Optical Properties of Amorphous Carbon Thin Films Fabricated Using a High-Energy-Impulse Magnetron-Sputtering Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
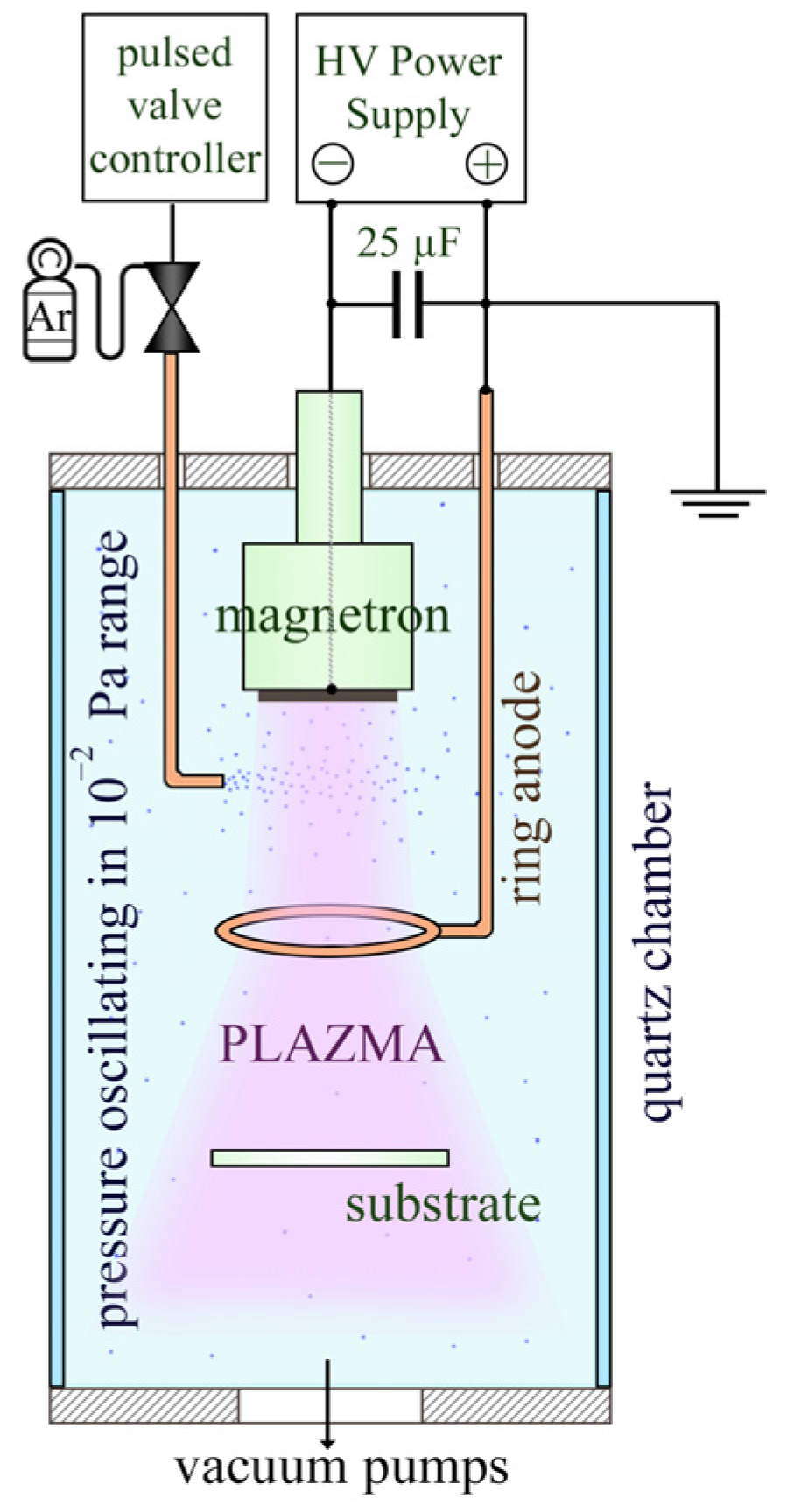
2.1. Sample Preparation
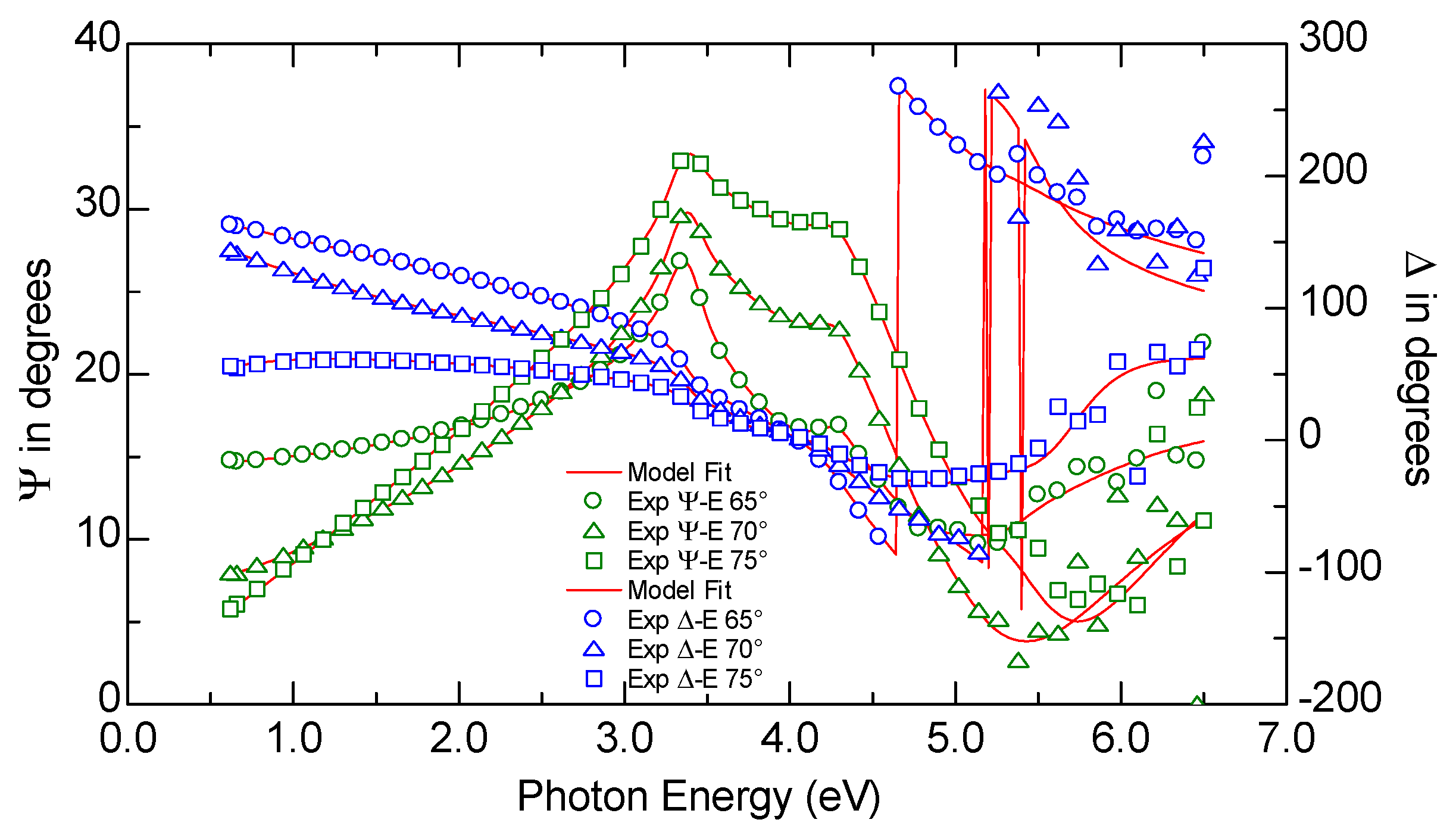
2.2. Sample Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Composition of the Fabricated a-C Films
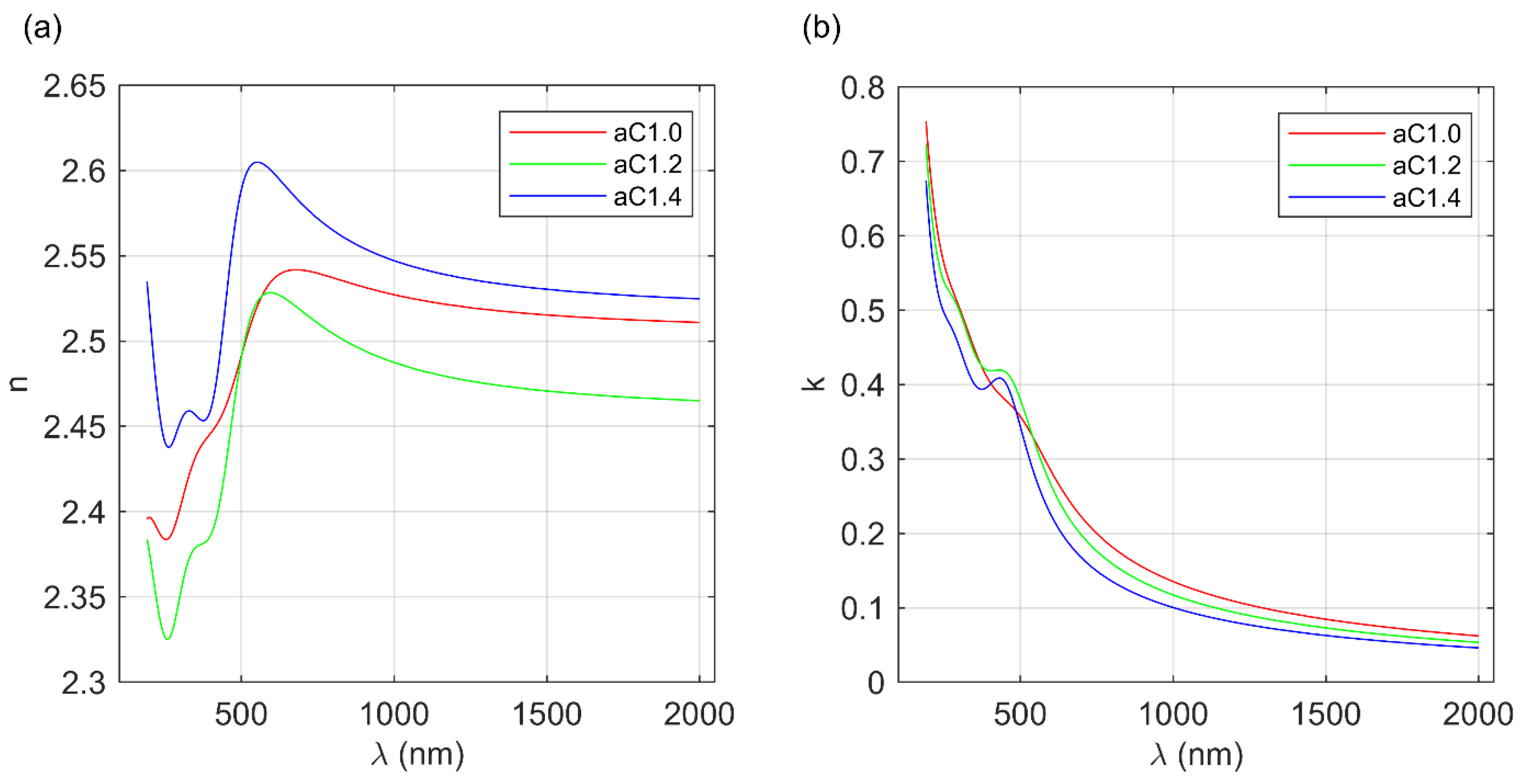
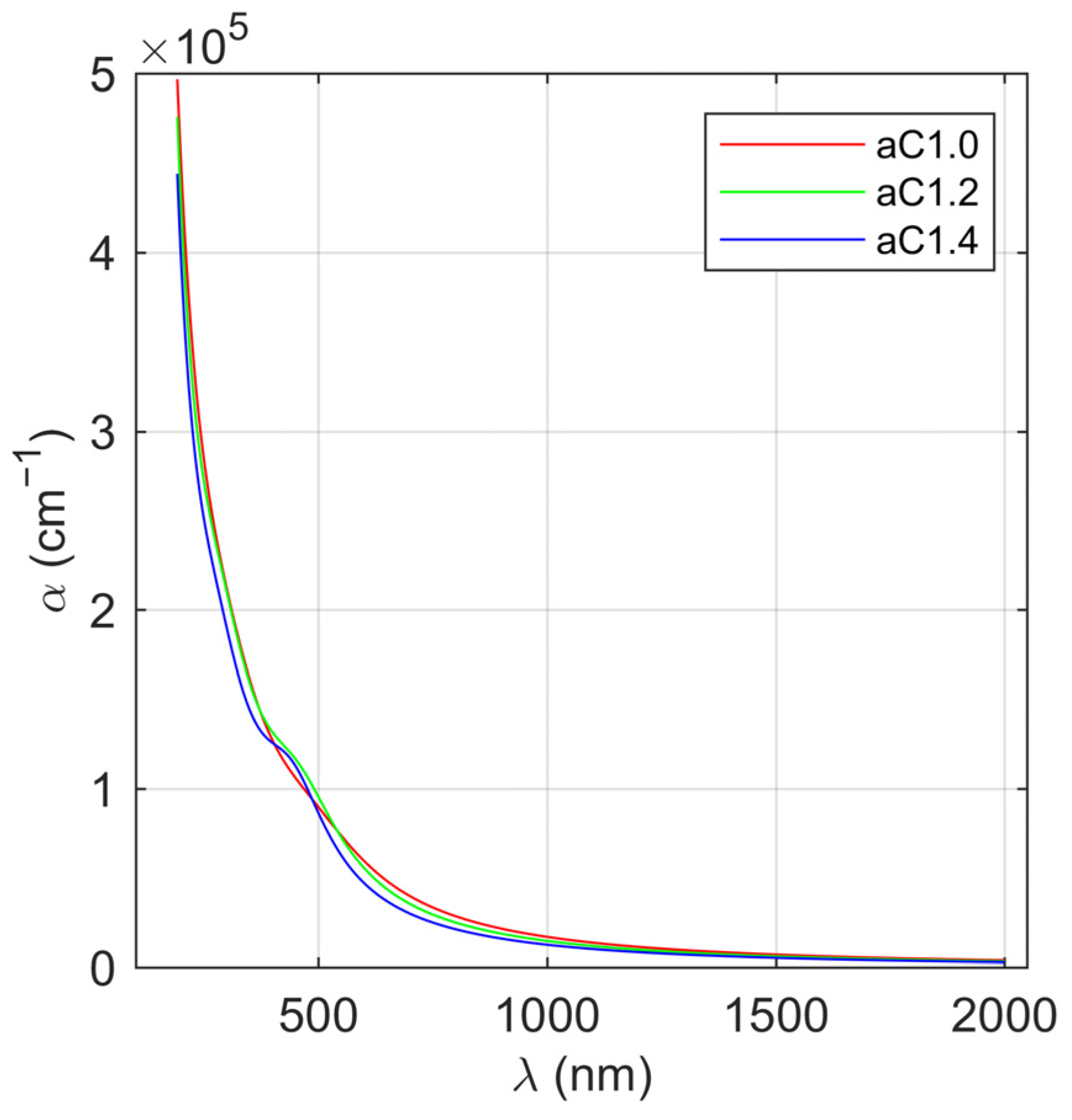
3.2. Optical Properties of the a-C Films
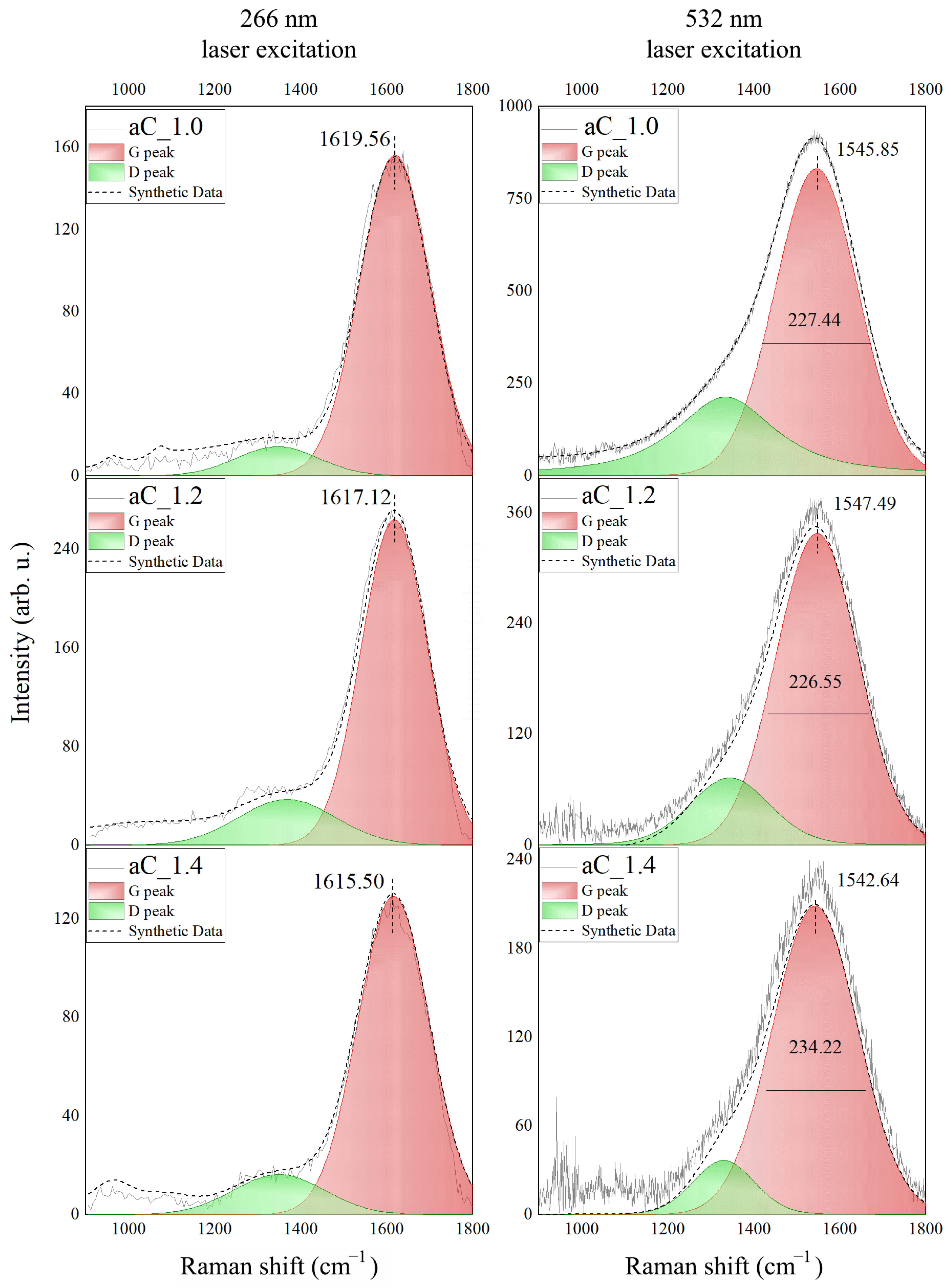
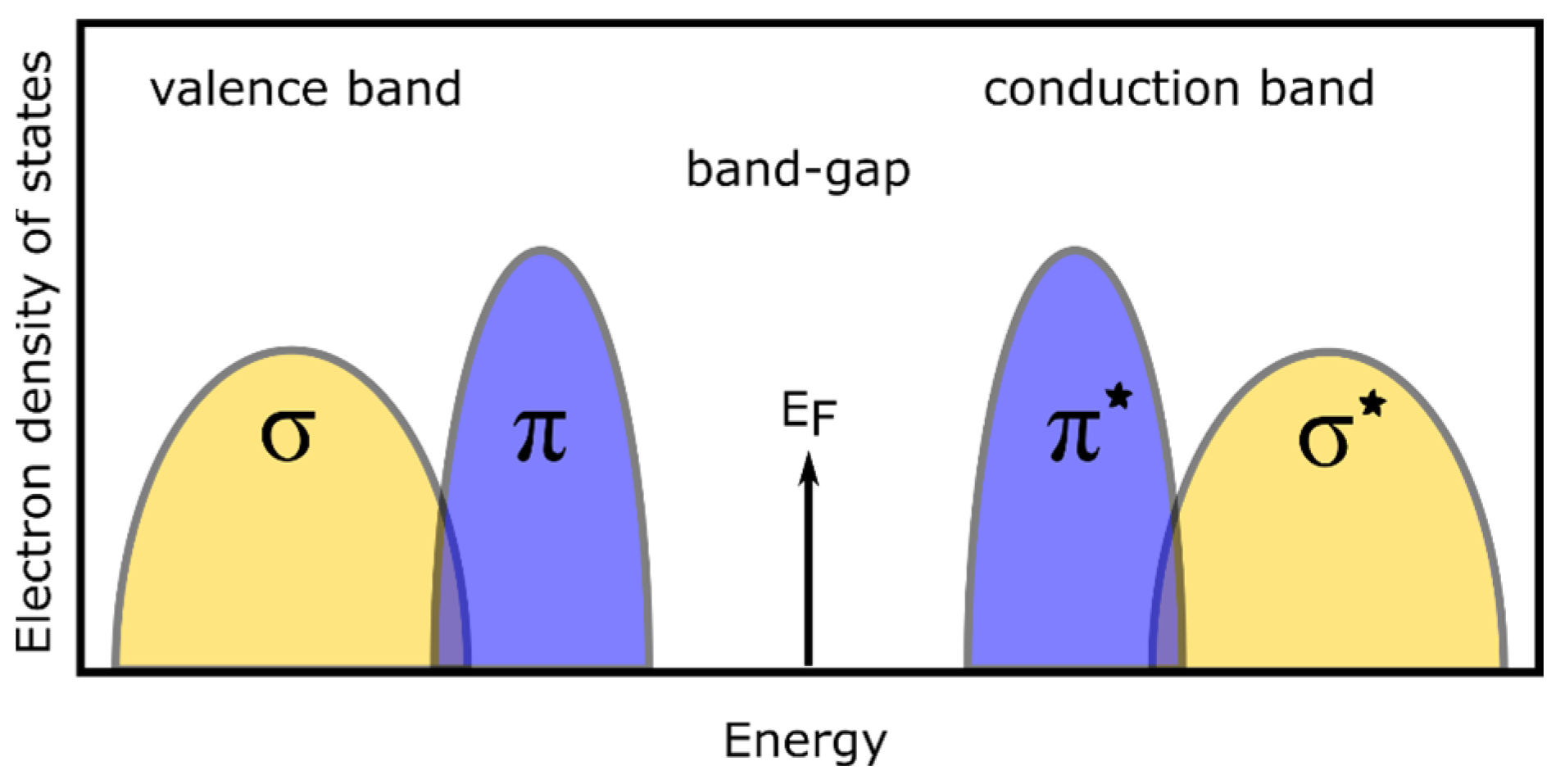
3.3. Structure of the a-C Films
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sample | Peak | Position (cm−1) | FWHM (cm−1) | Intensity (arb.u.) | sp3 Content GFWHM (%) | sp3 Content GPos. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aC1.0 | G266 | 1619.56 | 200.41 | 147.58 | 62 ± 6 | 69 ± 8 |
| D266 | 1413.24 | 212.00 | 18.05 | |||
| G532 | 1545.85 | 227.44 | 831.57 | |||
| D532 | 1334.02 | 276.16 | 213.26 | |||
| aC1.2 | G266 | 1617.18 | 185.18 | 249.54 | 58 ± 6 | 69 ± 8 |
| D266 | 1413.39 | 192.40 | 43.09 | |||
| G532 | 1547.49 | 226.55 | 337.40 | |||
| D532 | 1343.94 | 219.20 | 72.65 | |||
| aC1.4 | G266 | 1615.50 | 189.53 | 120.35 | 61 ± 6 | 73 ± 8 |
| D266 | 1410.11 | 172.52 | 17.65 | |||
| G532 | 1542.64 | 234.22 | 208.67 | |||
| D532 | 1329.93 | 167.84 | 36.66 |
References
- Ray, S. Magnetism and Spintronics in Carbon and Carbon Nanostructured Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Makarova, T. An Overview of the Magnetism of Metal Free Carbon-based Compounds and Materials. In Carbon Based Magnetism; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, J. Diamond-like amorphous carbon. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2002, 37, 129–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, I.; Bhatnagar, M.; Shukla, K.; Sarma, B.; Ranjan, M.; Sarma, A. Correlation of structural and optical properties of PVD grown amorphous carbon thin films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 75, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larruquert, J.; Rodríguez-de Marcos, L.; Méndez, J.; Martin, P.; Bendavid, A. High reflectance ta-C coatings in the extreme ultraviolet. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 27537–27549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koidl, P.; Wild, C.; Dischler, B.; Wagner, J.; Ramsteiner, M. Plasma Deposition, Properties and Structure of Amorphous Hydrogenated Carbon Films. Mater. Sci. Forum 1990, 52–53, 41–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waidmann, S.; Knupfer, M.; Fink, J.; Kleinsorge, B.; Robertson, J. Electronic structure studies of undoped and nitrogen-doped tetrahedral amorphous carbon using high-resolution electron energy-loss spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 3783–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhowalla, M.; Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J.; Amaratunga, G.A.J. Evolution of sp2 bonding with deposition temperature in tetrahedral amorphous carbon studied by Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 76, 1419–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.; Ravi, P. Properties of Amorphous Carbon; Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Guo, P.; Zhang, D.; Chen, R.; Zuo, X.; Ke, P.; Saito, H.; Wang, A. Influence of deposition temperature on the structure, optical and electrical properties of a-C films by DCMS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 503, 144310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohagheghpour, E.; Rajabi, M.; Gholamipour, R.; Larijani, M.M.; Sheibani, S. Correlation study of structural, optical and electrical properties of amorphous carbon thin films prepared by ion beam sputtering deposition technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, J.Y.; Tay, B.K.; Sheeja, D.; Lau, S.P.; Fu, Y.Q.; Chua, D.H.C.; Milne, W.I. Optical and electrical properties of amorphous carbon films deposited using filtered cathodic vacuum arc with pulse biasing. Thin Solid Film. 2004, 447–448, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.Y.; Cheng, X.R.; Wang, C.F.; Xue, Y.C.; Chen, Z.P. Structural, optical and electrical properties of amorphous carbon films deposited by pulsed unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Optik 2015, 126, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Alkhesho, I.; Zhou, H.; Duley, W.W. Optical and microstructural properties of diamond-like carbon films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2007, 16, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honglertkongsakul, K.; May, P.W.; Paosawatyanyong, B. Electrical and optical properties of diamond-like carbon films deposited by pulsed laser ablation. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2010, 19, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coşkun, Ö.D.; Zerrin, T. Optical, structural and bonding properties of diamond-like amorphous carbon films deposited by DC magnetron sputtering. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2015, 56, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldeeb, M.A.; Morgan, N.; Abouelsayed, A.; Amin, K.M.; Hassaballa, S. Correlation of acetylene plasma discharge environment and the optical and electronic properties of the hydrogenated amorphous carbon films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2019, 96, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicher, B.; Chodun, R.; Skowroński, Ł.; Trzcinski, M.; Kulikowski, K.; Zdunek, K. Design of thin DLC/TiO2 film interference coatings on glass screen protector using a neon–argon-based gas injection magnetron sputtering technique. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 123, 108859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicher, B.; Chodun, R.; Greczynski, G.; Lachowski, A.; Trzcinski, M.; Pshyk, A.V.; Król, K.; Kulikowski, K.; Skowroński, Ł.; Zdunek, K. Carbon ion self–sputtering attained by sublimation of hot graphite target and controlled by pulse injection of a neon–helium gas mixture. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 620, 156708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, M.; Shinagawa, T.; Kawai, S.; Umeno, M. Microstructure and optical band gap control of DLC film deposited by pulsed discharge plasma CVD. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2008, 17, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, A. Electrical and optical properties of diamond-like carbon. Thin Solid Film. 1999, 355–356, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewilogua, K.; Hofmann, D. History of diamond-like carbon films—From first experiments to worldwide applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 242, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, J. 60 years of DLC coatings: Historical highlights and technical review of cathodic arc processes to synthesize various DLC types, and their evolution for industrial applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 257, 213–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearnaley, G.; Arps, J.H. Biomedical applications of diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings: A review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 2518–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettington, A.H.; Smith, C. Optical properties and applications of diamond-like carbon coatings. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1992, 1, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Cai, W. Mechanical properties and anti-corrosion behavior of the diamond-like carbon films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, L.; Ojha, S.M. The growth of carbon films with random atomic structure from ion impact damage in a hydrocarbon plasma. Thin Solid Film. 1979, 58, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherine, Y.; Couderc, P. Electrical characteristics and growth kinetics in discharges used for plasma deposition of amorphous carbon. Thin Solid Film. 1986, 144, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowski, M.; Sokołowska, A.; Gokieli, B.; Michalski, A.; Rusek, A.; Romanowski, Z. Reactive pulse plasma crystallization of diamond and diamond-like carbon. J. Cryst. Growth 1979, 47, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassavetis, S.; Patsalas, P.; Logothetidis, S.; Robertson, J.; Kennou, S. Dispersion relations and optical properties of amorphous carbons. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2007, 16, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsov, V.; Macak, K.; Schneider, J.; Helmersson, U.; Petrov, I. A novel pulsed magnetron sputter technique utilizing very high target power densities. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 122, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarakinos, K.; Alami, J.; Konstantinidis, S. High power pulsed magnetron sputtering: A review on scientific and engineering state of the art. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 1661–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarakinos, K.; Braun, A.; Zilkens, C.; Mraz, S.; Schneider, J.M.; Zoubos, H.; Patsalas, P. Exploring the potential of high power impulse magnetron sputtering for growth of diamond-like carbon films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 2706–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiatrowski, A.; Kijaszek, W.; Posadowski, W.M.; Oleszkiewicz, W.; Jadczak, J.; Kunicki, P. Deposition of diamond-like carbon thin films by the high power impulse magnetron sputtering method. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 729, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iga, K.; Oda, A.; Kousaka, H.; Ohta, T. Formation of diamond-like carbon film using high-power impulse magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Film. 2019, 672, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Saka, K. Synthesis of hard diamond-like carbon films by double-pulse high-power impulse magnetron sputtering. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 108, 107996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Su, F.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Sun, J.; Lin, S. Hydrogen-free DLC films fabricated using superimposed HiPIMS-DCMS deposition system: Bias voltage effects. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 470, 129820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aijaz, A.; Sarakinos, K.; Lundin, D.; Brenning, N.; Helmersson, U. A strategy for increased carbon ionization in magnetron sputtering discharges. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2012, 23, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicher, B.; Chodun, R.; Trzcinski, M.; Nowakowska-Langier, K.; Skowronski, L.; Lachowski, A.; Zdunek, K. Applications insight into the plasmochemical state and optical properties of amorphous CNx films deposited by gas injection magnetron sputtering method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 565, 150540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinski, M.; Chodun, R.; Nowakowska-Langier, K.; Zdunek, K. Computational modelling of discharges within the impulse plasma deposition accelerator with a gas valve. Phys. Scr. 2014, T161, 014049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodun, R.; Nowakowska-Langier, K.; Wicher, B.; Okrasa, S.; Minikayev, R.; Zdunek, K. Reactive sputtering of titanium compounds using the magnetron system with a grounded cathode. Thin Solid Film. 2017, 640, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münz, W.-D.; Zufrass, T. Industrial scale deposition of well adherent superhard and low friction CDLC coatings grown by HIPIMS and anode assisted unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 387, 125485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.G.; Lai, Q.B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.M. Quantitative measurements of sp3 content in DLC films with Raman spectroscopy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 1995–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woollam, J.A. Guide to Using WVASE32®; Wextech Systems Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, H. Spectroscopic Ellipsometry. Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kovtun, A.; Jones, D.; Dell’Elce, S.; Treossi, E.; Liscio, A.; Palermo, V. Accurate chemical analysis of oxygenated graphene-based materials using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Carbon 2019, 143, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabchinskii, M.K.; Dideikin, A.T.; Kirilenko, D.A.; Baidakova, M.V.; Shnitov, V.V.; Roth, F.; Konyakhin, S.V.; Besedina, N.A.; Pavlov, S.I.; Kuricyn, R.A.; et al. Facile reduction of graphene oxide suspensions and films using glass wafers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streletskiy, O.A.; Zavidovskiy, I.A.; Balabanyan, V.Y.; Tsiskarashvili, A.V. Antibacterial properties of modified a-C and ta-C coatings: The effects of the sp2/sp3 ratio, oxidation, nitridation, and silver incorporation. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, D. A review on C1s XPS-spectra for some kinds of carbon materials, Fullerenes. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2020, 28, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowronski, L.; Ciesielski, A.; Olszewska, A.; Szczesny, R.; Naparty, M.; Trzcinski, M.; Bukaluk, A. Microstructure and Optical Properties of E-Beam Evaporated Zinc Oxide Films—Effects of Decomposition and Surface Desorption. Materials 2020, 13, 3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.; Ashcheulov, P.; Hubík, P.; Weiss, Z.; Klimša, L.; Kopeček, J.; Hrabovsky, J.; Veis, M.; Lorinčík, J.; Elantyev, I.; et al. Comparative determination of atomic boron and carrier concentration in highly boron doped nano-crystalline diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 135, 109837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, H.; Ohashi, Y.; Ishikawa, K.; Kondo, H.; Kato, T.; Kaneko, T.; Takeda, K.; Tsutsumi, T.; Hayashi, T.; Sekine, M.; et al. Gas-phase and film analysis of hydrogenated amorphous carbon films: Effect of ion bombardment energy flux on sp2 carbon structures. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 104, 107651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsalas, P. Optical properties of amorphous carbons and their applications and perspectives in photonics. Thin Solid Film. 2011, 519, 3990–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franta, D.; Nečas, D.; Zajíčková, L.; Buršíková, V.; Cobet, C. Combination of synchrotron ellipsometry and table-top optical measurements for determination of band structure of DLC films. Thin Solid Film. 2011, 519, 2694–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J.T. Amorphous and Liquid Semiconductors; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Jarosiński, Ł.; Pawlak, J.; Al-Ani, S.K.J. Inverse logarithmic derivative method for determining the energy gap and the type of electron transitions as an alternative to the Tauc method. Opt. Mater. 2019, 88, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, M.A.; Deringer, V.L.; Koskinen, J.; Laurila, T.; Csányi, G. Growth Mechanism and Origin of High sp3 Content in Tetrahedral Amorphous Carbon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 166101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chodun, R.; Skowronski, L.; Trzcinski, M.; Nowakowska-Langier, K.; Kulikowski, K.; Naparty, M.; Radziszewski, M.; Zdunek, K. The Amorphous Carbon Thin Films Synthesized by Gas Injection Magnetron Sputtering Technique in Various Gas Atmospheres. Coatings 2023, 13, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowronski, L.; Zdunek, K.; Nowakowska-Langier, K.; Chodun, R.; Trzcinski, M.; Kobierski, M.; Kustra, M.K.; Wachowiak, A.A.; Wachowiak, W.; Hiller, T.; et al. Characterization of microstructural, mechanical and optical properties of TiO2 layers deposited by GIMS and PMS methods. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 282, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowski, M. Influence of the pulse plasma chemical content on the crystallization of diamond under conditions of its thermodynamic instability. J. Cryst. Growth 1981, 54, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowski, M.; Sokolowska, A. Electric charge influence on the metastable phase nucleation. J. Cryst. Growth 1982, 57, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowska, A.; Zdunek, K.; Grigoriew, H.; Romanowski, Z. The structure and mechanical properties of carbon layers formed by crystallization from pulse plasma. J. Mater. Sci. 1986, 21, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifshitz, Y.; Kasi, S.R.; Rabalais, J.W.; Eckstein, W. Subplantation model for film growth from hyperthermal species. Phys. Rev. 1990, B41, 10468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifshitz, Y.; Lempert, G.D.; Grossman, E.; Avigal, I.; Uzan-Saguy, C.; Kalish, R.; Kulik, J.; Marton, D.; Rabalais, J.W. Growth mechanisms of DLC films from C+ ions: Experimental studies. Diam. Relat. Mat. 1995, 4, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | sp3 Content | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GFWHM | GPos. | XPS | |
| aC1.0 | 62 ± 6% | 69 ± 8% | 55 ± 3% |
| aC1.2 | 58 ± 6% | 68 ± 8% | 56 ± 3% |
| aC1.4 | 61 ± 6% | 73 ± 8% | 54 ± 6% |
| Sample | d (nm) | MSE (-) |
|---|---|---|
| aC1.0 | 32.1 ± 0.4 | 1.39 |
| aC1.2 | 22.1 ± 0.4 | 4.31 |
| aC1.4 | 21.5 ± 0.3 | 2.75 |
| Sample | Eg (eV) | Eg (nm) | m (-) |
|---|---|---|---|
| aC1.0 | 1.58 ± 0.03 | 785 ± 20 nm | 1.02 ± 0.02 |
| aC1.2 | 2.18 ± 0.03 | 569 ± 8 nm | 0.49 ± 0.05 |
| aC1.4 | 2.45 ± 0.02 | 506 ± 5 nm | 0.30 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skowronski, L.; Chodun, R.; Trzcinski, M.; Zdunek, K. Optical Properties of Amorphous Carbon Thin Films Fabricated Using a High-Energy-Impulse Magnetron-Sputtering Technique. Materials 2023, 16, 7049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16217049
Skowronski L, Chodun R, Trzcinski M, Zdunek K. Optical Properties of Amorphous Carbon Thin Films Fabricated Using a High-Energy-Impulse Magnetron-Sputtering Technique. Materials. 2023; 16(21):7049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16217049
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkowronski, Lukasz, Rafal Chodun, Marek Trzcinski, and Krzysztof Zdunek. 2023. "Optical Properties of Amorphous Carbon Thin Films Fabricated Using a High-Energy-Impulse Magnetron-Sputtering Technique" Materials 16, no. 21: 7049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16217049
APA StyleSkowronski, L., Chodun, R., Trzcinski, M., & Zdunek, K. (2023). Optical Properties of Amorphous Carbon Thin Films Fabricated Using a High-Energy-Impulse Magnetron-Sputtering Technique. Materials, 16(21), 7049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16217049








