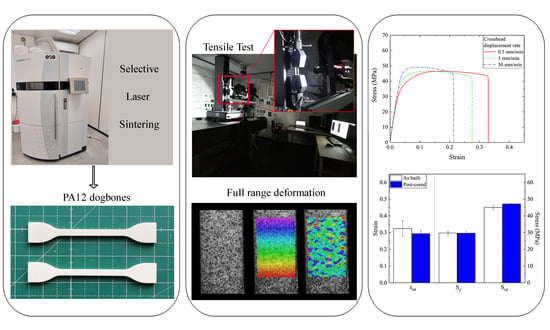
Effect of Strain Rates and Heat Exposure on Polyamide (PA12) Processed via Selective Laser Sintering
Abstract
Share and Cite
Morano, C.; Alfano, M.; Pagnotta, L. Effect of Strain Rates and Heat Exposure on Polyamide (PA12) Processed via Selective Laser Sintering. Materials 2023, 16, 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134654
Morano C, Alfano M, Pagnotta L. Effect of Strain Rates and Heat Exposure on Polyamide (PA12) Processed via Selective Laser Sintering. Materials. 2023; 16(13):4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134654
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorano, Chiara, Marco Alfano, and Leonardo Pagnotta. 2023. "Effect of Strain Rates and Heat Exposure on Polyamide (PA12) Processed via Selective Laser Sintering" Materials 16, no. 13: 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134654
APA StyleMorano, C., Alfano, M., & Pagnotta, L. (2023). Effect of Strain Rates and Heat Exposure on Polyamide (PA12) Processed via Selective Laser Sintering. Materials, 16(13), 4654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134654