Application of Metal-Based Catalysts for Semi-Hydrogenation of Alkynol: A Review
Abstract
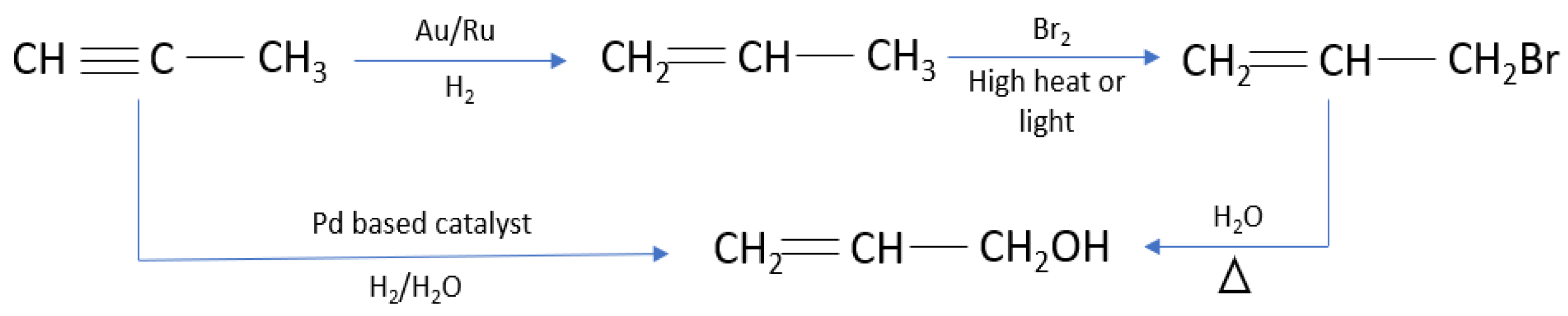
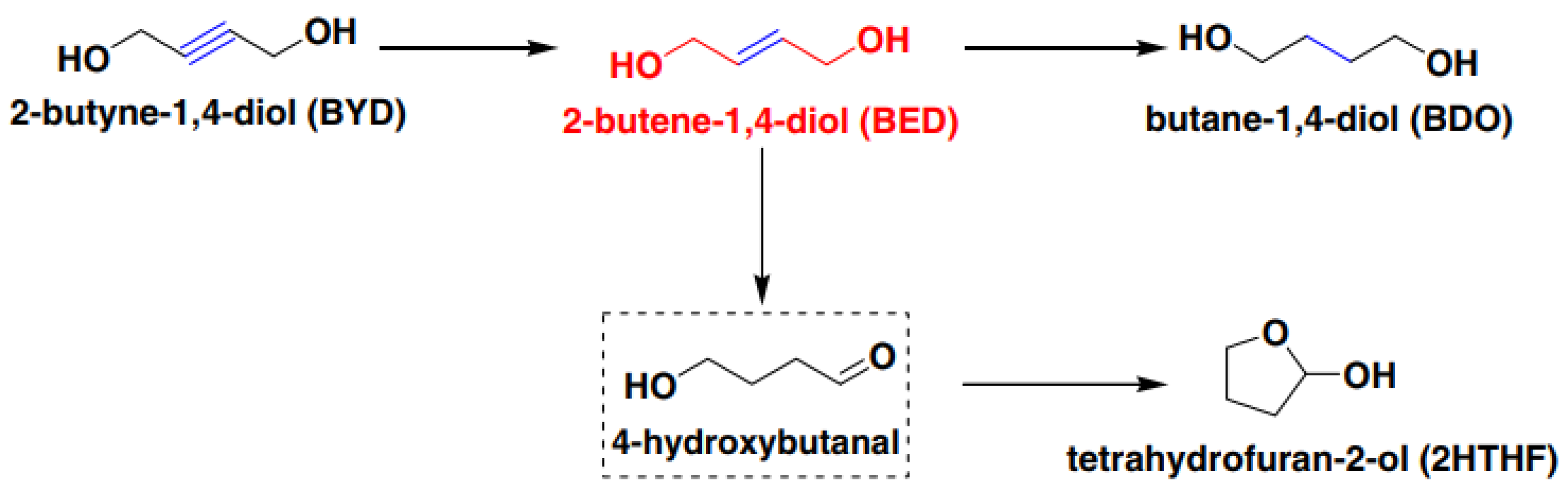
:1. Introduction
2. Semi-Hydrogenation of Alkynols over Noble Metal Catalysts
2.1. Pd-Based Catalysts
2.1.1. Lindlar Catalyst (Pd-Pb/CaCO3)
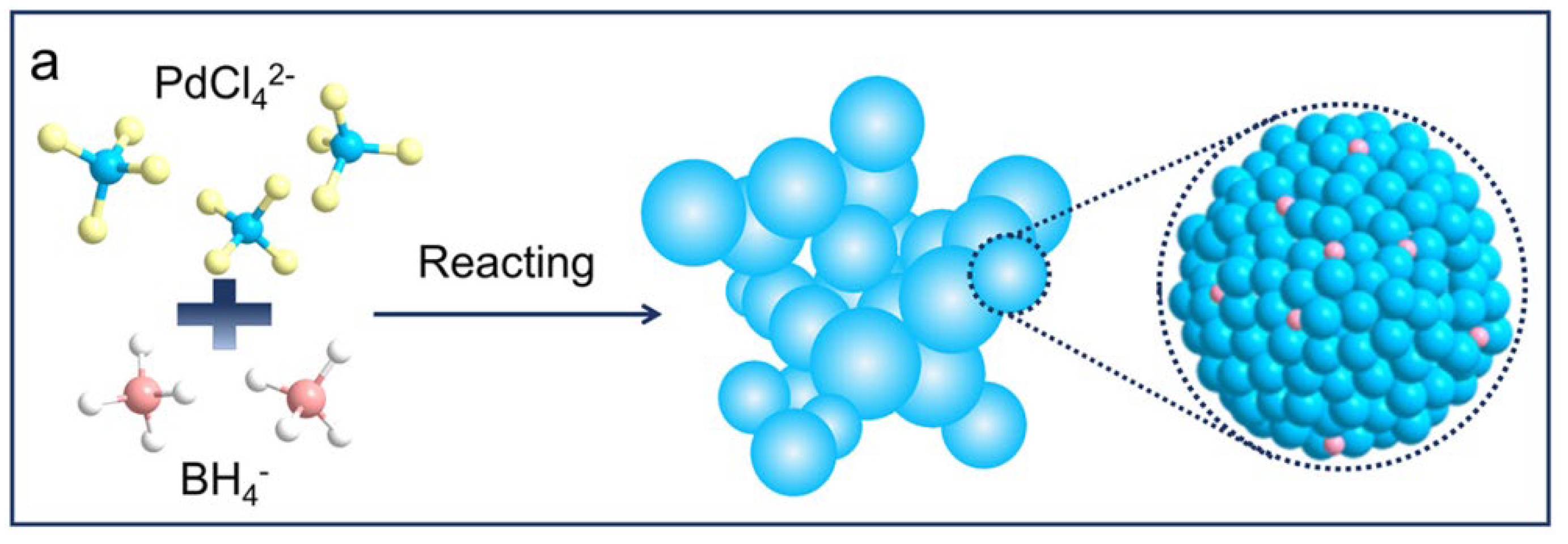
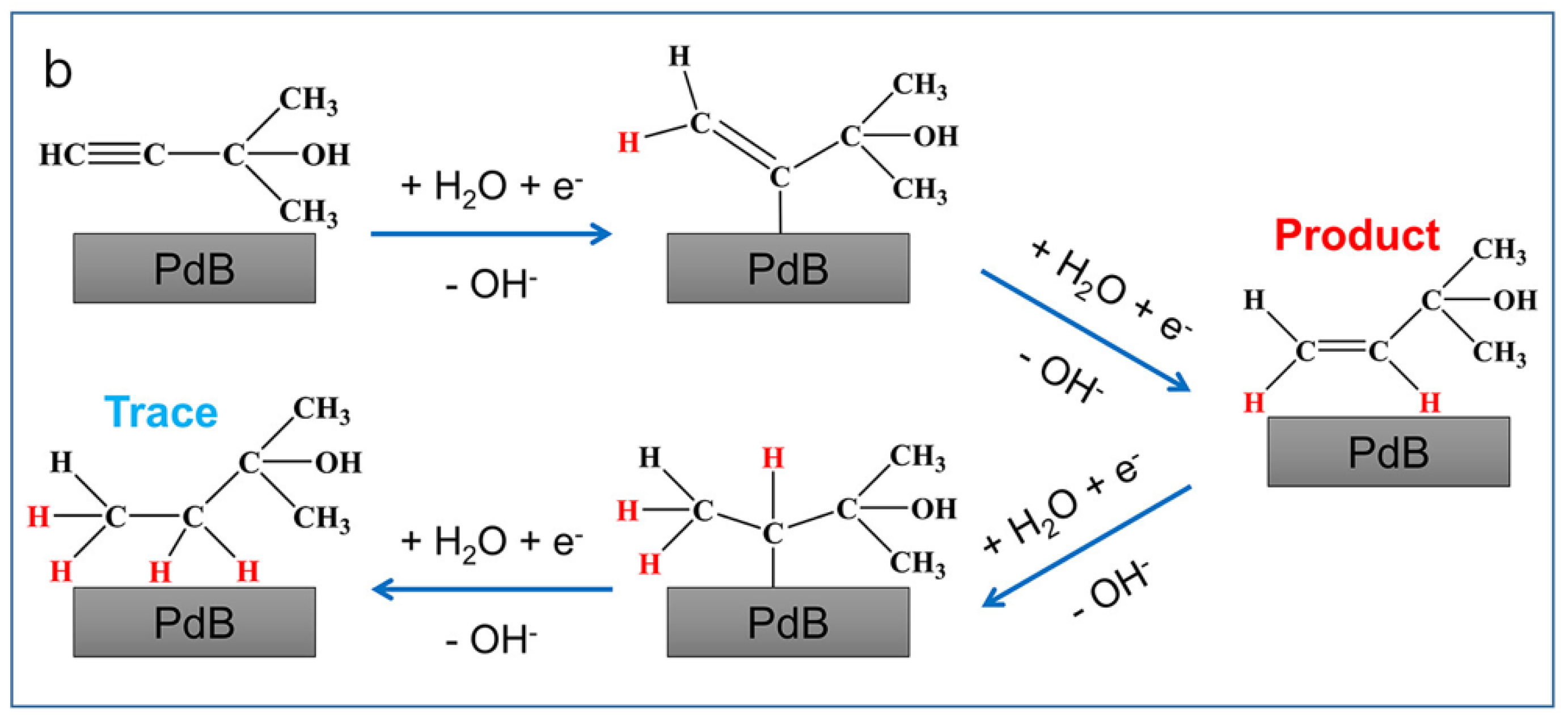
2.1.2. Pd-B Catalyst
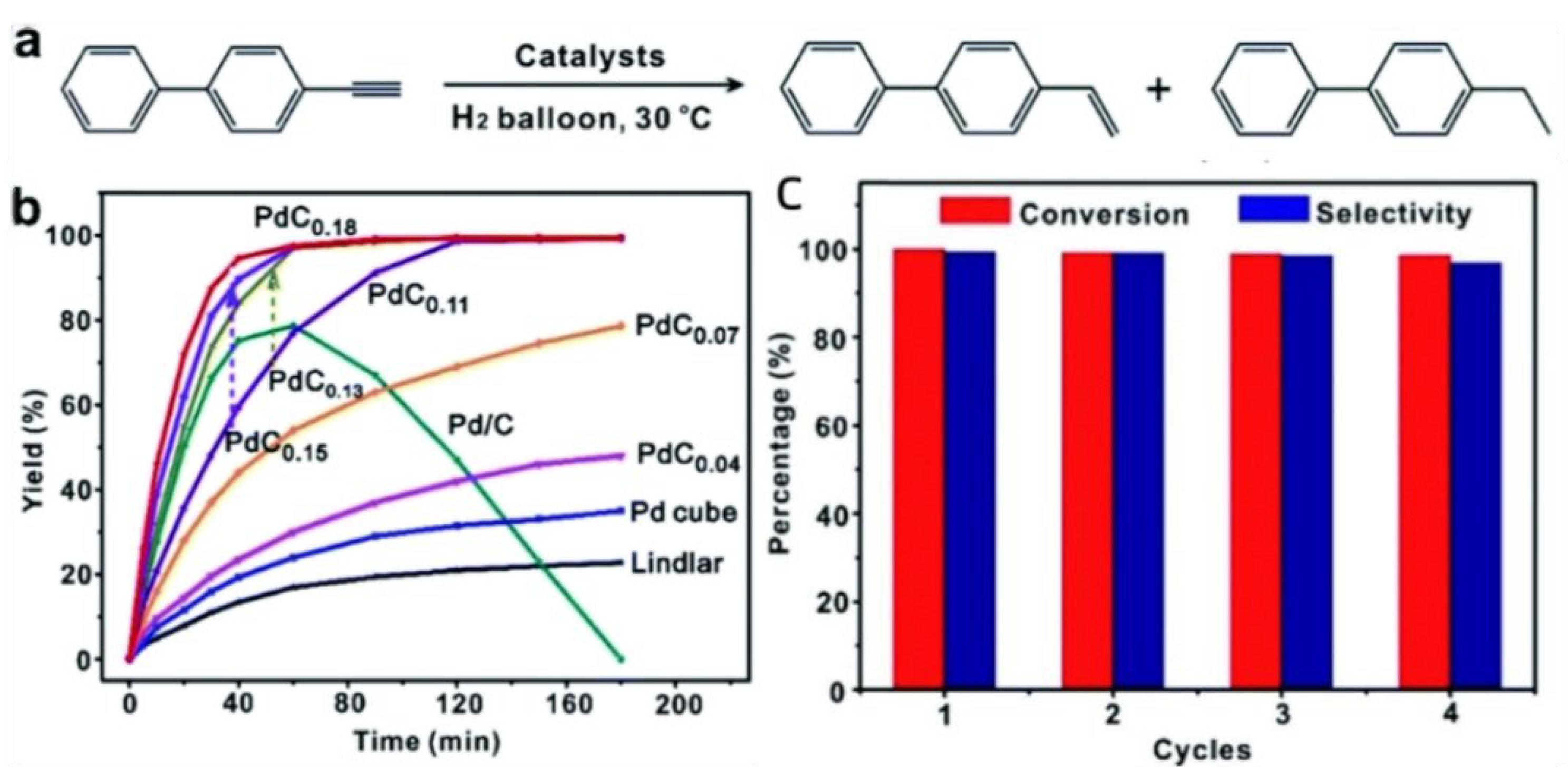
2.1.3. Pd-C Catalyst
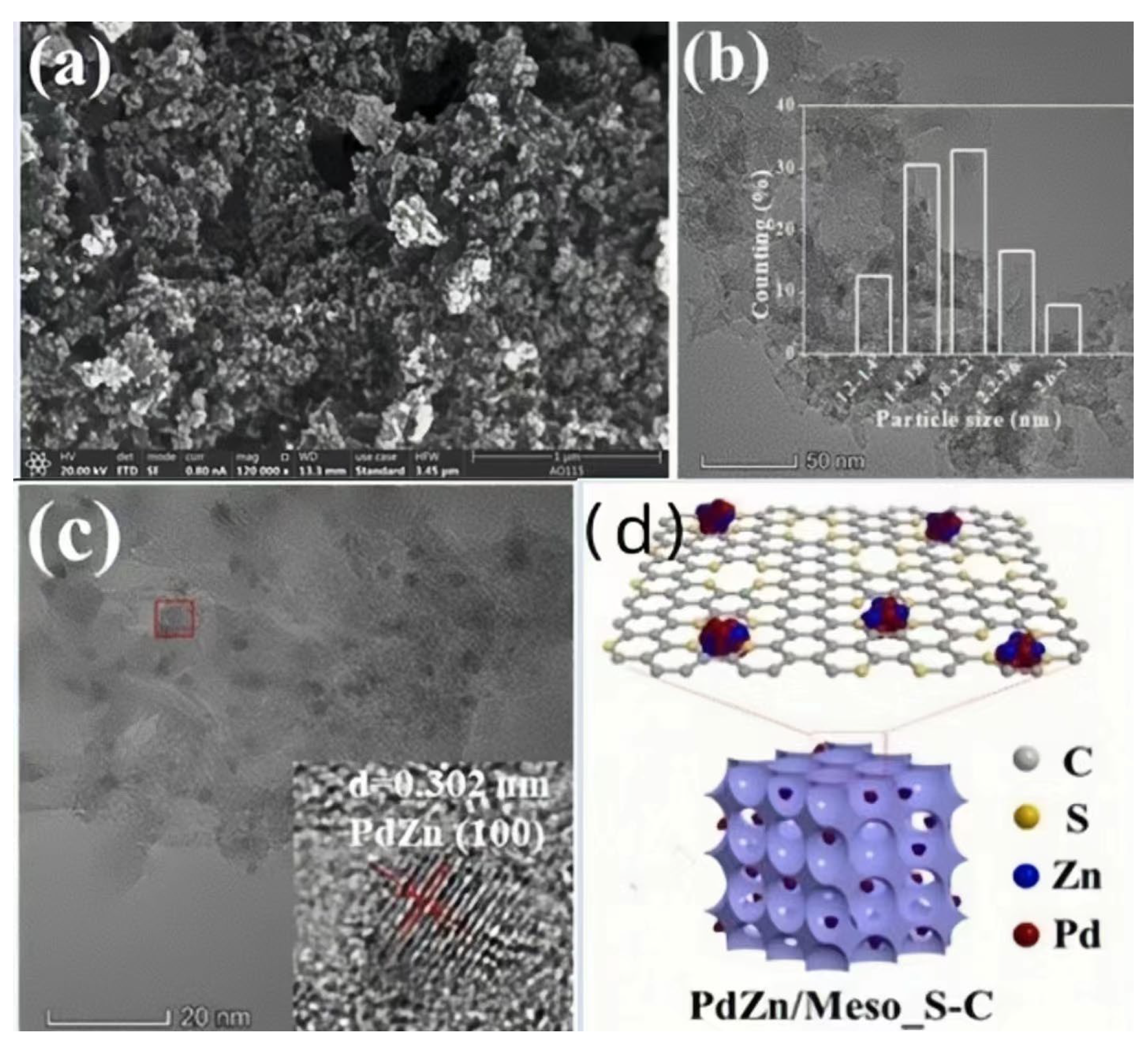
2.1.4. PdZn/Meso_S-C Catalyst
2.1.5. Pd-Enhanced Alkynol Hydrogenation on msAC
2.1.6. Other Catalysts
2.2. Pt-Based Catalysts
2.2.1. Pt{hkl} Catalysts
2.2.2. PtCl2/XPhos Catalyst System
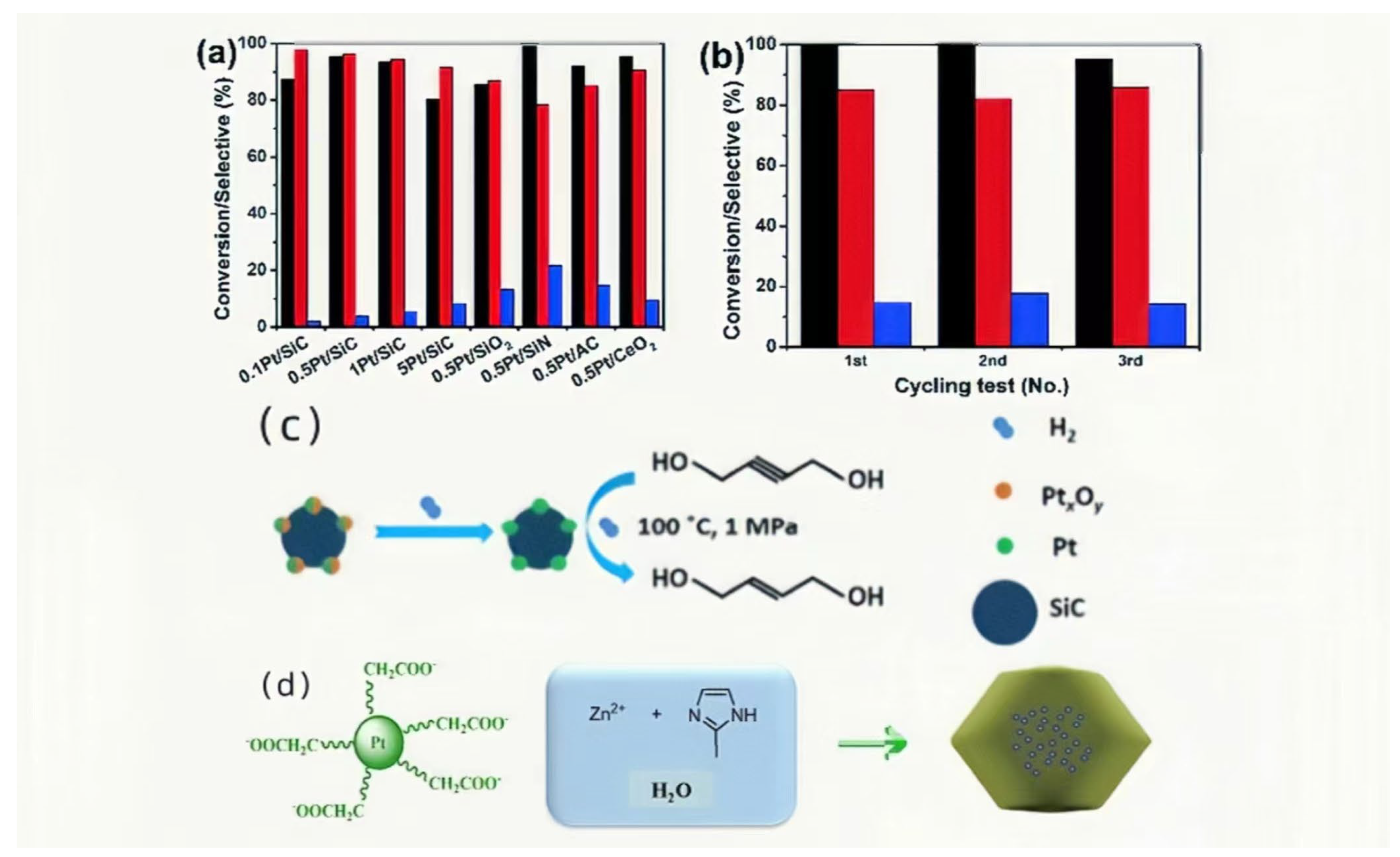
2.2.3. Pt/SiC Catalyst
2.2.4. Platinum NPs by Eschericha coli
2.3. Other Noble Metal
2.3.1. Au11Cl2(dppee)4]+ Nanocluster
2.3.2. Ru-Based Catalyst
3. Semi-Hydrogenation of Alkynols over Non-Noble Metal Catalysts
3.1. Ni-Based Catalyst
3.1.1. Raney-Ni Catalyst
3.1.2. Ni-Si Catalyst
3.1.3. Pristine Ni Catalyst
3.1.4. Other Heteroatom Participated Catalysts
3.2. Cu- and Zn-Based Catalyst
3.2.1. CuO-Fe2O3 on SiO2 and Al2O3 Base
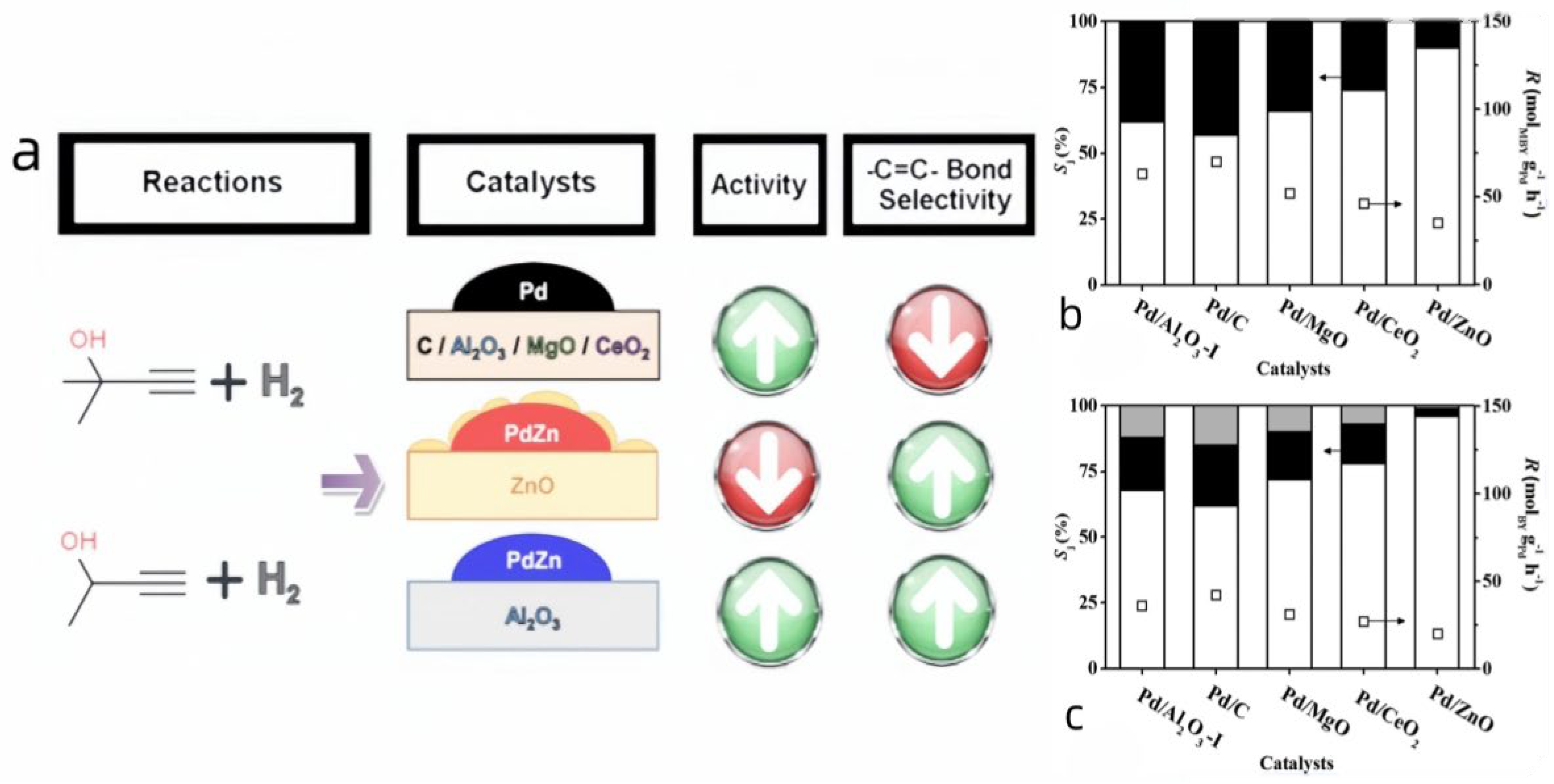
3.2.2. Pd-Zn on TiO2
3.2.3. Cu-Based Catalyst
3.2.4. Zn-Based Catalyst
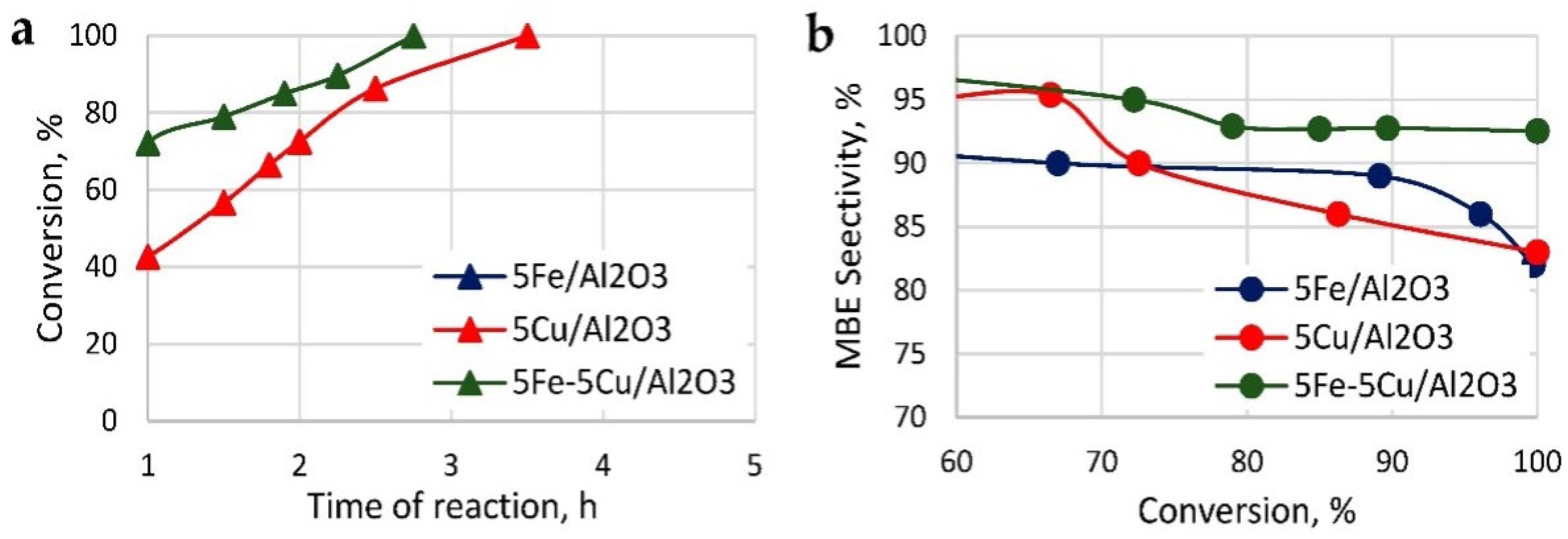
3.2.5. Fe-Based Catalyst
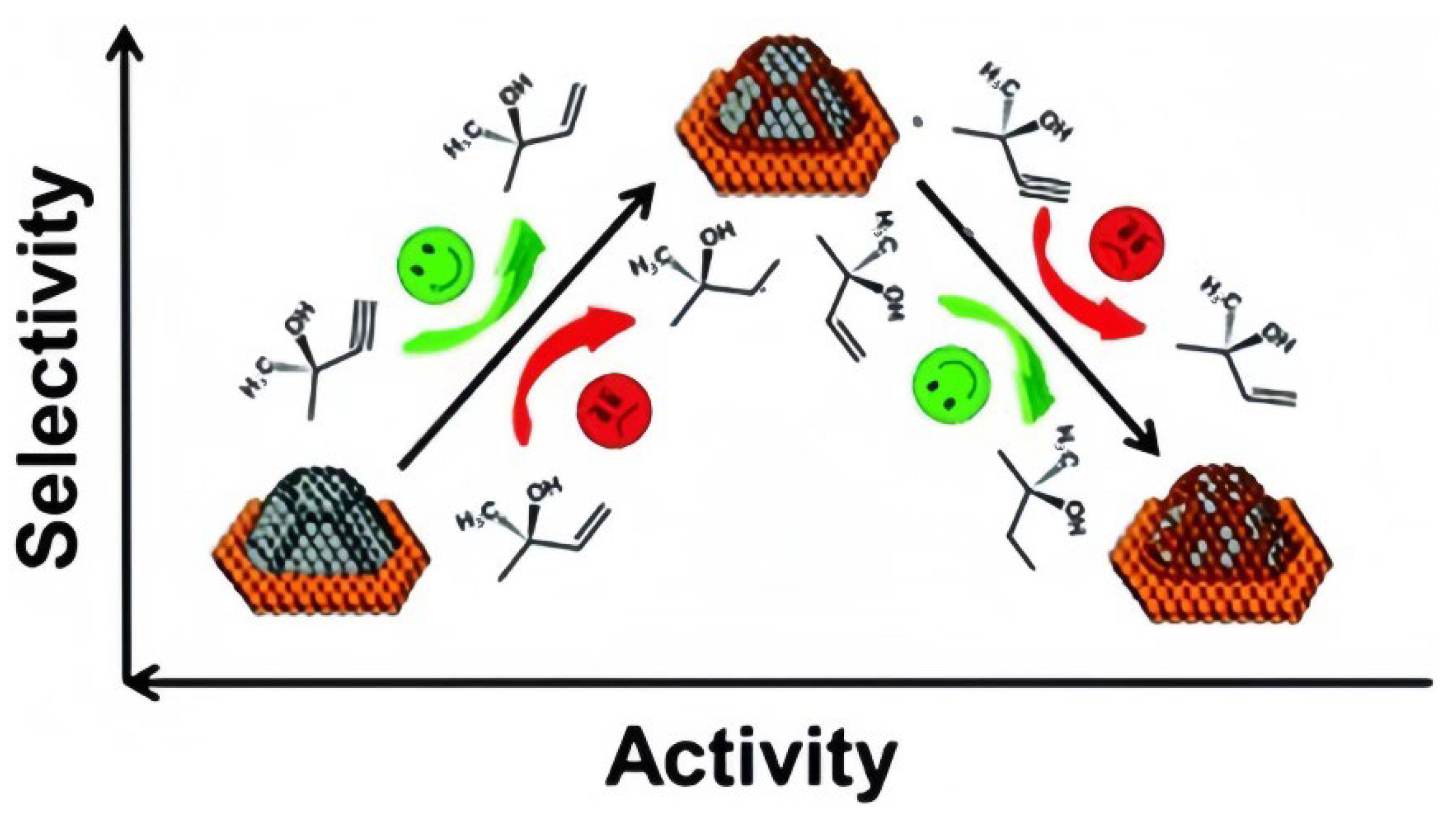
4. Comparative Analysis of Metal-Based Catalysts for Alkynol Hydrogenation
5. Conclusions and Outlook
5.1. Overview and Contributions
5.2. Discoveries on Noble Metal Catalysts
5.3. Insights on Non-Noble Metal Catalysts
5.4. Existing Research Gaps and Challenges
5.5. Future Perspectives and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, S.J.; Zhao, B.W.; Wang, Z.; Gong, Y.T.; Lu, G.F.; Ma, X.; Yu, L.L.; Wang, Y. Tuning the catalytic performance for the semi-hydrogenation of alkynols by selectively poisoning the active sites of Pd catalysts. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 4143–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.J.; Xiao, Q.; Li, J.H. Electro-/photocatalytic alkene-derived radical cation chemistry: Recent advances in synthetic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 7206–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Ropero, A.J.; Zawadzki, B.; Kowalewski, E.; Pieta, I.S.; Krawczyk, M.; Matus, K.; Lisovytskiy, D.; Srebowata, A. Continuous 2-Methyl-3-butyn-2-ol Selective Hydrogenation on Pd/gamma-Al2O3 as a Green Pathway of Vitamin A Precursor Synthesis. Catalysts 2021, 11, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.-n.; Gao, Y.; Du, X.; Bian, J.-l.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.-M.; Li, S.-Y. Characterization of the effect of cis-3-hexen-1-ol on green tea aroma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaicharla, T.; Zimmermann, B.M.; Oestreich, M.; Teichert, J.F. Using alcohols as simple H-2-equivalents for copper-catalysed transfer semihydrogenations of alkynes. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 13410–13413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherkasov, N.; Bai, Y.; Rebrov, E. Process Intensification of Alkynol Semihydrogenation in a Tube Reactor Coated with a Pd/ZnO Catalyst. Catalysts 2017, 7, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
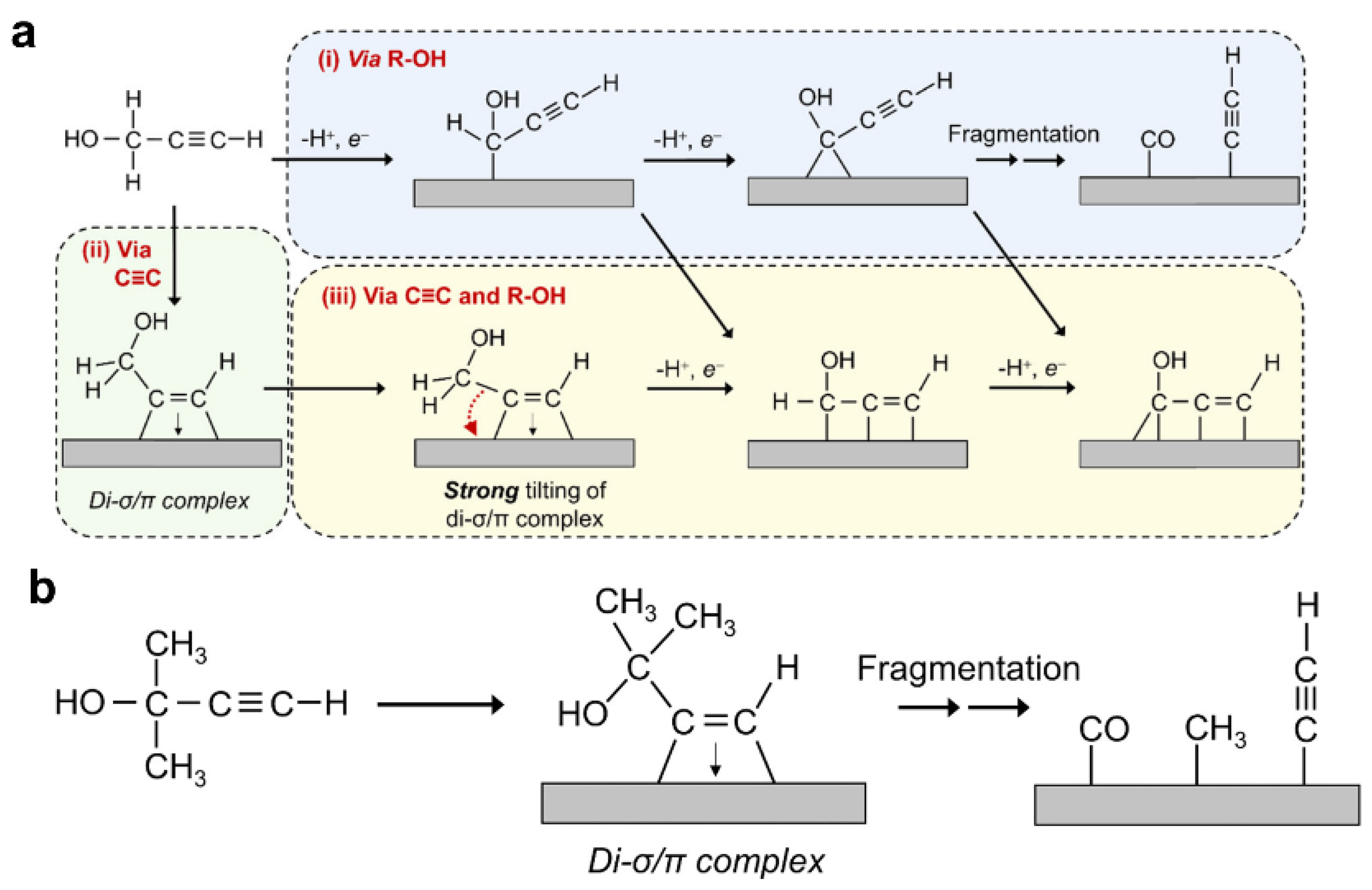
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Huang, K.; Ge, W.; Liu, Z.; Lian, C.; Liu, H.; Jiang, H.; Li, C. Dopant- and Surfactant-Tuned Electrode-Electrolyte Interface Enabling Efficient Alkynol Semi-Hydrogenation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 6516–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.D.; Ma, J.; Kui, B.; Zhu, G.P.; Jia, G.; Wu, F.F.; Gao, P.; Ye, W. Effect of Crystal Planes of Pd and the Structure of Interfacial Water on the Electrocatalytic Hydrogenation of Alkynes to Alkenes. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 5357–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.A.; Benkirane, O.; Claver, C.; Curulla-Ferre, D.; Godard, C. Advances in the preparation of highly selective nanocatalysts for the semi-hydrogenation of alkynes using colloidal approaches. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 12381–12403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, C.; Liang, C. Highly selective catalysts for the hydrogenation of alkynols: A review. Chin. J. Catal. 2021, 42, 2105–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, K.L.; Goldberger, J.E. Alkyne Hydrogenation Catalysis across a Family of Ga/In Layered Zintl Phases. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 52152–52159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncanson, I.T.; Sutherland, I.W.; Cullen, B.; Jackson, S.D.; Lennon, D. The hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol over a carbon-supported palladium catalyst. Catal. Lett. 2005, 103, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, F.; Nocchetti, M.; Bastianin, M.; Lavacchi, A.; Caporali, M.; Liguori, F. Robust Zirconium Phosphate-Phosphonate Nanosheets Containing Palladium Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalyst for Alkynes and Nitroarenes Hydrogenation Reactions. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 1750–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L.; Lang, J.; Yao, G.; Qin, T.; Ren, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; et al. Breaking scaling relationships in alkynol semi-hydrogenation by manipulating interstitial atoms in Pd with d-electron gain. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Bi, W.; Zhao, C.; Guo, Y.; Jin, M. PdCx nanocrystals with tunable compositions for alkyne semihydrogenation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 4714–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoshvili, L.Z.; Popov, A.Y.; Bykov, A.V.; Sidorov, A.I.; Kiwi-Minsker, L. Hybrid Pd-Nanoparticles within Polymeric Network in Selective Hydrogenation of Alkynols: Influence of Support Porosity. Molecules 2022, 27, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Zhang, J.; He, L.; Miao, R.; Shi, Y.; Ning, P. Selective Hydrogenation of Acetylene to Ethylene over the Surface of Sub-2 nm Pd Nanoparticles in Miscanthus sinensis-Derived Microporous Carbon Tubes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 11638–11648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Fernandez, A.; Pischetola, C.; Cardenas-Lizana, F. Gas Phase Catalytic Hydrogenation of C4 Alkynols over Pd/Al2O3. Catalysts 2019, 9, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogami, S.; Shida, N.; Iguchi, S.; Nagasawa, K.; Inoue, H.; Yamanaka, I.; Mitsushima, S.; Atobe, M. Mechanistic Insights into the Electrocatalytic Hydrogenation of Alkynes on Pt-Pd Electrocatalysts in a Proton-Exchange Membrane Reactor. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 5430–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.; Chang, S.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Ma, W.; Liu, Z.; An, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Highly selective electrocatalytic alkynol semi-hydrogenation for continuous production of alkenols. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberhauser, W.; Frediani, M.; Dehcheshmeh, I.M.; Evangelisti, C.; Poggini, L.; Capozzoli, L.; Moghadam, P.N. Selective Alkyne Semi-Hydrogenation by PdCu Nanoparticles Immobilized on Stereocomplexed Poly(lactic acid). Chemcatchem 2022, 14, e202101910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, S.; Kojima, Y.; Fudo, E.; Tanaka, A.; Kominami, H. Controlling the performance of a silver co-catalyst by a palladium core in TiO2-photocatalyzed alkyne semihydrogenation and H2 production. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 624, 118331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maazaoui, R.; Abderrahim, R.; Chemla, F.; Ferreira, F.; Perez-Luna, A.; Jackowski, O. Catalytic Chemoselective and Stereoselective Semihydrogenation of Alkynes to E-Alkenes Using the Combination of Pd Catalyst and ZnI2. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 7544–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Shi, C.; Wang, X.-B.; Li, W.-Y.; Liang, C. Intermetallic PdZn nanoparticles catalyze the continuous-flow hydrogenation of alkynols to cis-enols. Commun. Chem. 2021, 4, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Mao, S.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Chen, P.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. PdZn intermetallic on a CN@ZnO hybrid as an efficient catalyst for the semihydrogenation of alkynols. J. Catal. 2017, 350, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jin, J.; Ye, W.; Hu, C.; Hu, S.; Qi, Z.; Long, R.; Song, L.; Zhu, J.; et al. Controlling Au-Pd Surface on Au Nanocubes for Selective Catalytic Alkyne Semihydrogenation. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2018, 35, 1700377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadgeri, J.M.; Telkar, M.M.; Rode, C.V. Hydrogenation activity and selectivity behavior of supported palladium nanoparticles. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, X.; Papaefthimiou, V.; Pham-Huu, C.; Ritleng, V. Pd-functionalized polydopamine-coated polyurethane foam: A readily prepared and highly reusable structured catalyst for selective alkyne semi-hydrogenation and Suzuki coupling under air. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros-Soberanas, J.; Carlos Hernandez-Garrido, J.; Pedro Ceron-Carrasco, J.; Leyva-Perez, A. Selective semi-hydrogenation of internal alkynes catalyzed by Pd-CaCO3 clusters. J. Catal. 2022, 408, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukazawa, A.; Minoshima, J.; Tanaka, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kobori, Y.; Sato, Y.; Atobe, M. A New Approach to Stereoselective Electrocatalytic Semihydrogenation of Alkynes to Z-Alkenes using a Proton-Exchange Membrane Reactor. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11050–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zenner, J.; Johny, J.; Kaeffer, N.; Bordet, A.; Leitner, W. Electrocatalytic hydrogenation of alkenes with Pd/carbon nanotubes at an oil-water interface. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Attard, G.A.; Wain, A.J. Observation of Substituent Effects in the Electrochemical Adsorption and Hydrogenation of Alkynes on Pt{hkl} Using SHINERS. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 10999–11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bron, M.; Holze, R. Spectroelectrochemical investigation of the adsorption and oxidation of unsaturated C-4-alcohols. Surf. Sci. 2000, 457, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki-Arvela, P.; Murzin, D.Y. Effect of metal particle shape on hydrogen assisted reactions. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 618, 118140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, D.; Grepioni, F.; Walther, D.; Heubach, K.; Schmidt, A.; Imhof, W.; Gorls, H.; Klettke, T. From alkynols to alkynol complexes. A molecular assembly study. Organometallics 1997, 16, 4910–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.A.; Attard, G.A.; Deplanche, K.; Casadesus, M.; Huxter, S.E.; Macaskie, L.E.; Wood, J. Improving Selectivity in 2-Butyne-1,4-diol Hydrogenation using Biogenic Pt Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, M.; Shi, C.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Liang, C.; Si, R. Efficient selective hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol to 2-butene-1,4-diol by silicon carbide supported platinum catalyst. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Di, X.; Yin, D.; Li, W.; Liang, C. One-step synthesis of Pt@ZIF-8 catalyst for the selective hydrogenation of 1,4-butynediol to 1,4-butenediol. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Robinson, J.R.; Gao, Z.-H.; Wang, L.-S. Selective Semihydrogenation of Polarized Alkynes by a Gold Hydride Nanocluster. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 12501–12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekebergh, A.; Begon, R.; Kann, N. Ruthenium-Catalyzed E-Selective Alkyne Semihydrogenation with Alcohols as Hydrogen Donors. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 2966–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Yuan, T.Q.; Ren, X.H.; Rong, Z.M. Raney Ni as a Versatile Catalyst for Biomass Conversion. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 10508–10536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, K.; Williams, C.T.; Liang, C. Raney Ni–Si Catalysts for Selective Hydrogenation of Highly Concentrated 2-Butyne-1,4-diol to 2-Butene-1,4-diol. Catal. Lett. 2014, 144, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Meng, D.; Ji, H.; Sheng, H.; Chen, C.; Song, W.; Zhao, J. Visible-light-driven semihydrogenation of alkynes via proton reduction over carbon nitride supported nickel. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 304, 121004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albani, D.; Karajovic, K.; Tata, B.; Li, Q.; Mitchell, S.; Lopez, N.; Perez-Ramirez, J. Ensemble Design in Nickel Phosphide Catalysts for Alkyne Semi-Hydrogenation. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ma, F.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, H.; Yin, S.; Mian, I.; Tsubaki, N. Heteroatom Promoted Ni/Al2O3 Catalysts for Highly Efficient Hydrogenation of 1,4-Butynediol to 1,4-Butenediol. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 10072–10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhr, M.; Liang, H.; Allmendinger, L.; Buehler, R.; Napoli, F.E.; Ukaj, D.; Cokoja, M.; Jandl, C.; Kahlal, S.; Saillard, J.-Y.; et al. Catalytic Alkyne Semihydrogenation with Polyhydride Ni/Ga Clusters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202308790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Wen, X.; Nie, S.; Dong, J.; Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Bai, G. Fabrication of Ni3N nanorods anchored on N-doped carbon for selective semi-hydrogenation of alkynes. J. Catal. 2020, 382, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Chen, A. Selective hydrogenation of furfural and levulinic acid to biofuels on the ecofriendly Cu-Fe catalyst. Fuel 2014, 115, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Gong, X.; Ye, L.; Duan, X.; Yuan, Y. Synergistic effects of bimetallic Cu-Fe/SiO2 nanocatalysts in selective hydrogenation of diethyl malonate to 1,3-propanediol. J. Energy Chem. 2016, 25, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Wu, C.; Deng, L.B.; Zhang, R.R.; Zhou, S.S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Qiao, C.Z.; Tian, Y.J. Ni-Promoted Cu/ZSM-5 for selective hydrodeoxygenation of furfural to produce 2-Methylfuran. Fuel 2023, 353, 129233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shesterkina, A.A.; Strekalova, A.A.; Shuvalova, E.V.; Kapustin, G.I.; Tkachenko, O.P.; Kustov, L.M. CuO-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles Supported on SiO2 and Al2O3 for Selective Hydrogenation of 2-Methyl-3-Butyn-2-ol. Catalysts 2021, 11, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Wang, Z.; Jin, S.; Xiao, S.; Liu, S.; Hu, Z.; Chen, L.; Su, B. Highly Enhanced Catalytic Stability of Copper by the Synergistic Effect of Porous Hierarchy and Alloying for Selective Hydrogenation Reaction. Catalysts 2022, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okhlopkova, L.B.; Cherepanova, S.V.; Prosvirin, I.P.; Kerzhentsev, M.A.; Ismagilov, Z.R. Semihydrogenation of 2-methyl-3-butyn-2-ol on Pd-Zn nanoalloys: Effect of composition and heterogenization. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2018, 549, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhao, H.; Ma, H.; Li, B.; Kou, J.; Li, J.; Gao, M.; Zeng, G.; Fang, J.; Dong, Z. Ultrafine PdZn bimetallic nanoparticles anchored on sulfur-doped mesoporous carbon for the partial hydrogenation of alkynols. Catal. Today 2022, 405, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Fernandez, A.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Cazorla-Amoros, D.; Cardenas-Lizana, F. Zn-Promoted Selective Gas-Phase Hydrogenation of Tertiary and Secondary C4 Alkynols over Supported Pd. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 28158–28168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakas, N.J.; Neidig, M.L. Additive and Counterion Effects in Iron-Catalyzed Reactions Relevant to C-C Bond Formation. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 8493–8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.R.; Yan, K.L.; Cao, Y.Q.; Ge, X.H.; Zhou, X.G.; Yuan, W.K.; Chen, D.; Duan, X.Z. Mechanistic and Atomic-Level Insights into Semihydrogenation Catalysis to Light Olefins. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 12138–12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francova, D.; Tanchoux, N.; Gerardin, C.; Trens, P.; Prinetto, F.; Ghiotti, G.; Tichit, D.; Coq, B. Hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol on supported Pd catalysts obtained from LDH precursors. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 99, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joannet, E.; Horny, C.; Kiwi-Minsker, L.; Renken, A. Palladium supported on filamentous active carbon as effective catalyst for liquid-phase hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol to 2-butene-1,4-diol. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2002, 57, 3453–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, C.V. Catalytic hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol: Activity, selectivity and kinetics studies. J. Jpn. Pet. Inst. 2008, 51, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semagina, N.; Joannet, E.; Parra, S.; Sulman, E.; Renken, A.; Kiwi-Minsker, L. Palladium nanoparticles stabilized in block-copolymer micelles for highly selective 2-butyne-1,4-diol partial hydrogenation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 280, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, F.; Barbaro, P. Green semi-hydrogenation of alkynes by Pd@borate monolith catalysts under continuous flow. J. Catal. 2014, 311, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishwick, R.P.; Natividad, R.; Kulkarni, R.; McGuire, P.A.; Wood, J.; Winterbottom, J.M.; Stitt, E.H. Selective hydrogenation reactions: A comparative study of monolith CDC, stirred tank and trickle bed reactors. Catal. Today 2007, 128, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
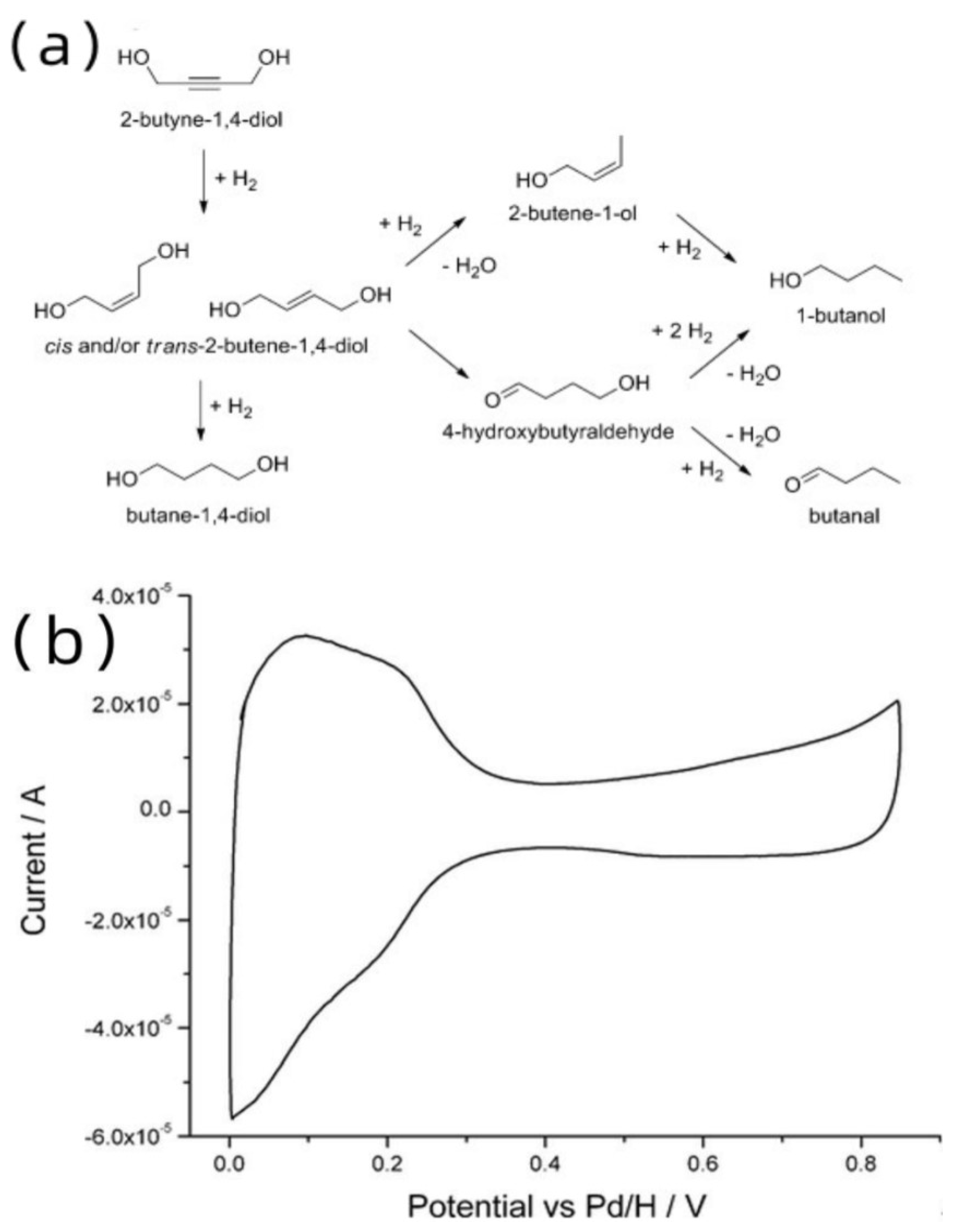
- Telkar, M.M.; Rode, C.V.; Jaganathan, R.; Rane, V.H.; Chaudhari, R.V. Platinum catalyzed hydrogenation of 2-butyne-1,4-diol. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2002, 187, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number | Reactant | Product | Time (min) | Conv. (%) | Sel. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 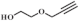 | 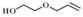 | 70 | 97.5 | 96.0 |
| 2 |  | 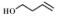 | 60 | 92.5 | 94.7 |
| 3 |  | 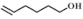 | 50 | >99 | 95.0 |
| 4 | 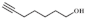 | 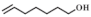 | 80 | >99 | 94.0 |
| 5 |  |  | 150 | 93.2 | 91.7 |
| 6 |  | 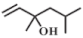 | 40 | 85.4 | 94.7 |
| 7 | 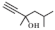 | 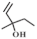 | 50 | 97.0 | 94.4 |
| 8 | 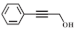 | 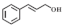 | 240 | 83.2 | 96.9 |
| Specific Properties of Various Thermal Catalysis Methods | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numbers | Catalyst | Reactants | Temperature (°C) | Pressure (MPa) | Reactor | Alkynol Conversion (%) | Enol Selectivity (%) | Reference |
| 1 | Pd-Pb/CaCO3 | 2-Methyl-3-butyn-2-ol | 80 | 0.1 | parr autoclave | 99 | 95 | [13] |
| 2 | Pd/Al2O3 | 2-methyl-3-butyn-2-ol | 100 | 0.1 | / | 99 | 95 | [18] |
| 3 | Pd-C | 2-methyl-1,4-diol | 65 | 0.3 | Büchi stirred | 65 (t = 100 min) | 73 (t = 100 min) | [12] |
| 4 | Pd/ZnO-400 | 2-methyl-1,4-diol | 80 | 2 | parr autoclave | 95.8 | 92.6 | [24] |
| 5 | PdZn/CN@ZnO | 2-methyl-3-butyn-2-ol | 35 | 0.5 | stainless steel autoclave | 99 | 96 | [25] |
| 6 | Pd-Au | 2-Methyl-3-butyn-2-ol | 30 | / | / | 98.2 | 98.9 | [26] |
| 7 | Pd-C(PVP) | 2-Butyne-1,4-diol | 100 | 2.24 | / | / | 99.6 | [27] |
| 8 | Pd@PDA@PUF | 1-butene 3-Methyl-3-ol | 25 | 0.1 | / | 98 | 95 | [28] |
| 9 | Pd-CaCO3 | 2-Butyne-1,4-dio | 50 | 2.1 | parr autoclave | / | 99.5 | [29] |
| Specific Properties of Various Electrocatalysis | ||||||||
| Numbers | Catalyst | Reactants | Faradaic Efficiency (%) | Electric Potential (V) | Reactor | Alkynol Conversion (%) | Enol Selectivity (%) | Reference |
| 10 | Pd-B | 2-methyl-3-butyn-2-ol | 39.0 | −1.0 | / | 94.5 | 90.2 | [7] |
| 11 | Pd | Diphenylacetylene | 99(current efficiency) | −0.09 | Proton-Exchange Membrane | / | / | [30] |
| 12 | Cu | 2-methyl-3-butyn-2-ol | 95 | −0.88 | Electrolytic tank | 93 | 97 | [20] |
| 13 | Pd/carbon nanotubes | Styrene | 95 | −0.65 | oil–water interface | 95 | / | [31] |
| Specific Properties of Photocatalysis | ||||||||
| Numbers | Catalyst | Reactants | Temperature (°C) | Light Source | Reactor | Alkynol Conversion (%) | Enol Selectivity (%) | Reference |
| 14 | Pd@Ag/TiO2 | 4-Octyne | / | high pressure mercury lamp | / | 99 | 99 | [22] |
| Number | Reactant | Obtauned a Cluster | Released b Product | Conversion c (%) | Z-Selectivity c (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 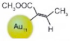 | 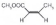 | >99 | 91 |
| 2 |  | 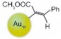 | 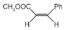 | >99 | 90 |
| 3 | 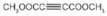 |  | 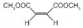 | >99 | 99 |
| 4 |  | 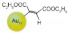 | 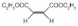 | >99 | 97 |
| 5 |  | None | None | / | / |
| 6 |  | None | None | / | / |
| Numbers | Catalyst | Reactants | Temperature (°C) | Pressure (MPa) | Reactor | Alkynol Conversion (%) | Enol Selectivity (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | Ni-Si | 2-Butyne-1,4-diol | 90 | 3.0 | high pressure fixed bed | 81.3 | 82.5 | [42] |
| 16 | Ni/Al2O3 | 2-Butyne-1,4-diol | / | 0.1 | / | 68.9 | 87.6 | [45] |
| 17 | Ni-Fe/Al2O3 | 2-methyl-1,4-diol | / | 0.1 | / | 82 | 93 | [45] |
| 18 | Ni-Ga | ethyne | 0 | 0.1 | NMR tubes | 67 | 77 | [46] |
| 19 | Ni3N | 1,2-diphenylethyne | 100 | 2 | stainless steel autoclave | 99 | 98 | [47] |
| Sample | Reactor | A/molMBY/molPd/s | S99/% | Y/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PdZn/TiO2 | microcapillary | 3.0 a | 96.9 | 95.9 |
| PdZn/TiO2 | batch | 1.2 b | 74.6 | 74.5 |
| Pd/TiO2 | microcapillary | 6.1 a | 93.9 | 92.9 |
| Pd/TiO2 | batch | 2.1 b | 64.6 | 65.7 |
| Pd+Pd/CaCO3 | Batch c | 0.09 c | / | 94.5 |
| No. | Catalyst | Type of Reaction | TOFs (s−1) | Conversion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Raney Ni | Thermos-catalysis | 14.7 | 96.7 | [42] |
| 2 | Raney 250-NiSix | 12.2 | 81.3 | ||
| 3 | Raney 350-NiSix | 11.6 | 84.8 | ||
| 4 | Raney 450-NiSix | 5.2 | 35.7 | ||
| 5 | Pdn/ND@G | Photo-catalytic | 10.5 | 99 | [57] |
| 6 | Pd/Mg(Al)O-imp | Thermos-catalysis | 20.6 | 90 | [58] |
| 7 | Pd/Mg(Al)O-nc | 12.3 | 90 |
| Serial No. | Catalyst | Selectivity to BED | TOFs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Raney Ni | 67.3 | 14.7 (s−1) | [42] |
| 2 | Raney 250-NiSix | 82.5 | 12.2 (s−1) | |
| 3 | Raney 350-NiSix | 80.4 | 11.6 (s−1) | |
| 4 | Raney 450-NiSix | 89.7 | 5.2 (s−1) | |
| 5 | bulk Pd/C catalyst | 5 | 0.29 | [27] |
| 6 | nanoparticles Pd/C catalyst | 99.6 | 3.1 | |
| 7 | 1% Pd/C | 5.0 | 2.9 | [60] |
| 8 | 1% Pd/Al2O3 | 6.0 | 2.0 | |
| 9 | 1% Pd/MgCO3 | 100.0 | 0.7 | |
| 10 | 1% Pd/BaCO3 | 100.0 | 0.7 | |
| 11 | 1% Pd/NH4-ZSM-5 10% | 100.0 | 0.6 | |
| 12 | 10% Ni_1% Pd/CaCO3 | 100.0 | 0.7 | |
| 13 | 1% Pd/CaCO3 | 100.0 | 1.2 | |
| 14 | 1% Pd/CaCO3 a | 83.0 | 1.5 | |
| 15 | 2 wt% Pd/ACF (active carbon fibers) | 97.0 | 12.0 | [59] |
| 16 | 3 wt% Pd/ACF | 97.0 | 12.0 | |
| 17 | 4 wt% Pd/ACF | 97.0 | 12.0 | |
| 18 | 5 wt% Pd/ACF | 97.0 | 12.0 | |
| 19 | Pd@PEO-b-P2VP micelles | 94.0 | 0.86 | [61] |
| 20 | Pd/Mg(Al)O-imp | 88.0 | 20.6 | [58] |
| 21 | Pd/Mg(Al)O-cop | 80 | 7.6 | |
| 22 | Pd/Mg(Al)O-nc | 86.1 | 12.3 | |
| 23 | Pd/Mg(Al)O-ncre | 79.4 | / | |
| 24 | Pd@ZPGly | 97.3 | 79 (h−1) | [13] |
| 25 | Pd@MonoBor | 75.5 | 466 (h−1) | [62] |
| 26 | Pd/Al2O3(Honeycomb) | 99.0 | 71 (h−1) | [63] |
| 27 | Pd/Al2O3(Packed-bed) | 93.9 | 125 (h−1) | |
| 28 | 1% Pd/Al2O3 | 6.0 | 2.02 (10−4 h−1) | [64] |
| 29 | 1% Pd/C | 5.0 | 2.92 (10−4 h−1) | |
| 30 | 5% Pd-2.5% Pd/CaCO3 | 77.0 | 1.92 (10−4 h−1) | |
| 31 | 1% Pt/CaCO3 b | 83.0 | 2.40 (10−4 h−1) | |
| 32 | 1% Pt/CaCO3 | 100.0 | 1.98 (10−4 h−1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Ma, Y.; Shi, Y.; Duan, F.; Wang, M. Application of Metal-Based Catalysts for Semi-Hydrogenation of Alkynol: A Review. Materials 2023, 16, 7409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16237409
Wang P, Ma Y, Shi Y, Duan F, Wang M. Application of Metal-Based Catalysts for Semi-Hydrogenation of Alkynol: A Review. Materials. 2023; 16(23):7409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16237409
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Pengxian, Yue Ma, Yiran Shi, Fangying Duan, and Meng Wang. 2023. "Application of Metal-Based Catalysts for Semi-Hydrogenation of Alkynol: A Review" Materials 16, no. 23: 7409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16237409
APA StyleWang, P., Ma, Y., Shi, Y., Duan, F., & Wang, M. (2023). Application of Metal-Based Catalysts for Semi-Hydrogenation of Alkynol: A Review. Materials, 16(23), 7409. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16237409






