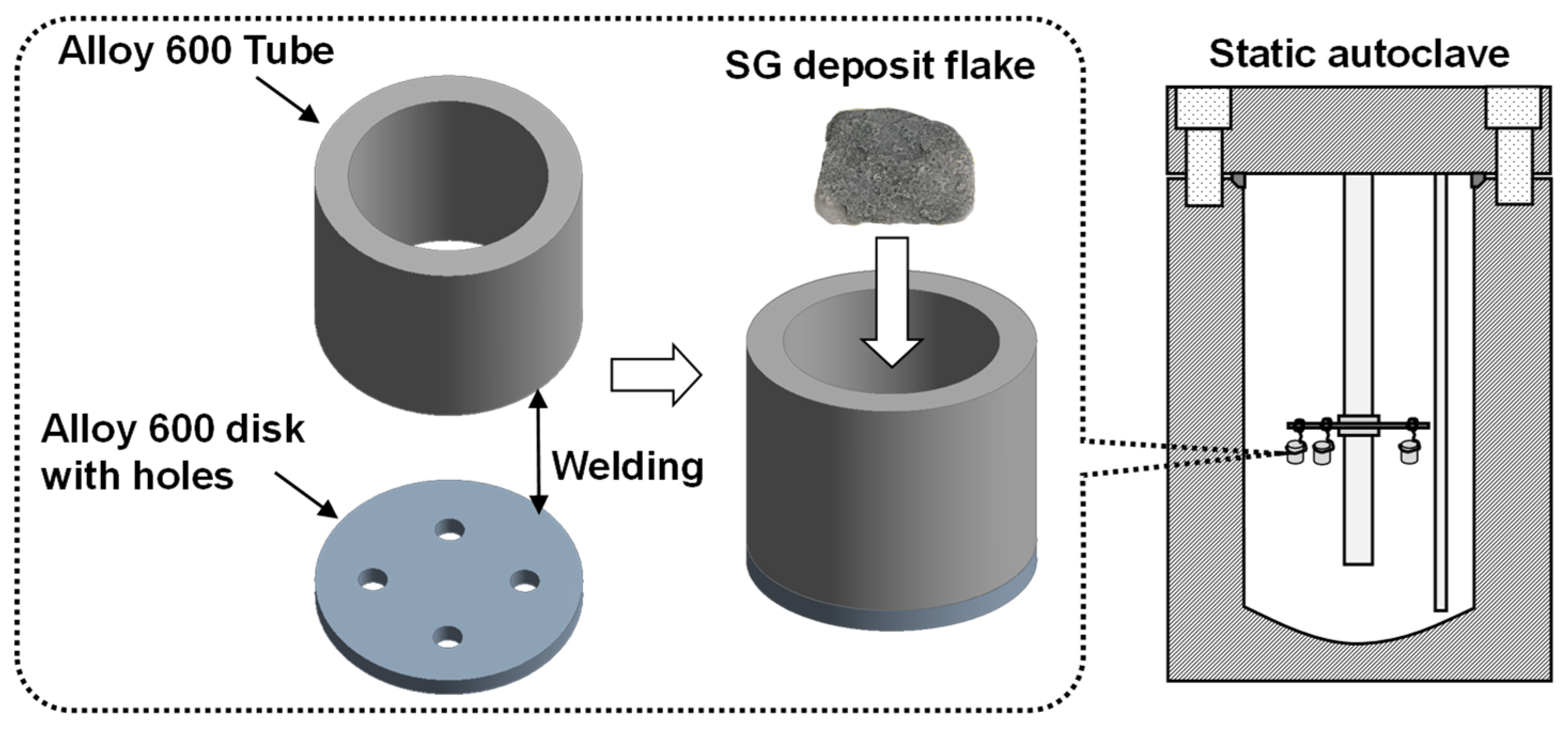
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
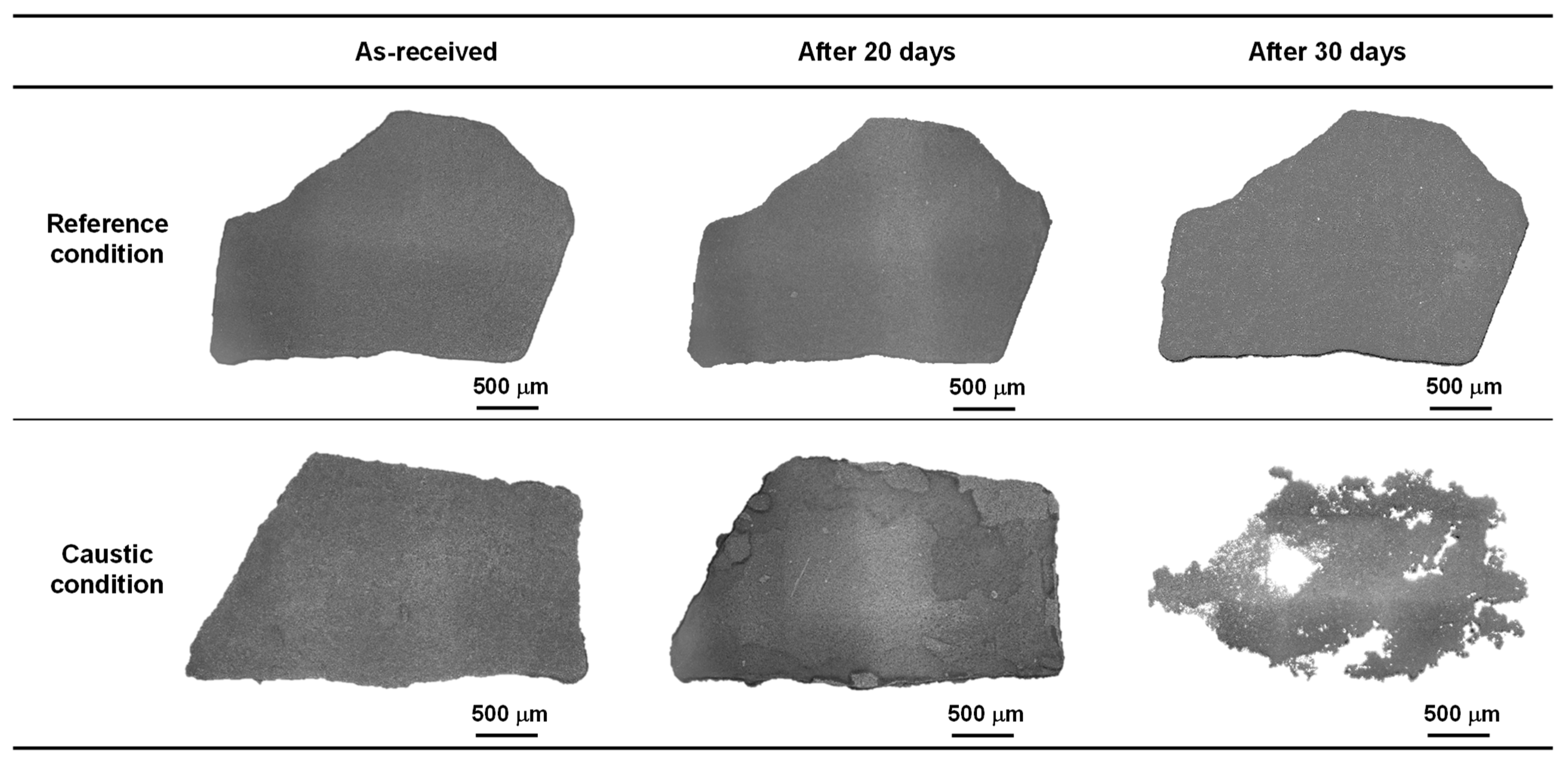
3.1. Dissolution Behavior of the SG Deposit Flakes
3.2. Thermodynamics for the Dissolution of the SG Deposit Flakes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeon, S.-H.; Hong, S.; Kwon, H.-C.; Hur, D.H. Characteristics of steam generator tube deposits in an operating pressurized water reactor. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 507, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapping, R.L.; Turner, C.W.; Thompson, R. Steam Generator Deposits—A Detailed Analysis and Some Inferences. Corrosion 1991, 47, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manahan, M.P. Mechanical behaviour of magnetite from the Oconee-2 and TMI-1 steam generators using miniaturized specimen technology. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 3415–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusev, B.A.; Efimov, A.A.; Aleshin, A.M.; Semenov, V.G.; Panchuk, V.V.; Martynov, V.V.; Maksimova, A.N. Morphology and Phase Composition of Oxide Films and Corrosion Product Deposits in the Steam Generator of a BN-800 Reactor Unit. Therm. Eng. 2022, 69, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, K.; Million-Picallion, L.; Delaunay, S.; Berger, G.; Lefèvre, G. Insights into the formation mechanism of hard sludge on the secondary side of PWR steam generators. Nucl. Mater. Energy 2022, 31, 101197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Pointeau, V.; Tevissen, E.; Chagnes, A. A review on clogging of recirculating steam generators in Pressurized-Water Reactors. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2017, 97, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prusek, T.; Moleiro, E.; Oukacine, F.; Adobes, A.; Jaeger, M.; Grandotto, M. Deposit models for tube support plate flow blockage in Steam Generators. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2013, 262, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.T.; Luo, J.L.; Lu, Y.C. A Mechanistic Study on Lead-Induced Passivity-Degradation of Nickel-Based Alloy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, C379–C389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehle, R.W.; Gorman, J.A. Quantitative Assessment of Submodes of Stress Corrosion Cracking on the Secondary Side of Steam Generator Tubing in Pressurized Water Reactors: Part 3. Corrosion 2004, 60, 115–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursier, J.B.; Dupin, M.; Sosset, P.; Rouillon, Y. Secondary side corrosion of French PWR steam generator tubing: Contribution of surface analyses to the understanding of the degradation process. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems—Water Reactors, Boston, MA, USA, 18–22 August 1999; TMS: Newport Beach, CA, USA, 1999; pp. 555–563. [Google Scholar]
- Fruzzetti, K. Pressurized Water Reactor Secondary Water Chemistry Guidelines–Revision 8; TR–3002010645; Electric Power Research Institute: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, C. Steam Generator Management Program: Effects of Different pH Control Agents on Pressurized Water Reactor Plant Systems and Components; TR–1019042; Electric Power Research Institute: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, D.H.; Lee, D.H.; Choi, M.S.; Song, M.H.; Han, J.H. Root causes of intergranular attack in an operating nuclear steam generator tube. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 375, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, D.H.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, D.H.; Song, M.H.; Han, J.H. Pitting Corrosion and its Countermeasures for Pressurized Water Reactor Steam Generator Tubes. Corrosion 2006, 62, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Johnson, B.; Bruemmer, S. Sulfur at crack tips in Alloy 600 service samples. In Workshop of Effects of Pb and S on the Performance of Secondary Side Tubing of Steam Generators in PWRs; Argon National Laboratory: Lemont, IL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- King, P.K.; Gonzalez, F.; Brown, J. Stress corrosion experience in steam generators at Bruce NGS. In Proceedings of the Sixth In-ternational Symposium on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems—Water Reactors, San Diego, CA, USA, 1–5 August 1993; TMS: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Cels, J.R. Stress Corrosion Cracking of Stainless Steel and Nickel Alloys at Controlled Potentials in 10% Caustic Soda Solutions at 550 °F. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1976, 123, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theus, G.J. Relationship Between Acid Intergranular Corrosion and Caustic Stress Corrosion Cracking of Alloy 600. Corrosion 1977, 33, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Ming, H.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, F.; He, G.; Wang, J.; Han, E.-H. Microstructure and stress corrosion cracking behavior of Alloy 690TT steam generator tubes with internal bulge defect. J. Nucl. Mater. 2022, 563, 153629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharasi, N.S.; Toppo, A.; Paul, V.T.; George, R.P.; Philip, J. Studies on the Susceptibility of Modified 9Cr-1Mo Steel to Stress Corrosion Cracking in Sodium Hydroxide Using Slow Strain Rate Testing Technique. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 2172–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Han, E.-H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ke, W. Localized corrosion behavior of scratches on nickel-base Alloy 690TT. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 1781–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, D.H.; Kim, J.S.; Baek, J.S.; Kim, J.G. Inhibition of Stress Corrosion Cracking of Alloy 600 in 10% Sodium Hydroxide Solution at 315 °C. Corrosion 2002, 58, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chou, L.; Shih, H. Factors affecting the electrochemical behavior and stress corrosion cracking of Alloy 690 in chloride environments. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 97, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, B.; Lu, Y.; Xin, L.; Wang, Z.; Shoji, T. The effect of normal force on fretting corrosion behavior of Inconel 690 in 3.5% sodium chloride. Mater. Charact. 2017, 131, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, K.; Wang, B.; Tian, R. A coupled model of corrosion of the steam generator heat transfer tube. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2022, 396, 111895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, S.; Long, F.; Korinek, A.; Smith, J. High resolution characterization of sulfur-assisted degradation in alloy 800. Corros. Sci. 2018, 140, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Carcea, A.G.; Newman, R.C. Pitting of steam-generator tubing alloys in solutions containing thiosulfate and sulfate or chloride. Faraday Discuss. 2015, 180, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, D.-H.; Wang, J.; Qin, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Hu, W.; Luo, J.-H. Sulfur induced corrosion (SIC) mechanism of steam generator (SG) tubing at micro scale: A critical review. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 233, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Shaehle, R.W. Effects of the valence of sulfur on passivation of Alloys 600, 690, and 800 at 25 °C and 95 °C. Corrosion 1999, 55, 355–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojinov, M.; Jäppinen, E.; Saario, T.; Sipilä, K.; Toivonen, A. Effect of lead and applied potential on corrosion of carbon steel in steam generator crevice solutions. Corros. Sci. 2019, 159, 108117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Luo, J.; Lu, Y. Passivity degradation of nuclear steam generator tubing alloy induced by Pb contamination at high temperature. J. Nucl. Mater. 2012, 429, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, D.H.; Choi, W.-I.; Song, G.D.; Jeon, S.-H.; Lim, S. Mechanistic insights into lead-accelerated stress corrosion cracking of Alloy 600. Corros. Sci. 2018, 145, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J. Corrosion and deposition on the secondary circuit of steam generators. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1455–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, M.; Gomez-Briceno, D.; Garcia-Mazario, M.; McIlree, A.R. Effect of silicon compounds on stress corrosion cracking pf Alloy 600 in caustic solutions. Corrosion 1999, 55, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lu, Z.; Huang, D.; Kong, D.; Zhao, G.; Congleton, J. Caustic stress corrosion cracking of nickel-rich, chromium-bearing alloys. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 963–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehle, R.W. Historical views on stress corrosion cracking of nickel-based alloys: The Coriou effect. In Stress Corrosion Cracking of Nickel-Based Alloys in Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactors; Feron, D., Staehle, R.W., Eds.; Elsevier: Duxford, UK, 2016; pp. 3–131. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.M.; Aral, K.; Theus, G.J. Computer-Calculated Potential pH Diagrams to 300 °C; NP–3137; Electric Power Research Institute: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1983; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Pourbaix, M. Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions; NACE: Houston, TX, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Varrin, R.D., Jr. Deposit accumulation in PWR steam generator. In Steam Generator for Nuclear Power Plants; Elsevier: Duxford, UK, 2017; pp. 323–363. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe, R. Steam Generator Management Program: Steam Generator Deposit Removal Strategies Sourcebook; TR-30020050902015; EPRI: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, D.H.; Choi, M.S.; Chung, H.S.; Kim, U.C. Optimum EDTA solvent chemistry for iron oxide removal at 150 °C. J. Nucl. Mater. 2002, 305, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coriou, H.; Grall, L.; Le Gall Vettier, S. Corrosion Fissurante Sous Contrainte de l’Inconel dans l’Eau à Haute Température; Report CEA no. 1521; CEA: Grenoble, France, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Copson, H.R.; Cheng, C.F. Some case histories of stress corrosion cracking of austenitic stainless steels associated with chlorides. Corrosion 1957, 13, 397t–404t. [Google Scholar]
- Copson, H.R. Effect of composition on stress corrosion cracking of some alloys containing nickel. In Physical Metallurgy of Stress Corrosion Fracture; Rhodin, T.N., Ed.; Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1959; pp. 247–272. [Google Scholar]


| Test Condition | NaOH Concentration (wt.%) | pH at 25 °C | Temperature (°C) | Test Duration (Day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference condition | 1.075 × 10−4 | 9.5 | 300 | 20, 30 |
| Caustic condition | 0.400 | 13.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hur, D.-H.; Song, G.-D.; Han, J.; Jeon, S.-H. On the Use of NaOH Solution to Simulate the Crevice Conditions of a Nuclear Steam Generator. Materials 2022, 15, 8471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238471
Hur D-H, Song G-D, Han J, Jeon S-H. On the Use of NaOH Solution to Simulate the Crevice Conditions of a Nuclear Steam Generator. Materials. 2022; 15(23):8471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238471
Chicago/Turabian StyleHur, Do-Haeng, Geun-Dong Song, Jeoh Han, and Soon-Hyeok Jeon. 2022. "On the Use of NaOH Solution to Simulate the Crevice Conditions of a Nuclear Steam Generator" Materials 15, no. 23: 8471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238471
APA StyleHur, D.-H., Song, G.-D., Han, J., & Jeon, S.-H. (2022). On the Use of NaOH Solution to Simulate the Crevice Conditions of a Nuclear Steam Generator. Materials, 15(23), 8471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238471







