The Effect of Cooling Rate on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Microalloyed Steel Plates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Thermo-Mechanical Processing
2.2. Microstructural Characterization
2.3. Hardness and Tensile Tests
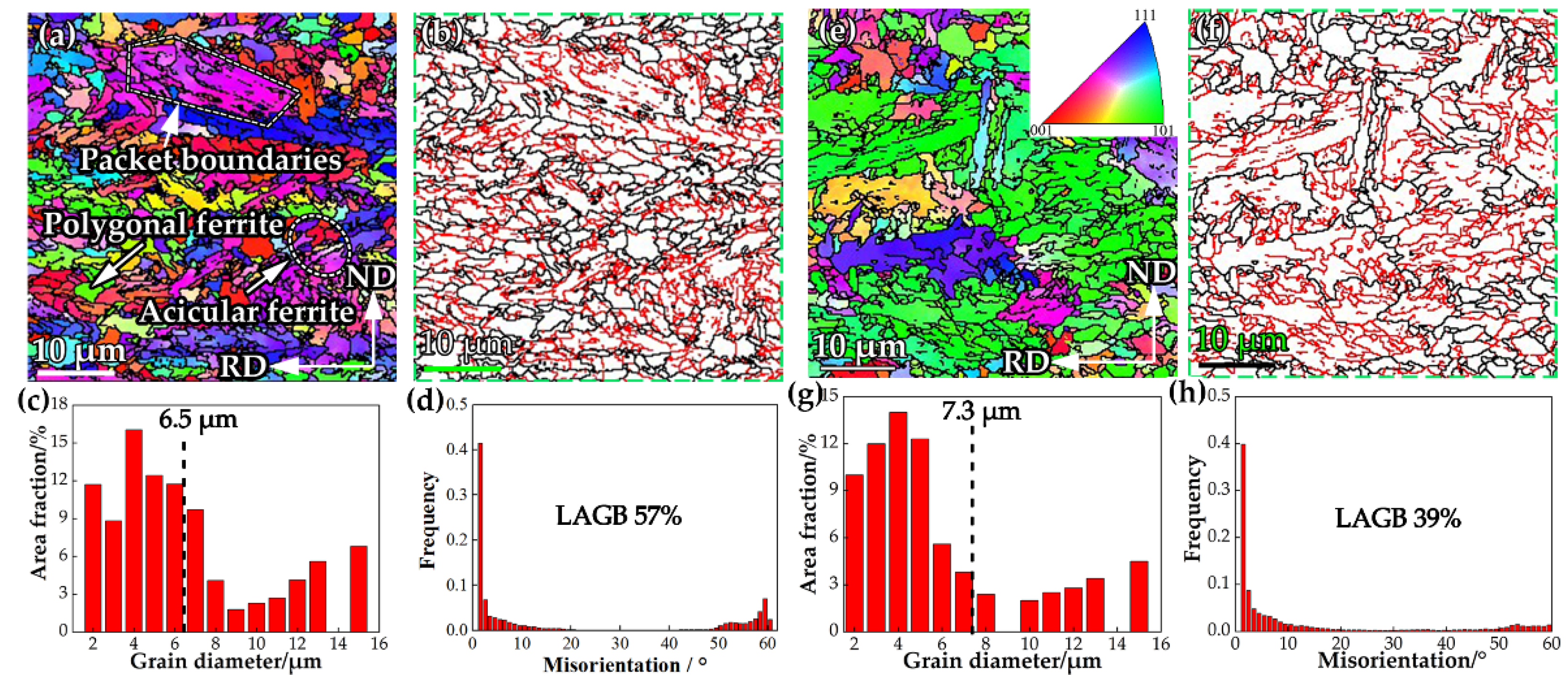
3. Results and Discussion
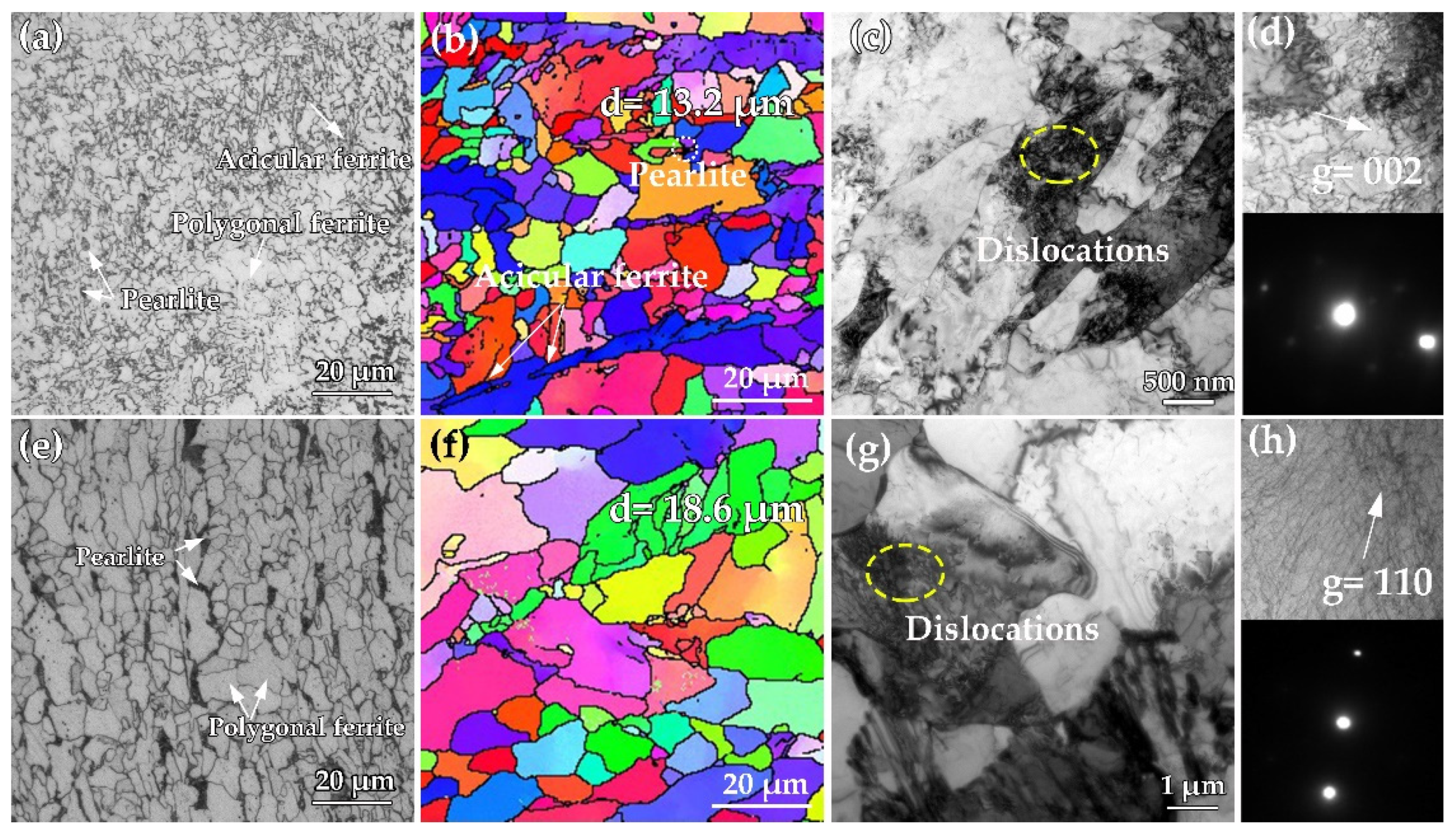
3.1. Microstructural Evolution
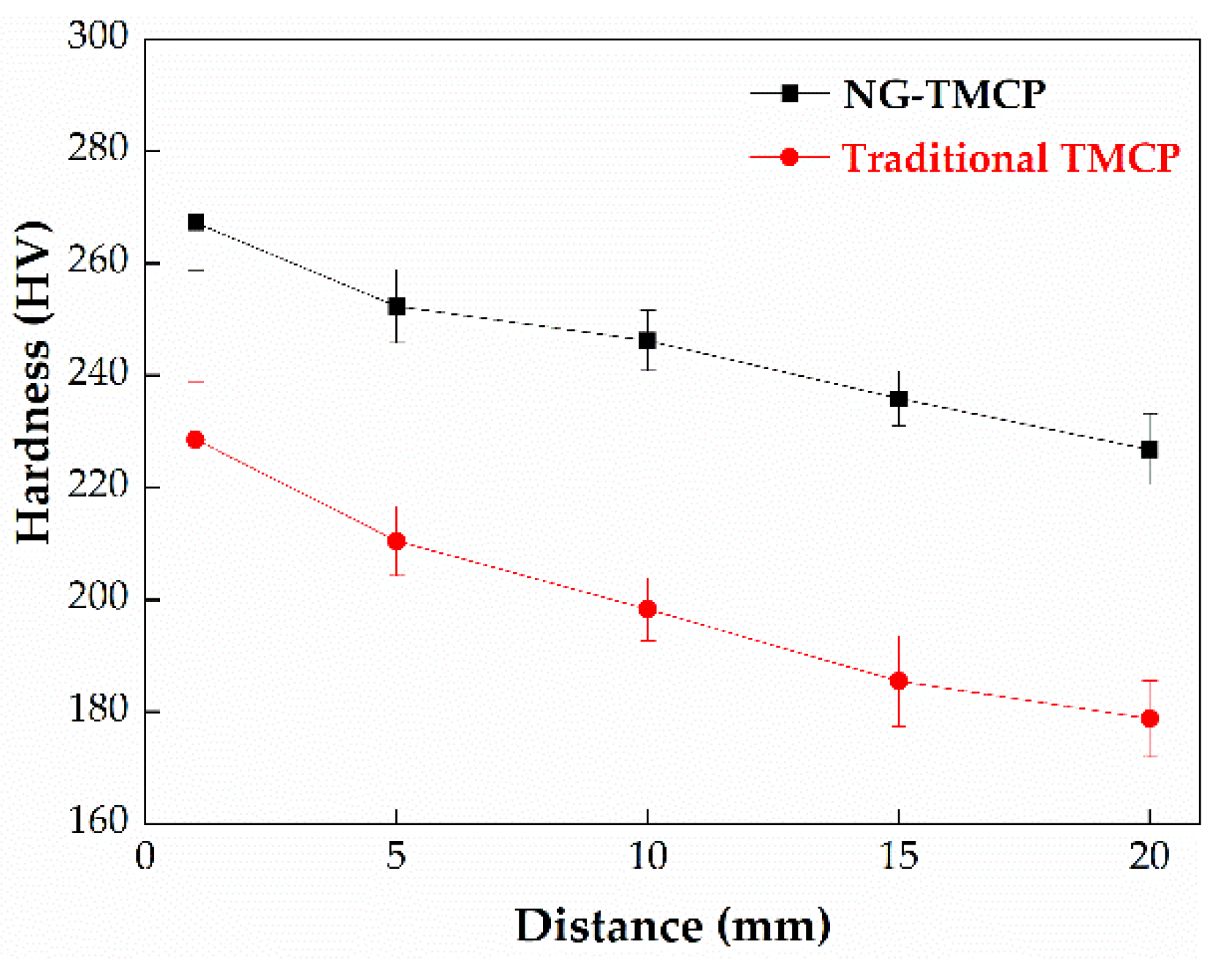
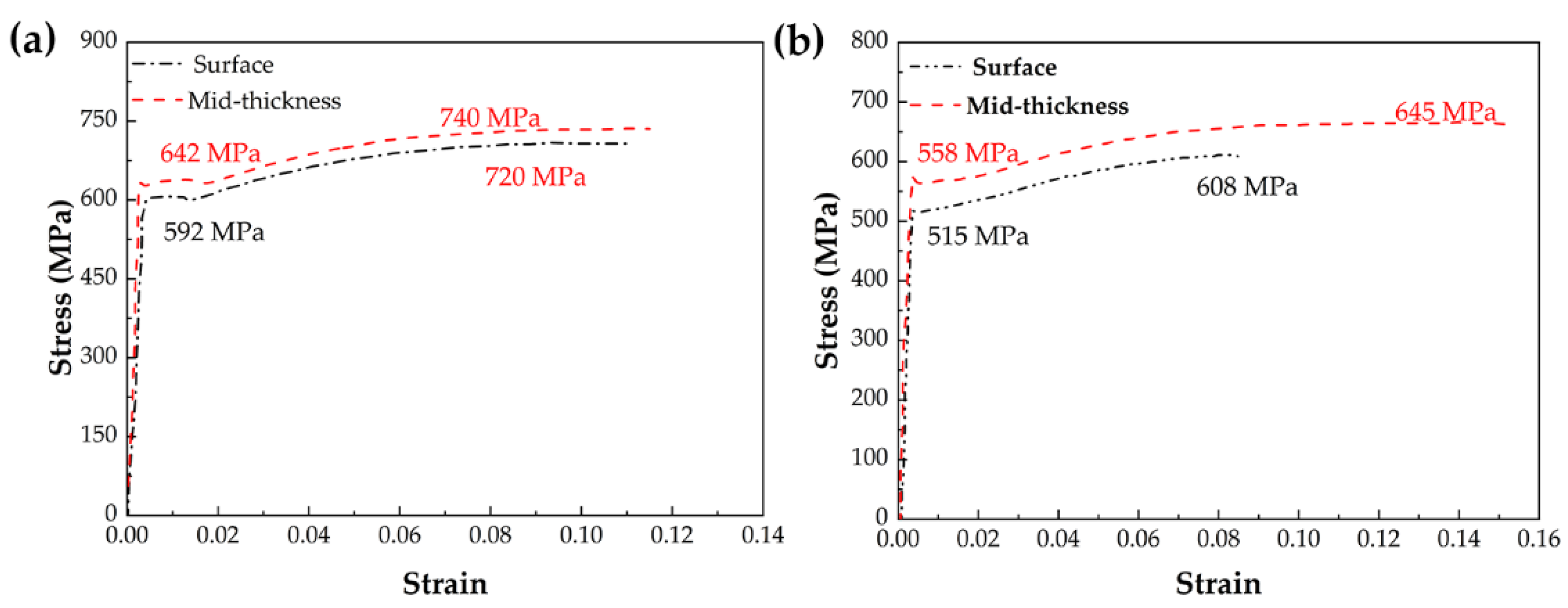
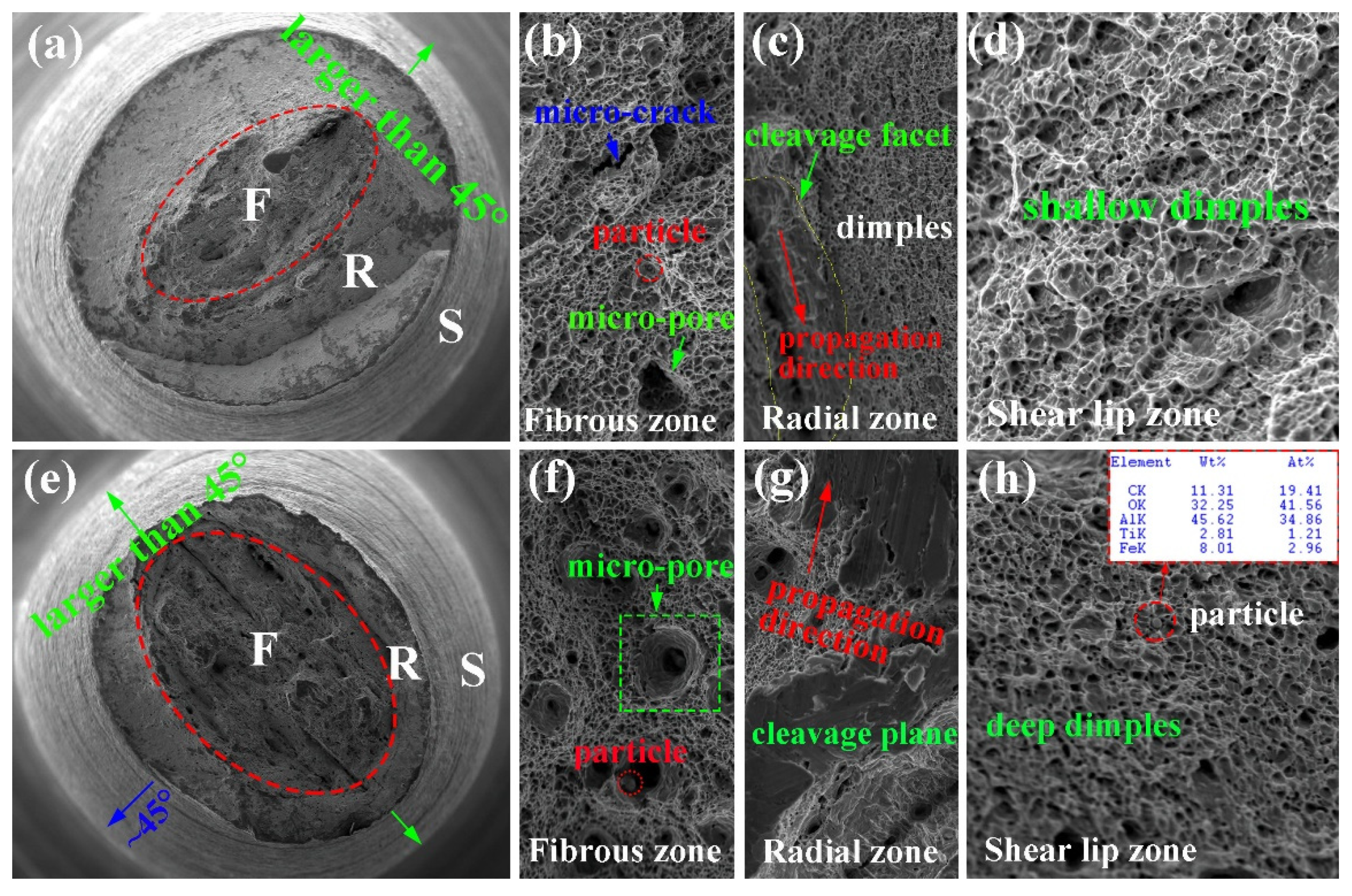
3.2. Mechanical Properties
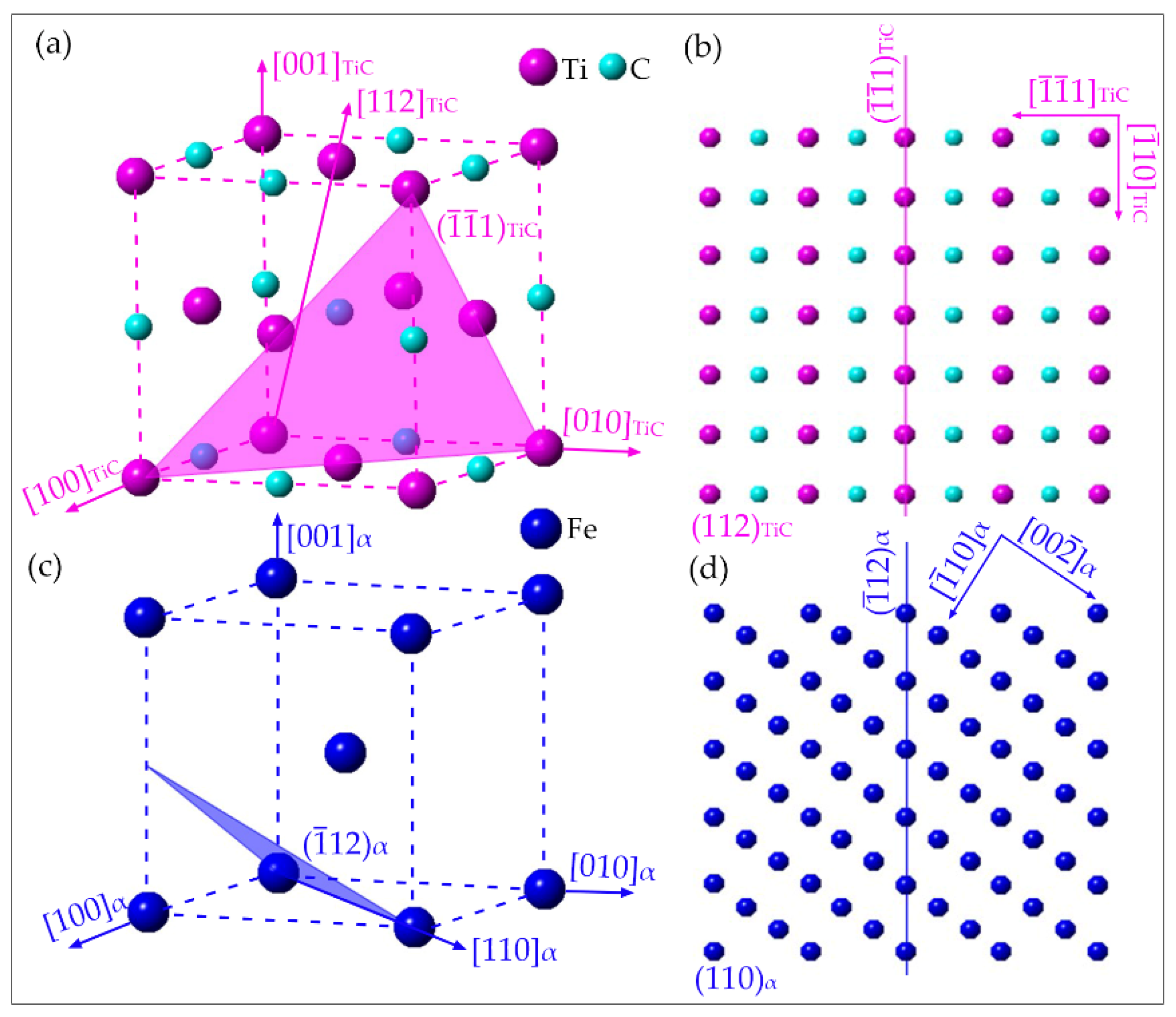
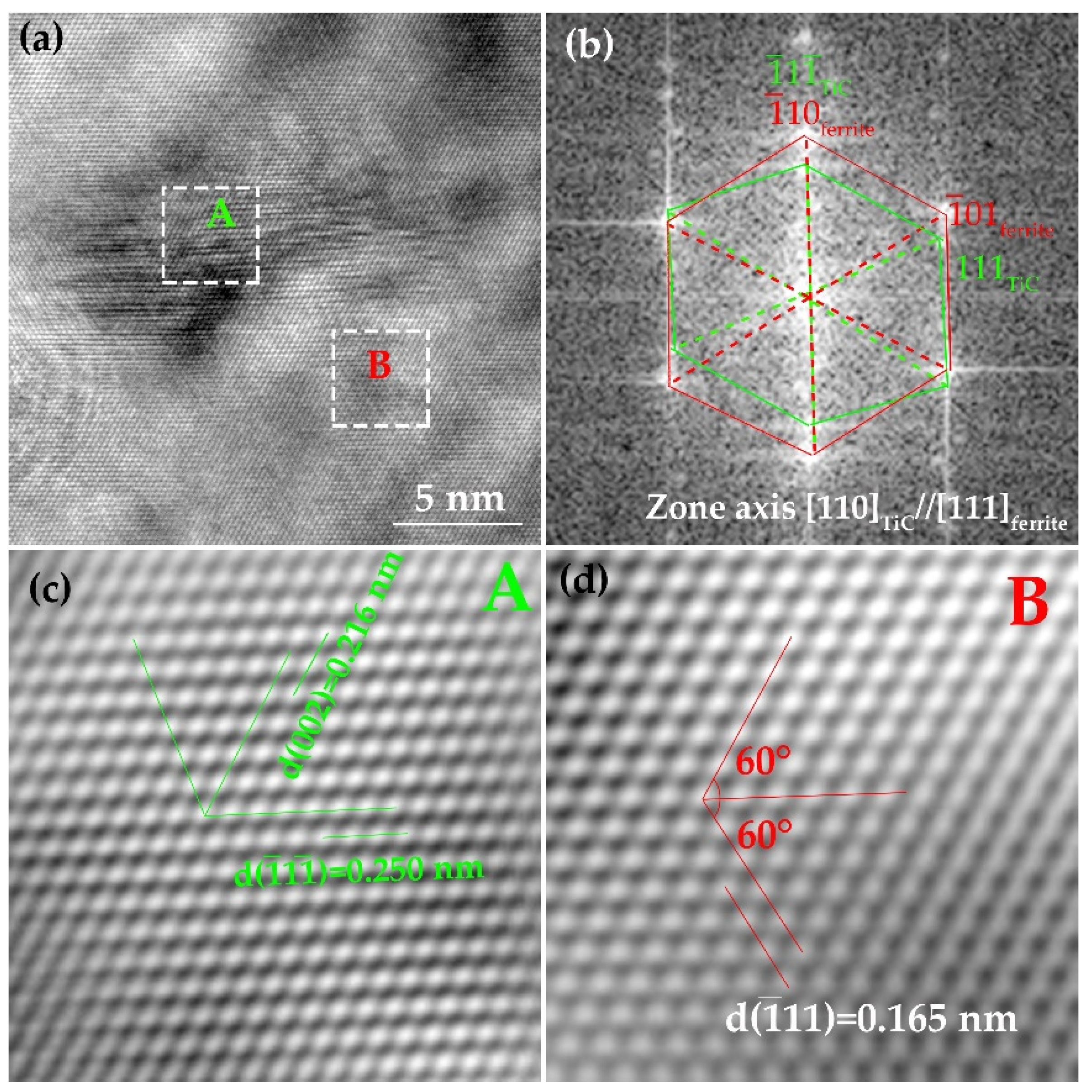
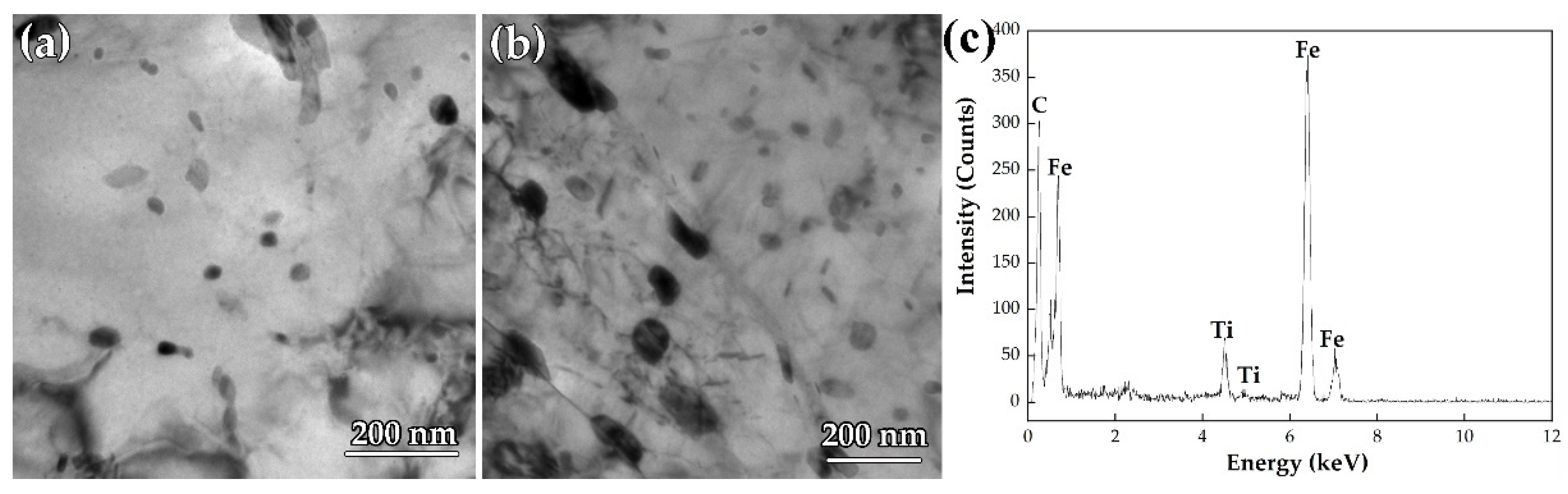
3.3. Precipitation Behavior
3.4. Strengthening and Toughing Mechanism
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- An excellent heavy steel plate has been obtained with a yield strength, tensile strength, and impact toughness of −20 ℃ of 592 MPa, 720 MPa, and 75 J, which is mainly devoted to grain refinement strengthening and precipitation strengthening.
- (2)
- The microstructure and mechanical properties of the heavy steel plate produced by UFC are more uniform compared with that by traditional accelerated cooling, for the cooling rate of UFC is uniform along the longitudinal direction of the thick plate.
- (3)
- The crystallographic characteristic of precipitates has been analyzed. The size of austenite strain-induced TiC is relatively large, and obeys the KS orientation relationship with the ferrite matrix, while for TiC formed in the supersaturated ferrite, the size is less than 5 nm, and obeys [112]MC//[110]α and // orientation relationship with the ferrite matrix.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Funakawa, Y.; Shiozaki, T.; Tomita, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Maeda, E. Development of high strength hot-rolled sheet steel consisting of ferrite and nanometer-sized carbides. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.J.; Li, D.Z.; Chen, J.; Tang, S.; Wang, G.D. The Effect of Initial Microstructure on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Intercritically Rolled Low-Carbon Microalloyed Steel Plates. Steel Res. Int. 2019, 90, 1900237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.B.; Liu, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.D. Effect of Rolling Temperature and Ultrafast Cooling Rate on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Steel Plate. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 3622–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Lei, C.S.; Tian, Q.; Deng, X.T.; Chen, L.; Gao, P.L.; Du, K.P.; Du, Y.; Yu, Y.G.; Wang, Z.D.; et al. Nanoscale cementite and microalloyed carbide strengthened Ti bearing low carbon steel plates in the context of newly developed ultrafast cooling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 698, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Wang, Z.D.; Deng, X.T.; Wang, G.D.; Misra, R.D.K. The Determining Role of Finish Cooling Temperature on the Microstructural Evolution and Precipitation Behavior in an Nb-V-Ti Microalloyed Steel in the Context of Newly Developed Ultrafast Cooling. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 1929–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.J.; Tang, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, G.D. Improving Toughness of Heavy Steel Plate by Deformation Distribution Under Low Finish Cooling Temperature. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 3682–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, K.; Ichikawa, K. Progress in thermomechanical control of steel plates and their commercialization. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2012, 13, 023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, T. The Physical Metallurgy of Microalloyed Steels, 1st ed.; The Institute of Materials: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Cai, Q.W.; Xie, B.S.; Ning, Z.; Zhou, X.C.; Li, G.S. Relationships among microstructure, precipitation and mechanical properties in different depths of Ti–Mo low carbon low alloy steel plate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 651, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, G.D. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of high strength microalloyed steels: Ultra-Fast Cooling (UFC) versus Accelerated Cooling (ACC). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 580, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Lei, C.S.; Deng, X.T.; Wang, Z.D.; Yu, Y.G.; Wang, G.D.; Misra, R.D.K. Precipitation strengthening in titanium microalloyed high-strength steel plates with new generation-thermomechanical controlled processing (NG-TMCP). J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 689, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.W.; Hong, S.G.; Huh, Y.H.; Lee, C.S. Role of rolling temperature in the precipitation hardening characteristics of Ti–Mo microalloyed hot-rolled high strength steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 615, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, G.D. Development of High Strength Plates with Low Yield Ratio by the Combination of TMCP and Inter-Critical Quenching and Tempering. Steel Res. Int. 2011, 82, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Du, L.X.; Xie, H.; Gao, X.H.; Misra, R.D.K. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TMCP heavy plate microalloyed steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 607, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemori, R.; Hasegawa, Y.; Hara, T.; Inoue, T.; Shinohara, Y.; Inoue, H.; Furuya, H. Steels for energy production and transport. Nippon Steel Technical Report. Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 2012, 101, 68–78. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Y.; Shang, C.J.; Song, X.; You, Y.; Li, C.; He, X.L. Properties and homogeneity of 550-MPa grade TMCP steel for ship hull. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2010, 17, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Cheng, B.; Chen, Y. Strengthening and Toughening of a Heavy Plate Steel for Shipbuilding with Yield Strength of Approximately 690 MPa. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.Q.; Bao, Y.P.; Xia, Z.H.; Luo, D.; Guo, A.M.; Wu, K.M. Toughening mechanisms of a high-strength acicular ferrite steel heavy plate. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2010, 17, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.G.; Wang, G.D.; Misra, R.D.K. Precipitation behavior of nanoscale cementite in hypoeutectoid steels during ultra fast cooling (UFC) and their strengthening effects. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 575, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.C.; Huang, X.F.; Atrens, A. Role of second phase cementite and martensite particles on strength and strain hardening in a plain C-Mn steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 549, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Li, G.; Mao, X.; Fang, K.M. Nanoscale Cementite Precipitates and Comprehensive Strengthening Mechanism of Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 3797–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.Z.; Wang, X.M.; Chen, L.; Yang, S.W.; Shang, C.J.; Misra, R.D.K. Influence of cooling rate on the precipitation behavior in Ti–Nb–Mo microalloyed steels during continuous cooling and relationship to strength. Mater. Charact. 2015, 102, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opiela, M.; Grajcar, A. Microstructure and Anisotropy of Plastic Properties of Thermomechanically-Processed HSLA-Type Steel Plates. Metals 2018, 8, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grajcar, A.; Morawiec, M.; Zalecki, W. Austenite Decomposition and Precipitation Behavior of Plastically Deformed Low-Si Microalloyed Steel. Metals 2018, 8, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Du, L.X.; Wang, J.J.; Gao, C.R. Effect of welding heat input on microstructures and toughness in simulated CGHAZ of V–N high strength steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 577, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Q.L.; Ma, M.T.; Wu, B.R. Microalloyed Steel-Physical and Mechanical Metallurgy, 1st ed.; Mechanical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.Y. The Microstructure of Materials and Its Electron Microscopy Analysis, 1st ed.; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, H.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Yang, J.R. The Nano Carbide Control: Design of Super Ferrite in Steels. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 8–91, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Jin, C.; Li, H.Z.; Hao, X.X.; He, Y.; Deng, X.T.; Wang, Z.D. Influence of cooling rate on phase transformation and precipitation behavior of Ti-bearing steel in continuous cooling process. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2021, in press. [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.L.; Wu, K.M.; Huang, G.; Nune, K.C.; Li, Y.; Cheng, L. Toughness improvement by Cu addition in the simulated coarse-grained heat-affected zone of high-strength low-alloy steels. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2016, 21, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| C | Mn | Si | Al | Ti | P | S | N | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.15 | 0.98 | 0.28 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.015 | 0.005 | 27 ppm | 48 ppm |
| No. | RTG 1 (°C) | NRTG 2 (°C) | Cooling Rate, °C/s | FCT 3, °C | Type of Cooling | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | Finish | Start | Finish | ||||
| A | 1150 | 1091 | 880 | 875 | 60 (45) | 590 (621) | 20 min, air cooling |
| B | 1150 | 1096 | 889 | 864 | 10 (5.8) | 598 (678) | 20 min, air cooling |
| Steel | Yield Strength, MPa | Tensile Strength, MPa | Elongation, % | Yield Ratio | Impact Toughness, J | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −20 °C | −40 °C | ||||||
| A | S 1 | 642 (5.2) | 740 (6.1) | 19.2 (1.3) | 0.87 (0.2) | 88.9 (3.6) | 68.9 (5.4) |
| M 2 | 592 (5.7) | 720 (5.9) | 17.3 (1.8) | 0.82 (0.2) | 75.3 (2.8) | 55.8 (5.1) | |
| B | S | 558 (2.8) | 645 (2.1) | 23.4 (0.9) | 0.86 (0.1) | 55.6 (5.6) | 30.6 (6.2) |
| M | 515 (4.3) | 608 (4.9) | 16.2 (1.2) | 0.85 (0.1) | 45.2 (4.2) | 28.2 (8.1) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Gao, X.; Deng, X.; Wang, Z. The Effect of Cooling Rate on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Microalloyed Steel Plates. Materials 2022, 15, 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041385
Li X, Li Q, Li H, Gao X, Deng X, Wang Z. The Effect of Cooling Rate on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Microalloyed Steel Plates. Materials. 2022; 15(4):1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041385
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaolin, Qian Li, Haozhe Li, Xiangyu Gao, Xiangtao Deng, and Zhaodong Wang. 2022. "The Effect of Cooling Rate on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Microalloyed Steel Plates" Materials 15, no. 4: 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041385
APA StyleLi, X., Li, Q., Li, H., Gao, X., Deng, X., & Wang, Z. (2022). The Effect of Cooling Rate on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Microalloyed Steel Plates. Materials, 15(4), 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15041385








