Improved Interlaminar Properties of Glass Fiber/Epoxy Laminates by the Synergic Modification of Soft and Rigid Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Epoxy Matrix Modified by CTBN
- Approximately 5 wt%, 8 wt%, and 10 wt% CTBN were added into the unmodified resin matrix based on epoxy resin, respectively.
- The unmodified and modified resin matrix were prepared with the weight ratio of epoxy resin:MTHPA:N, N-dimethylbenzylamine = 100:90:2.
- The mixture is placed in the rotation agitator (Thinky Mixer ARE-310) to be stirred and defoamed.
- The stirred liquid was slowly poured into the mold and put in the oven at 60 °C for vacuum defoaming for 30 min.
- The mold is placed into the oven for curing, and the procedure is conducted at 80 °C for 4 h, and then at 140 °C for 8 h.
2.3. Preparation of Resin Matrix with Synergic Toughening of Nano-SiO2 and CTBN
- Based on epoxy resin, CTBN with the optimal ratio was added, and nano-SiO2 with the additional amount of 0.25 wt%, 0.5 wt%, 0.75 wt%, and 1.0 wt% were added to tetrahydrofuran. Ultrasonic dispersion was carried out for 30 min.
- Corresponding quality epoxy resin was added into the tetrahydrofuran nano-SiO2 solution and stirred for 5 min.
- The tetrahydrofuran in the resin was removed successively by rotating the evaporation apparatus and vacuum oven. The curing agent and accelerator were added at the ratio of epoxy resin:MTHPA:N, N-dimethylbenzylamine = 100:90:2. For the following steps, refer to Section 2.2.
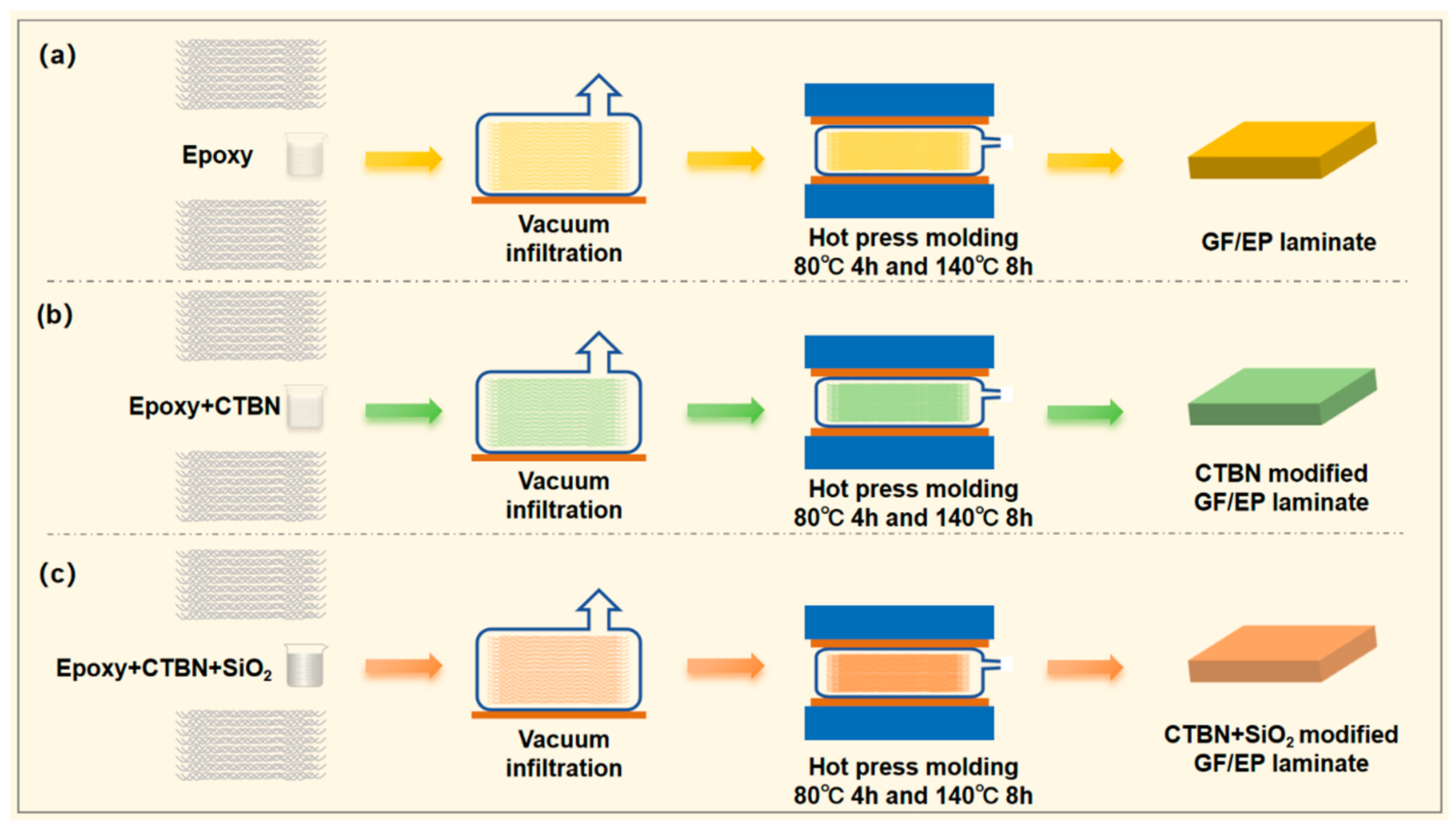
2.4. The Preparation of GF/EP Laminate Composites Toughened by Nano-SiO2 and CTBN
- The glass fiber cloth was cut into a rectangular fabric of the required size. The glass fiber cloth was washed with ethanol absolute (ethanol concentration ≥ 99.5%) and put into the oven for drying.
- According to the configuration of the resin matrix, the epoxy resin matrix with different components of nano-SiO2 and CTBN is prepared.
- Use a brush dipped in a small amount of glue to coat the glass fiber cloth, use a scraper to scrape off excess resin after coating, and then lay the 2nd~12th layer in turn.
- After the 12th layer is laid, spread polyimide with a thickness of 25 μm in the width direction as a prefab crack (this step is unnecessary for the preparation of shear strength laminate composite materials), and continue to apply the adhesive liquid on the remaining glass fiber cloth. The layering of the 13th to 24th layers is the same as layers 2nd to 12.
- After the 24th layer is covered, the system is put into a vacuum bag to vacuum and remove bubbles for 30 min. Put the system into the mold and use the hot press for hot pressing. The curing procedure is 80 °C 4 h and 140 °C 8 h. The thickness of the laminates was about 3 mm, with the fiber volume fraction of 60~65%.
2.5. Test and Characterization
2.5.1. Fracture Testing
2.5.2. Tensile Property Testing
2.5.3. SEM Observation of Section Morphology
2.5.4. GF/EP Laminates Interlayer Shear Strength Test
3. Results and Discussion
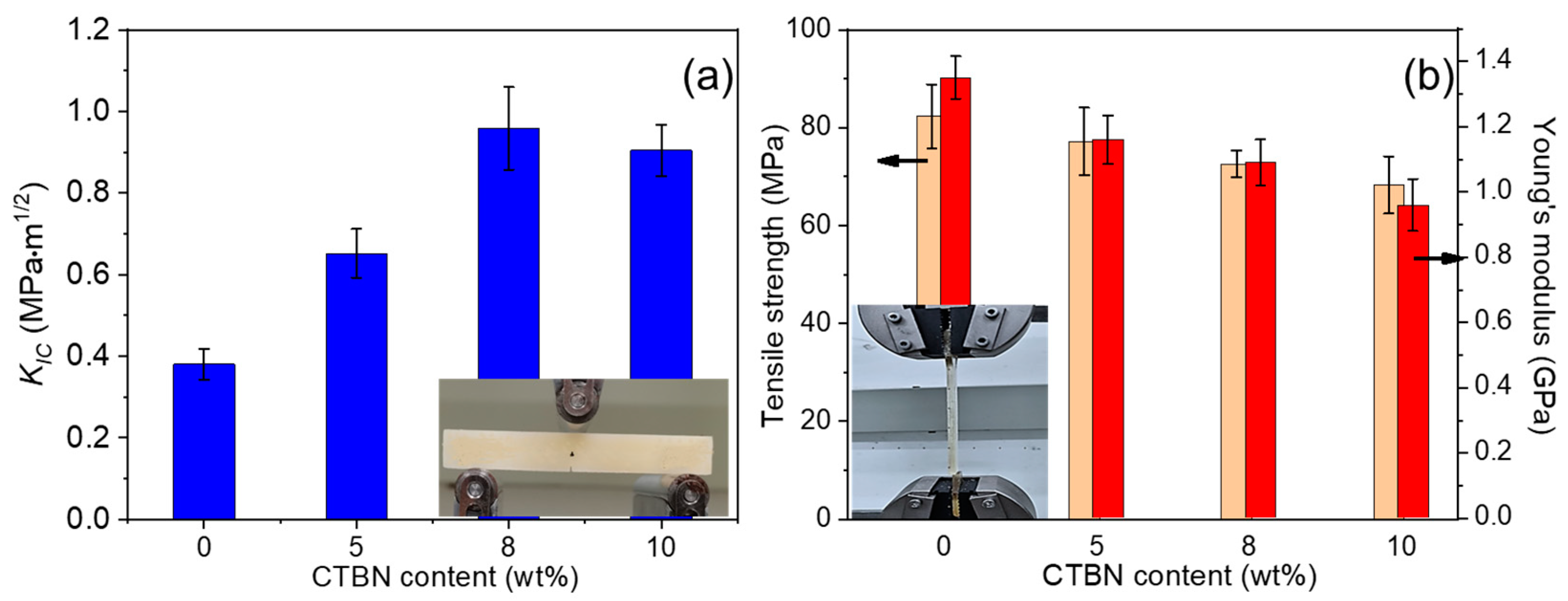
3.1. Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Matrix Modified by Particles
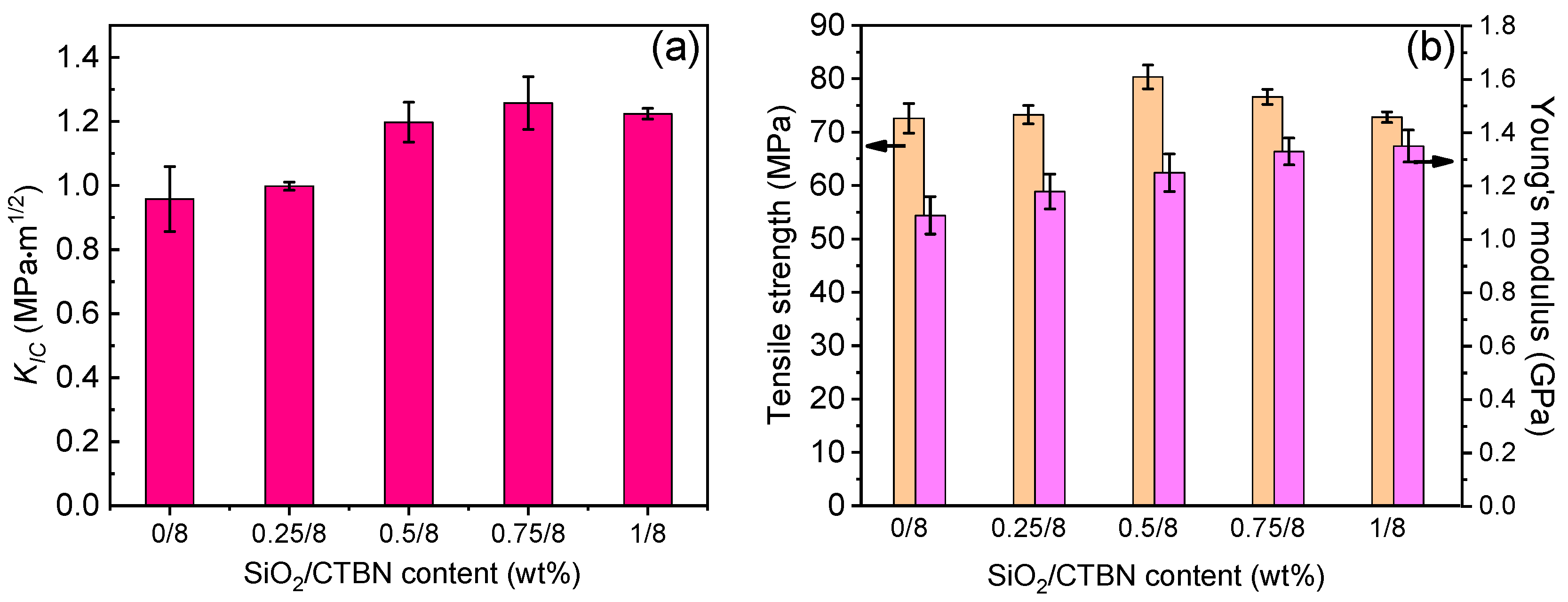
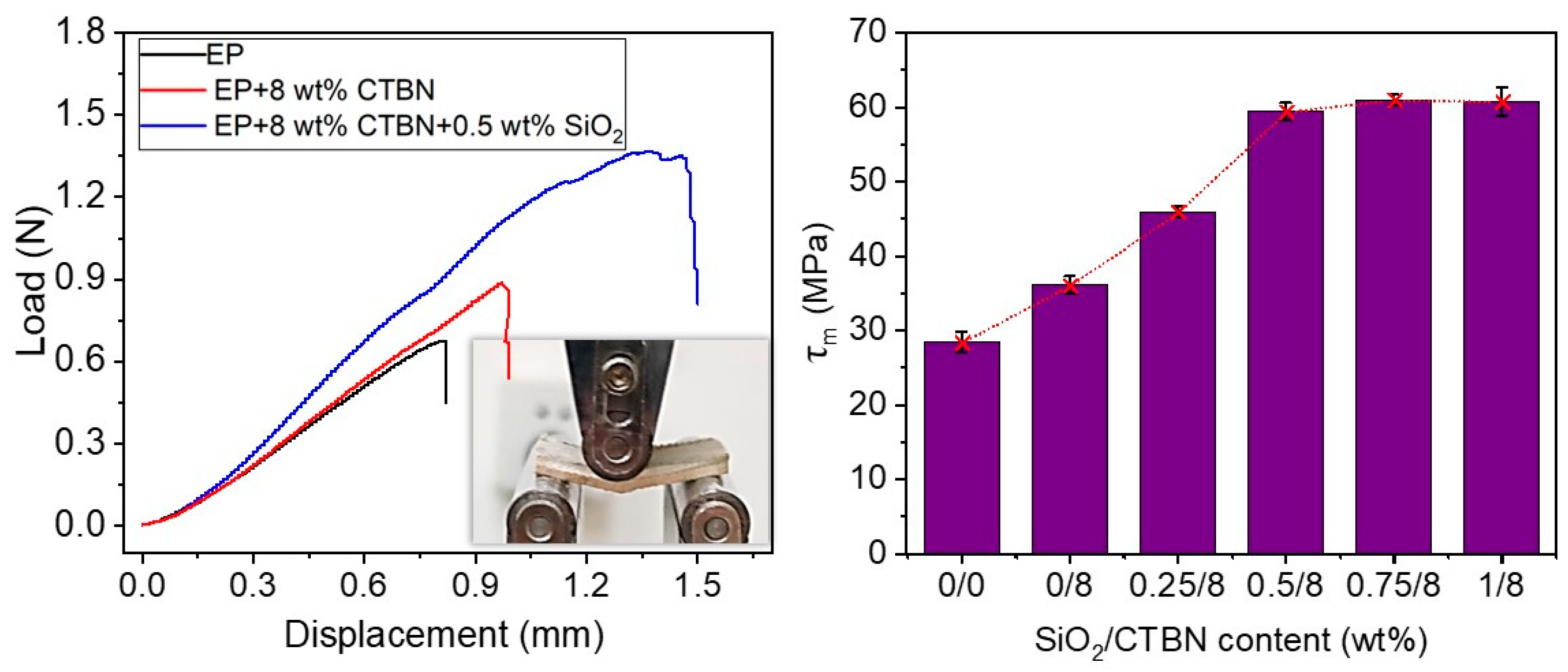
3.2. Interlayer Properties of GF/EP-Laminated Composites Toughened by SiO2 and CTBN
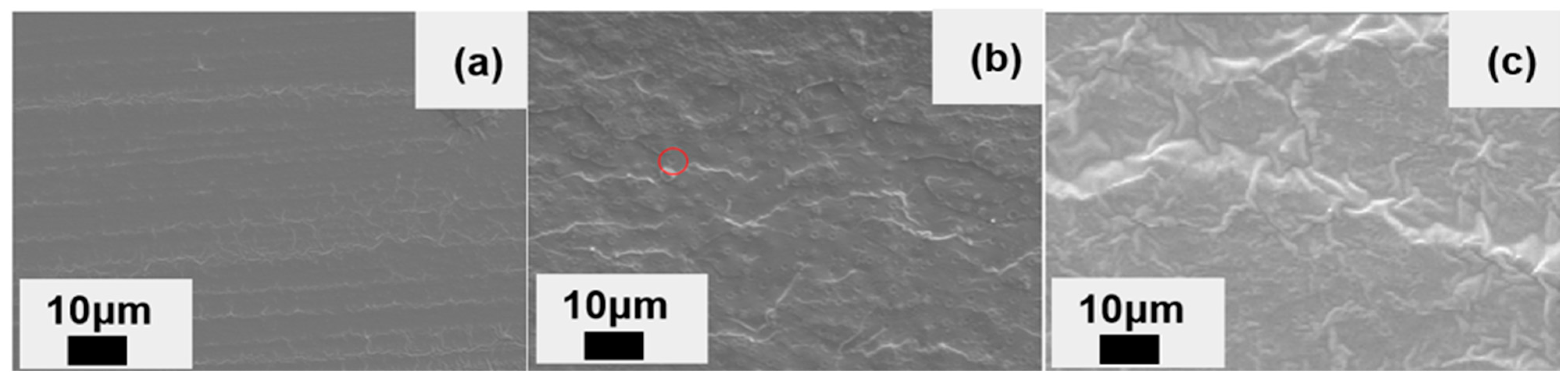
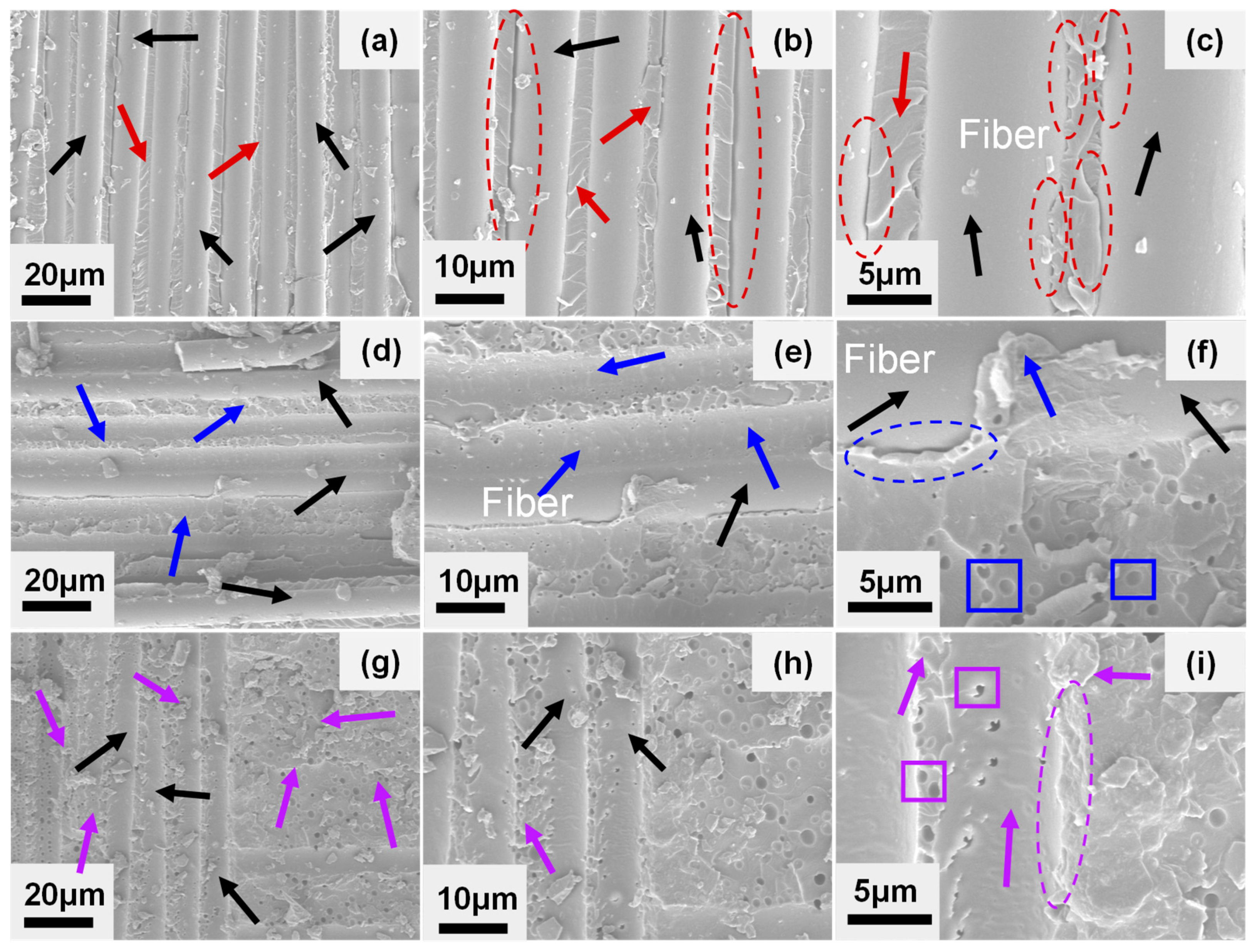
3.3. Fracture Behavior Analysis of GF/EP Laminate Composites Toughened by Nano-SiO2 and CTBN
4. Conclusions
- The epoxy resin can be successfully toughened by CTBN. The epoxy resin’s mode I fracture toughness increases by 150% when CTBN concentration is 8 wt%, but its strength and modulus drop by 11.8% and 19.3%, respectively.
- When flexible CTBN rubber particles and nano-SiO2 are used as synergistic toughening agents to toughen the epoxy resin base, when 8 wt% CTBN and 0.5 wt% nano-SiO2 are added to the resin, the fracture toughness of epoxy resin is increased by 215.8%. The tensile strength is only decreased by 2.3%, showing the best comprehensive performance.
- The synergistic toughening effect of 8 wt% CTBN and 0.5 wt% nano-SiO2 increased the GIC,Pro value of the GF/EP laminate composite by 86.8% and the interlaminate shear strength by 109.2%.
- The cross-section analysis of GF/EP-laminated composites shows that the addition of flexible CTBN rubber particles and rigid nano-SiO2 makes the interface adhesive failure of GF/EP-laminated composites change to matrix cohesion failure. When cracks expand in the interlayer matrix, the cavitation of the two particles and the plastic deformation of the matrix is the toughening mechanism of the interlayer properties of the composite.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karger-Kocsis, J.; Mahmood, H.; Pegoretti, A. Recent advances in fiber/matrix interphase engineering for polymer composites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 73, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, R.; Singh, K.K. Interlaminar fracture toughness characterization of laminated composites: A review. Polym. Rev. 2020, 60, 542–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, S.; Anand, A. Interleaving in Composites for High-Performance Structural Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 62, 16–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cicco, D.; Asaee, Z.; Taheri, F. Use of Nanoparticles for Enhancing the Interlaminar Properties of Fiber-Reinforced Composites and Adhesively Bonded Joints—A Review. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, F.; Hu, X.; Xiao, Y. Strain induced crack initiation and the subsequent crack propagation of fiber-reinforced resin composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 155, 106836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Santare, M.H.; Advani, S.G. Interlaminar shear strength of glass fiber reinforced epoxy composites enhanced with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 540–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.T.; Hossain, M.M.; Khomenko, A.; Haq, M.; Drzal, L.T.; Loos, A. Interlaminar reinforcement of glass fiber/epoxy composites with graphene nanoplatelets. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 70, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Du, X.; Liu, H.-Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Mai, Y.-W. Delamination toughening of carbon fiber/epoxy laminates by hierarchical carbon nanotube-short carbon fiber interleaves. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 140, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, F.; Aydin, M.; Avci, A. Mechanical properties of nano-SiO2 reinforced 3D glass fiber/epoxy composites. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 108, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, R.C.; Burghardt, T.; Maeder, E. Study on interfacial adhesion strength of single glass fibre/polypropylene model composites by altering the nature of the surface of sized glass fibres. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, N.; Wang, M.; Zhou, G.; Qiu, Y.; Wei, Y. Effect of polymer nanoparticle morphology on fracture toughness enhancement of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 234, 109749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Meng, X.; Aamir, R.M.; Lu, W.; Suo, T. Effects of loading rates on mode I interlaminar fracture toughness of carbon/epoxy composite toughened by carbon nanotube films. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 200, 108270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Yu, Y.; Liu, D.; He, M.; Li, G.; Yang, X. Enhanced interfacial and mechanical properties of high-modulus carbon fiber composites: Establishing modulus intermediate layer between fiber and matrix based on tailored-modulus epoxy. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 163, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Zhu, W.; Su, Q.; Li, G.; Yang, X. Correlation between compression strength and failure mechanism of carbon fiber composite with tailored modulus of amide acid/SiO2 synergistically stiffened epoxy matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 202, 108593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, P.J.L.; Sengottuvelu, R.; Natarajan, E. Assessments of Secondary Reinforcement of Epoxy Matrix-Glass Fibre Composite Laminates through Nanosilica (SiO2). Materials 2018, 11, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.C.; Mai, Y.-W. Failure mechanisms in toughened epoxy resins—A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1988, 31, 179–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ning, R. Effects of nanoparticles SiO2 on the performance of nanocomposites. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 2940–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Islam, M.S. Fabrication and characterization of TiO2-epoxy nanocomposite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 487, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kango, S.; Kalia, S.; Celli, A.; Njuguna, J.; Habibi, Y.; Kumar, R. Surface modification of inorganic nanoparticles for development of organic-inorganic nanocomposites—A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1232–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, R.; Pearson, R.A. Role of blend morphology in rubber-toughened polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 3945–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.Y.; Pearson, R.A.; Dimonie, V.L.; Shaffer, O.L.; ElAasser, M.S. The role of dispersed phase morphology on toughening of epoxies. Polymer 1997, 38, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, R.; Pearson, R.A. Role of particle cavitation in rubber-toughened epoxies: 1. Microvoid toughening. Polymer 1996, 37, 4529–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucknall, C.B.; Soares, V.L.P.; Yang, H.H.; Zhang, X.C. Rubber toughening of plastics: Rubber particle cavitation and its consequences. Macromol. Symp. 1996, 101, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, R.; Marouf, B.T.; Pearson, R.A. Rubber-toughened epoxies: A critical review. Polym. Rev. 2009, 49, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becu, L.; Maazouz, A.; Sautereau, H.; Gerard, J.F. Fracture behavior of epoxy polymers modified with core-shell rubber particles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 65, 2419–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbolat, M.Ç.; Katnam, K.B.; Soutis, C.; Potluri, P.; Sprenger, S.; Taylor, J. On mode-I and mode-II interlaminar crack migration and R-curves in carbon/epoxy laminates with hybrid toughening via core-shell rubber particles and thermoplastic micro-fibre veils. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 238, 109900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang Ngah, S.; Taylor, A.C. Fracture behaviour of rubber- and silica nanoparticle-toughened glass fibre composites under static and fatigue loading. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 109, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wu, F.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, J.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, Y. Improved interlaminar fracture toughness of carbon fiber/epoxy composites by a combination of extrinsic and intrinsic multiscale toughening mechanisms. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 252, 110503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Akbolat, M.Ç.; Katnam, K.B.; Zou, Z.; Potluri, P.; Sprenger, S.; Taylor, J. On the R-curve behaviour of carbon/epoxy laminates with core-shell rubber nanoparticle and micro-fibre veil hybrid toughening: Carbon vs. PPS veils. Polymer 2022, 254, 125081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povolo, M.; Maccaferri, E.; Cocchi, D.; Brugo, T.M.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Giorgini, L.; Zucchelli, A. Damping and mechanical behaviour of composite laminates interleaved with rubbery nanofibers. Compos. Struct. 2021, 272, 114228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccaferri, E.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Brugo, T.M.; Zucchelli, A.; Giorgini, L. Rubbery nanofibrous interleaves enhance fracture toughness and damping of CFRP laminates. Mater. Des. 2020, 195, 109049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccaferri, E.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Brugo, T.M.; Zucchelli, A.; Giorgini, L. Rubbery-Modified CFRPs with Improved Mode I Fracture Toughness: Effect of Nanofibrous Mat Grammage and Positioning on Tandelta Behaviour. Polymers 2021, 13, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adin, H.A.a.M.s. Effect of particles on tensile and bending properties of jute epoxy composites. Mater. Test. 2022, 64, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macan, J.; Paljar, K.; Burmas, B.; Spehar, G.; Leskovac, M.; Gajovic, A. Epoxy-matrix composites filled with surface-modified SiO2 nanoparticles. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 127, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Feng, Y.; Liao, Y.; Ye, Y.; Xie, X.; Mai, Y.W. Ultralow-Carbon Nanotube-Toughened Epoxy: The Critical Role of a Double-Layer Interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1204–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachid, H.B.; Noureddine, D.; Benali, B.; Adin, M.Ş. Effect of nanocomposites rate on the crack propagation in the adhesive of single lap joint subjected to tension. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2023, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.F.; Zhou, D.; Yeh, H.Y. Macro/microscopic fracture characterizations of SiO2/epoxy nanocomposites. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2008, 12, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domun, N.; Hadavinia, H.; Zhang, T.; Sainsbury, T.; Liaghat, G.H.; Vahid, S. Improving the fracture toughness and the strength of epoxy using nanomaterials—A review of the current status. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10294–10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccaferri, E.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Brugo, T.M.; Zucchelli, A.; Giorgini, L. Self-Assembled NBR/Nomex Nanofibers as Lightweight Rubbery Nonwovens for Hindering Delamination in Epoxy CFRPs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 1885–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D. 5045-14; Standard Test Methods for Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness and Strain Energy Release Rate of Plastic Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- ASTM D. 5528-01; Standard Test Method for Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Unidirectional Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2002.
- GB/T. 2567-2021; Test Methods for Properties of Resin Casting Body. CHINESE GB Standards: Shenzhen, China, 2021.
- JC/T. 773-2010; Fibre-Reinforced Plastics Composites-Determination of Apparent Interlaminar Shear Strength by Short-Beam Method. CHINESE GB Standards: Shenzhen, China, 2010.
- Adin, M.Ş. A parametric study on the mechanical properties of MIG and TIG welded dissimilar steel joints. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2023, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakre, P.R.; Lagoudas, D.C.; Riddick, J.C.; Gates, T.S.; Frankland, S.-J.V.; Ratcliffe, J.G.; Zhu, J.; Barrera, E.V. Investigation of the effect of single wall carbon nanotubes on interlaminar fracture toughness of woven carbon fiber-epoxy composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poel, G.V.; Goossens, S.; Goderis, B.; Groeninckx, G. Reaction induced phase separation in semicrystalline thermoplastic/epoxy resin blends. Polymer 2005, 46, 10758–10771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskizeybek, V.; Avci, A.; Gülce, A. The Mode I interlaminar fracture toughness of chemically carbon nanotube grafted glass fabric/epoxy multi-scale composite structures. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 63, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, S.; Kothmann, M.H.; Altstaedt, V. Carbon fiber-reinforced composites using an epoxy resin matrix modified with reactive liquid rubber and silica nanoparticles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 105, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.-P.; Xiao, H.-M.; Qu, C.-B.; Feng, Q.-P.; Fu, S.-Y.; Shindo, Y. Role of matrix modification on interlaminar shear strength of glass fibre/epoxy composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Tian, S.; Ren, J.; Huang, J.; Luo, L.; Du, B.; Zhang, T. Improved Interlaminar Properties of Glass Fiber/Epoxy Laminates by the Synergic Modification of Soft and Rigid Particles. Materials 2023, 16, 6611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196611
Liu J, Tian S, Ren J, Huang J, Luo L, Du B, Zhang T. Improved Interlaminar Properties of Glass Fiber/Epoxy Laminates by the Synergic Modification of Soft and Rigid Particles. Materials. 2023; 16(19):6611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196611
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jingwei, Shenghui Tian, Jiaqi Ren, Jin Huang, Lin Luo, Bing Du, and Tianyong Zhang. 2023. "Improved Interlaminar Properties of Glass Fiber/Epoxy Laminates by the Synergic Modification of Soft and Rigid Particles" Materials 16, no. 19: 6611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196611
APA StyleLiu, J., Tian, S., Ren, J., Huang, J., Luo, L., Du, B., & Zhang, T. (2023). Improved Interlaminar Properties of Glass Fiber/Epoxy Laminates by the Synergic Modification of Soft and Rigid Particles. Materials, 16(19), 6611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16196611








