Study on Microstructure of Fiber Laser Welding of CoCrCuFeNi High Entropy Alloy
Abstract
1. Introtuction
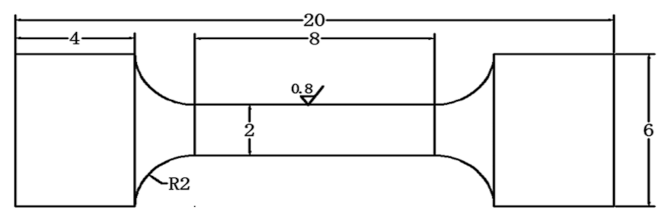
2. Materials and Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
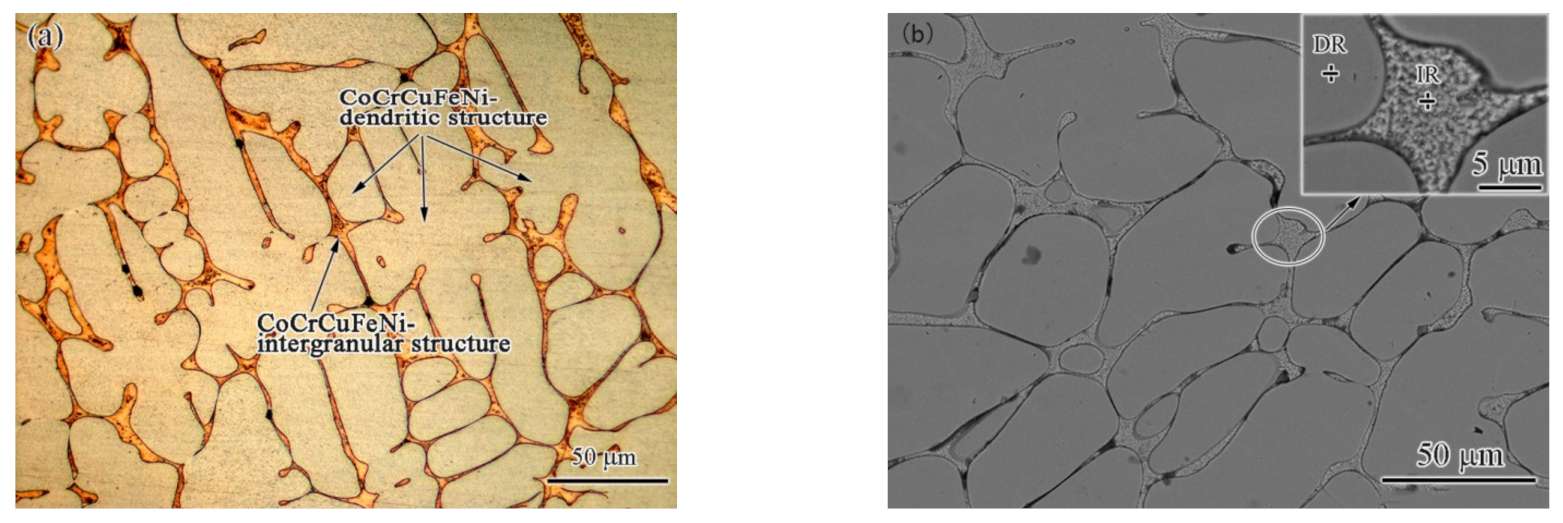
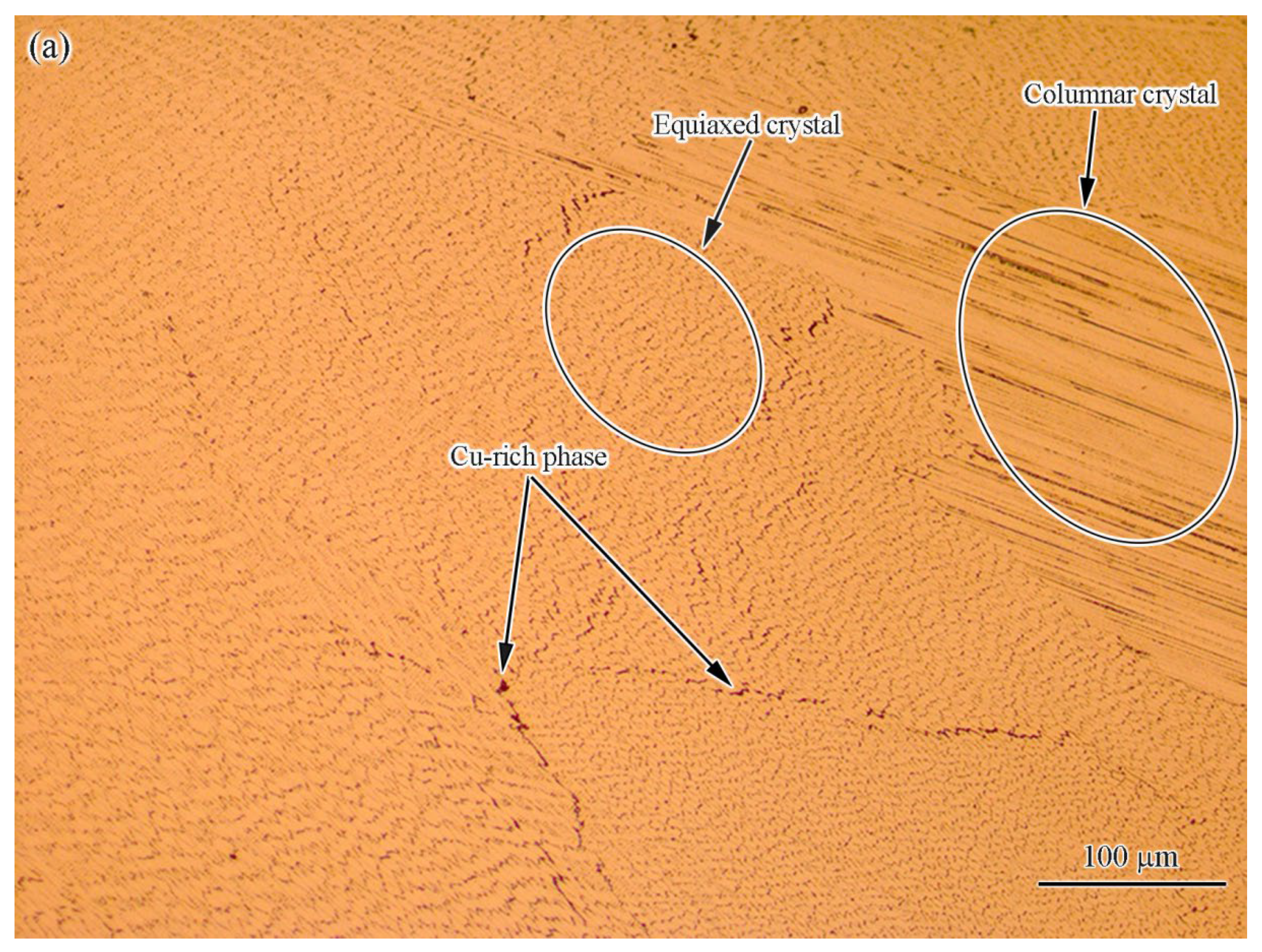
3.1. Basic Characteristics of Base Material
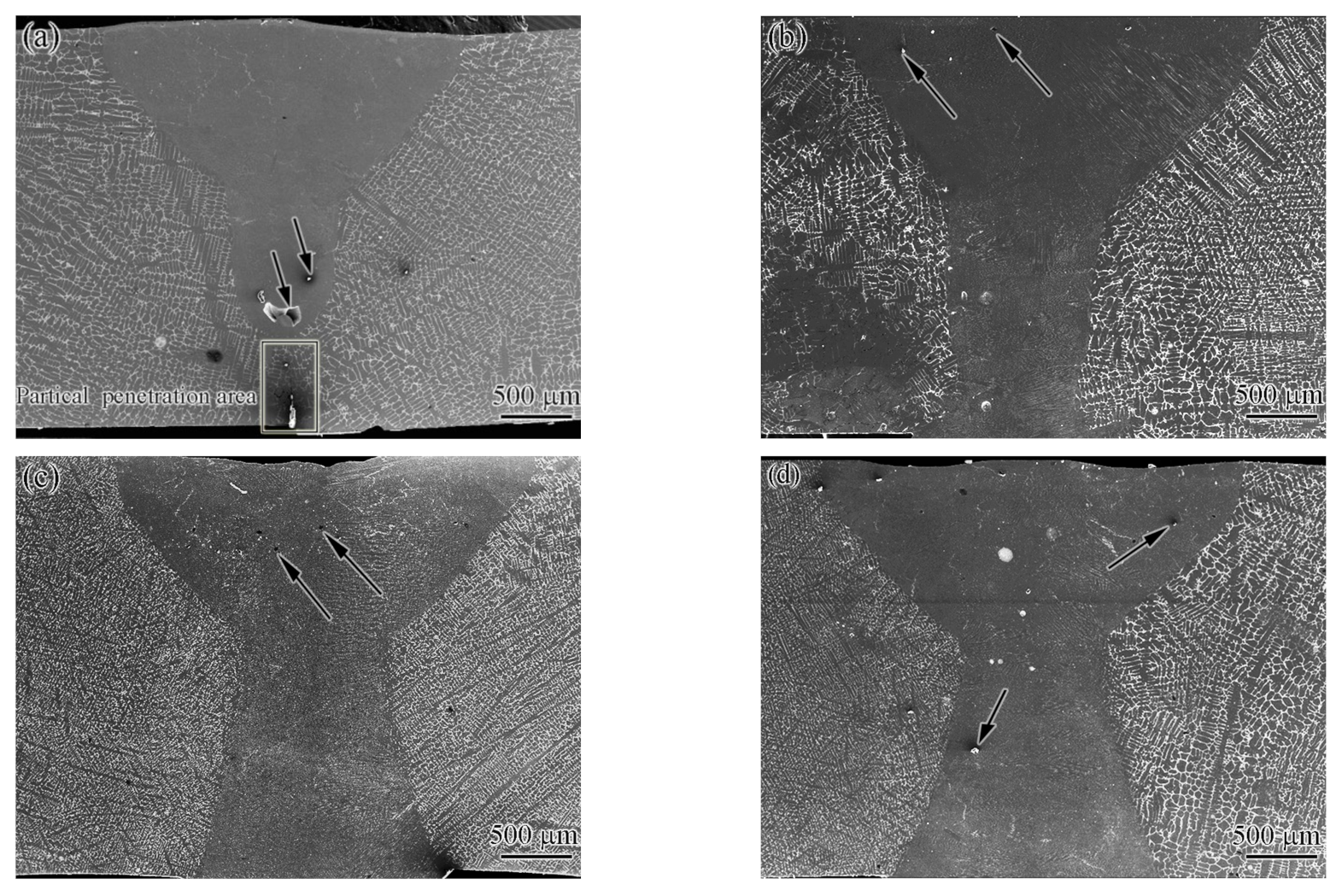
3.2. Weld Structure and Microstructure
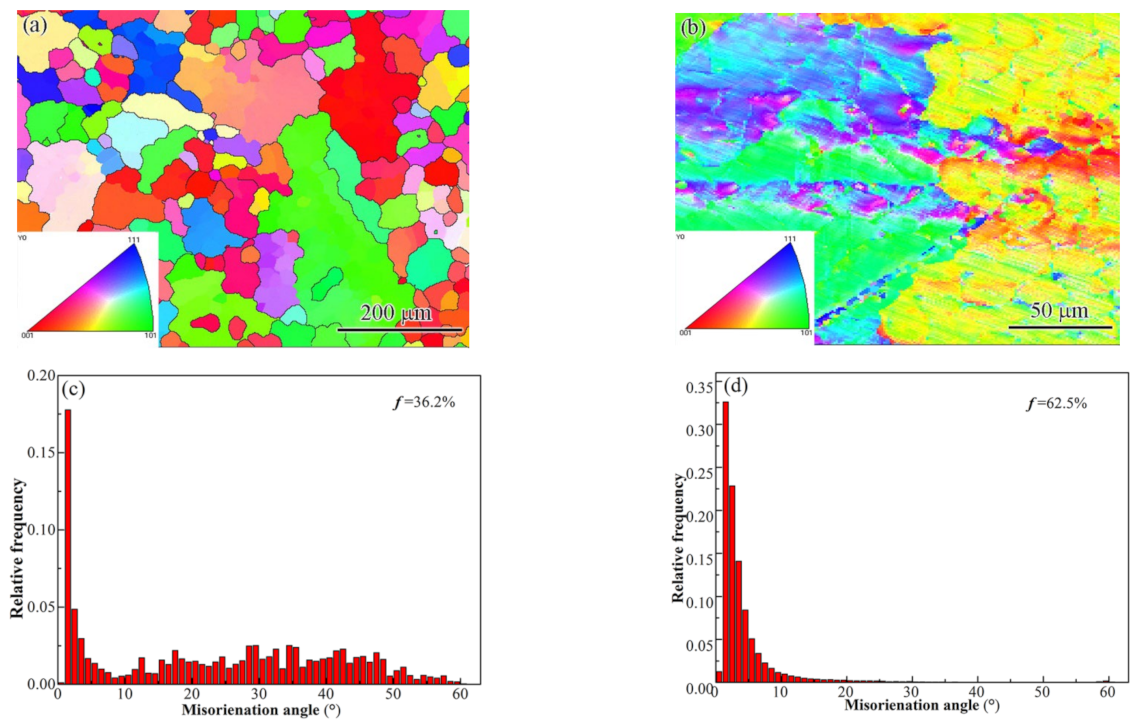
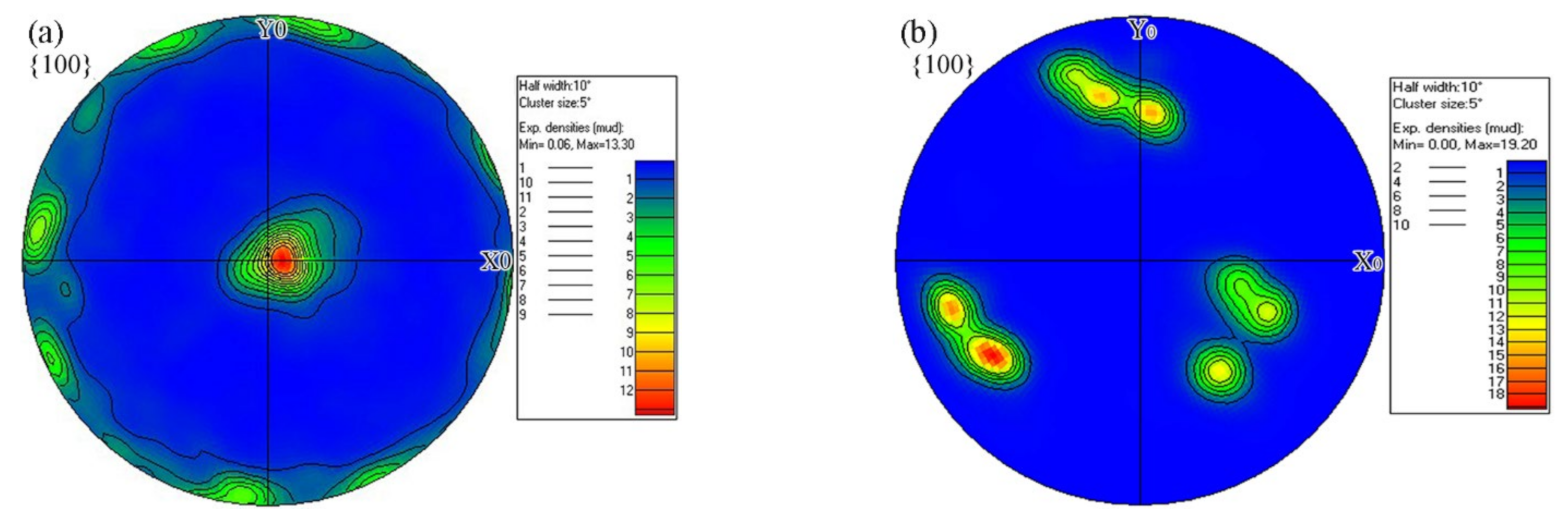
3.3. Misorientation Angle Analysis and Texture
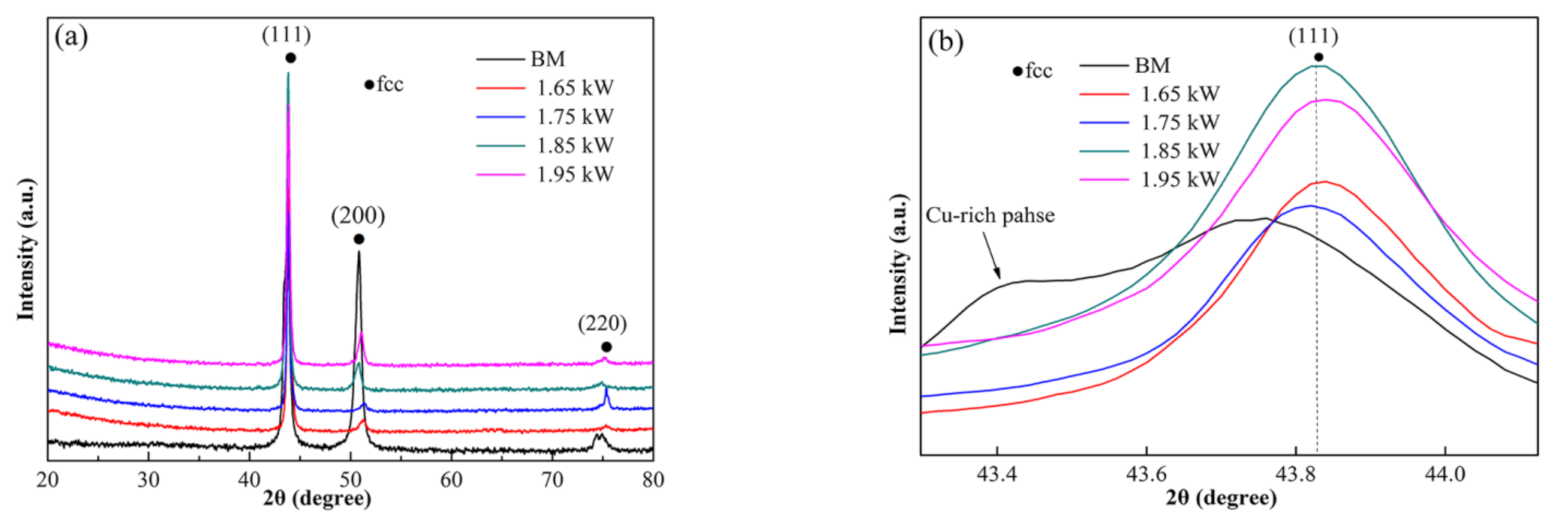
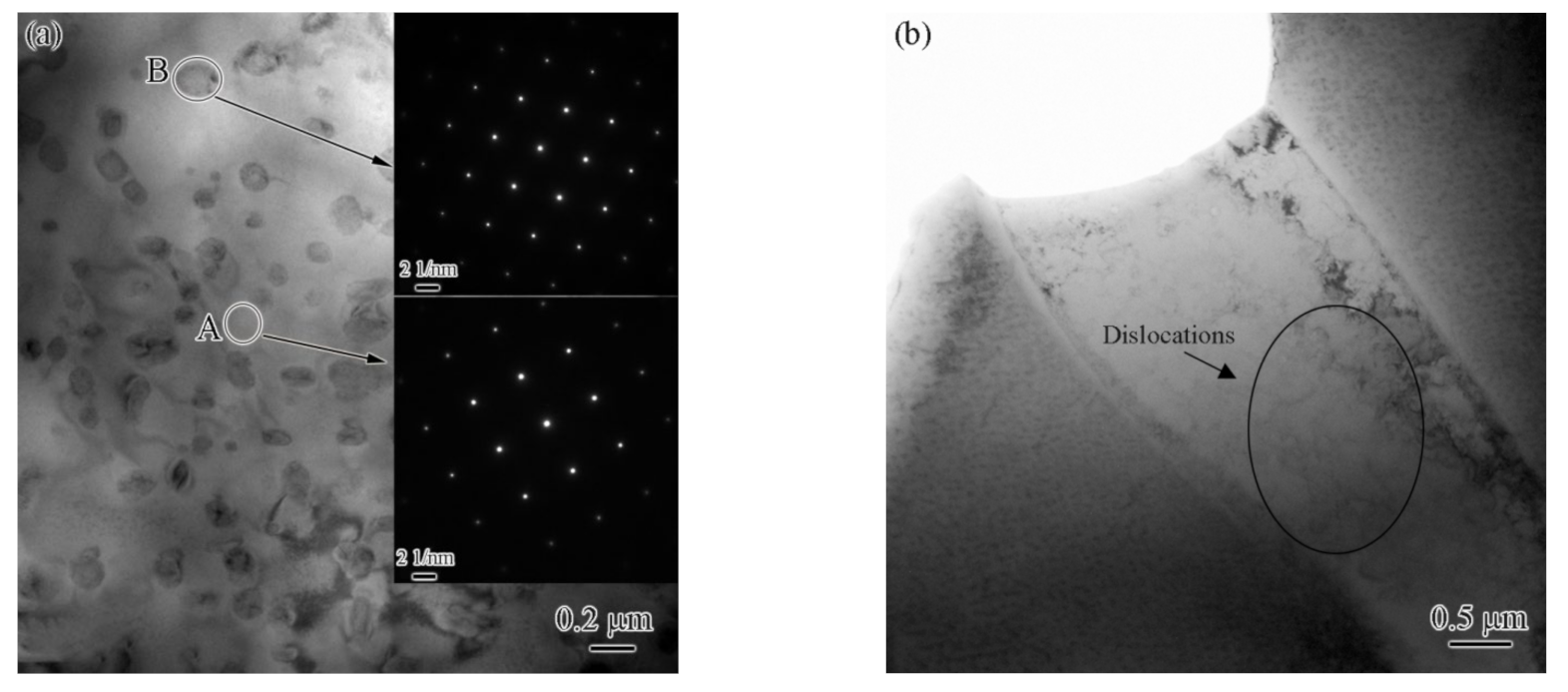
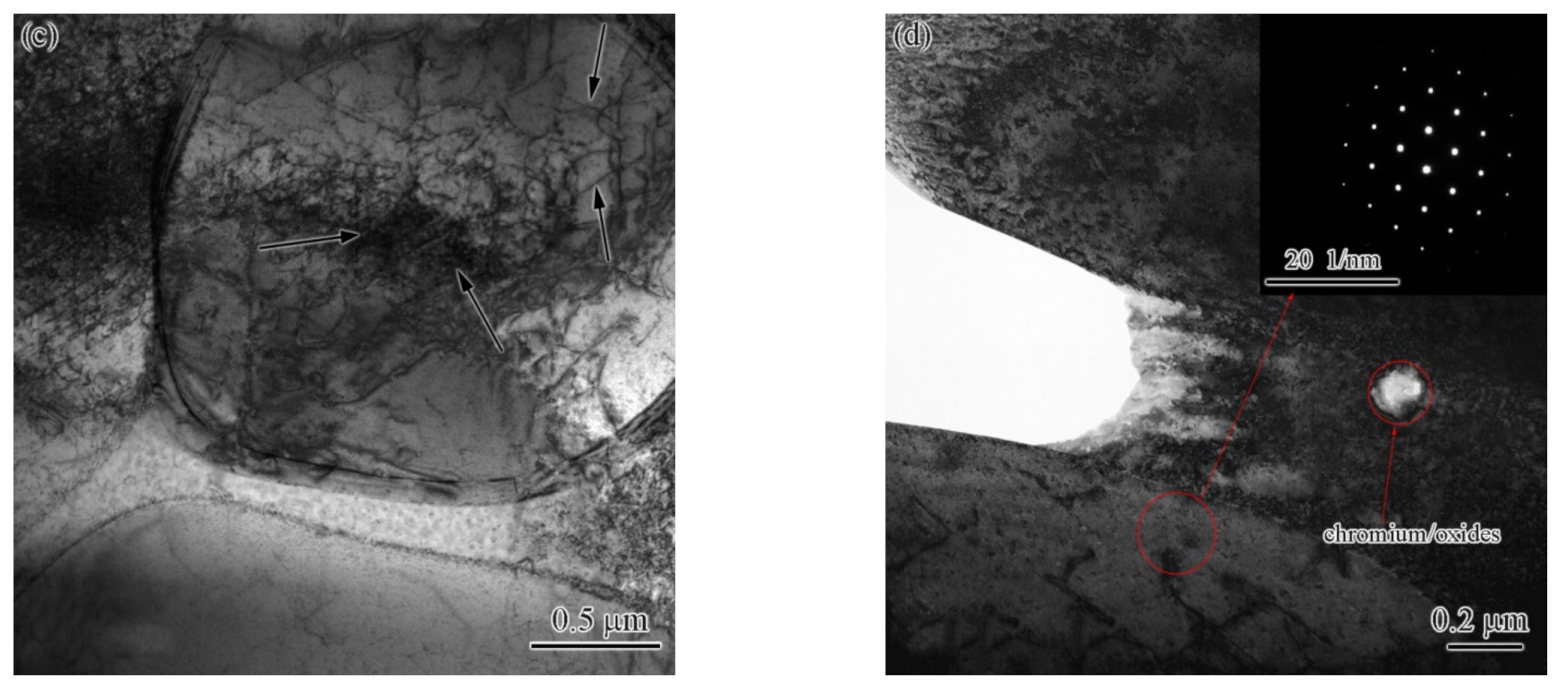
3.4. Analysis of Precipitated Phases and Dislocations
3.5. Mechanical Performance Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Three zones were formed in the welded joint: base metal, fusion zone, and partial melting zone.
- (2)
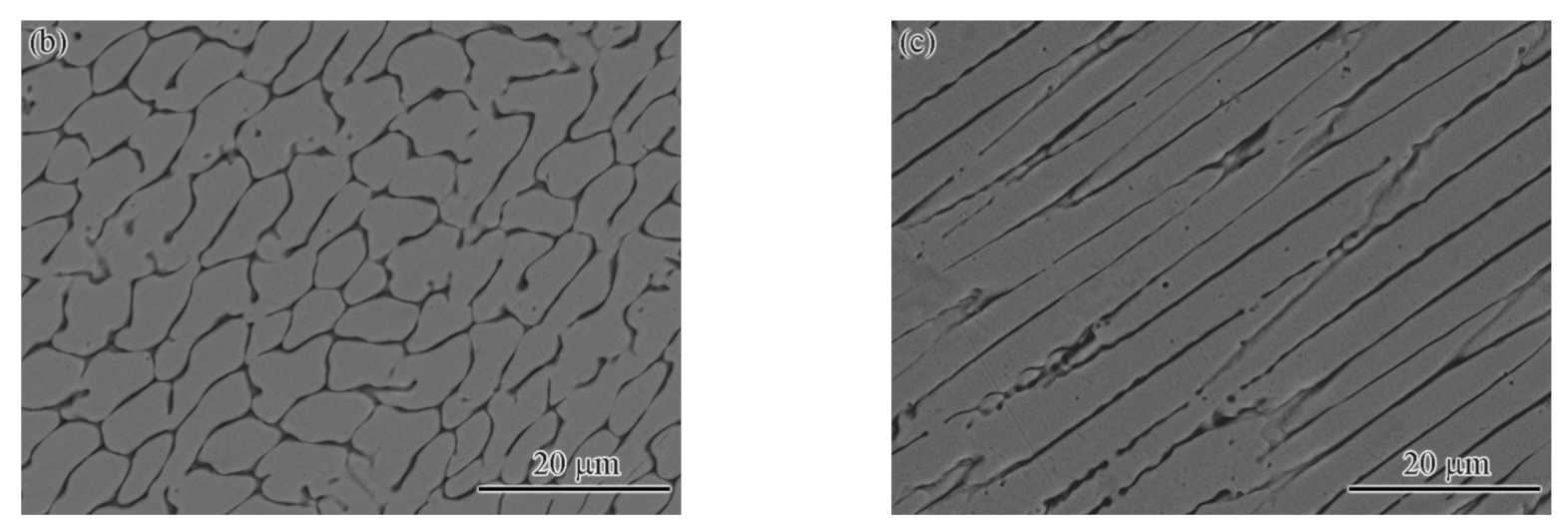
- The base metal exhibited a typical dendrite structure composed of the CoCrCuFeNi solid solution phase, and the Cu element segregated in the interdendrite, forming a Cu-rich phase. The content of Cu in the Cu-rich phase reached 79%.
- (3)
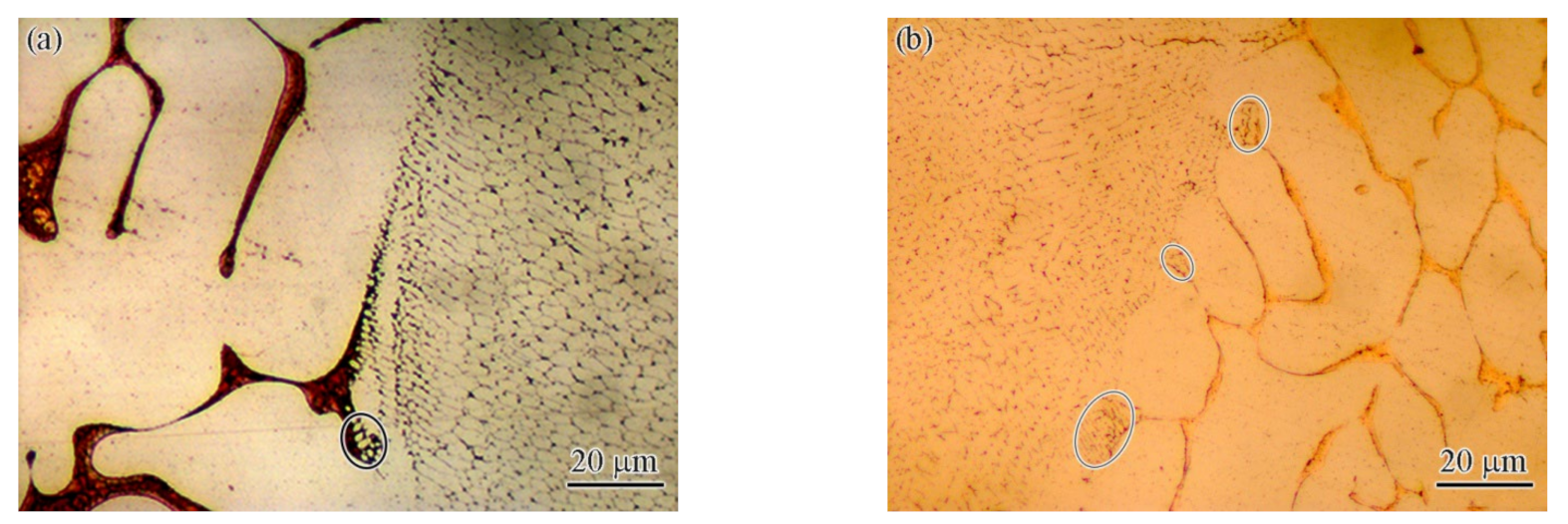
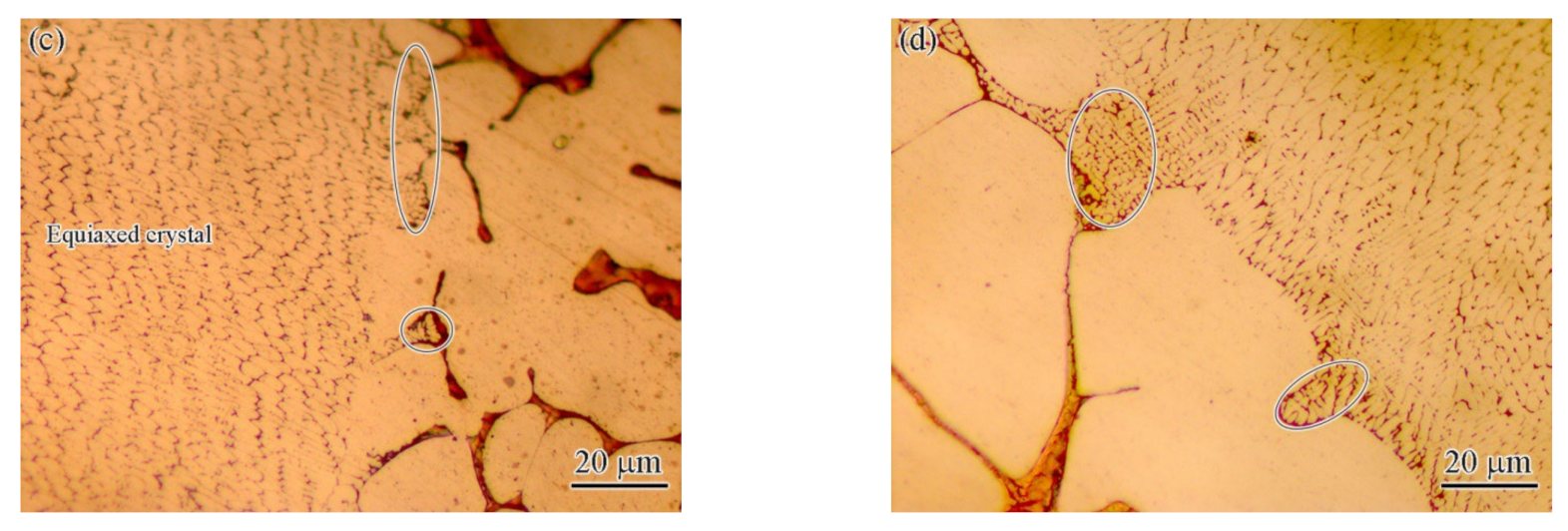
- The fusion zone was also composed of the CoCrCuFeNi solid solution phase and Cu-rich phase. The difference is that the solid solution phase consisted of fine equiaxed crystals (~10 μm) and columnar crystals. The Cu content of the copper-rich phase decreased significantly from 79.42 at.% to 22.24 at.%.
- (4)
- The partial melting zone (fusion line region) generated fine crystals present as spherical or fibrous shapes with a size of ~1 μm.
- (5)
- The low-angle grain boundary fraction was significantly increased from 36.2% in the BM to 62.5% in the FZ. High-density dislocations and dislocation pile-ups were produced at the same time.
- (6)
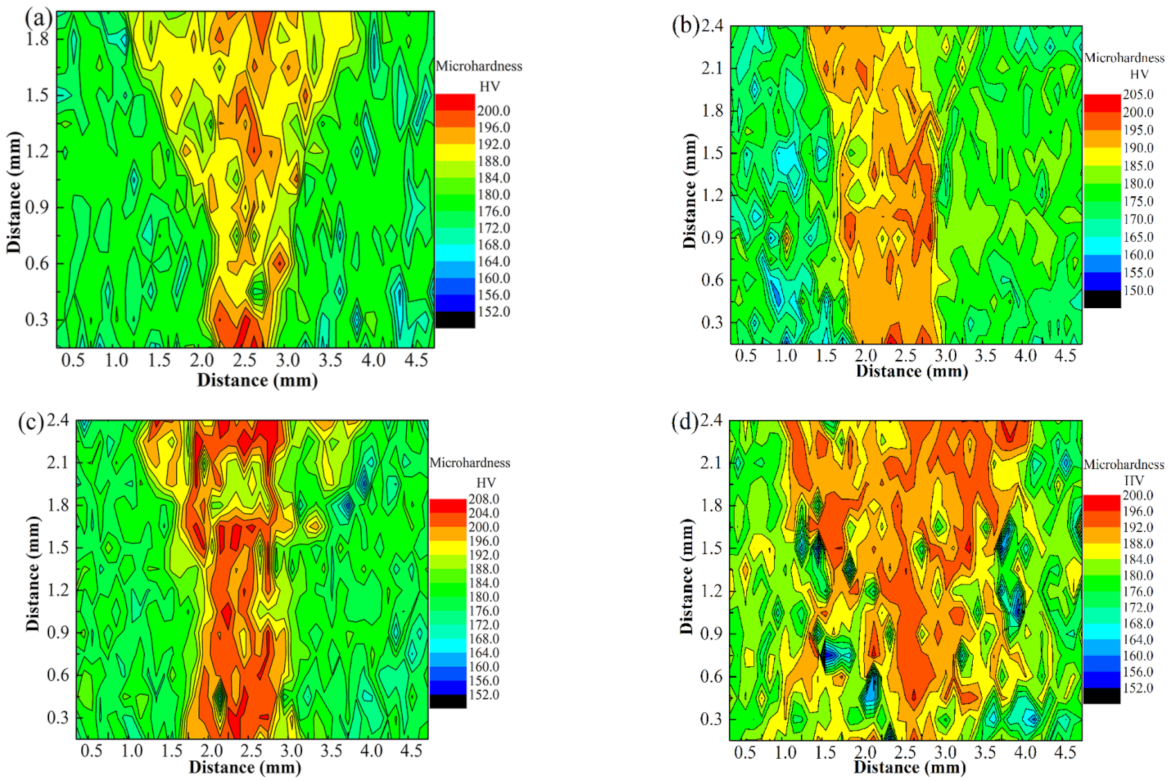
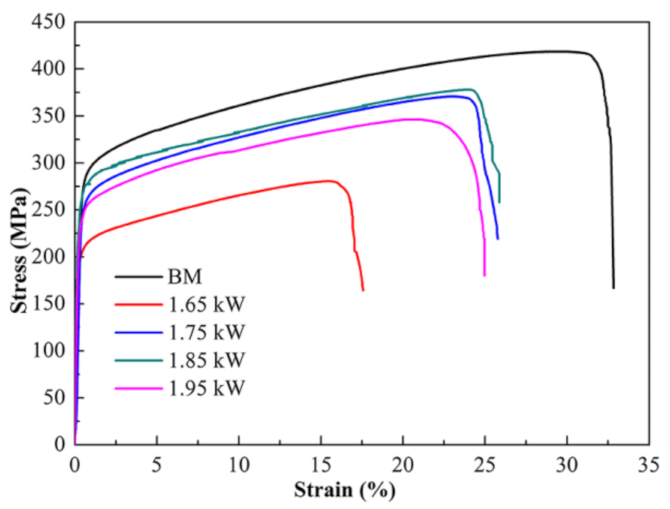
- Compared with the base metal, the hardness of FZ showed a significant increase. The UTS and elongation increased first and then decreased as the laser power was increased. The maximum value of the UTS exceeded that of the BM by 90%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.P.; Raabe, D.; Ritchie, R.O. High-entropy alloys. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, W. Recent progress in high-entropy alloys for catalysts: Synthesis, application and prospects. Mater. Today Energy 2021, 20, 100638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Dwivedi, V.K.; Dwivedi, S.P. Development of high entropy alloys: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Fang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Liu, B.; Sun, H.; Shao, Z.; Song, T. Research and development of welding methods and welding mechanism of high-entropy alloys: A review. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 28, 102503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdadi, N.; Primig, S.; Annasamy, M.; Cizek, P.; Hodgson, P.D.; Fabijanic, D.M. Dynamic recrystallization in AlXCoCrFeNi duplex high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 830, 154720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Parashar, A. Effect of lattice distortion and nanovoids on the shock compression behavior of (Co-Cr-Cu-Fe-Ni) high entropy alloy. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 209, 111402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Natu, H.; Balasundar, I.; Chelvane, A.; Niranjani, V.L.; Mohape, M.; Mahanta, G.; Gowtam, S.; Shanmugasundaram, T. Effect of copper on microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of laser-welded CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Sci. Technol. Weld Join. 2022, 27, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraju, S.; Bouzy, E.; Hazotte, A. Phase stability of a mechanically alloyed CoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1700095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Agrawal, P.; Rodrigues, T.A.; Lopes, J.G.; Schell, N.; Zeng, Z.; Mishra, R.S.; Oliveira, J.P. Gas tungsten arc welding of as-cast AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 2022, 223, 111176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, K.N.; Freitas, C.C.D.; Fanton, L.; Caram., R. Melting behavior and globular microstructure formation in semi-solid CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 52, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Fan, J.T.; Liu, D.J.; Zhang, M.D.; Yu, P.F.; Jing, Q.; Ma, M.Z.; Liaw, P.K.; Li, G.; Liu, R.P. The microstructural evolution and hardness of the equiatomic CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy in the semi-solid state. J. Alloy Compd. 2018, 745, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.P.; Zhang, W.Q.; Fu, H.M. Crack analysis of pulsed laser welding joint of high-entropy alloy CuCoCrFeNi thin sheet. Hot Work. Technol. 2017, 9, 234–237. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.P.; Zhang, W.Q.; Fu, H.M.; Luo, G.M. Study on microstructure and properties of laser welded joint of dissimilar high entropy alloy CuCoCrFeNi and AlCoCrFeNi. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 4, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, K.; Fu, L.; Shan, A.; Chen, Z. Effect of fiber laser welding on solute segregation and proprieties of CoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloy. J. Laser Appl. 2020, 32, 022005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Tarate, P.; Abhyankar, A.C.; Mohape, M.R.; Gowtam, D.S. High temperature wear in CoCrFeNiCux high entropy alloys: The role of Cu. Scr. Mater. 2019, 161, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Hu, L.; Luo, S.B.; Meng, L.J.; Geng, D.L.; Wei, B. Liquid phase separation and rapid dendritic growth of high-entropy CoCrCuFeNi alloy. Intermetallics 2016, 77, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Qin, Q.D.; Su, X.D. Diffusion bonding of CoCrFeNiCu high-entropy alloy to 304 stainless steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2021, 57, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.P. Study on Laser Weldability of CuCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy; Shenyang Ligong University: Shenyang, China, 2017; pp. 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Meng, Z.; Chen, B.; Tan, C.; Song, X.; Wang, G. Prediction of temperature field and residual stress of oscillation laser welding of 316LN stainless steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 145, 107493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, H.; Akbari, M. Investigating the effect of process parameters on the temperature field and mechanical properties in pulsed laser welding of Ti6Al4V alloy sheet using response surface methodology. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 106, 103267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, B.S.; Yeh, J.W.; Ranganathan, S. High-Entropy Alloys; Butterworth-Heinemann: Landon, UK, 2014; pp. 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, L.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Peng, Q.; He, X.; Sui, C. Partially unzipping carbon nanotubes: A route to synchronously improvefracture strength and toughness of nanocomposites inspired by pinning effect of screw. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.D.; Liu, N.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, P.J.; Xiang, H.F.; Wang, X.J. The effect of Ti addition on phase selection of CoCrCu0.5FeNi high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; David, S.A.; Leonard, D.N.; Feng, Z.; Bei, H. Microstructures and mechanical properties of a welded CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Sci. Technol. Weld Join. 2018, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdadi, N.; Primig, S.; Annasamy, M.; Cizek, P.; Hodgson, P.D.; Fabijanic, D.M. On the hot-worked microstructure of a face-centered cubic Al0.3 CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Scr. Mater. 2020, 178, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Song, Q.; Bao, Y. Microstructure evolution and machinal properties of friction stir welded FeCrNiCoMn high-entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashaev, N.; Ventzke, V.; Petrov, N.; Horstmann, M.; Zherebtsov, S.; Shaysultanov, D.; Sanin, V.; Stepanov, N. Fatigue behaviour of a laser beam welded CoCrFeNiMn-type high entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 766, 138358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; David, S.A.; Feng, Z.; Bei, Z. Weldability of a high entropy CrMnFeCoNi alloy. Scr. Mater. 2016, 124, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.G.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, M.J.; Madakashira, P.P.; Park, S.E.; Suh, J.Y.; Kim, D.I.; Hong, S.T.; Han, H.N. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded and laser welded high entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi. Met. Mater. Int. 2018, 24, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.; Park, C.; Kim, C.; Kim, H.; Kang, N. Effect of post weld heat treatment on weldability of high entropy alloy welds. Sci. Technol. Weld Join. 2018, 23, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Huang, R.; Sun, Y.; Tan, C.; Wu, L.; Chen, B.; Song, X.; Li, G. Microstructure and mechanical properties of fiber laser welded QP980/press-hardened 22MnB5 steel joint. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10079–10090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Co | Cr | Cu | Fe | Ni | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base metal | DR | 23.49 | 23.14 | 9.32 | 24.61 | 19.44 |
| IR | 3.71 | 4.17 | 79.42 | 4.38 | 8.32 | |
| Fusion zone | DR | 21.47 | 21.72 | 14.81 | 21.24 | 19.76 |
| IR | 19.31 | 19.07 | 22.24 | 19.71 | 19.67 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Q.; Wang, D.; Jiao, J.; Tang, G.; Li, Y. Study on Microstructure of Fiber Laser Welding of CoCrCuFeNi High Entropy Alloy. Materials 2022, 15, 8777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248777
Li J, Zhao H, Zhou N, Zhang Y, Qin Q, Wang D, Jiao J, Tang G, Li Y. Study on Microstructure of Fiber Laser Welding of CoCrCuFeNi High Entropy Alloy. Materials. 2022; 15(24):8777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248777
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Juan, Honglong Zhao, Nian Zhou, Yingzhe Zhang, Qingdong Qin, Daoyi Wang, Jianguo Jiao, Guoli Tang, and Yonghua Li. 2022. "Study on Microstructure of Fiber Laser Welding of CoCrCuFeNi High Entropy Alloy" Materials 15, no. 24: 8777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248777
APA StyleLi, J., Zhao, H., Zhou, N., Zhang, Y., Qin, Q., Wang, D., Jiao, J., Tang, G., & Li, Y. (2022). Study on Microstructure of Fiber Laser Welding of CoCrCuFeNi High Entropy Alloy. Materials, 15(24), 8777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248777






