Effect of Size-Distribution Environment on Breakage Parameters Using Closed-Cycle Grinding Tests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
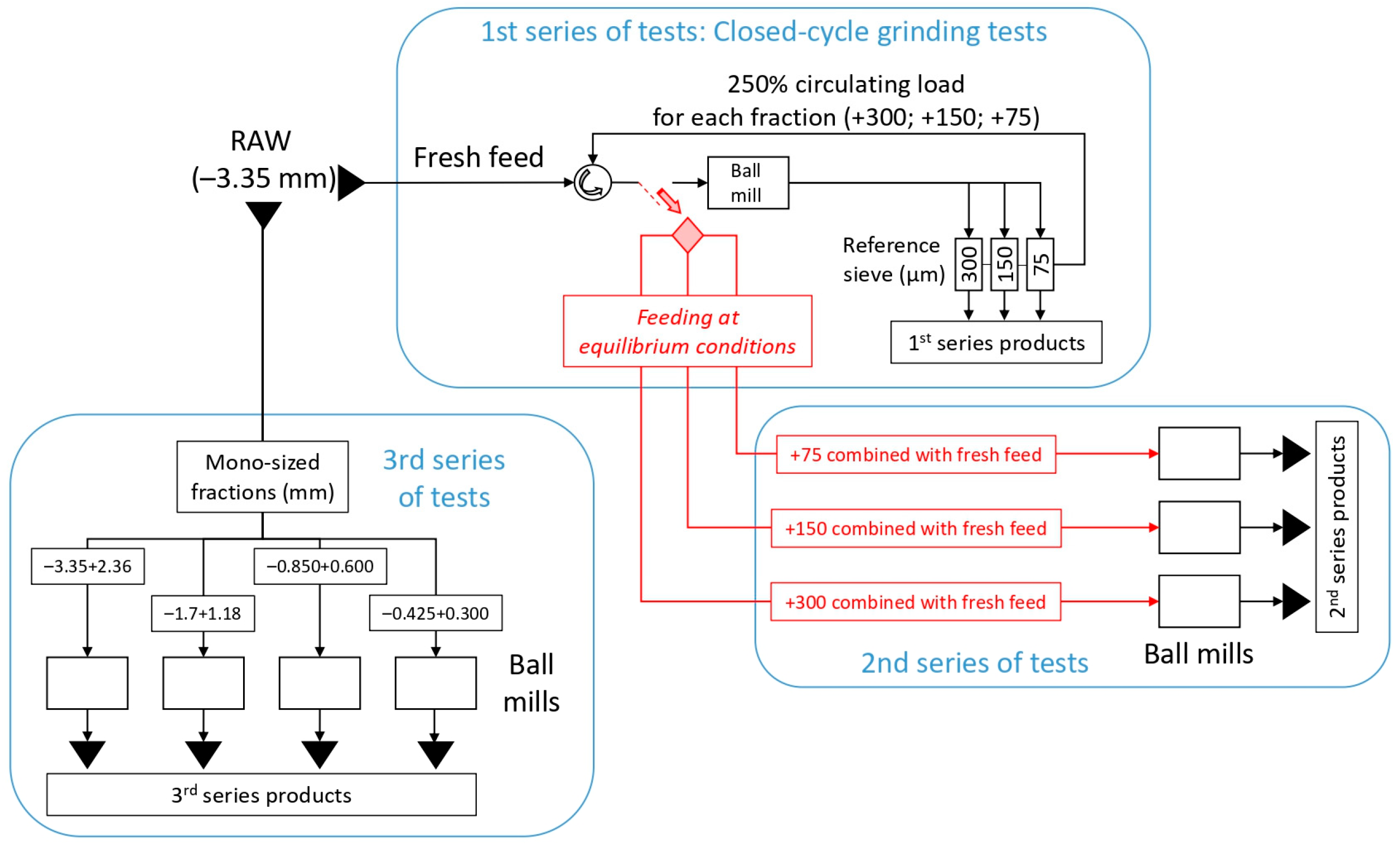
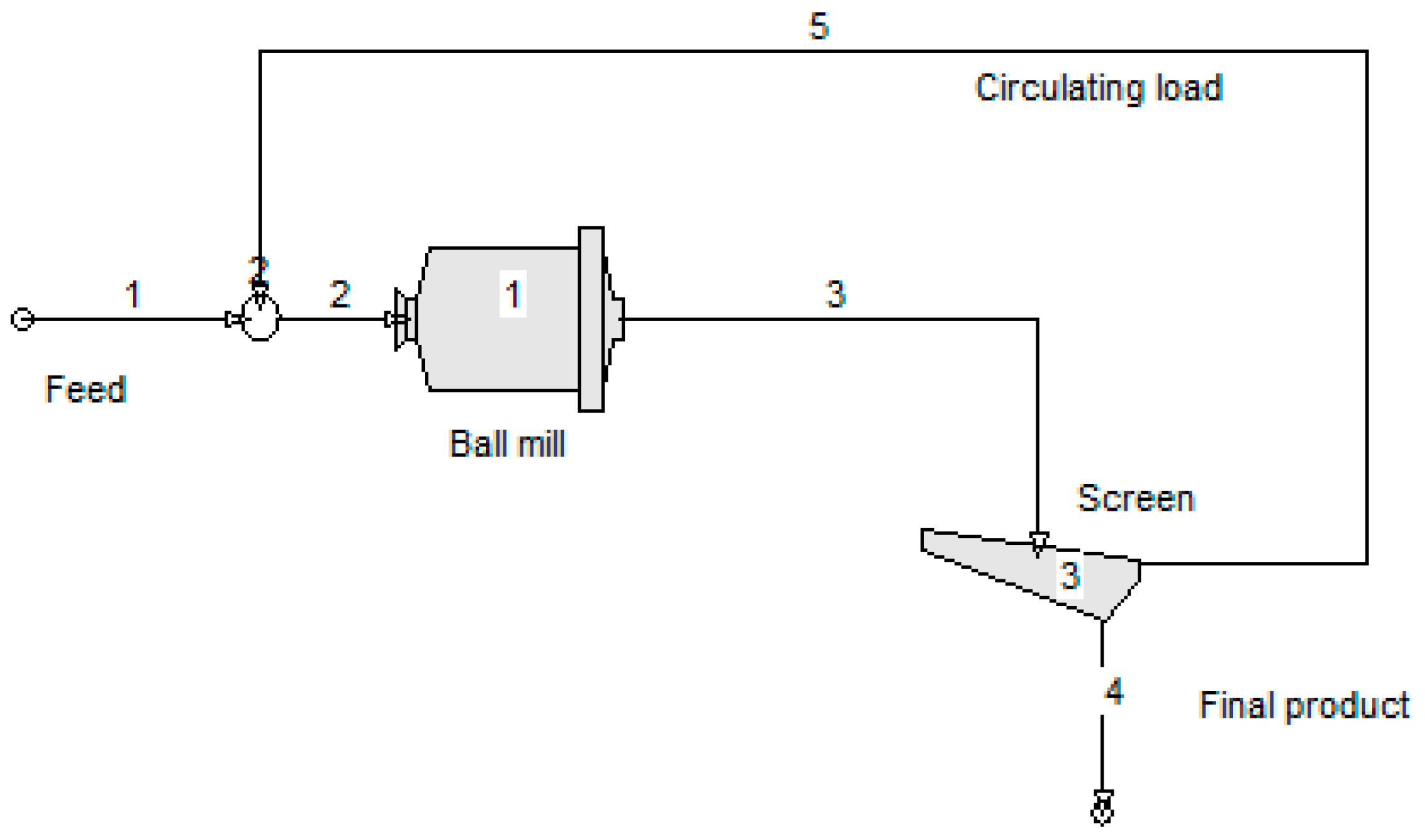
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
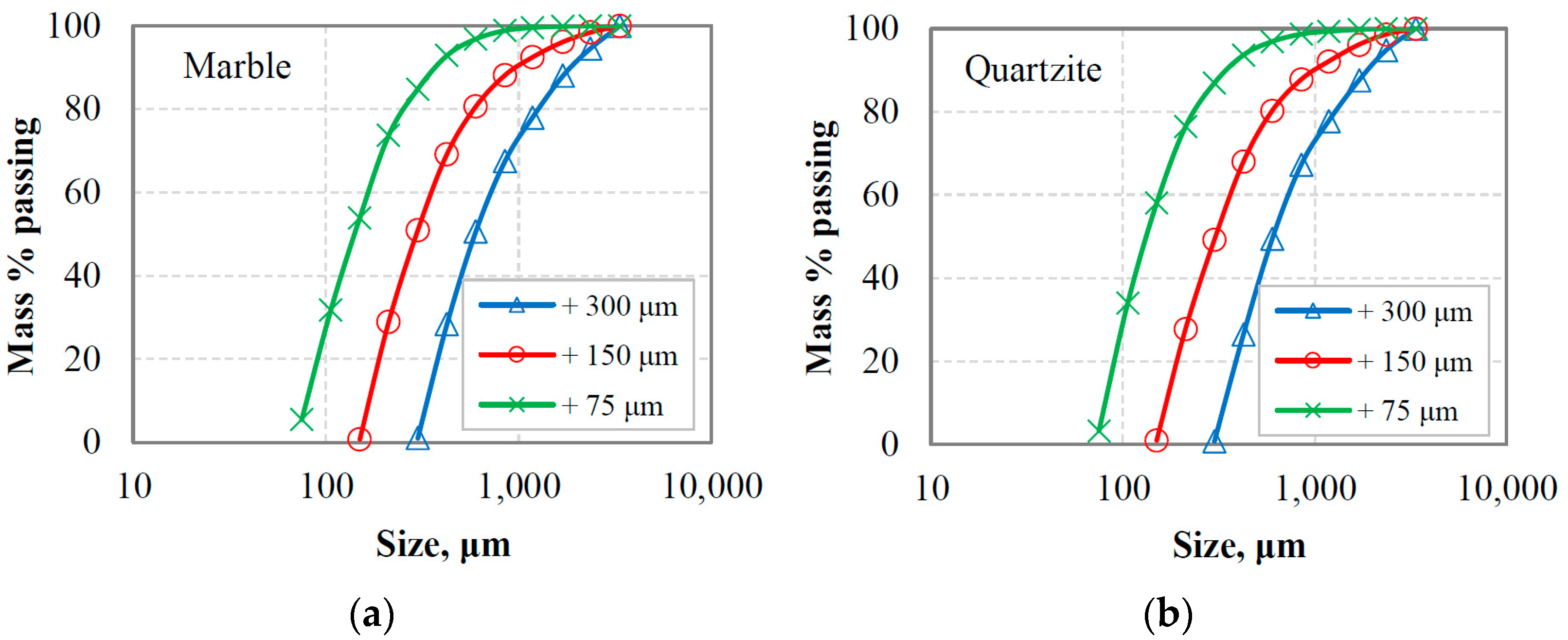
3.1. First Series of Tests
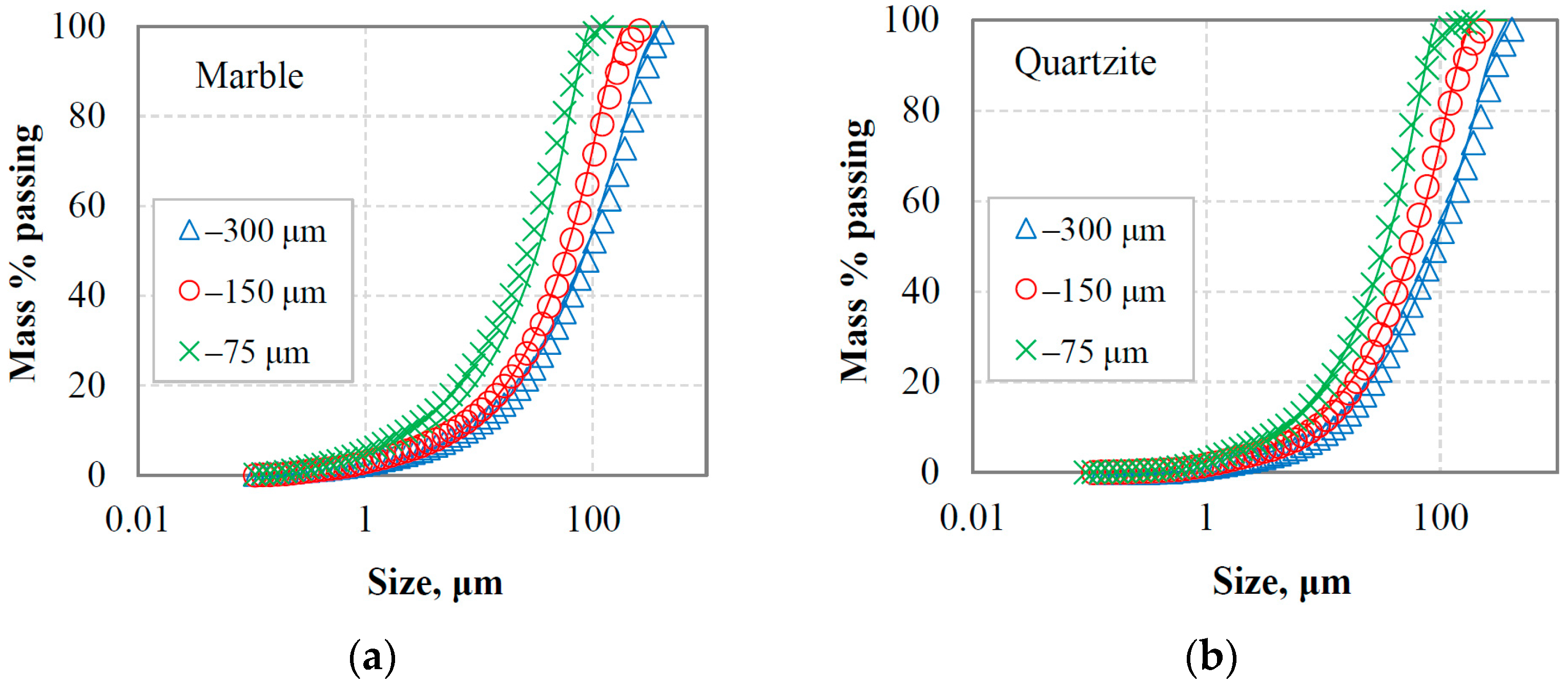
3.1.1. Examining the Fitting Accuracy of the Particle Size Distribution Models
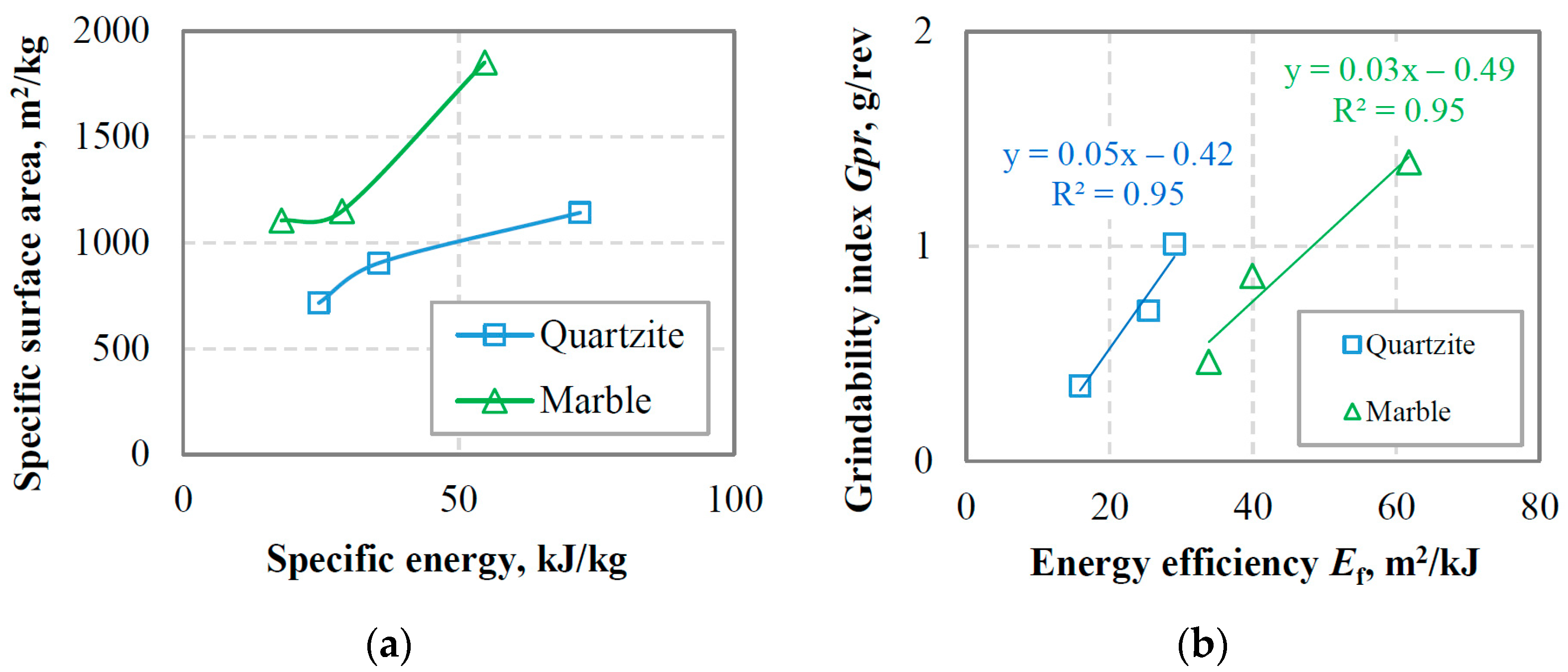
3.1.2. Calculation of Specific Surface Area and Energy Efficiency
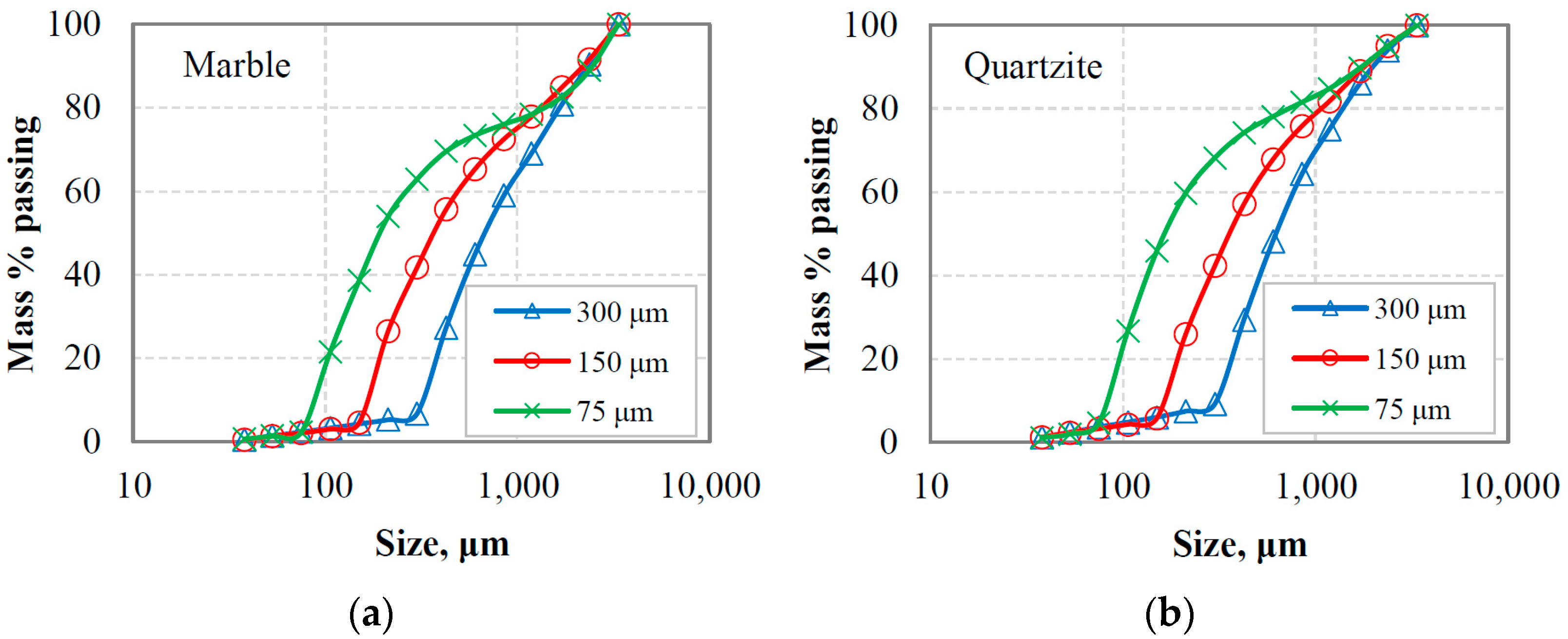
3.2. Second Series of Tests
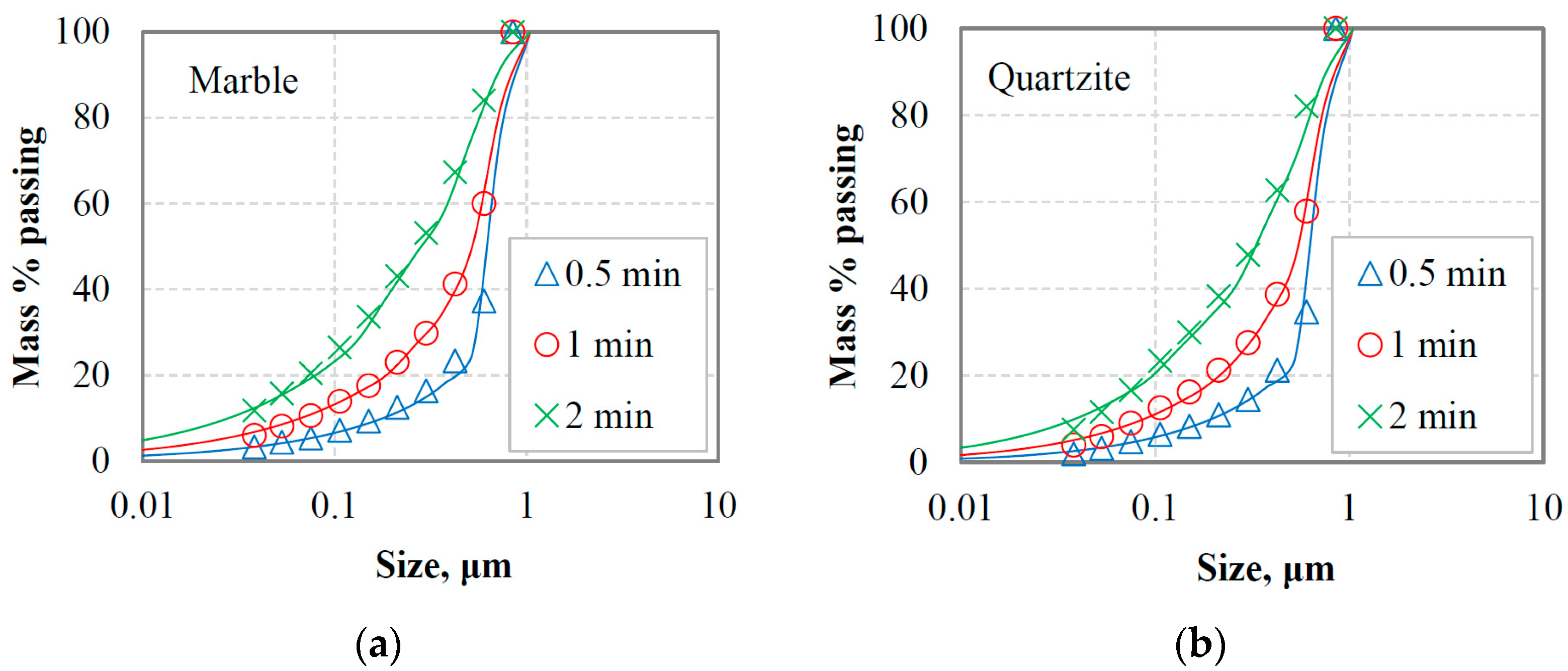
3.2.1. PSDs of the Equilibrium Feeding Materials
3.2.2. Modeling of Grinding Kinetics of Equilibrium Feeding Materials
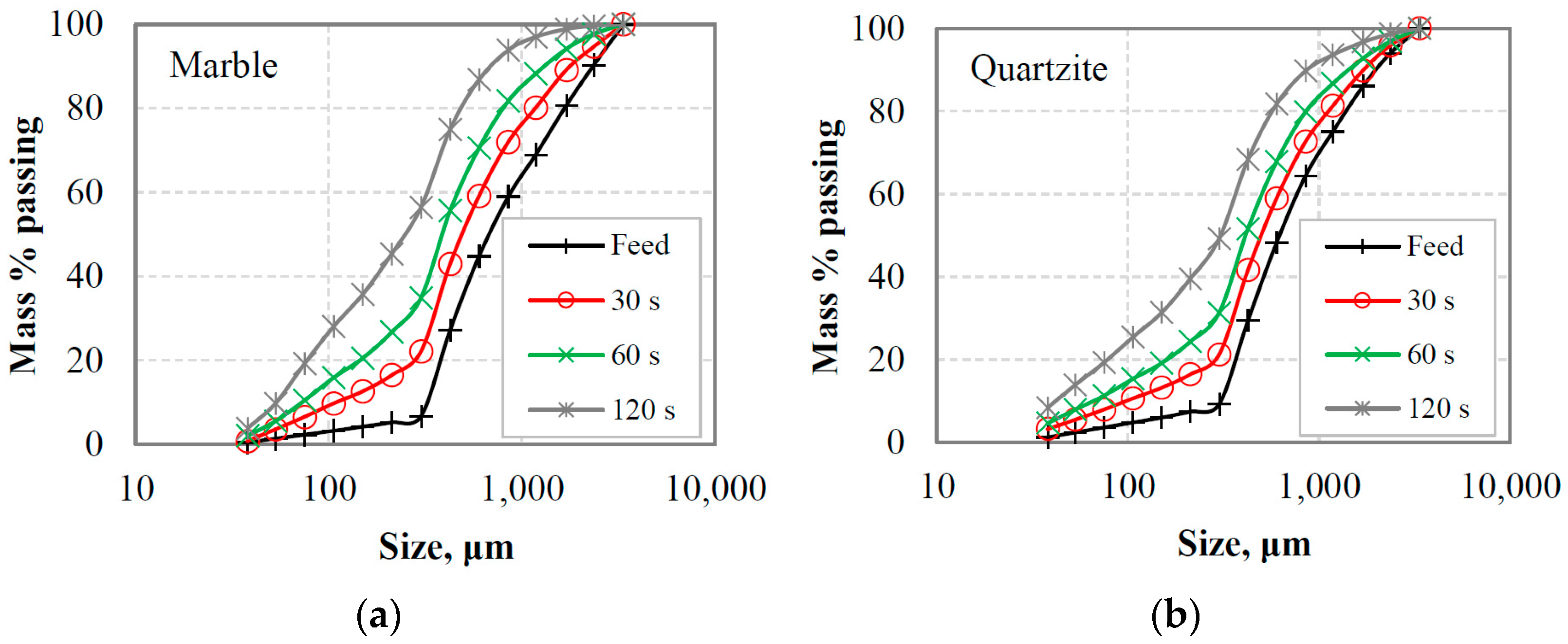
3.3. Third Series of Tests
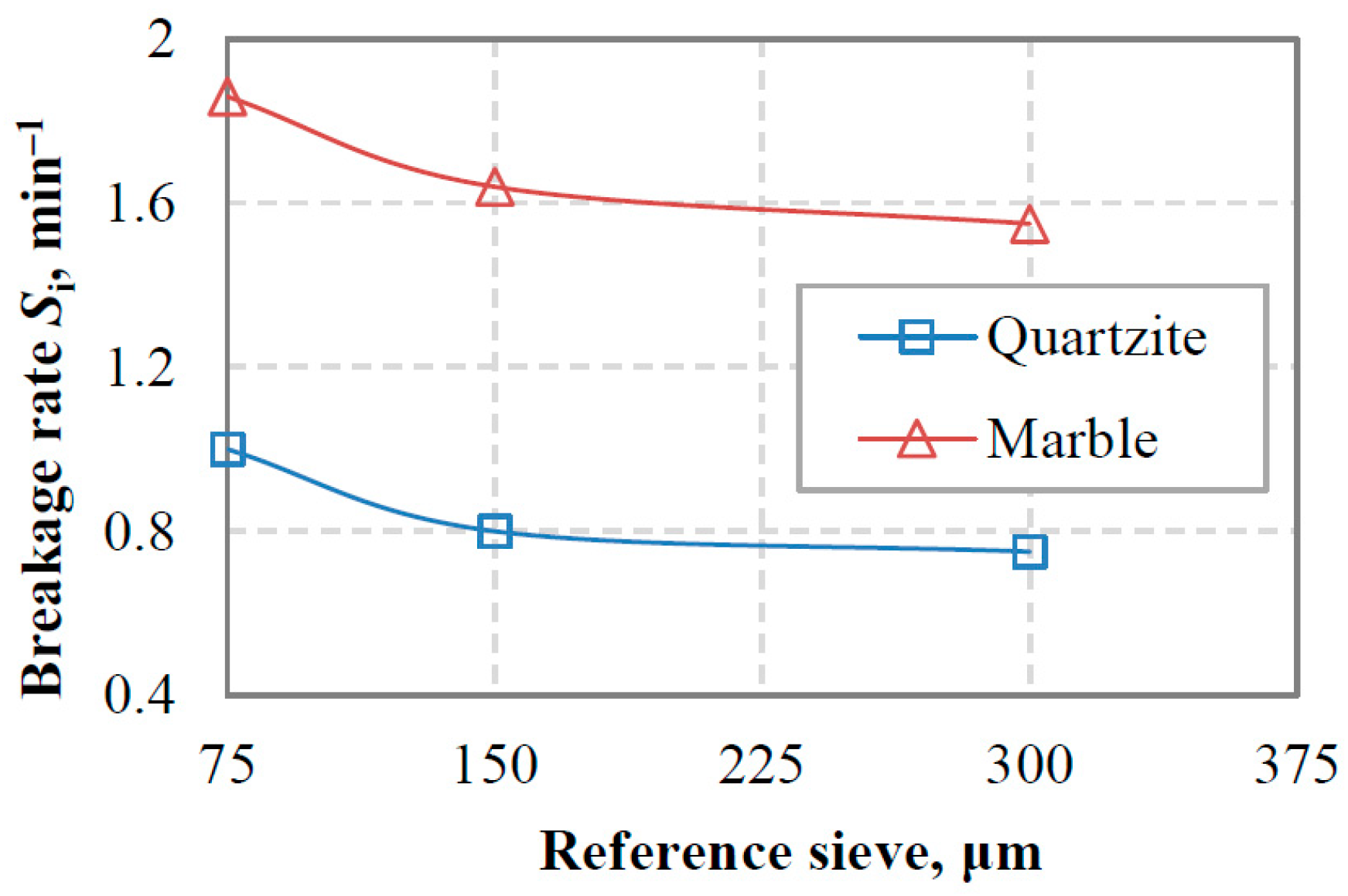
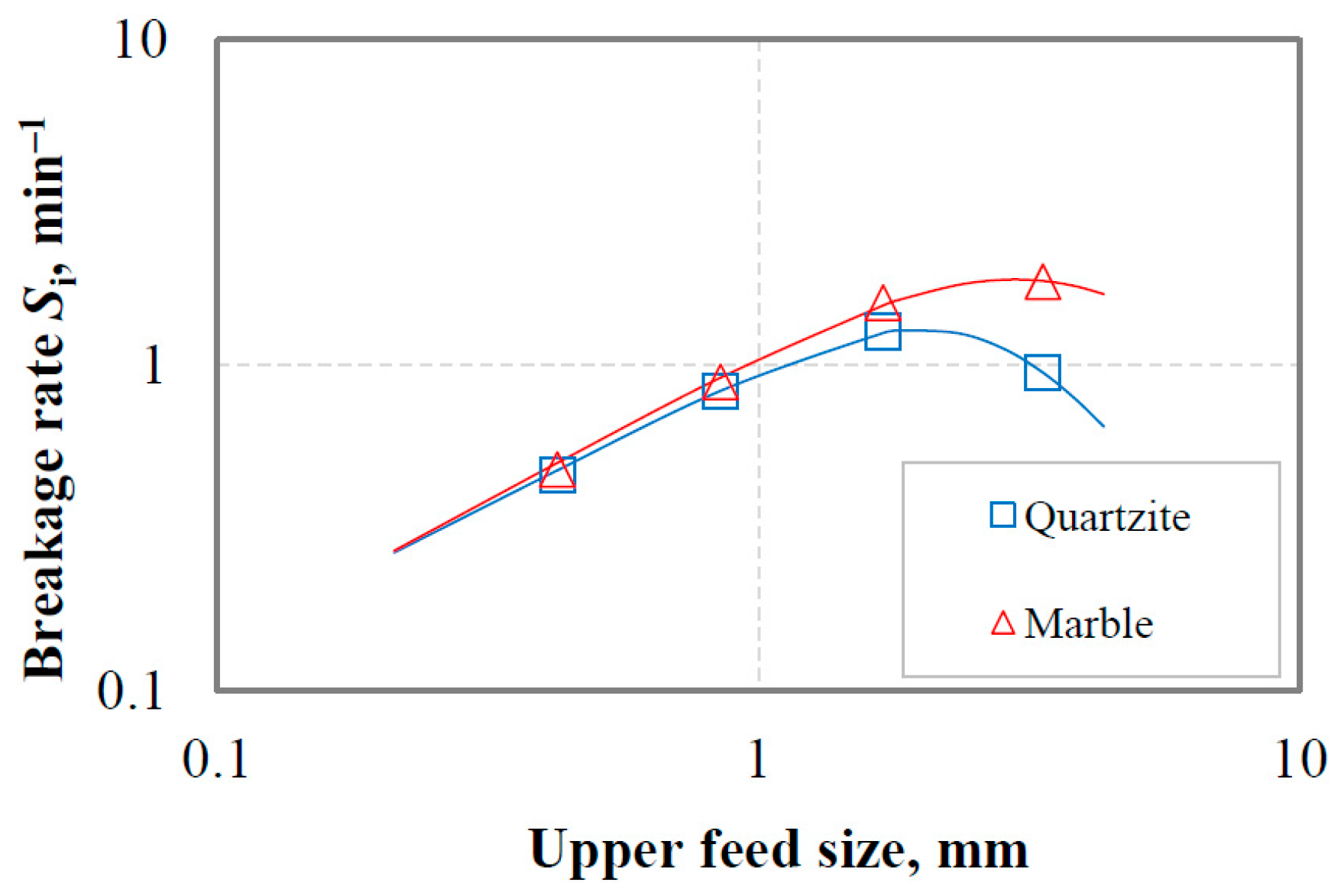
3.3.1. Determination of Breakage Parameters
3.3.2. Effect of Fines Accumulation on Breakage Rate of Coarse Particles
3.4. Simulation of the Closed-Cycle Grinding
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pural, Y.; Çelik, M.; Ozer, M.; Boylu, F. Effective circulating load ratio in mill circuit for milling capacity and further flotation process—Lab scale study. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. 2022, 58, 149916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, E.; Varouchakis, E.; Komnitsas, K. Reliability of the non-linear modeling in predicting the size distribution of the grinding products under different operating conditions. Min. Metall. Explor. 2023, 40, 1265–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltoniemi, M.; Kallio, R.; Tanhua, A.; Luukkanen, S.; Perämäki, P. Mineralogical and surface chemical characterization of flotation feed andproducts after wet and dry grinding. Miner. Eng. 2020, 156, 106500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeswiet, J.; Szekeres, A. Energy Consumption in Mining Comminution. Procedia CIRP 2016, 48, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, S. Helping to reduce mining industry carbon emissions: A step-by-step guide to sizing and selection of energy efficient high pressure grinding rolls circuits. Miner. Eng. 2022, 179, 107431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, A.J.; Forbes, E.; Verster, I.; Jokovic, V.; Awatey, B.; Parbhakar-Fox, A. Review on advances in mineral processing technologies suitable for critical metal recovery from mining and processing wastes. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 7, 100451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson, J.H.; Smith, M.H. Climate change and sustainability as drivers for the next mining and metals boom: The need for climate-smart mining and recycling. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 101205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamboliadis, E.T. Energy distribution in comminution: A new approach to the laws of Rittinger, Bond, and Kick. Can. Metall. Q. 2004, 43, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaña, M.; Gálvez, E.; Navarra, A.; Toro, N.; Cisternas, L.A. Optimization of the SAG Grinding Process Using Statistical Analysis and Machine Learning: A Case Study of the Chilean Copper Mining Industry. Materials 2023, 16, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, A.J. Mineral Crushing and Grinding Circuit—Their Simulation, Optimisation, Design and Control; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977; p. 342. [Google Scholar]
- Herbst, J.A.; Fuerstenau, D.W. Scale-up procedure for continuous grinding mill design using population balance models. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1980, 7, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, L.G.; Klimpel, R.R.; Luckie, P.T. Process Engineering of Size Reduction: Ball Milling; SME–AIME: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Ipek, H.; Göktepe, F. Determination of grindability characteristics of zeolite. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2011, 47, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.K.; Sharma, S. Analysis of ball mill grinding operation using mill power specific kinetic parameters. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, E.; Stamboliadis, E.; Komnitsas, K. Identification of optimal mill operating parameters during grinding of quartz with the use of population balance modelling. Kona Powder Part. J. 2017, 34, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K. An appraisal of the energy-size reduction relationships for mill scale-up design. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, L.G.; Luckie, P.T. Methods for determination of breakage distribution parameters. Powder Technol. 1972, 5, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimpel, R.R.; Austin, L.G. The back-calculation of specific rates of breakage and non-normalized breakage distribution parameters from batch grinding data. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1977, 4, 7–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, L.G.; Bagga, P. An analysis of fine dry grinding in ball mills. Powder Technol. 1981, 28, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hukki, R.T. Fundamentals of the closed grinding circuit. Eng. Min. J. 1979, 180, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Morrell, S. A method for predicting the specific energy requirement of comminution circuits and assessing their energy utilisation efficiency. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, A.; Valery, W. Closed circuit ball mill—Basics revisited. Miner. Eng. 2013, 43–44, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Ni, L.; Song, T.; Olson, J.; Zhao, J. An overview of operating parameters and conditions in hydrocyclones for enhanced separations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 206, 268–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhaffez, G.S.; Ahmed, A.A.; Ahmed, H.M. Effect of grinding media on the milling efficiency of a ball mill. Rud. Geol. Naft. Zb. 2022, 37, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, V.; Kruszelnicka, W. Relation between Scale-Up and Life Cycle Assessment for Wet Grinding Process of Pumice. Energies 2023, 16, 4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K. An appraisal of the linear first order kinetic model based ball mill design correlations. In Proceedings of the World Congress Particle Technology, Part II: Comminution, (6. European Symposium on Comminution), Nurnberg, Germany, 16–18 April 1986; Leschonski, K., Ed.; pp. 605–620. [Google Scholar]
- Rajamani, R.K.; Guo, D. Acceleration and deceleration of breakage rates in wet ball mills. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1992, 34, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, P.C. An improved method for estimating the feed-size breakage distribution functions. Powder Technol. 1982, 33, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerstenau, D.W.; Abouzeid, A.M.; Phatak, P.B. Effect of fine particles on the kinetics and energetics of grinding coarse particles. In Proceedings of the 119th AIME Annual Meeting, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, February 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, R.; Rajamani, R.K. Environment dependent breakage rates in ball milling. Powder Technol. 1995, 94, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 1936:2006; Natural Stone Test Methods. Determination of Real Density and Apparent Density, and of Total and Open Porosity. British Standard Institution (BSI): London, UK, 2017.
- Petrakis, E.; Komnitsas, K. Correlation between material properties and breakage rate parameters determined from grinding tests. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, G.G.; Oliva, J.; Guasch, E.; Anticoi, H.; Coello-Velázquez, A.L.; Menéndez-Aguado, J.M. Variability Study of Bond Work Index and Grindability Index on Various Critical Metal Ores. Metals 2021, 11, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, E.; Komnitsas, K. Effect of energy input in a ball mill on dimensional properties of grinding products. Min. Metall. Explor. 2019, 36, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wilkinson, D.; Patchigolla, K. Comparison of particle size distributions measured using different techniques. Part. Sci. Technol. 2005, 23, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuila, U.; Prasad, M. Specific surface area and pore-size distribution in clays and shales. Geophys. Prospect. 2012, 61, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, F.C. Crushing and grinding calculations. Br. Chem. Eng. 1961, 6, 378–385, 543–548. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Yan, D.S. Mineral Processing Design and Operations: An Introduction, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- King, R.P. Modeling and Simulation of Mineral Processing Systems; Butterworth–Heinemann Publications: Oxford, UK, 2001; p. 416. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, M.A.; King, R.P. The simulation of ore-dressing plants. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1984, 12, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T. Powder Sampling and Particle Size Determination; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; p. 682. [Google Scholar]
- Petrakis, E.; Karmali, V.; Bartzas, G.; Komnitsas, K. Grinding Kinetics of Slag and Effect of Final Particle Size on the Compressive Strength of Alkali Activated Materials. Minerals 2019, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeelnejad, L.; Siavashi, F.; Seyedmohammadi, J.; Shabanpour, M. The best mathematical models describing particle size distribution of soils. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coello-Velázquez, A.L.; Quijano Arteaga, V.; Menéndez-Aguado, J.M.; Pole, F.M.; Llorente, L. Use of the Swebrec Function to Model Particle Size Distribution in an Industrial-Scale Ni-Co Ore Grinding Circuit. Metals 2019, 9, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, B.A.; Finch, J. Will’s Mineral Processing Technology. An Introduction to the Practical Aspects of Ore Treatment and Mineral Recovery, 8th ed.; Butterworth–Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Taşdemir, A.; Taşdemir, T. A comparative study on PSD models for chromite ores comminuted by different devices. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2009, 26, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalinović, N.M. Calculation of energy required for grinding in a ball mill. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1989, 25, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aras, A.; Ozkan, A.; Aydogan, S. Correlations of bond and breakage parameters of some ores with the corresponding point load index. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2012, 29, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abazarpoor, A.; Halali, M. Investigation on the particle size and shape of iron ore pellet feed using ball mill and HPGR grinding methods. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2017, 53, 908–919. [Google Scholar]
- Hlobil, M.; Kumpová, I.; Hlobilová, A. Surface area and size distribution of cement particles in hydrating paste as indicators for the conceptualization of a cement paste representative volume element. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 134, 104798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, E.; Komnitsas, K. Development of a non-linear framework for the prediction of the particle size distribution of the grinding products. Min. Metall. Explor. 2021, 38, 1253–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, A.; Sinclair, S. The shape of product size distributions in stirred mills. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerstenau, D.W.; Abouzeid, A.-Z.M. Effect of fine particles on the kinetics and energetics of grinding coarse particles. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1991, 31, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kwon, J.; Kim, K.; Mun, M. Optimum choice of the make-up ball sizes for maximum throughput in tumbling ball mills. Powder Technol. 2013, 246, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, E.; Komnitsas, K. Effect of grinding media size on ferronickel slag ball milling efficiency and energy requirements using kinetics and attainable region approaches. Minerals 2022, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlepp, D.D.; Turner, P.A. Influence of circulating load and classification efficiency on mill throughput. In Proceedings of the SME Annual Meeting, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 26 February–2 March 1990; Society for Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration. Volume 10, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dündar, H.; Kalugin, A.; Delgado, M.; Palomino, A.; Türkistanli, A.; Aquino, B.; Lynch, A.J. Screens and cyclones in closed grinding circuits. Screens and cyclones in closed grinding circuits. In Proceedings of the XXVII International Mineral Processing Congress, Santiago, Chile, 20–24 October 2014; Gecamin: Santiago, Chile, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Frausto, J.J.; Ballantyne, G.R.; Runge, K.; Powell, M.S.; Wightman, E.M.; Evans, C.L.; Gonzalez, P.; Gomez, S. The effect of screen versus cyclone classification on the mineral liberation properties of a polymetallic ore. Miner. Eng. 2021, 169, 106930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
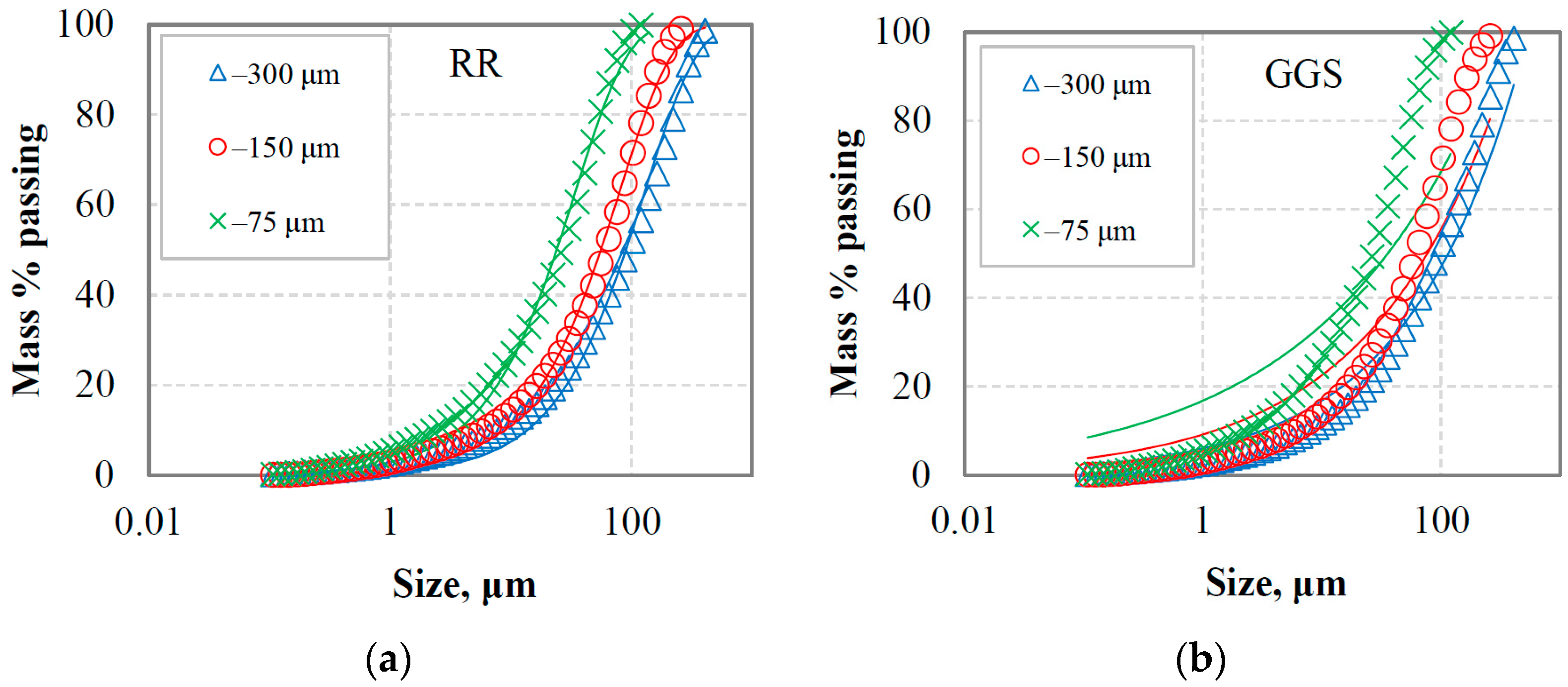

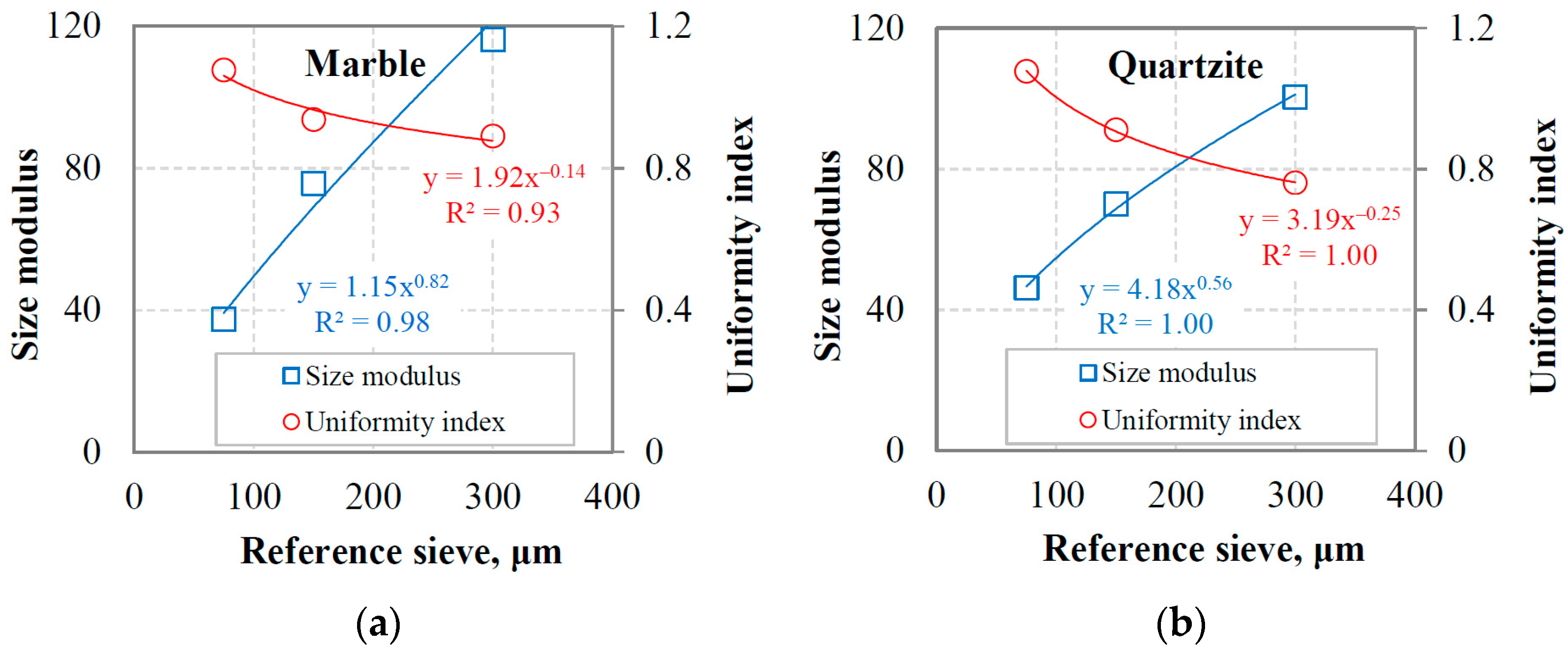



| Model | Index | Marble | Quartzite | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −300 μm | −150 μm | −75 μm | −300 μm | −150 μm | −75 μm | ||
| RR | R2 adj. | 0.997 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.997 |
| RMSE | 2.52 | 1.91 | 2.08 | 1.38 | 1.32 | 2.25 | |
| SE | 2.00 | 1.71 | 1.87 | 1.33 | 1.22 | 2.15 | |
| GGS | R2 adj. | 0.967 | 0.931 | 0.884 | 0.962 | 0.918 | 0.878 |
| RMSE | 6.45 | 10.29 | 14.39 | 7.21 | 11.57 | 15.02 | |
| SE | 6.22 | 9.95 | 13.94 | 6.87 | 11.16 | 14.55 | |
| Material | Product Size | BET | LD | d50 | ε | Ef |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μm | m2/kg | m2/kg | μm | kJ/kg | m2/kJ | |
| Marble | −300 | 1105 | 245 | 96.2 | 17.9 | 61.8 |
| −150 | 1149 | 296 | 61.2 | 28.8 | 39.9 | |
| −75 | 1852 | 556 | 26.7 | 54.7 | 33.8 | |
| Quartzite | −300 | 716 | 127 | 91.9 | 24.7 | 29.1 |
| −150 | 905 | 202 | 55.0 | 35.5 | 25.4 | |
| −75 | 1142 | 313 | 32.4 | 72.0 | 15.9 |
| Material | Si/3.35 | αΤ | α | μ | Λ | Φj | γ | β |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| min−1 | min−1 | mm | ||||||
| Marble | 1.81 | 1.09 | 0.90 | 3.71 | 3.10 | 0.63 | 0.73 | 3.30 |
| Quartzite | 0.95 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 2.76 | 3.15 | 0.73 | 0.85 | 3.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrakis, E. Effect of Size-Distribution Environment on Breakage Parameters Using Closed-Cycle Grinding Tests. Materials 2023, 16, 7687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247687
Petrakis E. Effect of Size-Distribution Environment on Breakage Parameters Using Closed-Cycle Grinding Tests. Materials. 2023; 16(24):7687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247687
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrakis, Evangelos. 2023. "Effect of Size-Distribution Environment on Breakage Parameters Using Closed-Cycle Grinding Tests" Materials 16, no. 24: 7687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247687
APA StylePetrakis, E. (2023). Effect of Size-Distribution Environment on Breakage Parameters Using Closed-Cycle Grinding Tests. Materials, 16(24), 7687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247687






