Effects of Polyethylene Glycol/Porous Silica Form-Stabilized Phase Change Materials on the Performance of Asphalt Binders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
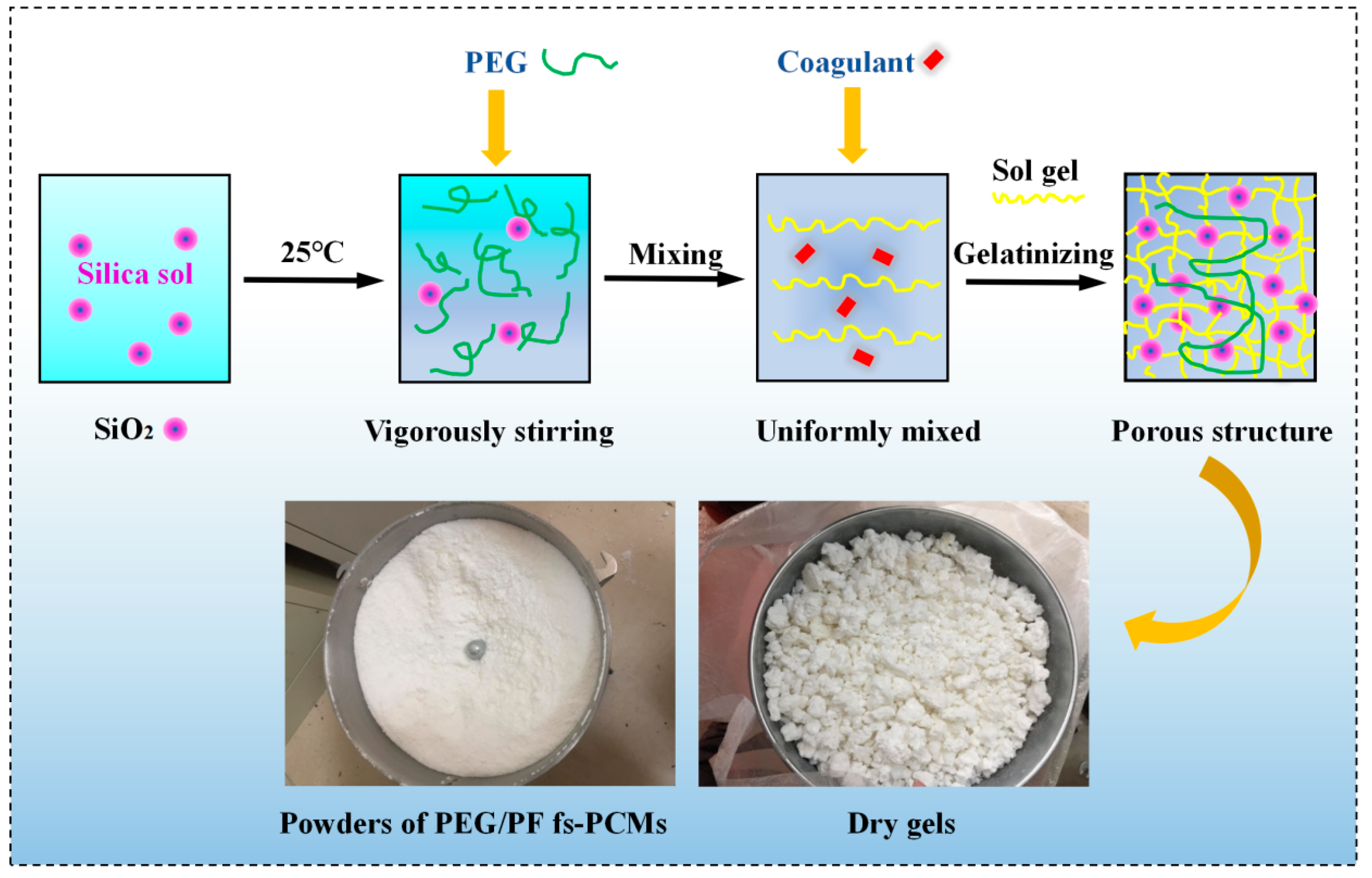
2.1. Preparation of PEG/PS-fs-PCMs
2.2. Preparation of PEG/PT fs-PCM-Modified Asphalt Binders
2.3. Characterization of Preparation of PEG/PS-fs-PCMs
2.3.1. SEM
2.3.2. DSC
2.3.3. FT-IR
2.3.4. TG
2.3.5. Leakage Test
2.4. Experimental Methods of the Modified Asphalt Binders
2.4.1. Conventional Properties Test
2.4.2. Dynamic Shear Rheometer Test (DSR)
2.4.3. Bending-Beam Rheometer Test (BBR)
2.4.4. Storage Stability Test
2.4.5. Temperature-Regulating Test
3. Results
3.1. Properties of PEG/PS-fs-PCMs
3.1.1. Morphology Characterization
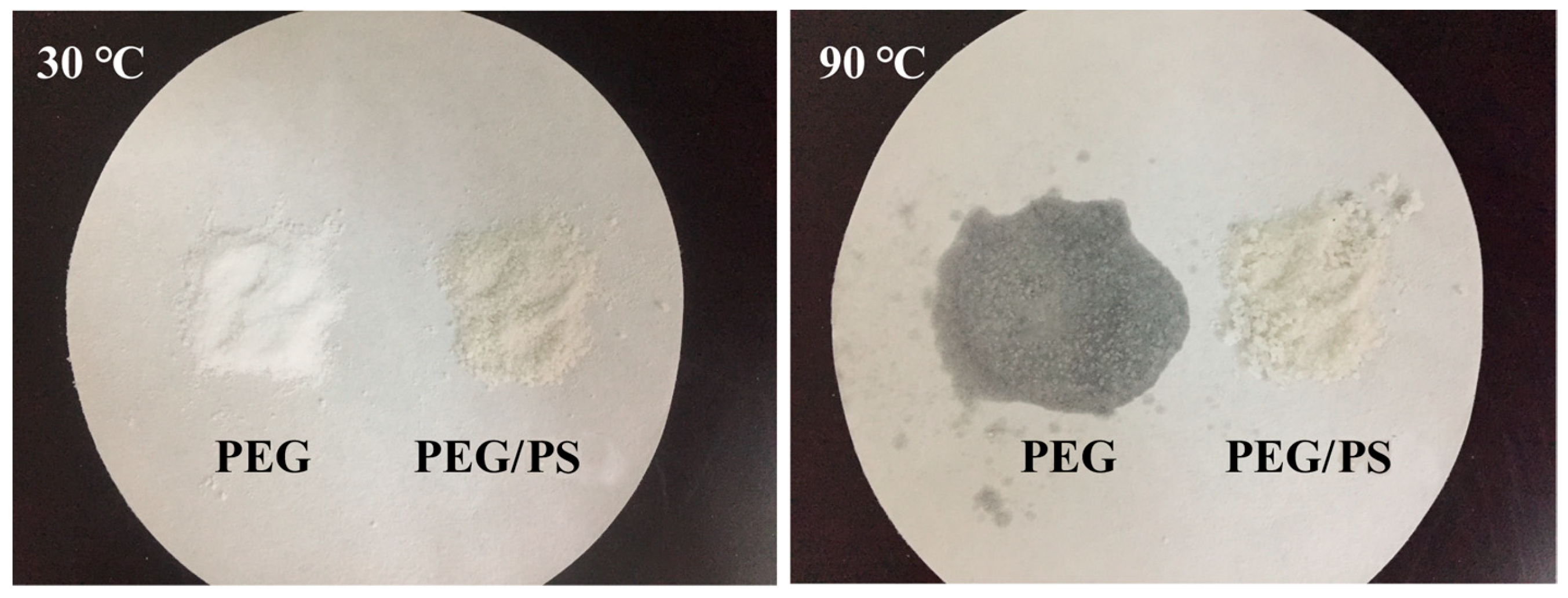
3.1.2. Form-Stability Property
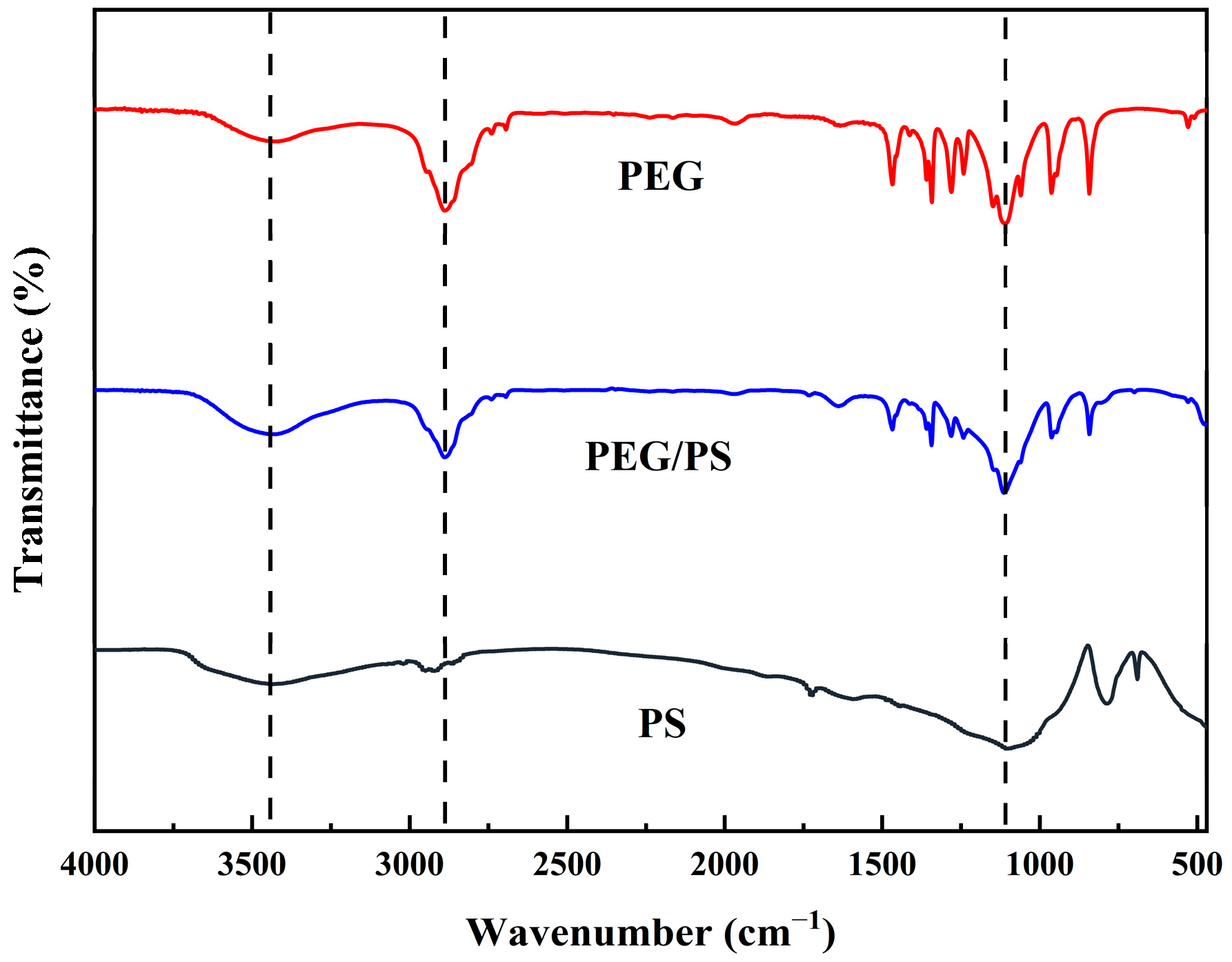
3.1.3. Chemical Structure
3.1.4. Thermal Property
3.1.5. Thermal Stability of PEG/PS-fs-PCMs
3.2. Performance of PEG/PS-fs-PCM-Modified Asphalt Binders
3.2.1. Conventional Physical Performance
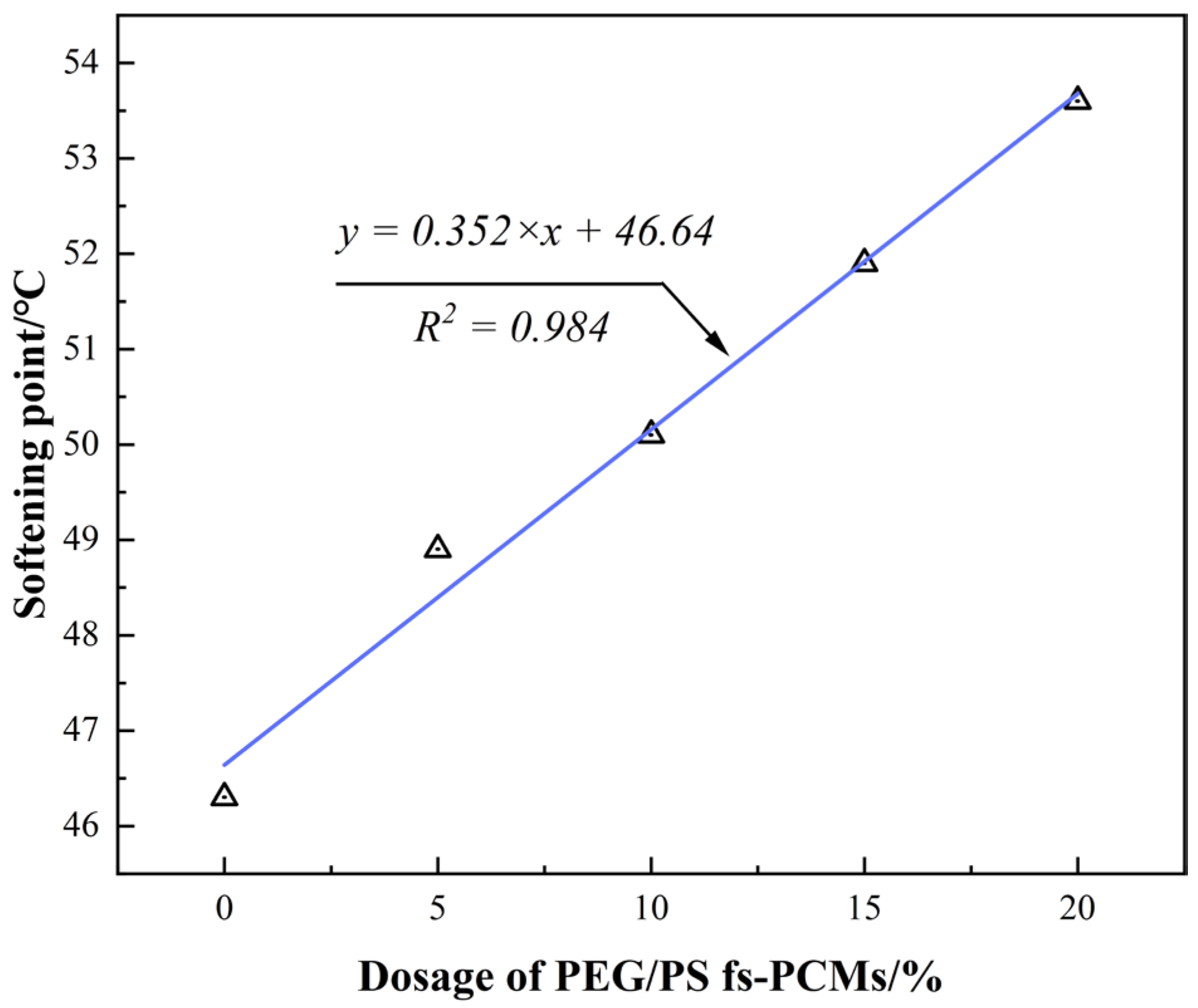
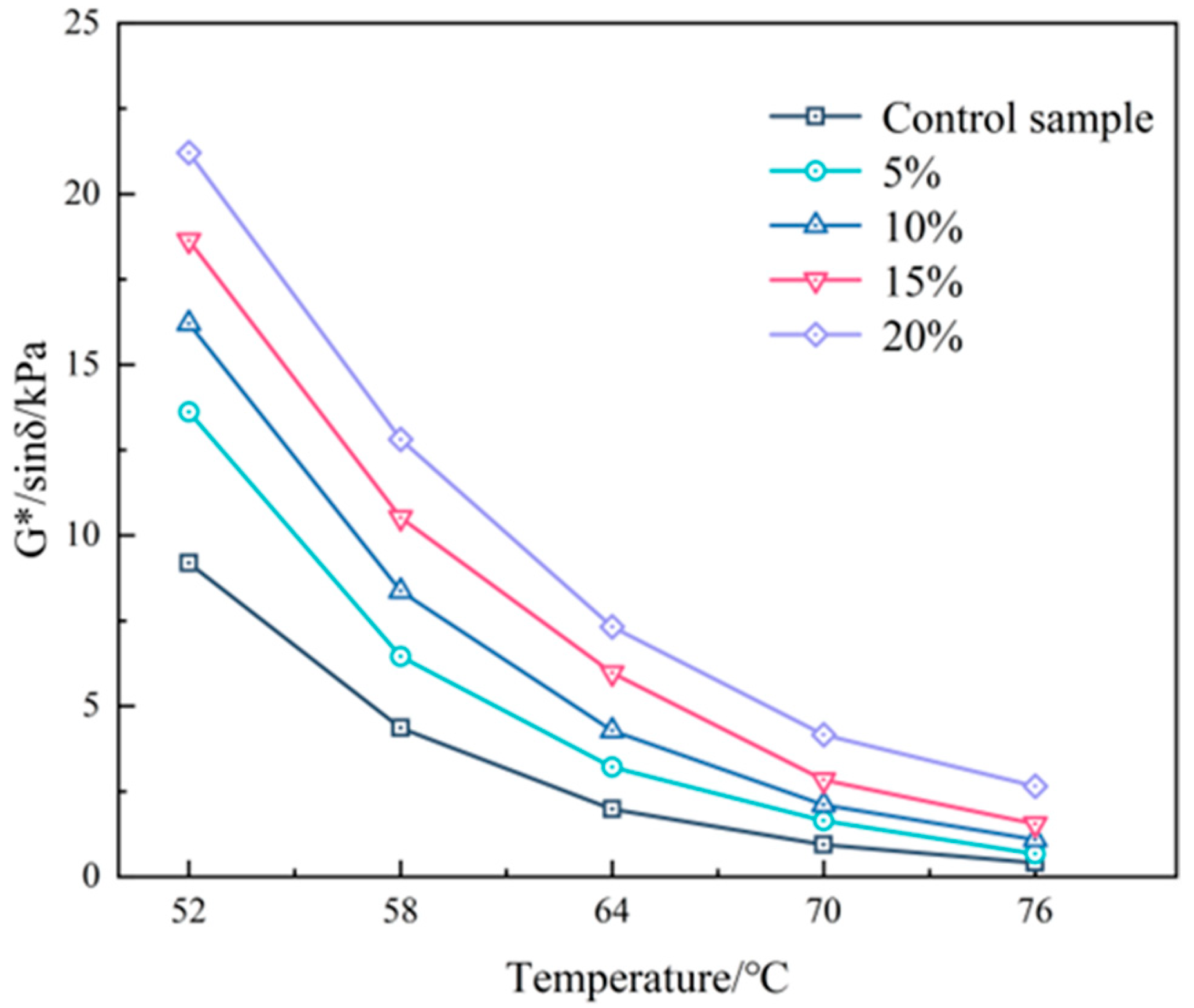
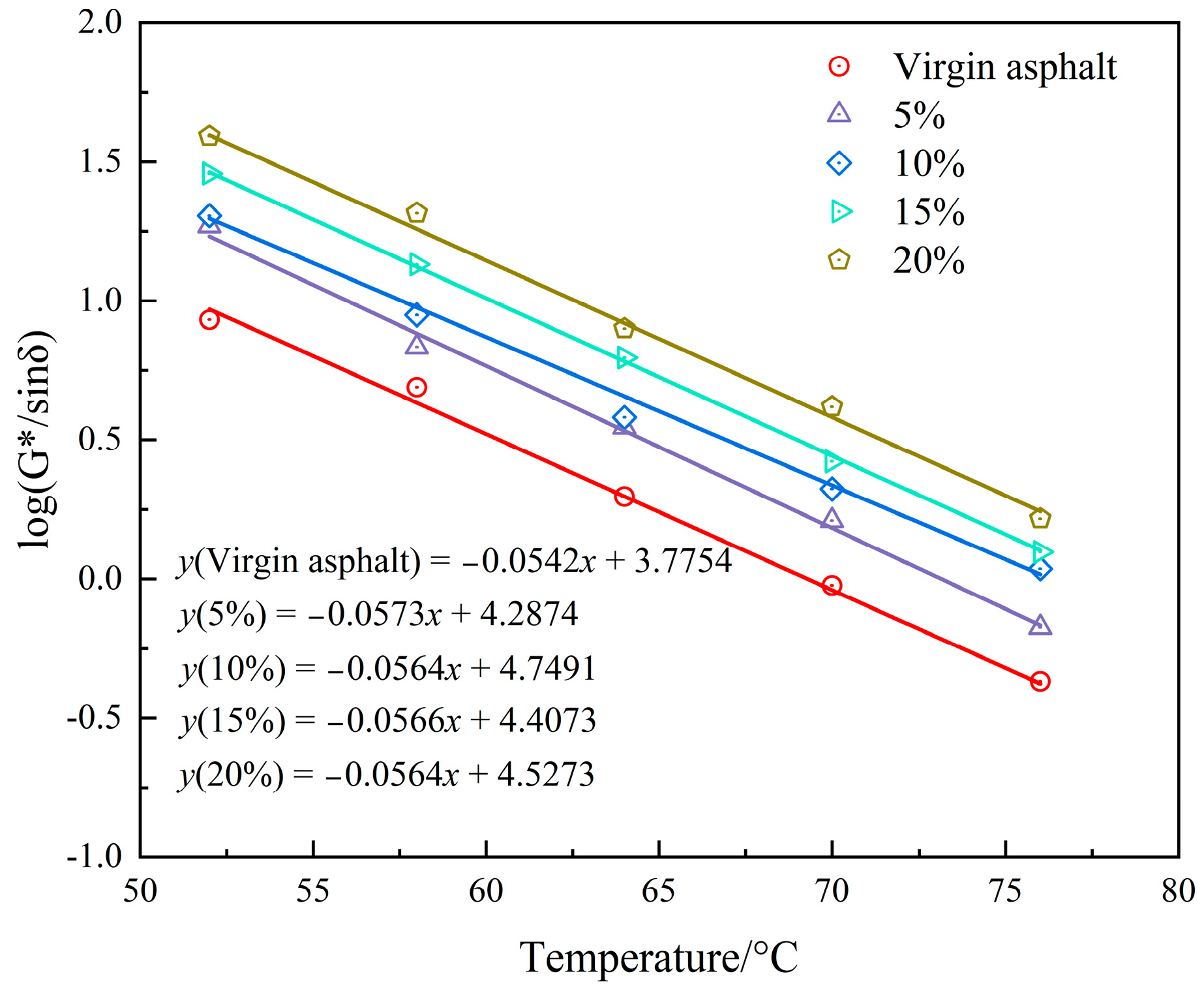
3.2.2. High-Temperature Performance
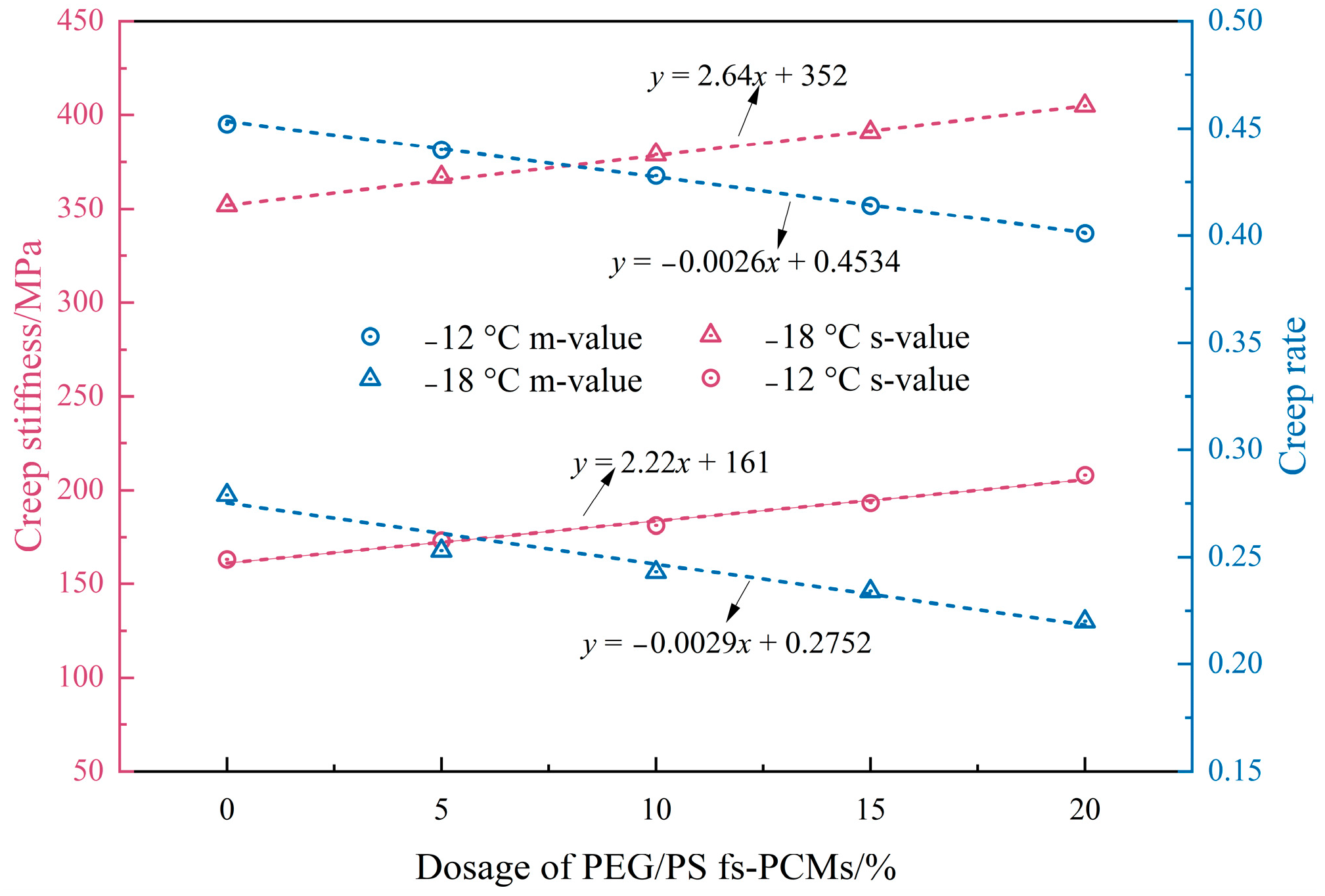
3.2.3. Low-Temperature Performance
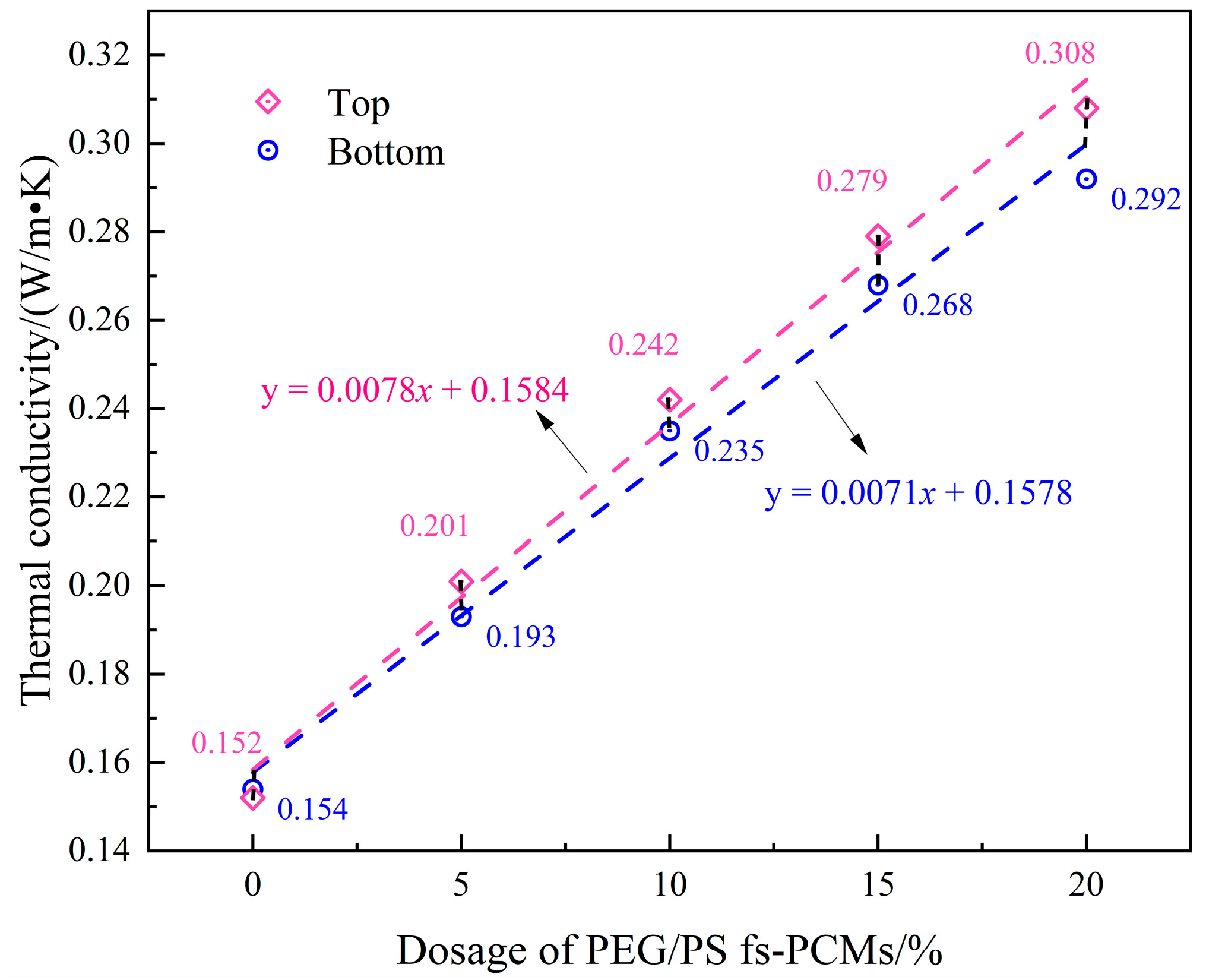
3.2.4. Compatibility Stability Performance
3.2.5. Temperature-Regulating Performance
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The prepared PEG/PS-fs-PCMs exhibit excellent thermal stability, commendable heat storage density, and appropriate phase-change temperatures for use as a thermoregulation modifier of an asphalt binder, as demonstrated via FT-IR, DSC, and TG experiments.
- (2)
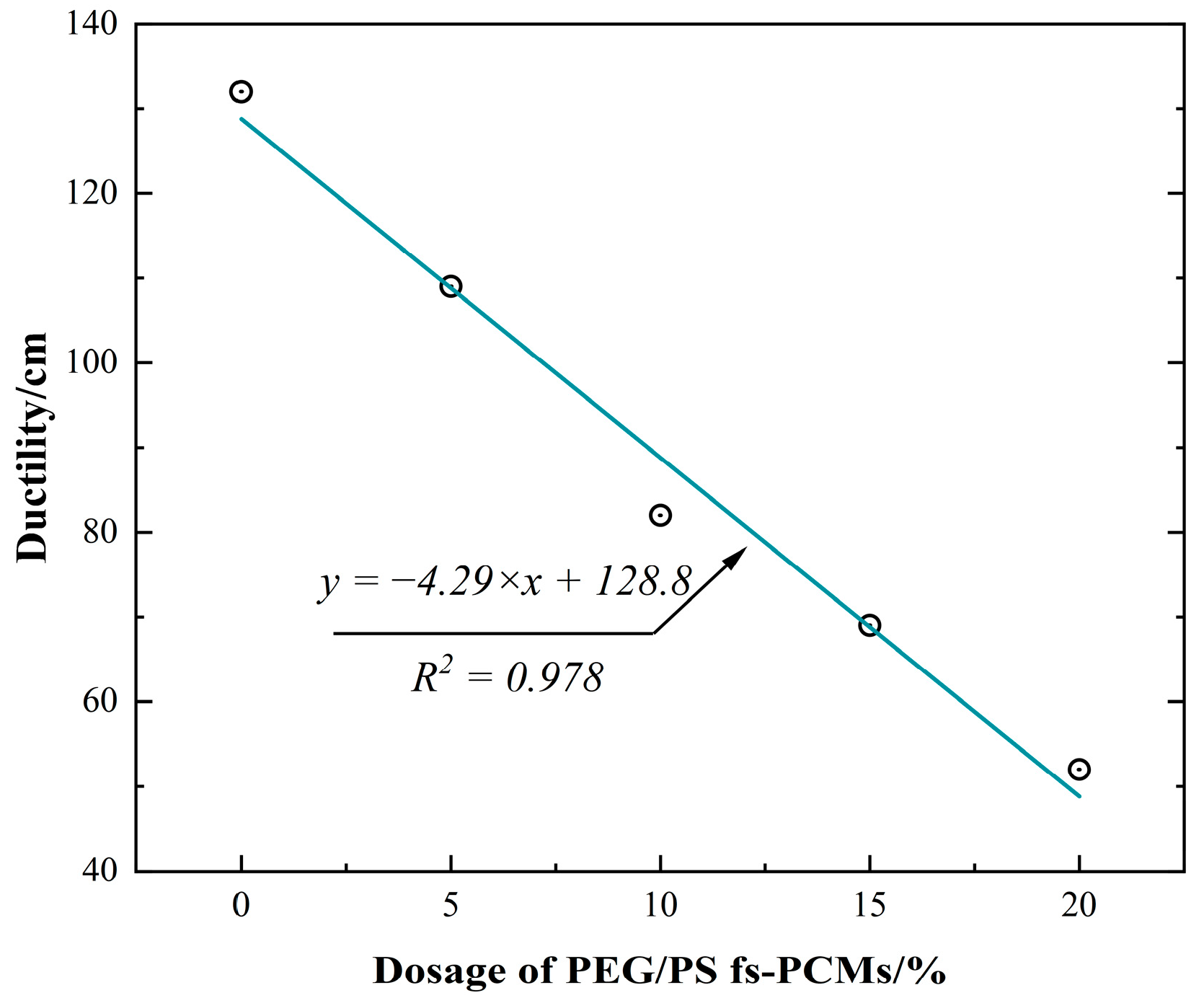
- Incorporating PEG/PS-fs-PCMs into the asphalt binder results in a decrease in the penetration and ductility, and an increase in the softening point. This may be attributed to the addition of PEG/PS-fs-PCMs weakening the cohesive force of the asphalt molecules, and limiting the ductility of the asphalt.
- (3)
- The rutting resistance index (G*/sinδ) of the asphalt binder improves with the increasing content of PEG/PS-fs-PCMs, and so does the failure temperature, suggesting that the addition of the fs-PCMs is beneficial in enhancing the rutting resistance of the asphalt binder at high temperatures.
- (4)
- The creep rate of the asphalt binder decreases, while the creep stiffness increases, due to the incorporation of PEG/PS-fs-PCMs, resulting in worse low-temperature properties. Therefore, it is not recommended to further increase the dosage of fs-PCMs.
- (5)
- Temperature regulation tests demonstrate that the addition of PEG/PS-fs-PCMs induces significant hysteresis in the asphalt binder temperature profiles, implying the outstanding temperature regulation capability of the fs-PCMs. The modified asphalt binder shows a maximum temperature difference of approximately 6.4 °C, compared to the virgin asphalt.
- (6)
- Overall, considering the high-temperature performance and excellent thermoregulation efficiency, the appropriate dosage may be determined to be 10%. Furthermore, an aging test and workability analysis will be performed in the future, for a more comprehensive evaluation of the performance of the PEG/PS-fs-PCM-modified asphalt binder.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Wan, J. Preparation of expanded graphite/polyethylene glycol composite phase change material for thermoregulation of asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Li, J.; Muhammad, Y.; Hou, D.; Zhang, F.; Yin, Y.; Duan, S. Effect of polystyrene grafted graphene nanoplatelets on the physical and chemical properties of asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; García Hernández, M.I.; Wang, Z.; Nie, S.; Zhang, G. Effect of ultraviolet radiation in different wavebands on bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 159, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddig, E.A.A.; Feng, C.P.; Ming, L.Y. Effects of ethylene vinyl acetate and nanoclay additions on high-temperature performance of asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhija, M.; Saboo, N.; Yadav, A.K.; Rath, C. Laboratory study on the suitability of nano-silica as a modifier for asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 302, 124406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadykova, A.Y.; Ilyin, S.O. Rheological and adhesive properties of nanocomposite bitumen binders based on hydrophilic or hydrophobic silica and modified with bio-oil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, M.; Wilmanski, A. Evaluation of Laboratory Methods of Determination of SBS Content in Polymer-Modified Bitumens. Materials 2020, 13, 5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Si, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H. Molecular dynamics study on influence of Nano-ZnO/SBS on physical properties and molecular structure of asphalt binder. Fuel 2020, 263, 116777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadykova, A.Y.; Ilyin, S.O. Bitumen improvement with bio-oil and natural or organomodified montmorillonite: Structure, rheology, and adhesion of composite asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 364, 129919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fan, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, M. Durability Evaluation Study for Crumb Rubber–Asphalt Pavement. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Pei, J.; Shen, C.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Hu, D. Performance and Reinforcement Mechanism of Modified Asphalt Binders with Nano-Particles, Whiskers, and Fibers. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Ma, B.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, H. Influence of NiTi alloy phase change heat-storage particles on thermophysical parameters, phase change heat-storage thermoregulation effect, and pavement performance of asphalt mixture. Renew. Energy 2019, 141, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Chen, S.-S.; Wei, K.; Liu, F.-W.; Zhou, X.-Y. Analysis of thermoregulation indices on microencapsulated phase change materials for asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Khan, Z.; Ghafoor, A. A review of performance enhancement of PCM based latent heat storage system within the context of materials, thermal stability and compatibility. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 115, 132–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, H.; Yan, L.; Yi, Z.; Min, X.; Hu, J. Preparation and Characterization of Microencapsulated Phase Change Materials with Binary Cores and Poly (allyl methacrylate) (PALMA) Shells Used for Thermo-regulated Fibers. Thermochim. Acta 2017, 655, 262–268. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Ma, B.; Wen, R.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Fang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X. Polyethylene glycol/Cu/SiO2 form stable composite phase change materials: Preparation, characterization, and thermal conductivity enhancement. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 58740–58748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Alva, G.; Huang, X.; Fang, G. Synthesis, characterization and properties of palmitic acid/high density polyethylene/graphene nanoplatelets composites as form-stable phase change materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 155, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Rao, Z. Experimental study on the thermal performance of graphene and exfoliated graphite sheet for thermal energy storage phase change material. Thermochim. Acta 2017, 647, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giropaloma, J.; Alshannaq, R.; Fernández, A.I.; Farid, M.M. Preparation and Characterization of Microencapsulated Phase Change Materials for Use in Building Applications. Materials 2015, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Hu, S.; Tian, J.; Li, Y. Laboratory investigation of phase change effect of polyethylene glycolon on asphalt binder and mixture performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 212, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zhou, X.Y.; Ma, B.; Ning, L.; Ren, J.P.; Chang, Y.J. The mechanism of different thermoregulation types of composite shape-stabilized phase change materials used in asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 547–558. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Ma, B.; Si, W.; Zhou, X.; Li, C. Preparation and analysis of composite phase change material used in asphalt mixture by sol–gel method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Riara, M.; Wan, J.; Li, Y. Thermal and rheological performance of asphalt binders modified with expanded graphite/polyethylene glycol composite phase change material (EP-CPCM). Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 194, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, M.R.; Refaa, Z.; Worlitschek, J.; Stamatiou, A.; Partl, M.N.; Bueno, M. Thermal and rheological characterization of bitumen modified with microencapsulated phase change materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 215, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarı, A.; Alkan, C.; Biçer, A. Synthesis and thermal properties of polystyrene-graft-PEG copolymers as new kinds of solid–solid phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 133, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, C.; Günther, E.; Hiebler, S.; Himpel, M. Complexing blends of polyacrylic acid-polyethylene glycol and poly(ethylene-co-acrylic acid)-polyethylene glycol as shape stabilized phase change materials. Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 64, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, H.; Cao, X.; Tang, B. Phase change characteristics of shape-stabilized PEG/SiO2 composites using calcium chloride-assisted and temperature-assisted sol gel methods. Solar Energy 2014, 103, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, K.; Wang, S.; Ma, B.; Wang, X.; Shi, W.; Xu, J. Effect of high-temperature-resistant epoxy resin/polyethylene glycol 2000 composite stereotyped phase change material particles on asphalt properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 300, 124007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Huang, H.; Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Sheng, X.; Li, X.; Lu, X.; Qu, J. Melamine foam/polyethylene glycol composite phase change material synergistically modified by polydopamine/MXene with enhanced solar-to-thermal conversion. Renew. Energy 2021, 171, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Zhu, H. Preparation and properties of polyethylene glycol/unsaturated polyester resin/graphene nanoplates composites as form-stable phase change materials. Thermochim. Acta 2018, 665, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, S.; Karaipekli, A.; Sarı, A.; Biçer, A. Polyethylene glycol (PEG)/diatomite composite as a novel form-stable phase change material for thermal energy storage. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X. Preparation and properties of palmitic acid/SiO2 composites with flame retardant as thermal energy storage materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2011, 95, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.T.; Li, J.H.; Ma, H.W.; Yang, J. The preparation of a green shape-stabilized composite phase change material of polyethylene glycol/SiO2 with enhanced thermal performance based on oil shale ash via temperature-assisted sol-gel method. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 132, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Ma, B.; Wen, R.; Min, X.; Huang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fang, M.; Wu, X. Preparation and performance of novel form-stable composite phase change materials based on polyethylene glycol/White Carbon Black assisted by super-ultrasound-assisted. Thermochim. Acta 2016, 638, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Deng, Y.; Guan, W.; Wang, X.; Qian, T. Preparation of paraffin/porous TiO2 foams with enhanced thermal conductivity as PCM, by covering the TiO2 surface with a carbon layer. Appl. Energy 2016, 171, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, N.; Nomura, T.; Zhu, C.; Habazaki, H.; Akiyama, T. Cotton-derived carbon sponge as support for form-stabilized composite phase change materials with enhanced thermal conductivity. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 192, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E20 T0606-2011; Softening Point of Bitumen (Ring-and-Ball Apparatus). Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- JTG E20 T0604-2011; Penetration of Bituminous Materials. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- JTG E20 T0605-2011; Ductility of Asphalt Materials. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.






| Test Indices | Technical Requirements | Measured Values | Specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Softening point (°C) | ≥46 | 48.1 | T0606-2011 |
| Dynamic viscosity (60 °C Pa s) | ≥180 | 223 | T0620-2011 |
| Ductility (10 °C cm) | ≥25 | 37 | T0605-2011 |
| Penetration (25 °C mm) | 60–80 | 66.3 | T0604-2011 |
| Samples | Tm (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) | Tc (°C) | ΔHc (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEG | 61.2 | 182.4 | 34.9 | 171.3 |
| PEG/PS-fs-PCMs | 61.5 | 121.6 | 33.8 | 114.7 |
| Samples | Control Sample | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.975 | 0.964 | 0.951 | 0.972 | 0.968 |
| Failure temperature | 68.1 °C | 73.2 °C | 77.4 °C | 78.1 °C | 82.2 °C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Pan, G.; He, L.; Zou, L. Effects of Polyethylene Glycol/Porous Silica Form-Stabilized Phase Change Materials on the Performance of Asphalt Binders. Materials 2023, 16, 5293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155293
Wang H, Pan G, He L, Zou L. Effects of Polyethylene Glycol/Porous Silica Form-Stabilized Phase Change Materials on the Performance of Asphalt Binders. Materials. 2023; 16(15):5293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155293
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hao, Gui Pan, Lihong He, and Ling Zou. 2023. "Effects of Polyethylene Glycol/Porous Silica Form-Stabilized Phase Change Materials on the Performance of Asphalt Binders" Materials 16, no. 15: 5293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155293
APA StyleWang, H., Pan, G., He, L., & Zou, L. (2023). Effects of Polyethylene Glycol/Porous Silica Form-Stabilized Phase Change Materials on the Performance of Asphalt Binders. Materials, 16(15), 5293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16155293





