Synthesis of FeSi–FeAl Composites from Separately Prepared FeSi and FeAl Alloys and Their Structure and Properties
Abstract
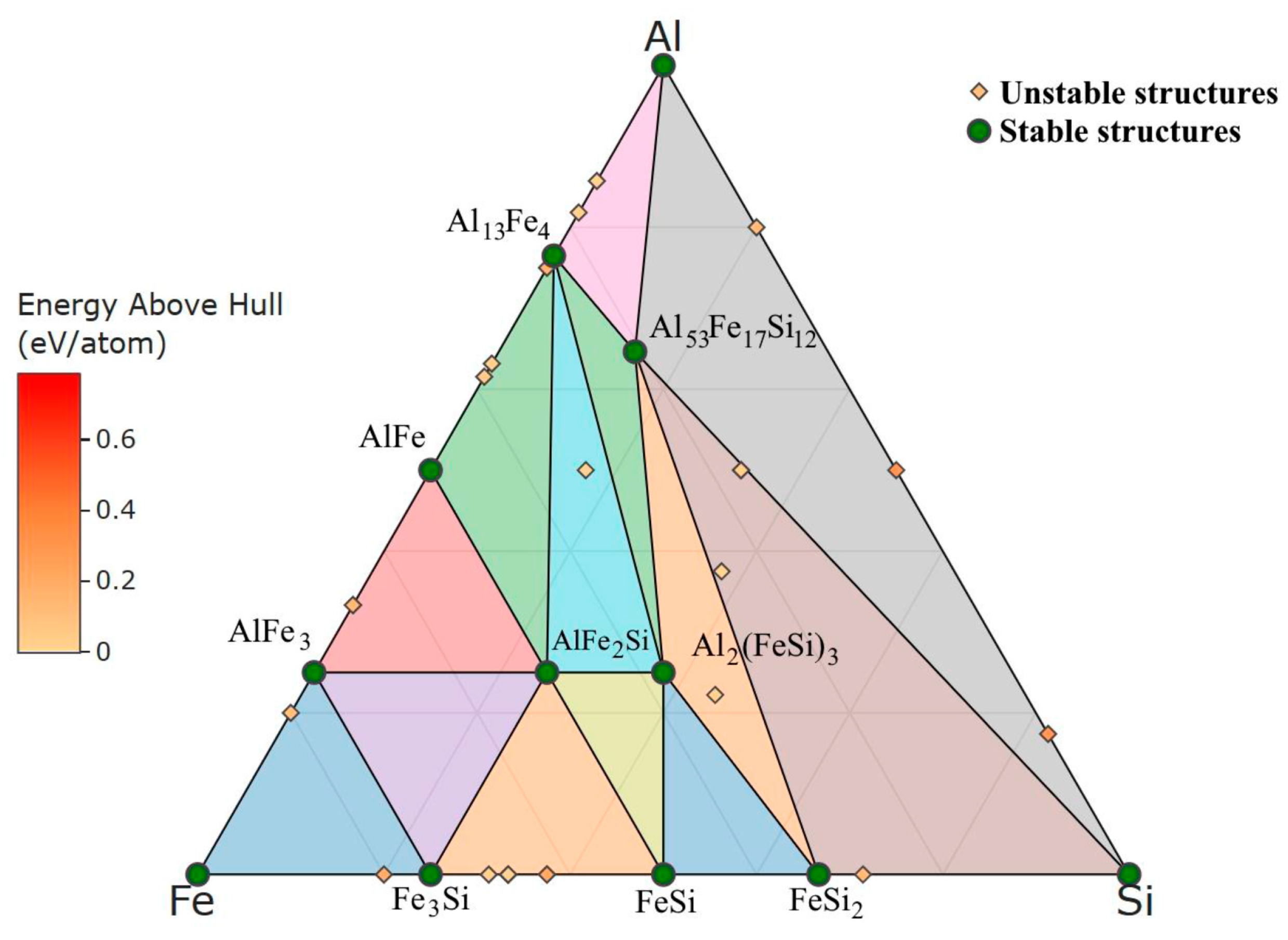
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
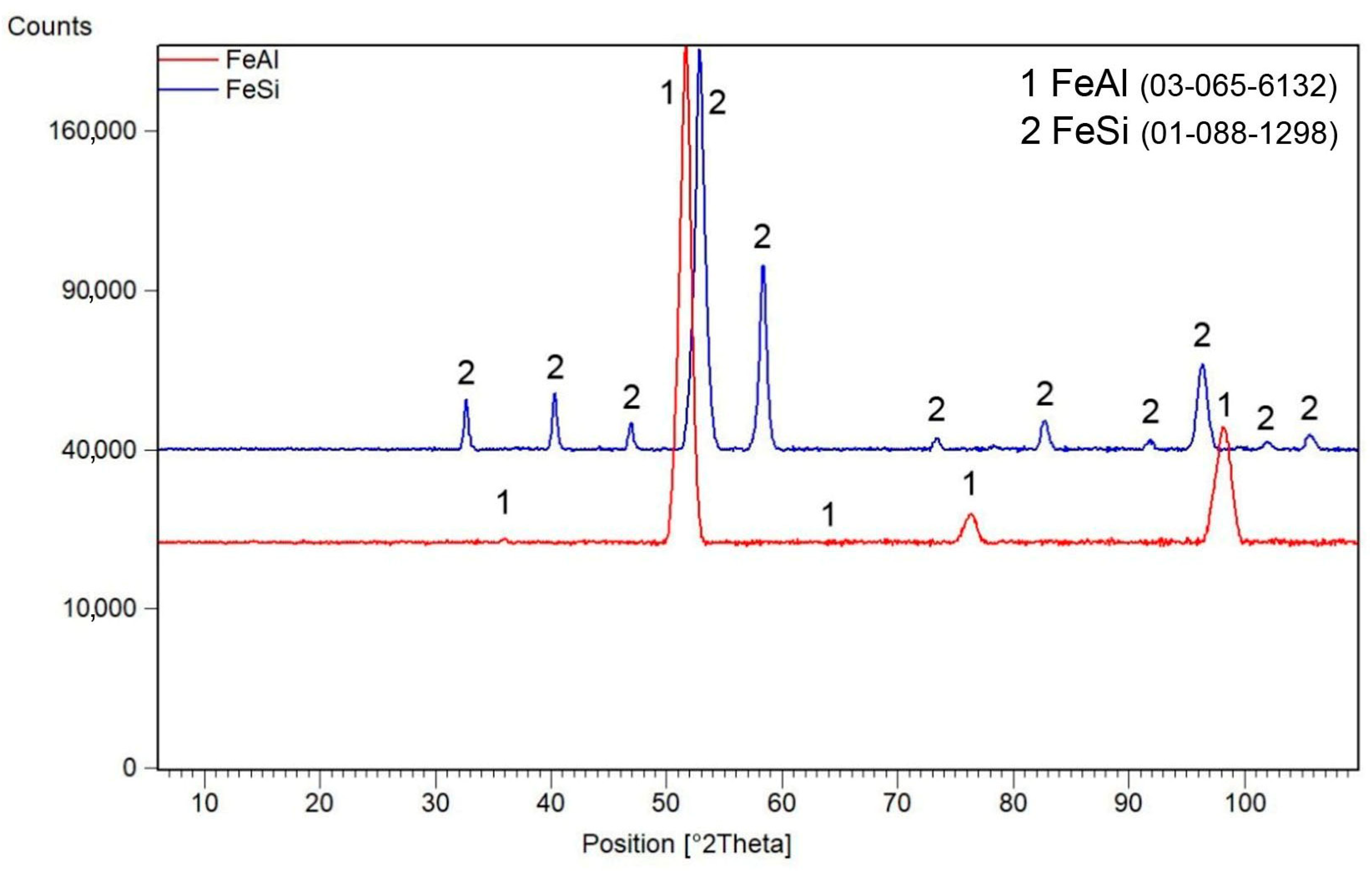
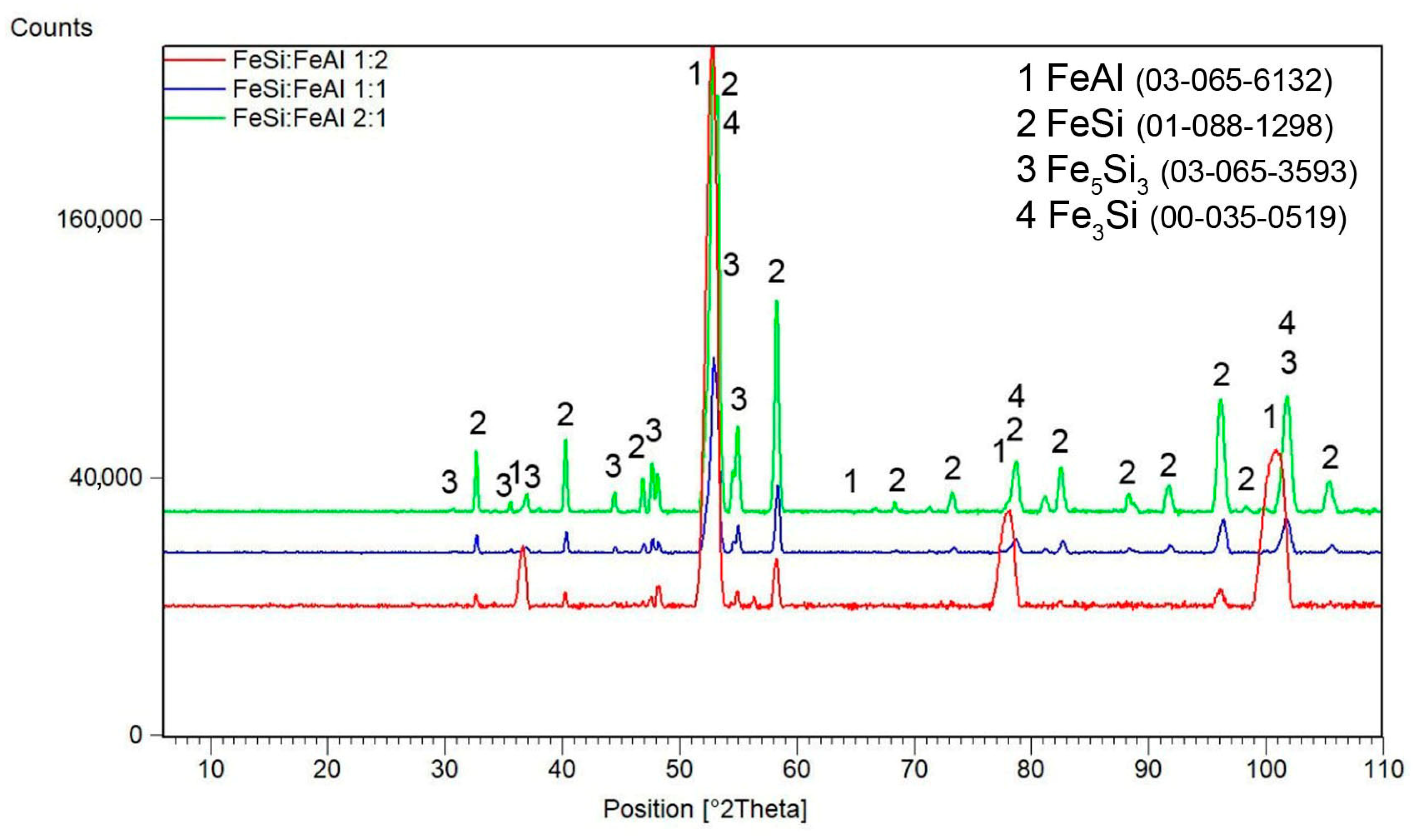
3.1. Phase Composition of Mechanically Alloyed Powders
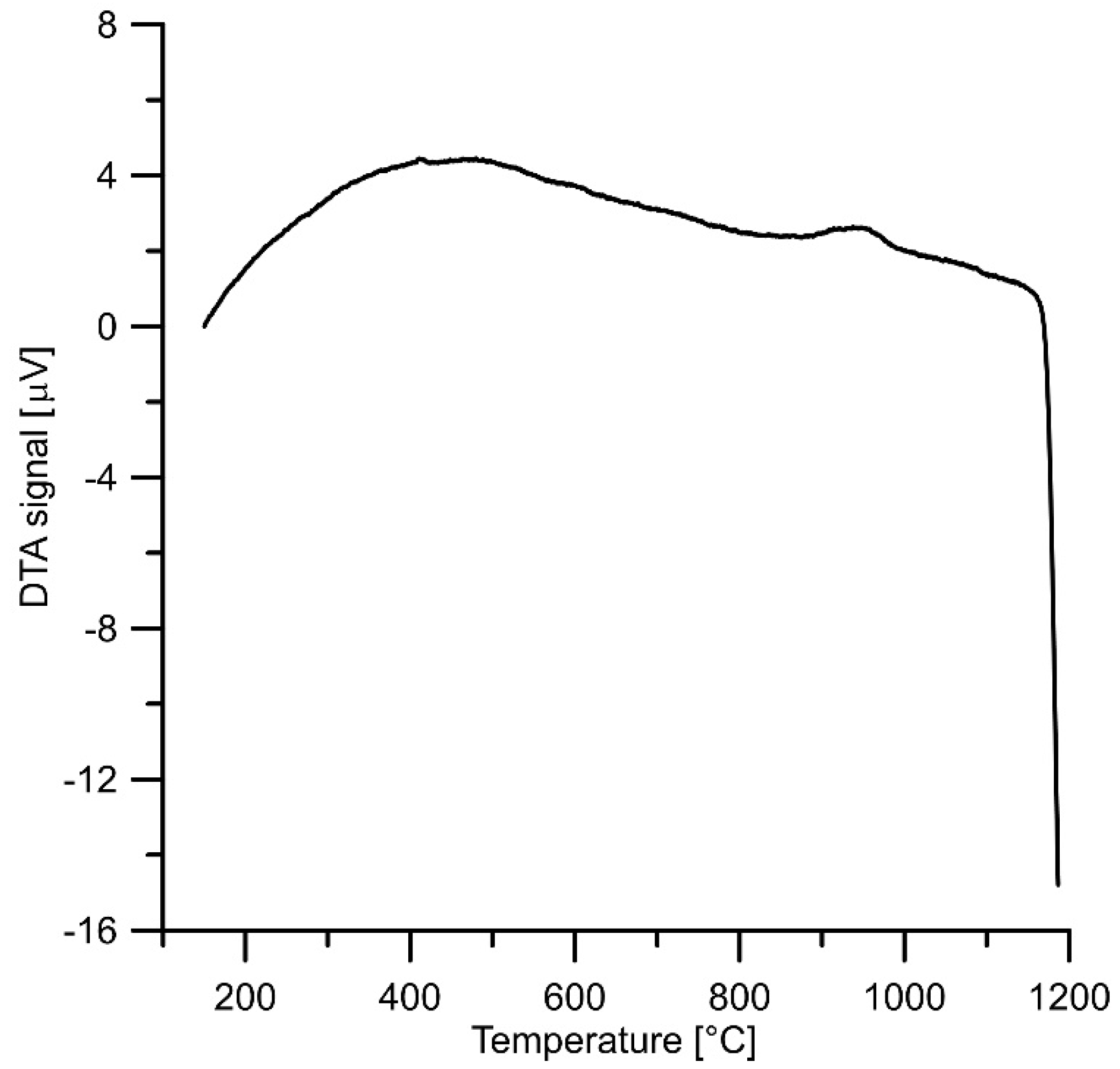
3.2. Thermal Analysis of FeSi–FeAl Mixture
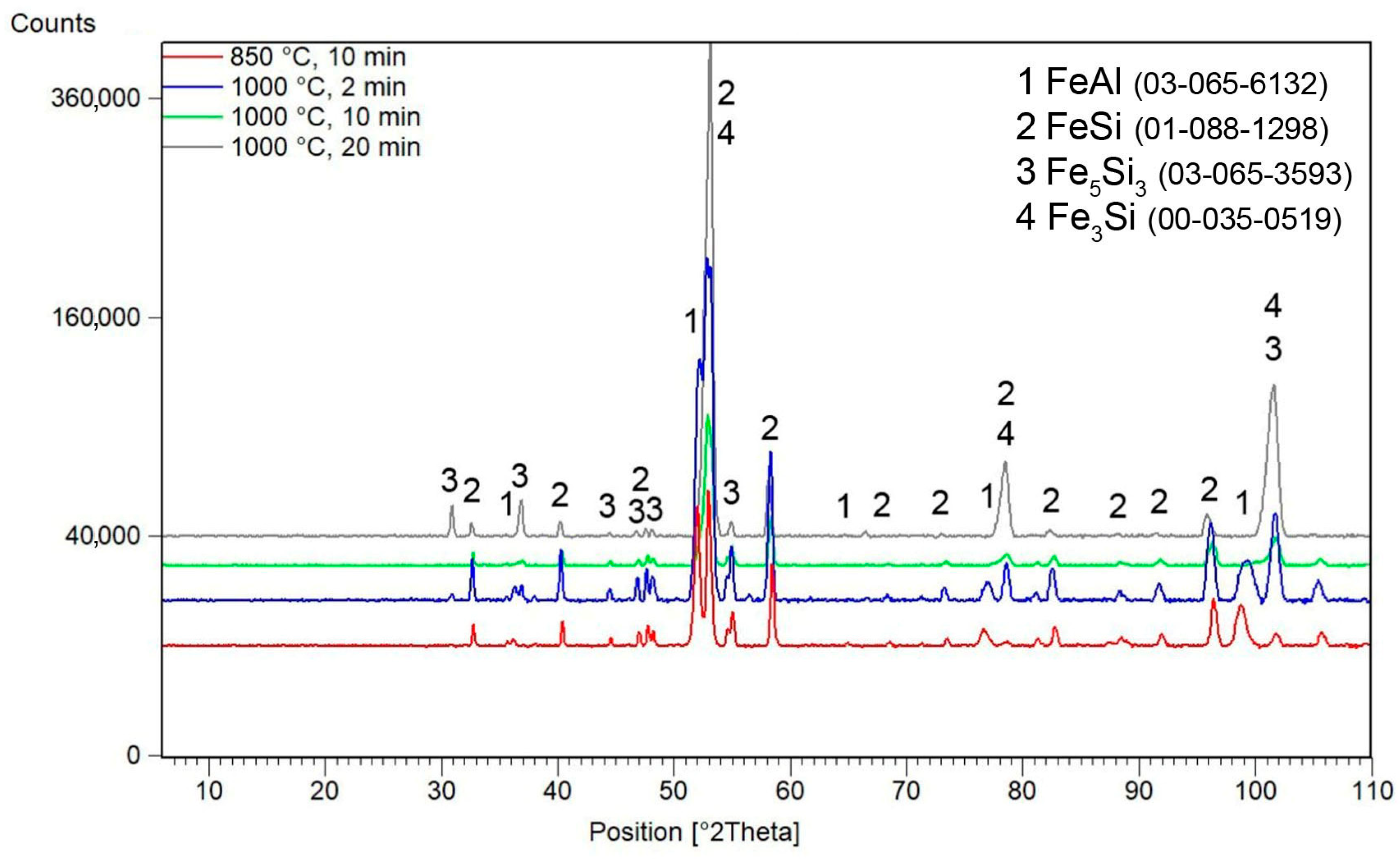
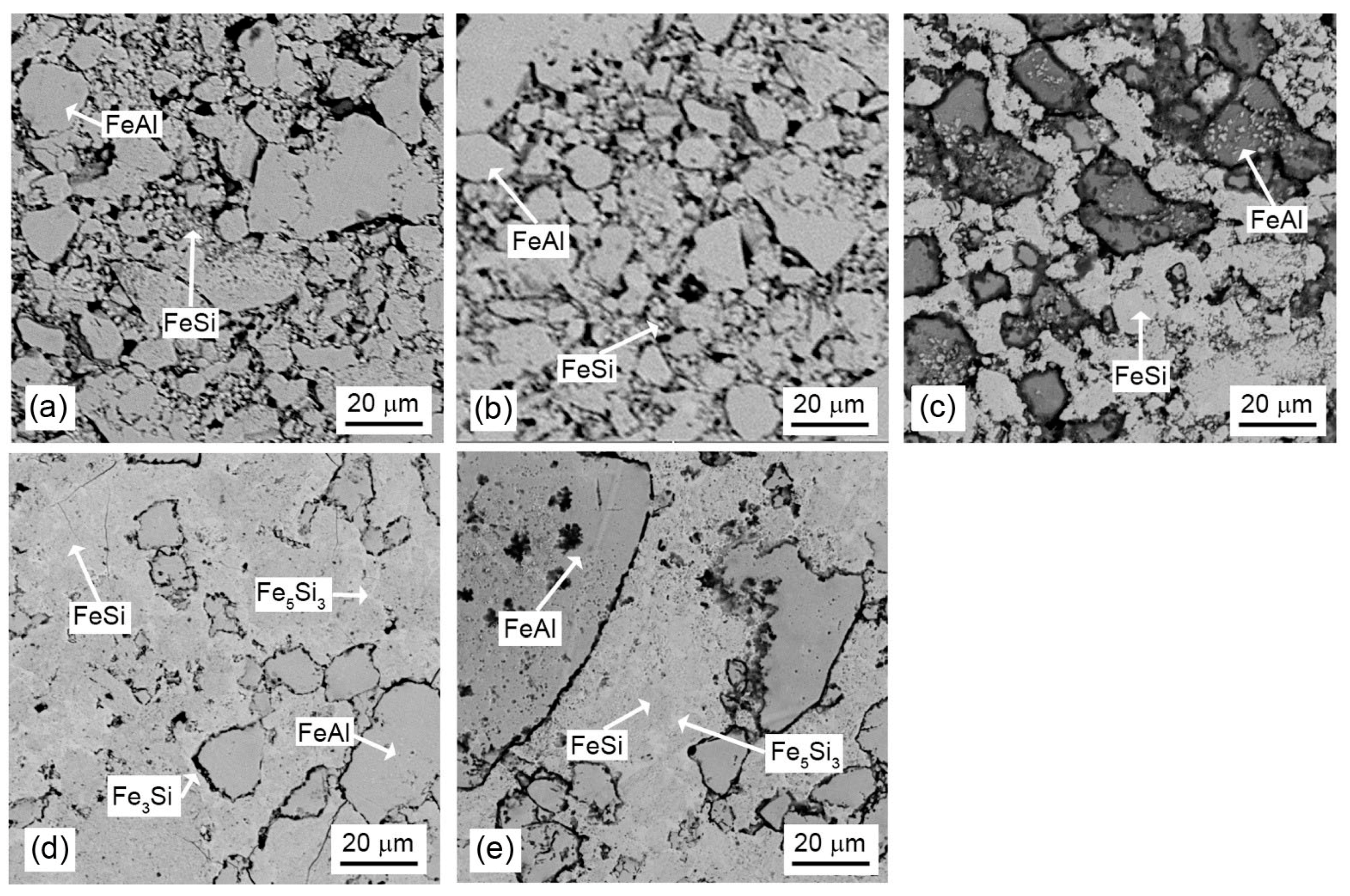
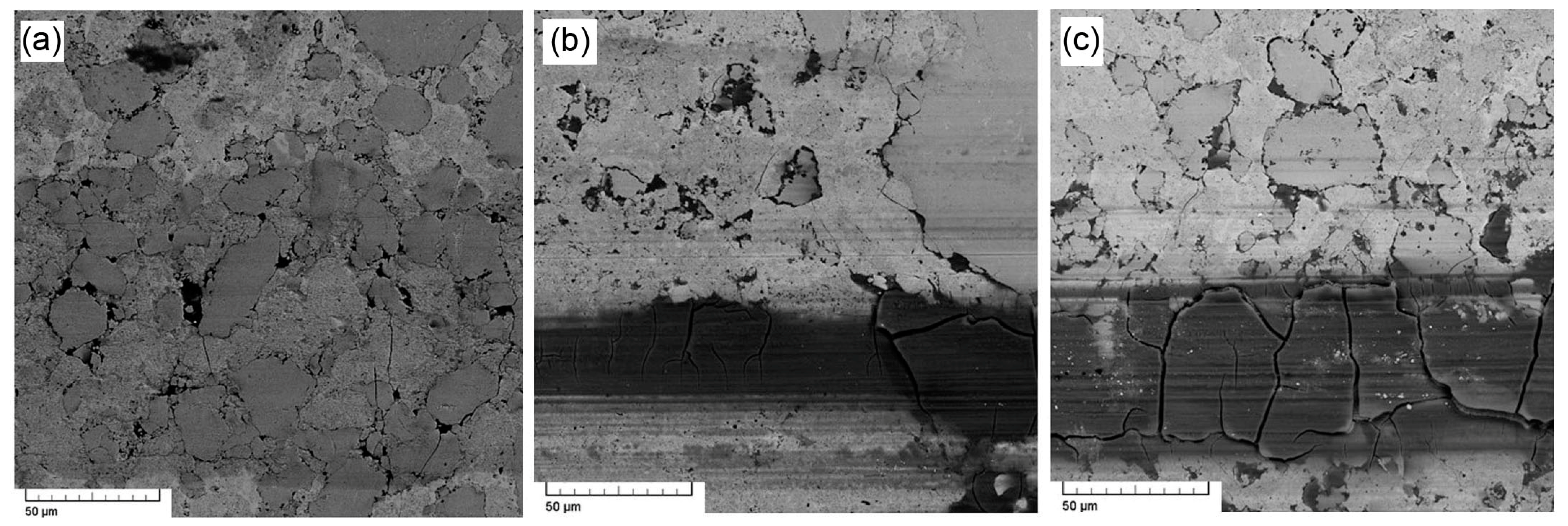
3.3. Microstructure and Phase Composition vs. Sintering Conditions
3.4. Microstructure and Phase Composition vs. FeSi:FeAl Ratio
3.5. Mechanical and Tribological Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://single-market-economy.ec.europa.eu/sectors/raw-materials/areas-specific-interest/critical-raw-materials_en (accessed on 7 December 2023).
- Rizzo, A.; Goel, S.; Luisa Grilli, M.; Iglesias, R.; Jaworska, L.; Lapkovskis, V.; Novak, P.; Postolnyi, B.O.; Valerini, D. The Critical Raw Materials in Cutting Tools for Machining Applications: A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Qi, Q.; Ma, M.; Han, R.; Shang, Q.; Yao, S. The formation mechanism of TiC/Ni composites fabricated by pressureless reactive sintering. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 97, 105524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufiiarov, V.; Erutin, D.; Borisov, E.; Popovich, A. Selective Laser Melting of Inconel 718/TiC Composite: Effect of TiC Particle Size. Metals 2022, 12, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemboub, S.; Boudebane, A.; Boudebane, S.; Bourbia, A.; Mezrag, S.; Gotor, F.J. Complex TiC-Ni-based composites joined to steel support by thermal explosion under load: Synthesis, microstructure and tribological behavior. Compos. Interfaces 2023, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, J.; Park, B.; Jo, I.; Lee, S.-K.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.-B.; Cho, S. Mechanical and Thermal Neutron Absorbing Properties of B4C/Aluminum Alloy Composites Fabricated by Stir Casting and Hot Rolling Process. Metals 2021, 11, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaislová, A.; Novák, P.; Cabibbo, M.; Jaworska, L.; Vojtěch, D. Development of TiAl–Si Alloys—A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzin-Nia, F.; Sterrett, T.; Sirney, R. Effect of machining on fracture toughness of corundum. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 2527–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, P.; Vanka, T.; Nová, K.; Stoulil, J.; Průša, F.; Kopeček, J.; Haušild, P.; Laufek, F. Structure and Properties of Fe–Al–Si Alloy Prepared by Mechanical Alloying. Materials 2019, 12, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Goldbeck, O.K. (Ed.) Fe—Si Iron—Silicon. In IRON—Binary Phase Diagrams; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; pp. 136–139. [Google Scholar]
- Nicheng, S.H.I.; Wenji, B.A.I.; Guowu, L.I.; Ming, X.; Jingsu, Y.; Zhesheng, M.A.; He, R. Naquite, FeSi, a New Mineral Species from Luobusha, Tibet, Western China. Acta Geol. Sin.—Engl. Ed. 2012, 86, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savva, N.; Minyuk, P.; Subbotnikova, T. Gupeiite Body in the Siberian Taiga (the Zone of Passage of the Tunguska Meteorite and the Vitim Bollid). Nat. Resour. 2022, 13, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudasov, Y.B.; Volkov, A.G.; Povzner, A.A.; Bajankin, P.V.; Bykov, A.I.; Dolotenko, M.I.; Guk, V.G.; Kolokol’chikov, N.P.; Krjuk, V.V.; Monakhov, M.P.; et al. Semiconductor–metal transition in FeSi in ultrahigh magnetic field. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2001, 298, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, S.; Tsuruoka, A.; Kimura, Y.; Isobe, T.; Nakajima, A. Influence of semiconductor crystallinity on a β-FeSi2 sensitized thermal cell. Solid-State Electron. 2019, 158, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Cui, X.; Wu, X.; Yang, J. Two-Dimensional Iron Silicide (FeSix) Alloys with Above-Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 2332–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunin, A.; Shevyrtalov, S.; Chichay, K.; Dikaya, O.; Barkovskaya, N.; Danilov, D.; Goikhman, A. Strong uniaxial magnetic anisotropy in Fe3Si thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 563, 170047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milekhine, V.; Onsøien, M.I.; Solberg, J.K.; Skaland, T. Mechanical properties of FeSi (ε), FeSi2 (ζα) and Mg2Si. Intermetallics 2002, 10, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chong, X.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, J. Stability, electronic structure, mechanical and thermodynamic properties of Fe-Si binary compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Goldbeck, O.K. (Ed.) Iron—Aluminium Fe—Al. In IRON—Binary Phase Diagrams; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; pp. 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Matysik, P.; Jóźwiak, S.; Czujko, T. Characterization of Low-Symmetry Structures from Phase Equilibrium of Fe-Al System—Microstructures and Mechanical Properties. Materials 2015, 8, 914–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochvíl, P. The history of the search and use of heat resistant Pyroferal© alloys based on FeAl. Intermetallics 2008, 16, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, P.; Baker, I. Effect of cooling rate on hardness of FeAl and NiAl. Metall. Trans. A 1990, 21, 2281–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 1–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, A.; Suhane, A. A critical review on mechanically alloyed high entropy alloys: Processing challenges and properties. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 052001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Mikami, M. Fabrication of Fe2VAl Alloy Powders by Short-term Mechanical Alloying. J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder Metall. 2008, 55, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, Z.A.; Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Ohyanagi, M. The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: A review of the spark plasma sintering method. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokita, M. Progress of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) Method, Systems, Ceramics Applications and Industrialization. Ceramics 2021, 4, 160–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulbert, D.M.; Anders, A.; Dudina, D.V.; Andersson, J.; Jiang, D.; Unuvar, C.; Anselmi-Tamburini, U.; Lavernia, E.J.; Mukherjee, A.K. The absence of plasma in “spark plasma sintering”. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 033305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp, J.; Semenov, A.; Eberhardt, O.; Nöthe, M.; Wallmersperger, T.; Kieback, B. Fundamental principles of spark plasma sintering of metals: Part II—About the existence or non-existence of the ‘spark plasma effect’. Powder Metall. 2020, 63, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubesh Kumar, D.; Selva babu, B.; Aravind Jerrin, K.M.; Joseph, N.; Jiss, A. Review of Spark Plasma Sintering Process. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 993, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, P.; Michalcová, A.; Voděrová, M.; Šíma, M.; Šerák, J.; Vojtěch, D.; Wienerová, K. Effect of reactive sintering conditions on microstructure of Fe–Al–Si alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 493, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, V. Al-Fe-Si (aluminum-iron-silicon). J. Phase Equilibria 2002, 23, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates-Rector, S.; Blanton, T. The powder diffraction file: A quality materials characterization database. Powder Diffr. 2019, 34, 34–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marder, R.; Estournès, C.; Chevallier, G.; Chaim, R. Numerical model for sparking and plasma formation during spark plasma sintering of ceramic compacts. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 4636–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadauria, N.; Pandey, S.; Pandey, P.M. Wear and enhancement of wear resistance—A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 2986–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, P.; Nová, K. Oxidation Behavior of Fe–Al, Fe–Si and Fe–Al–Si Intermetallics. Materials 2019, 12, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, M.; Artola, G.; Gorriño, A.; Angulo, C. Wear and Friction Evaluation of Different Tool Steels for Hot Stamping. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 3296398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toboła, D.; Brostow, W.; Czechowski, K.; Rusek, P. Improvement of wear resistance of some cold working tool steels. Wear 2017, 382–383, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Phase | Fe | Si | Al | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeAl | 47.5 ± 3.0 | 12.9 ± 2.8 | 37.5 ± 3.0 | 2.2 ± 0.2 |
| FeSi | 46.5 ± 0.4 | 41.0 ± 0.4 | 11.3 ± 0.3 | 1.4 ± 0.3 |
| Fe5Si3 | 60.1 ± 1.8 | 24.4 ± 3.6 | 13.4 ± 4.0 | 2.2 ± 0.3 |
| FeSi:FeAl Ratio | HV10 | f | w (mm3 N−1 m−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1:2 | 720 ± 38 | 0.466 | |
| 1:1 | 628 ± 33 | 0.539 | |
| 2:1 | 664 ± 33 | 0.473 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Novák, P.; Duda, J.; Průša, F.; Skotnicová, K.; Szurman, I.; Smetana, B. Synthesis of FeSi–FeAl Composites from Separately Prepared FeSi and FeAl Alloys and Their Structure and Properties. Materials 2023, 16, 7685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247685
Novák P, Duda J, Průša F, Skotnicová K, Szurman I, Smetana B. Synthesis of FeSi–FeAl Composites from Separately Prepared FeSi and FeAl Alloys and Their Structure and Properties. Materials. 2023; 16(24):7685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247685
Chicago/Turabian StyleNovák, Pavel, Jiří Duda, Filip Průša, Kateřina Skotnicová, Ivo Szurman, and Bedřich Smetana. 2023. "Synthesis of FeSi–FeAl Composites from Separately Prepared FeSi and FeAl Alloys and Their Structure and Properties" Materials 16, no. 24: 7685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247685
APA StyleNovák, P., Duda, J., Průša, F., Skotnicová, K., Szurman, I., & Smetana, B. (2023). Synthesis of FeSi–FeAl Composites from Separately Prepared FeSi and FeAl Alloys and Their Structure and Properties. Materials, 16(24), 7685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247685










