Physicochemical Aspects of Oxidative Consolidation Behavior of Manganese Ore Powders with Various Mn/Fe Mass Ratios for Pellet Preparation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
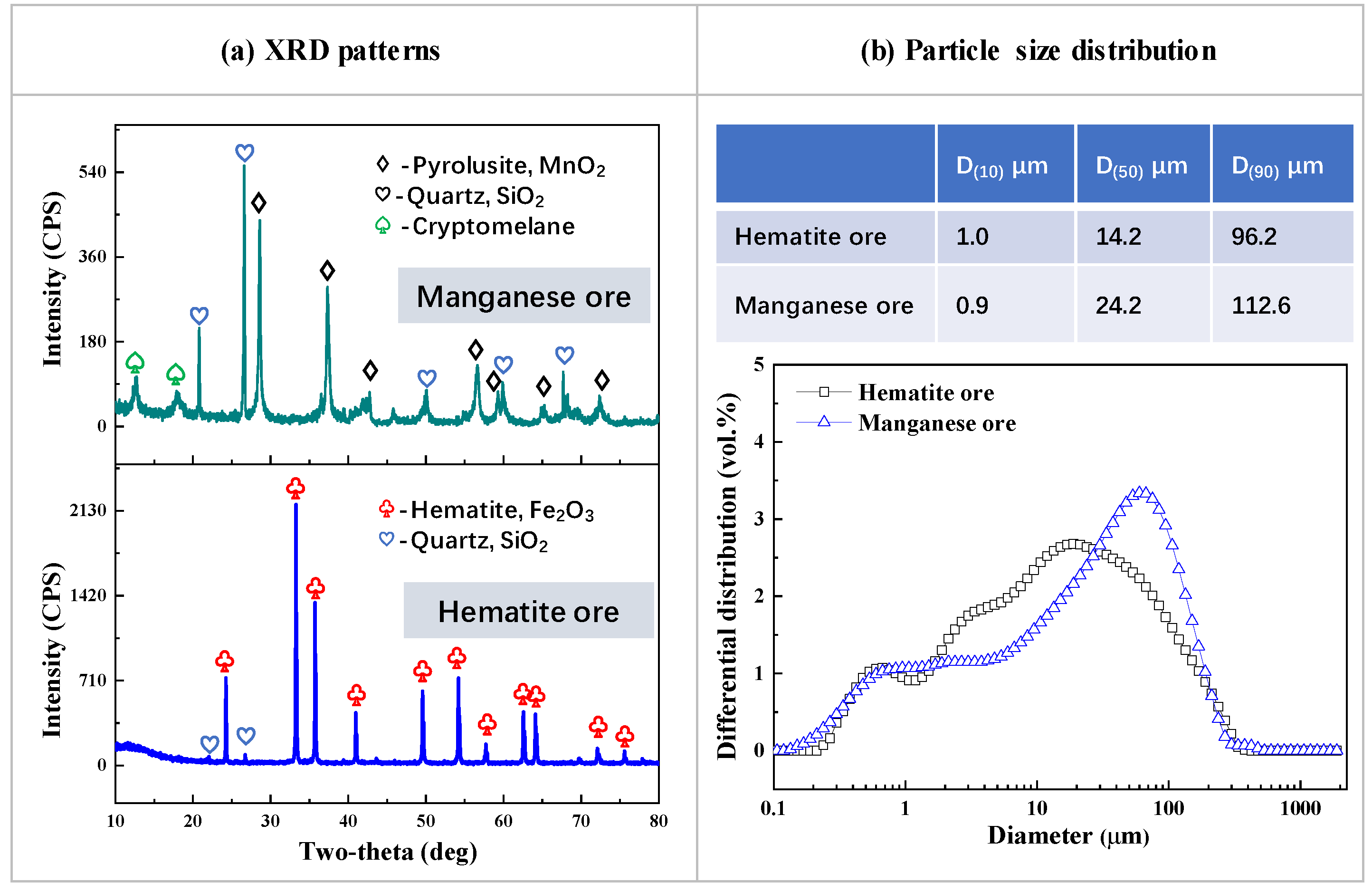
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
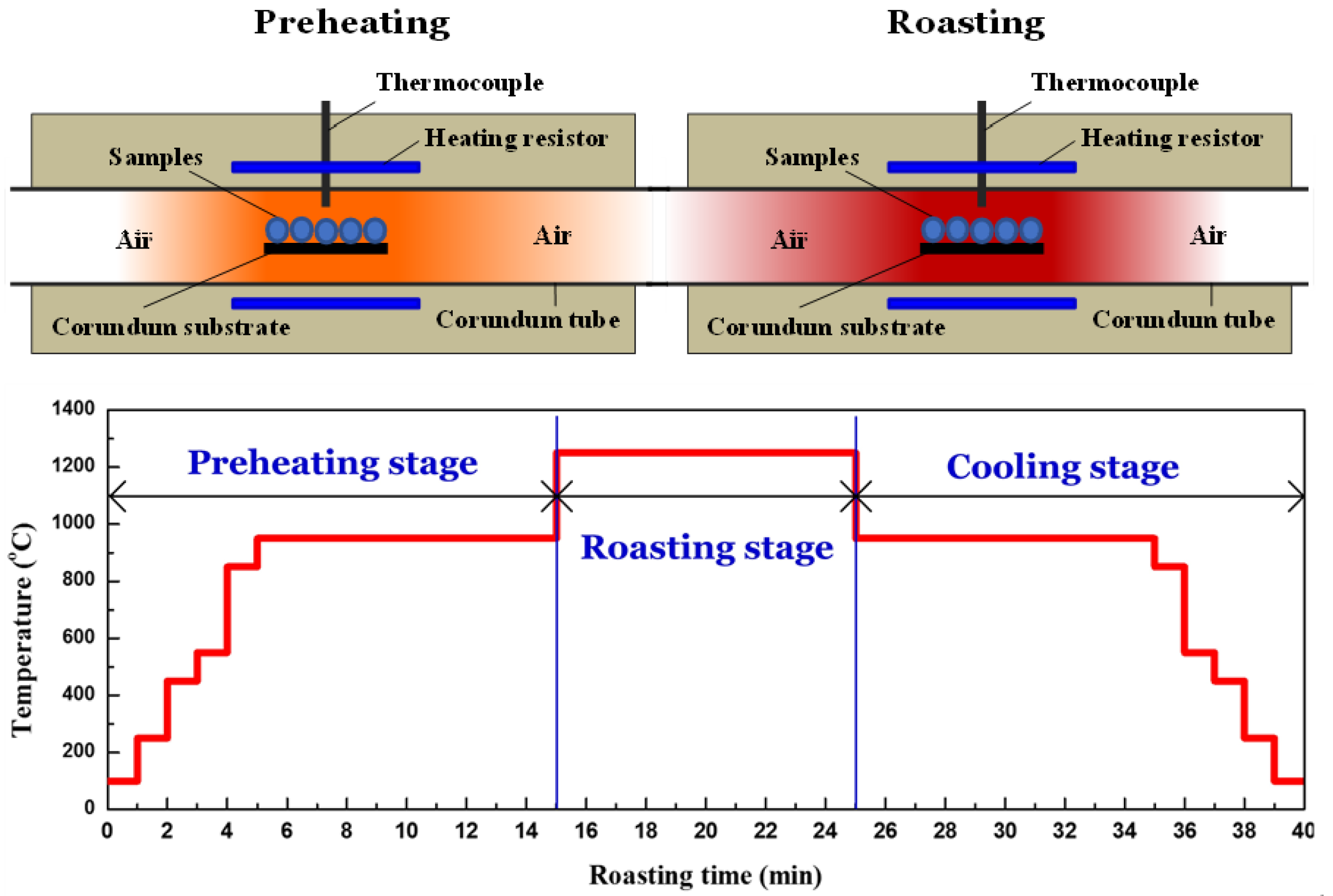
2.2.1. Oxidative Roasting Procedure for Pellet Preparation
2.2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
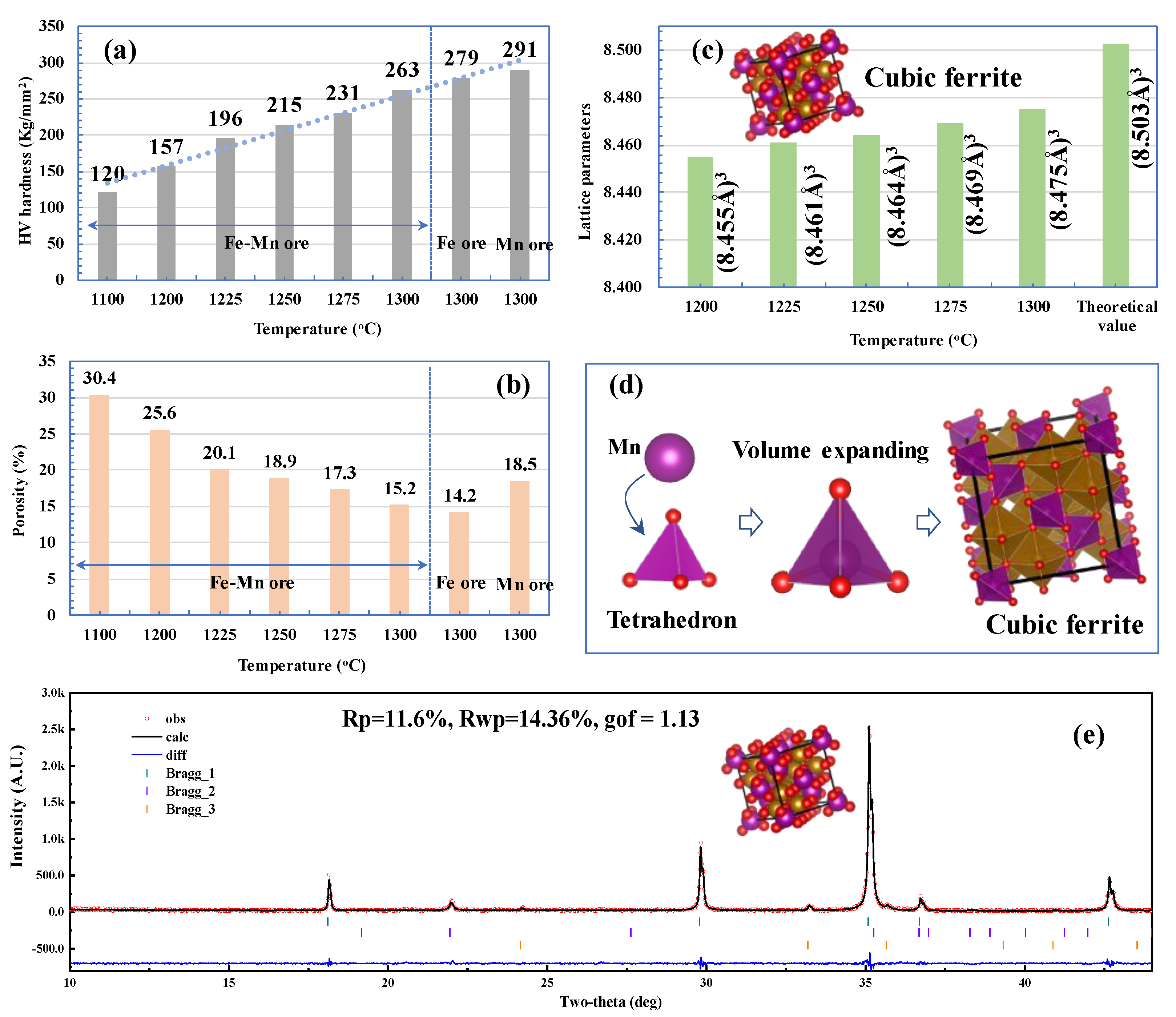
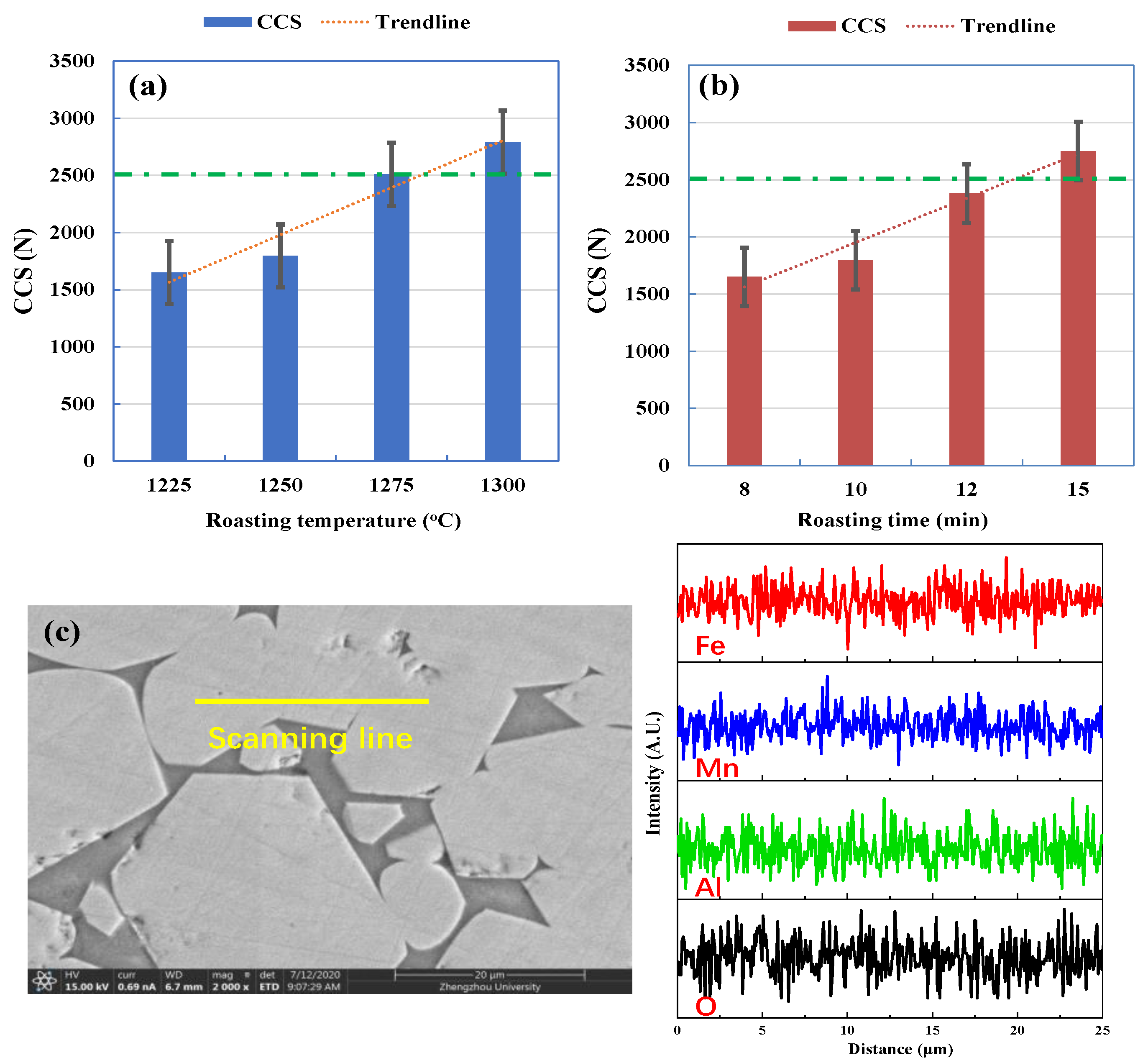
3.1. CCS Testing
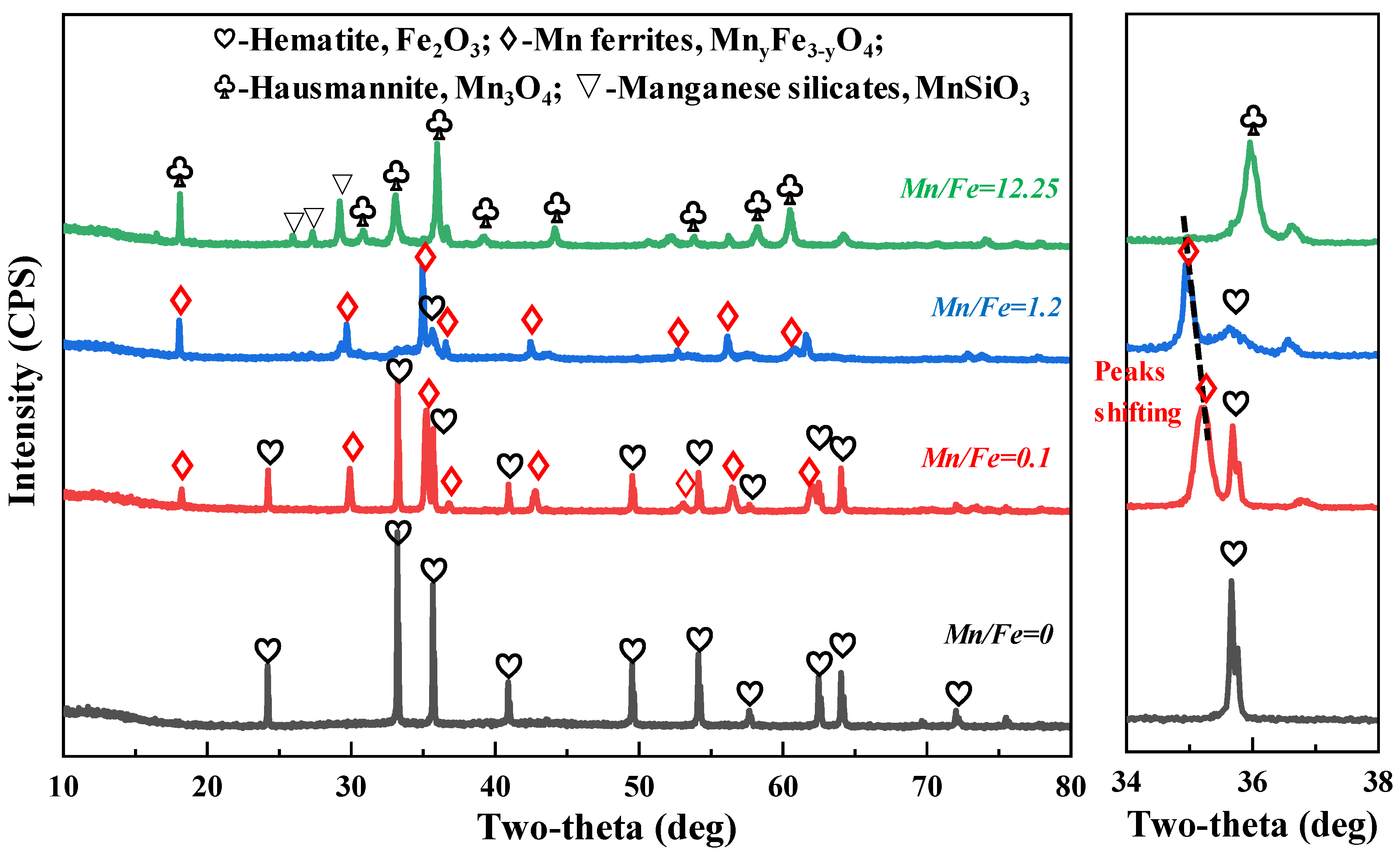
3.2. Phase Transformation
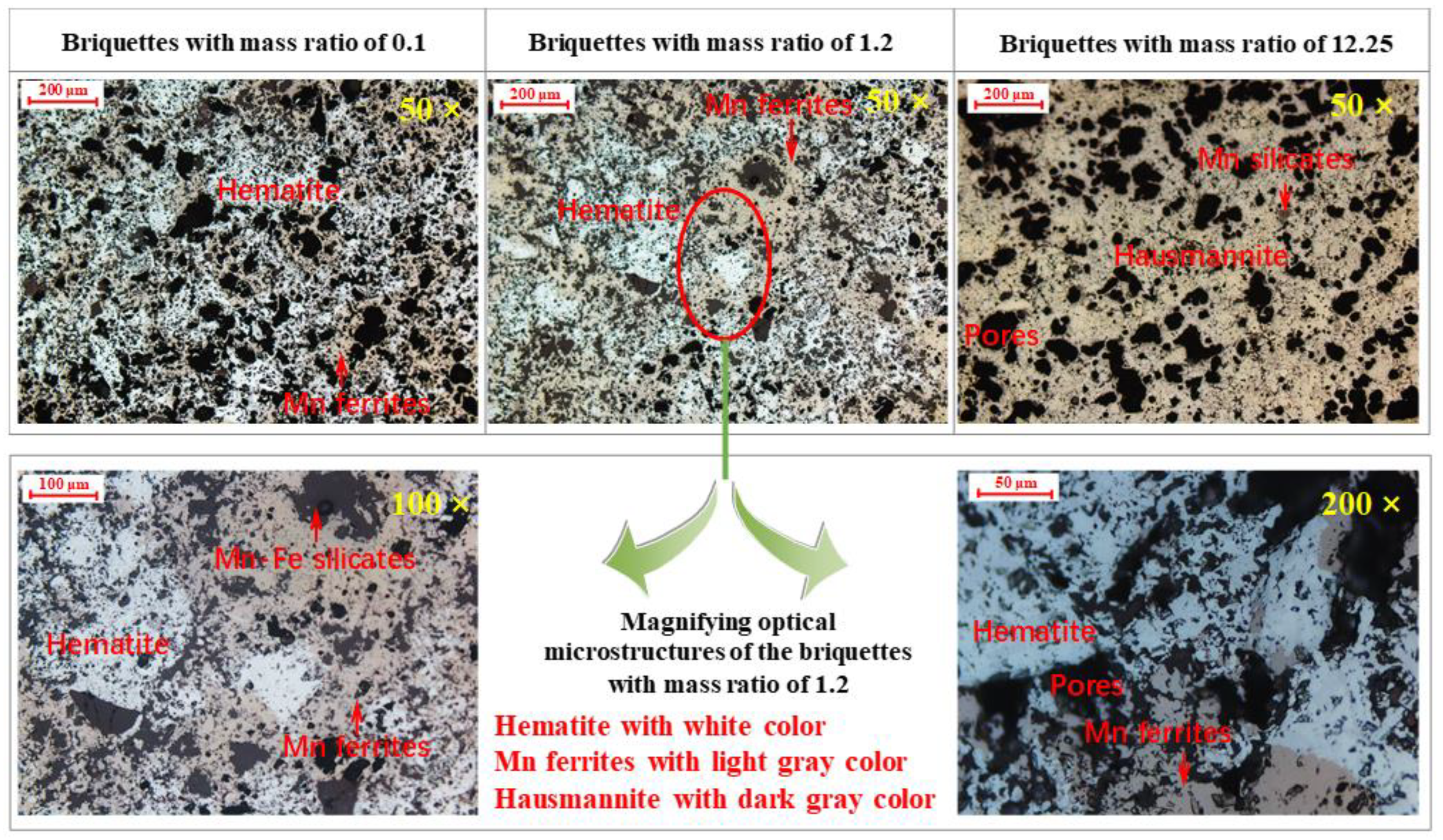
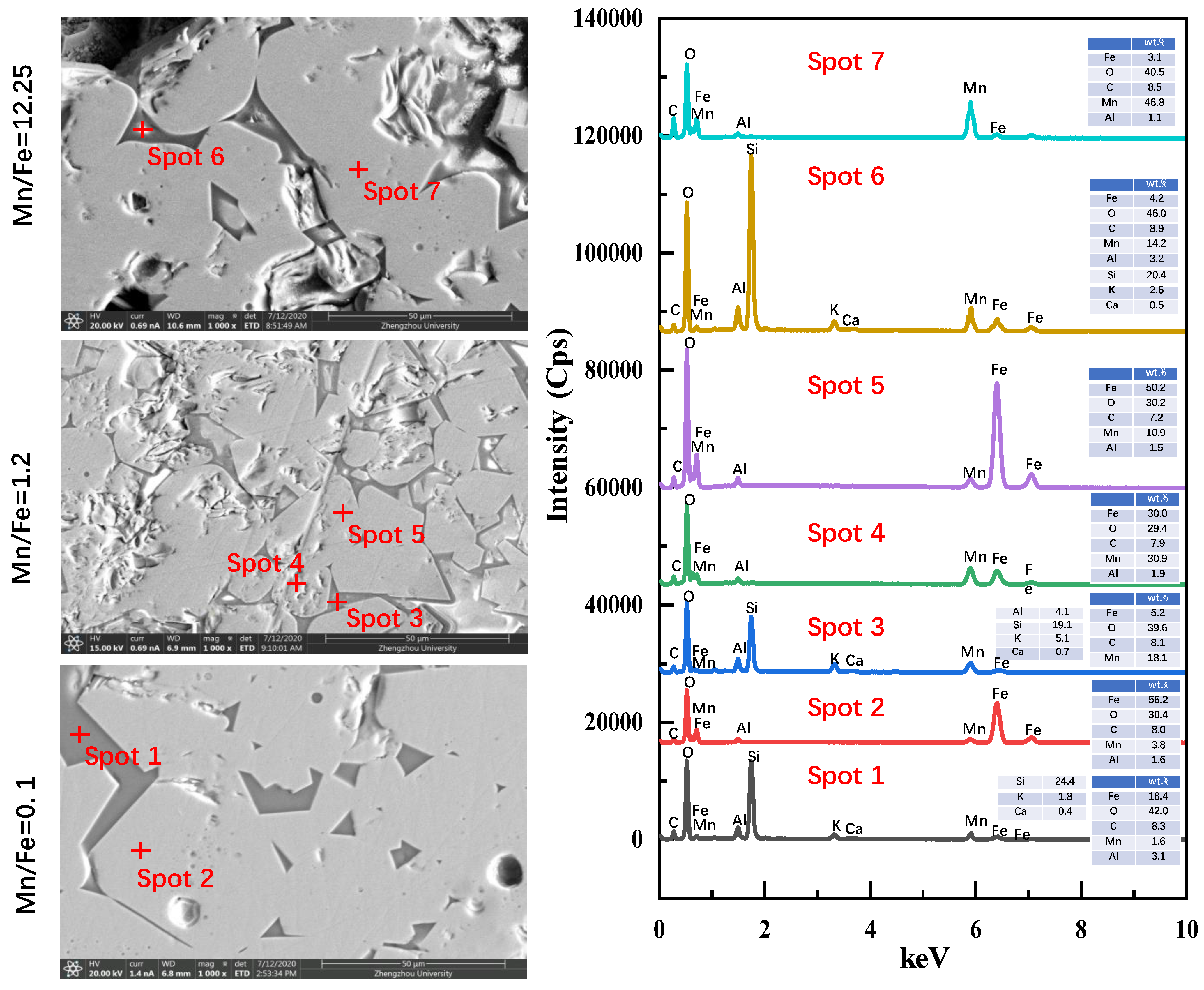
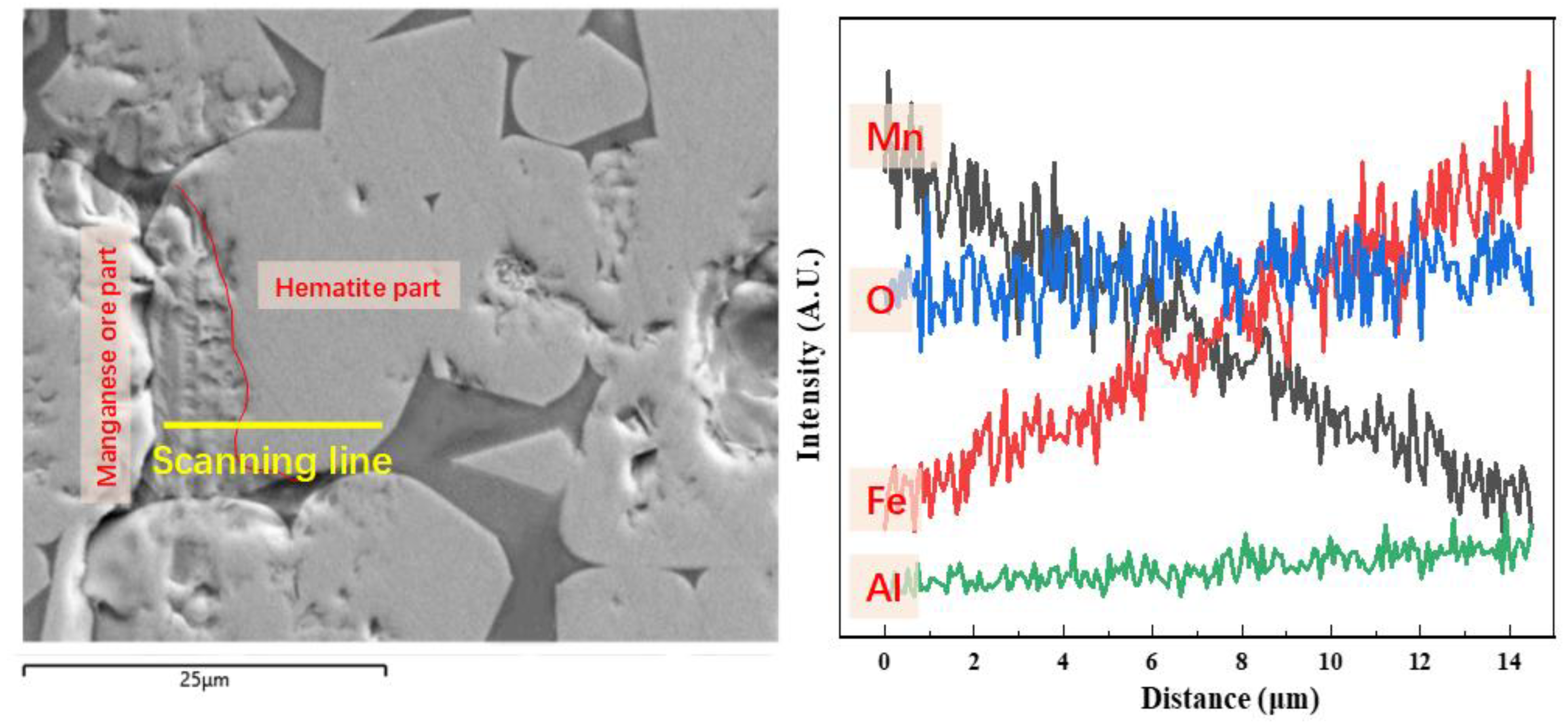
3.3. Morphology Evolution
3.4. Discussion of Mineralization
3.5. Suggestions for Consolidation of Fe-Mn Ore Pellets
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Manganese Institute. IMnI Annual Review. 2019. Available online: https://www.manganese.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/IMnI-2019-Annual-Review_ENG.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2020).
- Singh, V.; Ghosh, T.K.; Ramamurthy, Y.; Tathavadkar, V. Beneficiation and agglomeration process to utilize low-grade ferruginous manganese ore fines. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2011, 99, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, M.K.; Purcell, W.; Van Der Westhuizen, W.A. Recovery of manganese from ferruginous manganese ore using ascorbic acid as reducing agent. Miner. Eng. 2020, 154, 106406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Zhou, W.; Han, Y.; Li, Y. An innovative technology for full component recovery of iron and manganese from low grade iron-bearing manganese ore. Powder Technol. 2020, 373, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, M.; Su, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. Extraction and separation of manganese and iron from ferruginous manganese ores: A review. Miner. Eng. 2019, 131, 286–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Iqbal, Y.; Khan, I.; Ullah, A.; Sadiq, M.; Fahad, M.; Shah, K.H. Hydrometallurgical leaching and kinetic modeling of low-grade manganese ore with banana peel in sulfuric acid. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2021, 28, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Biswas, A. “Physicochemical processing of low grade ferruginous manganese ores”. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 158, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Yang, P. Introduction to and classification of manganese deposits of China. Ore Geol. Rev. 1999, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; El-Geassy, A.A.; Mishreky, M.; El-Geassy, A.-H.A. Crude steel directly from pre-reduced high manganese containing iron ore. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2014, 42, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Ghali, S.; El-Fawakhry, M.K.; El-Faramawy, H.; Eissa, M. Silicomanganese production utilising local manganese ores and manganese rich slag. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2014, 41, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Chakraborty, T.; Tripathy, S.K. A Review of Low Grade Manganese Ore Upgradation Processes. Miner. Process. Extr. Met. Rev. 2020, 41, 417–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Dai, S.-F.; Wang, P.; Ma, D.; Ni, B. Equilibrium kinetics of manganese-ore carbon-reduction between molten steel and slag. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2019, 46, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.-L.; Zhuang, C.-L. Carbothermal reduction characteristics of oxidized Mn ore through conventional heating and microwave heating. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2021, 28, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; You, Z.; Su, Z.; Luo, W.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. Consolidation Behavior of High-Fe Manganese Ore Sinters with Natural Basicity. Miner. Process. Extr. Met. Rev. 2016, 37, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Liu, L.; Pan, Y.; Zuo, H.; Wang, J.; Xue, Q. A review: Research progress of flux pellets and their application in China. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2021, 48, 1048–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavel, D.J.; Adema, A.; van der Stel, J.; Peeters, T.; Sietsma, J.; Boom, R.; Yang, Y. A comparative study of pellets, sinter and mixed ferrous burden behaviour under simulated blast furnace conditions. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2021, 48, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, G.; Tenório, J.A.S.; Jannotti, N., Jr.; Araújo, F.G.D.S. A geometallurgical comparison between lump ore and pellets of manganese ore. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 137, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, G.; Tenório, J.; Jannotti, N.; Araújo, F.D.S. Disintegration on heating of a Brazilian manganese lump ore. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 124, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.H.; Li, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.B.; He, G.Q.; Jiang, T. Induration mechanisms of oxidised pellets prepared from mixed magnetite–haematite concentrates. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2009, 36, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.-Q.; Yu, W.; Zhou, X.-L.; Pan, J. Strengthening pelletization of manganese ore fines containing high combined water by high pressure roll grinding and optimized temperature elevation system. J. Central South Univ. 2014, 21, 3485–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J. Pulverization mechanism and main minerals of fluxed manganese carbonate sintering. Chin. Manganese Ind. 1986, 4, 34–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; You, Z.; Su, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. Optimizing the Sintering Process of Low-Grade Ferromanganese Ores. In Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing, Conference Proceeding, San Antonio, TX, USA, 3–7 March 2013; pp. 527–534. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S. Sintering mineralization mechanism of the manganese ore. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 1990, 5, 45–52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.Y.; Hao, J.; Yang, S.; Lv, Q. Discussion on sintering technological parameter of manganese ore. Chin. Manganese Ind. 2011, 29, 24–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-Z.; Zhang, J.-L.; Liu, Z.-J.; Du, C.-B. Recent Advances and Research Status in Energy Conservation of Iron Ore Sintering in China. JOM 2017, 69, 2404–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4700: 2015. Iron Ore Pellets for Blast Furnace and Direct Reduction Feedstocks—Determination of the Crushing Strength. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/ (accessed on 4 February 2015).
- GB/T 24586-2009; Iron Ore or Pellet- Determination of Apparent Density, True Density, and Porosity. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, M.; Peng, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. Investigations on the MnO2-Fe2O3 system roasted in air atmosphere. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 2167–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Z.; Lu, M.; Peng, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. Formation mechanism of MnxFe3−xO4 by solid-state reaction of MnO2 and Fe2O3 in air atmosphere: Morphologies and properties evolution. Powder Technol. 2017, 313, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Han, G. Enhancing magnetism of ferrite via regulation of Ca out of sit A from spinel-type structure by adjusting the CaO/SiO2 mass ratio: Clean and value-added utilization of minerals. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 307, 122885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, G.; Zhang, B. Innovative methodology for co-treatment of mill scale scrap and manganese ore via oxidization roasting-magnetic separation for preparation of ferrite materials. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 6139–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Su, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. New understanding on separation of Mn and Fe from ferruginous manganese ores by the magnetic reduction roasting process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 444, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Test No. | Proportion (wt.%) | Mn/Fe Mass Ratio | Chemical Compositions of the Mixtures (wt.%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hematite Ore | Manganese Ore | TFe | TMn | CaO | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | Mn + Fe | ||
| H0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 64.76 | - | 0.14 | 0.08 | 1.7 | 4.65 | 64.76 |
| H1 | 93.6 | 6.4 | 0.05 | 60.89 | 3.04 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 1.87 | 4.86 | 63.93 |
| H2 | 88.0 | 12.0 | 0.1 | 57.44 | 5.75 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 2.02 | 5.04 | 63.19 |
| H3 | 82.9 | 17.1 | 0.15 | 54.37 | 8.16 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 2.15 | 5.21 | 62.53 |
| H4 | 78.4 | 21.6 | 0.2 | 51.61 | 10.32 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 2.27 | 5.36 | 61.94 |
| H5 | 74.3 | 25.7 | 0.25 | 49.12 | 12.28 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 2.38 | 5.49 | 61.40 |
| H6 | 70.6 | 29.4 | 0.3 | 46.86 | 14.06 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 2.48 | 5.61 | 60.92 |
| H7 | 64.1 | 35.9 | 0.4 | 42.90 | 17.17 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 2.65 | 5.83 | 60.07 |
| H8 | 53.9 | 46.1 | 0.6 | 36.71 | 22.03 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 2.92 | 6.16 | 58.74 |
| H9 | 46.3 | 53.7 | 0.8 | 32.07 | 25.68 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 3.12 | 6.41 | 57.74 |
| H10 | 40.4 | 59.6 | 1.0 | 28.49 | 28.49 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 3.28 | 6.60 | 56.98 |
| H11 | 35.7 | 64.3 | 1.2 | 25.61 | 30.74 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 3.40 | 6.76 | 56.36 |
| H12 | 30.2 | 69.9 | 1.5 | 22.25 | 33.39 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 3.55 | 6.94 | 55.64 |
| H13 | 25.9 | 74.1 | 1.8 | 19.67 | 35.42 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 3.66 | 7.08 | 55.08 |
| H14 | 23.6 | 76.4 | 2.0 | 18.26 | 36.52 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 3.72 | 7.16 | 54.78 |
| H15 | 19.0 | 81.0 | 2.5 | 15.48 | 38.70 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 3.85 | 7.31 | 54.19 |
| H16 | 15.7 | 84.3 | 3.0 | 13.44 | 40.31 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 3.93 | 7.42 | 53.72 |
| H17 | 13.1 | 86.9 | 3.5 | 11.87 | 41.54 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 4.00 | 7.50 | 53.41 |
| H18 | 8.0 | 92.0 | 5.0 | 8.79 | 43.96 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 4.14 | 7.67 | 52.75 |
| H19 | 0 | 100 | 12.25 | 3.90 | 47.80 | 0.26 | 0.18 | 4.35 | 7.93 | 51.70 |
| Ore Types | Main Consolidation Phase | Main Reactions | Microstructure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hematite ore | Hematite | Recrystallization of Fe2O3 | Fe2O3 particles connect to form bulk grains [19]. |
| Hematite and manganese ore mixture | Hematite, manganese ferrites | Recrystallization of Fe2O3 Equations (1)–(5) | Bulk particles contain both hematite and Mn ferrite phases, but the poorly crystallized Mn ferrites have apparent Mn and Fe element concentration gradients due to inadequate diffusion. |
| Manganese ore | Hausmannite, manganese silicates | Equations (1), (2) and (6) | Pyrolusite decomposes to hausmannite, many pores are formed, and hausmannite particles connect to form bulk grains. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, B.; Huang, J.; Ye, J.; Li, Y. Physicochemical Aspects of Oxidative Consolidation Behavior of Manganese Ore Powders with Various Mn/Fe Mass Ratios for Pellet Preparation. Materials 2022, 15, 1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051722
Zhang Y, Zhang B, Liu B, Huang J, Ye J, Li Y. Physicochemical Aspects of Oxidative Consolidation Behavior of Manganese Ore Powders with Various Mn/Fe Mass Ratios for Pellet Preparation. Materials. 2022; 15(5):1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051722
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuanbo, Bei Zhang, Bingbing Liu, Junjie Huang, Jing Ye, and Yuelong Li. 2022. "Physicochemical Aspects of Oxidative Consolidation Behavior of Manganese Ore Powders with Various Mn/Fe Mass Ratios for Pellet Preparation" Materials 15, no. 5: 1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051722
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, B., Liu, B., Huang, J., Ye, J., & Li, Y. (2022). Physicochemical Aspects of Oxidative Consolidation Behavior of Manganese Ore Powders with Various Mn/Fe Mass Ratios for Pellet Preparation. Materials, 15(5), 1722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051722








