Effect of Intercritical Annealing Time on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Low Carbon Medium Manganese Steel Subjected to Multi-Step Heat Treatment Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials Smelting and Rolling
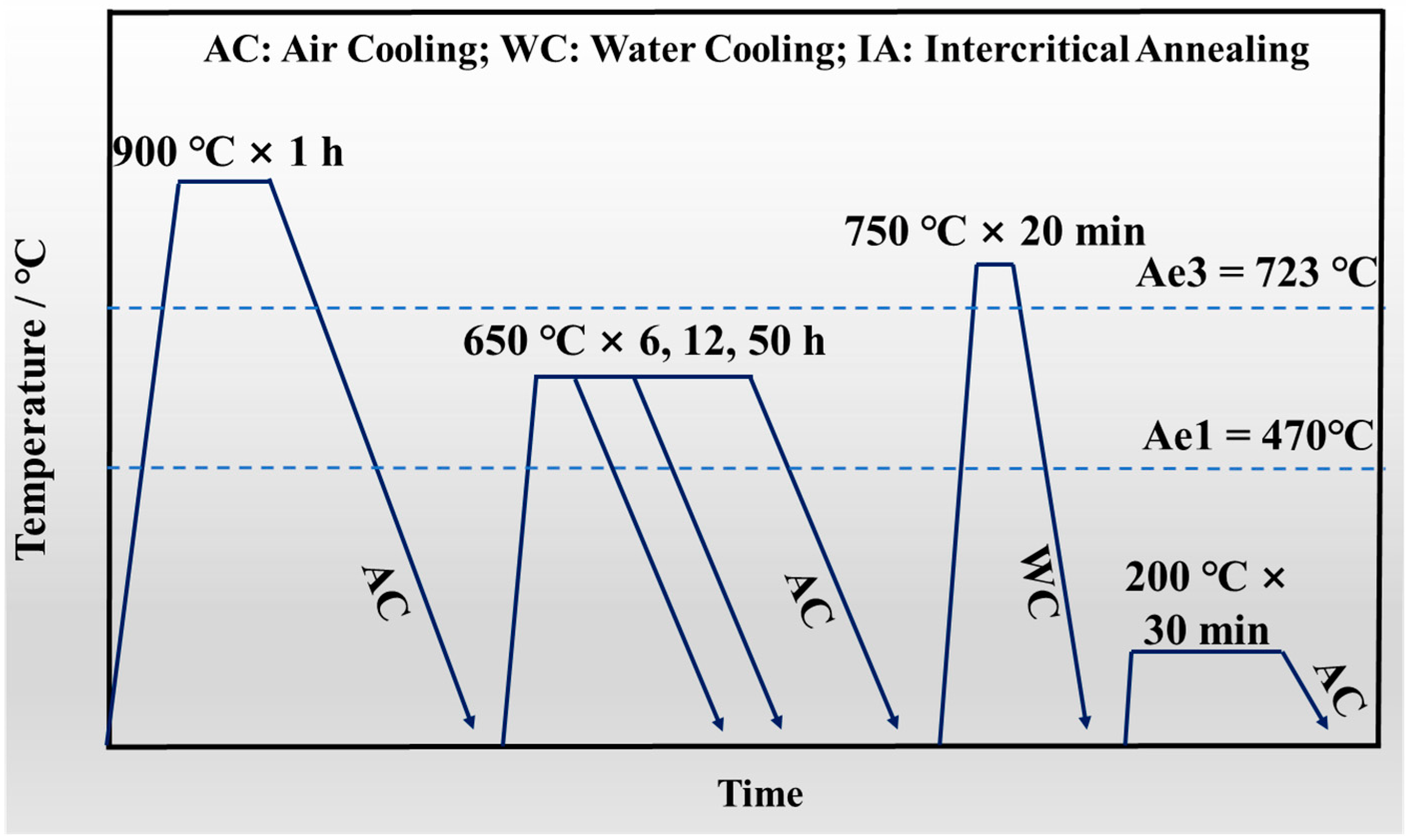
2.2. Heat Treatment Process
2.3. Microstructure Characterization
2.4. Secondary Phase Precipitation Characterization
2.5. Mechanical Property Tests
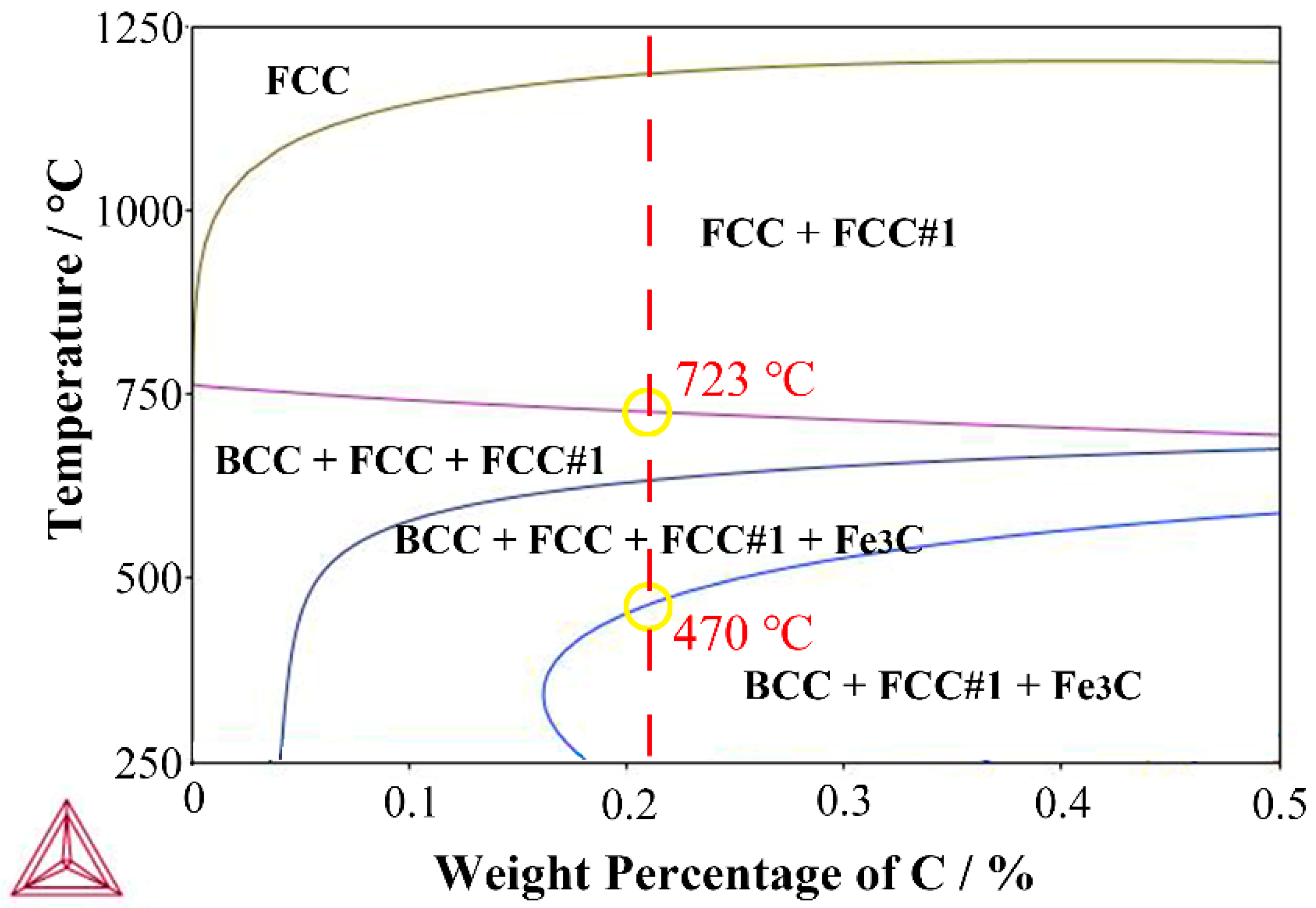
2.6. Phase Transformation Temperature Test
3. Results
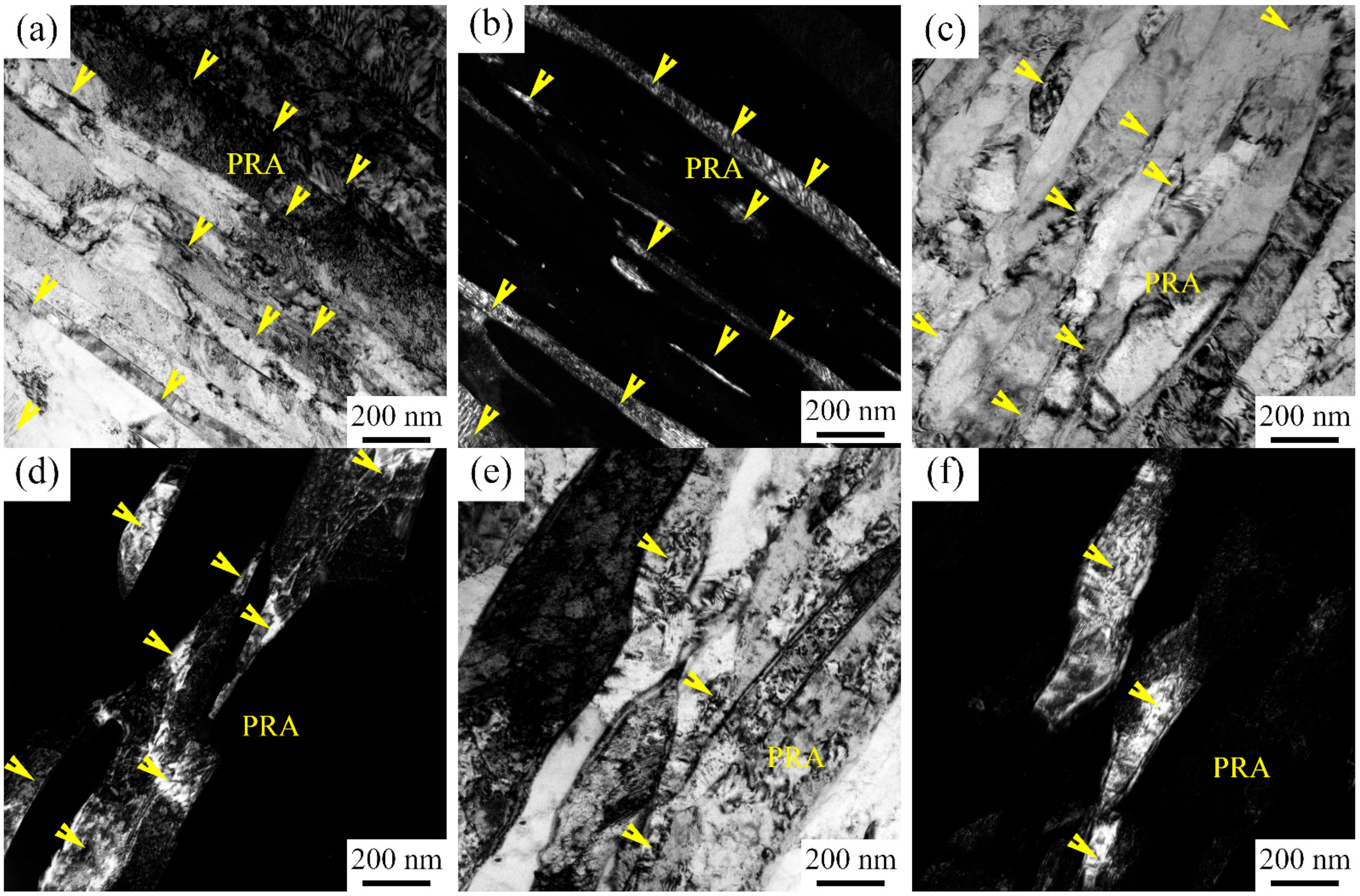
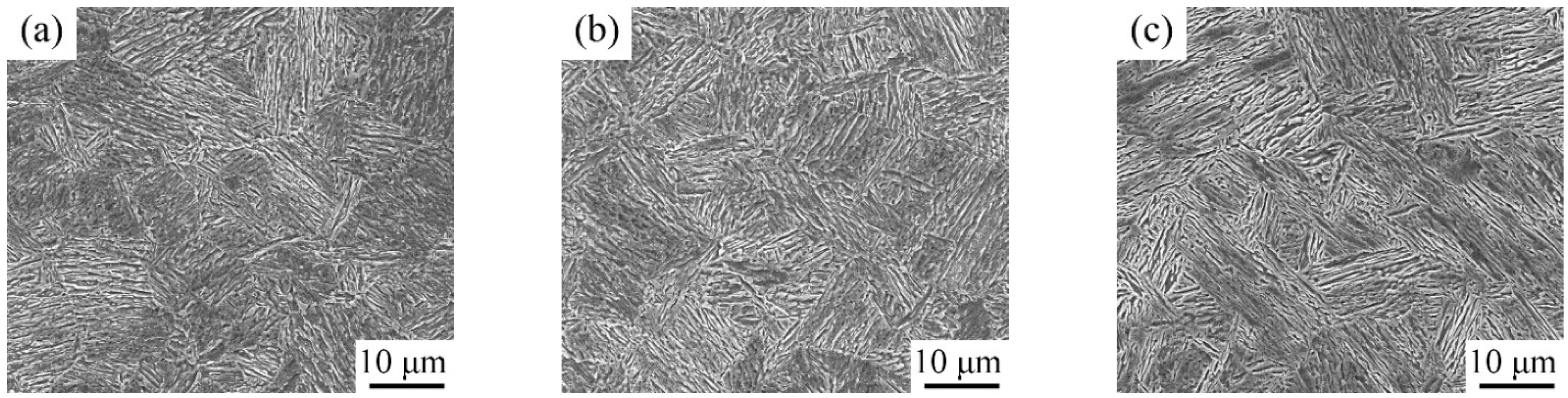
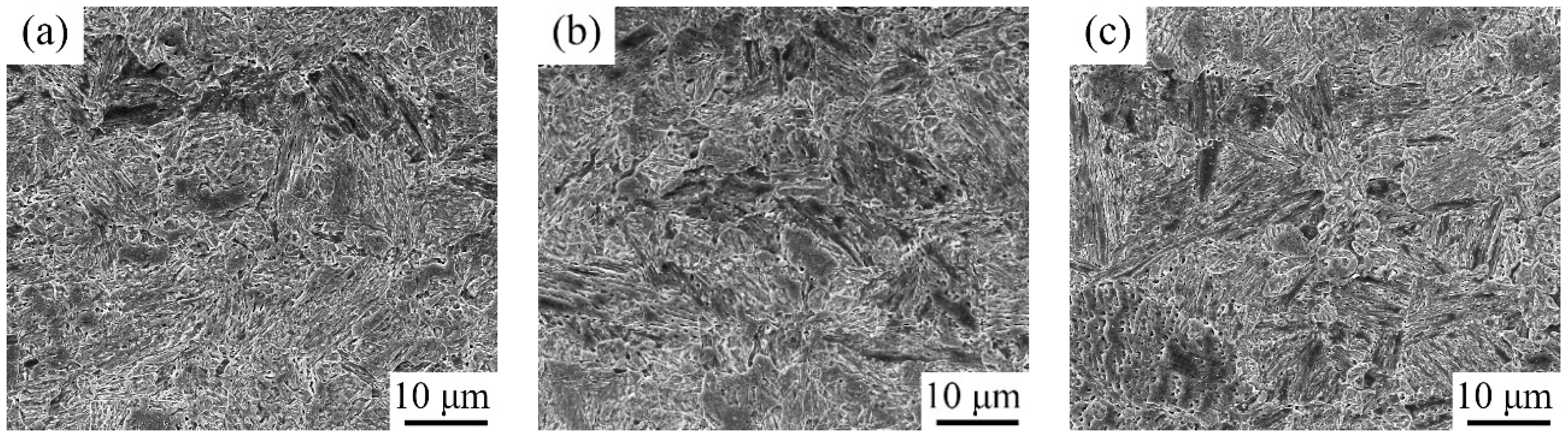
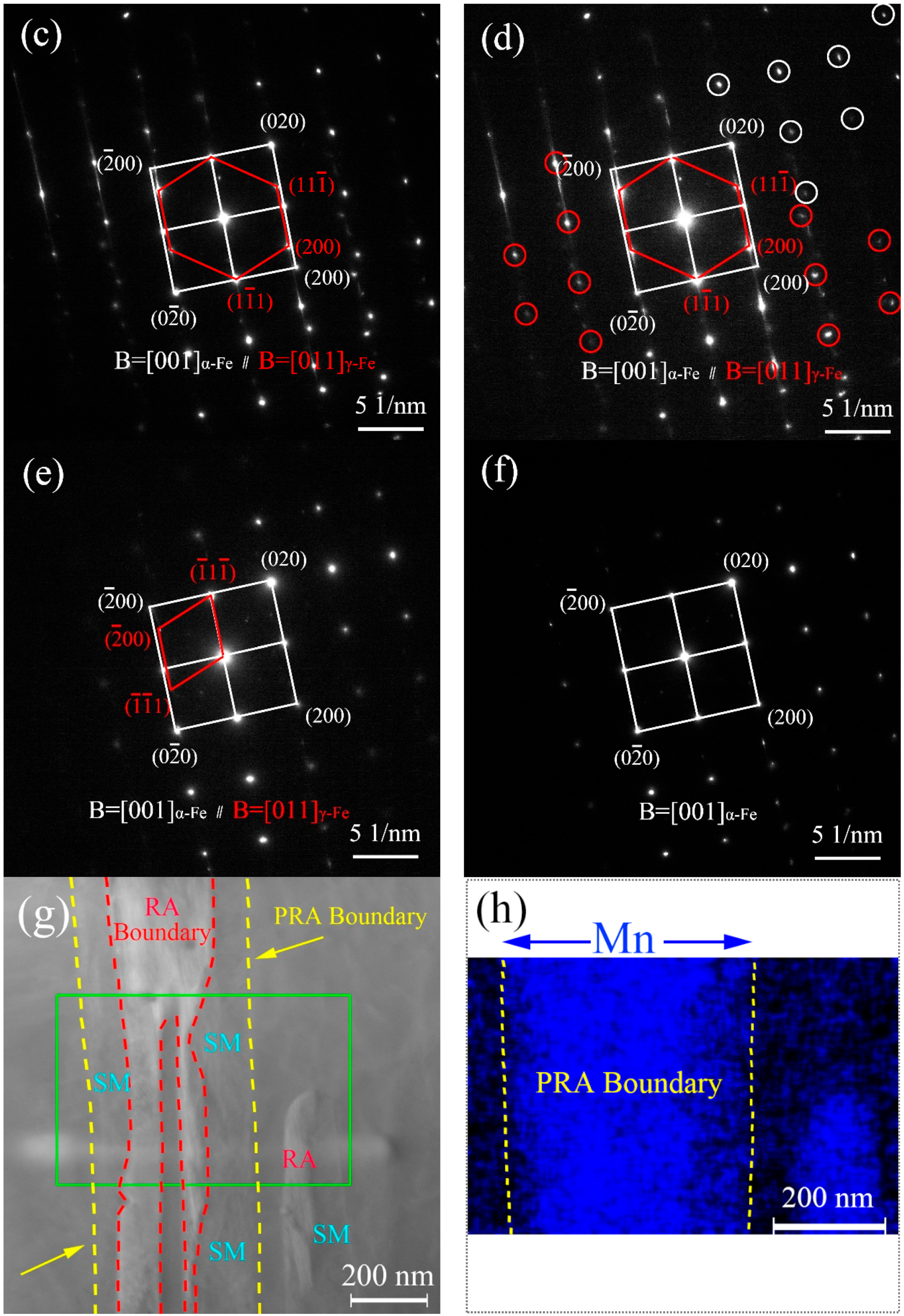
3.1. Microstructure Characterization after Being Subjected to IA at 650 °C
3.2. Microstructure Characterization after Being Tempered at 200 °C
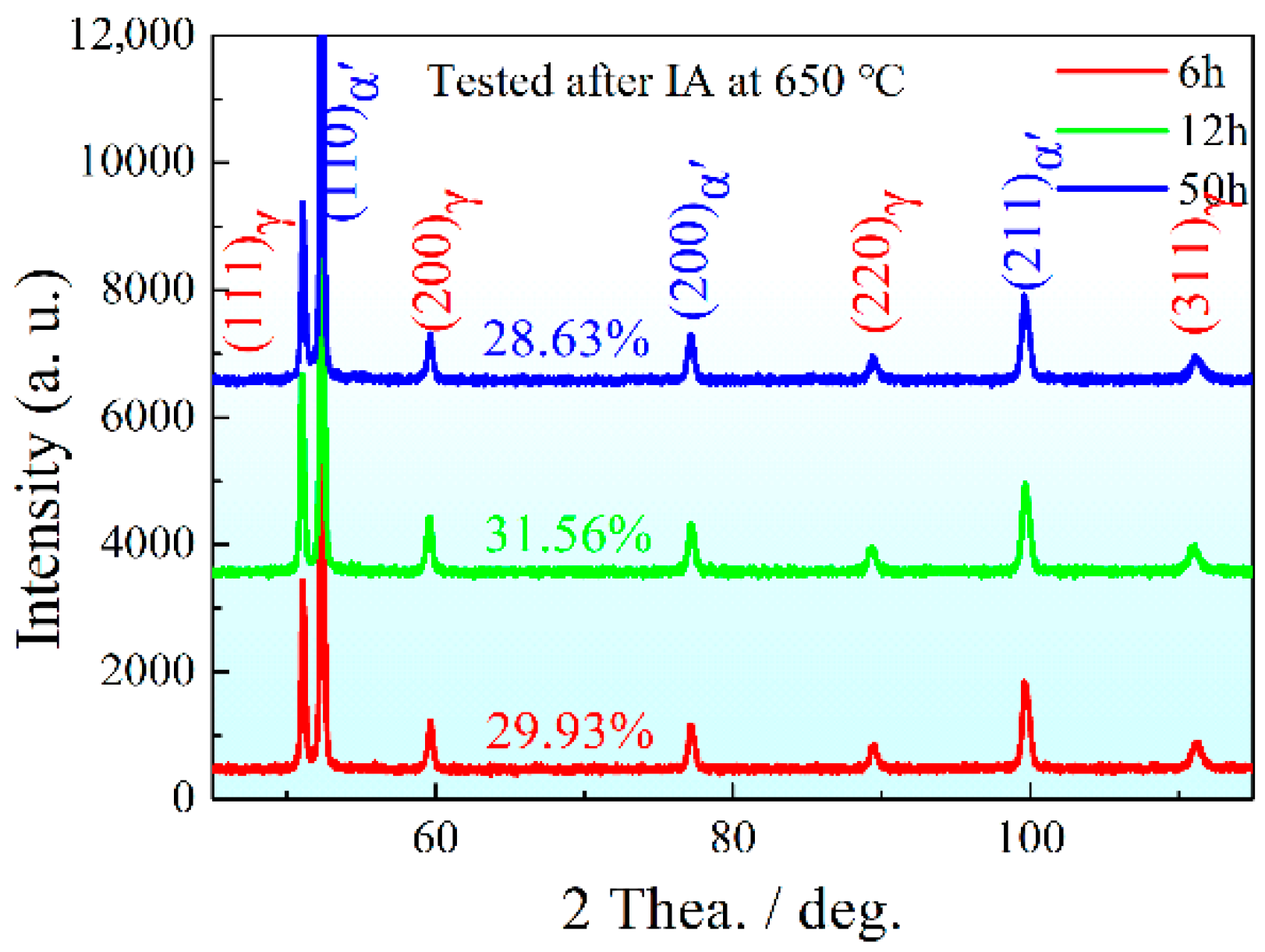
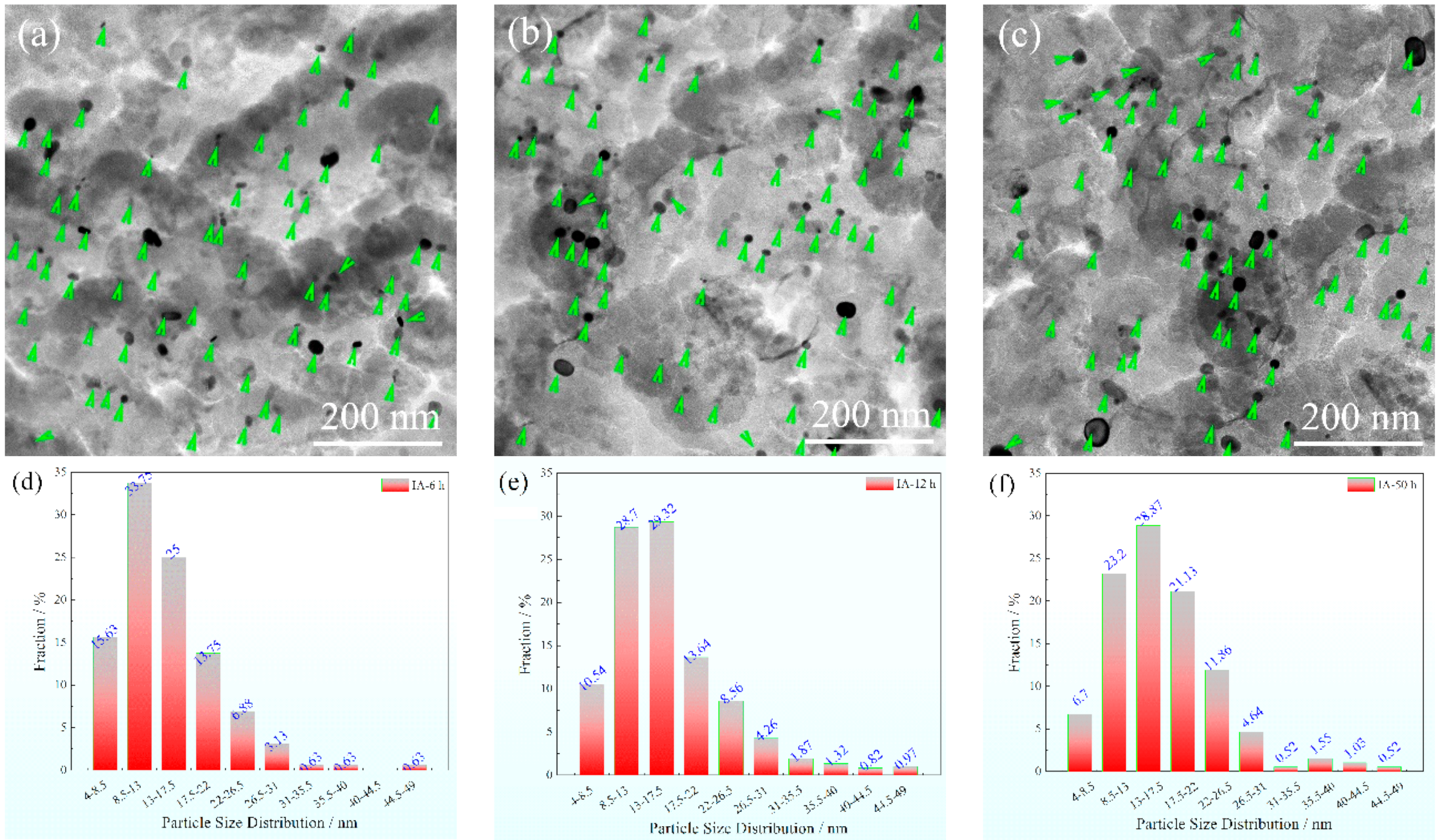
3.3. Precipitation Phase Evolution with Partition Time
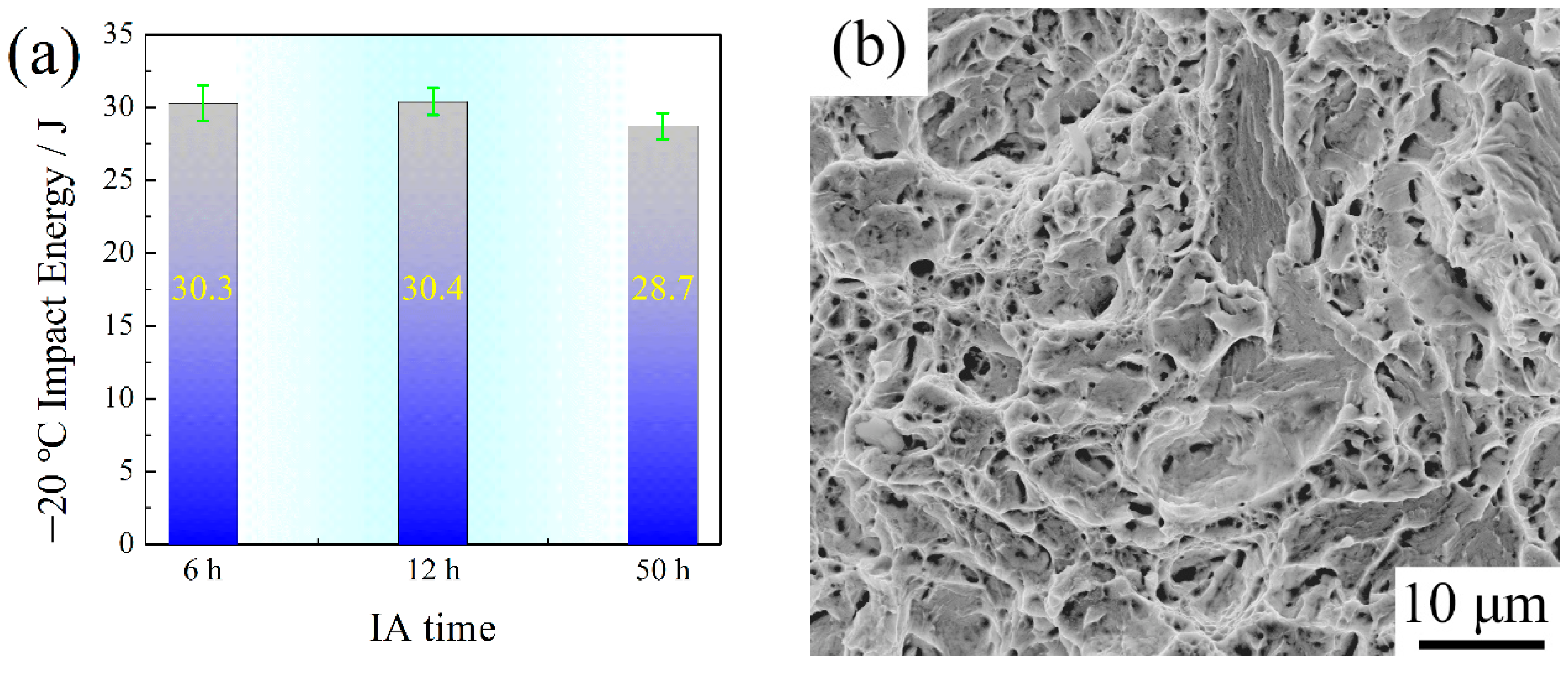
3.4. Mechanical Property Tests after Being Tempered at 200 °C
4. Discussion
4.1. Microstructure Evolution Varying with IA Time
4.2. Mechanical Property Evolution Varying with IA Time
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Although the 0.2C-5Mn steel was subjected to different durations of intercritical annealing, the mechanical properties showed little change, so the IA-6 h was preferred for real production.
- (2)
- With an increase in IA time, the contents of PRA were 28.63% at 6 h, 31.56% at 12 h and 28.63% at 50 h, respectively, and, after being tempered at 200 °C, the contents of RA were 6.68%, 6.13% and 3.84%, respectively. Finally, the microstructure was made up of PM, more than half, less than 10% of RA, and varying degrees of SM.
- (3)
- The mean (Ti, V, Mo)C particle size increases from about 14.27 nm to 15.65 nm as the IA time varied from 6 h to 50 h. Meanwhile, the Ostwald ripening and preservation at 750 °C jointly promoted the (Ti, V, Mo)C particle spheroidization.
- (4)
- The dislocation strengthening and (Ti, V, Mo)C precipitation strengthening increments were 679 and 104 MPa at IA-6 h, 660 and 102 MPa at IA-12 h, and 610 and 97 MPa, respectively. Although the superposed strength decreases with an increase in IA time, the high RA content, low EGS, and the high dissolution of (Ti, V, Mo)C jointly increased the yield strength from IA-6 h to IA-12 h, but decreased later.
- (5)
- The RA surrounded by SM had high stability and its low content caused the TRIP effect to decrease, leading to the low level of −20 °C toughness.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, J.; Du, L.X.; Sun, G.S.; Xie, H.; Misra, R.D.K. The determining role of reversed austenite in enhancing toughness of a novel ultra-low carbon medium manganese high strength steel. Scr. Mater. 2015, 104, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Du, L.X.; Xu, W.; Zhai, J.H.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Misra, R.D.K. Ensuring combination of strength, ductility and toughness in medium-manganese steel through optimization of nano-scale metastable austenite. Mater. Character. 2018, 136, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.G.; Mi, Z.L.; Xu, M.; Xiu, Q.; Li, J.; Jiang, H.T. Impact of intercritical annealing temperature and strain state on mechanical stability of retained austenite in medium Mn steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 725, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Sun, X.J.; Song, C.; Chen, H.; Tong, S.; Han, W.; Pan, F. Grain size-dependent mechanical properties of a high-manganese austenitic steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2019, 32, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noh, H.S.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, S.J. The effects of replacing Ni with Mn on hydrogen embrittlement in Cr-Ni-Mn-N austenitic steels. Corros. Sci. 2019, 152, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Luo, H.; Hu, C.; Pu, E.; Dong, H. Effects of intercritical annealing process on microstructures and tensile properties of cold-rolled 7Mn steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 685, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Liang, J.X.; Liu, Z.B.; Yang, Z.Y.; Sun, X.J.; Yong, Q.L. Effect of metastable austenite on mechanical property and mechanism cryogenic steel applied in oceaneering. Acta Metall. Sin. 2016, 52, 385–393. [Google Scholar]
- Nakada, N.; Mizutani, K.; Tsuchiyama, T.; Takaki, S. Difference in transformation behavior between ferrite and austenite formations in medium manganese steel. Acta Mater. 2014, 65, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedeva, N.I.; Park, M.S.; Van, A.D.C.; Medvedeva, J.E. First-principles study of Mn, Al and C distribution and their effect on stacking fault energies in fcc Fe. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 582, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, D.T.; Jiménez, J.A.; Bentley, J.; Raabe, D.; Wittig, J.E. The influence of stacking fault energy on the microstructural and strain-hardening evolution of Fe–Mn–Al–Si steels during tensile deformation. Acta Mater. 2015, 100, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.C.; Ding, H.; Misra, R.D.K.; Cai, Z.H. Microstructure-mechanical property relationship and austenite stability in medium-Mn TRIP steels: The effect of austenite-reverted transformation and quenching-tempering treatments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 682, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Li, B.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Liang, X.; Sun, X. Effect of intercritical annealing temperature on multiphase microstructure evolution in ultra-low carbon medium manganese steel. Mater. Charact. 2021, 173, 110920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Fazeli, F.; Scott, C.; Yan, X.; Liu, Z.; Qin, X.; Yue, S. Critical role of strain partitioning and deformation twinning on cracking phenomenon occurring during cold rolling of two duplex medium manganese steels. Scr. Mater. 2017, 130, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Shi, J.; Wang, C.; Cao, W.; Sun, X.; Dong, H. Experimental and numerical analysis on formation of stable austenite during the intercritical annealing of 5Mn steel. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 4002–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, G.; Zhang, K.; Sun, X.; Liang, X.; Yong, Q. Effect of Nb microalloying on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties in low carbon medium manganese steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 824, 141813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Matsui, Y.; Shibata, A.; Tsuji, N. Effect of thermomechanical processing at α+ γ two-phase temperatures on microstructure and mechanical property of 5Mn-0.1 C-2Si medium-manganese steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 743, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlazarov, A.; Gouné, M.; Bouaziz, O.; Hazotte, A. Critical factors governing the thermal stability of austenite in an ultra-fined grained medium-Mn steel. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2017, 97, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Gao, B.; Gui, X.; Hu, J.; He, J.; Tan, Z.; Bai, B. Correlation between microstructure and yield strength of as-quenched and Q&P steels with different carbon content (0.06–0.42 wt% C). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 753, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Song, C.; Chen, H.; Tong, S.; Han, W.; Pan, F. Evolution of microstructures and mechanical properties during solution treatment of a Ti–V–Mo-containing high-manganese cryogenic steel. Mater. Charact. 2018, 135, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messmer, R.P.; Briant, C.L. The role of chemical bonding in grain boundary embrittlement. Acta Mater. 1982, 30, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Peng, Y.; Kong, L.; Wang, Y. Effect of the deformation degree on the microstructure evolution of an austenite reverted transformation-annealed medium manganese steel. Metals 2020, 10, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Ning, B.; Qiao, Z.; Yan, Z.; Li, H. Precipitation behavior and martensite lath coarsening during tempering of T/P92 ferritic heat-resistant steel. Int. J. Met. Mater. 2014, 21, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Ju, X.; Yang, X. The measurement of the dislocation density using TEM. Mater. Charact. 2021, 175, 111065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Godet, S.; Jonas, J.J. Representation of misorientations in Rodrigues–Frank space: Application to the Bain, Kurdjumov–Sachs, Nishiyama–Wassermann and Pitsch orientation relationships in the Gibeon meteorite. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayron, C. Diffraction artefacts from twins and stacking faults, and the mirage of hexagonal, polytypes or other superstructures. Scr. Mater. 2021, 194, 113629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Z.D.; Sun, X.J.; Yong, Q.L.; Yang, J.W.; Li, Y.M.; Zhao, P.L. Development of Ti–V–Mo complex microalloyed hot-rolled 900-MPa-grade high-strength steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2015, 28, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, W.; Xu, W.; Bai, B.; Fang, H. Materialometrical approach of predicting the austenite formation temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 439, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xu, Y.B.; Hu, Z.P.; Gu, X.L.; Peng, F.; Tan, X.D.; Chen, S.Q.; Han, D.T.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wang, G.D. Austenite stability and its effect on the toughness of a high strength ultra-low carbon medium manganese steel plate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 675, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HajyAkbary, F.; Sietsma, J.; Böttger, A.J.; Santofimia, M.J. An improved X-ray diffraction analysis method to characterize dislocation density in lath martensitic structures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 639, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Sun, X.J.; Liang, X.K.; Liu, J.; Yong, Q.L. Effect of hot dolling deformation on microstructure and mechanical properties of a High-Ti wear-resistant steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2020, 56, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.F.; Zhao, J.; Cao, W.Q.; Shi, J.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Dong, H. Heat treatment effects on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a medium manganese steel (0.2 C–5Mn). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 532, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.Q.; Wang, C.; Shi, J.; Wang, M.Q.; Hui, W.J.; Dong, H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe–0.2 C–5Mn steel processed by ART-annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 6661–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.F.; Zhao, J.; Cao, W.Q.; Shi, J.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, J.; Dong, H. Tempering effects on the stability of retained austenite and mechanical properties in a medium manganese steel. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, C.; Hui, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Weng, Y. Effect of intercritical annealing time on hydrogen embrittlement of warm-rolled medium Mn steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 726, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| C | Si | Mn | Mo | Ti | V | P | S | Al | N | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.216 | 0.31 | 5.24 | 0.26 | 0.026 | 0.15 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.024 | 0.004 | Bal. |
| IA Time/h | Tensile Strength/MPa | Yield Strength/MPa | Yield Ratio | Uniform Elongation/% | Local Elongation/% | Total Elongation/% | Reduction in Area/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 1518.5 ± 2.5 | 1028.0 ± 12.5 | 0.677 | 7.8 ± 0 | 4.2 ± 0 | 12.0 ± 0.00 | 29.0 ± 0 |
| 12 | 1573.5 ± 21.5 | 1115.5 ± 24.5 | 0.709 | 8.5 ± 0.25 | 5.0 ± 0.25 | 13.5 ± 0.50 | 37.0 ± 0 |
| 50 | 1513.5 ± 11.5 | 1047.0 ± 24.0 | 0.692 | 9.3 ± 0.15 | 4.2 ± 0.15 | 13.5 ± 0.25 | 36.0 ± 0 |
| Element | IA-6 h | IA-12 h | IA-50 h |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.27 |
| Mn | 8.40 | 8.04 | 7.38 |
| Samples | ρ/m2 | Δσd/MPa | ΔσP/MPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IA-6 h | 5.644 × 1015 | 483 | 104 | 494 |
| IA-12 h | 5.348 × 1015 | 470 | 102 | 481 |
| IA-50 h | 4.760 × 1015 | 443 | 97 | 453 |
| Yield Strength/MPa | Tensile Strength/MPa | Total Elongation/% | Impact Energy/J | Microstructure | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 830~500 | 960 ± 30 | 20~45 | / | AM + RA | [14] |
| 550~675 | 850~1015 | 42~48 | / | AM + RA | [31] |
| 830~600 | 960 ± 30 | 20~45 | / | AM + RA | [32] |
| 530~630 | 960~1030 | 28~45 | / | α-F + RA | [33] |
| 550~825 | 1025~1100 | 48~58 | / | α-F + δ-F + RA | [34] |
| 1028.0~1115.5 | 1513.5~1573.5 | 12.0~13.5 | 30 (−20 °C) | SM + RA + PM | Our work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Ye, X.; Ren, S.; Zhang, K.; Liang, X.; Liu, G. Effect of Intercritical Annealing Time on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Low Carbon Medium Manganese Steel Subjected to Multi-Step Heat Treatment Process. Materials 2022, 15, 2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072425
Wang F, Ye X, Ren S, Zhang K, Liang X, Liu G. Effect of Intercritical Annealing Time on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Low Carbon Medium Manganese Steel Subjected to Multi-Step Heat Treatment Process. Materials. 2022; 15(7):2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072425
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Feilong, Xiaoyu Ye, Shoubin Ren, Kaihua Zhang, Xiaokai Liang, and Gang Liu. 2022. "Effect of Intercritical Annealing Time on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Low Carbon Medium Manganese Steel Subjected to Multi-Step Heat Treatment Process" Materials 15, no. 7: 2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072425
APA StyleWang, F., Ye, X., Ren, S., Zhang, K., Liang, X., & Liu, G. (2022). Effect of Intercritical Annealing Time on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Low Carbon Medium Manganese Steel Subjected to Multi-Step Heat Treatment Process. Materials, 15(7), 2425. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072425






