Supplementation of Polymeric Reservoirs with Redox-Responsive Metallic Nanoparticles as a New Concept for the Smart Delivery of Insulin in Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
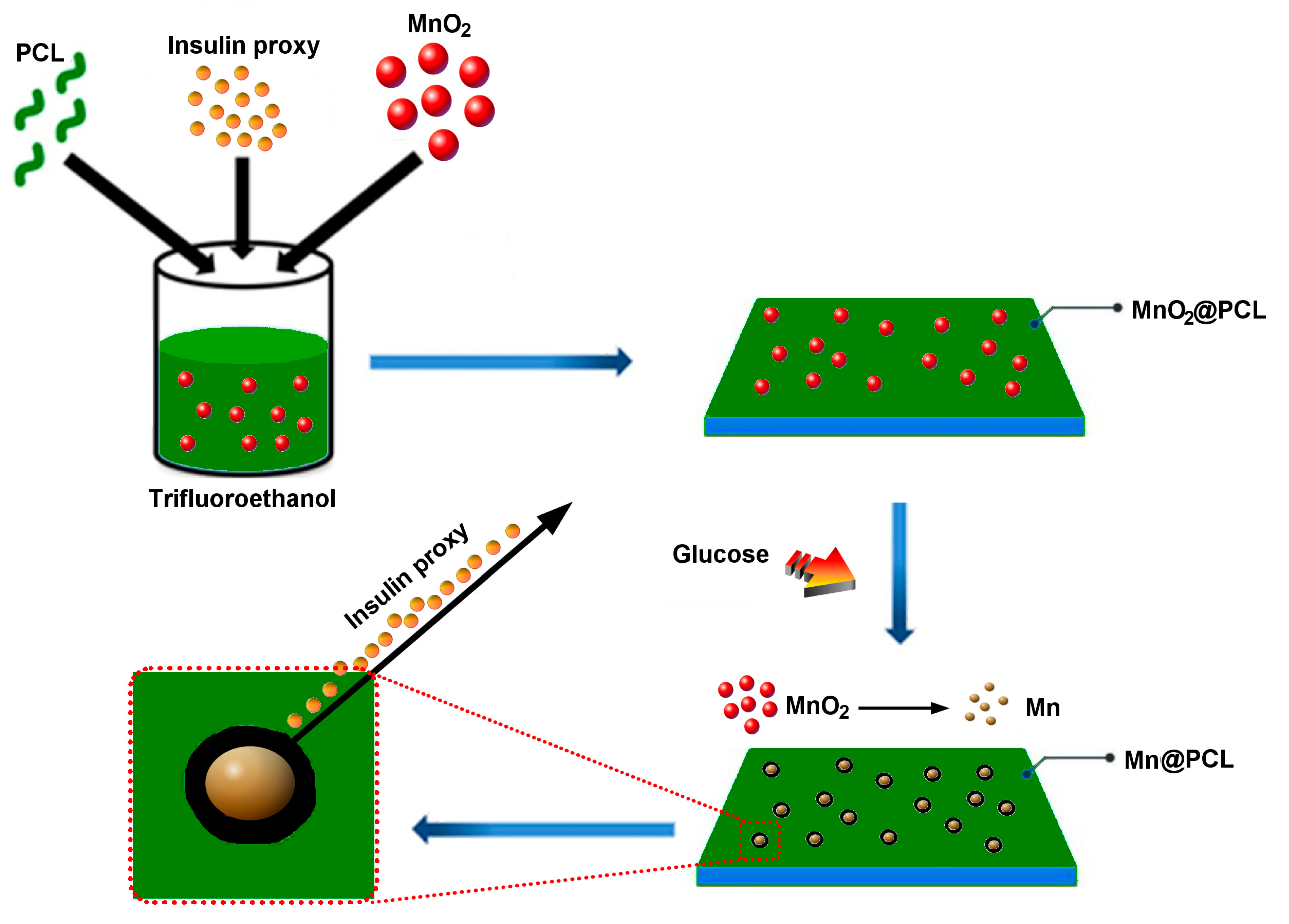
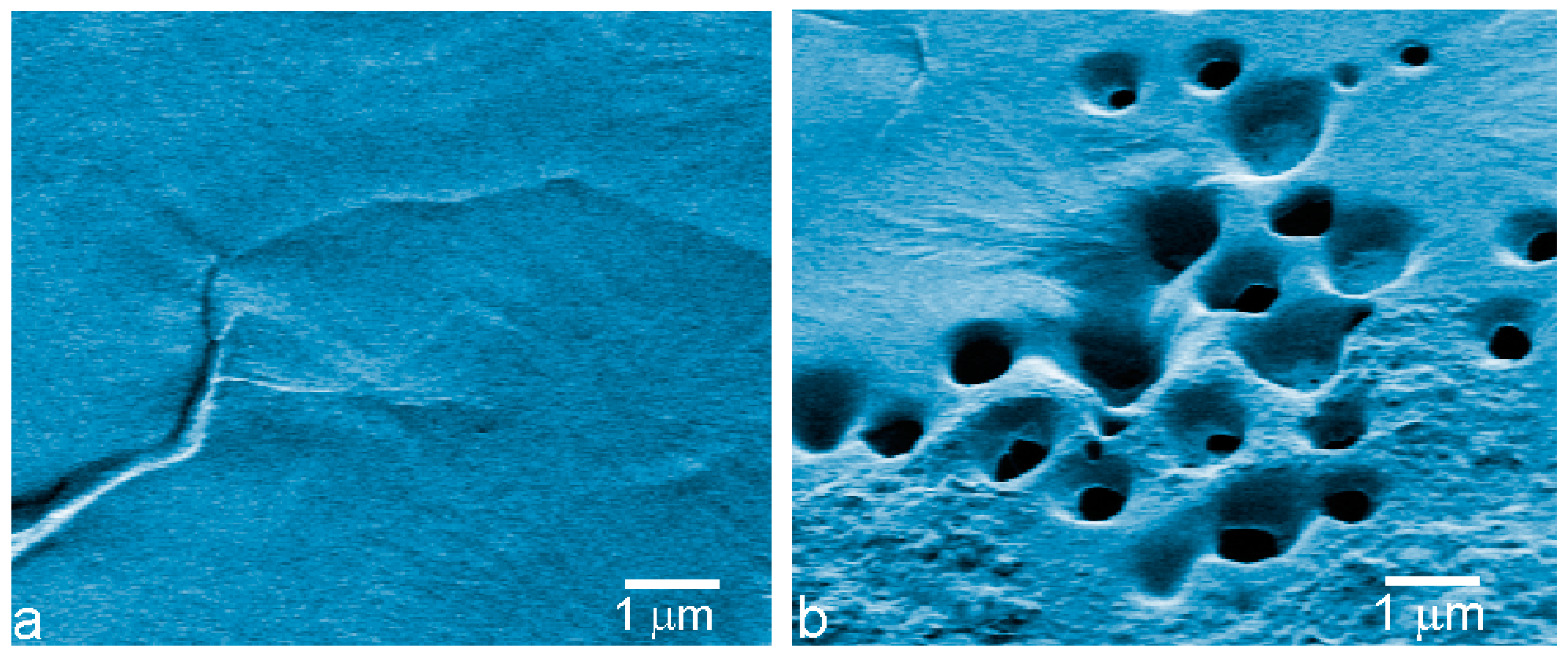
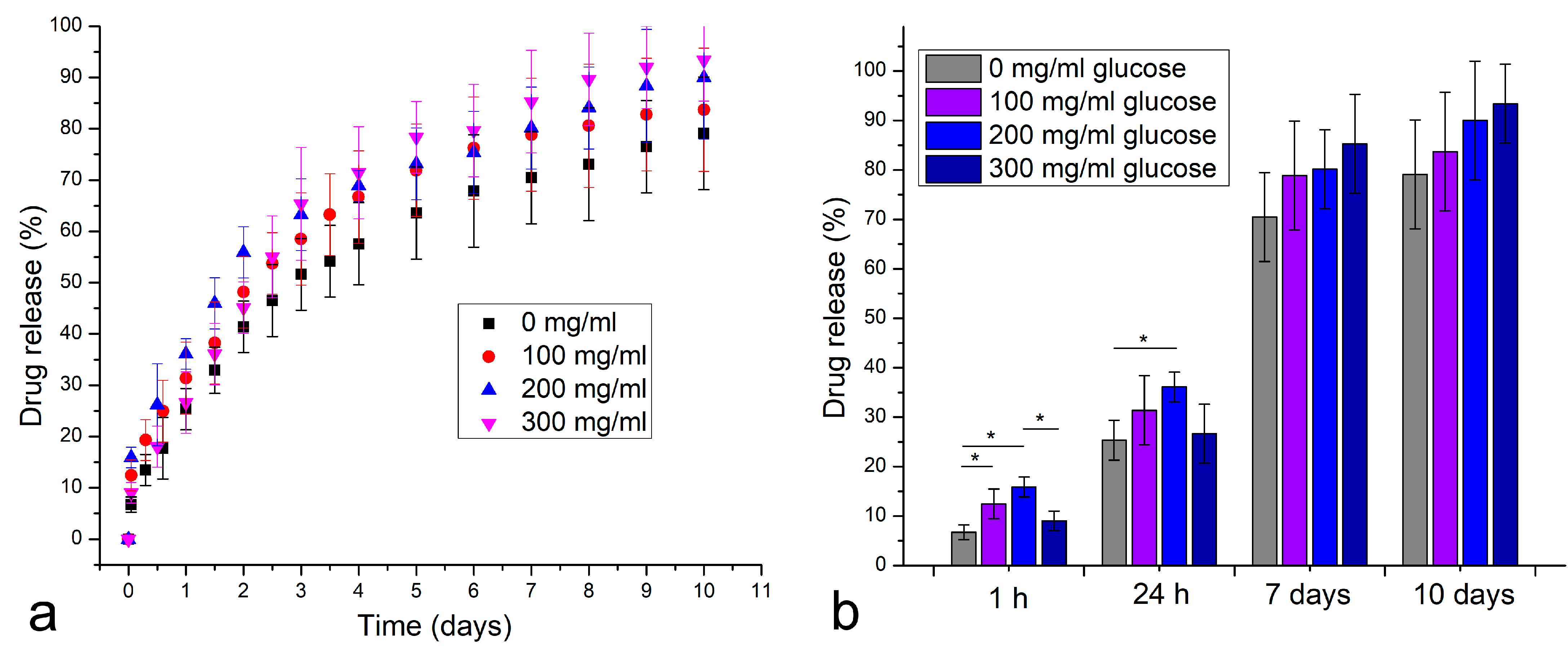
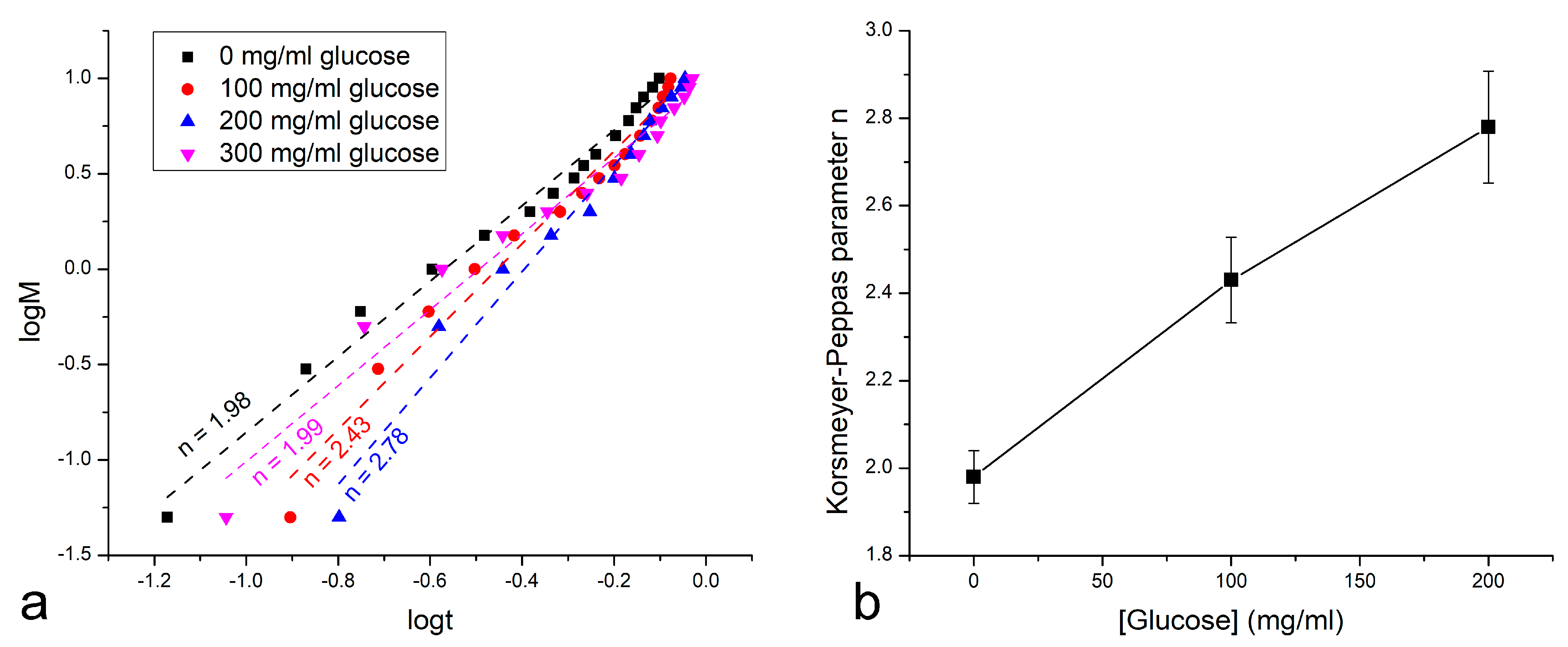
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Z.; Liu, S.; Kang, Y.; Wang, M. Glutathione- and pH-responsive nonporous silica prodrug nanoparticles for controlled release and cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 5859–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, K.; Wen, T.; Lao, S.; Quan, G.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. “Pincer movement”: Reversing cisplatin resistance based on simultaneous glutathione depletion and glutathione S-transferases inhibition by redox-responsive degradable organosilica hybrid nanoparticles. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2074–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, L.; Sandhu, J.K.; Harper, M.E.; Cuperlovic-Culf, M. Role of Glutathione in Cancer: From Mechanisms to Therapies. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milcovich, G.; Contessotto, P.; Marsico, G.; Pandit, A. Synthetic/ECM-inspired hybrid platform for hollow microcarriers with ROS-triggered nanoporation hallmarks. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, M.; Basu, S.M.; Yadava, S.K.; Sarviya, N.; Giri, J. A facile strategy for the preparation of polypropylene sulfide nanoparticles for hydrophobic and base-sensitive cargo. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Qian, J.; Guo, M.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Suo, A. Hydrazide-manganese coordinated multifunctional nanoplatform for potentiating immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 628, 968–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, B.; Jia, X.L.; Qi, J.L.; Yang, L.P.; Sun, W.H.; Yan, X.; Yang, S.K.; Cao, D.Y.; Du, Q.; Qi, X.R. Enhancing siRNA-based cancer therapy using a new pH-responsive activatable cell-penetrating peptide-modified liposomal system. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2385–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Mao, J.; Qian, S.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, B.; Mao, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Regulated extravascular microenvironment via reversible thermosensitive hydrogel for inhibiting calcium influx and vasospasm. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 21, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Wu, V.M.; Ghosh, S.; Uskoković, V. Gene Delivery Using Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles: Optimization of the Transfection Process and the Effects of Citrate and Poly(L-Lysine) as Additives. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 471, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskoković, V. An Odyssey at the Interface–A Study in the Stream of Consciousness. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 5150–5160. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, B.; Sefidbakht, Y.; Mozaffari-Jovin, S.; Gharachloo, B.; Mehraria, M.; Khodadadi, A.; Rezaei, M.; Ranaei-Siadat, S.O.; Uskoković, V. Hydroxyapatite as a Biomaterial—A Gift that Keeps on Giving. Drug Devel. Indust. Pharm. 2020, 46, 1035–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreira, A.S.; Gonçalves, F.A.M.M.; Mendonça, P.V.; Gil, M.H.; Coelho, J.F.J. Temperature and pH responsive polymers based on chitosan: Applications and new graft copolymerization strategies based on living radical polymerization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Sun, A.; Yang, J.; Cheng, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, H.; Ding, H.; Falahati, M. Development of doxorubicin-loaded chitosan–heparin nanoparticles with selective anticancer efficacy against gastric cancer cells in vitro through regulation of intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Arabian J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Panahi-Sarmad, M.; Vlierberghe, S.V.; Xu, R.; Hou, X.; Cui, Z.; Xiao, X. Multi-stimuli responsive shape memory behavior of dual-switch TPU/CB/CNC hybrid nanocomposites as triggered by heat, water, ethanol, and pH. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kang, S.-K. Principles for Controlling the Shape Recovery and Degradation Behavior of Biodegradable Shape-Memory Polymers in Biomedical Applications. Micromachines 2021, 12, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Miao, L.F.; Qian, L.L.; Wang, N.; Qi, M.M.; Zhang, Y.M.; Dang, S.P.; Wu, Y.; Wang, R.X. Molecular Mechanisms of Glucose Fluctuations on Diabetic Complications. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinnen, D. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists for Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Spectr. 2017, 30, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskoković, V.; Lee, K.; Lee, P.P.; Fischer, K.E.; Desai, T.A. Shape Effect in the Design of Nanowire-Coated Microparticles as Epithelial Drug Delivery Devices. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7832–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.B.; Patel, M.; Maahs, D.M.; Shah, V.N. Insulin delivery methods: Past, present and future. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Y.; DiSanto, R.; Sun, W.; Ranson, D.; Ligler, F.S.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Microneedle-array patches loaded with hypoxia-sensitive vesicles provide fast glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8260–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; He, D.; Cai, L.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Su, X. Alizarin Complexone Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Smart System Integrating Glucose-Responsive Double-Drugs Release and Real-Time Monitoring Capabilities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8358–8366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.; Li, M.; Ge, S.; Yang, J.; Sun, Q.; Xiong, L. Glucose-responsive biopolymer nanoparticles prepared by co-assembly of concanavalin A and amylopectin for insulin delivery. Indust. Crops Prod. 2018, 112, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Itoh, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Moro-Oka, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Miyahara, Y.; Suganami, T.; Matsumoto, A. Temperature-Stable Boronate Gel-Based Microneedle Technology for Self-Regulated Insulin Delivery. ACS Appl. Polymer Mater. 2020, 2, 2781–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Saha, B.; Vlachos, D.G. Pt catalysts for efficient aerobic oxidation of glucose to glucaric acid in water. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3815–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, G.; Onoguchi, A.; Tokoro, C. Preparation of copper nanoparticles for metal-metal bonding by aqueous reduction with d-glucose and PVP. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 209, 115210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, S.; Das, U.; Kc, S.; Mishra, S.; Sudarshan, M.; Saha, K.D.; Dey, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Narayana, Y. Synthesis of a novel glucose capped gold nanoparticle as a better theranostic candidate. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, P.; Fu, J.; Wallen, S.L. A simple and “green” method for the synthesis of Au, Ag, and Au–Ag alloy nanoparticles. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrekt, C.; Sørensen, K.H.; Lübcke, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Pan, C.; Bjerrum, N.J.; Ulstrup, J. 1.7 nm platinum nanoparticles: Synthesis with glucose starch, characterization and catalysis. ChemPhysChem 2010, 11, 2844–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.; Hsu, J.E.; Soslowsky, L.J. 6.618—Materials in Tendon and Ligament Repair. In Comprehensive Biomaterials; Ducheyne, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 257–279. [Google Scholar]
- Arun, Y.; Ghosh, R.; Domb, A.J. Biodegradable Hydrophobic Injectable Polymers for Drug Delivery and Regenerative Medicine. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, M.A.; Hutmacher, D.W. The return of a forgotten polymer- polycaprolactone in the 21st century. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1217–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimowska, A.; Morawska, M.; Bocho-Janiszewska, M. Biodegradation of poly(ε-caprolactone) in natural water environments. Pol. J. Chem. Tech. 2017, 19, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cercone, M.; Chevalier, J.; Kennedy, J.G.; Miller, A.D.; Fortier, L.A. Early Failure of a Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogel Implant with Osteolysis and Foreign Body Reactions in an Ovine Model of Cartilage Repair. Am. J. Sports Med. 2021, 49, 3395–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, J.D., Jr.; Mullarky, R.H.; Ryan, D.E. Tissue biocompatibility of kevlar aramid fibers and polymethylmethacrylate, composites in rabbits. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1987, 21, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bliley, J.M.; Marra, K.G. Polymeric Biomaterials as Tissue Scaffolds. In Stem Cell Biology and Tissue Engineering in Dental Sciences; Vishwakarma, A., Sharpe, P., Shi, S., Ramalingam, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zayed, M.A.; El-dek, S.I.; Ahmed, M.K.; Hady, M.A.; El Sherbiny, D.H.; Uskoković, V. Nanofibrous ε-Polycaprolactone Scaffolds Containing Ag-Doped Magnetite Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization and Biological Testing for Wound Dressing Applications in vitro and in vivo. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2070–2088. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.K.; Ramadan, R.; El-dek, S.I.; Uskoković, V. Complex Relationship between Alumina and Selenium-Doped Carbonated Hydroxyapatite as the Ceramic Additives to Electrospun Polycaprolactone Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 801, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohlmann, A.R.; Fonseca, F.N.; Paese, K.; Detoni, C.B.; Coradini, K.; Beck, R.C.; Guterres, S.S. Poly(ε-caprolactone) microcapsules and nanocapsules in drug delivery. Expert Opt. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 623–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskoković, V.; Drofenik, M. Gold-Embellished Mixed-Valence Manganite as a Smart, Self-Regulating Magnetoplasmonic Nanomaterial. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2021, 271, 124870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Feng, S.; Chen, J.; Feng, J.; Hou, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Weng, X.; Milcovich, G. Gold nanoparticles/electrochemically expanded graphite composite: A bifunctional platform toward glucose sensing and SERS applications. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 851, 113471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, P.; Zavattari, P.; Sanna, A.; Pretti, S.; Marcello, A.; Mannu, C.; Targhetta, C.; Bruno, G.; Songini, M. Zinc and Other Metals Deficiencies and Risk of Type 1 Diabetes: An Ecological Study in the High Risk Sardinia Island. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jouihan, H.A.; Cooksey, R.C.; Jones, D.; Kim, H.J.; Winge, D.R.; McClain, D.A. Manganese supplementation protects against diet-induced diabetes in wild type mice by enhancing insulin secretion. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balan, L.; Ghimbeu, C.M.; Vidal, L.; Guterl, C.V. Synthesis of manganese oxide nanostructures using visible light at room temperature. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, S.; Pauline, S. Synthesis, Structural and Morphological Characterization of CTAB-Mn3O4 by CO Precipitation Method. ChemTech Res. 2014, 6, 3813–3815. [Google Scholar]
- Baykal, A.; Koseoglu, Y.; Senel, M. Low temperature synthesis and characterization of Mn3O4 nano particles. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2007, 5, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Cherian, E.; Rajan, A.; Baskar, G. Synthesis of manganese dioxide nanoparticles using co-precipitation method and its antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Mod. Sci. Tech. 2016, 1, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Andal, V.; Buvaneswari, G. Effect of reducing agents in the conversion of Cu2O nanocolloid to Cu nanocolloid. Eng. Sci. Tech. Int. J. 2017, 20, 340–344. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Zhang, X.; Cai, H.; Cao, C. Sodium Alginate Mediated Route for the Synthesis of Monodisperse Silver Nanoparticles Using Glucose as Reducing Agents. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 2016, 45, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Yin, G.; Zeng, X.; Zhao, J.; Yao, G. Potential application of carbohydrate biomass in hydrometallurgy: One-pot reduction of metal oxides/salts under mild hydrothermal conditions. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 20747–20754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witzemann, E.J. Disodium phosphate as a catalyst for the quantitative oxidation of glucose to carbon dioxide with hydrogen peroxide. J. Biol. Chem. 1920, 45, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swensson, B.; Ek, M.; Gray, D.G. In Situ Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles in Paper by Reduction with Alkaline Glucose Solutions. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 9449–9452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, C.W. A Study of the Oxidation of d-Glucose with Air in a Saturated Solution of Barium Hydroxide. Master’s Thesis, University of Nebraska–Lincoln, Lincoln, NE, USA, 1929. Available online: https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/opentheses/62/ (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Witzemann, E.J. A new method of preparation and some interesting transformations of colloidal manganese dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1915, 37, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, C.F.; Bevan, E.J.; Smith, C. XLIX.—Reactions of the carbohydrates with hydrogen peroxide. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1898, 73, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoehr, H.A. The oxidation of carbohydrates with air. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1924, 46, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet-Aleta, J.; Calzada-Funes, J.; Hueso, J.L. Manganese oxide nano-platforms in cancer therapy: Recent advances on the development of synergistic strategies targeting the tumor microenvironment. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 29, 101628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, J.V.; Schulz-Vogt, H.N.; Dellwig, O.; Pollehne, F.; Schott, T.; Meeske, C.; Beier, S.; Jurgens, K. Biological manganese-dependent sulfide oxidation impacts elemental gradients in redox-stratified systems: Indications from the Black Sea water column. ISME J. 2022, 16, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Shan, X.; Pang, Z.; Song, P.; Niu, F.; Hu, L. Glucose-Responsive Microspheres as a Smart Drug Delivery System for Controlled Release of Insulin. Eur. J. Drug Metabol. Pharmacokin. 2020, 45, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uskoković, V. Mechanism of Formation Governs the Mechanism of Release of Antibiotics from Calcium Phosphate Powders and Cements in a Drug-Dependent Manner. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 3982–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganji, F.; Vasheghani-Farahani, S.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E. Theoretical Description of Hydrogel Swelling: A Review. Iran. Polym. J. 2010, 19, 375–398. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, C.G.; Gu, Z.W. Modification of the rates of chain cleavage of poly(ε-caprolactone) and related polyesters in the solid state. J. Control Release 1987, 4, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belbekhouche, S.; Charaabi, S.; Carbonnier, B. Glucose-sensitive capsules based on hydrogen-bonded (polyvinylpyrrolidone/phenylboronic–modified alginate) system. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 177, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, H.; Inagi, T. Partition of methyl orange between H2O and n-octanol. Membrane 1977, 2, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Liang, N.; Kawashima, Y.; Xia, D.; Cui, F. Hydrophobic ion pairing of an insulin-sodium deoxycholate complex for oral delivery of insulin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 3049–3056. [Google Scholar]
- Kurpiers, M.; Wolf, J.D.; Spleis, H.; Steinbring, C.; Jörgensen, A.M.; Matuszczak, B.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Lysine-Based Biodegradable Surfactants: Increasing the Lipophilicity of Insulin by Hydrophobic Ion Paring. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwalfenberg, G.K. The alkaline diet: Is there evidence that an alkaline pH diet benefits health? J. Environ. Public Health 2012, 2012, 727630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, N.J.; Bryant, M.G.; McCoy, C.P.; Trotter, J.L.; Turner, J. Multifunctional, Low Friction, Antimicrobial Approach for Biomaterial Surface Enhancement. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, L.A.; Silva, J.B.A.; Giulietti, M. Solubility of d-Glucose in Water and Ethanol/Water Mixtures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2007, 52, 2166–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, U.S.; Shetty, A.N. Simple glucose reduction route for one-step synthesis of copper nanofluids. Appl. Nanosci. 2014, 4, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, S.; Ali, N.; Tayyab, Z.; Shah, M.Y.; Yang, C.P.; Hu, J.F.; Kong, W.; Huang, Q.A.; Hayat, A.; Muhammad, M. Ionic liquid coated zerovalent manganese nanoparticles with stabilized and enhanced peroxidase-like catalytic activity for colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 035018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Jiao, R.; Liu, W.; Li, B.; Jin, Y. Visual detection of glucose by hydrogen peroxide test strips. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 4162–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Liu, F.; Fu, Q.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Guo, T.; et al. Hydrogen peroxide and glucose concentration measurement using optical fiber grating sensors with corrodible plasmonic nanocoatings. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Campbell, A.S.; Wang, J. Wearable non-invasive epidermal glucose sensors: A review. Talanta 2018, 177, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franc, A.; Muselík, J.; Sabadková, D.; Neumann, D. Preparation of pellets with controlled release of glucose as prevention of hypoglycaemia in paediatric patients. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 75, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Kahkoska, A.R.; Wang, J.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Insulin-Responsive Glucagon Delivery for Prevention of Hypoglycemia. Small 2017, 13, 1603028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uskoković, V. When 1 + 1 > 2: Nanostructured Composite Materials for Hard Tissue Engineering Applications. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 57, 434–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uskoković, V. Supplementation of Polymeric Reservoirs with Redox-Responsive Metallic Nanoparticles as a New Concept for the Smart Delivery of Insulin in Diabetes. Materials 2023, 16, 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020786
Uskoković V. Supplementation of Polymeric Reservoirs with Redox-Responsive Metallic Nanoparticles as a New Concept for the Smart Delivery of Insulin in Diabetes. Materials. 2023; 16(2):786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020786
Chicago/Turabian StyleUskoković, Vuk. 2023. "Supplementation of Polymeric Reservoirs with Redox-Responsive Metallic Nanoparticles as a New Concept for the Smart Delivery of Insulin in Diabetes" Materials 16, no. 2: 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020786
APA StyleUskoković, V. (2023). Supplementation of Polymeric Reservoirs with Redox-Responsive Metallic Nanoparticles as a New Concept for the Smart Delivery of Insulin in Diabetes. Materials, 16(2), 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16020786





