Microplastics in Wastewater by Washing Polyester Fabrics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fragments of Plastics and Polymers
Ageing of Polymers
3. Textiles—Source of Microplastic Pollution
- Creation of added value with low quality materials;
- Reduction in the plastic waste increase [56].
3.1. Textiles—The Release in the Washing Process
3.2. Wastewater and Microplastics
- mechanical;
- chemical;
- physico-chemical;
- biological; and
- chemico-biological.
4. Mitigation Measures for Microplastic Contamination
4.1. Prevention
4.2. Measures Proposed for The Production Process
4.3. Mechanical Means of Preventing the Release of Fibres during Use
4.4. Innovative Methods for the Direct Removal of Microparticles from the Aquatic Environment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Issac, M.N.; Balasubramanian, K. Effect of microplastics in water and aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19544–19562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marn, N.; Jusup, M.; Kooijman, S.; Klanjscek, T. Quantifying impacts of plastic debris on marine wildlife identifies ecological breakpoints. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kolbe, S. Microplastics or microfibers?—Conceptual confusion, Research Institute for Textiles and Clothing (FTB), Niederrhein University of Applied Sciences, Moenchengladbach, Germany. Tekstil 2018, 67, 235–236. [Google Scholar]
- Westphalen, H.; Abdelrasou, A. Challenges and treatment of microplastics in water. In Water Challenges of an Urbanizing World; Glavan, M., Ed.; InTech Open: London, UK, 2018; pp. 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Vassilenko, K.; Watkins, M.; Chastain, S.; Posacka, A.; Ross, P.S. Me, My Clothes and the Ocean: The Role of Textiles in Microfiber Pollution, Science Feature. Ocean Wise Conservation Association, Vancouver, QC, Canada, 16p. Available online: https://assets.ctfassets.net/fsquhe7zbn68/4MQ9y89yx4KeyHv9Svynyq/8434de64585e9d2cfbcd3c46627c7a4a/Research_MicrofibersReport_191004-e.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Carr, S.A.; Liu, J.; Tesoro, A.G. Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiounn, T.; Rhett, C.S. Advances and approaches for chemical recycling of plastic waste. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 1347–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Andrady, A.L.; Neal, M.A. Applications and societal benefits of plastics, Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B. Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, C.; Esteban, M.Á.; Cuesta, A. Microplastics in aquatic environments and their toxicological implications for fish. In Toxicology—New Aspects to This Scientific Conundrum; Larramendy, M.L., Soloneski, S., Eds.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 113–145. [Google Scholar]
- European Parliament’s Policy Department for Citizens’ Rights and Constitutional Affairs. The Environmental Impacts of Plastics and Micro-Plastics Use, Waste and Pollution: EU and National Measures—Study. 2020. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/STUD/2020/658279/IPOL_STU(2020)658279_EN.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Čatić, I.; Barić, G.; Cvjetičanin, N.; Galić, K.; Godec, D.; Grancarić, A.M.; Katavić, I.; Kovačić, T.; Raos, P.; Rogić, A. Polimeri—Od prapočetka do plastike i elastomera. Polimeri 2020, 31, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Vegt, A.K. From Polymers to Plastics; Delft University Press, VSSD: Delft, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sazali, N.; Ibrahim, H.; Jamaludin, A.S.; Mohamed, M.A.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Abidin, M.N.Z. A short review on polymeric materials concerning degradable polymers. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 788, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Material Properties of Plastics. Available online: https://application.wiley-vch.de/books/sample/3527409726_c01.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Nmazai, H. Polymers in our daily life. BioImpacts 2017, 7, 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- Maddah, H.A. Polypropylene as a promising plastic: A review. Am. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Eyerer, P. Plastics: Classification, characterization, and economic data. In Polymers—Opportunities and Risks I. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Eyerer, P., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrady, A.L. Persistence of plastic litter in the oceans. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Bergmann, M., Gutow, L., Klages, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Yousif, E.; Haddad, R. Photodegradation and photostabilization of polymers, especially polystyrene: Review. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambert, S.; Sinclair, C.J.; Bradley, E.L.; Boxall, A.B.A. Effects of environmental conditions on latex degradation in aquatic systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julienne, F.; Delorme, N.; Lagarde, F. From macroplastics to microplastics: Role of water in the fragmentation of polyethylene. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjan, V.P.; Goel, S. Degradation of Low-Density Polyethylene Film Exposed to UV Radiation in Four Environments. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2019, 23, 04019015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.D. Microbiological deterioration and degradation of synthetic polymeric materials: Recent research advances. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2003, 52, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, J.; Kraak MH, S.; Parsons, J.R. Plastics in the Marine Environment: The Dark Side of a Modern Gift. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 220, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Faravelli, T.; Pinciroli, M.; Pisano, F.; Bozzano, G.; Dente, M.; Ranzi, E. Thermal degradation of polystyrene. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2001, 60, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.; Shin, G.; Lee, M.; Koo, J.M.; Jeon, H.; Ok, Y.S.; Hwang, D.S.; Hwang, S.Y.; Oh, D.X.; Park, J. Biodegradable chito-beads replacing non-biodegradable microplastics for cosmetics. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 6953–6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, L.W.; White, J.W.; Cohen, P.H.; Biermann, P.J. A materials aging problem in theory and practice. Johns Hopkins APL Tech. Dig. 2000, 21, 575–581. [Google Scholar]
- Richaud, E.; Verdu, J. Aging behavior and modeling studies of unsaturated polyester resin and unsaturated polyester resin-based blends. In Unsaturated Polyester Resins: Fundamentals, Design, Fabrication, and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 199–231. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02568819/document (accessed on 28 November 2021).
- Salopek Čubrić, I.; Čubrić, G.; Potočić Matković, V.M. Behavior of Polymer Materials Exposed to Aging in the Swimming Pool: Focus on Properties That Assure Comfort and Durability. Polymers 2021, 13, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.R. Polymer ageing: Physics, chemistry or engineering? Time to reflect. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2006, 9, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
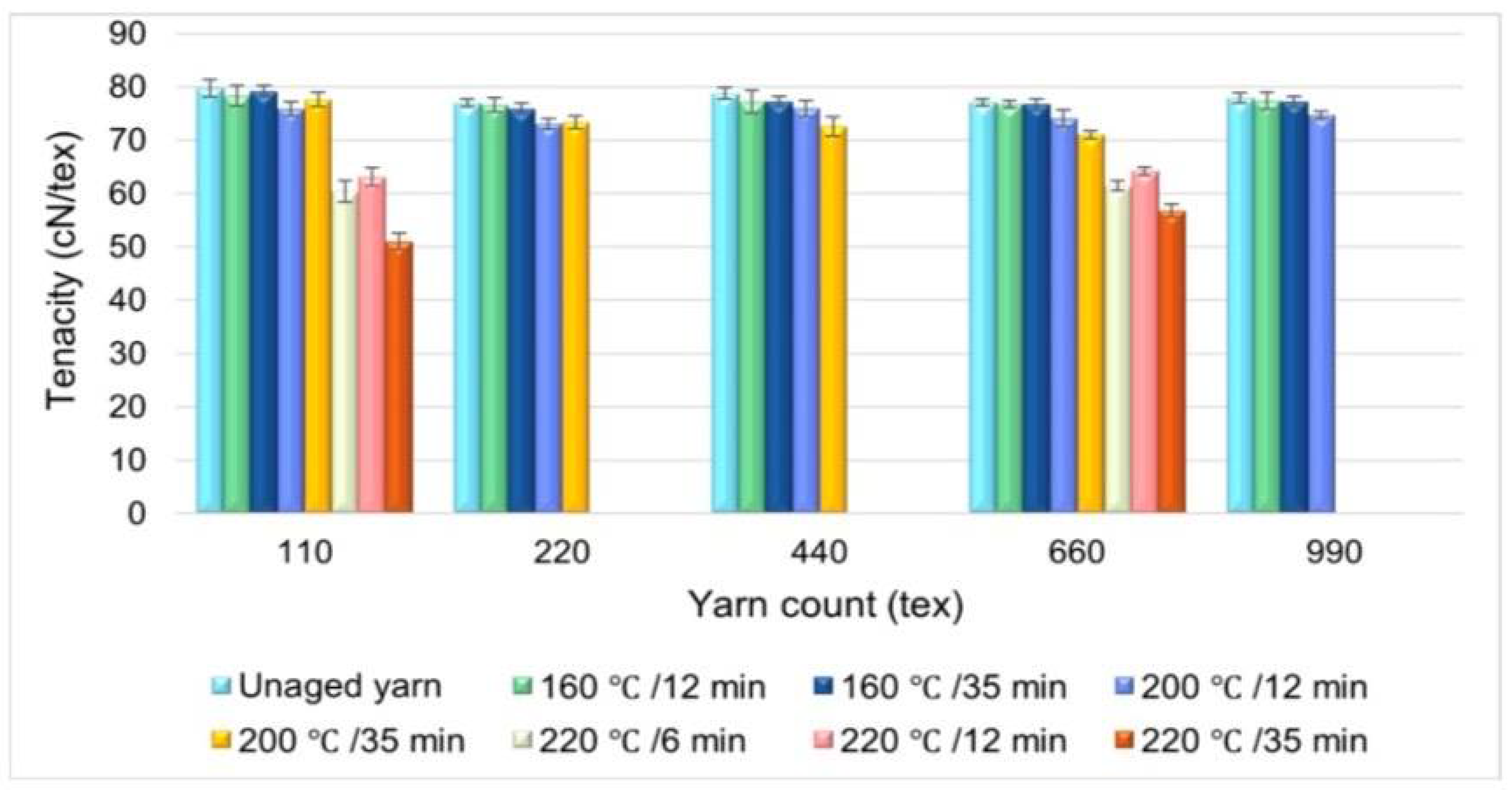
- Lemmi, T.S.; Barburski, M.; Kabziński, A.; Frukacz, K. Effect of thermal aging on the mechanical properties of high tenacity polyester yarn. Materials 2021, 14, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, S.; Levenstam Arturin, O.; Hanning, A.-C. Microplastics Shedding from Polyester Fabrics, Mistra Future Fashion Report No 2017:1, SEREA. 2017. Available online: http://mistrafuturefashion.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/MFF-Report-Microplastics.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Manshoven, S.; Smeets, A.; Malarciuc, C.; Tenhunen, A.; Mortensen, L.F. Microplastic Pollution from Textile Consumption in Europe, Eionet Report—ETC/CE 2022/1. Available online: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/etc-ce/products/etc-ce-products/etc-ce-report-1-2022-microplastic-pollution-from-textile-consumption-in-europe (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Sillanpää, M.; Sainio, P. Release of polyester and cotton fibers from textiles in machine washings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19313–19321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Falco, F.; Cocca, M.C.; Avella, M.; Thompson, R.C. Microfiber Release to Water, Via Laundering, and to Air, via Everyday Use: A Comparison between Polyester Clothing with Differing Textile Parameters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3288–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvão, A.; Aleixo, M.; De Pablo, H.; Lopes, C.; Raimundo, J. Microplastics in wastewater: Microfiber emissions from common household laundry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26643–26649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaylarde, C.; Baptista-Neto, J.A.; da Fonseca, E.M. Plastic microfibre pollution: How important is clothes’ laundering? Heliyon 2021, 7, e07105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, E.; Nowack, B.; Mitrano, D. Polyester Textiles as a Source of Microplastics from Households: A Mechanistic Study to Understand Microfiber Release During Washing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7036–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, T.; Mitrano, D.M.; Heuberger, M.; Hufenus, R.; Nowack, B. Systematic Study of Microplastic Fiber Release from 12 Different Polyester Textiles during Washing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4847–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, F.; Di Pace, E.; Cocca, M.; Avella, M. The contribution of washing processes of synthetic clothes to microplastic pollution. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volgare, M.; De Falco, F.; Avolio, R.; Castaldo, R.; Errico, M.E.; Gentile, G.; Ambrogi, V.; Cocca, M. Washing load influences the microplastic release from polyester fabrics by affecting wettability and mechanical stress. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathinamoorthy, R.; Balasaraswathi, S.R. A review of the current status of microfiber pollution research in textiles. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 2021, 33, 364–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Kwon, M.; Park, M.-J.; Kim, J. Characterization of Microplastics Released Based on Polyester Fabric Construction during Washing and Drying. Polymers 2021, 13, 4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čurlin, M.; Pušić, T.; Vojnović, B.; Dimitrov, N. Particle Characterization of Washing Process Effluents by Laser Diffraction Technique. Materials 2021, 14, 7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöpel, B.; Stamminger, R. A Comprehensive Literature Study on Microfibres from Washing Machines. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2019, 56, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.; Laitala, K.; Klepp, I.G. Microfibres from apparel and home textiles: Prospects for including microplastics in environmental sustainability assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayo, J.; Ramos, B.; López-Castellanos, J.; Rojo, D.; Olmos, S. Lack of Evidence for Microplastic Contamination from Water-Soluble Detergent Capsules. Microplastics 2022, 1, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haap, J.; Classen, E.; Beringer, J.; Mecheels, S.; Gutmann, J.S. Microplastic Fibers Released by Textile Laundry: A New Analytical Approach for the Determination of Fibers in Effluents. Water 2019, 11, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luogo, B.D.P.; Salim, T.; Zhang, W.; Hartmann, N.B.; Malpei, F.; Candelario, V.M. Reuse of Water in Laundry Applications with Microand Ultrafiltration Ceramic Membrane. Membranes 2022, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Mateo, C.; van der Meer, Y.; Seide, G. Analysis of the polyester clothing value chain to identify key intervention points for sustainability. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Mitrano, D.M.; Heuberger, M.; Hufenus, R.; Nowack, B. The origin of microplastic fiber in polyester textiles: The textile production process matters. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 121970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, A. Man-made fibers continue to grow. Text. World 2015, 165, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, A.; Scherer, C.; Brennholt, N.; Reifferscheid, G.; Wagner, M. PET microplastics do not negatively affect the survival, development, metabolism and feeding activity of the freshwater invertebrate Gammarus pule. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccardo, M.; Provenza, F.; Grazioli, E.; Cavallo, A.; Terlitti, A.; Renzi, M. PET microplastics toxicity on marine key species is influenced by pH, particle size and food variations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čorak, I.; Pušić, T.; Tarbuk, A. Enzimi za hidrolizu poliestera. Tekstil 2019, 68, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Kärkkäinen, N.; Sillanpää, M. Quantification of different microplastic fibres discharged from textiles in machine wash and tumble drying. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 16253–16263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesa, F.S.; Turra, A.; Checon, H.H.; Leonardi, B.; Baruque-Ramos, J. Laundering and textile parameters influence fibers release in household washings. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Qiao, F.; Lei, K.; Li, H.; Kang, Y.; Cui, S.; An, L. Microfiber release from different fabrics during washing. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney Almroth, B.; Åström, L.; Roslund, S.; Petersson, H.; Johansson, M.; Persson, N. Quantifying shedding of synthetic fibers from textiles; a source of microplastics released into the environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartline, N.L.; Bruce, N.J.; Karba, S.N.; Ruff, E.O.; Sonar, S.U.; Holden, P.A. Microfiber masses recovered from conventional machine washing of new or aged garments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11532–11538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Napper, I.E.; Thompson, R.C. Release of synthetic microplastic plastic fibres from domestic washing machines: Effects of fabric type and washing conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corami, F.; Rosso, B.; Bravo, B.; Gambaro, A.; Barbante, C. A novel method for purification, quantitative analysis and characterization of microplastic fibers using Micro-FTIR. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belzagui, F.; Crespi, M.; Álvarez, A.; Gutiérrez-Bouzán, C.; Vilaseca, M. Microplastics’ emissions: Microfibers’ detachment from textile garments. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soljačić, I.; Pušić, T. Njega Tekstila, Dio 1: Čišćenje u Vodenim Medijima, Zagreb, Tekstilno-Tehnološki Fakultet; Sveučilišta u Zagrebu: Zagreb, Croatia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sinner, H. Ueber das Waschen mit Haushaltwaschmaschinen: In Welchem Umfange Erleichtern Haushaltwaschmachinen und—Geraete das Waeschewaschen im Haushalt? Haus und Heim: Hamburg, Germany, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, W.; Gong, R.H.; Ding, X.; Xue, Y.; Li, P.; Fan, W. Optimizing a laundering program for textiles in a front-loading washing machine and saving energy. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konstadinos Abeliotis, K.; Amberg, C.; Candan, C.; Ferri, A.; Osset, M.; Owens, J.; Stamminger, R. Trends in laundry by 2030. Househ. Pers. Care Today 2015, 10, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Alfieri, F.; Cordella, M.; Stamiminger, R.; Bues, A. Durability Assessment of Products: Analysis and Testing of Washing Machines, JCR Technical Reports. Available online: https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/bitstream/JRC114329/jrc114329_task_3_durability_final_v3.0.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Kelly, M.R.; Lant, N.J.; Kurr, M.; Burgess, J.G. Importance of water-volume on the release of microplastic fibers from laundry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 20, 11735–11744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.; Okoffo, E.D.; O’Brien, J.W.; Ribeiro, F.; Wang, X.; Wright, S.L.; Samanipour, S.; Rauert, C.; Alajo Toapanta, T.Y.; Albarracin, R.; et al. Airborne emissions of microplastic fibres from domestic laundry dryers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapp, K.J.; Miller, R.Z. Electric clothes dryers: An underestimated source of microfiber pollution. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Danyang, T.; Zhang, K.; Xu, S.; Lin, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, J.; Yim, T.; Giesy, J.P.; Leung, K.M.Y. Microfibers Released into the Air from a Household Tumble Dryer. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Pirc, U.; Vidmar, M.; Mozer, A.; Kržan, A. Emissions of Microplastic Fibers from Microfiber Fleece during Domestic Washing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 22206–22211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, E.G.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Ma, L.; Zeng, E.Y.; Shi, H. A Review of Microplastics in Table Salt, Drinking Water, and Air: Direct Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3740–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, S.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Turner, A.; Kelly, F.J.; Dominguez, A.O.; Jaafarzadeh, N. Distribution and potential health impacts of microplastics and microrubbers in air and street dusts from Asaluyeh County, Iran. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Falco, F.; Gullo, M.P.; Gentile, G.; Di Pace, E.; Cocca, M.; Gelabert, L.; Brouta-Agnésa, M.; Rovira, A.; Escudero, R.; Villalba, R.; et al. Evaluation of microplastic release caused by textile washing processes of synthetic fabrics. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano, M.C.; Pawlak, J.J.; Daystar, J.; Ankeny, M.; Cheng, J.J.; Venditti, R.A. Microfibers generated from the laundering of cotton, rayon and polyester based fabrics and their aquatic biodegradation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines woldwide: Sources and sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilenko, E.; Watkins, M.; Chastain, S.; Mertens, J.; Posacka, A.M.; Patankar, S.; Ross, P.S. Domestic laundry and microfiber pollution: Exploring fiber shedding from consumer apparel textiles. PLoS ONE 2020, 16, e0250346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.Q.; Xiao, M.R.; Ma, Y.; Niu, H.; Zhang, G.S. Polyester microfiber and natural organic matter impact microbial communities, carbon-degraded enzymes, and carbon accumulation in a clayey soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Koistinen, A.; Setälä, O. Solutions to microplastic pollution—Removal of microplastics from wastewater effluent with advanced wastewater treatment technologies. Water Res. 2017, 123, 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- Sol, D.; Laca, A.; Laca, A.; Diaz, M. Microplastics in Wastewater and Drinking Water Treatment Plants: Occurrence and Removal of Microfibres. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Madhanraj, K.; Vishal, D. Removal of microplastics from wastewater: Available techniques and way forward. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3689–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-Manjón, A.; Martínez-Díez, R.; Sol, D.; Laca, A.; Laca, A.; Rancaño, A.; Díaz, M. Long-Term Occurrence and Fate of Microplastics in WWTPs: A Case Study in Southwest Europe. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Nord, N.B.; Baster, K.; Vollertsen, J. Microplastics removal from treated wastewater by a biofilter. Water 2020, 12, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Lu, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Occurrence and Characteristics of Microplastics in a Wastewater Treatment Plant. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, R.; Subramanian, R.B. Synthetic textile and microfiber pollution: A review on mitigation strategies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 41596–41611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, A.; Classon, S. Analysis of Microplastic Prevention Methods from Synthetic Textiles. iGEM LUND 2017. Available online: http://2017.igem.org/wiki/images/2/2c/T--Lund---Analysis_of_Microplastic_Prevention_Methods_from_Synthetic_Textiles.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- De Falco, F.; Gentile, G.; Avolio, R.; Errico, M.E.; Di Pace, E.; Ambrogi, V.; Avella, M.; Cocca, M. Pectin based finishing to mitigate the impact of microplastics released by polyamide fabrics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar, P.S.; Fontana, D.G.; Zoccola, M. Sustainable Superheated Water Hydrolysis of Black Soldier Fly Exuviae for Chitin Extraction and Use of the Obtained Chitosan in the Textile Field. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 8884–8893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukawa, S.; Kasai, M.; Mizuta, Y. Modification of Polyester Fabrics Using Chitosan. Sen’i Gakkaishi 1995, 51, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flinčec Grgac, S.; Tarbuk, A.; Dekanić, T.; Sujka, W.; Draczyński, Z. The Chitosan Implementation into Cotton and Polyester/Cotton Blend Fabrics. Materials 2020, 13, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korica, M.; Peršin, Z.; Trifunović, S.; Mihajlovski, K.; Nikolić, T.; Maletić, S.; Fras Zemljič, L.; Kostić, M.M. Influence of Different Pretreatments on the Antibacterial Properties of Chitosan Functionalized Viscose Fabric: TEMPO Oxidation and Coating with TEMPO Oxidized Cellulose Nanofibrils. Materials 2019, 26, 3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.-T.; Chen, L.; Ji, J.-M.; Huang, Y.-L.; Chen, D.-H. Antibacterial Properties of Cotton Fabrics Treated with Chitosan. Text. Res. J. 2003, 73, 1103–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz Atay, H. Antibacterial activity of chitosan-based systems. In Functional Chitosan: Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications; Jana, S., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 457–489. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega-Ortiz, H.; Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, B.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Jimenez, L.I. Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan and the Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes of Poly(acrylic acid)-Chitosan. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2010, 53, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walawska, A.; Filipowska, B.; Rybicki, E. Dyeing Polyester and Cotton-Polyester Fabrics by Means of Direct Dyestuffs after Chitosan Treatment. Fibers Text. East. Eur. 2003, 11, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Najafzadeh, N.; Habibi, S.; Ghasri, M.A. Dyeing of Polyester with Reactive Dyestuffs Using Nano-Chitosan. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2018, 13, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dey, T.K.; Md, U.; Mamun, J. Detection and removal of microplastics in wastewater: Evolution and impact. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 16925–16947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Kong, T.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Biodegradation of Microplastic Derived from Poly(ethylene terephthalate) with Bacterial Whole-Cell Biocatalysts. Polymers 2018, 10, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Categories | Common Applications | Specific Density [g/cm3] |
|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE-LDPE, LLDPE) | Plastic bags, six-pack rings, bottles | 0.91–0.93 |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Rope, bottle caps, netting | 0.90–0.92 |
| Foamed polystyrene (PS) | Cups, buoy | 0.01–1.05 |
| Polystyrene (PS) | Plastic utensils, food containers, packaging | 1.04–1.09 |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) | Bags, tubes | 1.16–1.30 |
| Polyamide or nylon (PA) | Ropes | 1.13–1.15 |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | Beverage bottles | 1.34–1.39 |
| Polyester resin + fibreglass | Textiles | >1.35 |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Electronic compounds | 1.20–1.22 |
| Cellulose acetate (CA) | Filter cigarettes | 1.22–1.24 |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Teflon items, tubes | 2.10–2.30 |
| Textile parameters | Type of fibres | Hydrophilic fibres release more fibres than synthetic ones The strength can also affect tearing |
| Yarn properties | Yarns with more twists and longer filaments release less microfibres | |
| Structure of fabric | Thermally cut fabrics release less than mechanically cut fabrics The influence of knitted and woven structure is not entirely clear | |
| Ageing of fabric | The impact is not predictable because the garment does not pass a complete lifecycle | |
| External parameters | Washing machine | Vertical drum machines contribute more to the release than horizontal ones, although this is related to the bath ratio |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šaravanja, A.; Pušić, T.; Dekanić, T. Microplastics in Wastewater by Washing Polyester Fabrics. Materials 2022, 15, 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072683
Šaravanja A, Pušić T, Dekanić T. Microplastics in Wastewater by Washing Polyester Fabrics. Materials. 2022; 15(7):2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072683
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠaravanja, Ana, Tanja Pušić, and Tihana Dekanić. 2022. "Microplastics in Wastewater by Washing Polyester Fabrics" Materials 15, no. 7: 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072683
APA StyleŠaravanja, A., Pušić, T., & Dekanić, T. (2022). Microplastics in Wastewater by Washing Polyester Fabrics. Materials, 15(7), 2683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072683








