A Review on the Analysis of Thermal and Thermodynamic Aspects of Grain Refinement of Aluminum-Silicon-Based Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Objectives
- Reducing the grain size compared to other elements.
- Solidification by thermal analysis, including phenomena and parameters that take place during solidification at slow rate (~1 °C/s).
- The alloy microstructure and whether there is an effect on the alloy mechanical behavior.
- Intermetallic formation. Once the grain refiner is present in the alloy, the intermetallics associated with the additions become an integral part of the microstructure. Therefore, it is then possible to study them under various experimental conditions. In addition, it is possible to study the interaction of these intermetallics with the different components of the microstructure.
- The interaction between the Sr modifier and the grain refiner (Al-10Ti, Al-5Ti-1B, Al-4B), the interaction between silicon and titanium, and their competing influence on the morphology of the eutectic silicon, on the size of the grains and on the shape of the dendritic α-Al phase.
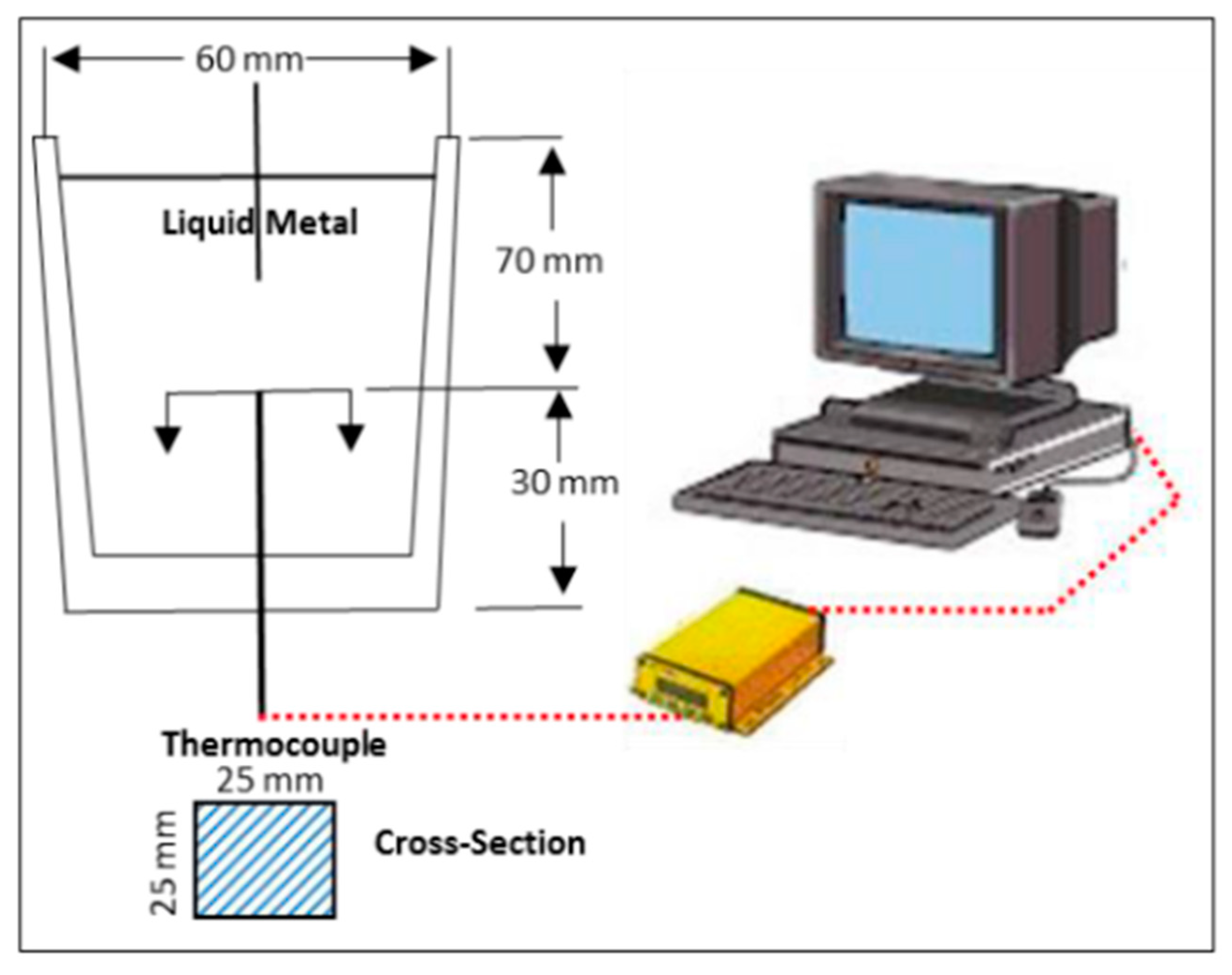
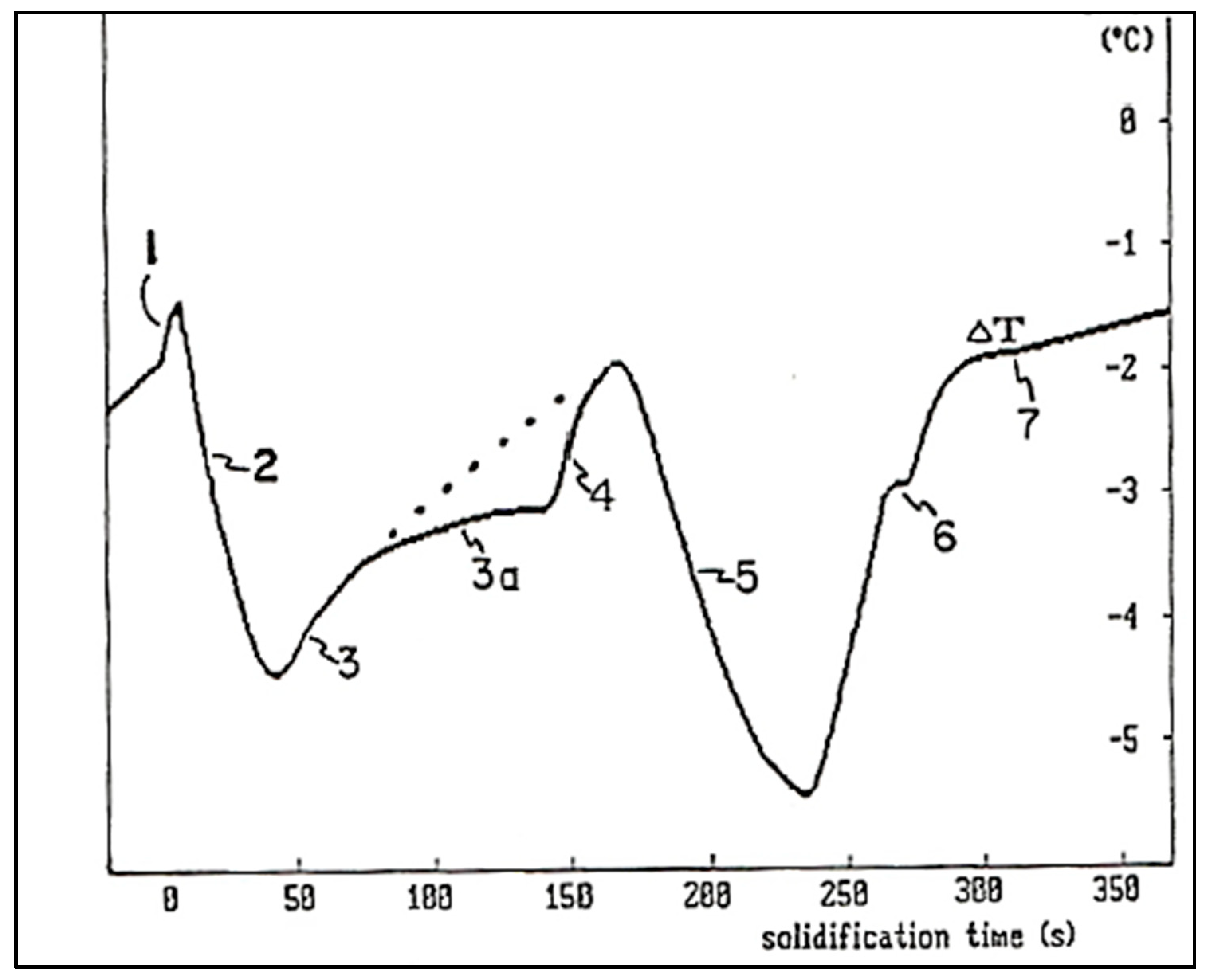
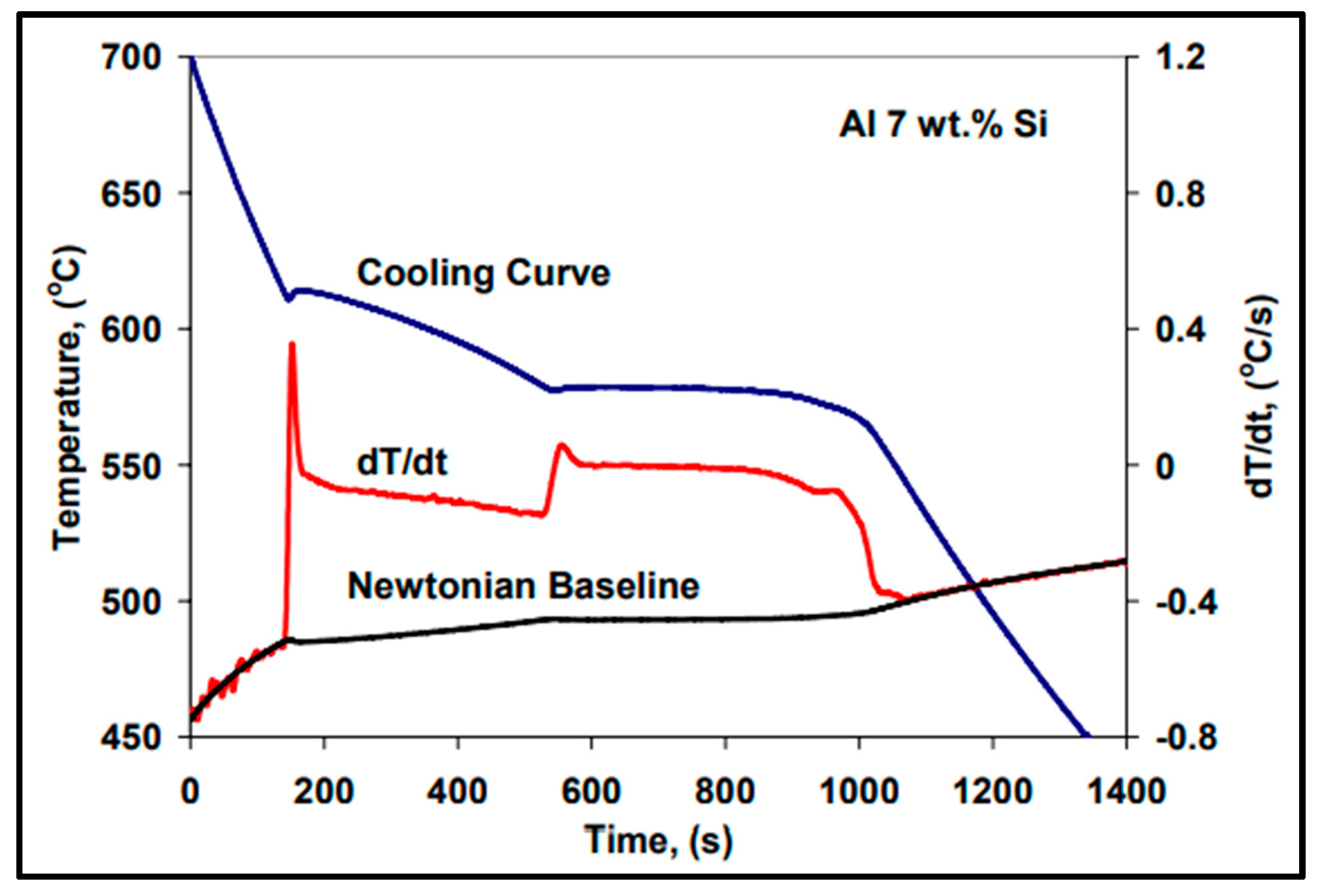
2.1. Thermal Analysis Method
2.2. Thermal Concept
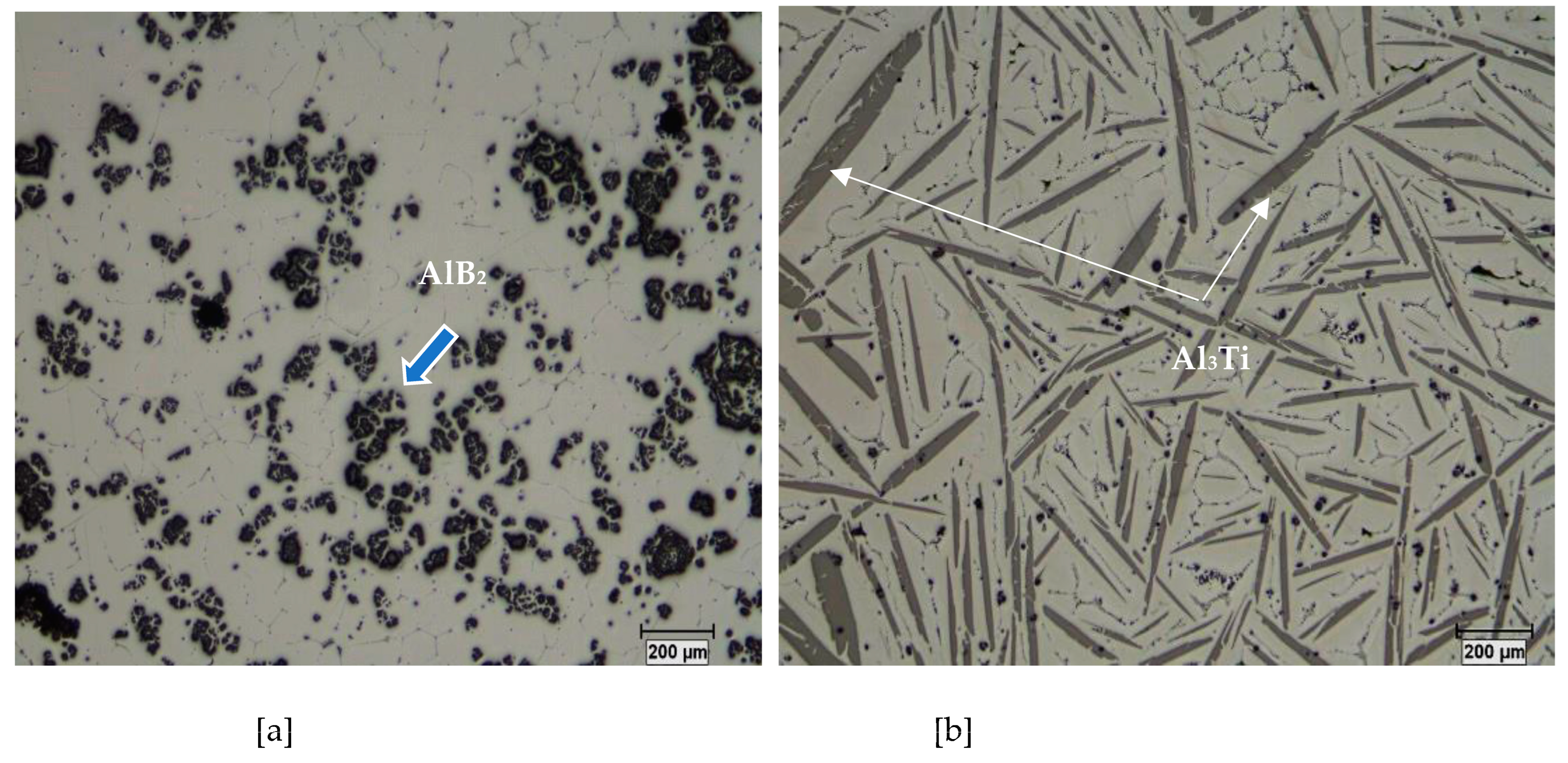
3. Al-B and Al-Ti Systems
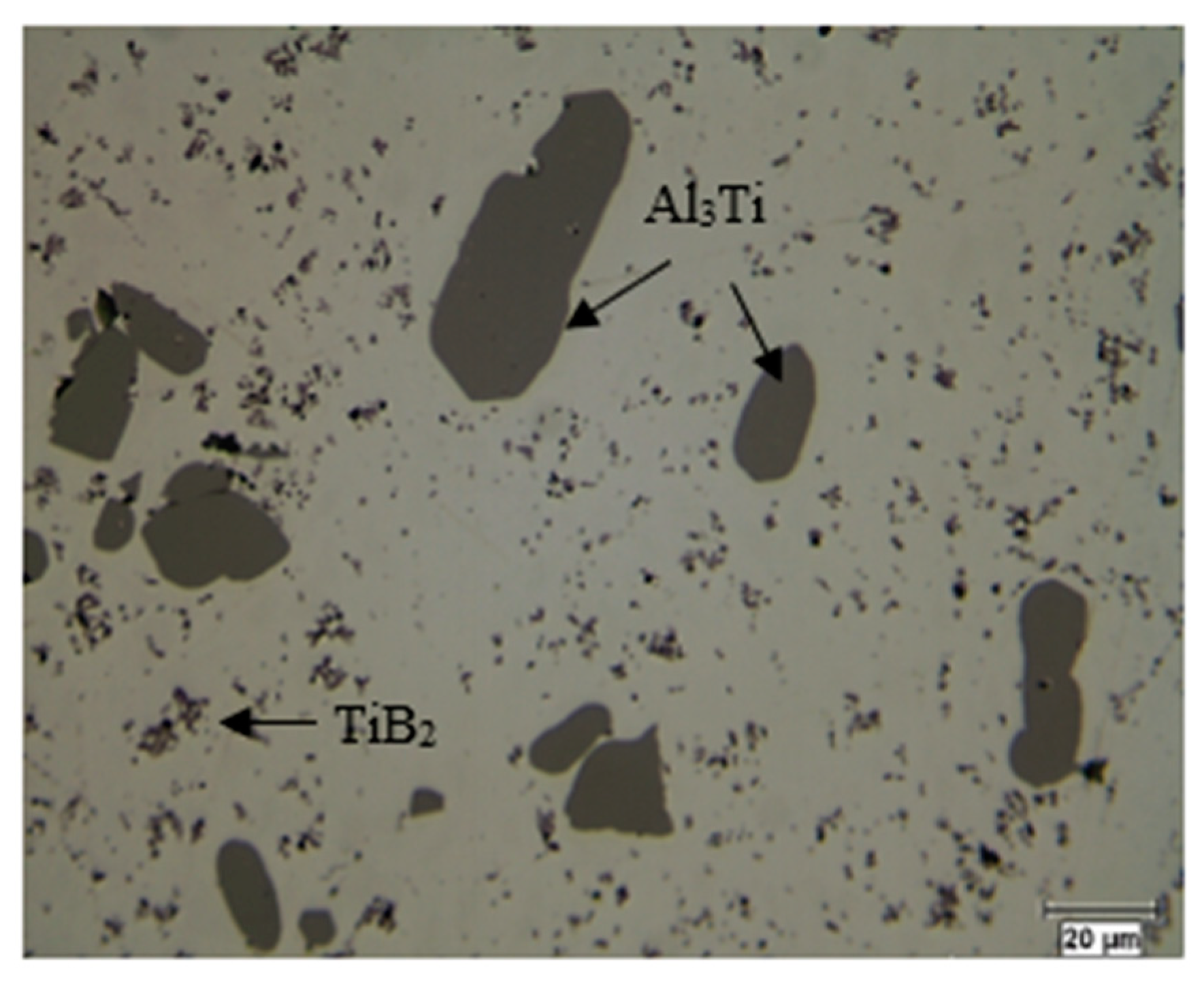
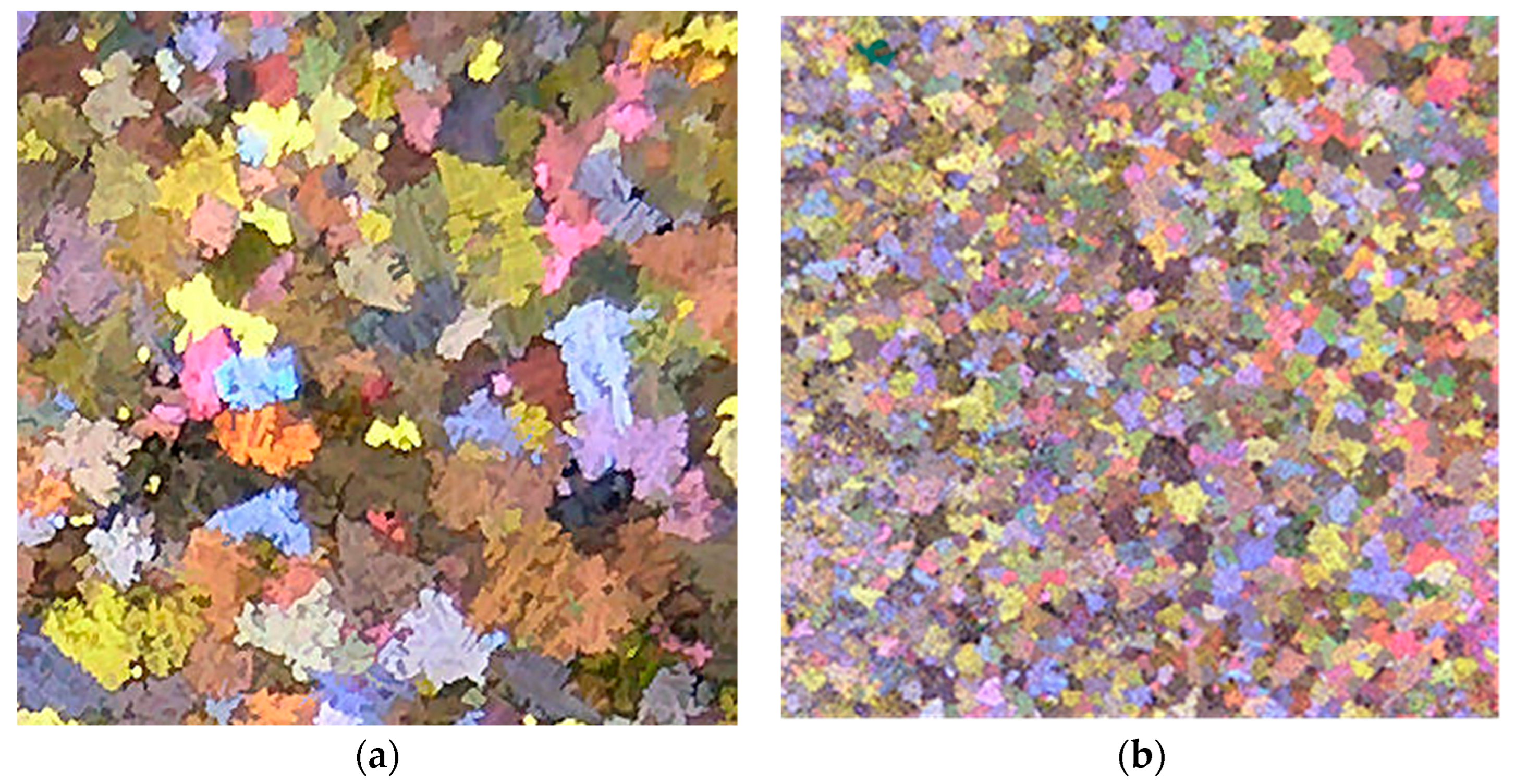
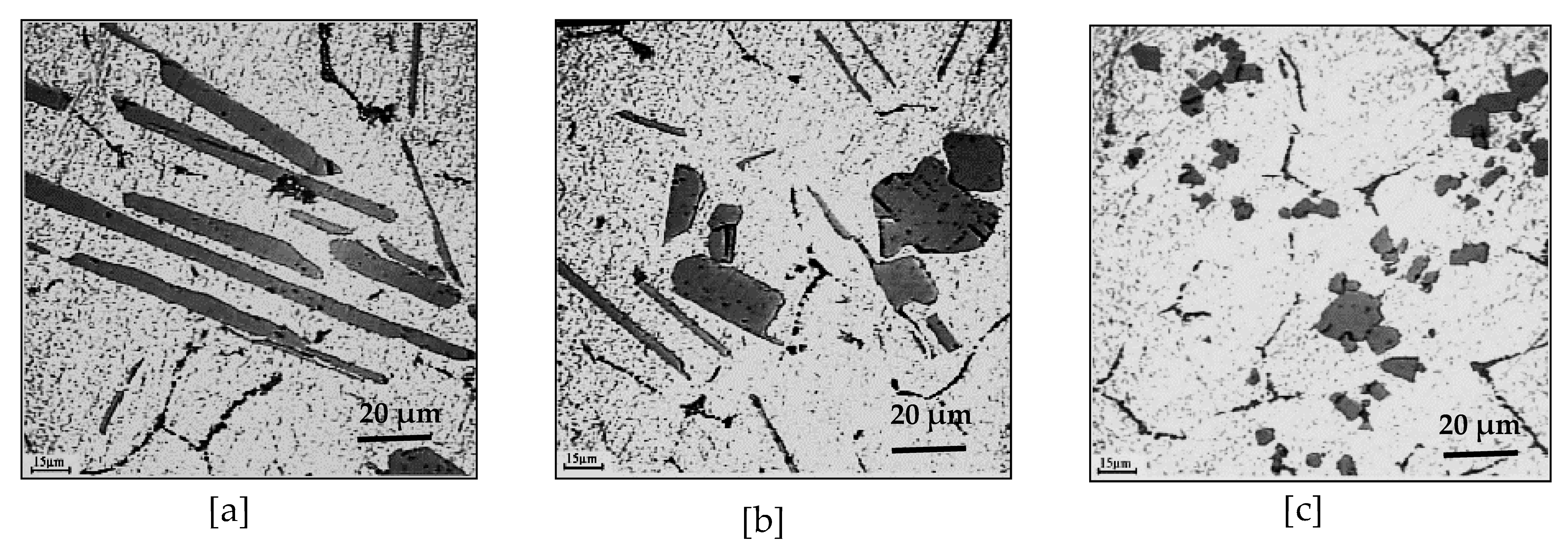
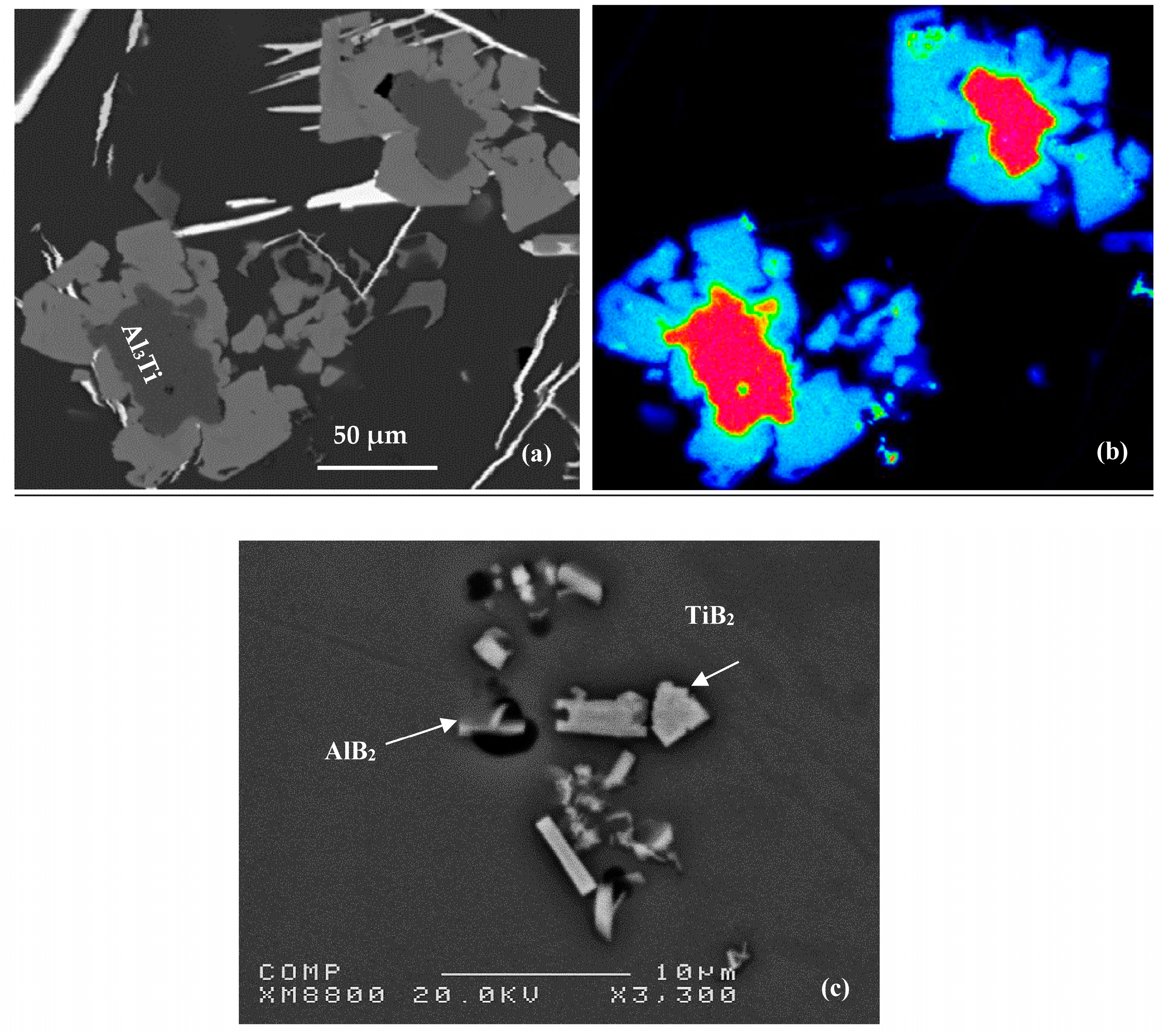
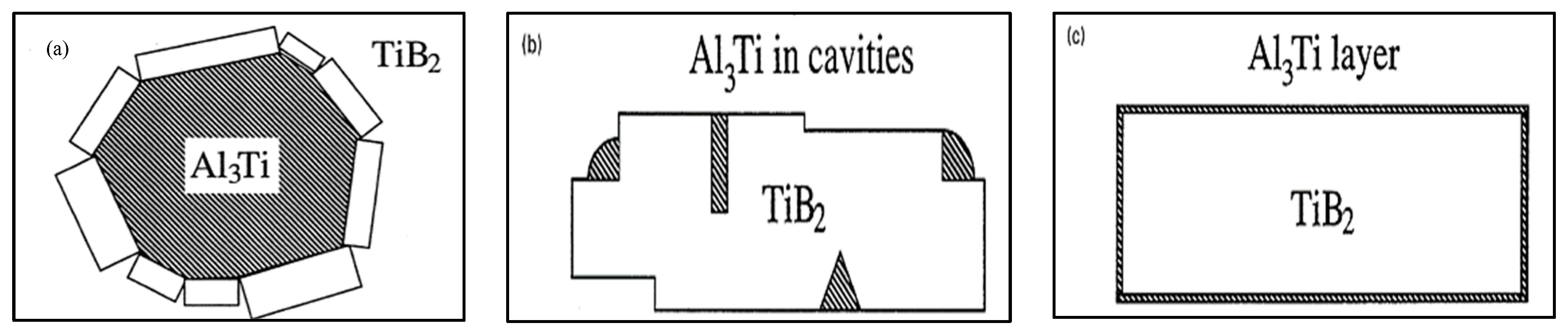
4. Al-Ti-B System
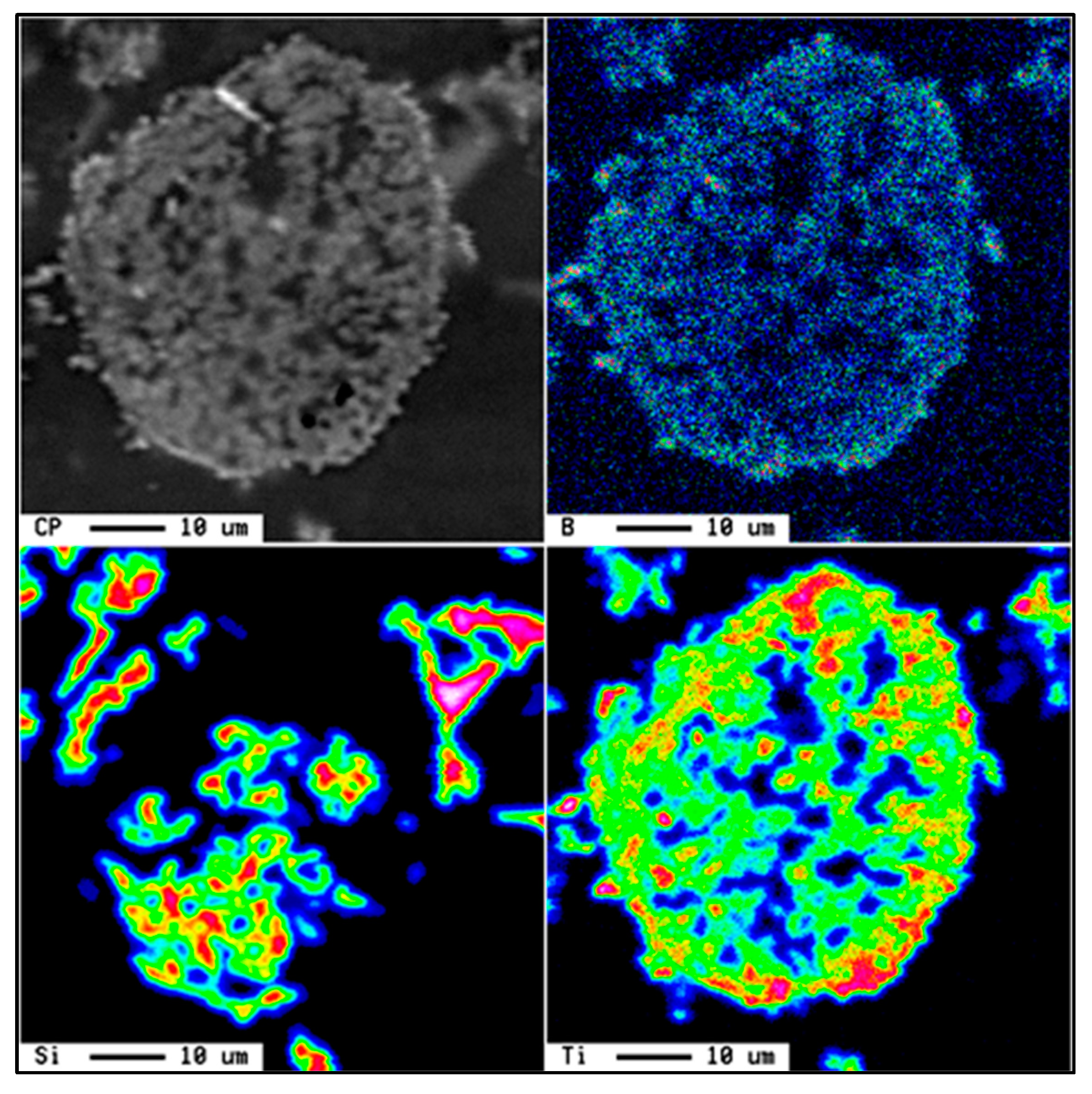
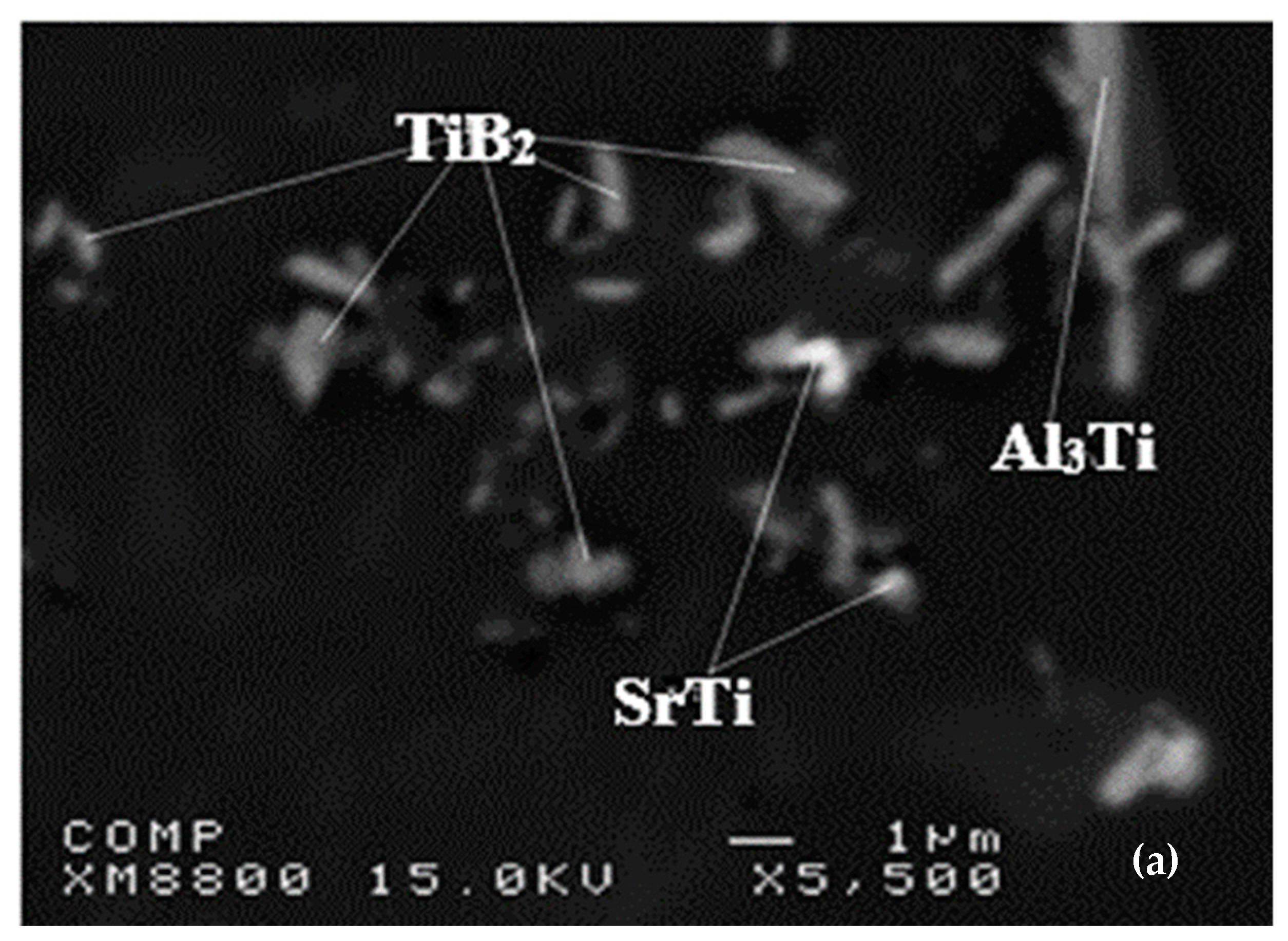
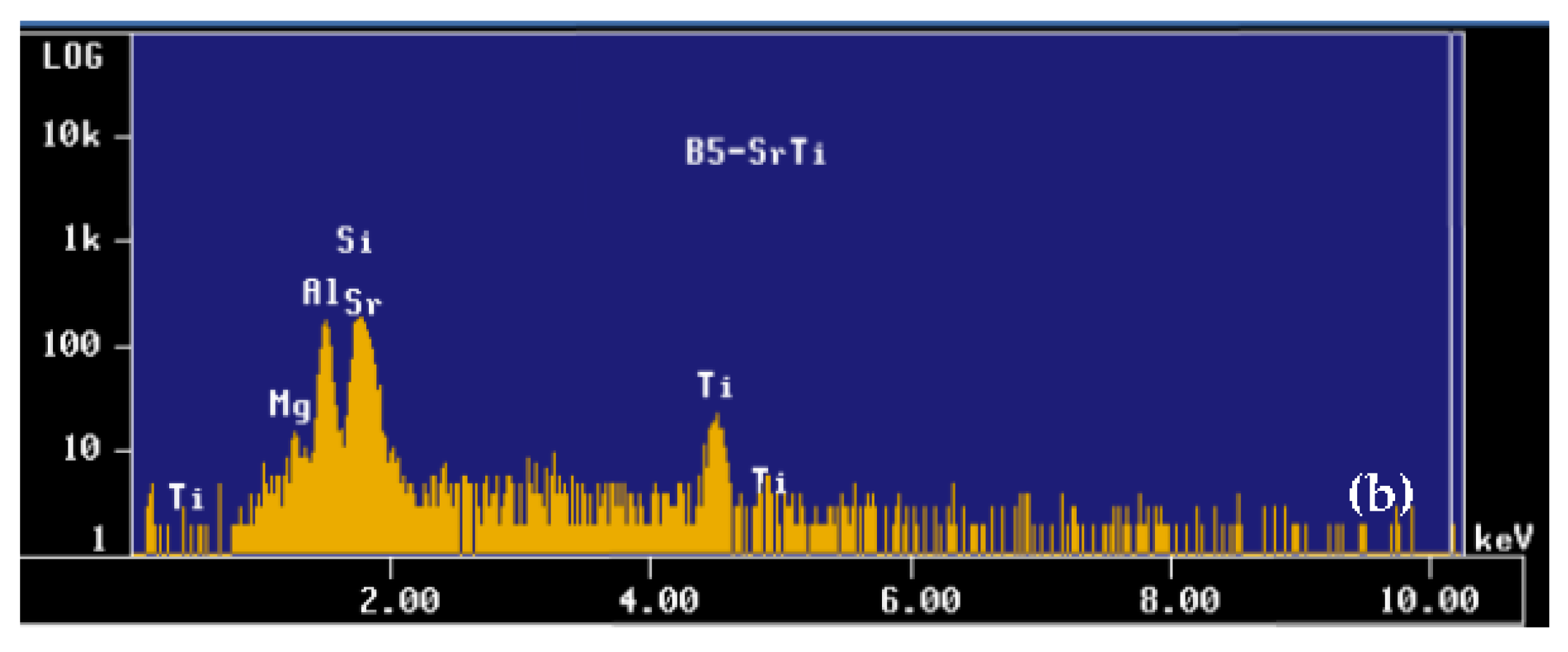
 Ti6Si2B. Figure 7 shows the X-ray mapping of the Al-Ti-Si-B phase.
Ti6Si2B. Figure 7 shows the X-ray mapping of the Al-Ti-Si-B phase.5. Al-Ti-C System
 Al4C3 +3 Ti
Al4C3 +3 Ti
 3Ti3AlC + Al
3Ti3AlC + Al
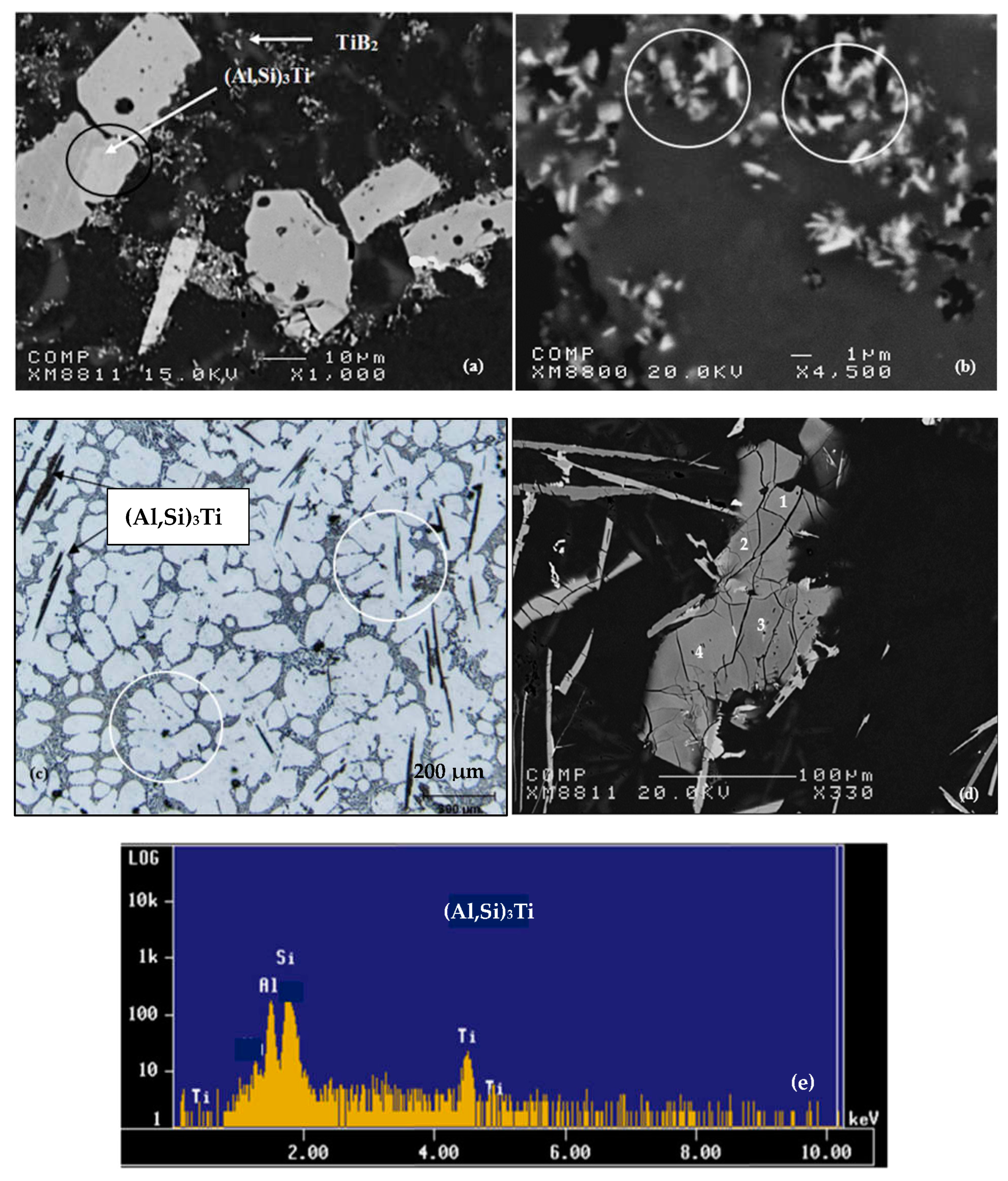
6. Si-TiAl3 Interaction
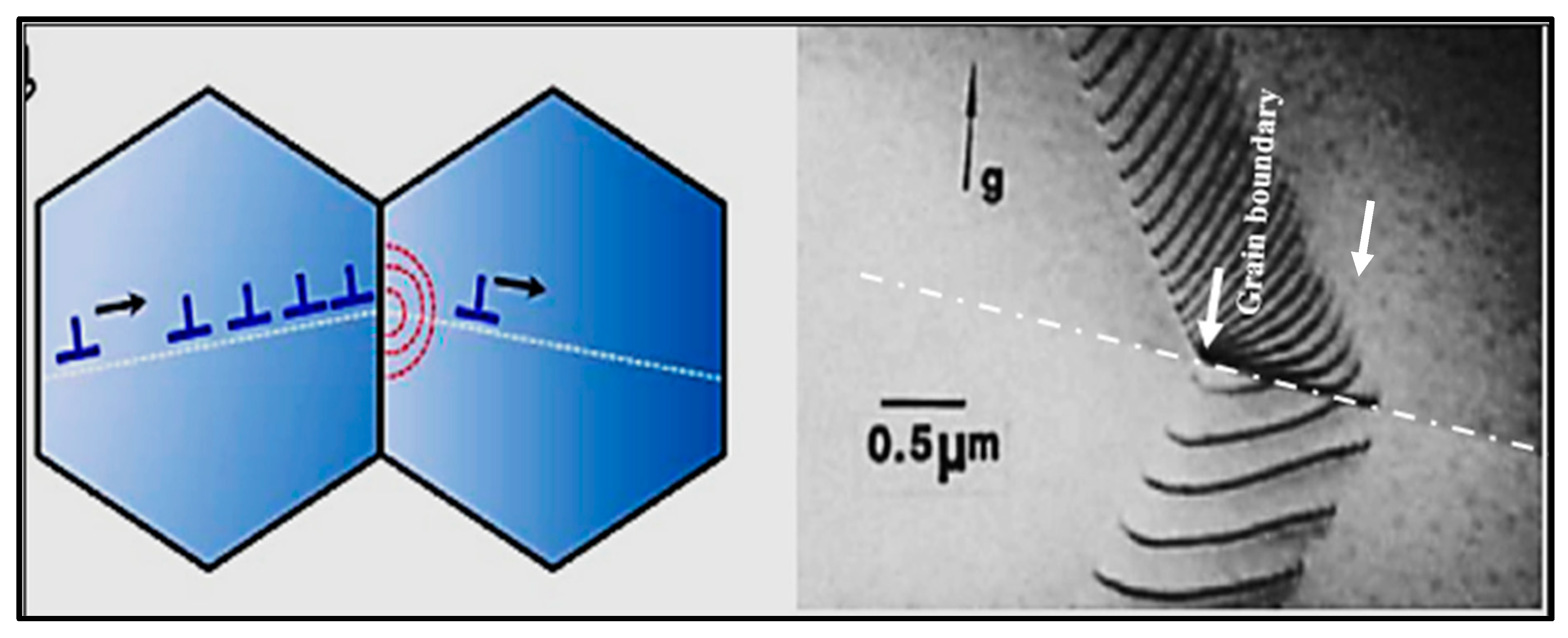
7. Nucleation Phenomenon
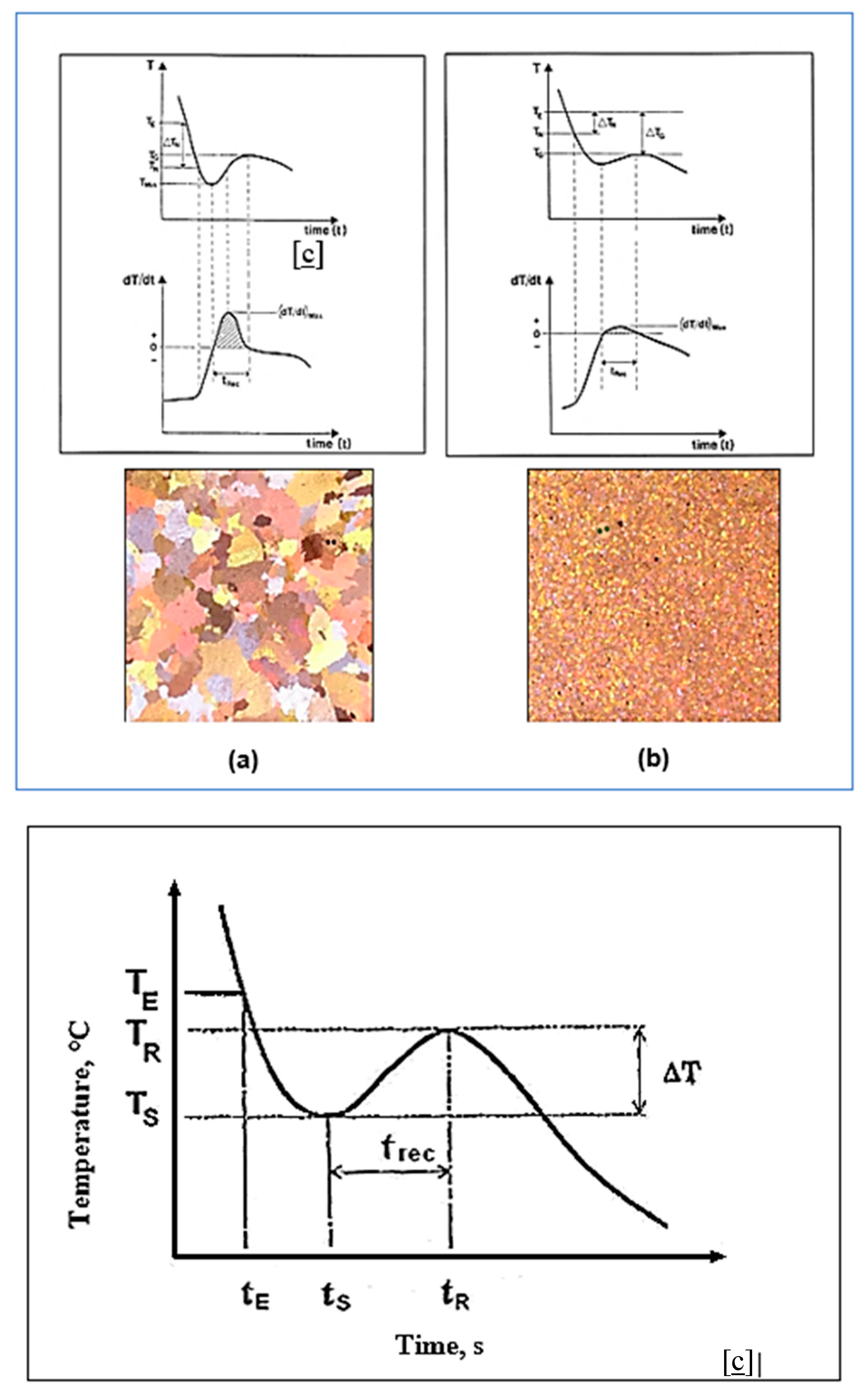
8. Solidification Parameters
- TE = The liquidus equilibrium temperature.
- TG = The steady state growth temperature of the molten metal.
- TN = The onset of nucleation temperature.
- TMIN = The temperature at which the newly nucleated crystals have grown to such an extent that the latent heat released swings out of equilibrium. The period of time required for this reaction is termed the recalescence period (tRec).
9. Calculation of Solid Fraction
- -
- QL: latent heat of solidification (J);
- -
- V: volume of the sample (m3);
- -
- ρ: volumetric mass (kg/m3);
- -
- Cp: specific heat of metal (J/kg °C);
- -
- T: temperature of the metal (°C);
- -
- t: time (s);
- -
- h: coefficient of heat transfer (J/m2s °C);
- -
- A: surface (m2);
- -
- T0: ambient temperature (°C).
10. Duplex Theory of Nucleation
11. Combined Effect of Ti/B and Sr
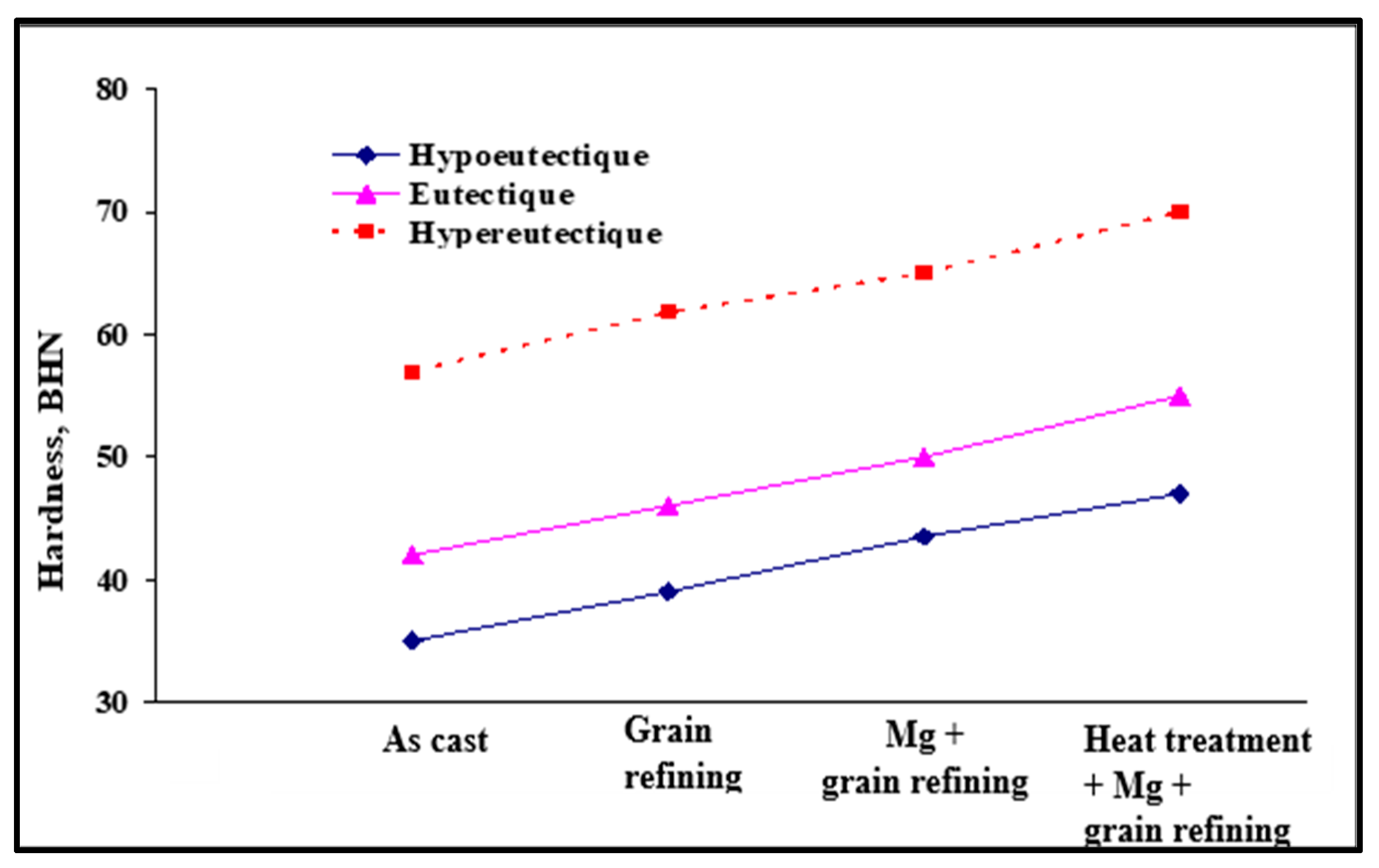
12. Grain Size–Mechanical Properties Relationship
- Re0.2: conventional elastic limit (MPa);
- σ0: constant (MPa);
- k: parameter whose value depends on the metal;
- d: grain size (mm or µm).
13. Conclusions
- 1-
- Undercooling and recalescence temperatures increase with the initial increase in titanium concentration. If the concentration reaches approximately 0.25%, a rapid decrease in these temperatures is observed. Thereafter, the temperatures increase again with Ti concentration and eventually become constant.
- 2-
- The undercooling parameter decreases as a function of the Ti concentration and, from a concentration of around 0.20%, this parameter becomes zero.
- 3-
- For the recalescence temperature parameter, for a concentration of more than 0.20% Ti, it can be zero. Otherwise, the number of experimental results is insufficient to determine the exact variation.
- 4-
- The presence of excess silicon in Al-Si alloys leads to a strong interaction between titanium and silicon. This high affinity leads to the formation of (Al,Si)3Ti-type phases, weakening the nucleation opportunities of the dendritic phase and consequently reducing the degree of grain refinement. The titanium disilicate phase tends to form more when the liquid metal is held for long periods.
- 5-
- For master alloys, residual titanium Ti in alloy A356 reacts with boron B to form TiB2, which subsequently acts as an active seed alongside AlB2 for the α-Al phase.
- 6-
- A combined treatment (refining and modification) is more advantageous for the grain size and the shape of the eutectic Si than when the treatments are carried out individually. This is quite evident in the case of the addition of strontium and titanium in the form of master alloys to the A356 alloy.
- 7-
- The introduction of AlB2 in the form of Al-4%B in alloys containing traces of titanium leads to the reaction between boron and titanium to form TiB2. Grain refining is achieved primarily with TiB2 rather than AlB2, or both, depending on the Ti content in the given alloy.
- 8-
- When strontium is added, the boron reacts with the strontium to form compounds of the SrB6 type, which is supposed to be a very weak refiner. The affinity between titanium and boron is higher than the affinity existing between boron and strontium.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maxwell, I.; Hellawell, A. The constitution of the system Al-Ti-B with reference to aluminum-base alloys. Met. Trans. 1972, 3, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backerud, L.; Yidong, S. Grain refining mechanisms in aluminum as a result of additions of titanium and boron, Part I. Aluminium 1991, 67, 780–785. [Google Scholar]
- Vatne, H.E. Efficient grain refinement of ingots of commercial wrought aluminum alloys Part I: Method for grain refining. Aluminium 1999, 75, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Easton, M.; StJohn, D. Grain refinement of aluminum alloys: Part 1. The nucleant and solute paradigms—A review of the literature. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1999, 30, 1613–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.P.; Pearson, J. Factors affecting the grain-refinement of aluminum using titanium and boron additives. Met. Trans. B 1976, 7, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigworth, G.K.; Guzowski, M.M. Grain refining of hypoeutectic Al-Si alloys. AFS Trans. 1985, 172, 907–912. [Google Scholar]
- Kearns, M.A.; Thistlethwaite, S.R.; Cooper, P.S. Recent advances in understanding the mechanism of aluminum grain refinement by TiBAl master alloys. In Light Metals, Proceedings of the Annual Meeting and Exhibition of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society (TMS), Anaheim, CA, USA, 4–8 February 1996; Hale, W., Ed.; TMS: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1996; pp. 713–720. [Google Scholar]
- Spittle, J.A.; Keeble, J.M.; Al Meshhedani, M. A study of grain refinement efficiency in Al-Si alloy castings. In Proceedings of the 4th Decennial International Conference on Solidification Processing, Sheffield, UK, 7–10 July 1997; pp. 273–276. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Sritharan, T.; Seow, H. Grain refinement of DIN226 alloy at high titanium and boron inoculation levels. Scr. Mater. 1996, 35, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, E.; Golbahar, B.; Samuel, A.M.; Doty, H.W.; Valtierra, S.; Samuel, F.H. Effect of grain refiner on the tensile and impact properties of Al–Si–Mg cast alloys. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrašinović, A.; Tomić, M. Functional and Environmental Advantage of Cleaning Ti5B1 Master Alloy. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 9, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Kandalova, E.; Nikitin, V. Grain refining performance of Al-Ti master alloys with different microstructures. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatne, H.E.; Hakonsen, A. The effect of chemical composition on the as-cast grain size of aluminum alloys. Alum. Trans. 2000, 2, 257–266. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, P.; Greer, A.L.; Worth, J.; Evans, P.V.; Kearns, M.A.; Fisher, P.; Green, A.H. New studies of nucleation mechanisms in aluminium alloys: Implications for grain refinement practice. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1998, 14, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigworth, G.K. The grain refining of aluminum and phase relationship in the Al-Ti-B system. Met. Trans. A 1984, 15, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigworth, G.K. Communication on mechanism of grain refinement in aluminum. Scr. Mater. 1996, 34, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.; Cooper, P. A review of the basics of grain refining. In Proceedings of the Sixth Australian Asian Pacific Conference on Aluminium Cast House Technology, Sydney, Australia, 26–29 July 1999; Minerals, Metals & Materials Society: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1999; pp. 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Backerud, L.; Gustafson, P.; Johnsson, M. Grain refining mechanisms in aluminium as a result of additions of titanium and boron, Part II. Aluminium 1991, 67, 910–915. [Google Scholar]
- Guzowski, M.M.; Sigworth, G.K.; Sentner, D.A. The role of boron in the grain refinement of aluminum with titanium. Met. Trans. A 1987, 18, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcantonio, J.A.; Mondolfo, L.F. The nucleation of aluminium by several intermetallic compounds. J. Inst. Met. 1970, 98, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson, M.; Bäckerud, L. Nucleants in grain refined aluminium after addition of Ti- and B-containing master alloys. Int. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 83, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.S.; Nunes, C.A.; Rodrigues, G.; Suzuki, P.A.; Coelho, G.C.; Grytsiv, A.; Rogl, P. Ti6Si2B a new ternary phase in the Ti-Si-B System. Intermetallic 2004, 12, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haida, M.A.; Ghaneya, A.A.; Niazi, A. Development and evaluation of Al-Ti-C master alloys as grain refiner for aluminium. In Light Metals, Proceedings of the Annual Meeting and Exhibition of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society (TMS), Anaheim, CA, USA, 4–8 February 1996; Hale, W., Ed.; TMS: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1996; pp. 729–736. [Google Scholar]
- Banerji, A.; Reif, W. Development of Al-Ti-C grain refiners containing TiC. Met. Trans. A 1986, 17, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.L.; Cooper, P.S.; Meredith, M.W.; Schneider, W.; Schumacher, P.; Spittle, J.A.; Tronche, A. Grain refinement of aluminium alloys by inoculation. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2003, 5, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondel, P.A.; Arnberg, L. Grain refinement of an Al-10% Si alloy by Ti-additions. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, Trondheim, Norway, 22–27 June 1992; pp. 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Youdelis, W.V.; Yang, C.S. Ti(Al, Si)3 compound formation in non-equilibrated Al-Ti-Si alloy. Met. Sci. 1980, 14, 500–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahle, A.K.; Tøndel, P.A.; Paradies, C.J.; Arnberg, L. Effect of grain refinement on the fluidity of two commercial Al-Si foundry alloys. Met. Mater. Trans. A 1996, 27, 2305–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, R.; Correa, E.R.; de Andrade Bastos, M. Effects of grain refinement on feeding mechanisms in A356 aluminum alloy. AFS Trans. 1998, 106, 401–409. [Google Scholar]
- Dahle, A.K.; St. John, D.H.; Attavanich, P.; Taopetch, P. Grain formation in AlSi7Mg0.35 foundry alloy at low superheat. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2000; Volume 331–337, pp. 271–276. [Google Scholar]
- Cibula, A. The mechanism of grain refinement of sand castings in aluminium alloys. J. Inst. Met. 1950, 76, 321–360. [Google Scholar]
- Cibula, A. The grain refinement of aluminium alloy castings by additions of titanium and boron. J. Inst. Met. 1951, 80, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Z.; Hwang, I.; Pan, S.; Li, X.J. Nano-manufacturing, scalable manufacturing of AgCu40 (wt%)–WC nanocomposite Microwires. JOM (J. Occup. Med.) 2018, 6, 031008. [Google Scholar]
- Mondolfo, L.F.; Barlock, J.G. Effect of superheating on structure of some aluminum alloys. Met. Trans. B 1975, 6, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossley, F.A.; Mondolfo, L.F. Mechanism of grain refinement in aluminum alloys. J. Met. Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Metall. Eng. 1951, 191, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-D.; Lee, Z.-H. The effect of grain refining and oxide inclusion on the fluidity of Al-4.5Cu-0.6Mn and A356 alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2003, 360, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, M.; Pillai, U.T.S.; Pai, B.C.; Damodaran, A.D.; Dwarakadasa, E.S. Mechanical properties of cast Al-7Si-0.3Mg (LM 25/356) alloy. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 1998, 11, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kori, S.A.; Murty, B.S.; Chakraborty, M. Influence of silicon and magnesium on grain refinement in aluminium alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1999, 15, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutt, J.; Easton, M.; Hogan, L.; StJohn, D. The effect of nucleant particles and alloy chemistry on the grain structure of aluminium castings. In Proceedings of the 4th Decennial International Conference on Solidification Processing, Sheffield, UK, 7–10 July 1997; pp. 268–272. [Google Scholar]
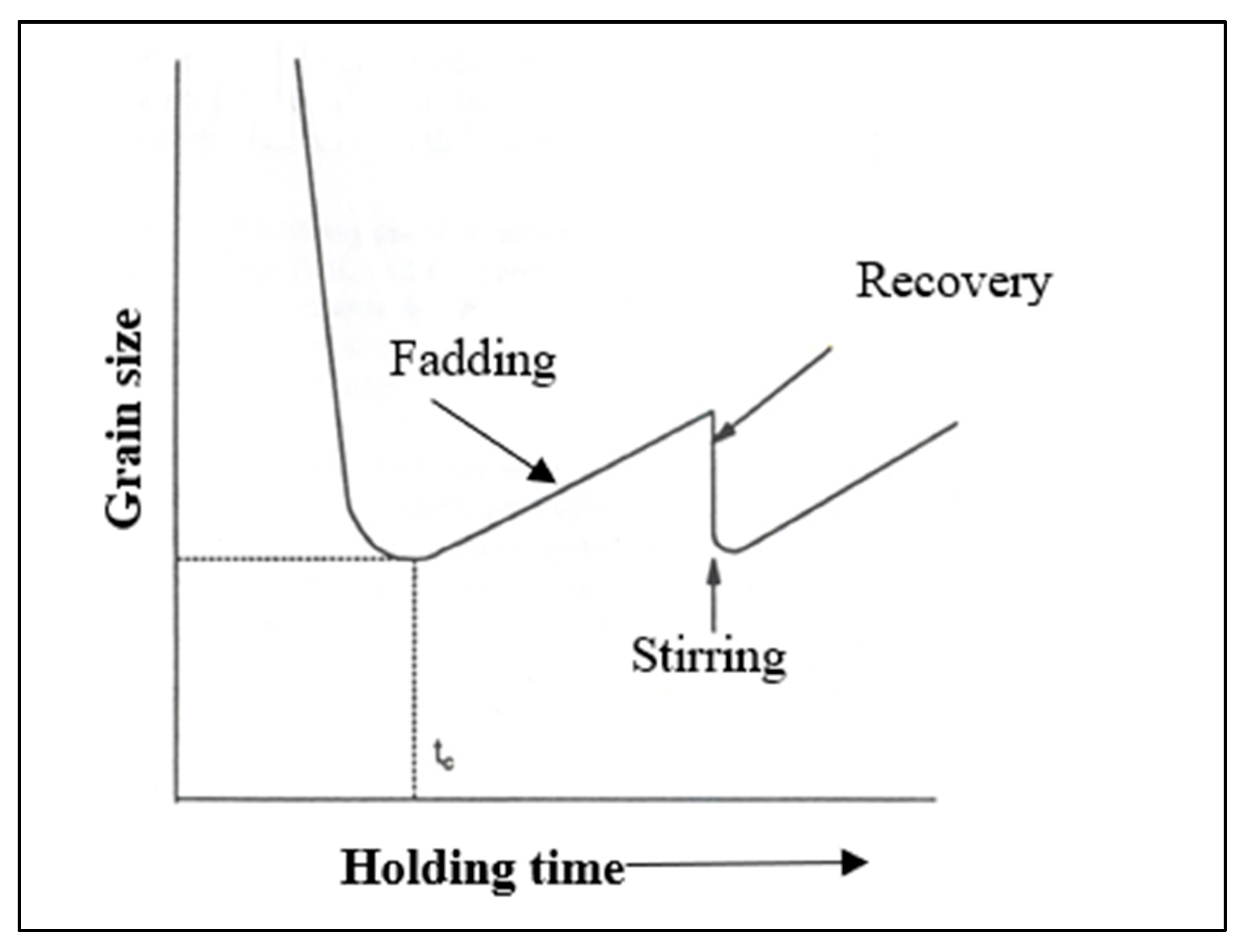
- Birch, M.E.J.; Fisher, P. Mechanism of fade in grain refining of aluminium with titanium boron aluminium. In Solidification Processing; Becht, J., Jones, H., Eds.; The Institute of Metals: London, UK, 1988; pp. 500–502. [Google Scholar]
- Spittle, J.A.; Sadli, S. The influence of zirconium and chromium on the grain-refining efficiency of Al-Ti-B inoculants. Cast Met. 1995, 7, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, W.; Kearns, M.A.; McGarry, M.J.; Whitehead, A.J. A comparison of the behaviour of AlTiB and AlTiC grain refiners. In Light Metals; Welch, B., Ed.; TMS: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1998; pp. 953–961. [Google Scholar]
- Kori, S.A.; Murty, B.S.; Chakraborty, M. Grain refinement of aluminium and its alloys by heterogeneous nucleation and alloying. Int. Mater. Rev. 2002, 47, 3–29. [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson, M. Influence of Si and Fe on the grain refinement of aluminium. Int. J. Mater. Res. 1994, 85, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.A.; Wang, H.; StJohn, D.H.; Bainbridge, I.F. Anomalous grain coarsening behaviour in grain-refined aluminium alloys cast using low superheat. In Light Metals, Proceedings of the 130th TMS Annual Meeting Light Metals 2001, New Orleans, LA, USA, 11–15 February 2001; Angier, J., Ed.; TMS: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2001; pp. 935–941. [Google Scholar]
- Tronche, A.; Greer, A.L. Effect of Solute on the Grain Structures of Al-Ti-B and Al-Ti-C Grain-Refined Al Alloys; Continuous Congress: Francfort, Germany, 2000; pp. 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Backerud, L.; Johnsson, M. The relative importance of nucleation and growth mechanisms to control grain size in various aluminum alloys. In Light Metals, Proceedings of the Annual Meeting and Exhibition of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society (TMS), Anaheim, CA, USA, 4–8 February 1996; Hale, W., Ed.; TMS: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1996; pp. 679–685. [Google Scholar]
- Easton, M.A.; StJohn, D.H. The effect of alloy content on the grain refinement of aluminium alloys. In Light Metals; Angier, J., Ed.; TMS: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2001; pp. 927–933. [Google Scholar]
- Spittle, J.A.; Sadli, S. Effect of alloy variables on grain refinement of binary aluminium alloys with Al-Ti-B. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1995, 11, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youdelis, W.V.; Yang, C.S. Non-peritectic grain refinement of aluminum by titanium. Aluminium 1980, 56, 411–413. [Google Scholar]
- Dorlot, J.M.; Baïlon, J.P.; Masounave, J. Des Matériaux; Édition de l’École Polytechnique de Montréal: Montreal, QC, Canada, 1986; 467p. [Google Scholar]
- Kashyap, K.T.; Chandrashekar, T. Effects and mechanisms of grain refinement in aluminium alloys. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2001, 24, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCartney, D.G. Grain refining of aluminium and its alloys using inoculants. Int. Mater. Rev. 1989, 34, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, N.; Lu, L.; Lai, M. Application of thermodynamic calculation in the in-situ process of Al/TiB2. Composite Structures. Compos. Struct. 1999, 47, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backerud, L. How does a good grain refiner work? Light Met. Age 1983, 41, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sparkman, D.; Kearney, A. Breakthrough in aluminum alloy thermal analysis technology for process control. AFS Trans. 1994, 102, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Gowri, S. Comparison of thermal analysis parameters of 356 and 359 alloys. AFS Trans. 1994, 102, 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson, M. Grain refinement of aluminium studied by use of a thermal analytical technique. Thermochim. Acta 1995, 256, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, F.; Wettinck, E. Study of the grain refinement of A356 and its control by thermal analysis. Aluminium 1996, 72, 442–447. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.X.; Li, X.C. Grain refinement of Al-7Si alloys and the efficiency assessment by recognition of cooling curves. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2003, 34, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonnier, J. Microprocessor assisted thermal analysis testing of aluminum alloy structures. AFS Trans. 1984, 92, 907–922. [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson, M.; Backerud, L.; Sigworth, G.K. Study of the mechanism of grain refinement of aluminium after additions of Ti- and B-containing master alloys. Metall. Trans. A 1993, 24, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloria, D.; Gruzleski, J.E. Time as a control parameter in determination of grain size of 319 Al-Si-Cu foundry alloy. AFS Trans. 1999, 107, 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Backerud, L.; Chai, G.; Tamminen, J. Solidification Characteristics of Aluminum Alloys Vol. 2: Foundry Alloys; AFS/Skanaluminium: Des Plaines, IL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Louvo, A. The development of melt quality control systems based on derivative thermal analysis and the microcomputer. In Thermal Analysis of Molten Aluminum—A New In-Process Technique for Quality Control, Proceedings of the AFS/CMI Conference, Rosemont, IL, USA, 11–12 December 1984; Cast Metals Institute: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 1985; pp. 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhya, K.G.; Stefanescu, D.M.; Lieu, K.; Yeager, D.P. Computer-aided cooling curve analysis: Principles and applications in metal casting. AFS Trans. 1989, 97, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Emadi, D.; Whiting, L.V. Determination of solidification characteristics of Al-Si alloys by thermal analysis. AFS Trans. 2002, 110, 285–296. [Google Scholar]
- Fras, E.; Kapturkiewicz, W.; Burbielko, A.; Lopez, H.F. A new concept in thermal analysis of castings. AFS Trans. 1993, 101, 505–511. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, A.M.; Mohamed, S.S.; Doty, H.W.; Valtierra, S.; Samuel, F.H. Effect of melt temperature on the effectiveness of the grain refining in Al-Si castings. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 7626219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sigworth, G.K. Fundamentals of grain refining in aluminum alloy castings. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Molten Aluminum Processing, Des Plaines, IL, USA, February 1986; American Foundrymen’s Society: Des Plaines, IL, USA, 1986; pp. 75–99. [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie, R.I.L. Studies on the fading behavior of Al-Ti-B master alloys and grain refinement mechanism using LiMCA. In Light Metals; TMS: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1995; pp. 859–868. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, P.; Greer, A.L. Studies of the action of grain-refining particles in aluminium alloys. In Light Metals; TMS: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1995; pp. 869–877. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, P.; Greer, A.L. Devitrification of the stable Al-Rich amorphous alloy Al85Y8Ni5Co2. Key Eng. Mater. 1993, 81–83, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, P.S.; Samuel, F.H.; Gruzleski, J.E. Experimental study on pore nucleation by inclusions in aluminum castings. In Proceedings of the Ninety-Nine Annual Meeting, Schaumburg, IL, USA, 1995; American Foundrymen’s Society: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 1995; pp. 555–564. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, P.S.; Samuel, F.H.; Gruzleski, J.E. Studies on addition of inclusions to molten aluminum using a novel technique. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 1995, 26, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, P.S.; Samuel, F.H.; Gruzleski, J.E.; Kosto, T.J. Studies on the mechanism of grain-refinement in aluminium. In Light Metals, Proceedings of the Technical Sessions Presented by the TMS Light Metals Committee at the 123rd TMS Annual Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 27 February–3 March 1994; Mannweiler, U., Ed.; Wayne Hale Minerals, Metals & Materials Society: San Francisco, CA, USA; pp. 1039–1045.
- Mohanty, P.S.; Samuel, F.H.; Gruzleski, J.E. Mechanism of Heterogeneous Nucleation of Pores in Metals and Alloys. Metall. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 1993, 24, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, P.S.; Samuel, F.H.; Gruzleski, J.E. Role of inclusions on pore nucleation in aluminium casting alloys. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Light Metals Processing and Applications, Quebec City, QC, USA, 29 August–1 September 1993; Bickert, C., Ed.; Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum: Montreal, QC, Canada, 1993; pp. 273–282. [Google Scholar]
- Naess, S.E.; Berg, O. On Grain Refinement in Aluminium Alloys. Int. J. Mater. Res. 1974, 65, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornish, A.J. The influence of boron on the mechanism of grain refinement in dilute aluminium-titanium alloys. Met. Sci. 1975, 9, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio-Lozano, J.; Suarez-Pena, B. Effect of the addition of refiners and/or modifiers on the microstructure of die cast Al-12Si alloys. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Sun, G. Mutual poisoning effect between Sr and B in Al–Si casting alloys. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Katgerman, L. Distribution of trace elements in a modified and grain refined aluminium–silicon hypoeutectic alloy. Micron 2010, 41, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Peña, B.; Asensio-Lozano, J. Microstructure and mechanical property developments in Al–12Si gravity die castings after Ti and/or Sr additions. Mater. Charact. 2006, 57, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.W.; Kim, S.W.; Kumai, S. Effects of solidification structure on tear resistance of Al-7%Si-0.4% Mg cast alloys. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2004, 27, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.F.; Samuel, E.; Samuel, A.M.; Al-Ahmari, A.M.A.; Samuel, F.H. Metallurgical parameters controlling the microstructure and hardness of Al–Si–Cu–Mg base alloys. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2130–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbahar, B.; Samuel, E.; Samuel, A.M.; Doty, H.W.; Samuel, F.H. On thermal analysis, macrostructure and microstructure of grain refined al–si–mg cast alloys: Role of sr addition. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2014, 27, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.J.; Ginebra, M.P.; Manero, J.M.; Planell, J.A. Formation of α-Widmanstätten structure: Effects of grain size and cooling rate on the Widmanstätten morphologies and on the mechanical properties in Ti6Al4V alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 329, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, M.; Sun, C.; He, Y. Effects of particle size and distribution on the mechanical properties of SiC reinforced Al–Cu alloy composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 528, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.D. Effect of grain size on the tensile properties of magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 459, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigworth, G.K. Theoretical and practical aspects of the modification of Al-Si alloys. AFS Trans. 1983, 91, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Bowen, P.; Knott, J.F. Fatigue performance of a cast aluminium alloy Al-7Si-Mg with surface defects. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivkumar, S.; Ricci, S., Jr.; Steenhoff, B.; Apelian, D.; Sigworth, G. An experimental study to optimize the heat treatment of A356 alloy. AFS Trans. 1989, 97, 791–810. [Google Scholar]









| Alloy | Al | Si | Cu | Mg | Fe | Mn | Zn | Ti | Sr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A356.2 | bal. | 6.78 | 0.02 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0 |
| Spot # | Al | Ti | Si |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 71.340 | 23.412 | 2.68 |
| 2 | 71.445 | 23.497 | 2.70 |
| 3 | 71.576 | 23.019 | 2.09 |
| 4 | 71.847 | 23.653 | 1.66 |
| Number | TiB2 | Al3Ti | α-Al |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | <1120> {0001} | <110> {112} | <110> {111} |
| 2 | <1120> {0001} | <210> {112} | <110> {111} |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samuel, E.; Samuel, A.M.; Songmene, V.; Samuel, F.H. A Review on the Analysis of Thermal and Thermodynamic Aspects of Grain Refinement of Aluminum-Silicon-Based Alloys. Materials 2023, 16, 5639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165639
Samuel E, Samuel AM, Songmene V, Samuel FH. A Review on the Analysis of Thermal and Thermodynamic Aspects of Grain Refinement of Aluminum-Silicon-Based Alloys. Materials. 2023; 16(16):5639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165639
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamuel, Ehab, Agnes M. Samuel, Victor Songmene, and Fawzy H. Samuel. 2023. "A Review on the Analysis of Thermal and Thermodynamic Aspects of Grain Refinement of Aluminum-Silicon-Based Alloys" Materials 16, no. 16: 5639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165639
APA StyleSamuel, E., Samuel, A. M., Songmene, V., & Samuel, F. H. (2023). A Review on the Analysis of Thermal and Thermodynamic Aspects of Grain Refinement of Aluminum-Silicon-Based Alloys. Materials, 16(16), 5639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165639








