Hybrid Dispersion Model Characterization of PAZO Azopolymer Thin Films over the Entire Transmittance Spectrum Measured in the UV/VIS/NIR Spectral Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Samples and Measurement of Their Transmittance Spectra T(λ)
2.2. Common Techniques for Characterization of Thin Films Only from T(λ)
2.3. Hybrid Dispersion Model for Characterization of Amorphous Thin Films Only from T(λ)
3. Results
3.1. Results from Characterizations of the PAZO Polymer Films Using HDM and T(λ)
3.2. Characteristics of the PAZO Polymer Films Derived from HDM Results and DMs for n(λ) or k(λ)
3.3. Results about the Thickness Characteristics and the Accuracy of the Film Characterizations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nikolova, L.; Ramanujam, P.S. Polarization Holography; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 64–89. [Google Scholar]
- Priimagi, A.; Shevchenko, A. Azopolymer-Based Micro- and Nanopatterning for Photonic Applications. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2014, 52, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Azo Polymers: Synthesis, Functions and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.; Cao, L.; Liu, Y.; Tan, X. A Review of Polarization-Sensitive Materials for Polarization Holography. Materials 2020, 13, 5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lvov, Y.; Yamada, S.; Kunitake, T. Non-linear optical effects in layer-by-layer alternate films of polycations and an azobenzene-containing polyanion. Thin Solid Film. 1997, 300, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casson, J.; Wang, H.; Roberts, J.; Parikh, A.; Robinson, J.; Johal, M. Kinetics and interpenetration of ionically self-assembled dendrimer and PAZO multilayers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dante, S.; Advincula, R.; Frank, C.; Stroeve, P. Photoisomerization of Polyionic Layer-by-Layer Films Containing Azobenzene. Langmuir 1999, 15, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Yan, D.; Shi, W.; Ma, J.; Yan, H.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.; Duan, X. Layer-by-layer ultrathin films of azobenzene-containing polymer/layered double hydroxides with reversible photoresponsive behavior. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 5678–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, Q.; Gomes, P.; Raposo, M.; Giacometti, J.; Oliveira, O.; Ribeiro, P. Influence of ionic interactions on the photoinduced birefringence of poly[1-[4-(3-Carboxy-4-hydroxyphenylazo) benzene sulfonamido]-1,2-ethanediyl, sodium salt] films. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 2659–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, Q.; Ribeiro, P.; Oliveira, O., Jr.; Raposo, M. Long-term stability at high temperatures for Birefringence in PAZO/PAH layer-by-layer films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1470–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madruga, C.; Filho, P.; Andrade, M.; Gonçalves, M.; Raposo, M.; Ribeiro, P. Birefringence dynamics of poly{1-[4-(3-carboxy-4-hydroxyphenylazo) benzenesulfonamido]-1,2-ethanediyl, sodium salt} cast films. Thin Solid Film. 2011, 519, 8191–8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelchev, L.; Ivanov, D.; Blagoeva, B.; Nazarova, D. Optical anisotropy induced at five different wavelengths in azopolymer thin films: Kinetics and spectral dependence. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 376, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarova, D.; Nedelchev, L.; Ivanov, D.; Blagoeva, B.; Berberova, N.; Stoykova, E.; Mateev, G.; Kostadinova, D. Laser induced optically and thermally reversible birefringence in azopolymers. Proc. SPIE 2017, 10226, 1022608. [Google Scholar]
- Berberova-Buhova, N.; Nedelchev, L.; Mateev, G.; Stoykova, E.; Strijkova, V.; Nazarova, D. Influence of the size of Au nanoparticles on the photoinduced birefringence and diffraction efficiency of polarization holographic gratings in thin films of azopolymer nanocomposites. Opt. Mater. 2021, 121, 111560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcione, R.; Roldan, M.V.; Pellegri, N.; Goyanes, S.; Ledesma, S.A.; Capeluto, M.G. Increase of SRG modulation depth in azopolymers-nanoparticles hybrid materials. Opt. Mater. 2021, 115, 111015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelchev, L.; Mateev, G.; Strijkova, V.; Salgueiriño, V.; Schmool, D.S.; Berberova-Buhova, N.; Stoykova, E.; Nazarova, D. Tunable Polarization and Surface Relief Holographic Gratings in Azopolymer Nanocomposites with Incorporated Goethite (α-FeOOH) Nanorods. Photonics 2021, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoilova, A.; Mateev, G.; Nazarova, D.; Nedelchev, L.; Stoykova, E.; Blagoeva, B.; Berberova, N.; Georgieva, S.; Todorov, P. Polarization holographic gratings in PAZO polymer films doped with particles of biometals. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 411, 113196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, P.; Jonas, A.; Laschewsky, A.; Legras, R. Ultrathin polymer coatings by complexation of polyelectrolytes at interfaces: Suitable materials, structure and properties. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2000, 21, 319–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelchev, L.; Nazarova, D.; Mateev, G.; Berberova, N. Birefringence induced in azopolymer (PAZO) films with different thickness. Proc. SPIE 2015, 9447, 94471I. [Google Scholar]
- Lilova, V.; Trifonova, Y.; Stoilova, A.; Georgieva, S.; Todorov, P. Optical properties of PAZO polymer composite films doped with particles of a novel copper hydantoin complex. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2021, 56, 1192–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Stoilova, A.; Lilova, V.; Ivanova, V.; Trifonova, Y.; Dimov, D. Optical properties of electrospray deposited PAZO polymer films doped with GeTe4–Cu chalcogenide particles. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2022, 57, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel, O.; Ohlídal, M. Optical Characterization of Thin Solid Films, 1st ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Leal, J.M.; Prieto-Alcon, R.; Angel, J.A.; Minkov, D.A.; Marquez, E. Influence of substrate absorption on the optical and geometrical characterization of thin dielectric films. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 7300–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanepoel, R. Determination of surface roughness and optical constants of inhomogeneous amorphous silicon films. J. Phys. E Sci. Instrum. 1984, 17, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkov, D. Flow-graph approach for optical analysis of planar structures. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 7698–7703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minkov, D.A.; Gavrilov, G.M.; Angelov, G.V.; Moreno, G.M.D.; Vazquez, C.G.; Ruano, S.M.F.; Marquez, E. Optimization of the envelope method for characterization of optical thin film on substrate specimens from their normal incidence transmittance spectrum. Thin Solid Film. 2018, 645, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkov, D.A.; Angelov, G.; Nestorov, R.; Nezhdanov, A.; Usanov, D.; Kudryashov, M.; Mashin, A. Optical characterization of AsxTe100-x Films Grown by Plasma Deposition Based on the Advanced Optimizing Envelope Method. Materials 2020, 13, 2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkov, D.; Marquez, E.; Angelov, G.; Gavrilov, G.; Ruano, S.M.F.; Saugar, E. Further increasing the accuracy of characterization of a thin dielectric or semiconductor film on a substrate from its interference transmittance spectrum. Materials 2021, 14, 4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellison, G.E.; Modine, F.A. Parameterization of the optical functions of amorphous materials in the interband region. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 371–373, Erratum in Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc–Lorentz Dispersion Formula, Technical Note. Spectroscopic Ellipsometry TN11. Available online: https://www.horiba.com/fileadmin/uploads/Scientific/Downloads/OpticalSchool_CN/TN/ellipsometer/Tauc–Lorentz_Dispersion_Formula.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2022).
- New Amorphous Dispersion Formula, Technical Note. Spectroscopic Ellipsometry TN12. Available online: https://www.horiba.com/fileadmin/uploads/Scientific/Downloads/OpticalSchool_CN/TN/ellipsometer/New_Amorphous_Dispersion_Formula.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2022).
- Dkhilalli, F.; Borchani, S.M.; Rasheed, M.; Barille, M.; Guidara, K.; Megdiche, M. Structural, dielectric, and optical properties of the zinc tungstate ZnWO4 compound. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 6297–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foldyna, M.; Postava, K.; Bouchal, J.; Pitora, J.; Yamaguchi, T. Model dielectric function of amorphous materials including Urbach tail. Proc. SPIE 2003, 5445, 301–305. [Google Scholar]
- Márquez, E.; Ruíz-Pérez, J.J.; Ballester, M.; Márquez, A.P.; Blanco, E.; Minkov, D.; Fernandez, S.M.; Saugar, E. Optical Characterization of H-Free a-Si Layers Grown by rf-Magnetron Sputtering by Inverse Synthesis Using Matlab: Tauc–Lorentz–Urbach Parameterization. Coatings 2021, 11, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodruguez-deMarcos, L.; Larruquert, J.I. Analytic optical-constant model derived from Tauc–Lorentz and Urbach tail. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 28561–28572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ballester, M.; García, M.; Márquez, A.P.; Blanco, E.; Fernández, S.M.; Minkov, D.; Katsaggelos, A.K.; Cossairt, O.; Willomitzer, F.; Marquez, E. Application of the Holomorphic Tauc–Lorentz–Urbach Function to Extract the Optical Constants of Amorphous Semiconductor Thin Films. Coatings 2022, 12, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemple, S.H.; DiDomenico, M., Jr. Behavior of the Electronic Dielectric Constant in Covalent and Ionic Materials. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter. 1971, 3, 1338–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemple, S.H. Refractive-index behavior of amorphous semiconductors and glasses. Phys. Rev. B 1973, 7, 3767–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbach, F. The Long-Wavelength Edge of Photographic Sensitivity and of the Electronic Absorption of Solids. Phys. Rev. 1953, 92, 1324–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacalis, N.; Economou, E.N.; Cohen, M.H. Simple derivation of exponential tails in the density of states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1988, 37, 2714–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J. Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous Ge and Si. Mater. Res. Bull. 1966, 3, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, E.A.; Mott, N.F. Conduction in non-crystalline systems V. Conductivity, optical absorption and photoconductivity in amorphous semiconductors. Philos. Mag. A 1970, 22, 903–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenzel, O. Optical Coatings: Material Aspects in Theory and Practice, 1st ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 35–51. [Google Scholar]
- Marquez, E.; Díaz, J.M.; García-Vázquez, C.; Blanco, E.; Ruiz-Pérez, J.J.; Minkov, D.A.; Angelov, G.V.; Gavrilov, G.M. Optical characterization of amine-solution-processed amorphous chalcogenide thin films by the use of transmission spectroscopy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 721, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haryński, L.; Olejnik, A.; Grochowska, K.; Siuzdak, K. A facile method for Tauc exponent and corresponding electronic transitions determination in semiconductors directly from UV–Vis spectroscopy data. Opt. Mater. 2022, 127, 112205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, M.; Márquez, A.P.; García-Vázquez, C.; Díaz, J.M.; Blanco, E.; Minkov, D.; Fernández-Ruano, S.M.; Willomitzer, F.; Cossairt, O.; Márquez, E. Energy-band-structure calculation by below-band-gap spectrophotometry in thin layers of non-crystalline semiconductors: A case study of unhydrogenated a-Si. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2022, 594, 121803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refractive Index.Info. Available online: https://refractiveindex.info/?shelf=glass&book=BK7&page=SCHOTT/ (accessed on 23 October 2022).
- Mujahid, M.; Srivastava, D.S.; Gupta, S.; Avasthi, D.K. Estimation of optical band gap and carbon cluster sizes formed in heavy ion irradiated polycarbonate. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2005, 74, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaka, K.; Jacob, M.V. Effects of Iodine Doping on Optoelectronic and Chemical Properties of Polyterpenol Thin Films. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
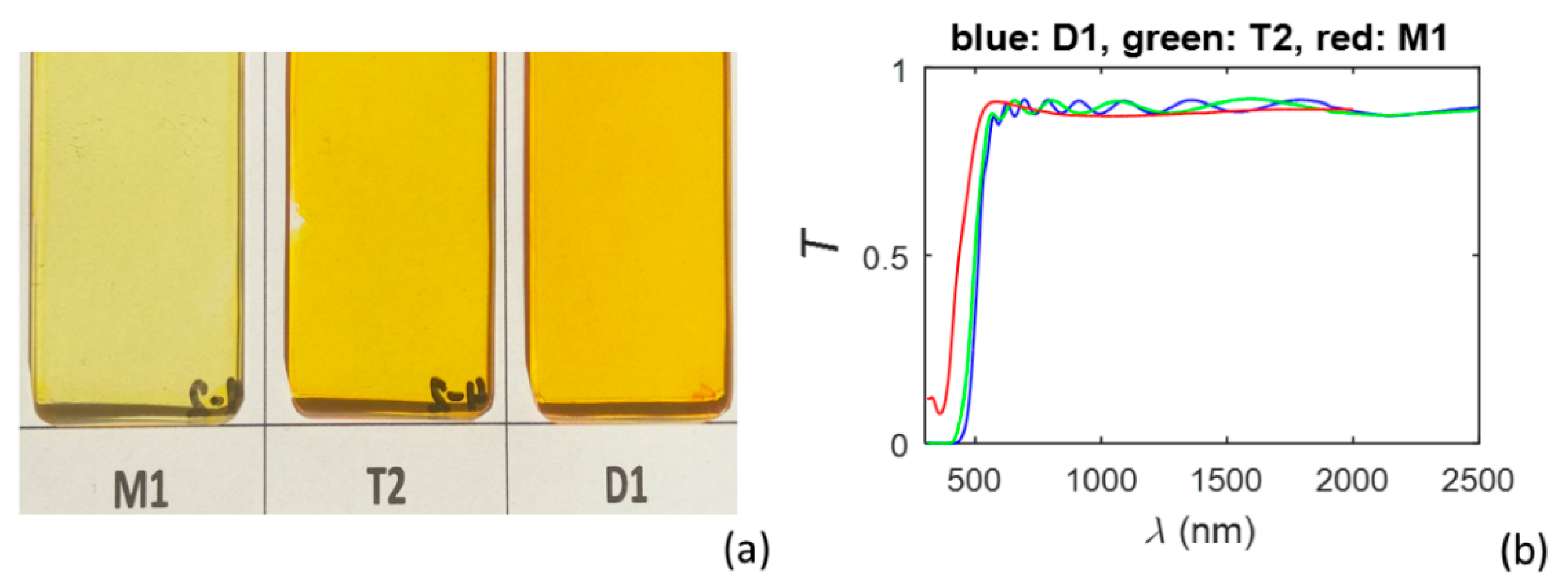

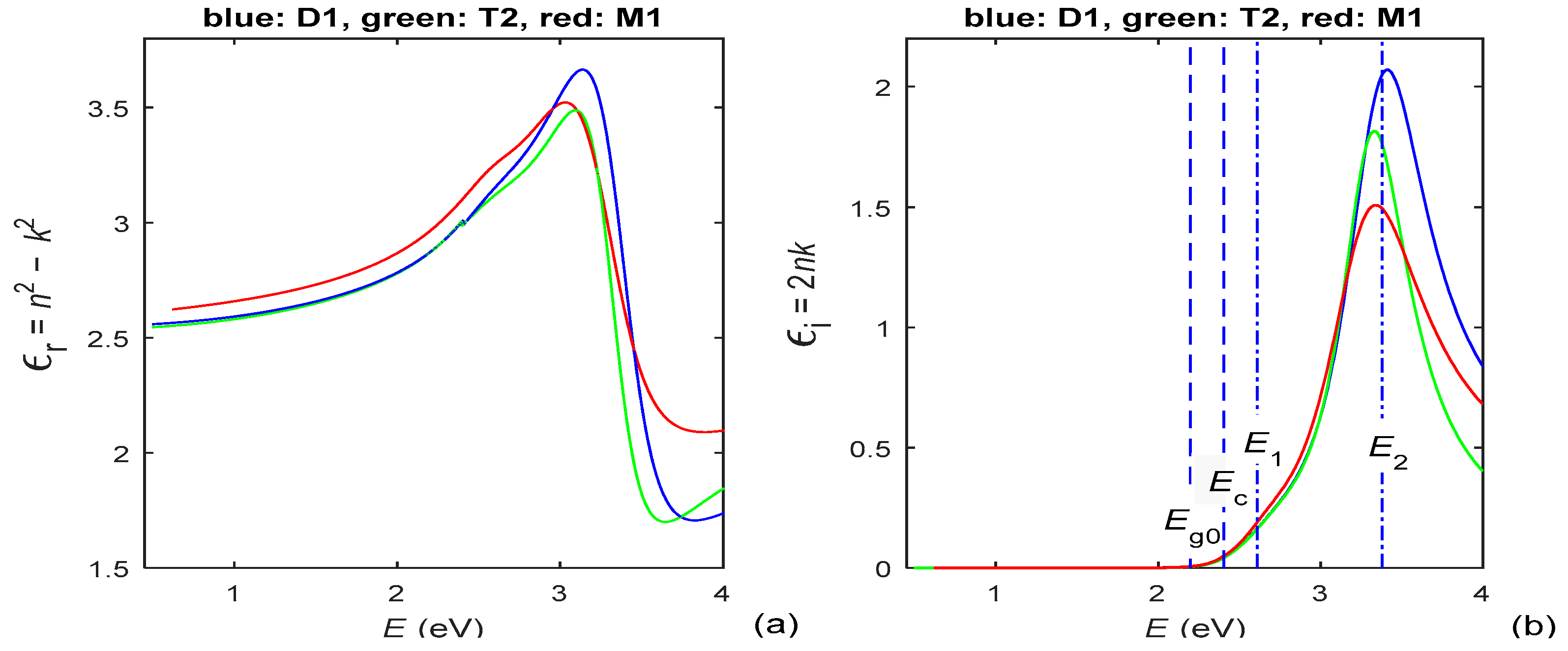
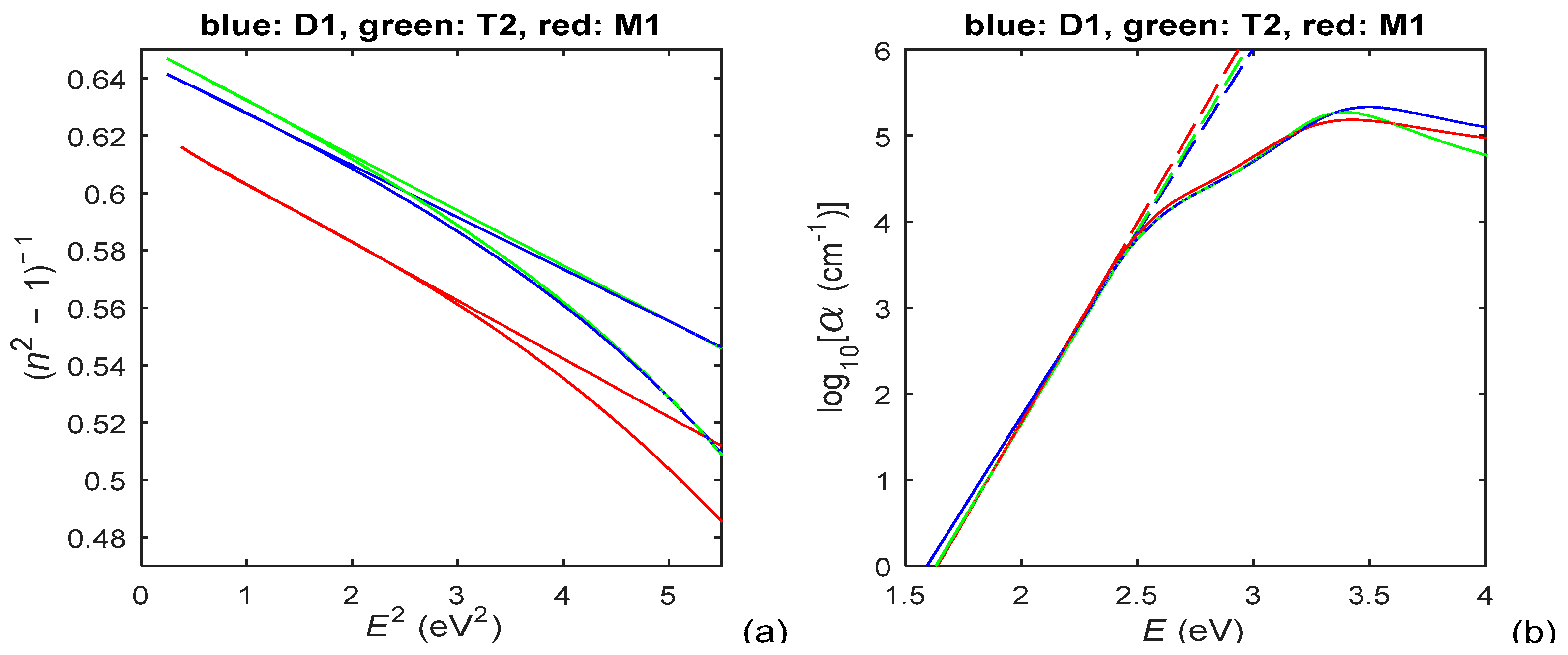
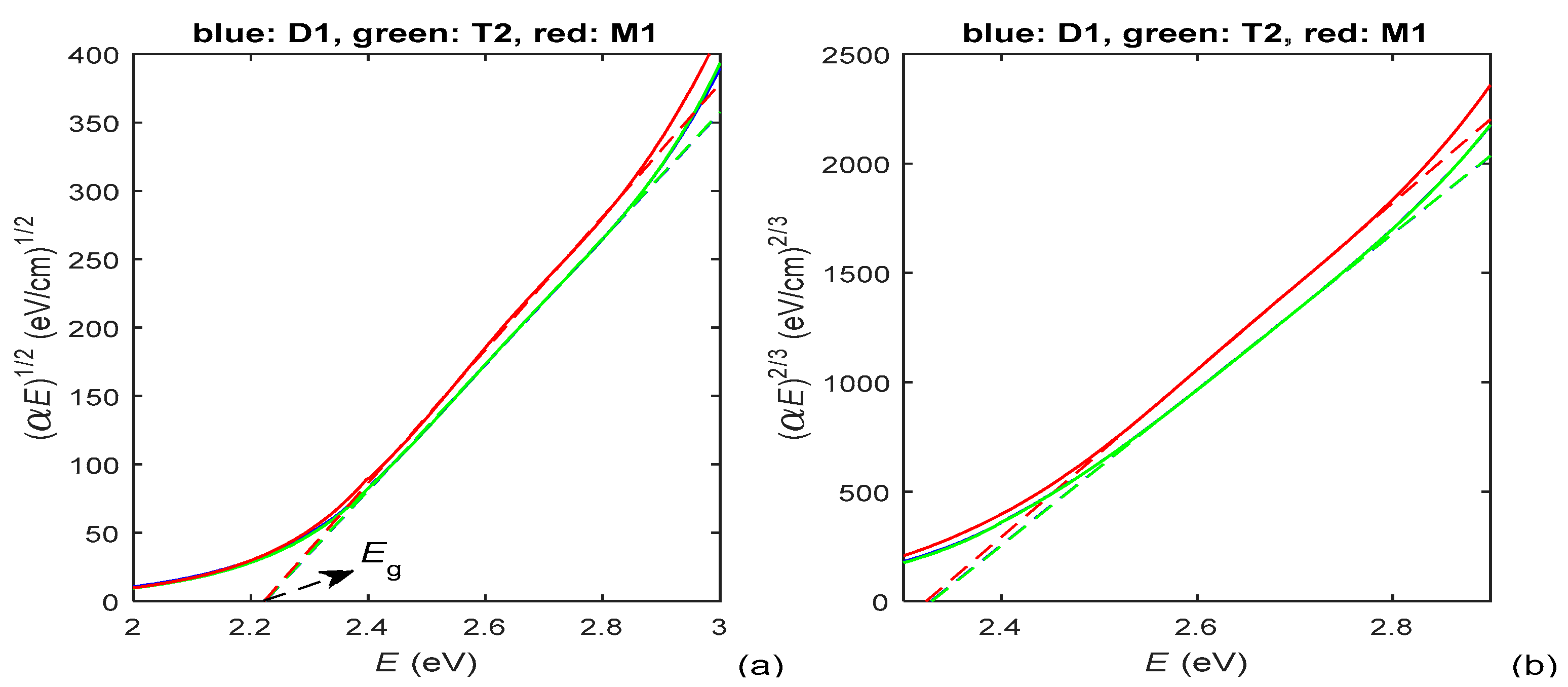
| Film | HDM for min(E) ≤ E < Ec, HDM for Ec ≤ E ≤ max(E) | Eg0 (eV) | Ec (eV) | EU (meV) | f1 ×0.001 | E1 (eV) | B1 (eV) | f2 ×0.001 | E2 (eV) | B2 (eV) | εr (∞) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | TLUF, NADF.2osc | 2.20 | 2.40 | 101.5 | 15.2 | 2.61 | 0.36 | 36.6 | 3.37 | 0.34 | 2.27 |
| T2 | TLUF, TL.2osc | 2.13 | 2.40 | 96.8 | 2154 | 2.67 | 0.72 | 7061 | 3.31 | 0.54 | 2.35 |
| M1 | TLUF, NADF.2osc | 2.02 | 2.23 | 93.8 | 9.12 | 2.62 | 0.30 | 37.7 | 3.27 | 0.39 | 2.43 |
| Film | E0 (eV) | Ed (eV) | n(0) | Eg (eV) | p | EM (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 5.97 | 9.25 | 1.60 | 2.225 | 1.77 | 6.30 |
| T2 | 5.83 | 8.94 | 1.59 | 2.224 | 1.84 | 6.09 |
| M1 | 5.55 | 8.90 | 1.61 | 2.223 | 1.76 | 5.78 |
| Film, | Dispersion Model | (nm) | (nm) | F | (F−FHDM)/F (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1, 1693 | TLUF | 32.2 | 1684 | −0.555 | 1.63 | 2.3 |
| TLUR | 32.3 | 1684 | −0.573 | 1.78 | 10.4 | |
| TL.2osc | 33.8 | 1682 | −0.673 | 2.99 | 46.8 | |
| NADF.2osc | 33.5 | 1682 | −0.685 | 2.34 | 31.9 | |
| HDM | 32.2 | 1684 | −0.555 | FHDM = 1.59 | ||
| T2, 992.4 | TLUF | 31.9 | 988.3 | −0.413 | 1.14 | 17.5 |
| TLUR | 31.3 | 985.8 | −0.665 | 1.52 | 38.0 | |
| TL.2osc | 36.4 | 986.3 | −0.614 | 2.14 | 94.4 | |
| NADF.2osc | 31.4 | 986.7 | −0.574 | 1.47 | 35.6 | |
| HDM | 31.9 | 988.3 | −0.413 | FHDM = 0.944 | ||
| M1, - | TLUF | 0.0 | 162.2 | 4.40 | 74.8 | |
| TLUR | 0.0 | 163.7 | 14.9 | 92.6 | ||
| TL.2osc | 30.3 | 157.2 | 1.49 | 40.1 | ||
| NADF.2osc | 25.6 | 159.6 | 1.15 | 3.3 | ||
| HDM | 25.6 | 159.6 | FHDM = 1.11 |
| Parameter | n | k | n | k | n | k | Eg (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| From | λ = 440 nm | λ = 1000 nm | λ = 2500 nm | ||||
| [20] | [1.85, 1.9] | [0.07, 0.075] | [1.56, 1.64] | [0.003, 0.014] | [1.45, 1.5] | [0.01, 0.02] | [2.45, 2.6] |
| [21] | [1.22, 1.42] | [0.024, 0.06] | [1.26, 1.45] | [0.01, 0.06] | - | - | [1.35, 1.75] |
| this study | [1.80, 1.85] | [0.09, 0.105] | [1.61, 1.64] | [1.1, 1.5]×10−7 | [1.59, 1.60] | 0 | [2.22, 2.23] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minkov, D.; Nedelchev, L.; Angelov, G.; Marquez, E.; Blagoeva, B.; Mateev, G.; Nazarova, D. Hybrid Dispersion Model Characterization of PAZO Azopolymer Thin Films over the Entire Transmittance Spectrum Measured in the UV/VIS/NIR Spectral Region. Materials 2022, 15, 8617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238617
Minkov D, Nedelchev L, Angelov G, Marquez E, Blagoeva B, Mateev G, Nazarova D. Hybrid Dispersion Model Characterization of PAZO Azopolymer Thin Films over the Entire Transmittance Spectrum Measured in the UV/VIS/NIR Spectral Region. Materials. 2022; 15(23):8617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238617
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinkov, Dorian, Lian Nedelchev, George Angelov, Emilio Marquez, Blaga Blagoeva, Georgi Mateev, and Dimana Nazarova. 2022. "Hybrid Dispersion Model Characterization of PAZO Azopolymer Thin Films over the Entire Transmittance Spectrum Measured in the UV/VIS/NIR Spectral Region" Materials 15, no. 23: 8617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238617
APA StyleMinkov, D., Nedelchev, L., Angelov, G., Marquez, E., Blagoeva, B., Mateev, G., & Nazarova, D. (2022). Hybrid Dispersion Model Characterization of PAZO Azopolymer Thin Films over the Entire Transmittance Spectrum Measured in the UV/VIS/NIR Spectral Region. Materials, 15(23), 8617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238617








