Advances in Titanium/Polymer Hybrid Joints by Carbon Fiber Plug Insert: Current Status and Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Background
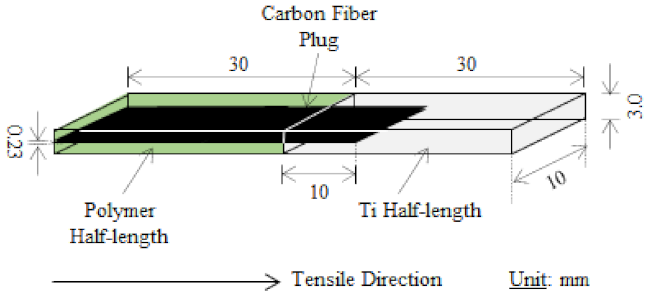
2. Introducing CF Plug for Increased UTS of Titanium/Polymer Joints
2.1. Ti/CF Half-Length: Assembly by Spot Welding and Examination
2.2. Polymer/CF Half-Length: Assembly
2.3. Tensile Testing and Analysis
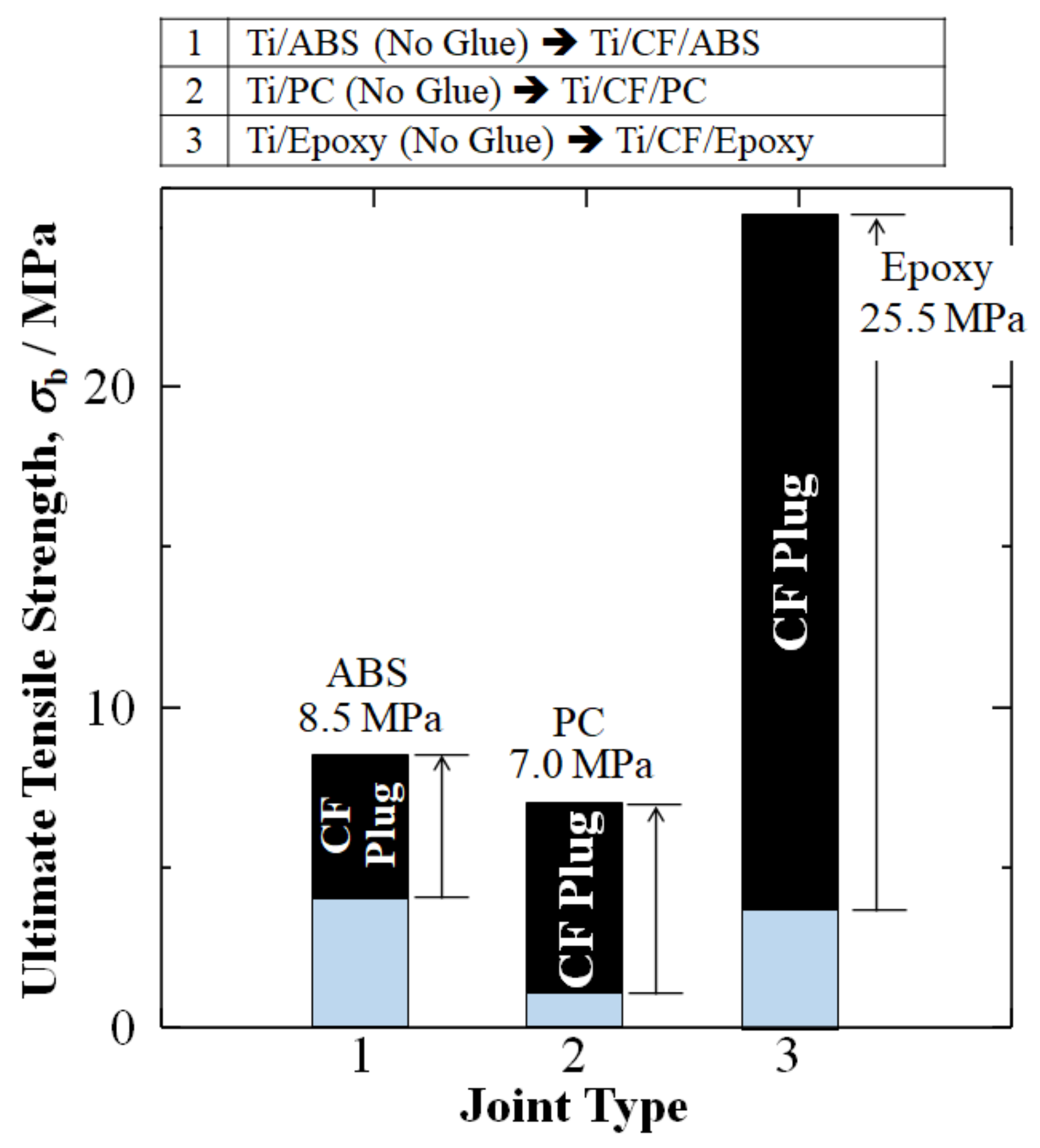
2.4. Results of Addition of CF Plug to Increase Tensile Stress of Ti/Polymer Joints
3. Activating CF Plug with HLEBI to Increase UTS for Ti/CF/Thermoplastic Joints
3.1. HLEBI Method
3.2. Increase in UTS by HLEBI Activation
3.3. Results for Normalized (Corrected) cσb (cUTS) for CFRP Cross-Sectional Area Fraction by Rule of Mixtures
3.4. Activation by HLEBI Increasing Adhesion of Carbon Fibers with Thermoplastic
4. Ti/CF Half-Length: Metallographic Changes Due to Spot Welding
4.1. Ti/CF Half-Length: Metallographic Process
4.2. Ti/CF Half-Length: Diffusion
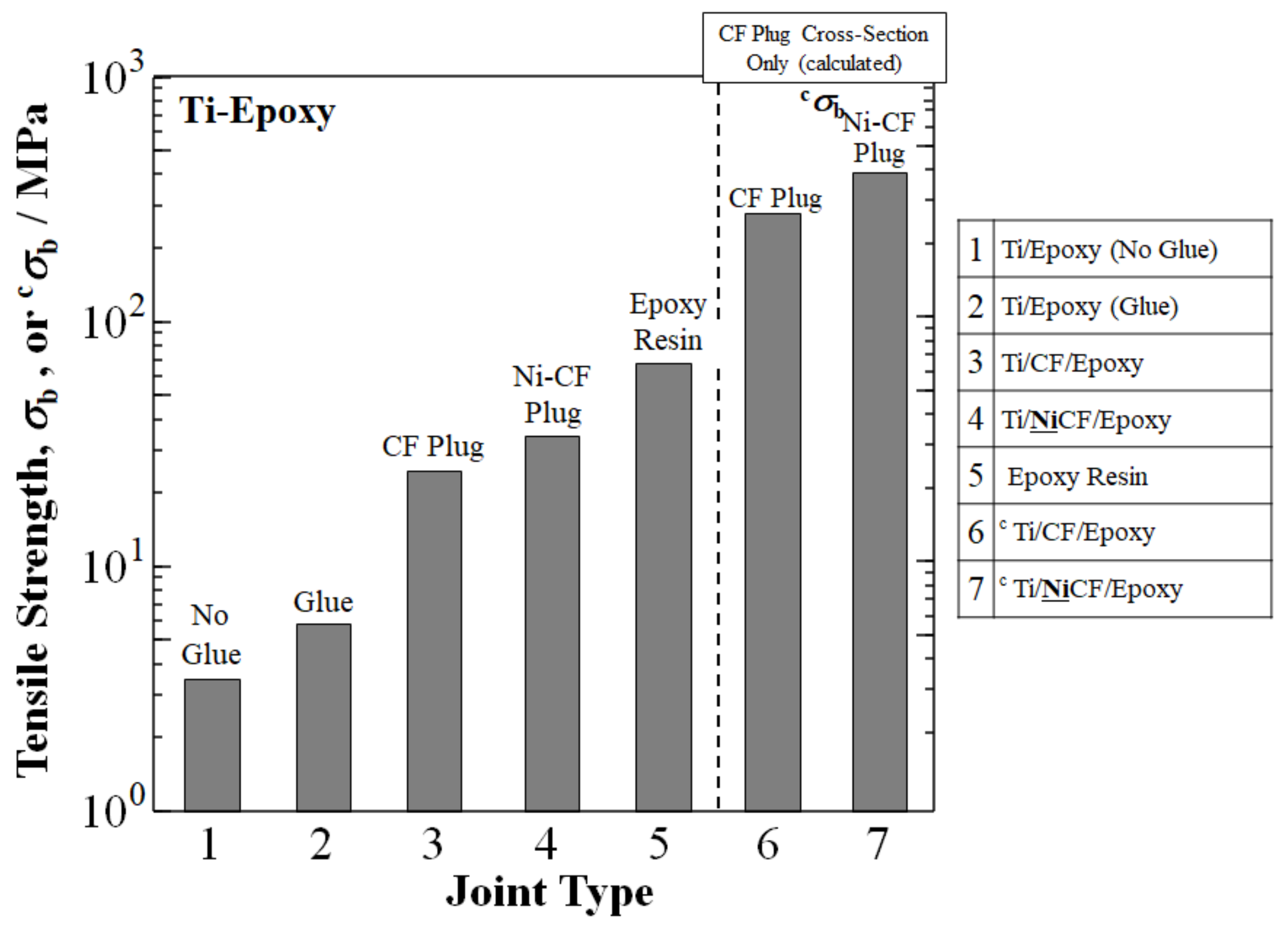
5. Developments in Thermoset Ti/CF/Epoxy Joints
Metallographic Process of Increasing Adhesion by Ni Coating on Ti/CF Half-Length for Ti/NiCF/Epoxy Joints
6. Summary of Our Research Increasing UTS of Ti/TP and Ti/Epoxy Joints
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.; Xian, G.; Li, H. Tension-tension fatigue performance of a large-diameter pultruded carbon/glass hybrid rod. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 120, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z. Life cycle cost analysis of FRP cables for long-span cable supported bridges. Structures 2020, 25, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fahmy, M.F.; Guan, S.; Pan, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Zhao, T. Properties and applications of FRP cable on long-span cable-supported bridges: A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 190, 107934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z. Fatigue life assessment of FRP cable for long-span cable-stayed bridge. Compos. Struct. 2018, 210, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Xian, G.; Li, C.; Huang, X.; Xin, M. Effect of fiber hybridization types on the mechanical properties of carbon/glass fiber reinforced polymer composite rod. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2021, 2021, 1974620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.-L.; Xian, G.; Wu, G.; Raman, R.S.; Al-Saadi, S. Durability study on interlaminar shear behaviour of basalt-, glass- and carbon-fibre reinforced polymer (B/G/CFRP) bars in seawater sea sand concrete environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 985–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallab, N.J.; Jacobs, J.J. Biomaterials Science: An Introduction to Materials in Medicine, Part 1, 3rd ed.; Ratner, B.D., Hoffman, A.S., Schoen, F.J., Lemons, J.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Tokyo, Japan, 2013; ISBN 978-0-12-374626-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mouritz, A.P. Introduction to Aerospace Materials; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 1–14. ISBN 978-1-85573-946-8. [Google Scholar]
- Faudree, M.C. Relationship of graphite-polyimide composites to galvanic processes. Soc. Adv. Mater. Process Eng. (SAMPE) J. 1991, 2, 1288–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, H.; Faudree, M.C.; Matsumuara, Y.; Jimbo, I.; Nishi, Y. Tensile Strength of a Ti/Thermoplastic ABS Matrix CFRTP Joint Connected by Surface Activated Carbon Fiber Cross-Weave Irradiated by Electron Beam. Mater. Trans. 2016, 57, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, H.; Faudree, M.C.; Enomoto, Y.; Takase, S.; Kimura, A.; Tonegawa, A.; Jimbo, I.; Salvia, M.; Nishi, Y. Enhanced tensile strength of Titanium/Polycarbonate joint connected by electron beam activated cross-weave carbon fiber clothinsert. Mater. Trans. 2017, 58, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, K. Reduction of Stress Concentration Factor (SCF) on the Bolted Joint Connection for a Large Wind Turbine Rotor Blade through Various Design Modifications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitoune, R.; Collombet, F. Numerical prediction of the thrust force responsible of delamination during the drilling of the long-fibre composite structures. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davim, J.P.; Reis, P.; António, C.C. Experimental study of drilling glass fiber reinforced plastics (GFRP) manufactured by hand lay-up. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2004, 64, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, R.; Shibata, M.; Todoroki, A. Improving performance of GFRP/aluminum single lap joints using bolted/co-cured hybrid method. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K. “At forty cometh understanding”: A review of some basics of adhesion over the past four decades. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2003, 23, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Su, X.; Chen, Y.; Tian, Z. Joint formation and fracture characteristics of laser welded (bolted) CFRP/TC4 joints. J. Manuf. Processes 2019, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Tan, C.; Wu, Z.; Wu, L.; Gong, X.; Chen, B.; Song, X.; Feng, J. Influence of defocus distance on laser joining of CFRP to titanium alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 124, 106006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, J.; Tan, C.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, L.; Chen, B.; Song, X. Effect of laser texturing on mechanical strength and microstructural properties of hot-pressing joining of carbon fiber reinforced plastic to Ti6Al4V. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 65, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Su, J.; Feng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.; Song, X. Laser joining of CFRTP to titanium alloy via laser surface texturing. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2020, 34, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Su, J.; Zhu, B.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Chen, B.; Song, X.; Feng, J. Effect of scanning speed on laser joining of carbon fiber reinforced PEEK to titanium alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 129, 106273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashaev, N.; Ventzke, V.; Riekehr, S.; Dorn, F.; Horstmann, M. Assessment of alternative joining techniques for Ti–6Al–4V/CFRP hybrid joints regarding tensile and fatigue strength. Mater. Des. 2015, 81, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, J.; Zou, Q.; Ye, Y.; Xu, Z.; Sheng, L. Carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites and TC4 alloy laser assisted joining with the metal surface laser plastic-covered method. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 213, 108738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Jiao, J.; Xu, J.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Xia, H.; Tian, R.; et al. Effects of laser hybrid interfacial pretreatment on enhancing the carbon fiber reinforced thermosetting composites and TC4 alloy heterogeneous joint. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 30, 103142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Absi, C.; Alsinani, N.; Lebel, L.L. Carbon fiber reinforced poly(ether ether ketone) rivets for fastening composite structures. Compos. Struct. 2022, 280, 114877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tie, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, M. Tensile properties analysis of CFRP-titanium plate multi-bolt hybrid joints. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 35, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, Q. Damage behavior investigation of CFRP/Ti bolted joint during interference fit bolt dynamic installation progress. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 111, 104454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-T.; Akkerman, R.; Xiong, J.-J.; Luo, C.-Y.; Du, Y.-S. Evaluation of insert design on the performance of repaired composite-Ti alloy joints. Compos. Struct. 2019, 230, 111506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zuo, Y.; Huo, L.; Qiu, J.; Zuo, D. Numerical and experimental investigation of fitting tolerance effects on damage and failure of CFRP/Ti double-lap single-bolt joints. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Cao, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Dynamic behavior of CFRP/Ti single-lap pinned joints under longitudinal electromagnetic dynamic loading. Compos. Struct. 2018, 184, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Zhao, P.; Ren, R.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, X.; Ji, S. Enhanced resistance-welding hybrid joints of titanium alloy/thermoplastic composites using a carbon-nanotube lamina. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2019, 101, 107611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Wang, H.; Tao, J.; Zhang, X. Interface strengthening mechanisms of Ti/CFRP fiber metal laminate after adding MWCNTs to resin matrix. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 171, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tao, J.; Jin, K. The effect of MWCNTs with different diameters on the interface properties of Ti/CFRP fiber metal laminates. Compos. Struct. 2021, 266, 113818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forced CFRP and Ti6Al4V multi-material joints. Mater. Des. 2021, 210, 110118.
- Tamura, R.; Yasuda, K. Ultrasonic joining of carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic and Ti alloy. In Proceedings of the 2018 Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) CPMT Symposium Japan (ICSJ2018), Kyoto, Japan, 19–21 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Skiles, J.A.; Wightman, J.P. Heat-resistant thermoplastic/chromic acid anodized Ti-6Al-4V single lap bond evaluation. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 1988, 8, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiles, J.A.; Wightman, J.P. Heat-resistant thermoplastic/chromic acid anodized Ti-6Al-4V single lap bond evaluation. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 1988, 8, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, F.; Hu, X. A simple and effective resin pre-coating treatment on grinded, acid pickled and anodised substrates for stronger adhesive bonding between Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy and CFRP. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2022, 432, 128072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Li, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Zhong, S.; Long, W. Low residual stress C/C composite-titanium alloy joints brazed by foam interlayer. Ceram. Int. 2021, 48, 5260–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmeyer, J.; dos Santos, J.; Amancio-Filho, S.T. Effect of the friction riveting process parameters on the joint formation and performance of Ti alloy/short-fibre reinforced polyether ether ketone joints. Mater. Des. 2014, 60, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugauer, F.P.; Kandler, A.; Meyer, S.P.; Wunderling, C.; Zaeh, M.F. Induction-based joining of titanium with thermoplastics: Creation and examination of titanium-thermoplastic connections. Prod. Eng. 2019, 13, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, S.; Dang, C. Investigation of shear failure load in ultrasonic additive manufacturing of 3D CFRP/Ti structures. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 56, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, I.; Tan, C.; Tan, K. Bio-inspired patterned adhesive single-lap joints for CFRP and titanium. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 224, 109182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Faudree, M.C.; Kitahara, D.; Takase, S.; Matsumura, Y.; Jimbo, I.; Salvia, M.; Nishi, Y. A Novel Joint of 18-8 Stainless Steel and Aluminum by Partial Welding Process to Ni-Plated Carbon Fiber Junction. Mater. Trans. 2020, 61, 2292–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Inui, S.; Shiraishi, K.; Ishii, S.; Kasai, A.; Matsumura, Y.; Nishi, Y. Preparation of Ti/CFRTP joint strengthened by carbon fiber cloth. J. Adv. Sci. 2016, 28, 11001. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishi, Y.; Uchida, H.T.; Faudree, M.C.; Kaneko, S.; Kimura, H. Fracture toughness of CF-Plug joints of Ti and epoxy matrix CFRP. Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Key Engineering Materials (ICKEM 2019). Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 821, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Nishi, Y. Critical Implant Length of Carbon Fiber in Transparent Adhesive Polymer for Tensile Fracture Test. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 2005, 69, 1021–1025. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishi, Y.; Kitagawa, S.; Faudree, M.C.; Uchida, H.T.; Kanda, M.; Takase, S.; Kaneko, S.; Endo, T.; Tonegawa, A.; Salvia, M.; et al. Improvements of strength of layered polypropylene reinforced by carbon fiber by its sizing film and electron beam under protective nitrogen gas atmosphere. In Carbon Related Materials; Kaneko, S., Aono, M., Pruna, A., Can, M., Mele, P., Ertugrul, M., Endo, T., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 279–302. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, S.; Kimura, H.; Uchida, H.T.; Faudree, M.C.; Tonegawa, A.; Kaneko, S.; Salvia, M.; Nishi, Y. A New Process of Thermoplastic Polypropylene Reinforced by Interlayered Activated Carbon Fiber Treated by Electron Beam Irradiation under Nitrogen Gas Atmosphere with Oxygen Prior to Assembly and Hot-Press. Mater. Trans. 2019, 60, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, M.; Gao, S.; Mäder, E.; Sharma, H.; Wei, L.Y.; Bijwe, J. Carbon fiber surfaces and composite interphases. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 102, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, M.; Bernardo, C.; Nardin, M. Mechanical, surface and interfacial characterisation of pitch and PAN-based carbon fibres. Carbon 2000, 38, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvir, H.; Jopp, J.; Gottlieb, M. Estimation of polymer–surface interfacial interaction strength by a contact AFM technique. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 304, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Kim, B.-J. Roles of acidic functional groups of carbon fiber surfaces in enhancing interfacial adhesion behavior. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 408, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minegishi, A.; Okada, T.; Kanda, M.; Faudree, M.C.; Nishi, Y. Tensile Shear Strength Improvement of 18-8 Stainless Steel/CFRP Joint Irradiated by Electron Beam Prior to Lamination Assembly and Hot-Pressing. Mater. Trans. 2015, 56, 1169–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oguri, K.; Iwataka, N.; Tonegawa, A.; Hirose, Y.; Takayama, K.; Nishi, Y. Misting-free diamond surface created by sheet electron beam irradiation. J. Mater. Res. 2001, 16, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguri, K.; Irisawa, Y.; Tonegawa, A.; Nishi, Y. Influences of electron beam irradiation on misting and related surface condition on sapphire lens. J. Intell. Mater. Struct. 2006, 17, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, Y.; Oguri, K.; Fujita, K.; Takahashi, M.; Omori, Y.; Tonegawa, A.; Honda, N.; Ochi, M.; Takayama, K. Effects of electron beam irradiation on time to clear vision of misted dental mirror glass. J. Mater. Res. 1998, 13, 3368–3371. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Oguri, K.; Takahashi, T.; Kadowaki, A.; Tonegawa, A.; Nishi, Y. Influences of Electron Beam Irradiation on Misting for Transparent Polycarbonate Resin. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 2004, 68, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishi, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Salvia, M. Effects of electron beam irradiation on Charpy impact value of GFRP. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 1924–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faudree, M.C.; Nishi, Y.; Gruskiewicz, M. Effects of Electron Beam Irradiation on Charpy Impact Value of Short Glass Fiber (GFRP) Samples with Random Distribution of Solidification Texture Angles from Zero to 90 Degrees. Mater. Trans. 2012, 53, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanda, M.; Miyazawa, Y.; Uyama, M.; Nishi, Y. Creation of Adhesive Force between Laminated Sheets of Aluminum and Polyurethane by Homogeneous Low Energy Electron Beam Irradiation Prior to Hot-Press. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 1795–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uyama, M.; Fujiyama, N.; Okada, T.; Kanda, M.; Nishi, Y. High Adhesive Force between Laminated Sheets of Copper and Polyurethane Improved by Homogeneous Low Energy Electron Beam Irradiation (HLEBI) Prior to Hot-Press. Mater. Trans. 2014, 55, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishi, Y.; Uyama, M.; Kawazu, H.; Takei, H.; Iwata, K.; Kudoh, H.; Mitsubayashi, K. Effects of Electron Beam Irradiation on Adhesive Force of Laminated Sheet of High Strength Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and Bio-Adaptable Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Mater. Trans. 2012, 53, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishi, Y.; Faudree, M.C.; Quan, J.; Yamazaki, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Ogawa, S.; Iwata, K.; Tonegawa, A.; Salvia, M. Increasing Charpy Impact Value of Polycarbonate (PC) Sheets Irradiated by Electron Beam. Mater. Trans. 2018, 59, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitagawa, S.; Kimura, H.; Uchida, H.T.; Faudree, M.C.; Kaneko, S.; Endoh, T.; Salvia, M.; Nishi, Y. A new strengthening process of thermoplastic polypropylene reinforced by interlayered activated sizing film-free carbon fiber treated by electron beam irradiation under oxygen-rich nitrogen gas prior to assembly and hot-press. J. Compos. Mater. 2021, 55, 2975–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, A.; Nishi, Y. Improved strength in carbon fiber reinforced plastics due after electron beam irradiation. Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishi, Y.; Ishii, S.; Inui, S.; Kasai, A.; Faudree, M.C. Impact Value of CFRP/Ti Joint Reinforced by Nickel Coated Carbon Fiber. Mater. Trans. 2014, 55, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshitake, N.; Mizutani, A.; Kimura, A.; Toriyama, T.; Oguri, K.; Tonegawa, A. Effects of sheet electron beam irradiation on aircraft design stress of carbon fiber. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, Y.; Sato, H.; Iwata, K. Effects of homogeneous irradiation of electron beam with low potential on adhesive strength of polymethyl methacrylate composite sheet covered with nylon-6 film. J. Mater. Res. 2009, 24, 3503–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenhusz, R.; Reimer, L. Schichtdickenabhangigkeit der warmerzeugungdurch elektronenbestrahlung im energiebereich zwischen 9 und 100 keV (layer thickness dependency of heat generation by electron irradiation in the energy range between 9 and 100 keV). Z. Angew. Phys. 1967, 23, 396–404. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Lokensgard, E. Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications, 6th ed.; Cengage Learning: Clifton Park, NY, USA, 2016; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay, D.; Sharma, R.C.; Chakraborti, N. The Ti-Co-C system (titanium-cobalt-carbon). J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2000, 21, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancarevic, M.; Zinkevich, M.; Aldinger, F. Thermodynamic description of the Ti–O system using the associate model for the liquid phase. Comput. Coupling Phase Diagr. Thermochem. 2007, 31, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, H.; Koiwa, M. Diffusion in titanium. ISIJ Int. 1991, 31, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarian, S. Diffusion of Carbon in TiC. J. Appl. Phys. 1968, 39, 3305–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Omori, S.-I. Diffusion of Carbon in TiC. Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met. 1975, 16, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shackelford, J.F. Introduction to Materials Science for Engineers, 5th ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 194, 207, 208. [Google Scholar]
- Calderon, N.R.; Voytovych, R.; Narciso, J.; Eustathopoulos, N. Wetting dynamics versus interfacial reactivity of AlSi alloys on carbon. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 45, 2150–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastin, G.F.; Reick, G.D. Diffusion in the titanium-nickel system: II. Calculations of chemical and intrinsic diffusion coefficients. Metall. Trans. 1974, 5, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barksdale, J. Titanium. In The Encyclopedia of Chemical Elements; Hampel, C.A., Ed.; Reinhold Book Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1968; pp. 732–738, LCCN 68-29938. [Google Scholar]






| Diffusion Coefficients, D (cm2/s) in Ti | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dof C in a-Ti | Dof C in b-Ti | ||
| T (K) | D (cm2/s) | T (K) | D (cm2/s) |
| 1113 | 9 × 10−11 | 1693 | 8 × 10−5 |
| 873 | 2 × 10−12 | 1353 | 2 × 10−6 |
| D of O in a-Ti | Dof O in b -Ti | ||
| 1113 | 0.2 to 2 × 10−9 | 1693 | 1 × 10−6 |
| 873 | 6 × 10−13 | 1173 | 0.6 to 1 × 10−7 |
| Dof Ti in Ti (self diffusion) | |||
| 1693 | 6 × 10−8 | ||
| 1173 | 6 × 10−10 | ||
| Treated CF-Plug over | Treated CF-Plug over Ti/Polymer (No Glue) Joints | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated CF-Plug Joints | sb (MPa) | Joint | sb (MPa) |
| Ti/CF/ABS | 8.5 | Ti/ABS (No Glue) | 4 |
| Ti/EBCF/ABS | 18.2 | Ti/EBCF/ABS | 18.2 |
| imp. | 114% | imp. | 355% |
| Ti/CF/PC | 7 | Ti/PC (No Glue) | 1 |
| Ti/EBCF/PC | 21 | Ti/EBCF/PC | 21 |
| imp. | 200% | imp. | 2000% |
| Ti/CF/Epoxy | 25.5 | Ti/Epoxy (No Glue) | 3.5 |
| Ti/NiCF/Epoxy | 35 | Ti/NiCF/Epoxy | 35 |
| imp. | 37% | imp. | 900% |
| Treated CF-Plug over | Treated CF-Plug over [Ti/Polymer] (No Glue) Joints | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated CF-Plug Joints | csb (MPa) | Joint | csb or sb (MPa) |
| cTi/CF/ABS | 55 | Ti/ABS (No Glue) | 4 |
| cTi/EBCF/ABS | 140 | cTi/EBCF/ABS | 140 |
| imp. | 154% | imp. | 3400% |
| cTi/CF/PC | 21 | Ti/PC (No Glue) | 1 |
| cTi/EBCF/PC | 195 | cTi/EBCF/PC | 195 |
| imp. | 829% | imp. | 19,400% |
| cTi/CF/Epoxy | 283 | Ti/Epoxy (No Glue) | 3.5 |
| cTi/NiCF/Epoxy | 413 | cTi/NiCF/Epoxy | 413 |
| imp. | 45% | imp. | 11,700% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faudree, M.C.; Uchida, H.T.; Kimura, H.; Kaneko, S.; Salvia, M.; Nishi, Y. Advances in Titanium/Polymer Hybrid Joints by Carbon Fiber Plug Insert: Current Status and Review. Materials 2022, 15, 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093220
Faudree MC, Uchida HT, Kimura H, Kaneko S, Salvia M, Nishi Y. Advances in Titanium/Polymer Hybrid Joints by Carbon Fiber Plug Insert: Current Status and Review. Materials. 2022; 15(9):3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093220
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaudree, Michael C., Helmut Takahiro Uchida, Hideki Kimura, Satoru Kaneko, Michelle Salvia, and Yoshitake Nishi. 2022. "Advances in Titanium/Polymer Hybrid Joints by Carbon Fiber Plug Insert: Current Status and Review" Materials 15, no. 9: 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093220
APA StyleFaudree, M. C., Uchida, H. T., Kimura, H., Kaneko, S., Salvia, M., & Nishi, Y. (2022). Advances in Titanium/Polymer Hybrid Joints by Carbon Fiber Plug Insert: Current Status and Review. Materials, 15(9), 3220. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093220