Integrating a Top-Gas Recycling and CO2 Electrolysis Process for H2-Rich Gas Injection and Reduce CO2 Emissions from an Ironmaking Blast Furnace
Abstract
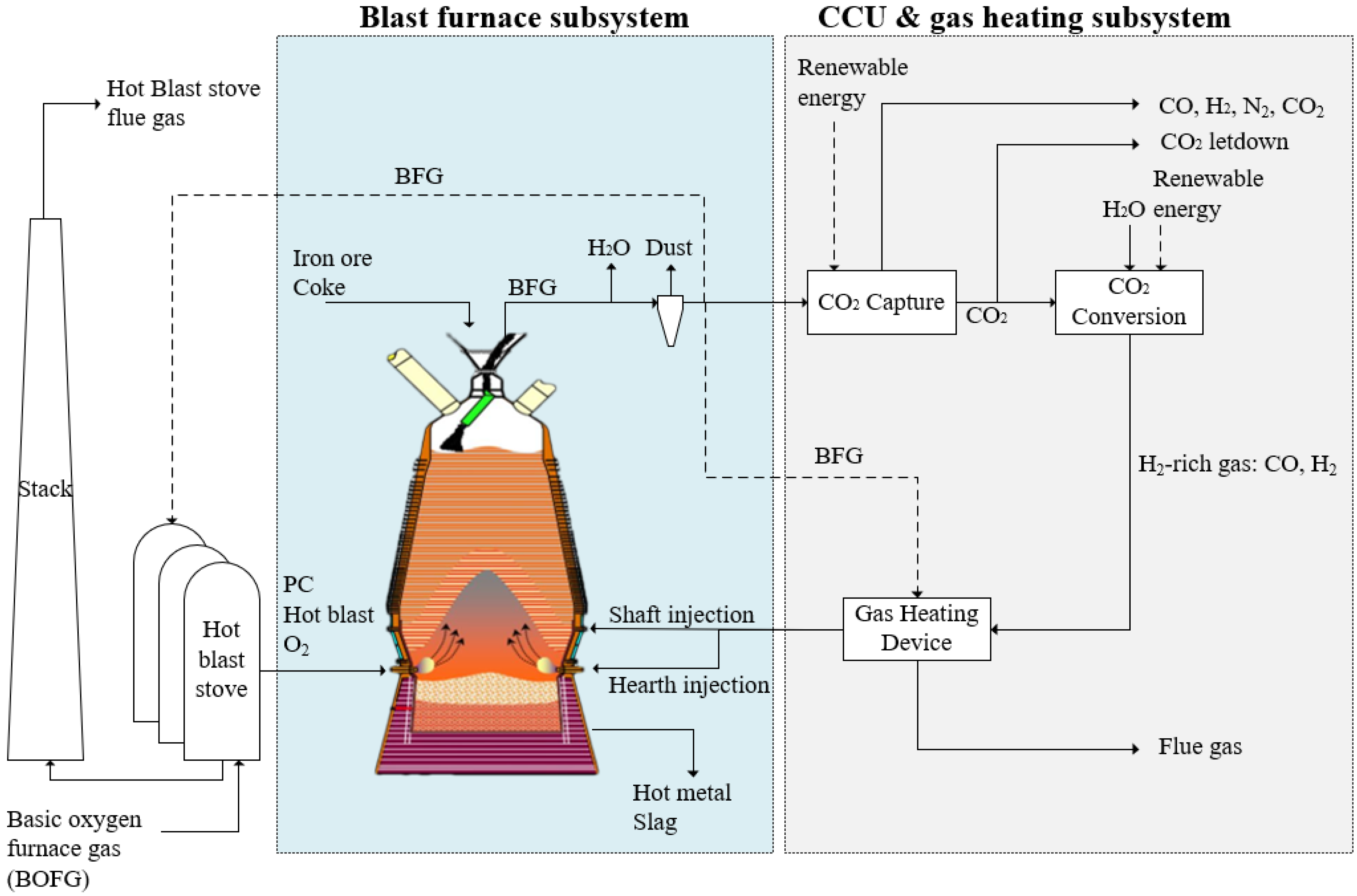
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Degree of indirect reduction depends on the reducing gas concentration of BF bosh gas, which is estimated by an empirical equation, as shown in Equation (1) [36]:
- For the amine absorption CO2 capture unit: 30% monoethanolamine (MEA) concentration was used for CO2 capture in this study. The capture unit recovered 90% CO2 in BFG, and the CO2 purity was >99%; the general thermal energy requirement for capture was assumed to be around 1000 kWh/tCO2 (3.6 GJ/ tCO2) [37,38,39]. Any additional CO2 captured and not converted was assumed to be released as per current operation or could be sent to CO2 storage routes, shown as CO2 letdown in Figure 1.
- The electrochemical CO2 conversion unit was treated in the model as a simplified input–output model. Assumptions for the material and energy balance in the CO2 conversion unit were based on laboratory demonstration data with additional inputs from literature sources. Briefly, the model was based on multiple two-cell vapour fed electrolyser stacks with the capacity to treat 50 tCO2 per day; further details can be found in our other report [33]. The current density of the electrolyser was altered from 2.68 V at 0 A/m2 to 3.59 V at 1862 A/m2 to produce the H2-rich gas with different H2/CO compositions.
- The electricity consumption for CO2 conversion is proportional to the H2 generation, which can be estimated as in Equation (2) [33]:
- efficiency of the gas heating device was 85%;
- The hot blast stove system uses two stoves on-gas and one stove on-blast, and the efficiency of the hot blast stoves was 75%.
2.1. Thermodynamic Calculations of H2-Rich Gas Injection BF
2.1.1. Raceway
2.1.2. Dripping, Cohesive, and High-Temperature Zones over 1000 °C
2.1.3. Shaft Zone Temperature between 800 and 1000 °C
2.2. Thermal Calculations of H2-Rich Gas Injection BF
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Results of the Thermodynamic Model
3.2. BF Simulation Conditions and Validation
3.3. Effect of H2 Injection on Coke Consumption Rate
3.4. Effect on H2 Utilisation Efficiency
3.5. Effects on CO2 Emissions and Energy Consumption
4. Conclusions
- The desired shaft gas injection temperature should not exceed 1000 °C to suppress the endothermic FeO reduction reaction by H2-rich gas.
- Injecting H2 to BF hearth has a better effect on coke rate reduction than that of injection to the shaft. The lowest H2 consumption to save 1 kg of coke was estimated to be 7.9 m3/tHM.
- H2 utilisation efficiency dropped significantly with increasing H2 content, and the increase in CO utilisation efficiency was limited. Further research should focus on improving H2 utilisation efficiency with a high H2 injection rate.
- Considering H2 utilisation efficiency and the degree of indirect reduction by H2 and CO, the proper H2 injection rate should be from around 50 to 80 m3/tHM.
- Introducing H2-rich gas injection can reduce CO2 emissions of the iron-making process by up to 262 m3/tHM compared with a traditional BF. However, injecting too much H2 would hinder CO2 emission reduction due to its requirement of preheating outside the BF.
- The energy consumption of this proposed process was higher than that of the traditional BF. Although coke consumption was reduced by 43 kg/tHM more than that of the traditional BF, net energy consumption increased with the amount of injected hydrogen due to the high electricity consumption in the CO2 capture and electrolyser. Developing a CO2 conversion unit with higher efficiency but less energy consumption is strongly recommended.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Abbreviations | |
| BF | Blast furnace |
| PCI | Pulverised coal injection |
| CCU | CO2 capture and conversion unit |
| RAFT | Raceway adiabatic flame temperature |
| tHM | Tonne of hot metal |
| Roman and Greek symbols | |
| Energy, kWh/tHM or kgce/tHM | |
| Volume of gas, m3/tHM | |
| T | Temperature, °C |
| Specific heat capacity, kJ/m3°C | |
| Reaction equilibrium constant of reduction stage i; i = I, II, III | |
| G | Gibbs free energy, kJ/mol |
| Volume fraction of gas component | |
| Utilisation efficiency of CO in stage i, i = 1, 2, 3 | |
| Utilisation efficiency of H2 in stage i, i = 1, 2, 3 | |
| Minimal CO required for iron ores reduction, mol | |
| Minimal H2 required for iron ores reduction, mol | |
| Volume reaction of CO or H2 in reducing gas entering the BF shaft | |
| Overall gas utilisation efficiency for H2-rich reducing gas in the BF | |
| Proportion of H2 and CO in the total amount of gas entering the bosh and shaft. | |
| Sensible heat of material, kJ/tHM | |
| Enthalpy of material, kJ/tHM | |
| Degree of direct reduction | |
| Degree of indirect reduction | |
| Iron content in hot metal | |
| Enthalpy of reaction, kJ/tHM | |
| Weight fraction of solid material | |
| Total H2 injection volume to the BF, m3/tHM | |
References
- Xu, K. Low carbon economy and iron and steel industry. Iron Steel 2010, 45, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo, N.; Moya, J.A. Prospective scenarios on energy efficiency and CO2 emissions in the European Iron & Steel industry. Energy 2013, 54, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, A.; Senk, D. New Trends in Coal Conversion: Combustion, Gasification, Emissions, and Coking; Woodhead Publishing: Sawson, UK, 2019; pp. 367–404. [Google Scholar]
- Danloy, G.; Berthelemot, A.; Grant, M.; Borlée, J.; Sert, D.; Van Der Stel, J.; Jak, H.; Dimastromatteo, V.; Hallin, M.; Eklund, N.; et al. ULCOS-Pilot testing of the Low-CO2 Blast Furnace process at the experimental BF in Luleå. Rev. Métall.-Int. J. Metall. 2009, 106, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, K.; Hallin, M.; Burstrom, E. ULCORED SP 12 Concept for minimized CO2 emission. Metall. Res. Technol. 2009, 106, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Material Economics. Industrial Transformation 2050: Pathways to Net-Zero Emisisons from EU Heavy Industry. 2019. Available online: https://materialeconomics.com/publications/industrial-transformation-2050 (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Chisalita, D.-A.; Petrescu, L.; Cobden, P.; van Dijk, H.E.; Cormos, A.-M.; Cormos, C.-C. Assessing the environmental impact of an integrated steel mill with post-combustion CO2 capture and storage using the LCA methodology. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogami, H.; Kashiwaya, Y.; Yamada, D. Simulation of Blast Furnace Operation with Intensive Hydrogen Injection. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, T.; Kawabata, H.; Ono-Nakazato, H.; Kurosaka, A. Fundamental Experiments on the H2 Gas Injection into the Lower Part of a Blast Furnace Shaft. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, S14–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinegar, H.K.; Moats, M.S.; Sohn, H.Y. Process Simulation and Economic Feasibility Analysis for a Hydrogen-Based Novel Suspension Ironmaking Technology. Steel Res. Int. 2011, 82, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.; Devisme, O.; Patisson, F.; Ablitzer, D. A laboratory study of the reduction of iron oxides by hydrogen. arXiv 2008, arXiv:08032831. [Google Scholar]
- Spreitzer, D.; Schenk, J. Reduction of Iron Oxides with Hydrogen—A Review. Steel Res. Int. 2019, 90, 1900108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, Y.; Lyu, Q.; Li, J.; Lan, C.; Liu, X. Effect of Hydrogen Addition on Reduction Kinetics of Iron Oxides in Gas-injection BF. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.-b.; Wang, C.; Dong, J.-j.; Jiao, K.-x.; Xu, R.-s. Reduction kinetics of iron oxide pellets with H2 and CO mixtures. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2015, 22, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Nogami, H.; Yagi, J.-I. Numerical Analysis on Injection of Hydrogen Bearing Materials into Blast Furnace. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, C.; Wendelstorf, J.; Turek, T. Modeling and simulation of hydrogen injection into a blast furnace to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 154, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Qie, Y.; Liu, X.; Lan, C.; Li, J.; Liu, S. Effect of hydrogen addition on reduction behavior of iron oxides in gas-injection blast furnace. Thermochim. Acta 2017, 648, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watakabe, S.; Miyagawa, K.; Matsuzaki, S.; Inada, T.; Tomita, Y.; Saito, K.; Osame, M.; Sikström, P.; Ökvist, L.S.; Wikstrom, J.-O. Operation Trial of Hydrogenous Gas Injection of COURSE50 Project at an Experimental Blast Furnace. ISIJ Int. 2013, 53, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, Y.; Lyu, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Lan, C.; Zhang, S.; Yan, C. Effect of Hydrogen Addition on Softening and Melting Reduction Behaviors of Ferrous Burden in Gas-Injection Blast Furnace. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 2622–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, Z.-J.; Zhang, W.-l.; Zhu, H.-b.; Zhang, J.-h.; Pang, Q.-h. Reduction behavior of iron-bearing burdens in hydrogen-rich stream. Iron Steel 2020, 55, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, J.; Grönkvist, S. A comparison of two hydrogen storages in a fossil-free direct reduced iron process. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 28657–28674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydrogen Council. Path to Hydrogen Competitiveness: A Cost Perspective. 2020. Available online: https://hydrogencouncil.com/en/path-to-hydrogen-competitiveness-a-cost-perspective/ (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Uribe-Soto, W.; Portha, J.-F.; Commenge, J.-M.; Falk, L. A review of thermochemical processes and technologies to use steelworks off-gases. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rocha, E.P.; Guilherme, V.S.; de Castro, J.A.; Sazaki, Y.; Yagi, J.-I. Analysis of synthetic natural gas injection into charcoal blast furnace. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2013, 2, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Halim, K.S.A. Theoretical Approach to Change Blast Furnace Regime with Natural Gas Injection. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2013, 20, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinkel, V.; Kieberger, N.; Bürgler, T.; Rechberger, H.; Fellner, J. Influence of waste plastic utilisation in blast furnace on heavy metal emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 94, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Tafalla, B.; Martínez-Ferrero, E.; Franco, F.; Palomares-Gil, E. Applications of Carbon Dots for the Photocatalytic and Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO2. Molecules 2022, 27, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Sa, R.; Lv, H.; Yang, S.; Yuan, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, R. Covalent organic framework hosting metalloporphyrin-based carbon dots for visible-light-driven selective CO2 reduction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küngas, R. Review—Electrochemical CO2 Reduction for CO Production: Comparison of Low- and High-Temperature Electrolysis Technologies. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 044508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvanian, A.M.; Sadeghi, N.; Rafiee, A.; Shearer, C.J.; Jafarian, M. Application of porous materials for CO2 reutilization: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacourt, C.; Ridgway, P.; Kerr, J.; Newman, J. Design of an Electrochemical Cell Making Syngas (CO + H2) from CO2 and H2O reduction at Room Temperature. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 155, B42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Jiao, F. Electrochemical CO2 reduction: Electrocatalyst, reaction mechanism, and process engineering. Nano Energy 2016, 29, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Li, M.; Idros, M.N.; Wu, Y.; Wang, G.; Rufford, T.E. Is Maximising Current Density Always the Optimum Strategy in Electrolyser Design for Electrochemical CO2 Conversion to Chemicals? 2021. Available online: https://chemrxiv.org/engage/chemrxiv/article-details/61a7235f7848050092a110b4 (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- De Ras, K.; Van de Vijver, R.; Galvita, V.V.; Marin, G.B.; Van Geem, K.M. Carbon capture and utilization in the steel industry: Challenges and opportunities for chemical engineering. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2019, 26, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, J.A.; Takano, C.; Yagi, J.-i. A theoretical study using the multiphase numerical simulation technique for effective use of H2 as blast furnaces fuel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2017, 6, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Fundamental Study and Process Optimization of the Oxygen Blast Furnace Ironmaking. Doctoral Dissertation, Northeastern University, Shenyang, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, N.-S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, I.Y.; Jang, K.R.; Shim, J.-G. A study of the CO2 capture pilot plant by amine absorption. Energy 2012, 47, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, M.; Adjiman, C.S.; Bardow, A.; Anthony, E.J.; Boston, A.; Brown, S.; Fennell, P.S.; Fuss, S.; Galindo, A.; Hackett, L.A.; et al. Carbon capture and storage (CCS): The way forward. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1062–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Cho, H.; Yun, S.; Jang, M.-G.; Oh, S.-Y.; Binns, M.; Kim, J.-K. Process design and optimization of MEA-based CO2 capture processes for non-power industries. Energy 2019, 185, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari, S.R.; Balaji, C.P.; Karunamurthy, K. Carbon Capture and Storage Using Renewable Energy Sources: A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 573, 12004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aresta, M.; Dibenedetto, A.; Angelini, A. The use of solar energy can enhance the conversion of carbon dioxide into energy-rich products: Stepping towards artificial photosynthesis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2013, 371, 20120111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBrien, M.; Serrenho, A.C.; Allwood, J. Potential for energy savings by heat recovery in an integrated steel supply chain. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 103, 592–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazanek, E.; Jasienska, S.; Brachucy, A.; Bryk, C. The influence of hydrogen in the gas mixture of hydrogen and CO on the dynamics of the reduction process. Metal. Odlew. 1982, 8, 53–70. [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowski, K.; Mondal, K.; Lorethova, H.; Stonawski, L.; Szymanski, T.; Wiltowski, T. Effect of gas composition on the kinetics of iron oxide reduction in a hydrogen production process. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2005, 30, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozwiak, W.; Kaczmarek, E.; Maniecki, T.; Ignaczak, W.; Maniukiewicz, W. Reduction behavior of iron oxides in hydrogen and carbon monoxide atmospheres. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 326, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Ferrous Metallurgy; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bernasowski, M. Theoretical Study of the Hydrogen Influence on Iron Oxides Reduction at the Blast Furnace Process. Steel Res. Int. 2014, 85, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, M. The Reduction of Wustite with High Oxygen Enrichment and High Injection of Hydrogenous Fuel. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Chu, M.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yagi, J. Mathematical simulation and life cycle assessment of blast furnace operation with hydrogen injection under constant pulverized coal injection. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China GB/T 2589-2020; General Principles for Calculation of the Comprehensive Energy Consumption. Standardization Administration of China: Bijing, China, 2020.












| Operating Parameters | |
|---|---|
| PCI rate (kg/tHM) | 137 |
| Blast temperature, °C | 1052 |
| Humidity of hot blast, g/m3 | 12.93 |
| Top gas temperature, °C | 161 |
| Hearth injection temperature, °C | 1250 |
| Shaft injection temperature, °C | 900 |
| Parameter | Prediction | Industrial | Top Gas | Prediction | Industrial |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coke rate, kg/tHM | 386 | 386 | CO, % | 25.1 | 24.9 |
| Blast, Nm3/tHM | 1060 | 1089 | CO2, % | 21.1 | 20.0 |
| Slag rate, kg/tHM | 364 | 373 | H2, % | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| Burden input, kg/tHM | 1676 | 1676 | N2, % | 50.0 | 53 |
| RAFT, °C | 2205 | 2195 | Rd | 0.46 | - |
| Composition | Tfe | FeO | SiO2 | CaO | MgO | TiO2 | S | Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sinter 1 | 55.85 | 9.59 | 5.25 | 10.35 | 2.19 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 2.5 |
| Sinter 2 | 55.85 | 9.2 | 5.26 | 10.27 | 2.2 | 0.27 | - | 2.5 |
| Pellet | 61.92 | 1.46 | 5.31 | 1.45 | - | 1.58 | - | 0.98 |
| Ti ore | 40.27 | - | 9.07 | 2.05 | - | 10.78 | - | 1.69 |
| Dust | 39.80 | 2.58 | 4.05 | 2.04 | 0.83 | 0 | - | 1.31 |
| Composition | Fixed C | H2O | FeO | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | N | O | H | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coke | 86.06 | 4.50 | 1.6 | 0.39 | 4.49 | 3.69 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.21 | 0.33 | 1.80 |
| PCI | 71.15 | 0 | 0.03 | 1.98 | 8.4 | 7.93 | 0.18 | 0.34 | 3.16 | 2.10 | 0.30 |
| Composition | Fe | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hot metal | 95.14 | 4.12 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.136 | 0.023 | 0.129 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, J.; Hao, L.; Rufford, T.E.; Rudolph, V.; Wang, G. Integrating a Top-Gas Recycling and CO2 Electrolysis Process for H2-Rich Gas Injection and Reduce CO2 Emissions from an Ironmaking Blast Furnace. Materials 2022, 15, 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062008
Hu Y, Qiu Y, Chen J, Hao L, Rufford TE, Rudolph V, Wang G. Integrating a Top-Gas Recycling and CO2 Electrolysis Process for H2-Rich Gas Injection and Reduce CO2 Emissions from an Ironmaking Blast Furnace. Materials. 2022; 15(6):2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062008
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yichao, Yinxuan Qiu, Jian Chen, Liangyuan Hao, Thomas Edward Rufford, Victor Rudolph, and Geoff Wang. 2022. "Integrating a Top-Gas Recycling and CO2 Electrolysis Process for H2-Rich Gas Injection and Reduce CO2 Emissions from an Ironmaking Blast Furnace" Materials 15, no. 6: 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062008
APA StyleHu, Y., Qiu, Y., Chen, J., Hao, L., Rufford, T. E., Rudolph, V., & Wang, G. (2022). Integrating a Top-Gas Recycling and CO2 Electrolysis Process for H2-Rich Gas Injection and Reduce CO2 Emissions from an Ironmaking Blast Furnace. Materials, 15(6), 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062008






