Crystallinity and Oscillatory Shear Rheology of Polyethylene Blends
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- -
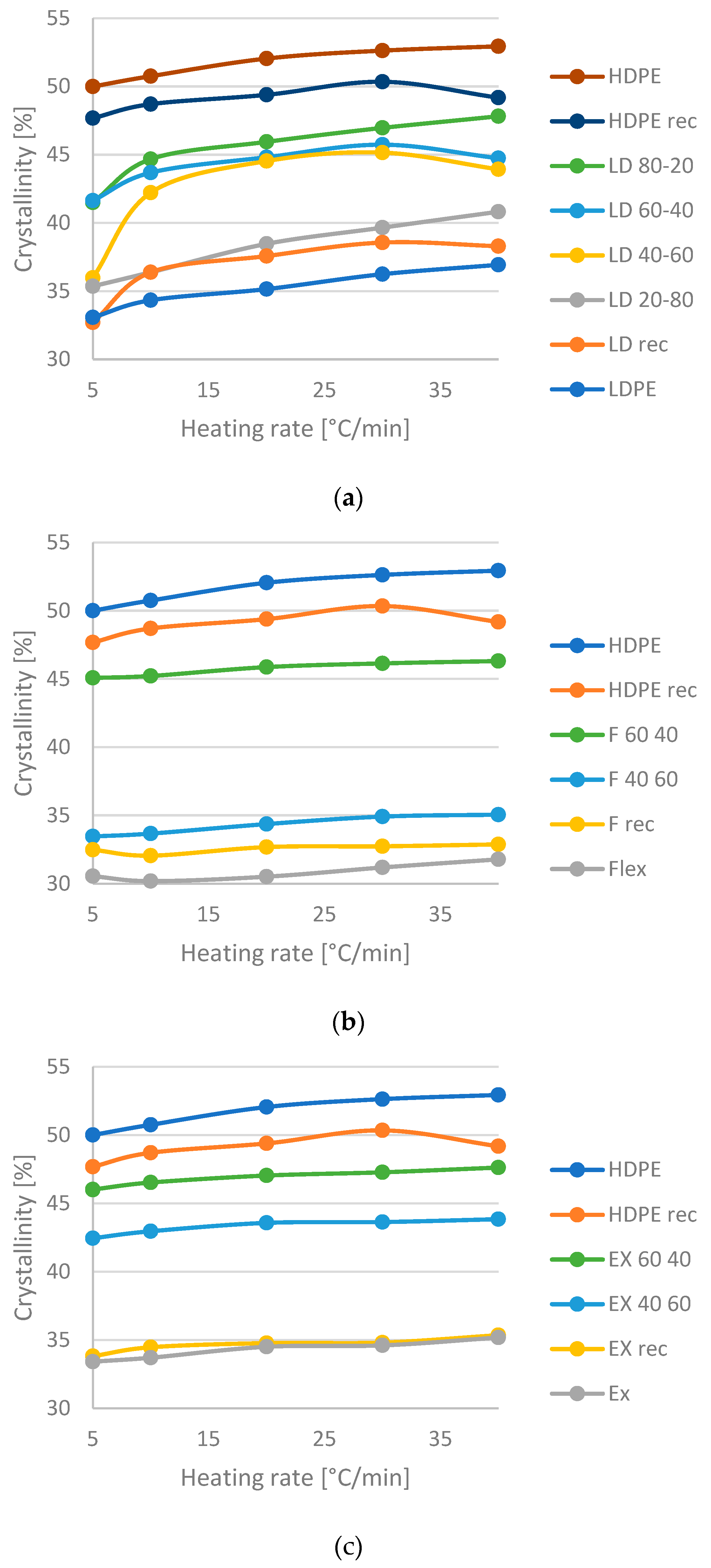
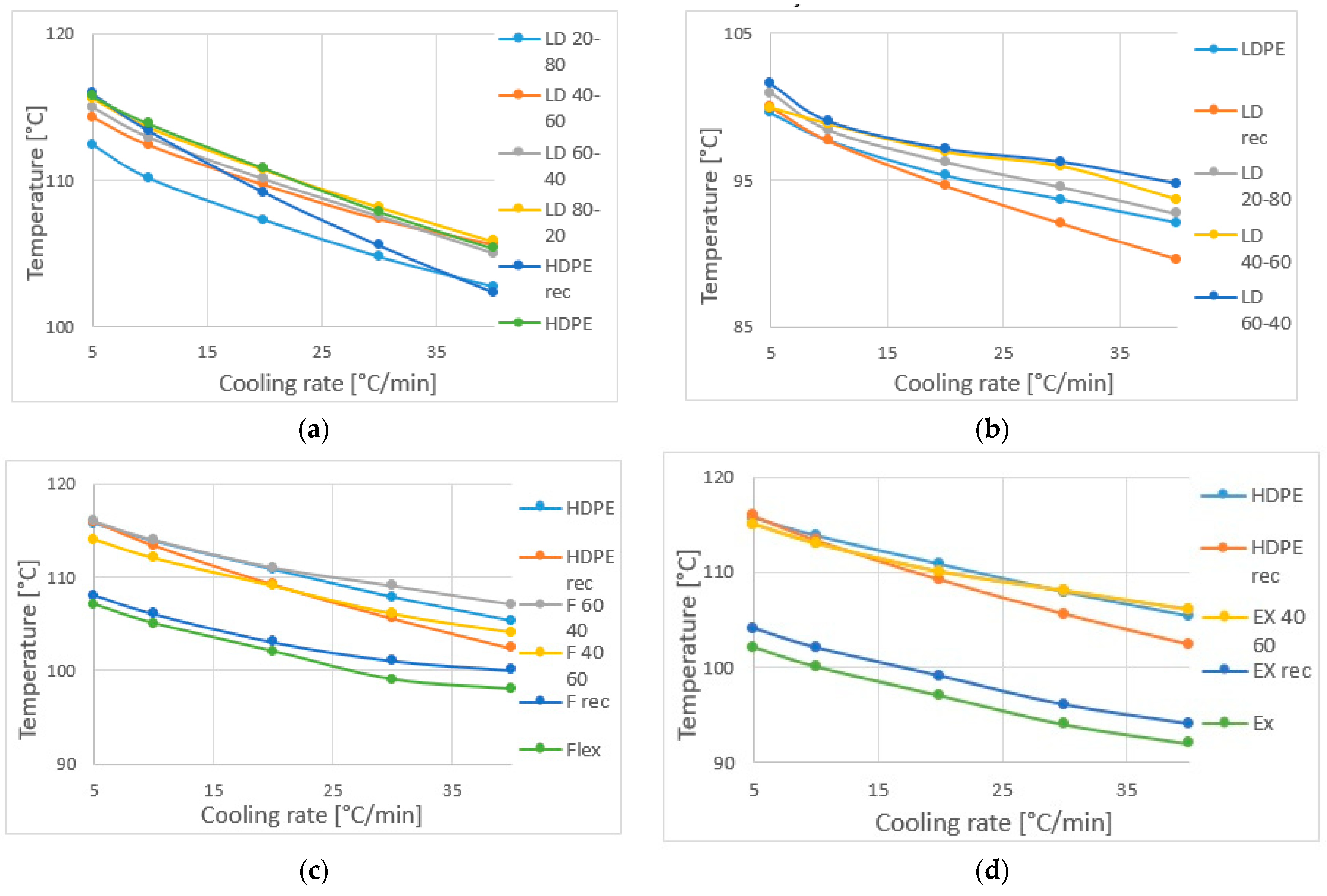
- The one-peak melting endotherm of the 80–20% HDPE-LDPE blend could indicate miscibility in the solid phase, while the other HDPE-LDPE blends with two-peak curves are partially or not miscible.
- -
- All the HDPE-LLDPE blends have a one-peak melting, which can indicate co-crystallization. However, according to the peak temperature and the height of the peak (degree of crystallinity) of the 40–60% HDPE-LLDPE butylene blend is immiscible, while all the other HDPE-LLDPE blends are miscible in solid phase.
- -
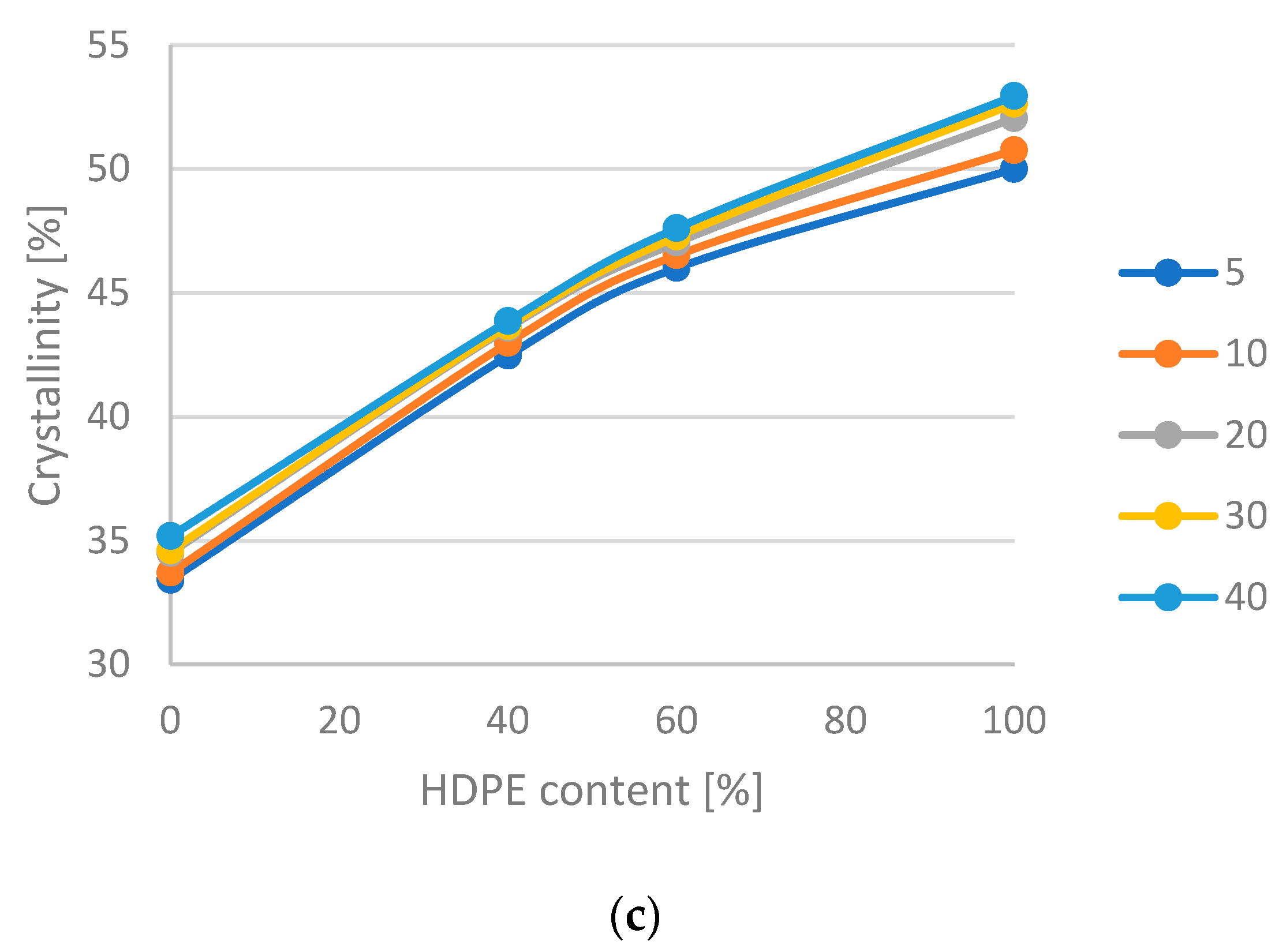
- According to the change in crystallinity, the HDPE-LDPE blends have more phase inversions, the HDPE-LLDPE butylene blends have a phase inversion between 40 and 60% HDPE content, while the HDPE-LLDPE hexane blends have no or below 40% HDPE content.
- -
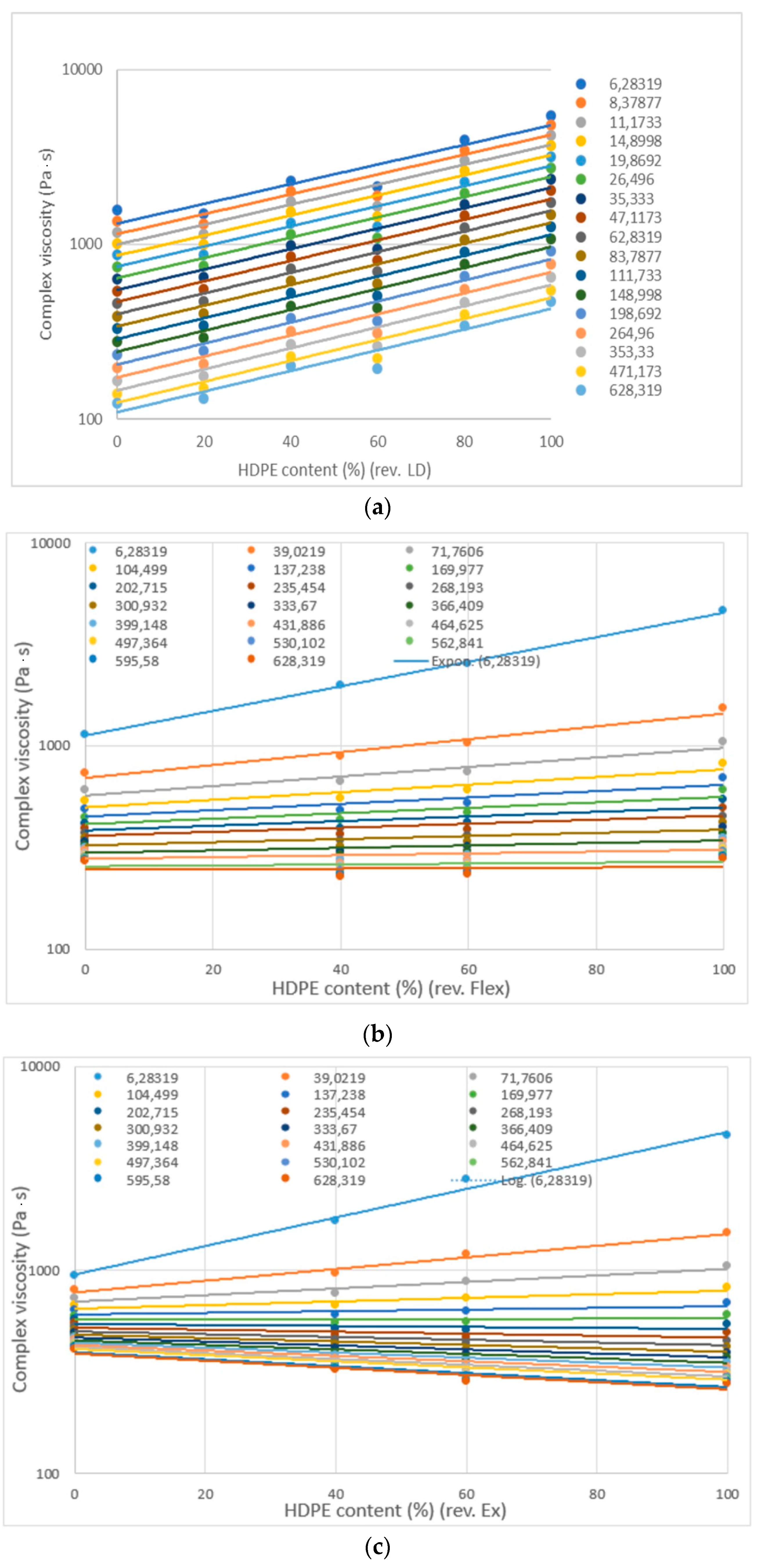
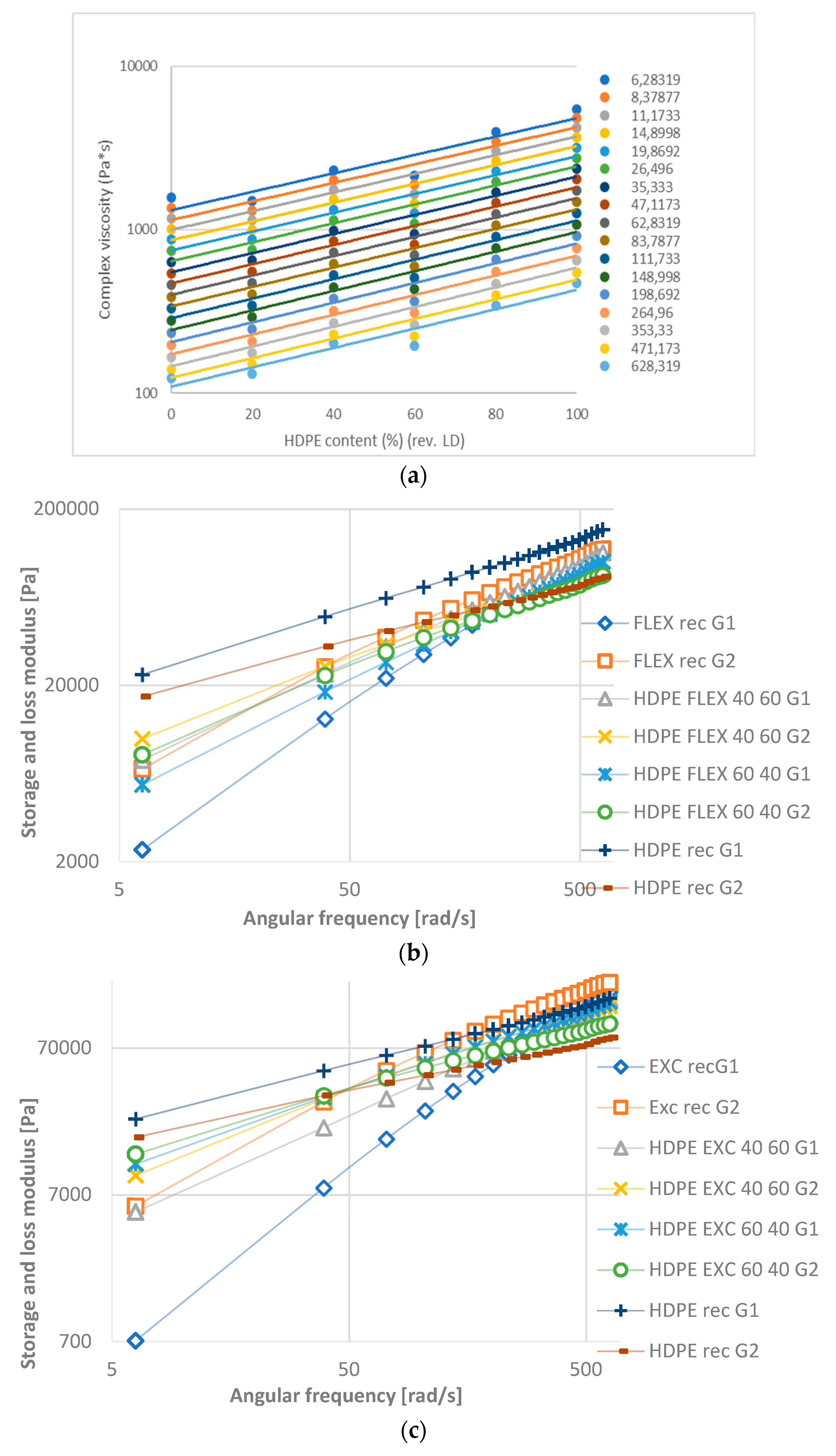
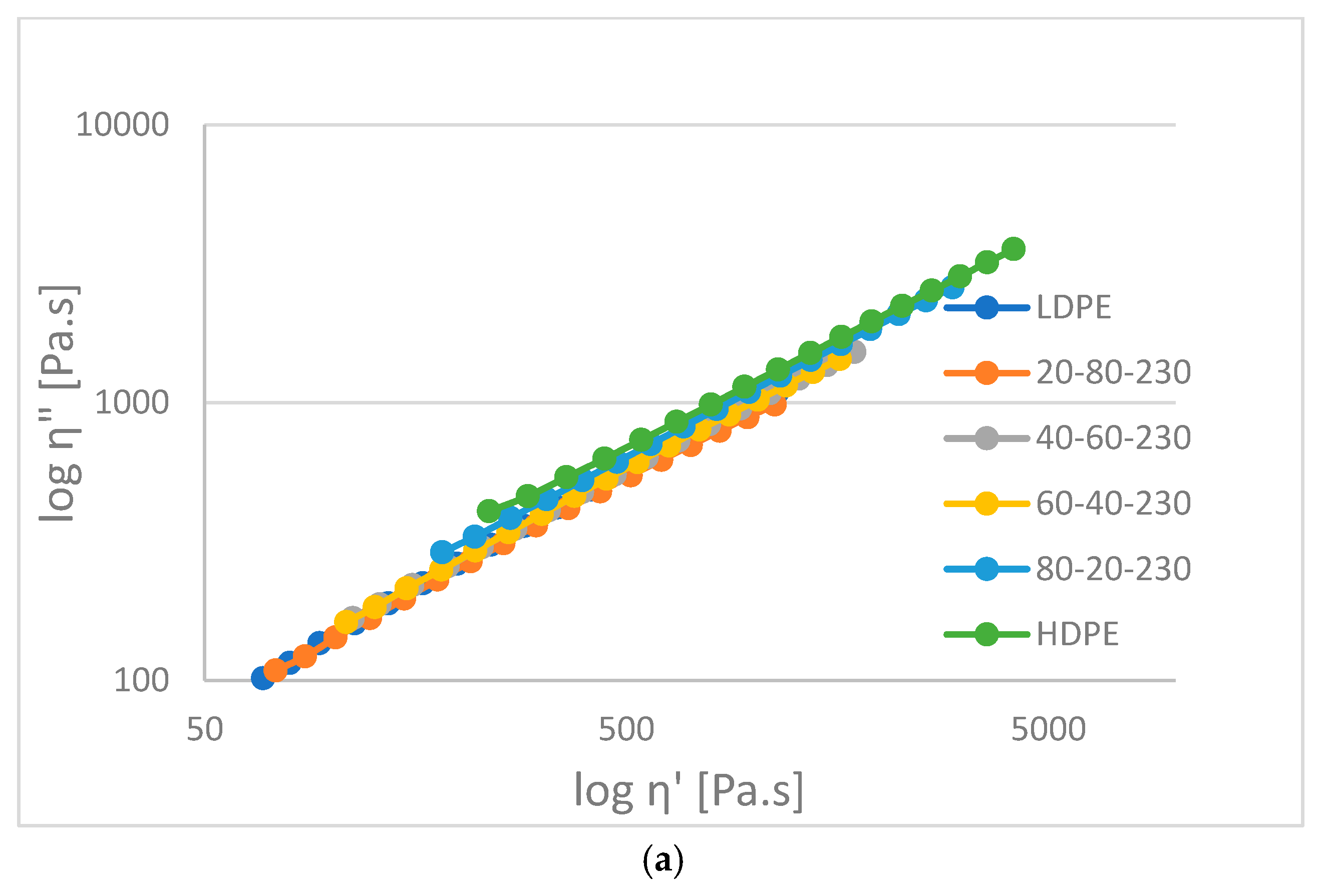
- In general, complex viscosity decreases with angular frequency. For HD-LD blends the curves are parallel, while for HD-LLDPE blends are not (they have intersection).
- -
- The complex viscosity shows linear behavior with composition, but some blends have a significant negative deviation. At lower frequency values, complex viscosity is influenced more by angular frequency than at higher frequencies.
- -
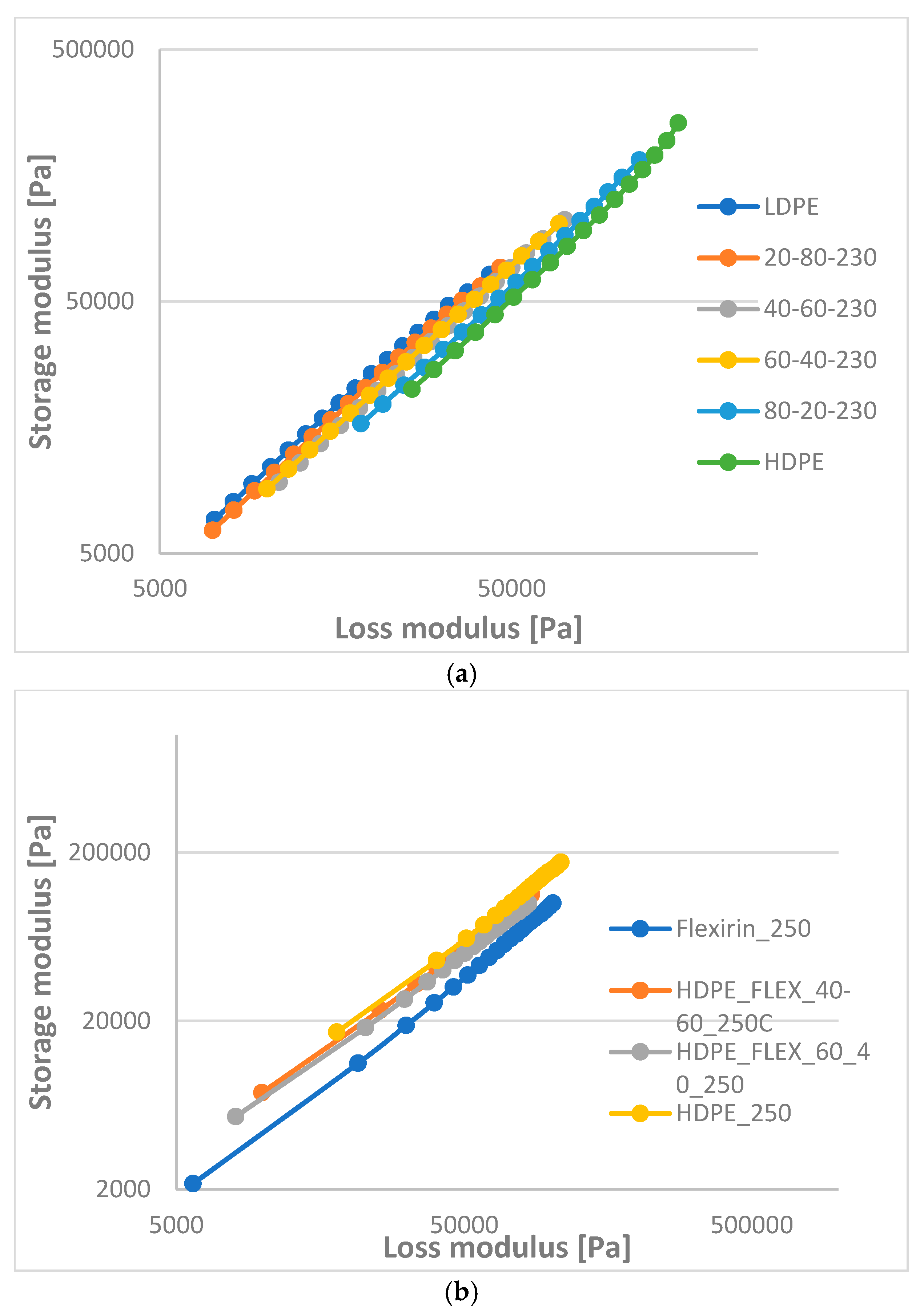
- The storage and loss modulus increase in function of angular frequency. The curves of HD-LD blends are parallel, while those of HD-LLDPEs have intersections.
- -
- In the liquid phase, according to rheological measurements, the HDPE-LDPE blends are not or partially miscible, while the HDPE-LLDPE blends are probably miscible.
- -
- The results can be used in industry, for example, in the recycling of mixed polyethylene waste, from which new polyethylene mixtures are made. These mixtures can contribute to the application of covering cables in the automotive industry, where the recycling rate is of particular importance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, K.; Lee, B.H.; Hwang, K.M.; Lee, H.; Choe, S. Rheological and mechanical properties in polyethylene blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1998, 38, 1969–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, J.A.; Keßner, U.; Stadler, F.J. Hermorheological behavior of polyethylene: A sensitive probe to molecular structure. Rheol. Acta 2011, 50, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Alique, E.; Vega, J.F.; Robledo, N.; Nieto, J.; Martínez-Salazar, J. Study of the effect of the molecular architecture of the components on the melt rheological properties of polyethylene blends. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, D. Crystallization behavior of blends of high-density polyethylene with novel linear low-density polyethylene. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1997, 198, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkhel, G.; Banerjee, A.; Bhattacharya, P. Rheological and mechanical properties of LDPE/HDPE blends. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2006, 45, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.K. Effect of cocrystallization on kinetic parameters of high-density polyethylene/linear low-density polyethylene blend. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 61, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Denn, M.M. Blends of linear and branched polyethylenes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2000, 40, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utracki, L.A.; Favis, B.D. Polymer alloys and blends. Handb. Polym. Sci. Technol. 1989, 4, 121–185. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, P.; Silva, M.H.; Cavalcanti, S.N.; Freitas, D.M.; Araújo, J.P.; Oliveira, A.D.; Mélo, T.J. Rheological properties of high-density polyethylene/linear low-density polyethylene and high-density polyethylene/low-density polyethylene blends. Polym. Bull. 2021, 79, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, J.; He, J. Rheological and thermal properties of m-LLDPE blends with m-HDPE and LDPE. Polymer 2002, 43, 3811–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.J.; Barham, P.J.; Keller, A.; Rosney, C.C.A. Phase segregation in melts of blends of linear and branched polyethylene. Polymer 1991, 32, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamo, R.G.; Graessley, W.W.; Krishnamoorti, R.; Lohse, D.J.; Londono, J.D.; Mandelkern, L.; Stehling, F.C.; Wignall, G.D. Small angle neutron scattering investigations of melt miscibility and phase segregation in blends of linear and branched polyethylenes as a function of the branch content. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanem, B.S.; Stori, A. Investigation of phase behaviour in the melt in blends of single-site based linear polyethylene and ethylene–1-alkene copolymers. Polymer 2001, 42, 4309–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, T.; Hussein, I.A. Rheological study of the influence of Mw and comonomer type on the miscibility of m-LLDPE and LDPE blends. Polymer 2002, 43, 6911–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, T.; Hussein, I.A. Melt miscibility and mechanical properties of metallocene LLDPE blends with HDPE: Influence of Mw of LLDPE. Polym. J. 2006, 38, 1114–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.Y.; Qi, L.Y.; Tao, G.L.; Liu, C.L. Dynamic rheological behavior of two LDPE/HDPE binary blending melts. Polym. Bull. 2015, 72, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.J.; Williams, M.C.; Choi, P. A molecular dynamics study of the effects of branching characteristics of LDPE on its miscibility with HDPE. Polymer 2002, 43, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, B.B. Application of differential thermal analysis to polyethylene blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1965, 9, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Somani, R.H.; Sics, I.; Hsiao, B.S.; Kolb, R.; Fruitwala, H.; Ong, C. Shear-induced crystallization precursor studies in model polyethylene blends by in-situ rheo-SAXS and rheo-WAXD. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 4845–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, S.; Birley, A.W. Blends of polyolefins: Characteristic melting and crystallization data. Adv. Polym. Technol. J. Polym. Process. Inst. 1990, 10, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelkern, L. The effect of molecular weight on the crystallization, melting, and morphology of long-chain molecules. J. Polym. Sci. Part C Polym. Symp. 1967, 15, 129–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwag, H.; Rana, D.; Cho, K.; Rhee, J.; Woo, T.; Lee, B.H.; Choe, S. Binary blends of metallocene polyethylene with conventional polyolefins: Rheological and morphological properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2000, 40, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Abe, S. LLDPE/LDPE blends. I. Rheological, thermal, and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 3153–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamo, R.G.; Londono, J.D.; Mandelkern, L.; Stehling, F.C.; Wignall, G.D. Phase behavior of blends of linear and branched polyethylenes in the molten and solid states by small-angle neutron scattering. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.L.; Hill, M.J.; Barham, P.J. Morphology, melting behaviour and co-crystallization in polyethylene blends: The effect of cooling rate on two homogeneously mixed blends. Polymer 1999, 40, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wignall, G.D.; Londono, J.D.; Lin, J.S.; Alamo, R.G.; Galante, M.J.; Mandelkern, L. Morphology of blends of linear and long-chain-branched polyethylenes in the solid state: A study by SANS, SAXS, and DSC. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 3156–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Shi, Y.; Tang, Y.; Luo, C.; Hou, L.; Ren, M.; Zheng, C.; Liu, L.Z. CRYSTAF, DSC and SAXS Study of the Co-Crystallization, Phase Separation and Lamellar Packing of the Blends with Different Polyethylenes. Polymers 2023, 15, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatelli, A.A. Characterization of multicomponent polyethylene blends by differential scanning calorimetry. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1979, 23, 3071–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, I.A. Melt miscibility and mechanical properties of metallocene linear low-density polyethylene blends with high-density polyethylene: Influence of comonomer type. Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, J.F.; Otegui, J.; Ramos, J.; Martínez-Salazar, J. Effect of molecular weight distribution on Newtonian viscosity of linear polyethylene. Rheol. Acta 2012, 51, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.C.; Stadler, F.J. Classification of thermorheological complexity for linear and branched polyolefins. Rheol. Acta 2018, 57, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, F.J.; Chen, S.; Chen, S. On “modulus shift” and thermorheological complexity in polyolefins. Rheol. Acta 2015, 54, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaidullin, N.M.; Salakhov, I.I.; Borisenko, V.N.; Tavtorkin, A.N.; Nifant’ev, I.E. Structural, rheological, and mechanical properties of binary compounds based on high-density polyethylene and linear low-density polyethylene. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2020, 93, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, I.A. Influence of composition distribution and branch content on the miscibility of m-LLDPE and HDPE blends: Rheological investigation. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 2024–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zou, H.; Liang, M.; Liu, P. Rheological, thermal, and morphological properties of low-density polyethylene/ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene and linear low-density polyethylene/ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.J.; Barham, P.J. Liquid-liquid phase separation in blends containing copolymers produced using metallocene catalysts. Polymer 1997, 38, 5595–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordinejad, A.K.; Jafari, S.H. Miscibility analysis in LLDPE/LDPE blends via thermorheological analysis: Correlation with branching structure. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, T.; Hussein, I.A. Effect of short chain branching of LDPE on its miscibility with linear HDPE. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2004, 289, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, C.B.B.; Siqueira, D.D.; Araújo, E.M.; Wellen, R.M.R. Tailoring PS/PPrecycled blends compatibilized with SEBS. Evaluation of rheological, mechanical, thermomechanical and morphological characters. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 075316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Rana, S.K.; Deopura, B.L. Crystallization behavior of high-density polyethylene/linear low-density polyethylene blend. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1992, 44, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Rana, S.K.; Deopura, B.L. Crystallization kinetics of high-density polyethylene linear low-density polyethylene blend. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1994, 51, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Shen, H.; Xie, B.; Yang, W.; Yang, M. Crystallization and fracture behaviors of high-density polyethylene/linear low-density polyethylene blends: The influence of short-chain branching. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Rana, S.K.; Deopura, B.L. Mechanical properties and morphology of high-density polyethylene/linear low-density polyethylene blend. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1992, 46, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.L.; Hill, M.J.; Barham, P.J.; Van der Pol, A.; Kip, B.J.; Ottjes, R.; Van Ruiten, J. A study of the phase behaviour of polyethylene blends using micro-Raman imaging. Polymer 2001, 42, 2121–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, C.C.; Hill, M.J.; Odell, J.A. Absence of isothermal thickening for a blend of linear and branched polyethylene. Polymer 1993, 34, 3402–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.R.; Kyu, T.; Stein, R.S. Characterization and properties of polyethylene blends I. Linear low-density polyethylene with high-density polyethylene. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1987, 25, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Cho, K.; Ahn, T.K.; Choe, S.; Kim, I.J.; Park, I.; Lee, B.H. Solid-state relaxations in linear low-density (1-octene comonomer), low-density, and high-density polyethylene blends. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1997, 35, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Tashiro, K.; Gose, N.; Imanishi, K.; Izuchi, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Imai, M.; Ohashi, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ohoyama, K. Spatial distribution of chain stems and chain folding mode in polyethylene lamellae as revealed by coupled information of DSC, FT-IR, SANS, and WANS. Polym. J. 1999, 31, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Z.; Zhong, L. Elongation properties of polyethylene melts. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 2490–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfer, Y.; Winter, H.H. Effect of branch distribution on rheology of LLDPE during early stages of crystallization. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 8974–8981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.L.P.; Soares, J.B.; Penlidis, A. HDPE/LLDPE reactor blends with bimodal microstructures—Part II: Rheological properties. Polymer 2003, 44, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, A.M.; Jaroslav, B.; David, B. Low dose cosmic radiation effects on polycarbonate. Perner’s Contacts 2019, 2, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Ádám, B.; Polgár, B.; Nagy, D. The effect of different printing parameters on mechanical and thermal properties of PLA specimens. Gradus 2020, 7, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorottya, N.; Krisztian, B. Rheological study of high and linear low density polyethylene blends. Perner’s Contacts 2019, 2, 206. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.W.; Xie, B.H.; Yang, W.; Yang, M.B. Thermal and rheological properties of polyethylene blends with bimodal molecular weight distribution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 2145–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, P.; Behravesh, A.H.; Haghtalab, A.; Rizvi, G.; Pop-Iliev, R.; Goharpei, F. Effect of mixing intensity on foaming behavior of LLDPE/HDPE blends in thermal induced batch process. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2016, 55, 949–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ádám, B.; Weltsch, Z. Thermal and Mechanical Assessment of PLA-SEBS and PLA-SEBS-CNT Biopolymer Blends for 3D Printing. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berczeli, M.; Weltsch, Z. Enhanced wetting and adhesive properties by atmospheric pressure plasma surface treatment methods and investigation processes on the influencing parameters on HIPS polymer. Polymers 2021, 13, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.molgroupchemicals.com/userfiles/products/40/40_tds_hu.pdf?v=1695373226 (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Technical Datasheet. Polyethylene Tipolen FB 243-51. LDPE for Film. Available online: https://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:vt3bogM5REMJ:https://www.molgroupchemicals.com/userfiles/products/13/13_tds_en.pdf+&cd=2&hl=hu&ct=clnk&gl=hu (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Exceed™ 3518CB Cast. Performance Polymer. Available online: https://exxonmobilchemical.ulprospector.com/en-US/ds243873/Exceed%E2%84%A2%203518CB%20Cast.aspx?I=58933&U=1 (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Flexirene® CL 10 U. Available online: https://plastics.ulprospector.com/datasheet/e87911/flexirene-cl-10-u (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- ISO 11357-1:2009; Plastics—Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)—Part 1: General Principles. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/41637.html (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- ARES-G2. Available online: https://www.tainstruments.com/ares-g2/ (accessed on 19 September 2023).






| Name of Raw Material | Investigated Property | |
|---|---|---|
| MFR Values (g/10 min) | Density at 23 °C (kg/m3) | |
| HDPE TIPELIN FA 381-10 | 0.28 | 937 |
| LDPE TIPOLEN FB 243-51 | 0.75 | 921 |
| LLDPE Exceed 3518 | 3.5 | 918 |
| LLDPE Flexirine CL10U | 2.5 | 918 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagy, D.; Weltsch, Z. Crystallinity and Oscillatory Shear Rheology of Polyethylene Blends. Materials 2023, 16, 6402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196402
Nagy D, Weltsch Z. Crystallinity and Oscillatory Shear Rheology of Polyethylene Blends. Materials. 2023; 16(19):6402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196402
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagy, Dorottya, and Zoltán Weltsch. 2023. "Crystallinity and Oscillatory Shear Rheology of Polyethylene Blends" Materials 16, no. 19: 6402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196402
APA StyleNagy, D., & Weltsch, Z. (2023). Crystallinity and Oscillatory Shear Rheology of Polyethylene Blends. Materials, 16(19), 6402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196402






