Determination of Buckling Behavior of Web-Stiffened Cold-Formed Steel Built-Up Column under Axial Compression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
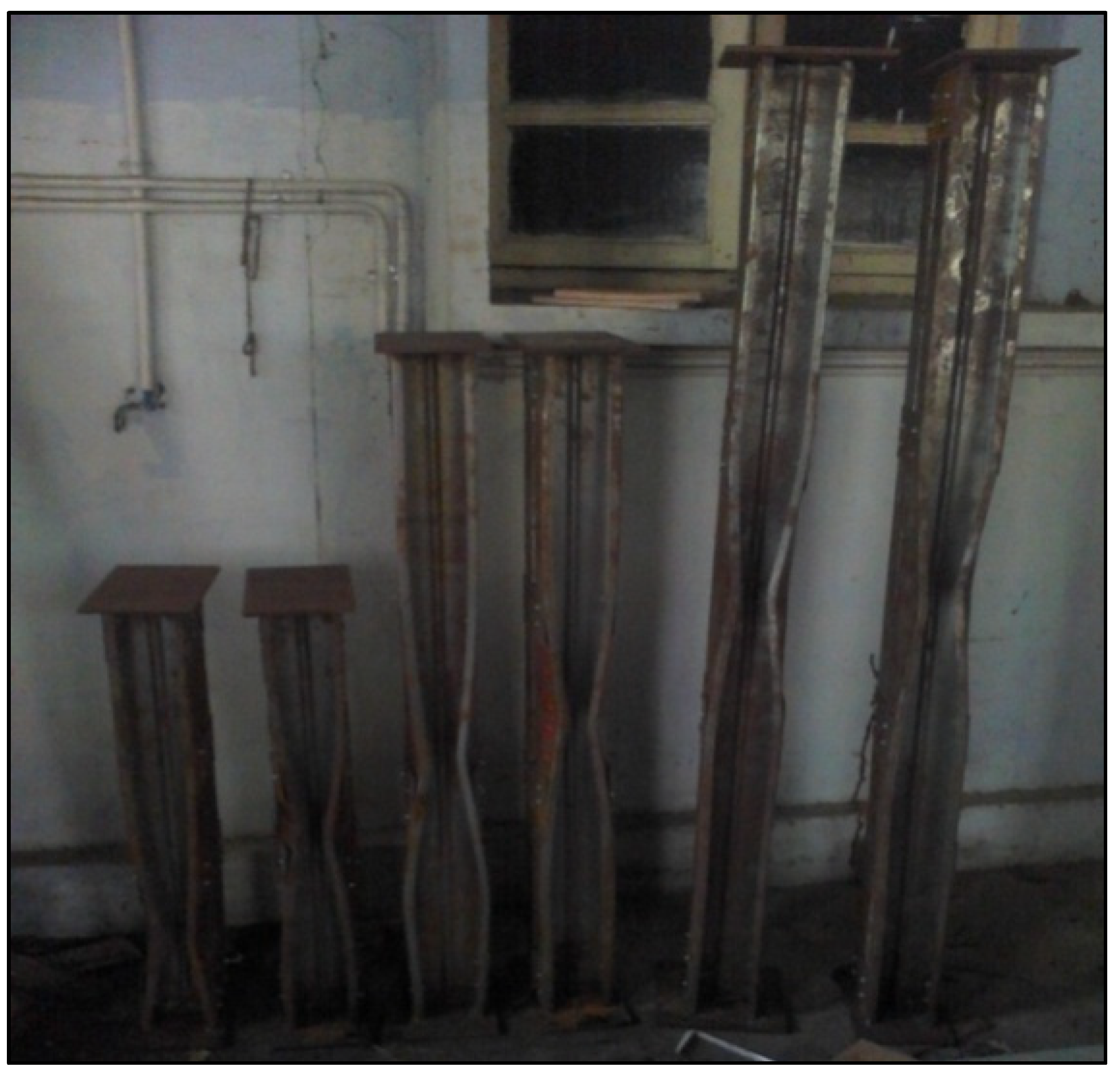
2.1. Selection of Specimen
2.2. Properties of the Specimen
2.3. Validation of the Selected Specimen with GBTUL
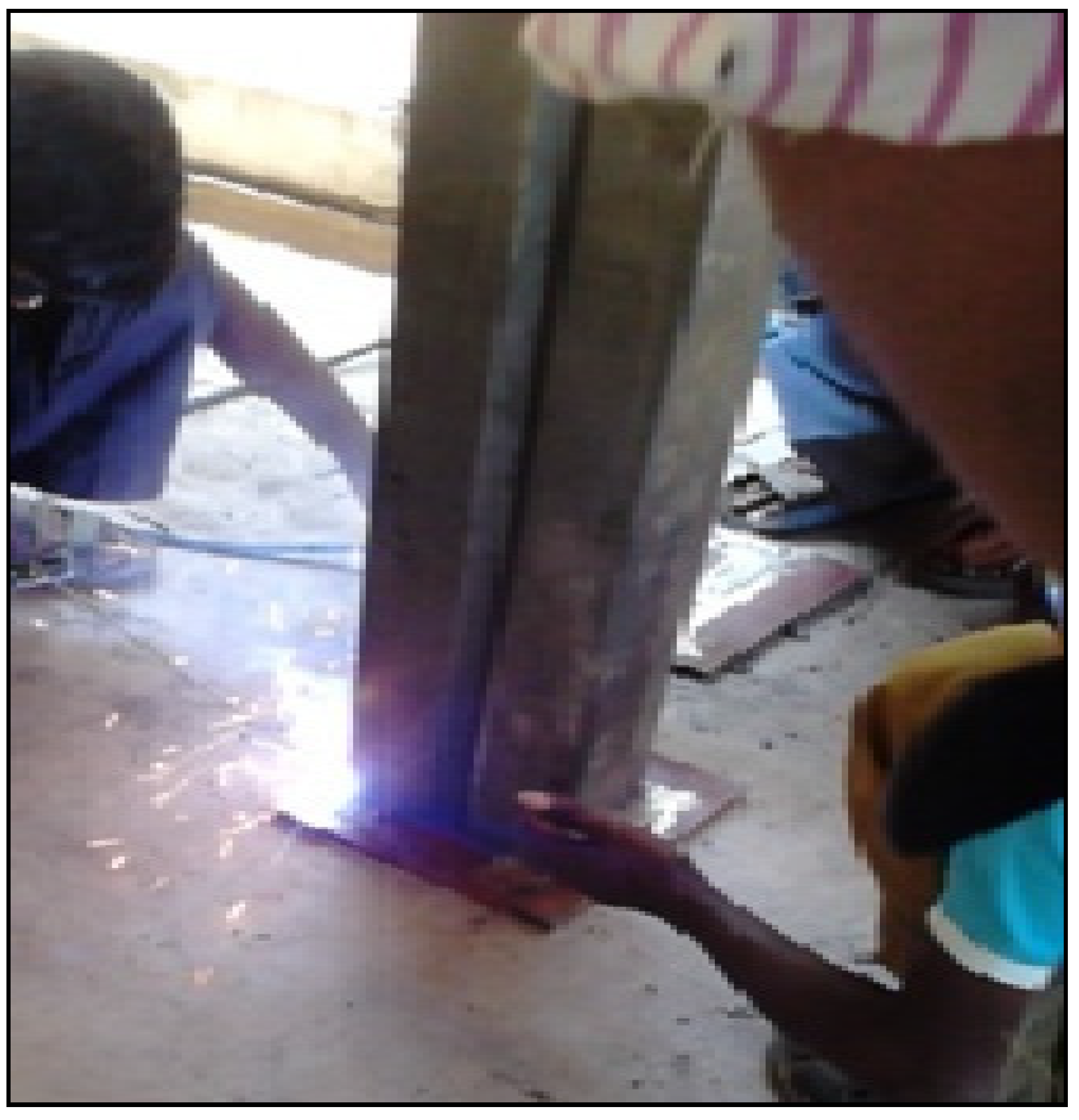
2.4. Testing of Specimen
2.5. DSM (Direct Strength Method) Approach
2.6. Modeling of Specimen Using FEM
2.6.1. Finite Element Modeling
2.6.2. Incorporation of Material Parameter
2.6.3. Selecting the End Condition and Loading
3. Results and Discussion
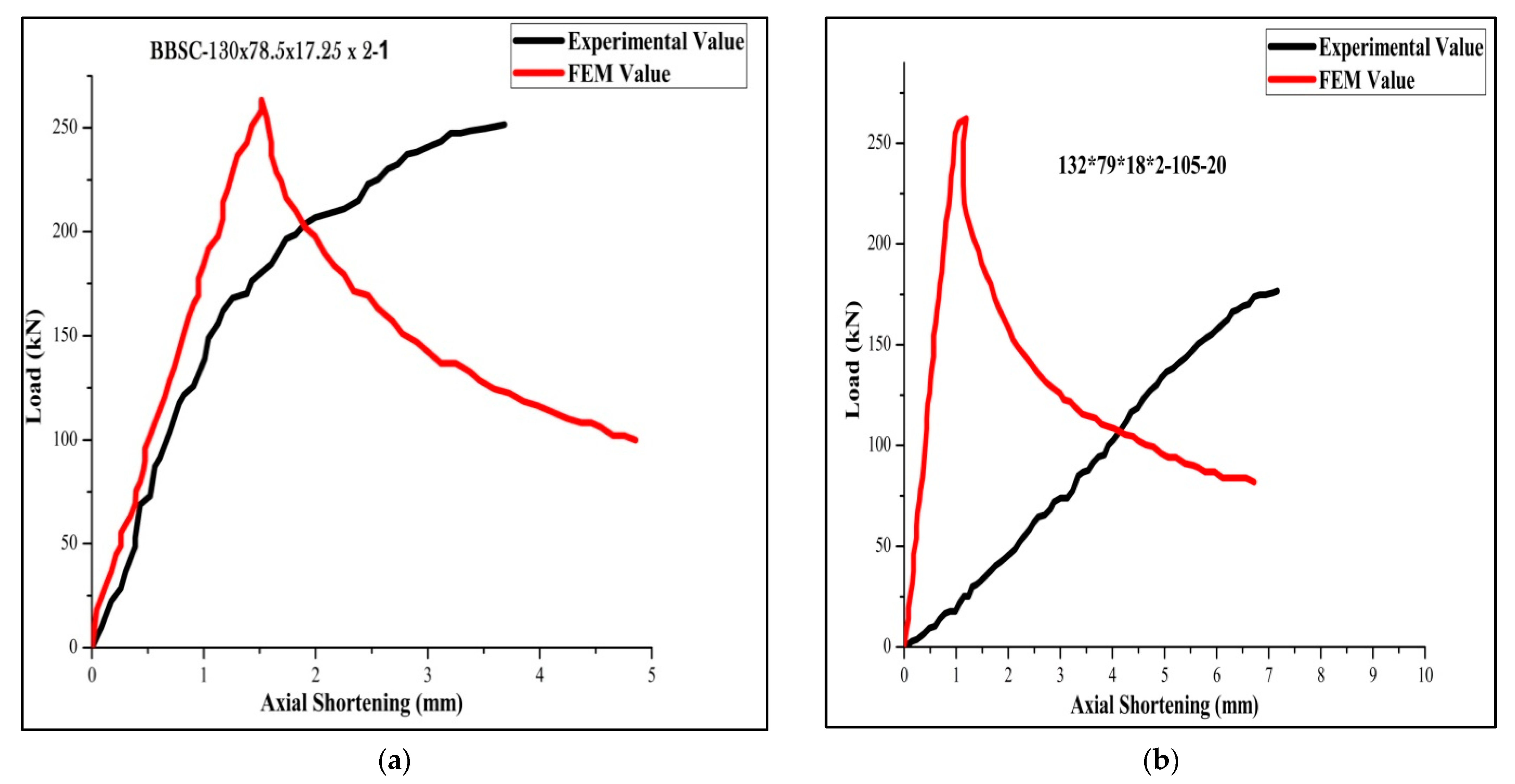
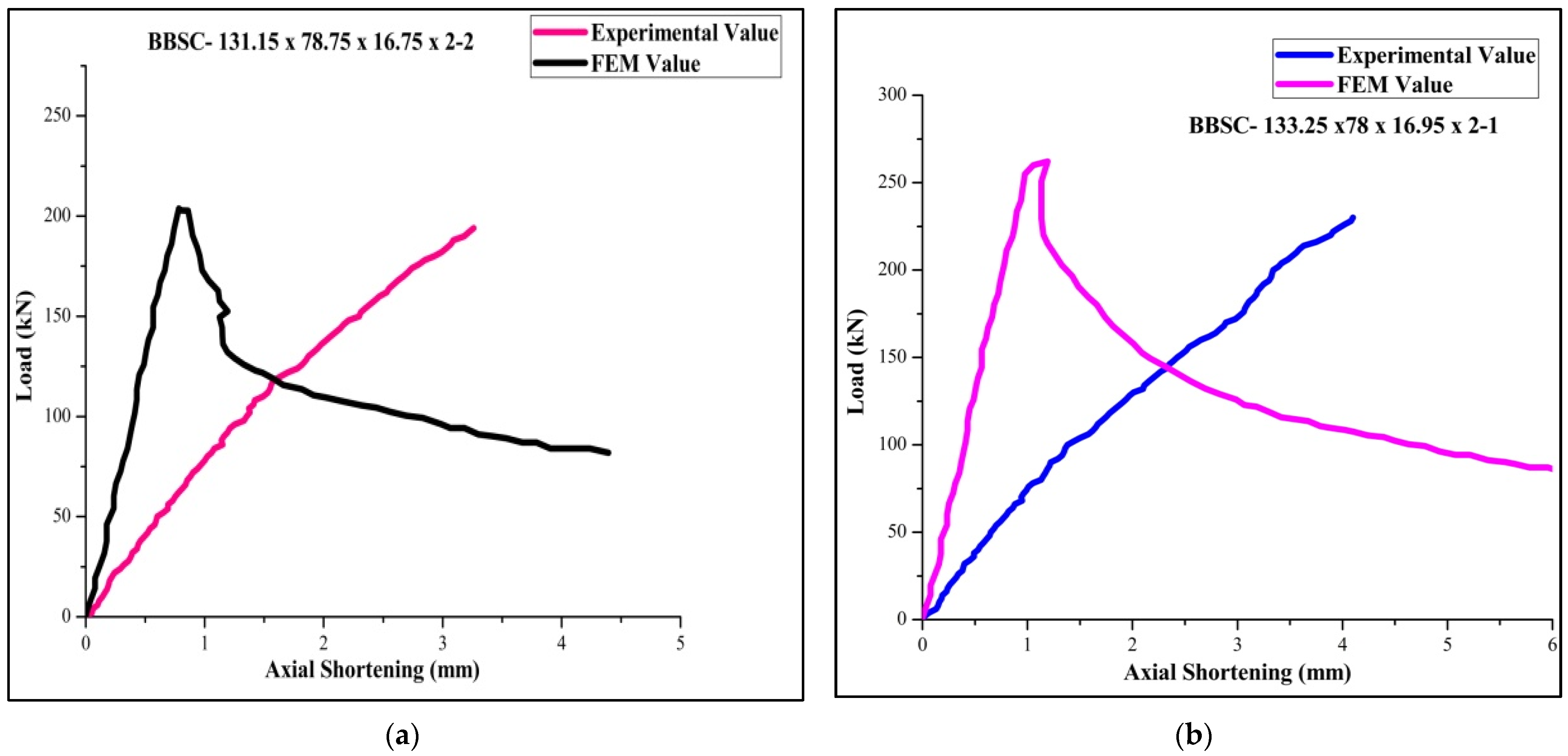
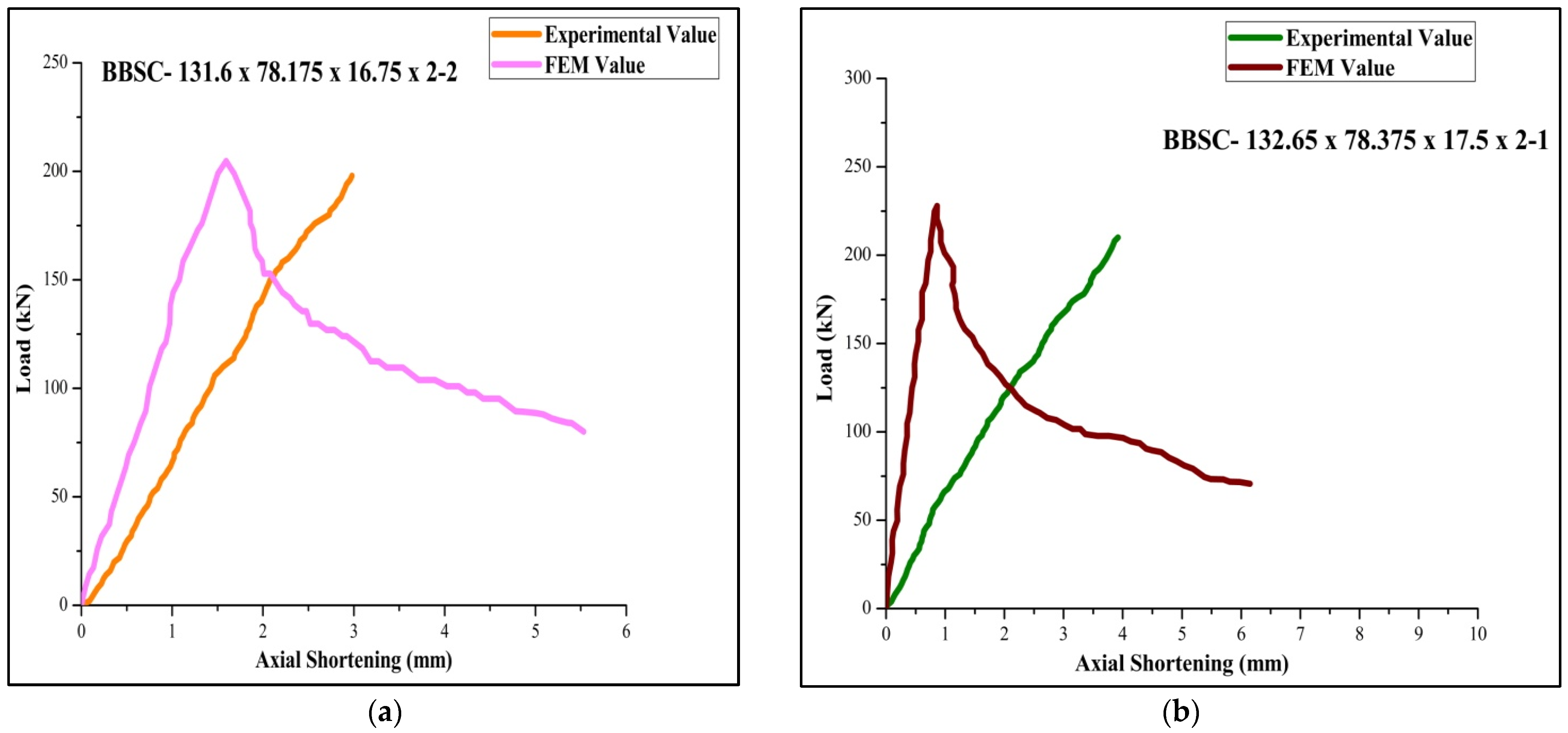
3.1. Validation of Experimentally Tested Specimen with FEM and DSM
3.2. Load Bearing Capacity vs. Axial Shortening Performance
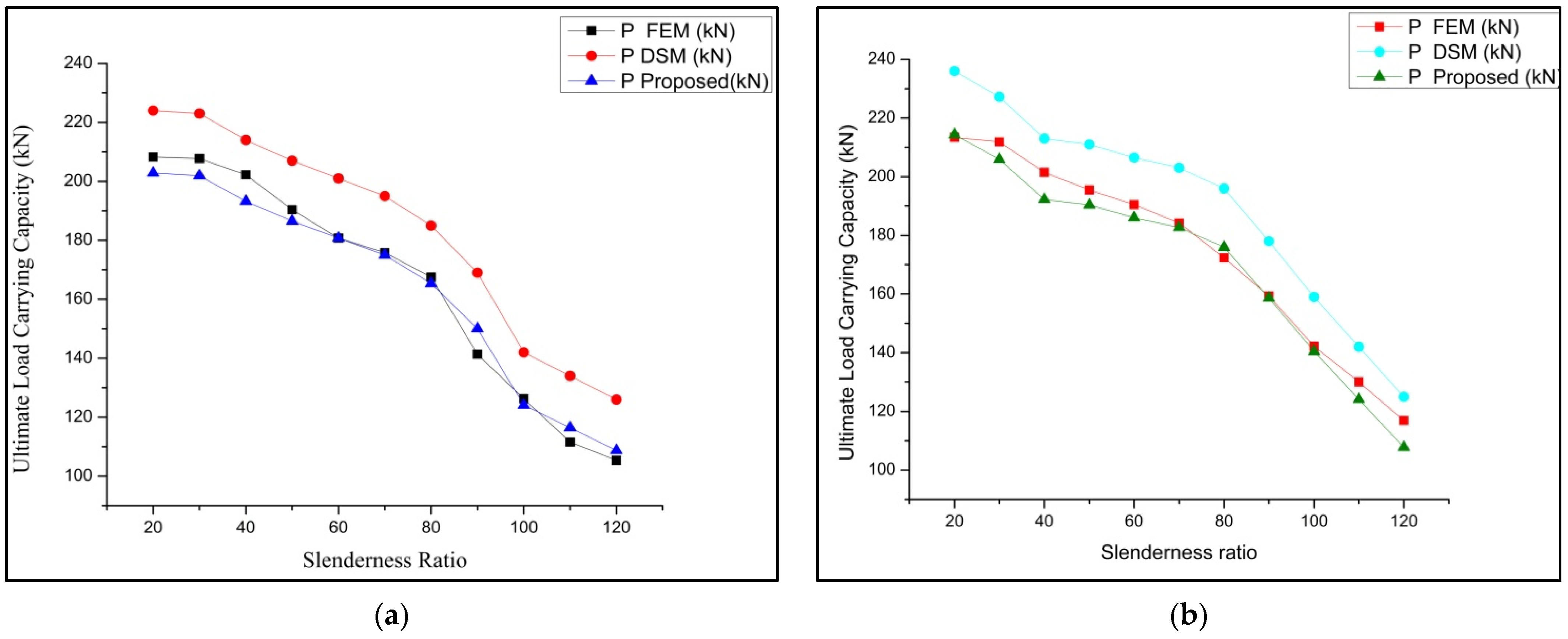
3.3. Comparison of DSM vs. FEM
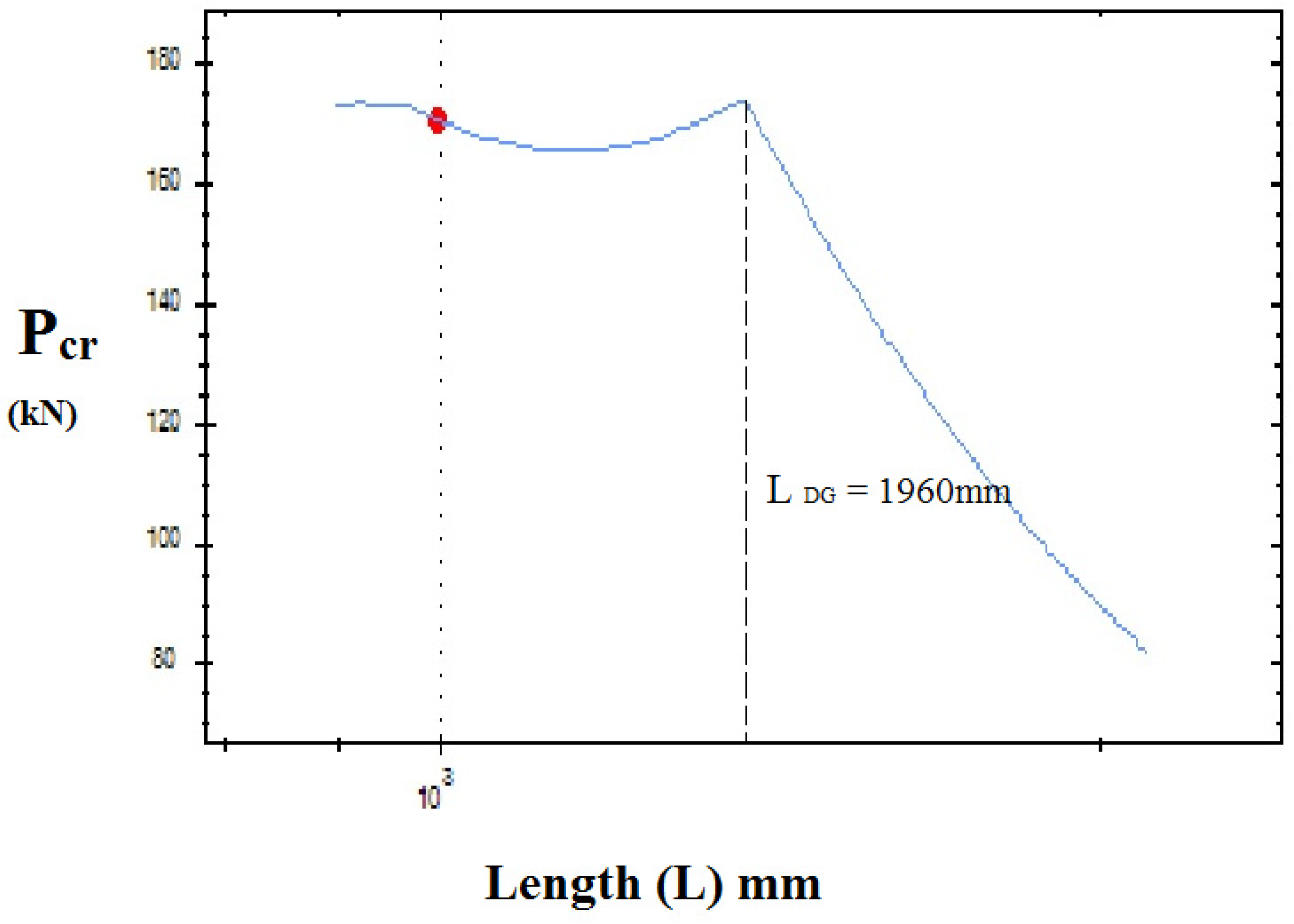
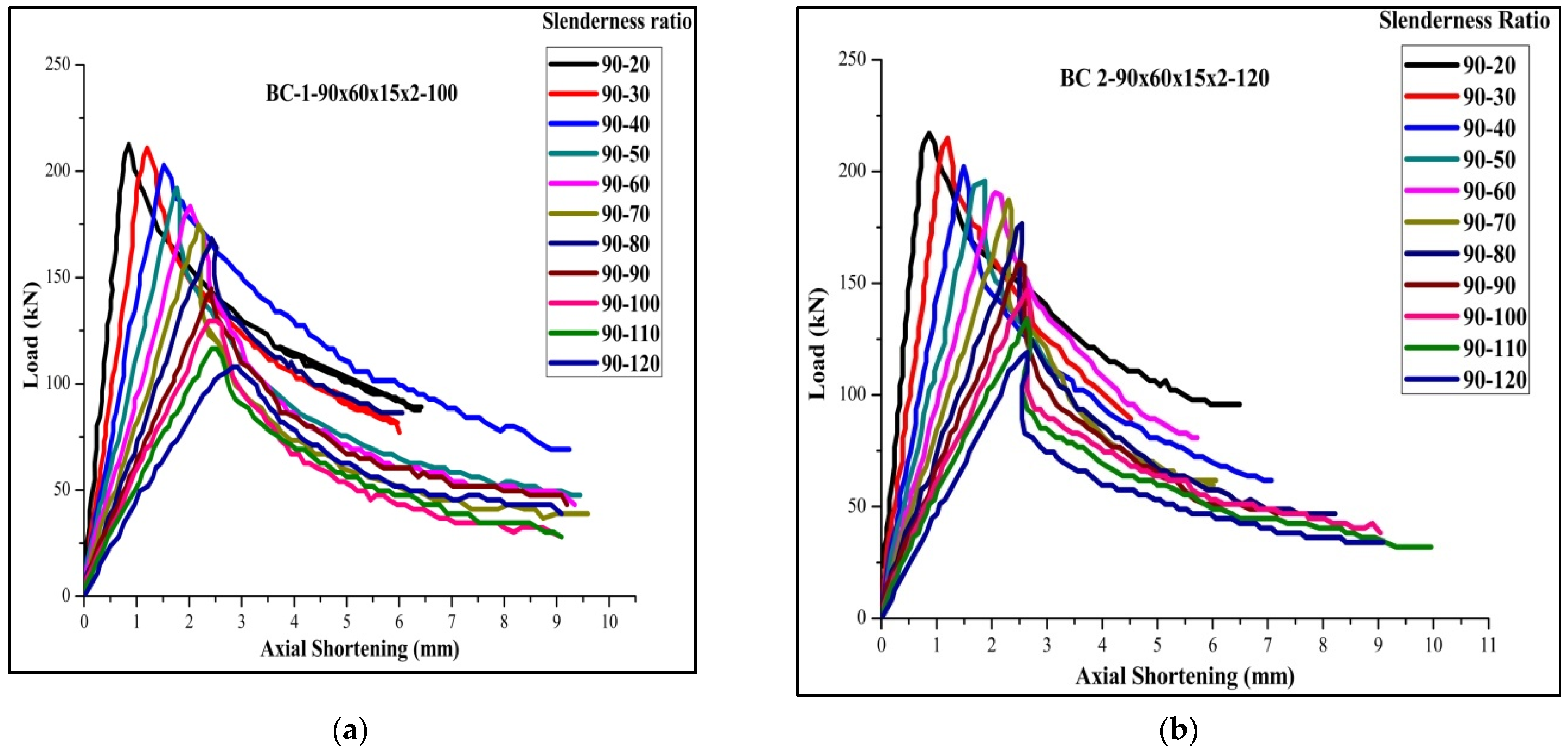
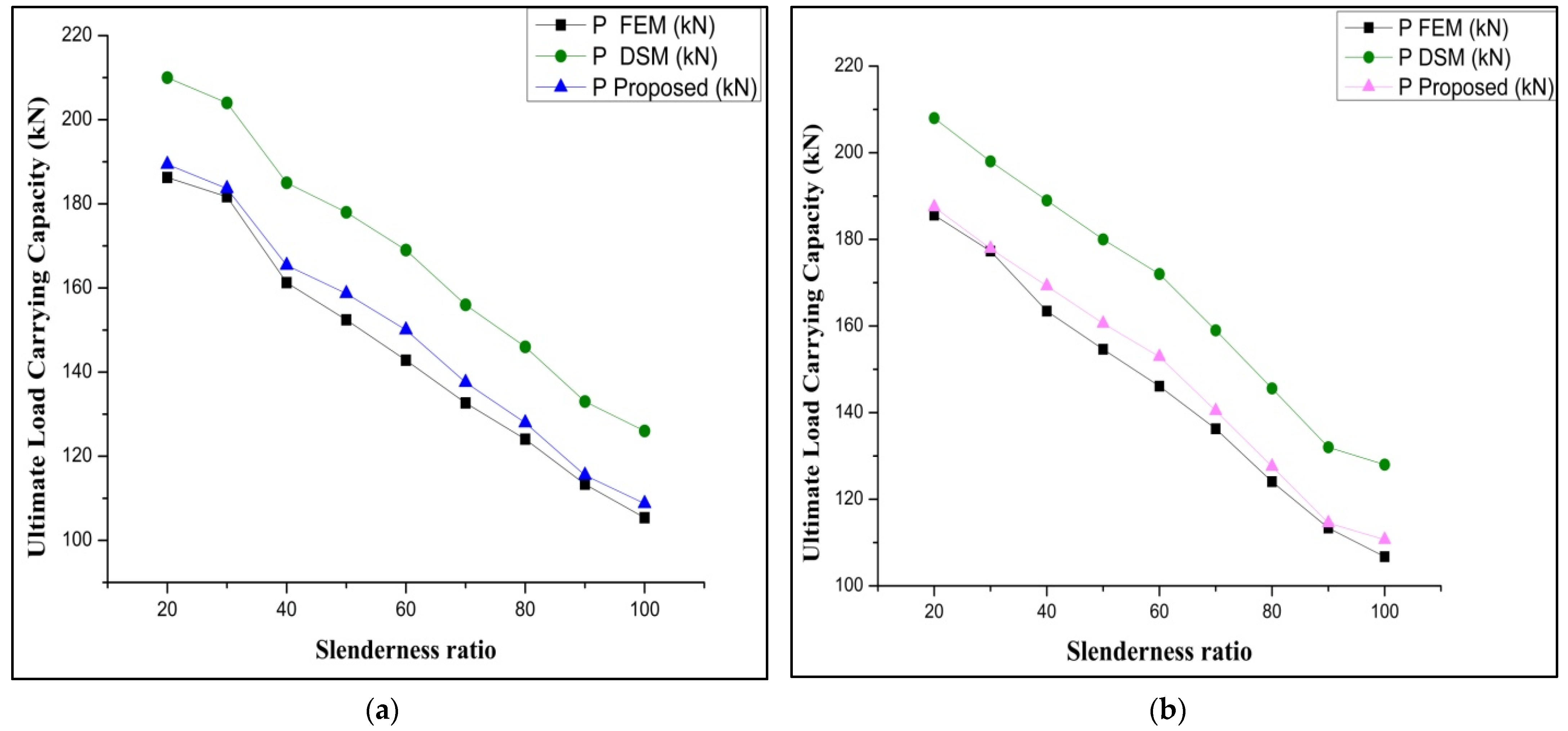
3.4. Parametric Study
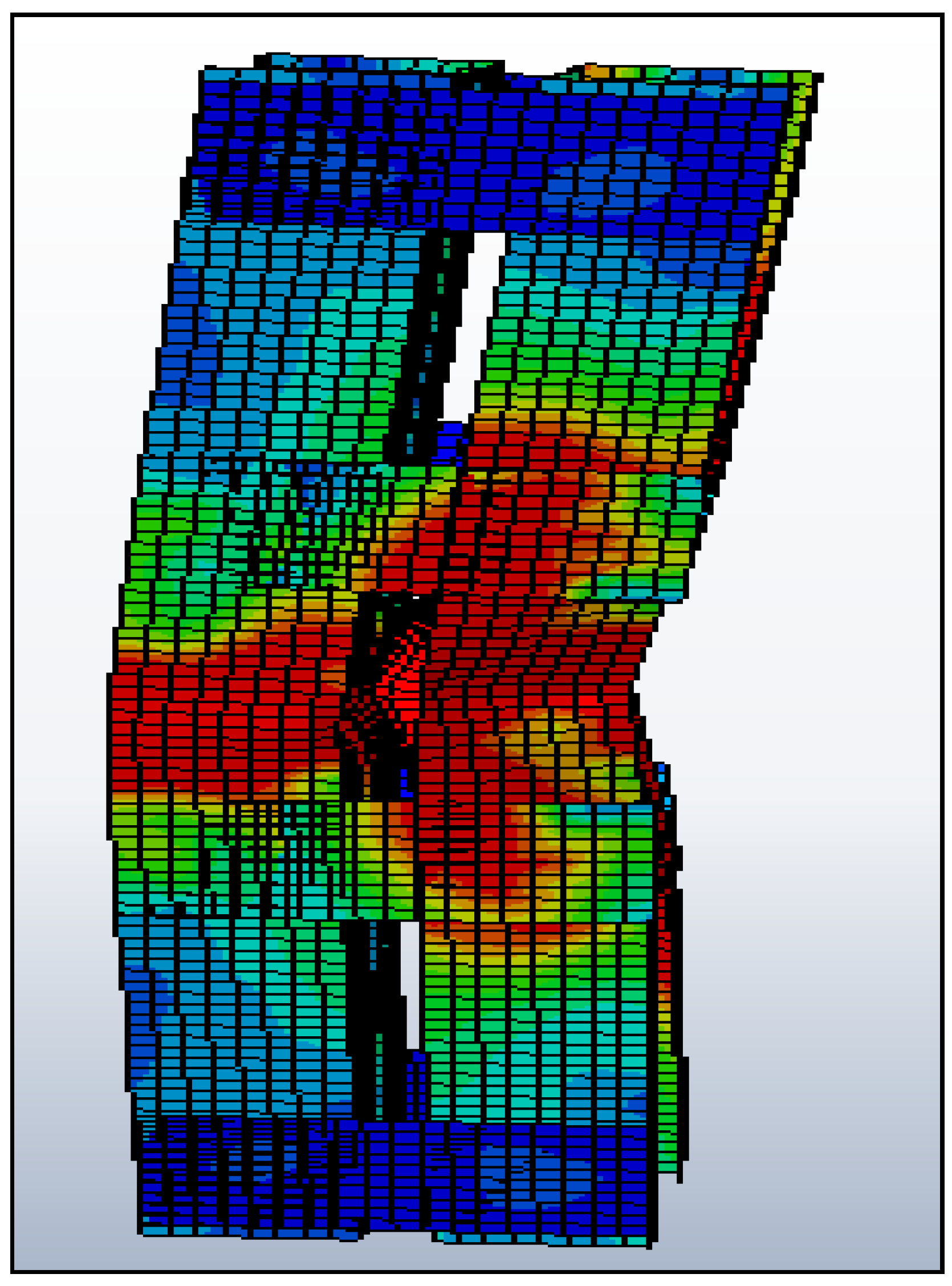
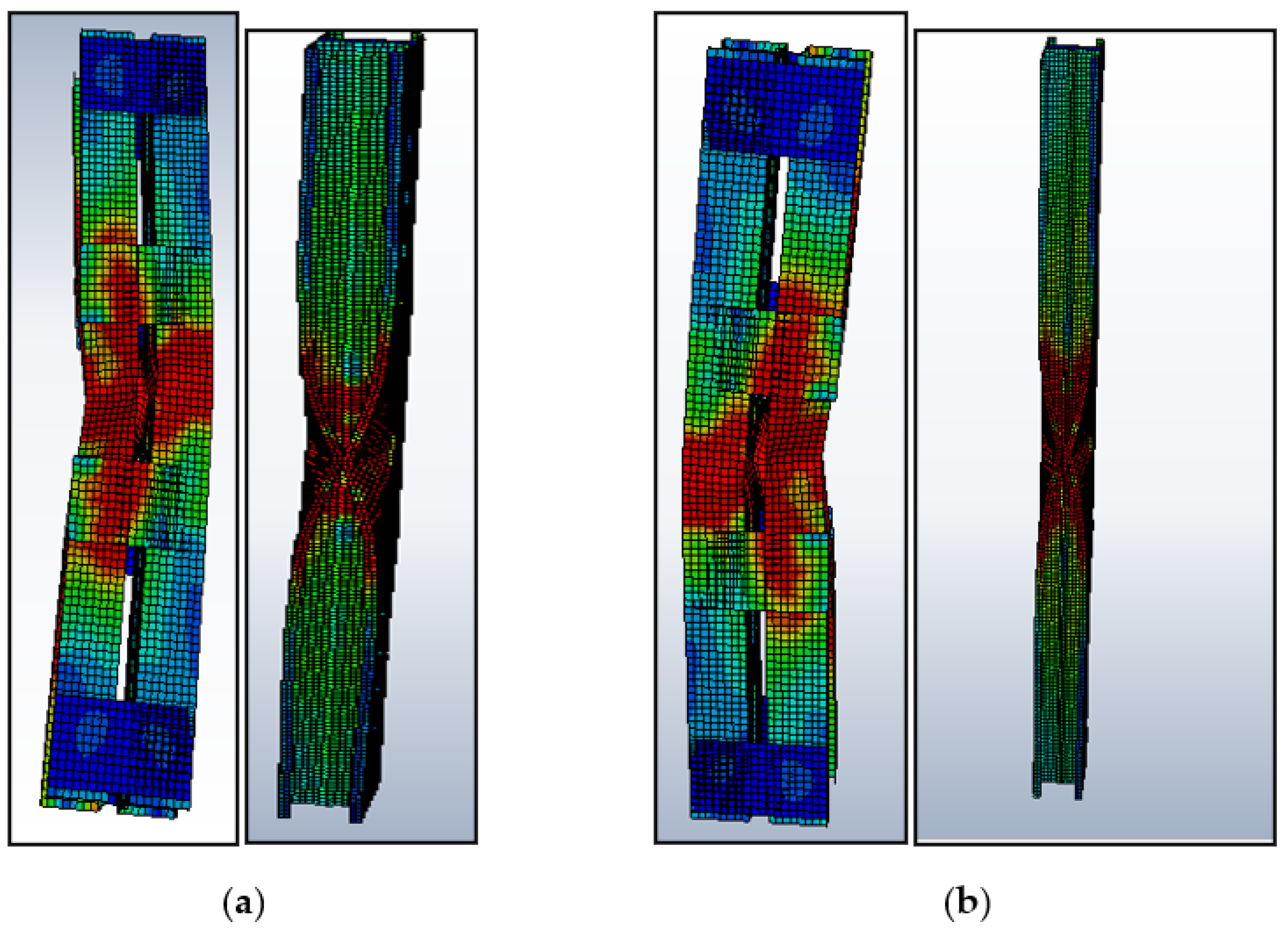
Buckling Mode
3.5. Results of Parametric Study
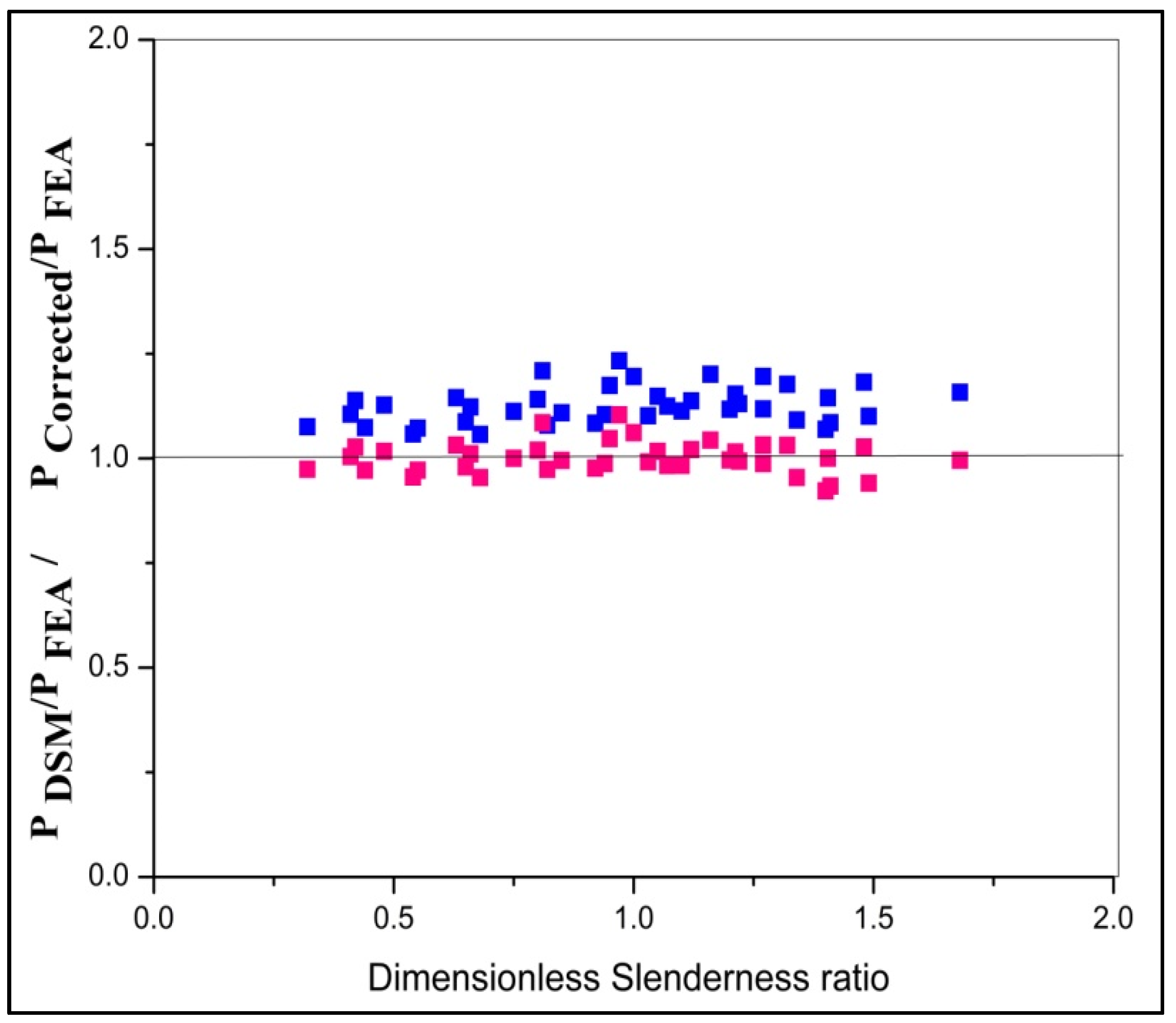
3.6. Discussion
- The experimental method shows that the load-carrying capacity is governed by residual stress, slenderness ratio, and battened width.
- The buckling mode started with local buckling and ended up with a combination of local and distortional with respect to slenderness ratio. The buckling mode started with local buckling and ended up with the combination of local and distortional for slenderness ratio.
- Increasing the slenderness ratio from 20 to 30 and 30 to 40, the resistance against loading decreased by the nominal verge of 10 percent for the experimental specimen. The failure of the column is predicted for a lower slenderness ratio (≤30) may be local or a combination of local and flexural buckling. For the higher-order slenderness ratio (>30), the buckling will combine local, distortional, and flexural buckling modes.
- The experimental specimen subjected to buckling mode was matched with the FEA specimen from the validation study. Therefore, for the tedious situation, such as for the CFS back-to-back stiffened column, the observed value for a larger slenderness ratio can be predicted by finding out the product of 1.072 with PFEM (analytical value).
- From the theoretical study, it can be inferred that the DSM analysis is found to be conservative with the inclusion of service load and predicted the column’s strengthen equation, which calculates the failure load irrespective of the thickness and slenderness ratio.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AISI-S100:2007; North American Specification for the Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structural Members Specifications. American Iron Steel Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Salem, A.; Aghoury, M.; Dib, F.H.; Hanna, M. Ultimate capacity of I-slender section columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2004, 60, 1193–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalochairetis, K.; Gantes, C. Numerical and analytical investigation of collapse loads of laced built-up columns. Comput. Struct. 2011, 89, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, R.; Thenmozhi, R.; Jayagopal, L. Flexural -Torsional Buckling Tests of Cold-Formed Lipped Channel Beams Under Restrained Boundary Conditions. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2015, 19, 2134–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondal, J.; Niazi, M. Stability of built-up beams and columns with thin-walled members. J. Constr. Steel Res. 1990, 16, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslani, F.; Goel, S.C. An Analytical Criterion for Buckling Strength of Built-up Compression Members. Eng. J. 1991, 28, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, K.; Ting, T.; Lau, H.H.; Lim, J. Nonlinear behavior of axially loaded back-to-back built-up cold-formed steel un-lipped channel sections. Steel Compos. Struct. 2018, 28, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Ting, T.; Lau, H.H.; Lim, J. Experimental investigation into the behaviour of back-to-back gapped built-up cold-formed steel channel sections under compression. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2018, 147, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Ting, T.; Lau, H.H.; Lim, J. Effect of thickness on the behaviour of axially loaded back-to-back cold-formed steel built-up channel sections -Experimental and numerical investigation. Structures. 2018, 28, 327–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AS/NZS 4600:2005; Australian/New Zealand Standard—Cold Formed Steel Structures. SAI Global: Singapore, 2005.
- Sani, M.S.H.M.; Muftah, F.; Tan, C.S. Experimental Analysis of Cold-Formed Steel C-Sections with the Notch Subjected to Axial Compression. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurocode 3- Design of Steel Structures—Part 1-3: General Rules—Supplementary Rules for Cold-Formed Members and Sheeting vol. Part 1-3. 2006. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/2f1f2ecc-0d2a-481d-a432-9d833ea1861f/en-1993-1-3-2006 (accessed on 9 March 2022).
- Anbarasu, M.; Kumar, S.B.; Sukumar, S. Study on the effect of ties in the intermediate length Cold Formed Steel (CFS) columns. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2013, 46, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Aghoury, M.A.; Salem, A.H.; Hanna, M.T.; Amoush, E.A. Ultimate capacity of battened columns composed of four equal slender angles. Thin-Walled Struct. 2013, 63, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Aghoury, M.A.; Salem, A.H.; Hanna, M.T.; Amoush, E.A. Experimental investigation for the behaviour of battened beam-columns composed of four equal slender angles. Thin-Walled Struct. 2010, 48, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, I.; Schueremans, L.; Pyl, L. Composed columns from cold-formed steel Z-profiles: Experiments and code-based predictions of the overall compression capacity. Eng. Struct. 2012, 37, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, I.; Schueremans, L.; Pyl, L.; Vandewalle, L. Experimental investigation of built-up double-Z members in bending and compression. Thin-Walled Struct. 2012, 53, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbarasu, M.; Kanagarasu, K.; Sukumar, S. Investigation on the behaviour and strength of cold-formed steel web stiffened built-up battened columns. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 4029–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraman, M.; Anuradha, R.; Awoyera, P.O.; Gobinath, R. Numerical simulation and specification provisions for buckling characteristics of a built-up steel column section subjected to axial loading. Eng. Struct. 2020, 207, 110256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, C.H.T.; Lau, H.H. Compression Test on Cold-Formed Steel Built-Up Back-to-Back Channels Stub Columns. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 201, 2900–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schafer, B.W.; Peköz, T. Computational modeling of cold-formed steel: Characterizing geometric imperfections and residual stresses. J. Constr. Steel Res. 1998, 47, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankanamge, N.D.; Mahendran, M. Behaviour and design of cold-formed steel beams subject to lateral–torsional buckling. Thin-Walled Struct. 2012, 51, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, J.; Hajirasouliha, I.; Becque, J.; Eslami, A. Optimum design of cold-formed steel beams using Particle Swarm Optimisation method. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2016, 122, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinis, P.B.; Camotim, D. Cold-formed steel columns undergoing local–distortional coupling: Behaviour and direct strength prediction against interactive failure. Comput. Struct. 2015, 147, 181–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Hajirasouliha, I.; Becque, J. Experimental investigation of local-flexural interactive buckling of cold-formed steel channel columns. Thin-Walled Struct. 2018, 125, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathy, K.C.K.; Kumar, M.v.A. Unstiffened Elements as Limiting Case of Distortional Buckling of Partially Stiffened Elements. J. Struct. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.v.A.; Kalyanaraman, V. Interaction of Local, Distortional, and Global Buckling in CFS Lipped Channel Compression Members. J. Struct. Eng. 2018, 144, 04017192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.A.; Sahoo, D.R.; Jain, A.K. Numerical Study on the Structural Integrity of Built-up Cold-Formed Steel Battened Columns; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2020; pp. 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherbouche, S.; Megnounif, A. Numerical study and design of thin walled cold formed steel built-up open and closed section columns. Eng. Struct. 2019, 179, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.A.; Sahoo, D.R.; Jain, A.K. Influence of chord compactness and slenderness on axial compression behavior of built-up battened CFS columns. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayanand, S.; Anbarasu, M. Effect of Spacers on Ultimate Strength and Behavior of Cold-Formed Steel Built-up Columns. Procedia Eng. 2017, 173, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbarasu, M. Behaviour of cold-formed steel built-up battened columns composed of four lipped angles: Tests and numerical validation. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2020, 23, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-H.; Young, B. Finite element analysis and design of cold-formed steel built-up closed section columns with web stiffeners. Thin-Walled Struct. 2018, 131, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunalan, S.; Mahendran, M. Improved design rules for fixed ended cold-formed steel columns subject to flexural–torsional buckling. Thin-Walled Struct. 2013, 73, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, A.D.; Dinis, P.B.; Camotim, D.; Providência, P. On the relevance of local–distortional interaction effects in the behaviour and design of cold-formed steel columns. Comput. Struct. 2015, 160, 57–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cava, D.; Camotim, D.; Dinis, P.B.; Madeo, A. Numerical investigation and direct strength design of cold-formed steel lipped channel columns experiencing local–distortional–global interaction. Thin-Walled Struct. 2016, 105, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, P.; Arun, N. Behaviour of Partially Closed Stiffened Cold-Formed Steel Compression Member. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 3865–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Z.; Roy, K.; Mares, J.; Sham, C.-W.; Chen, B.; Lim, J.B.P. Deep learning-based axial capacity prediction for cold-formed steel channel sections using Deep Belief Network. Structures 2021, 33, 2792–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, E.; Fard, S.E.; Zandi, Y.; Samali, B. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of an Innovative Method for Strengthening Cold-Formed Steel Profiles in Bending throughout Finite Element Modeling and Application of Neural Network Based on Feature Selection Method. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanthasamy, E.; Alsanat, H.; Poologanathan, K.; Gatheeshgar, P.; Corradi, M.; Thirunavukkarasu, K.; Dissanayake, M. Web Crippling Behaviour of Cold-Formed High Strength Steel Unlipped Channel Beams. Buildings 2022, 12, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Lau, H.H.; Fang, Z.; Masood, R.; Ting, T.C.; Lim, J.B.; Lee, V.C. Effects of corrosion on the strength of self-drilling screw connections in cold-formed steel structures-experiments and finite element modeling. Structures 2022, 36, 1080–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Roy, K.; Fang, Z.; Lim, J.B.P. A Critical Review on Optimization of Cold-Formed Steel Members for Better Structural and Thermal Performances. Buildings 2022, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbarasu, M.; Murugapandian, G. Experimental study on cold-formed steel web stiffened lipped channel columns undergoing distortional–global interaction. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABAQUS (2010), Version 6.10; SIMULIA: Providence, RI, USA, 2010.
- ASTM: 370–92; Standard Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1996.
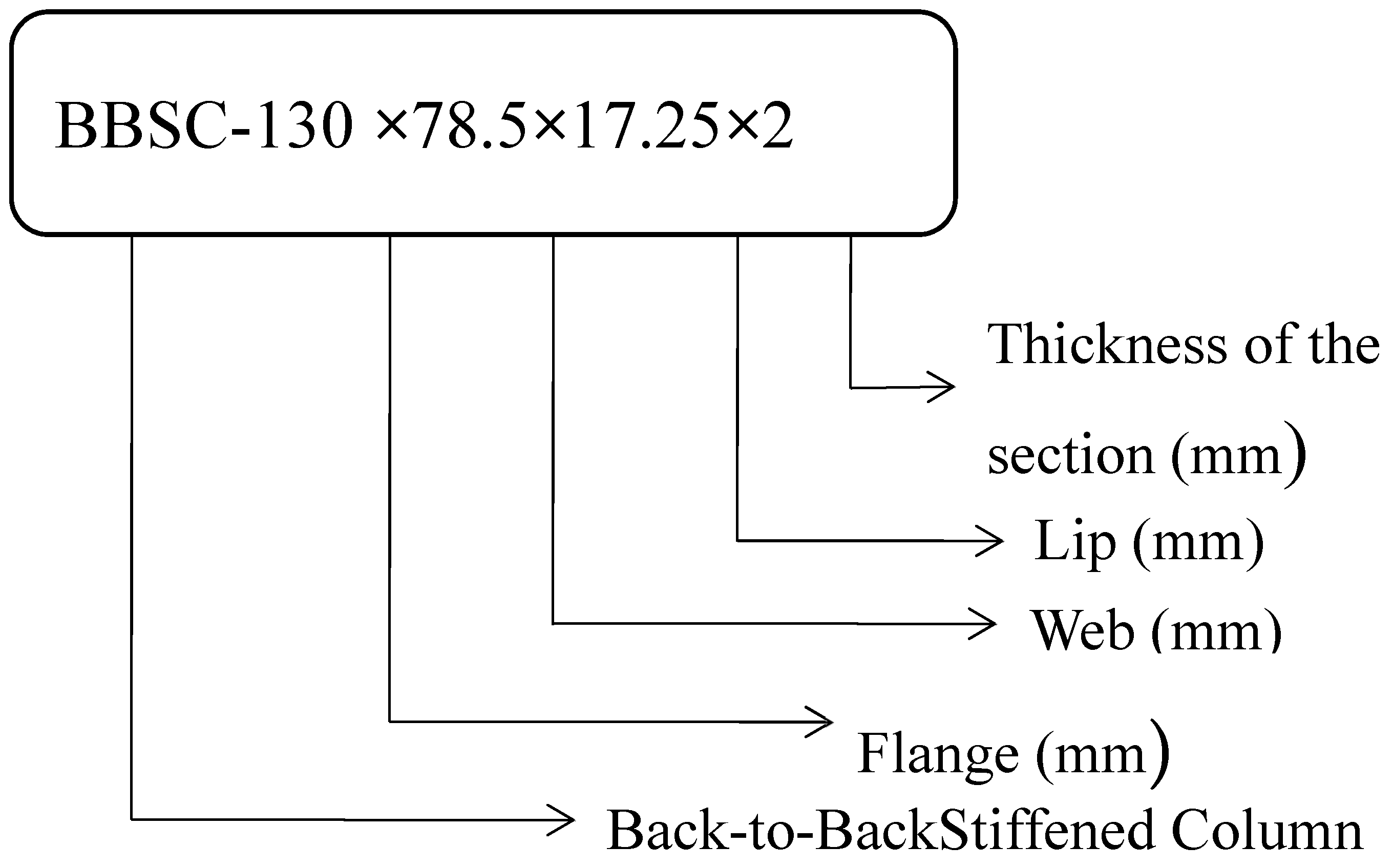










| Lipped c-Section with Web Stiffener | One or Two Intermediate Stiffeners: |
|---|---|
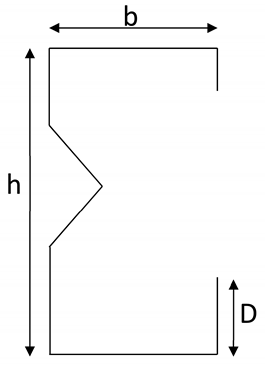 | h/t < 489 |
| b/t < 160 | |
| 6 < D/t < 33 | |
| 1.3 < h/b < 2.7 | |
| 0.05 < D/b < 0.41 | |
| E/fy > 340 (fy < 593 MPa or 6050 kg/cm2) |
| No. | Specimen ID BBSC-BW×Bf×D-t | Young’s Modulus E (GPa) | Tension Stress fy (MPa) | Failure Stress fu (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Loading Condition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BBSC-130×78.5×17.25×2 | 200 | 316 | 350 | 28 | Pinned end condition |
| 2 | BBSC-132.5×78.75×16.75×2 | |||||
| 3 | BBSC-131.15×78.75×16.75×2 | |||||
| 4 | BBSC-131.6×78.175×16.75×2 | |||||
| 5 | BBSC-131.6×78×16.95×2 | |||||
| 6 | BBSC-132.65×78.375×17.5×2 |
| S.I.NO. | Specimen ID Boundary Condition-Specimen ID | Slenderness Ratio | Thickness t (mm) | Battened Width b (mm) | Web bW (mm) | Flange bf (mm) | Lip d1 & d2 (mm) | Length (mm) | Spacing between Chords S (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BC-1-1 | 20 | 2 | 105 | 78.5 | 130 | 17.25 | 995 | 26 |
| 2 | BC-2-1 | 30 | 2 | 105 | 78.5 | 130 | 17.25 | 1492.5 | 26.5 |
| 3 | BC-1-2 | 20 | 2 | 104.5 | 79 | 130.5 | 17.10 | 995 | 25.2 |
| 4 | BC-2-2 | 30 | 2 | 104.5 | 79 | 130.5 | 17.10 | 1492.5 | 25.7 |
| 5 | BC-1-3 | 20 | 2 | 104.5 | 78.6 | 129.5 | 17.12 | 998 | 27 |
| 6 | BC-2-3 | 30 | 2 | 104.5 | 78.8 | 129.3 | 17.15 | 1492 | 26.7 |
| 7 | BC-3-1 | 20 | 2 | 149 | 78.75 | 132.5 | 16.75 | 990 | 27 |
| 8 | BC-4-1 | 30 | 2 | 149 | 78.76 | 132.5 | 16.75 | 1485 | 26.5 |
| 9 | BC-3-2 | 20 | 2 | 149 | 78.78 | 132.7 | 16.8 | 995 | 26 |
| 10 | BC-4-2 | 30 | 2 | 149 | 78.32 | 132.6 | 16.65 | 1492 | 26.2 |
| 11 | BC-3-3 | 20 | 2 | 149 | 77.75 | 132.52 | 16.76 | 1485 | 25 |
| 12 | BC-4-3 | 30 | 2 | 149 | 78.72 | 132.51 | 16.81 | 1485 | 26.5 |
| 13 | BC-5-1 | 30 | 2 | 105 | 78.75 | 131.15 | 16.75 | 1470 | 25 |
| 14 | BC- 6-1 | 40 | 2 | 105 | 78.75 | 131.23 | 16.754 | 1960 | 25.6 |
| 15 | BC-5-2 | 30 | 2 | 105 | 78.753 | 131.15 | 16.751 | 1468 | 24 |
| 16 | BC-6-2 | 40 | 2 | 105 | 78.75 | 131.14 | 16.746 | 1956 | 23.5 |
| 17 | BC-5-3 | 30 | 2 | 105 | 78.745 | 131.15 | 16.752 | 1469 | 24.2 |
| 18 | BC-6-3 | 40 | 2 | 105 | 78.746 | 131.15 | 16.656 | 1964 | 24.7 |
| 19 | BC-7-1 | 30 | 2 | 150 | 78.175 | 131.56 | 16.75 | 1472 | 27 |
| 20 | BC-8-1 | 40 | 2 | 150 | 78.174 | 131.55 | 16.746 | 1964 | 26.25 |
| 21 | BC-7-2 | 30 | 2 | 150 | 78.25 | 132 | 16.752 | 1462 | 26 |
| 22 | BC-8-2 | 40 | 2 | 150 | 78.175 | 131.62 | 16.748 | 1949 | 26.5 |
| 23 | BC-7-3 | 30 | 2 | 150 | 78.173 | 131.62 | 16.762 | 1468 | 25 |
| 24 | BC-8-3 | 40 | 2 | 150 | 78.175 | 131.63 | 16.752 | 1957 | 25.2 |
| 25 | BC-9-1 | 30 | 2 | 105 | 78 | 133.25 | 16.95 | 1472 | 27 |
| 26 | BC-10-1 | 40 | 2 | 105 | 78.23 | 133.25 | 16.95 | 1964 | 26.5 |
| 27 | BC-9-2 | 30 | 2 | 105 | 78.2 | 133.25 | 17 | 1472 | 26 |
| 28 | BC-10-2 | 40 | 2 | 105 | 78.3 | 133.25 | 16.95 | 1964 | 26.46 |
| 29 | BC-9-3 | 30 | 2 | 105 | 78.15 | 133.25 | 16.95 | 1472 | 25 |
| 30 | BC-10-3 | 40 | 2 | 105 | 78 | 133.25 | 16.95 | 1964 | 27 |
| 31 | BC-11-1 | 30 | 2 | 150 | 78.38 | 132.65 | 17.5 | 1965 | 29.5 |
| 32 | BC-12-1 | 40 | 2 | 150 | 78.375 | 132.65 | 17.46 | 2620 | 29.62 |
| 33 | BC-11-2 | 30 | 2 | 150 | 78.42 | 132.65 | 17.45 | 1965 | 28.5 |
| 34 | BC-12-2 | 40 | 2 | 150 | 78.4 | 132.65 | 17.53 | 2620 | 29.25 |
| 35 | BC-11-3 | 30 | 2 | 150 | 78.35 | 132.65 | 17.52 | 1965 | 31 |
| 36 | BC-12-3 | 40 | 2 | 150 | 78.37 | 132.65 | 17.5 | 2620 | 32.5 |
| 30 | BC-10-3 | 40 | 2 | 105 | 78 | 133.25 | 16.95 | 1964 | 27 |
| 31 | BC-11-1 | 30 | 2 | 150 | 78.38 | 132.65 | 17.5 | 1965 | 29.5 |
| 32 | BC-12-1 | 40 | 2 | 150 | 78.375 | 132.65 | 17.46 | 2620 | 29.62 |
| 33 | BC-11-2 | 30 | 2 | 150 | 78.42 | 132.65 | 17.45 | 1965 | 28.5 |
| 34 | BC-12-2 | 40 | 2 | 150 | 78.4 | 132.65 | 17.53 | 2620 | 29.25 |
| 35 | BC-11-3 | 30 | 2 | 150 | 78.35 | 132.65 | 17.52 | 1965 | 31 |
| 36 | BC-12-3 | 40 | 2 | 150 | 78.37 | 132.65 | 17.5 | 2620 | 32.5 |
| No. | Specimen ID Boundary Condition-Specimen ID | Slenderness Ratio | PEXP (kN) | PFEM (kN) | PDSM (kN) | PFEM/PEXP | PFEM/PDSM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BC-1-1 | 20 | 250 | 263 | 269 | 1.052 | 0.978 |
| 2 | BC-2-1 | 30 | 242 | 259 | 263 | 1.070 | 0.985 |
| 3 | BC-1-2 | 20 | 248 | 261 | 265.3 | 1.052 | 0.984 |
| 4 | BC-2-2 | 30 | 236 | 257.2 | 262.4 | 1.090 | 0.980 |
| 5 | BC-1-3 | 20 | 252 | 263 | 265.2 | 1.044 | 0.992 |
| 6 | BC-2-3 | 30 | 238 | 258 | 264.5 | 1.084 | 0.975 |
| 7 | BC-3-1 | 20 | 264 | 273 | 276 | 1.034 | 0.989 |
| 8 | BC-4-1 | 30 | 220 | 242 | 252 | 1.100 | 0.960 |
| 9 | BC-3-2 | 20 | 268 | 275 | 279 | 1.026 | 0.986 |
| 10 | BC-4-2 | 30 | 216 | 254 | 258 | 1.176 | 0.984 |
| 11 | BC-3-3 | 20 | 258 | 270 | 275 | 1.047 | 0.982 |
| 12 | BC-4-3 | 30 | 242 | 258 | 262 | 1.066 | 0.985 |
| 13 | BC-5-1 | 30 | 234 | 244 | 252 | 1.043 | 0.968 |
| 14 | BC-6-1 | 40 | 192 | 210 | 224 | 1.094 | 0.938 |
| 15 | BC-5-2 | 30 | 230 | 240 | 252 | 1.043 | 0.952 |
| 16 | BC-6-2 | 40 | 194 | 208 | 219 | 1.072 | 0.950 |
| 17 | BC-5-3 | 30 | 232 | 242 | 251 | 1.043 | 0.964 |
| 18 | BC-6-3 | 40 | 196 | 206 | 212.5 | 1.051 | 0.969 |
| 19 | BC-7-1 | 30 | 226 | 247 | 256 | 1.093 | 0.965 |
| 20 | BC-8-1 | 40 | 196 | 213.2 | 230 | 1.088 | 0.927 |
| 21 | BC-7-2 | 30 | 230 | 247 | 252 | 1.074 | 0.980 |
| 22 | BC-8-2 | 40 | 198 | 207 | 214 | 1.045 | 0.967 |
| 23 | BC-7-3 | 30 | 228 | 247 | 249.5 | 1.083 | 0.990 |
| 24 | BC-8-3 | 40 | 192 | 208.5 | 212.5 | 1.086 | 0.981 |
| 25 | BC-9-1 | 30 | 230 | 253 | 257 | 1.100 | 0.984 |
| 26 | BC-10-1 | 40 | 206 | 219.25 | 226.32 | 1.064 | 0.969 |
| 27 | BC-9-2 | 30 | 226 | 249 | 252 | 1.102 | 0.988 |
| 28 | BC-10-2 | 40 | 206 | 214.5 | 224 | 1.041 | 0.958 |
| 29 | BC-9-3 | 30 | 236 | 251 | 259 | 1.064 | 0.969 |
| 30 | BC-10-3 | 40 | 206 | 219.25 | 227.89 | 1.064 | 0.962 |
| 31 | BC-11-1 | 30 | 250 | 272.5 | 282 | 1.090 | 0.966 |
| 32 | BC-12-1 | 40 | 210 | 228.33 | 236 | 1.087 | 0.968 |
| 33 | BC-11-2 | 30 | 242 | 264.5 | 272.4 | 1.093 | 0.971 |
| 34 | BC-12-2 | 40 | 210 | 228.33 | 234.23 | 1.087 | 0.975 |
| 35 | BC-11-3 | 30 | 246 | 263.2 | 276 | 1.070 | 0.954 |
| 36 | BC-12-3 | 40 | 210 | 228.33 | 235 | 1.087 | 0.972 |
| Mean | 1.072 | 0.971 | |||||
| Standard Deviation | 0.030 | 0.027 | |||||
| Coefficient of Variation | 0.028 | 0.025 | |||||
| No. | Specimen ID BC 1-BW×Bf× D-t-bw | Batten Width (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Spacing between Chords (mm) | Ultimate Strength fu (N/mm2) and Poisson’s Ratio | Slenderness Ratio | Young’s Modulus (N/mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BC 1-90×60×15-2-60.27 | 60.27 | 2 | 25 | 305 and 0.3 | 20-120 | 2 × 105 |
| 2 | BC 2-90×60×15-2-120 | 120 | 2 | 25 | 20-120 | ||
| 3 | BC 3-150×75×15-2-150 | 150 | 2 | 73 | 20-100 | ||
| 4 | BC 4-150×75×15-2-105 | 105 | 2 | 73 | 20-100 |
| No. | Specimen ID | Slenderness Ratio | PFEM (KN) | PDSM (kN) | PCorrected (kN) | PCorrected /PFEM | PDSM /PFEM | Failure Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BC 1-90×60×15×2-60.27-20-4 | 20 | 208.250 | 224.000 | 202.830 | 0.974 | 1.076 | NL + ND + NE |
| 2 | BC 1-90×60×15×2-60.27-30-5 | 30 | 207.719 | 223.000 | 201.870 | 0.972 | 1.074 | NL + ND + NE |
| 3 | BC 1-90×60×15×2-60.27-40-5 | 40 | 202.221 | 214.000 | 193.230 | 0.956 | 1.058 | NL + ND + NE |
| 4 | BC 1-90×60×15×2-60.27-50-5 | 50 | 190.381 | 207.000 | 186.510 | 0.980 | 1.087 | NL + ND + NE |
| 5 | BC 1-90×60×15×2-60.27-60-6 | 60 | 180.738 | 201.000 | 180.750 | 1.000 | 1.112 | NL + ND + NE |
| 6 | BC 1-90×60×15×2-60.27-70-6 | 70 | 175.848 | 195.000 | 174.990 | 0.995 | 1.109 | ND + NE |
| 7 | BC 1-90×60×15×2-60.27-80-7 | 80 | 167.495 | 185.000 | 165.390 | 0.987 | 1.105 | ND + NE |
| 8 | BC 1-90×60×15×2-60.27-90-8 | 90 | 141.358 | 169.000 | 150.030 | 1.061 | 1.196 | ND + NE |
| 9 | BC 1-90×60×15×2-60.27-100-9 | 100 | 126.266 | 142.000 | 124.110 | 0.983 | 1.125 | ND + NE |
| 10 | BC 1-90×60×15×2-60.27-110-10 | 110 | 111.572 | 134.000 | 116.430 | 1.044 | 1.201 | ND + NE |
| 11 | BC 1-90×60×15×2-60.27-120-10 | 120 | 105.377 | 126.000 | 108.750 | 1.032 | 1.196 | ND + NE |
| 12 | BC 2-90×60×15×2-120-20-4 | 20 | 213.432 | 236.000 | 214.350 | 1.004 | 1.106 | NL + ND + NE |
| 13 | BC 2-90×60×15×2-120-30-5 | 30 | 211.901 | 227.200 | 205.902 | 0.972 | 1.072 | NL + ND + NE |
| 14 | BC 2-90×60×15×2-120-40-5 | 40 | 201.476 | 213.000 | 192.270 | 0.954 | 1.057 | NL + ND + NE |
| 15 | BC 2-90×60×15×2-120-50-5 | 50 | 195.485 | 211.000 | 190.350 | 0.974 | 1.079 | NL + ND + NE |
| 16 | BC 2-90×60×15×2-120-60-6 | 60 | 190.488 | 206.500 | 186.030 | 0.977 | 1.084 | NL + ND + NE |
| 17 | BC 2-90×60×15×2-120-70-6 | 70 | 184.242 | 203.000 | 182.670 | 0.991 | 1.102 | ND + NE |
| 18 | BC 2-90×60×15×2-120-80-7 | 80 | 172.343 | 196.000 | 175.950 | 1.021 | 1.137 | ND + NE |
| 19 | BC 2-90×60×15×2-120-90-8 | 90 | 159.321 | 178.000 | 158.670 | 0.996 | 1.117 | ND + NE |
| 20 | BC 2-90×60×15×2-120-100-9 | 100 | 142.187 | 159.000 | 140.430 | 0.988 | 1.118 | ND + NE |
| 21 | BC 2-90×60×15×2-120-110-10 | 110 | 130.060 | 142.000 | 124.110 | 0.954 | 1.092 | ND + NE |
| 22 | BC 2-90×60×15×2-120-120-10 | 120 | 116.872 | 125.000 | 107.790 | 0.922 | 1.070 | ND + NE |
| 23 | BC 3-150×75×15-2-20-150-5 | 20 | 186.273 | 210.000 | 189.390 | 1.017 | 1.127 | NL + ND + NE |
| 24 | BC 3-150×75×15-2-20-150-5 | 30 | 181.683 | 204.000 | 183.630 | 1.011 | 1.123 | NL + ND + NE |
| 25 | BC 3-150×75×15-2-20-150-5 | 40 | 161.259 | 185.000 | 165.390 | 1.026 | 1.147 | NL + ND + NE |
| 26 | BC 3-150×75×15-2-20-150-6 | 50 | 152.433 | 178.000 | 158.670 | 1.041 | 1.168 | NL + ND + NE |
| 27 | BC 3-150×75×15-2-20-150-7 | 60 | 142.812 | 169.000 | 150.030 | 1.051 | 1.183 | NL + ND + NE |
| 28 | BC 3-150×75×15-2-20-150-8 | 70 | 132.662 | 156.000 | 137.550 | 1.037 | 1.176 | ND + NE |
| 29 | BC 3-150×75×15-2-20-150-10 | 80 | 124.053 | 146.000 | 127.950 | 1.031 | 1.177 | ND + NE |
| 30 | BC 3-150×75×15-2-20-150-11 | 90 | 113.355 | 133.000 | 115.470 | 1.019 | 1.173 | ND + NE |
| 31 | BC 3-150×75×15-2-20-150-12 | 100 | 105.377 | 126.000 | 108.750 | 1.032 | 1.196 | ND + NE |
| 32 | BC 4-150×75×15-2-20-105-5 | 20 | 185.596 | 208.000 | 187.470 | 1.010 | 1.121 | NL + ND + NE |
| 33 | BC 4-150×75×15-2-20-105-5 | 30 | 177.289 | 198.000 | 177.870 | 1.003 | 1.117 | NL + ND + NE |
| 34 | BC 4-150×75×15-2-20-105-5 | 40 | 163.444 | 189.000 | 169.230 | 1.035 | 1.156 | NL + ND + NE |
| 35 | BC 4-150×75×15-2-20-105-6 | 50 | 154.630 | 180.000 | 160.590 | 1.039 | 1.164 | NL + ND + NE |
| 36 | BC 4-150×75×15-2-20-105-7 | 60 | 146.100 | 172.000 | 152.910 | 1.047 | 1.177 | NL + ND + NE |
| 37 | BC 4-150×75×15-2-20-105-8 | 70 | 136.274 | 159.000 | 140.430 | 1.030 | 1.167 | ND + NE |
| 38 | BC 4-150×75×15-2-20-105-10 | 80 | 124.053 | 145.600 | 127.566 | 1.028 | 1.174 | ND + NE |
| 39 | BC 4-150×75×15-2-20-105-11 | 90 | 113.355 | 132.000 | 114.510 | 1.010 | 1.164 | ND + NE |
| 40 | BC 4-150×75×15-2-20-105-12 | 100 | 106.743 | 128.000 | 110.670 | 1.037 | 1.199 | ND + NE |
| Mean | 0.978 | 1.101 | ||||||
| Standard Deviation | 0.027 | 0.031 | ||||||
| Coefficient of Variation | 0.028 | 0.028 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohan, M.; Ramachandran, A.; Amran, M.; Borovkov, A. Determination of Buckling Behavior of Web-Stiffened Cold-Formed Steel Built-Up Column under Axial Compression. Materials 2022, 15, 2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15092968
Mohan M, Ramachandran A, Amran M, Borovkov A. Determination of Buckling Behavior of Web-Stiffened Cold-Formed Steel Built-Up Column under Axial Compression. Materials. 2022; 15(9):2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15092968
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohan, Muthuraman, Anuradha Ramachandran, Mugahed Amran, and Aleksey Borovkov. 2022. "Determination of Buckling Behavior of Web-Stiffened Cold-Formed Steel Built-Up Column under Axial Compression" Materials 15, no. 9: 2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15092968
APA StyleMohan, M., Ramachandran, A., Amran, M., & Borovkov, A. (2022). Determination of Buckling Behavior of Web-Stiffened Cold-Formed Steel Built-Up Column under Axial Compression. Materials, 15(9), 2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15092968








