Behavior of Mold Electromagnetic Stirring for Round Bloom Castings and Its Eccentric Stirring Problem
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model
2.1. Coupling Model
- (1)
- Ignoring the effects of mold taper, mold vibration, strand curvature, and solidification shrinkage on the flow and temperature state of the internal molten steel, the casting process is steady state with constant casting speed, superheat degree, and cooling conditions.
- (2)
- The molten steel is considered as an incompressible Newtonian fluid and the thermal parameters such as density, viscosity, specific heat and thermal conductivity are treated as constants.
- (3)
- (4)
- The magnetic Reynolds number Rm is much less than 1 in the mold metallurgical process, i.e., the influence of the molten steel flow on the magnetic field is negligible.
- (5)
- Under the low-frequency condition of M-EMS, the period of the alternating current controlling the change of magnetic field is much smaller than the momentum response time of the molten steel, so the time-varying electromagnetic force can be replaced by the time-averaged electromagnetic force under the harmonic magnetic field [32].
- (6)
- The Joule heat from M-EMS and the heat from the solid-state phase change after solidification are much smaller than the latent heat of solidification, and their effects on heat transfer and solidification are ignored.
2.2. Boundary Conditions
2.2.1. Electromagnetic Field
- Three pairs of coil windings are loaded with a three-phase alternating current; the phase difference of each phase is 120°.
- The magnetic flux lines are parallel to the boundary at the external surfaces of the surrounding air unit.
- Insulation boundary conditions are imposed between the electromagnetic stirrer coil and the iron core.
2.2.2. Flow and Solidification
2.3. Solver Setting
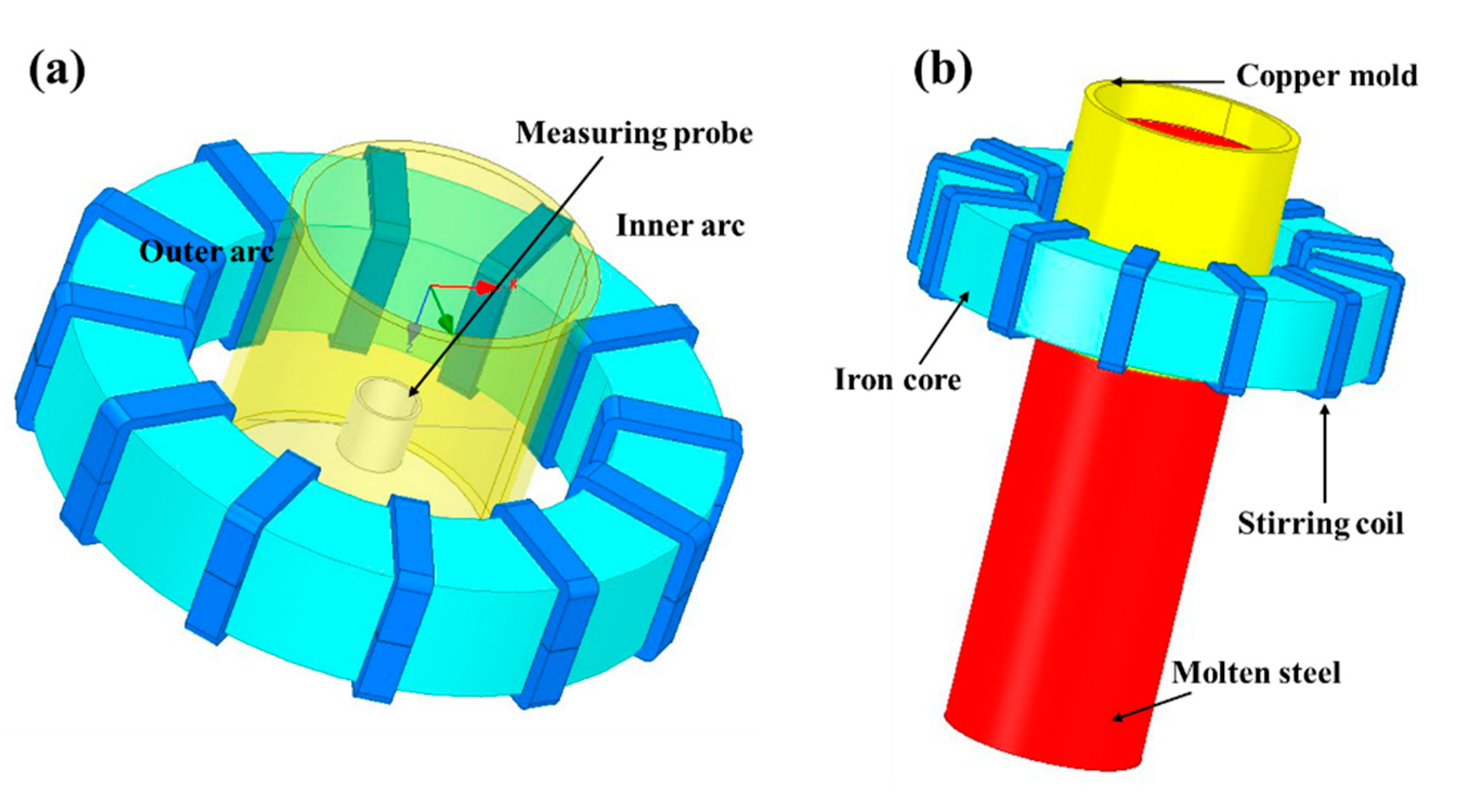
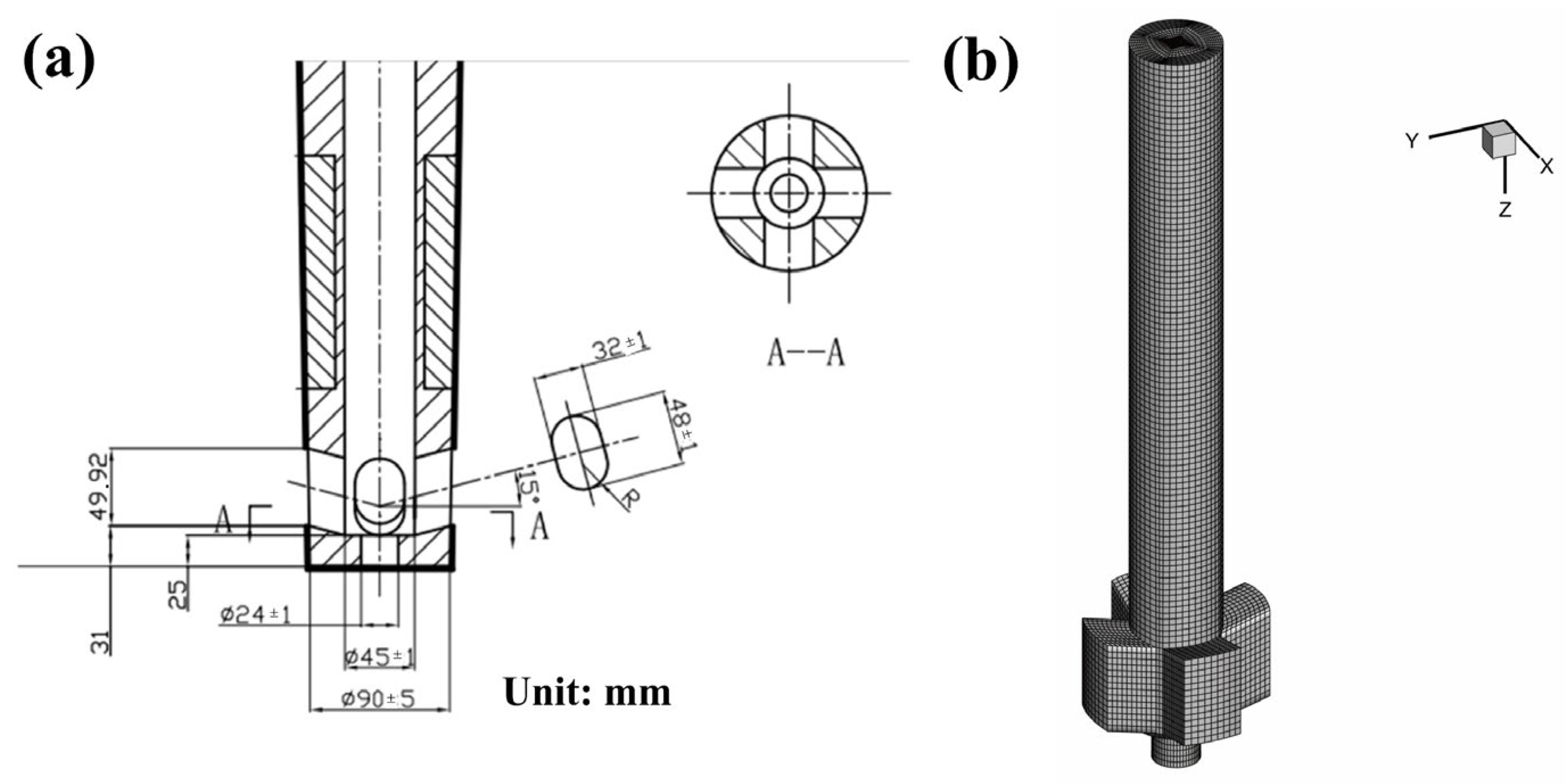
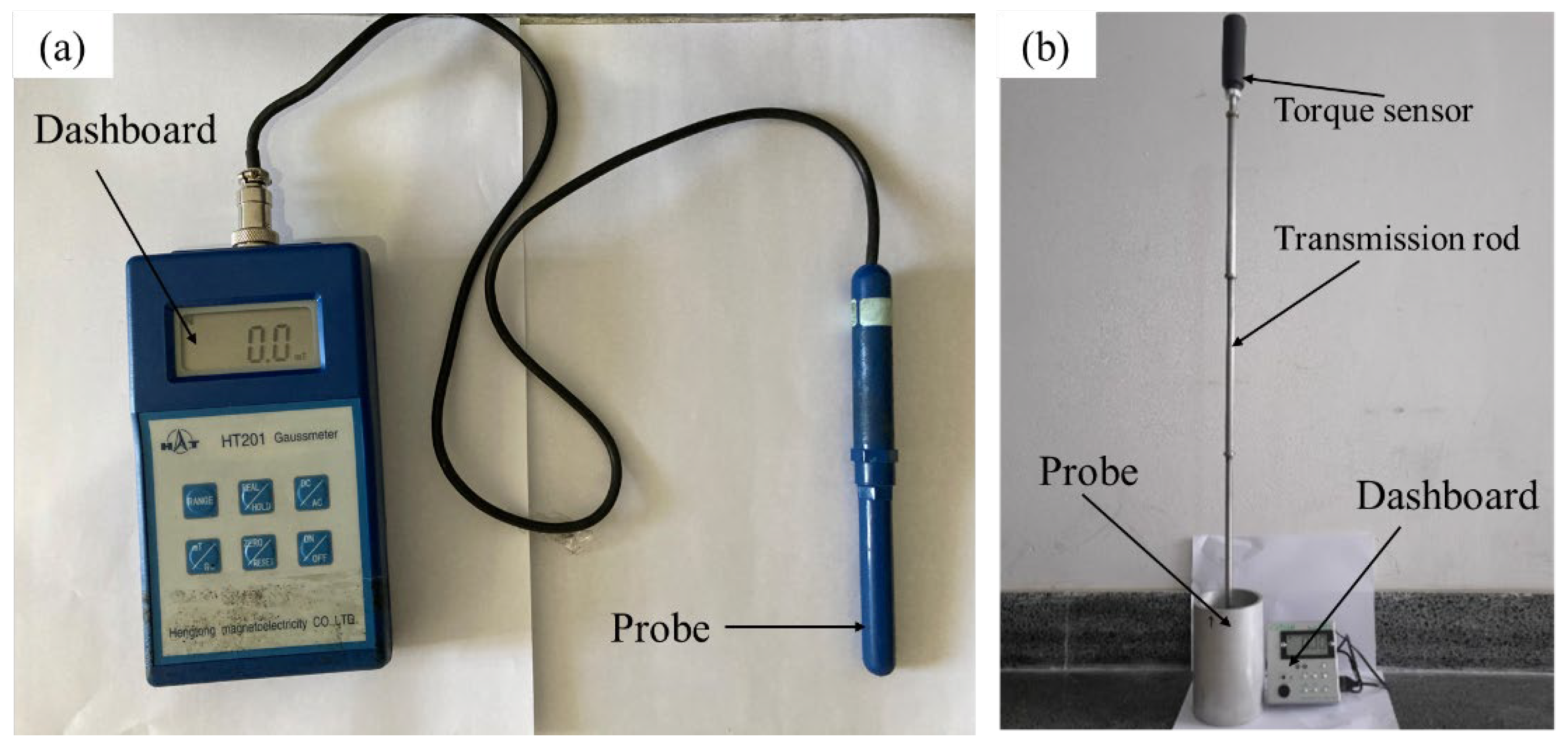
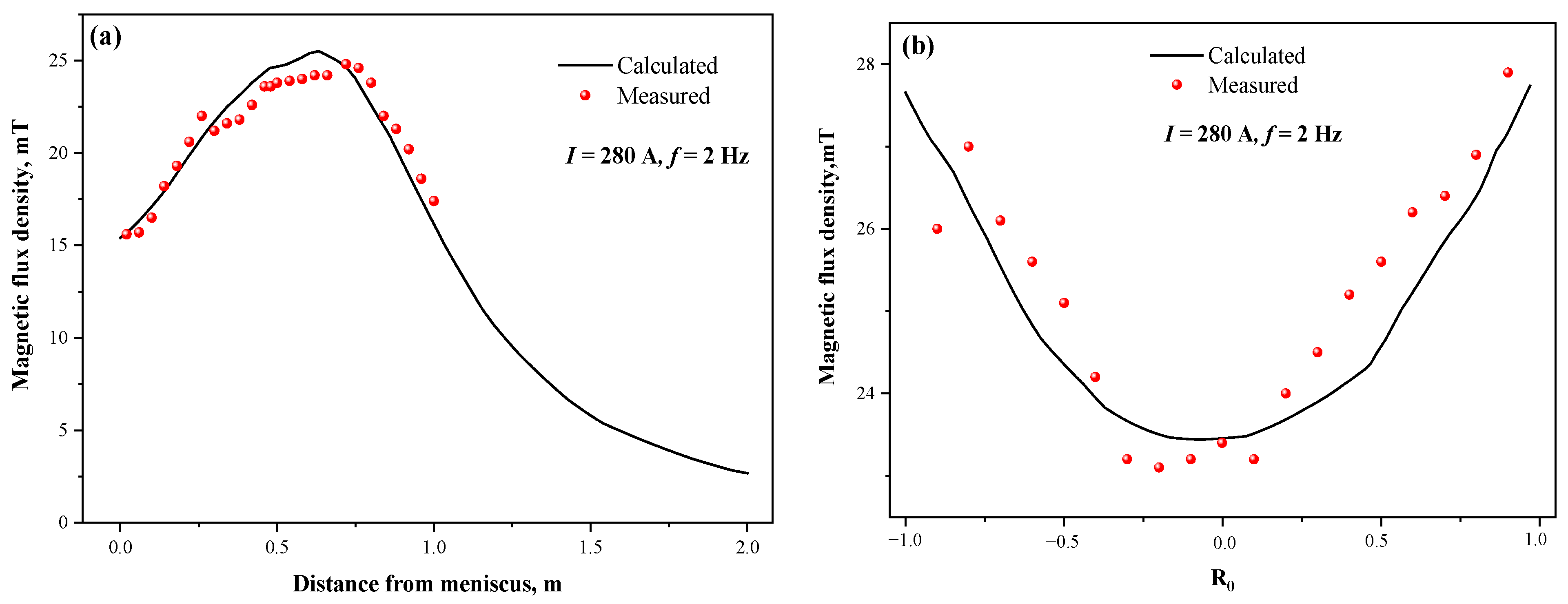
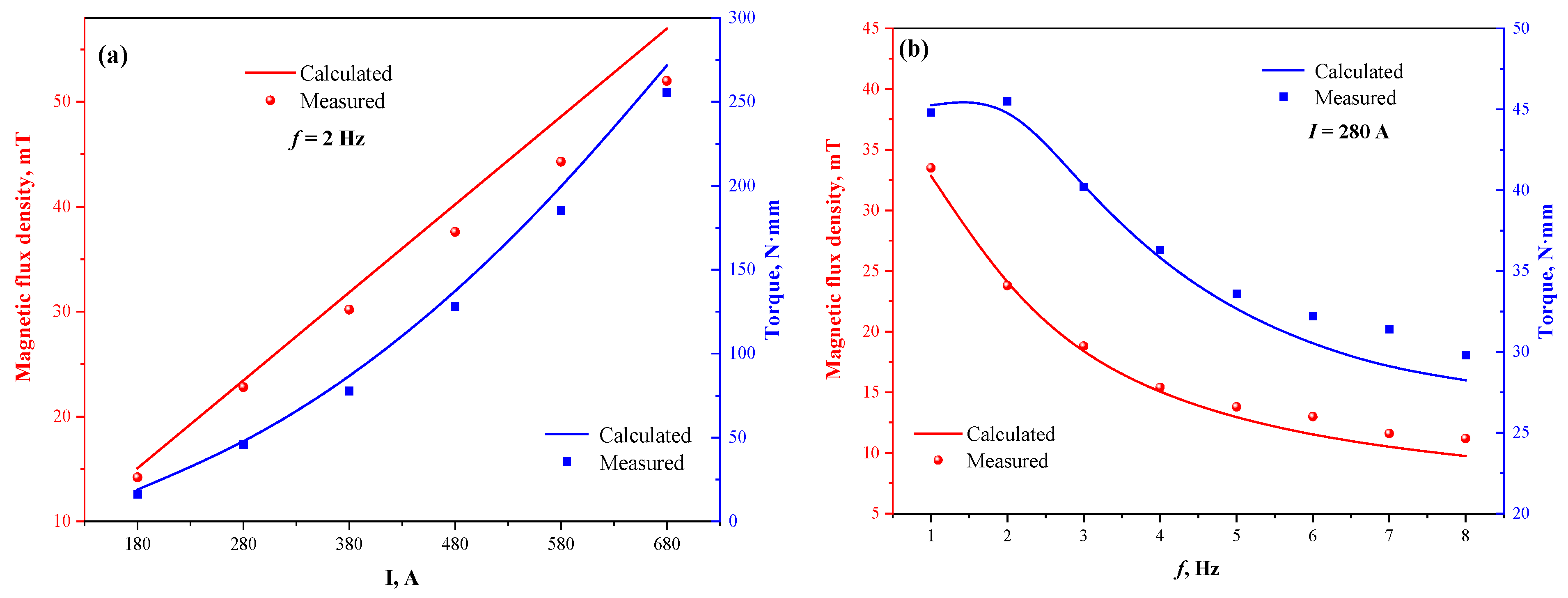
2.4. Numerical Model Validation
3. Behavior of M-EMS for Round Blooms
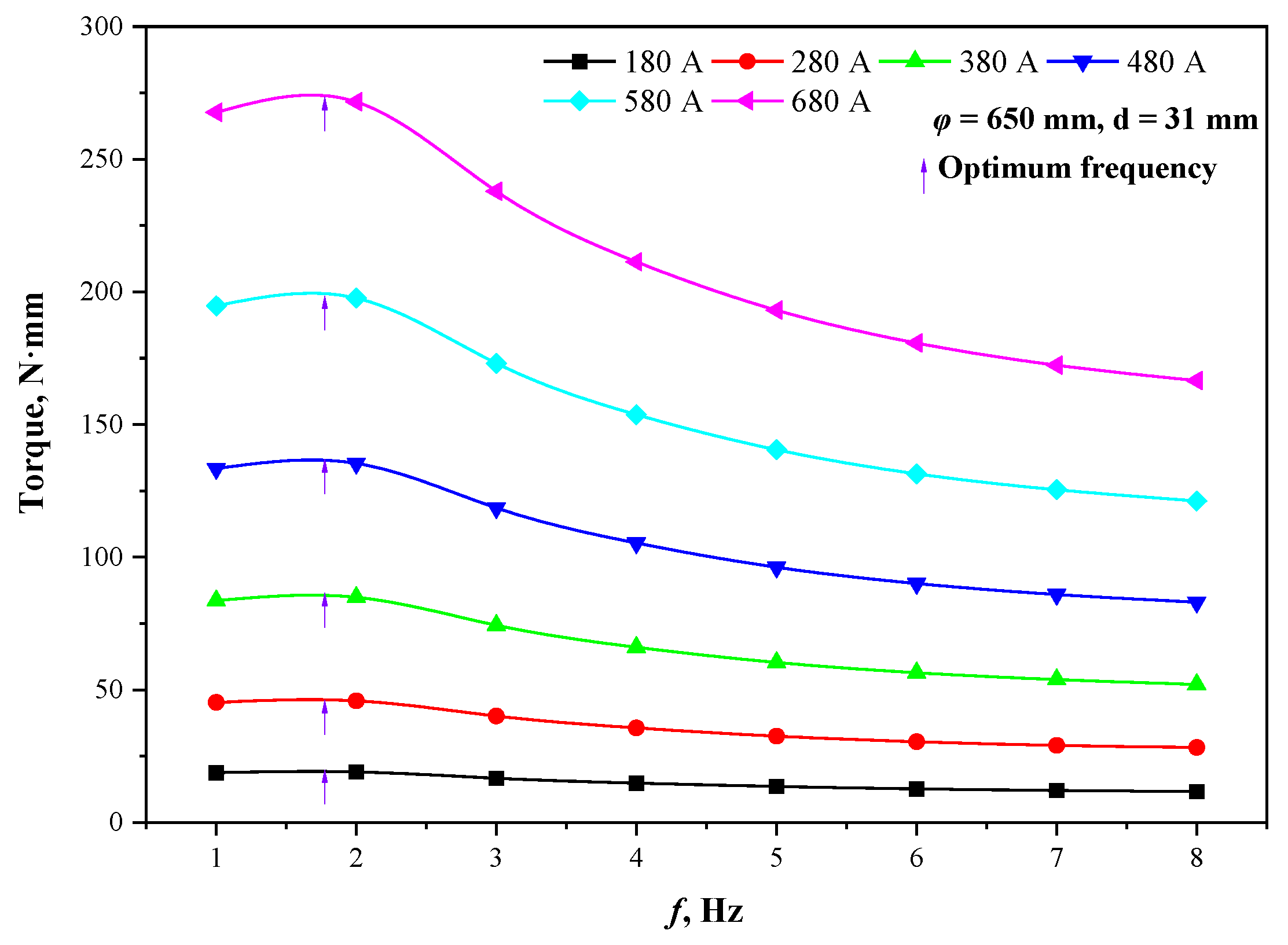
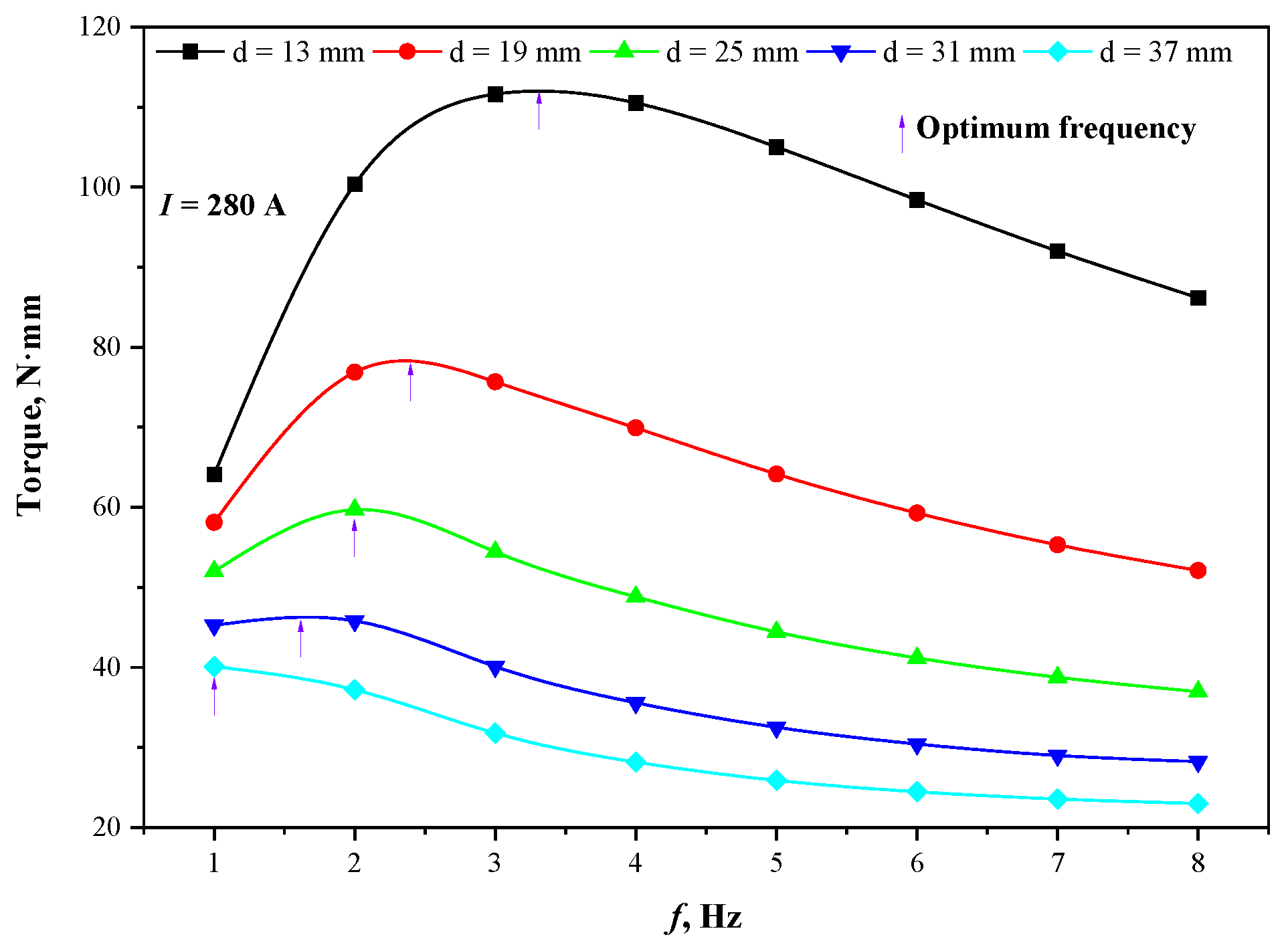
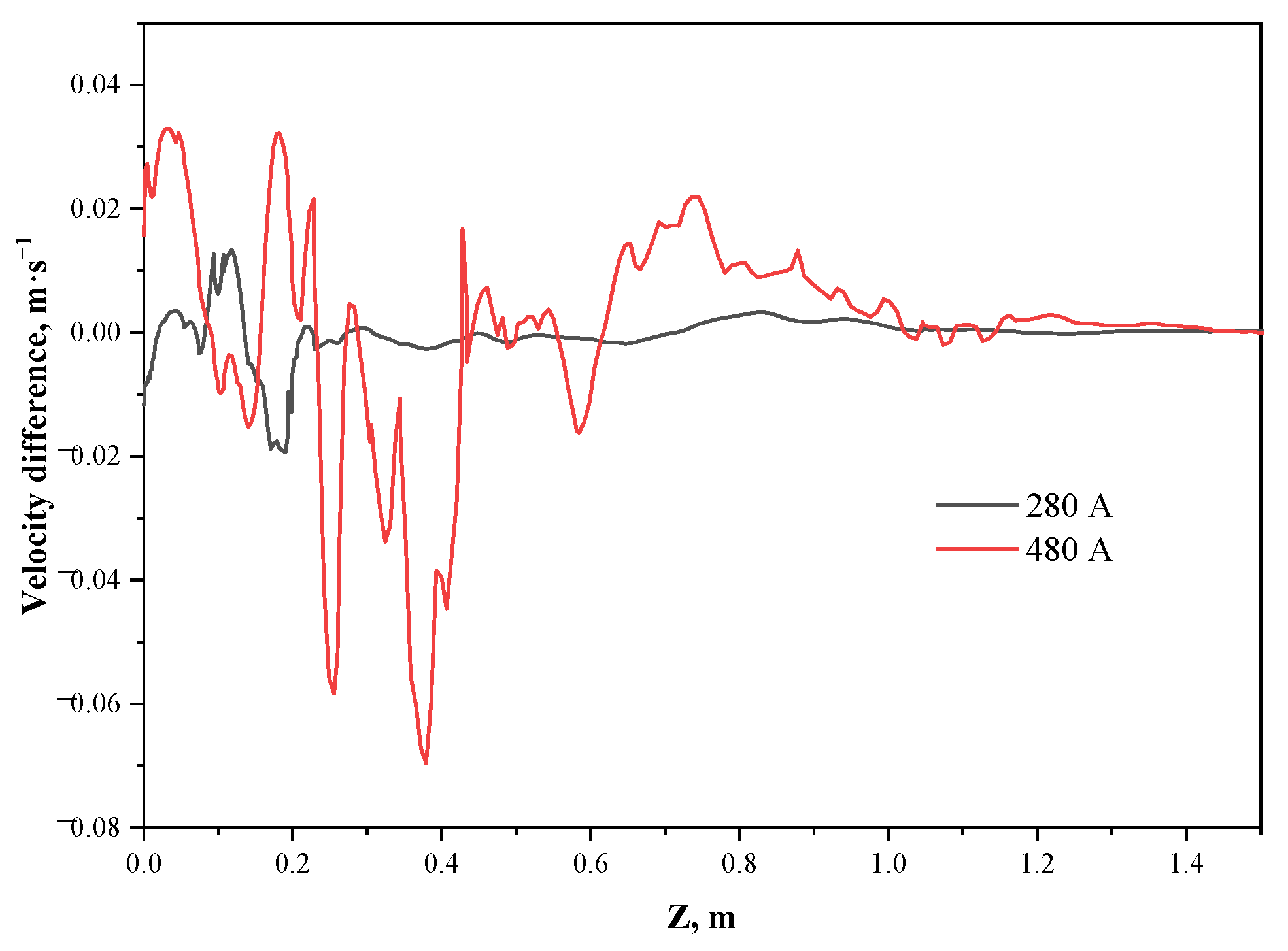
3.1. Effect of Current Parameters
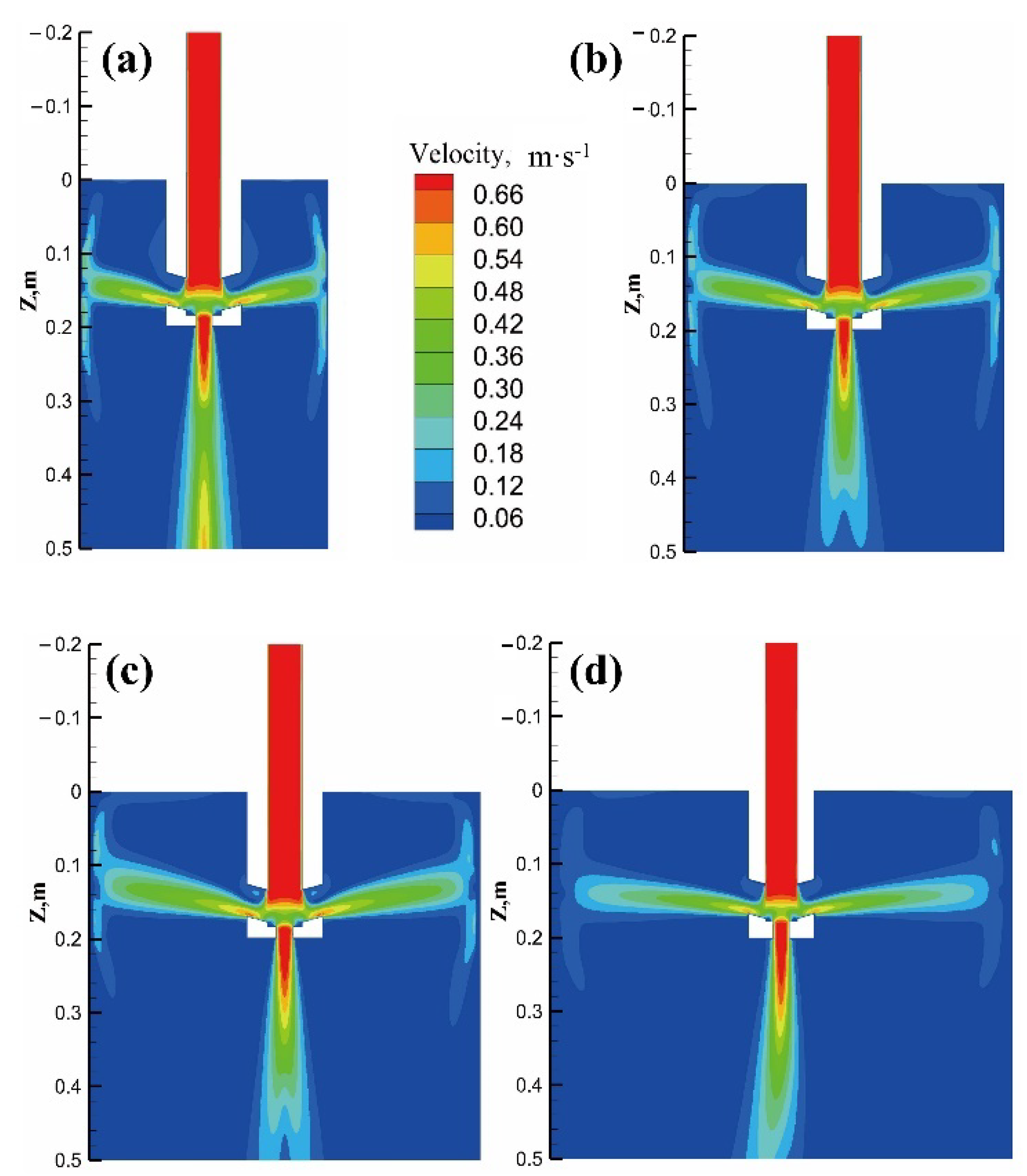
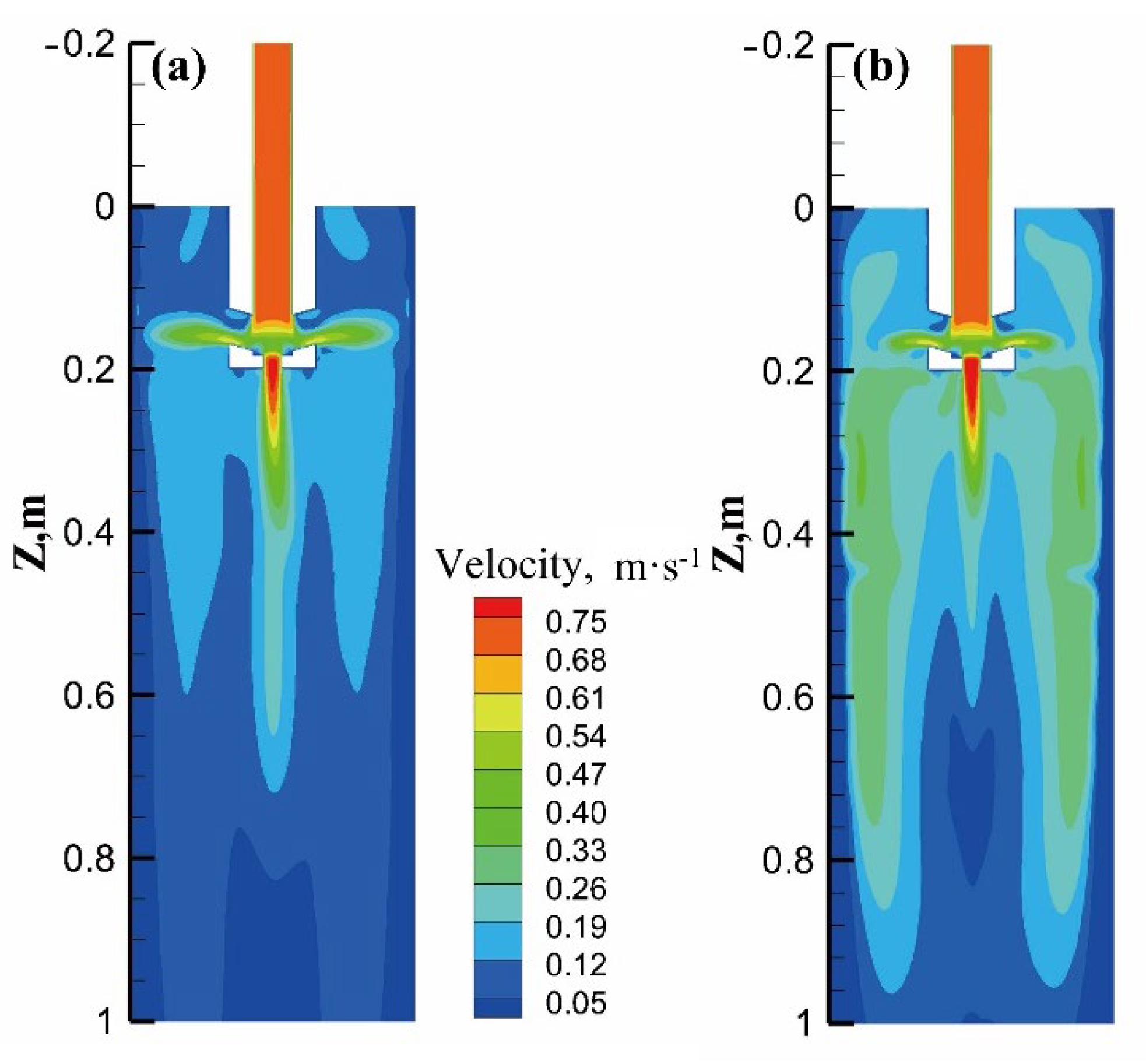
3.2. Influence of Copper Tube Thickness and Round Bloom Section
4. Exploration of Size Effect and Eccentric Stirring for Round Bloom
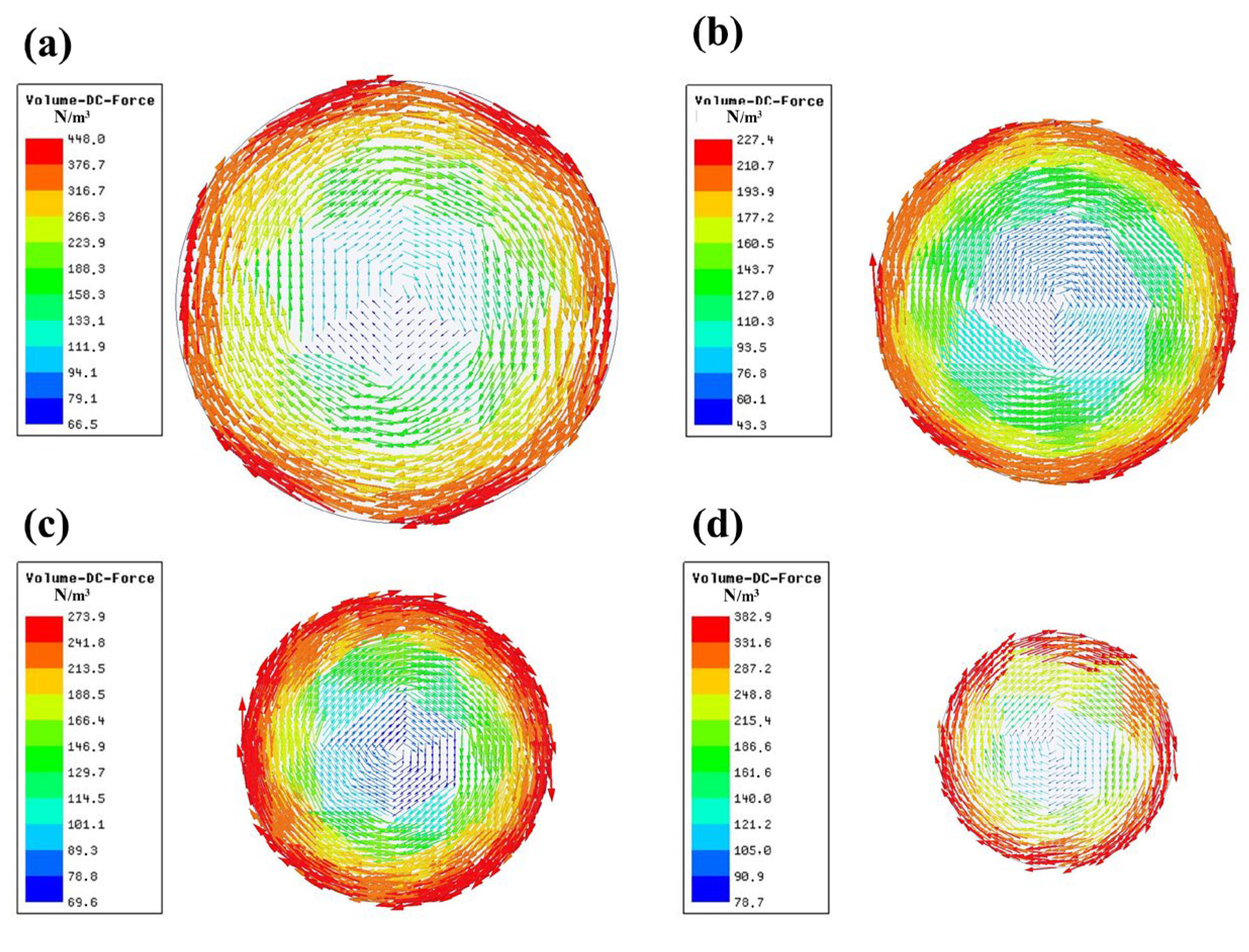
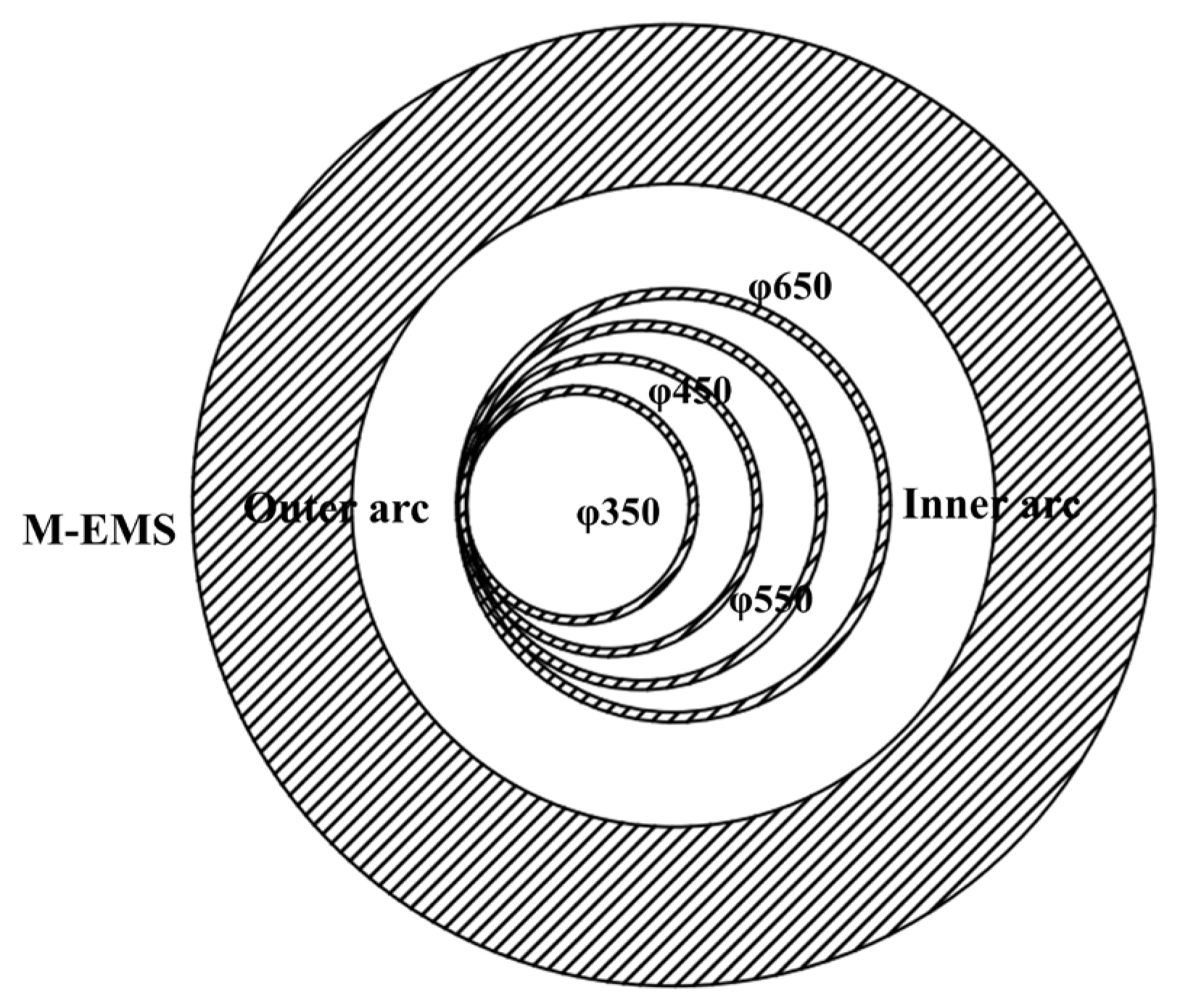
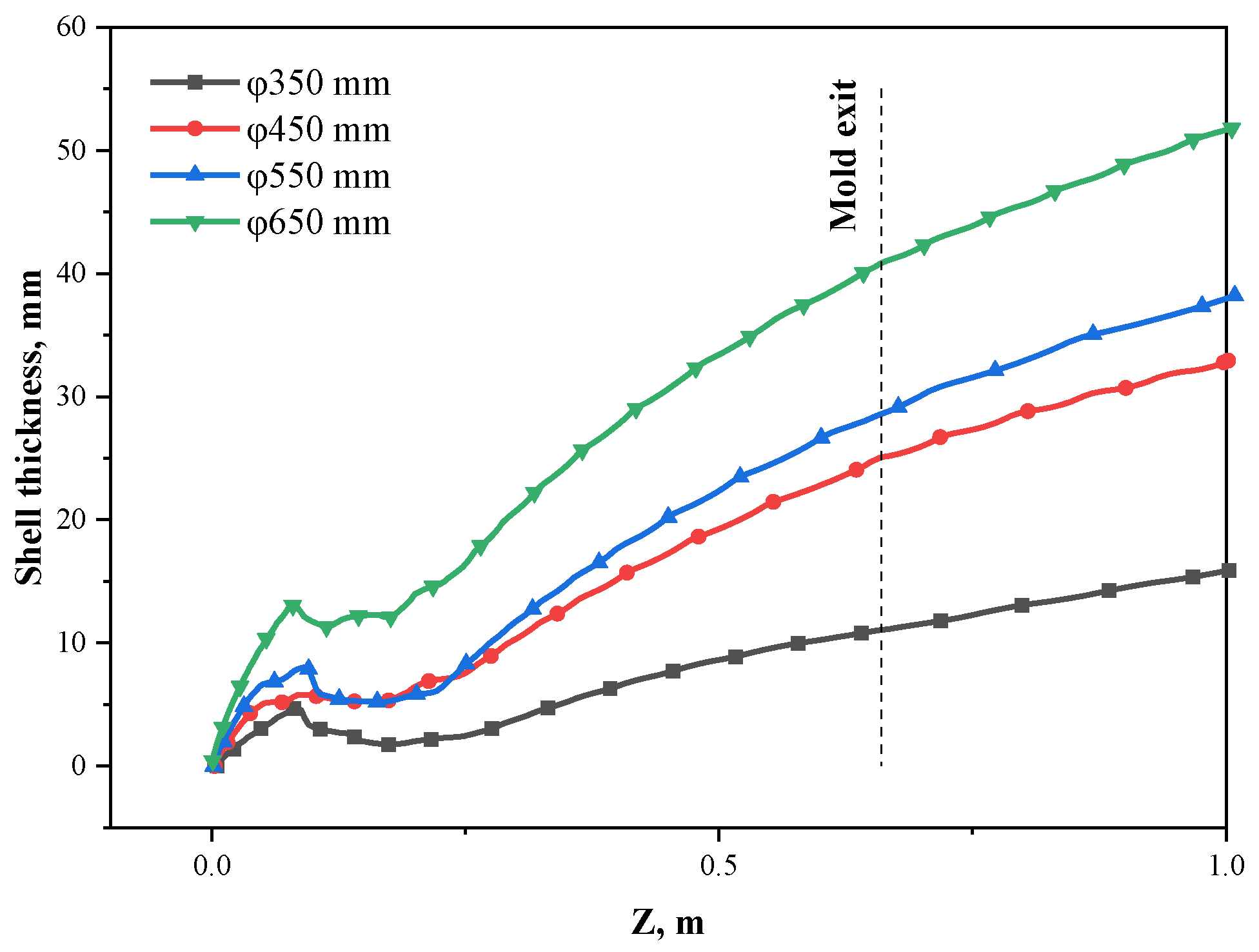
4.1. Effects of Section Size
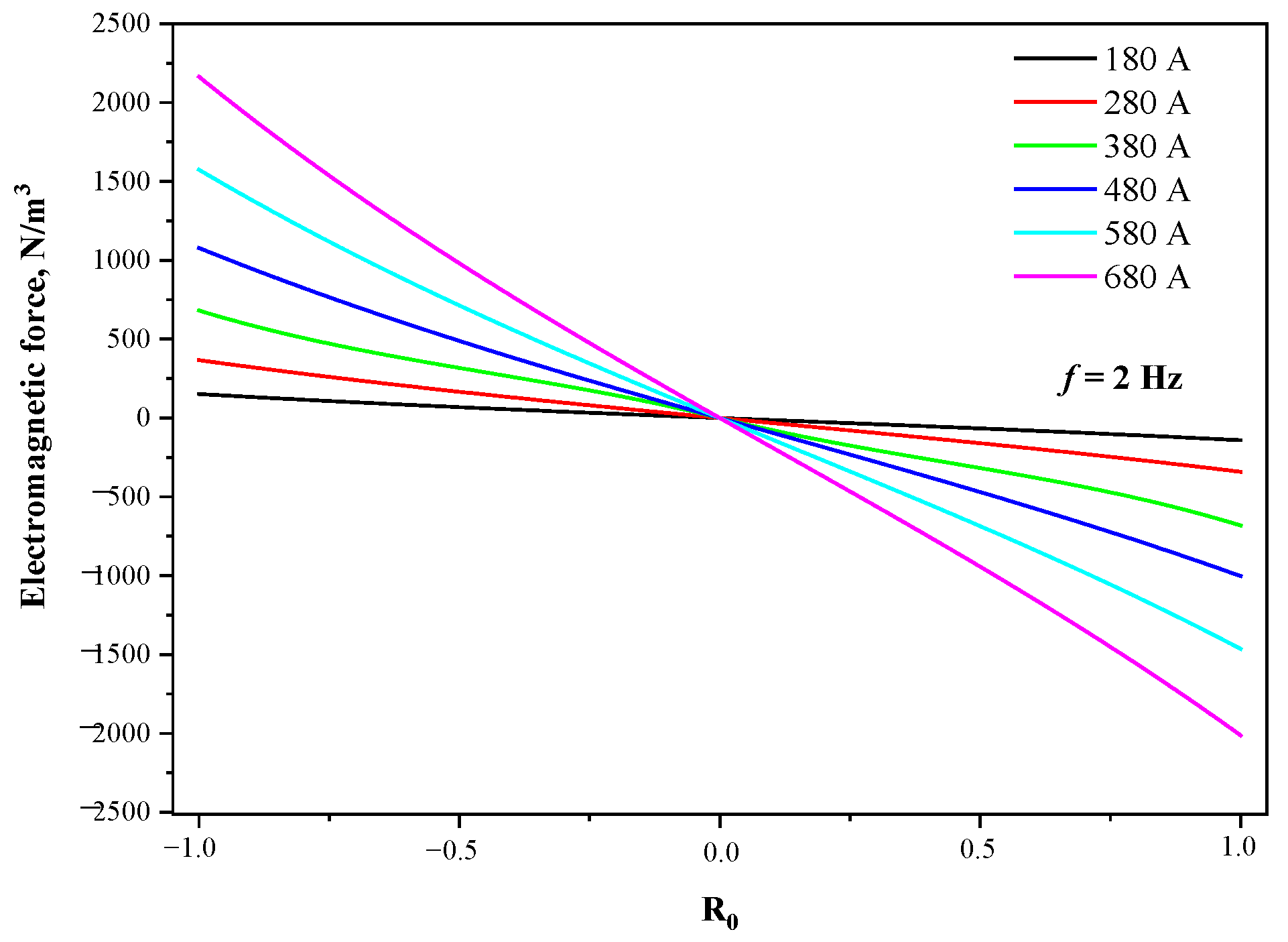
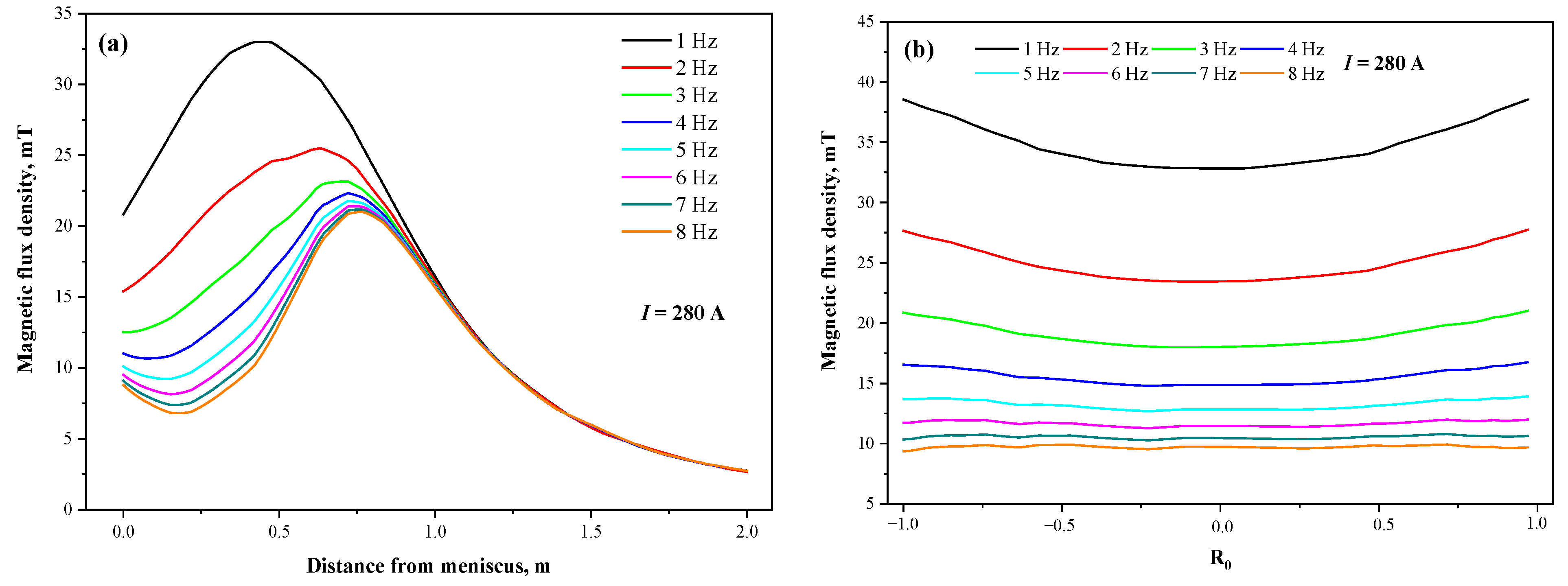
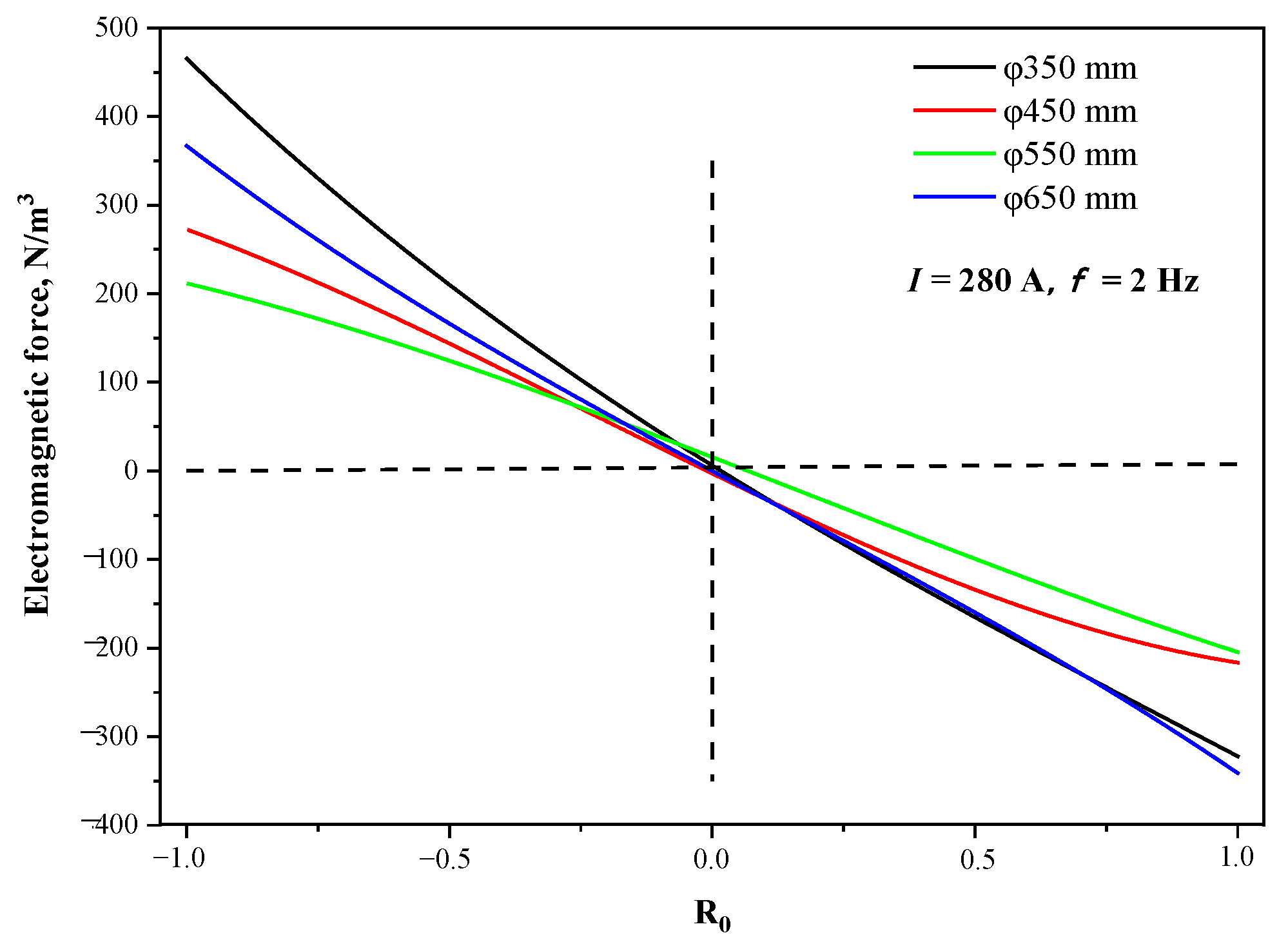
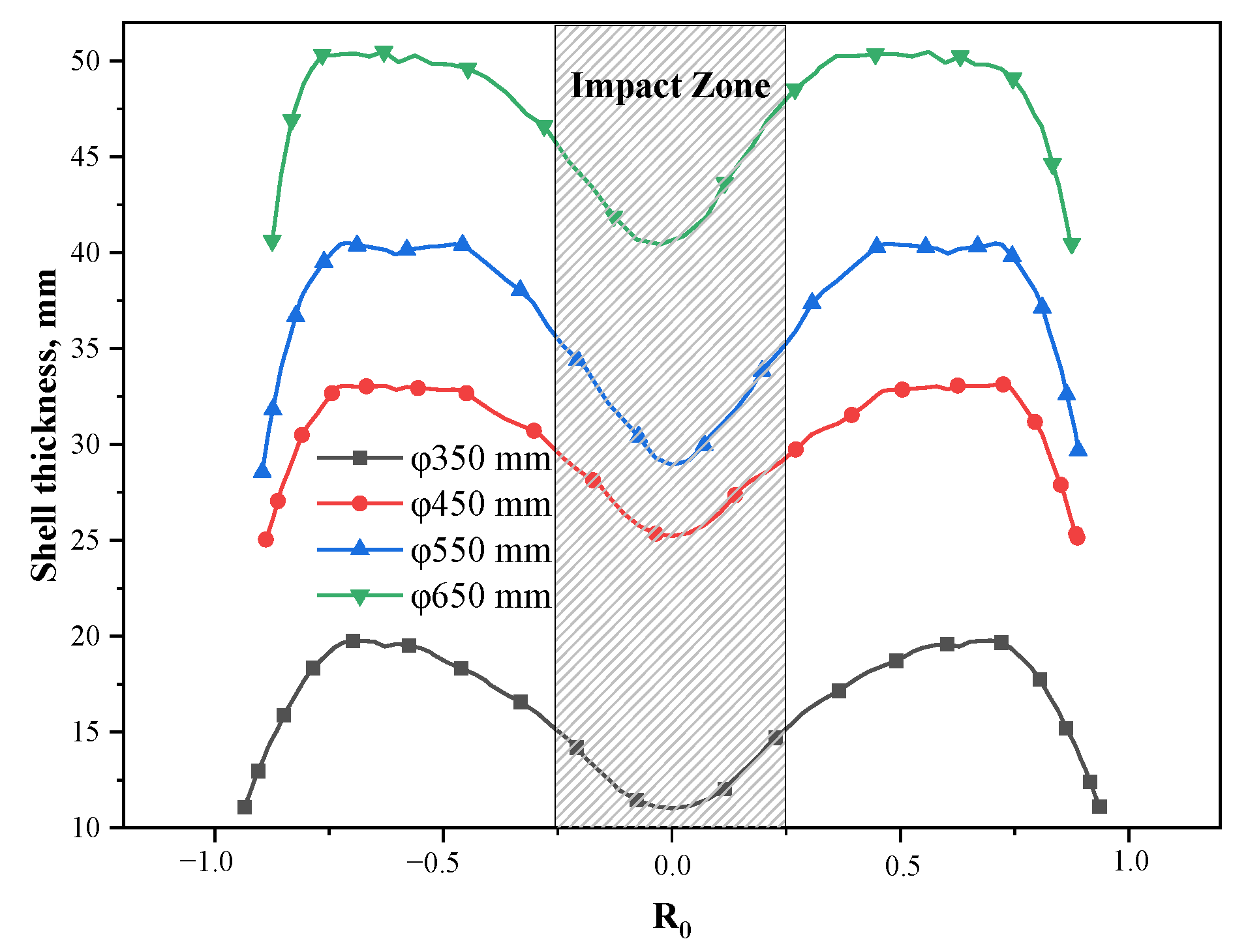
4.2. Eccentric Stirring
5. Conclusions
- ●
- With the increase in current frequency, the magnetic flux density decreases, but the electromagnetic torque increases and then decreases, and the same optimal stirring frequency exists for the same M-EMS structure for round blooms at any current intensity. The torque value and electromagnetic force both grow as a quadratic function of the current intensity, and the electromagnetic torque, which drives the molten steel flow, can directly characterize the real M-EMS performance.
- ●
- The mold copper tube has a significant magnetic shielding effect on the M-EMS. The stirring intensity decreases rapidly as the tube thickness increases, and the optimal stirring frequency decreases as well. In fact, the center of the stirrer deviates from the geometric center of the strand, which results in the eccentric stirring phenomenon. It reveals the magnetic shielding effect of the mold copper tube and the magnetic field loss of the air between the stirrer and the inner and outer arcs of the copper, which lead to the stirring intensity and the eccentric stirring phenomenon.
- ●
- When the Φ650 mm SMS-Concast casting machine casting blooms with the section size of Φ350 mm, the washing effect on the upper region of the inner arc side and the lower region of the outer arc side is stronger, so that the temperature of the inner and outer arcs shows alternating differences, and the jet flow from the five-port nozzle can suppress the difference in initial solidification symmetry between the inner and outer arcs of the round bloom caused by eccentric stirring.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrea, M.; Carlo, T. The Danieli Large-Size Round Bloom Casters; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.Q.; Wen, G.Y.; Chen, W.Q.; Liu, Y.L. The design features and application of special large section round bloom caster. Cont. Cast. 2018, 43, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.G.; Ji, C.; Zhu, M.Y. Numerical Simulation of Continuous Casting Round Blooms with Different Solidification End Reduction Strategies. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2021, 52, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyama, E.; Uchida, T.; Morikawa, M.; Saito, S. A method of shrinkage prediction and its application to steel casting practice. Int. J. Cast Metal Res. 1982, 7, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Minakawa, S.; Samarasekera, I.V.; Weinberg, F. Centerline porosity in plate castings. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1985, 16, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.P.; Wang, Z.Y.; Qiu, H. Numerical Simulation of Fluid Flow and Solidification in a Vertical Round Bloom Caster Using a Four-port SEN with Mold and Strand Electromagnetic Stirring. ISIJ Int. 2020, 60, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xiao, H.; Shen, H.F.; Chen, X.Q.; Chen, L.; Lan, P.; Zhang, J.Q. Effect of Mold Electromagnetic Stirring on the Gear Steel Solidification Behavior of its Large-sized Round Casting. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 57, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.P.; Chen, Y.Q.; Qiu, H.; Wang, Z.Y. Numerical simulation of coupled fluid flow and solidification in a curved round bloom continuous caster with a combined rotary electromagnetic stirring. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2022, 49, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.W.; Xu, C.J.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.B.; Wu, H.J. The simulation of mould metallurgical behaviour under electromagnetic stirring for vertical large bloom. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2021, 48, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turewicz, P.; Baake, E.; Umbrashko, A. Numerical simulation of electromagnetic stirring in continuous casting of wires. Compel 2011, 30, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, S.; Zhang, L.F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.D.; Zhang, J.Y. Effect of Electromagnetic Stirring on Inclusions in Continuous Casting Blooms of a Gear Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2021, 52, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, H.B.; Zhong, Y.B.; Ren, Z.M.; Lei, Z.S. Numerical Simulation for the Influence of EMS Position on Fluid Flow and Inclusion Removal in a Slab Continuous Casting Mold. ISIJ Int. 2020, 60, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javurek, M.; Barna, M.; Gittler, P.; Rockenschaub, K.; Lechner, M. Flow modelling in continuous casting of round bloom strands with electromagnetic stirring. Steel Res. Int. 2008, 79, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.J.; Wei, N.; Bao, Y.P.; Wang, G.X.; Xiao, C.P.; Liu, J.J. Effect of M-EMS on the solidification structure of a steel billet. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 2011, 18, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, H.; Miyazawa, K.; Matsumiya, T. Numerical modeling of columnar to equiaxed transition with consideration of molten steel flow. Int. J. Cast Metal Res. 2003, 15, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.P.; Xu, M.G.; Qiu, S.T.; Zhang, H. Numerical simulation of fluid flow in a round bloom mold with in-mold rotary electromagnetic stirring. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2012, 43, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.P.; Zhang, J.M.; Liu, Q.; Yin, Y.B. Magnetohydrodynamic calculation for electromagnetic stirring coupling fluid flow and solidification in continuously cast billets. Steel Res. Int. 2017, 88, 1700067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, L.B.; Nadalon, J.E.A.; Contini, A.C.; Barroso, R.C. Modeling of solidification in continuous casting round billet with mold electromagnetic stirring (M-EMS). Steel Res. Int. 2017, 88, 1600319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Lan, P.; Tang, H.Y.; Tie, Z.P.; Zhang, J.Q. Study on the electromagnetic field, fluid flow, and solidification in a bloom continuous casting mold by numerical simulation. Steel Res. Int. 2018, 89, 1800071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Tu, T.S.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z.M. Effect of final electromagnetic stirring on solidification microstructure of GCr15 bearing steel in simulated continuous casting. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2020, 27, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.F. Measurement and Calculation of Magnetic Flux Density During Mold Electromagnetic Stirring on a Continuous Casting Bloom Mold. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2022, 53, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, M.H.; Wang, T.M.; Li, J.; Li, T.J.; Jin, J.Z. Numerical simulation of horizontal continuous casting process of round copper billet with electromagnetic stirring. Int. J. Cast Metal Res. 2011, 24, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.Z.; Chen, D.F.; Xia, W.T.; Wang, H.D.; Han, Z.W. Numerical simulation of electromagnetic field in round bloom continuous casting with final electromagnetic stirring. Metals 2018, 8, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, X.; Li, X.; Liu, F.B.; Li, H.B.; Jiang, Z.H. Optimisation of electromagnetic field and flow field in round billet continuous casting mould with electromagnetic stirring. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2015, 42, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Q.; Zhu, M.Y. Influence of electromagnetic stirring on transport phenomena in round billet continuous casting mould and macrostructure of high carbon steel billet. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2012, 39, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.H.; Liu, C.; Ni, H.W. Effect of electromagnetic stirrer position on mold metallurgical behavior in a continuously cast bloom. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.H.; Bao, Y.P.; Wang, M.; Yang, Q. Electromagnetic torque detecting for optimization of in-mould electromagnetic stirring in the billet and bloom continuous casting. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2019, 46, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Xiao, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, H.S.; Zhang, J.Q. Analysis on electromagnetic field of continuous casting mold including a new integral method for calculating electromagnetic torque. Metals 2019, 9, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Li, S.X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.Q.; Wang, X.S.; Zhang, J.Q. Overall Mold Metallurgical Behavior Under Electromagnetic Stirring for Round Bloom Casting Process. Iron Steel 2019, 54, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Aboutalebi, M.R.; Guthrie, R.I.L.; Seyedein, S.H. Mathematical modeling of coupled turbulent flow and solidification in a single belt caster with electromagnetic brake. Appl. Math. Model 2007, 31, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tie, Z.P.; Xiao, H.; Zhu, J.L.; Tang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.Q. Optimizing of Submerged Entry Nozzle for Bloom Continuous Casting Based on Physical and Numerical Simulation. Steel Res. Int. 2022, 93, 2200402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felten, F.; Fautrelle, Y.; Terrail, Y.D.; Metais, O. Numerical modelling of electromagnetically-driven turbulent flows using LES methods. Appl. Math. Model 2004, 28, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, W.P.; Launder, B.E. The calculation of low-Reynolds-number phenomena with a two-equation model of turbulence. Int. J. Heat. Mass Tran. 1973, 16, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, S.X.; Zhang, Z.; Tie, Z.P.; Dong, Y.N.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.Q. Effect of Combined Stirring Modes on the Solidification Behavior of a Special Steel Bloom Casting. J. Mech. Eng. 2020, 56, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Tie, Z.P.; Li, S.X.; Lan, P.; Tang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.Q. Effect of M-EMS Current Intensity on the Subsurface Segregation and Internal Solidification Structure for Bloom Casting of 42CrMo Steel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2021, 48, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, S.X.; Tie, Z.P.; Liu, H.S.; Tang, H.Y.; Lan, P.; Zhang, J.Q. Effect of different types of nozzles on swirling flow development and shell growth behavior in a bloom casting mold. AIST 2019, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Zhang, X.M.; Li, L.; Lan, P.; Tang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.Q. Representation and effect of mushy zone coefficient on coupled flow and solidification simulation during continuous casting. Chin. J. Eng 2019, 41, 199. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, M.; Pandey, J.C. Optimisation of electromagnetic stirring in continuously cast steel billets using ultrasonic C-scan imaging technique. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2008, 35, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.H.; Yan, Q.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Chen, J.X. Safety thickness of solidified shell at mold export of heavy section continuous casting billet. Iron Steel 2014, 49, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, L.; Zhao, J.X.; Qiu, S.T.; Tang, W.D.; Yang, L.Z. Numerical simulation of flow and heat transfer in a continuous casting round bloom with eccentric M-EMS. Iron Steel 2020, 55, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, L.; Zhao, J.X.; Qiu, S.T. Effects of Eccentric Mold Electromagnetic Stirring on Continuous Casting Large Steel Round Blooms. Mater. Trans. 2020, 61, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Governing Equations | Symbols |
|---|---|
| , Magnetic flux density [Tesla] | |
| , Electric field strength [V·m−1] | |
| , Time [s] | |
| , Induced electric field strength [A·m−2] | |
| , Induced charge density [C·m−3] | |
| , Induced magnetic flux density [A·m−1] | |
| , Induced current intensity [A·m−2] | |
| , Conductivity [S·m−1] | |
| , Magnetic permeability [H·m−1] | |
| , Electromagnetic force density [N·m−3] | |
| , Real part of the complex number | |
| , Conjugate complex number of | |
| , Density of molten steel [kg·m−3] | |
| , Velocity of molten steel [m·s−1] | |
| , Static pressure [Pa] | |
| , Effect viscosity coefficient [kg·m−1·s−1] | |
| , Laminar viscosity coefficient [kg·m−1·s−1] | |
| , Turbulent viscosity coefficient [kg·m−1·s−1] | |
| , Acceleration of gravity [m·s−2] | |
| , Turbulent kinetic energy [m2·s−2] | |
| , Turbulent energy dissipation rate [m2·s−3] | |
| , from the low Reynolds k-ε model [33] | |
| , Thermal expansion coefficient | |
| , Local temperature [K] | |
| , Reference temperatures [K] | |
| , Liquid volume fraction | |
| , 0.001 | |
| , 1 × 108 | |
| , Pull velocity [m·s−1] | |
| , Liquidus temperature [K] | |
| , Solidus temperature [K] | |
| , Enthalpy [J·kg−1] | |
| , Effective thermal conductivity [W·m−1·K−1] | |
| , Reference enthalpy [J·kg−1] | |
| , Specific heat [J·kg−1·K−1] | |
| , Latent heat [J·kg−1] | |
| , Laminar thermal conductivity [W·m−1·K−1] | |
| , Turbulent Prandtl number [0.85] |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inside and outside diameter of the nozzle (mm) | 45, 90 | Molten steel Density (kg·m−3) | 7020 |
| Effective length of mold (mm) | 660 | Molten steel Viscosity (kg·m−1·s−1) | 0.0062 |
| Section (mm) | Φ350, Φ450, Φ550, Φ650 | Molten steel Specific heat (J·kg−1·K−1) | 750 |
| Thickness of copper (mm) | 25, 25, 29, 31 | Molten steel Latent heat (J·kg−1) | 268,000 |
| Casting speed (m·min−1) | 0.72, 0.42, 0.30, 0.21 | Superheat degree (K) | 30 |
| Mold cooling water (L·min−1) | 2800, 4500, 4600, 4600 | Solidus temperature (K) | 1710 |
| Second cooling ratio (L·kg−1) | 0.25, 0.18, 0.18, 0.18 | Liquidus temperature (K) | 1768 |
| Thermal conductivity (W·(m·K)−1) | 29 | / | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, J. Behavior of Mold Electromagnetic Stirring for Round Bloom Castings and Its Eccentric Stirring Problem. Materials 2022, 15, 8814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248814
Wang P, Xiao H, Zhang Z, Li S, Zhang J. Behavior of Mold Electromagnetic Stirring for Round Bloom Castings and Its Eccentric Stirring Problem. Materials. 2022; 15(24):8814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248814
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Pu, Hong Xiao, Zhuang Zhang, Shaoxiang Li, and Jiaquan Zhang. 2022. "Behavior of Mold Electromagnetic Stirring for Round Bloom Castings and Its Eccentric Stirring Problem" Materials 15, no. 24: 8814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248814
APA StyleWang, P., Xiao, H., Zhang, Z., Li, S., & Zhang, J. (2022). Behavior of Mold Electromagnetic Stirring for Round Bloom Castings and Its Eccentric Stirring Problem. Materials, 15(24), 8814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248814





