Model Investigation of Argon Injection into Liquid Steel at Ladle Furnace Station with Using of Innovative Module
Abstract
1. Introduction
- ability to generate the required gas column structure in the liquid steel ensuring effective mixing thereof with possibly limited impact on the steel mirror and the metal-slag interface,
- ability to create large quantities of the possibly fine gas bubbles and, consequently, create gas dispersion with a high degree in liquid steel volume,
- striving to reduce inert gas consumption while ensuring process efficiency.
2. Research Object and Research Methodology
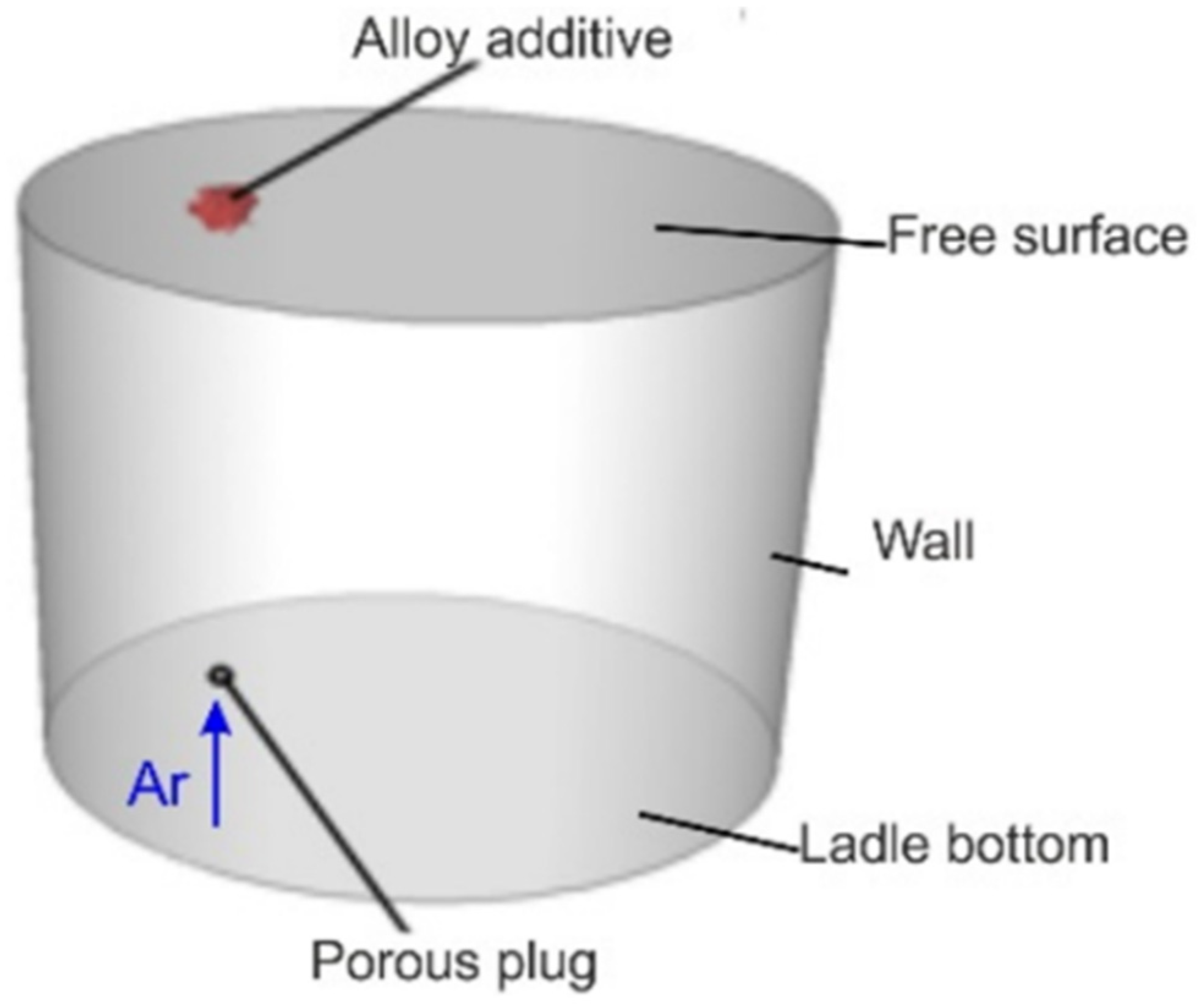
2.1. Numerical Modelling
- Liquid steel flow is turbulent.
- Argon injection for forced convection makes flow two-phase one.
- Neglecting the presence of the slag-protecting metal—the metal surface was modelled as the flat free surface.
- Liquid steel’s natural convection influence on the mixing process is negligible.
- Alloy additive addition to liquid steel bath results in multi-component flow.
- Flow parameters associated with gas injection and alloy additive (tracer) addition are changing over time resulting in unstable liquid flow.
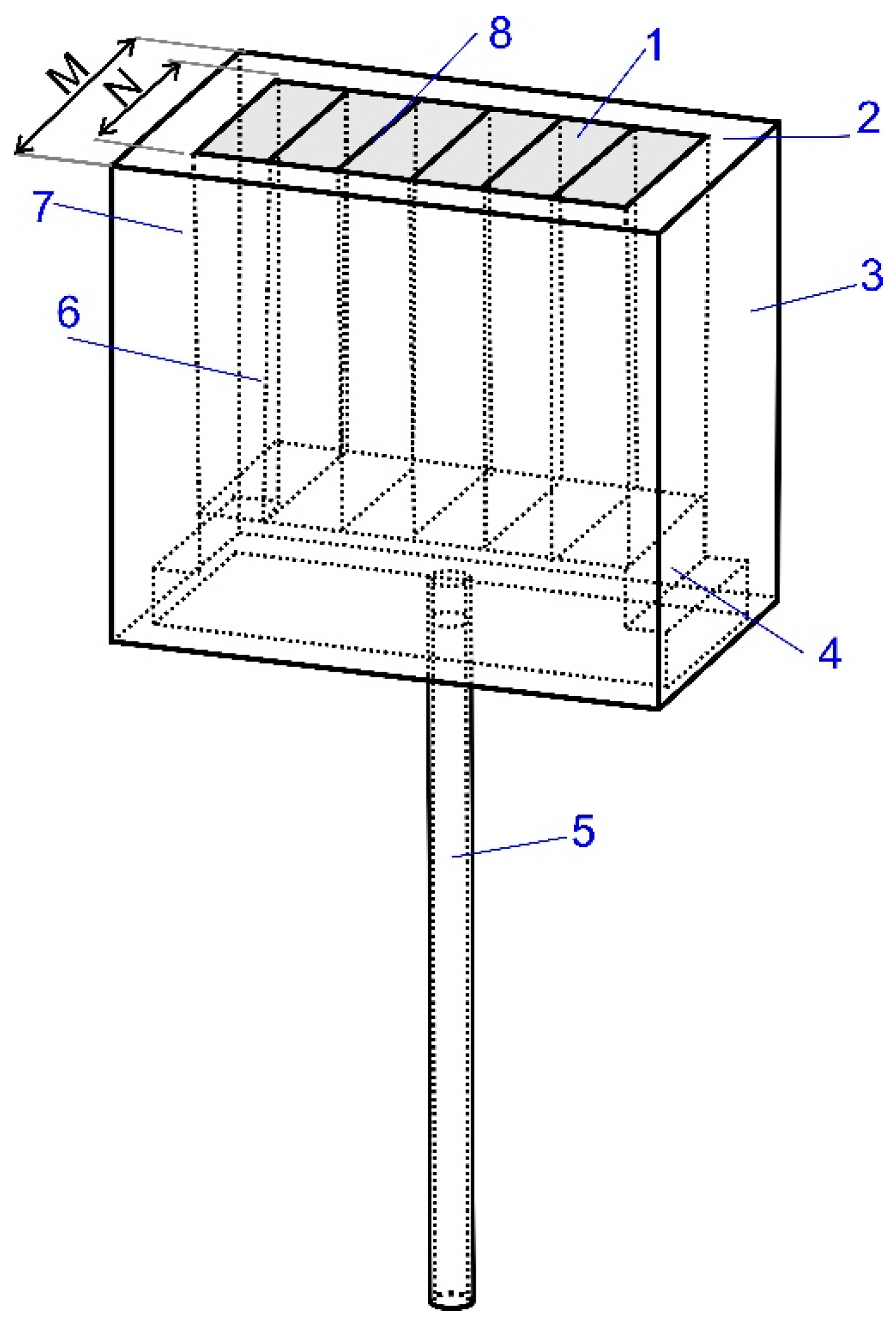
- Argon is injected through a porous plug of slotted type (number of slots—12) and innovative module at a defined mass flow rate (Qm), generating bubbles of a defined diameter.
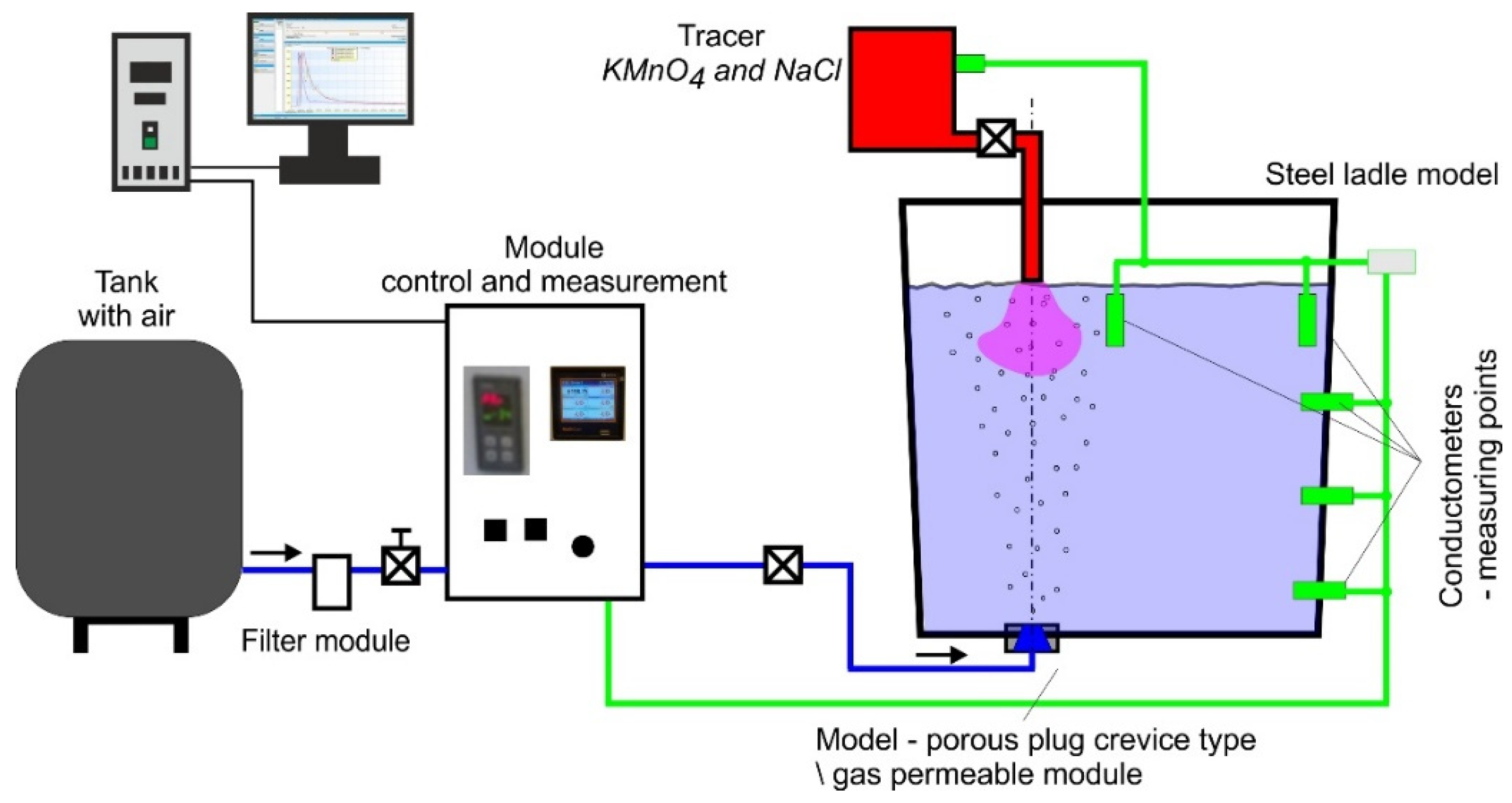
2.2. Physical Modelling
3. Results and Discussions
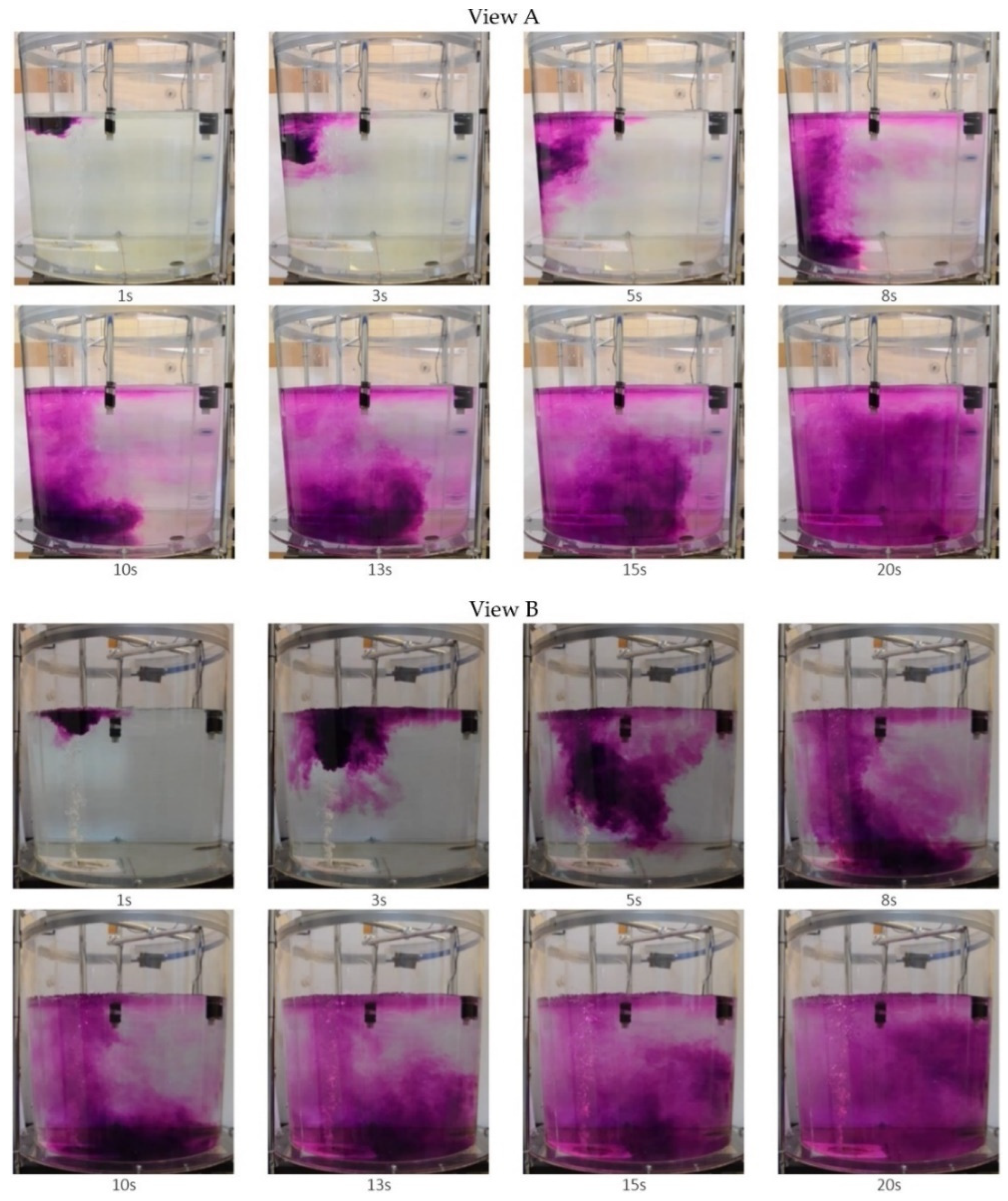
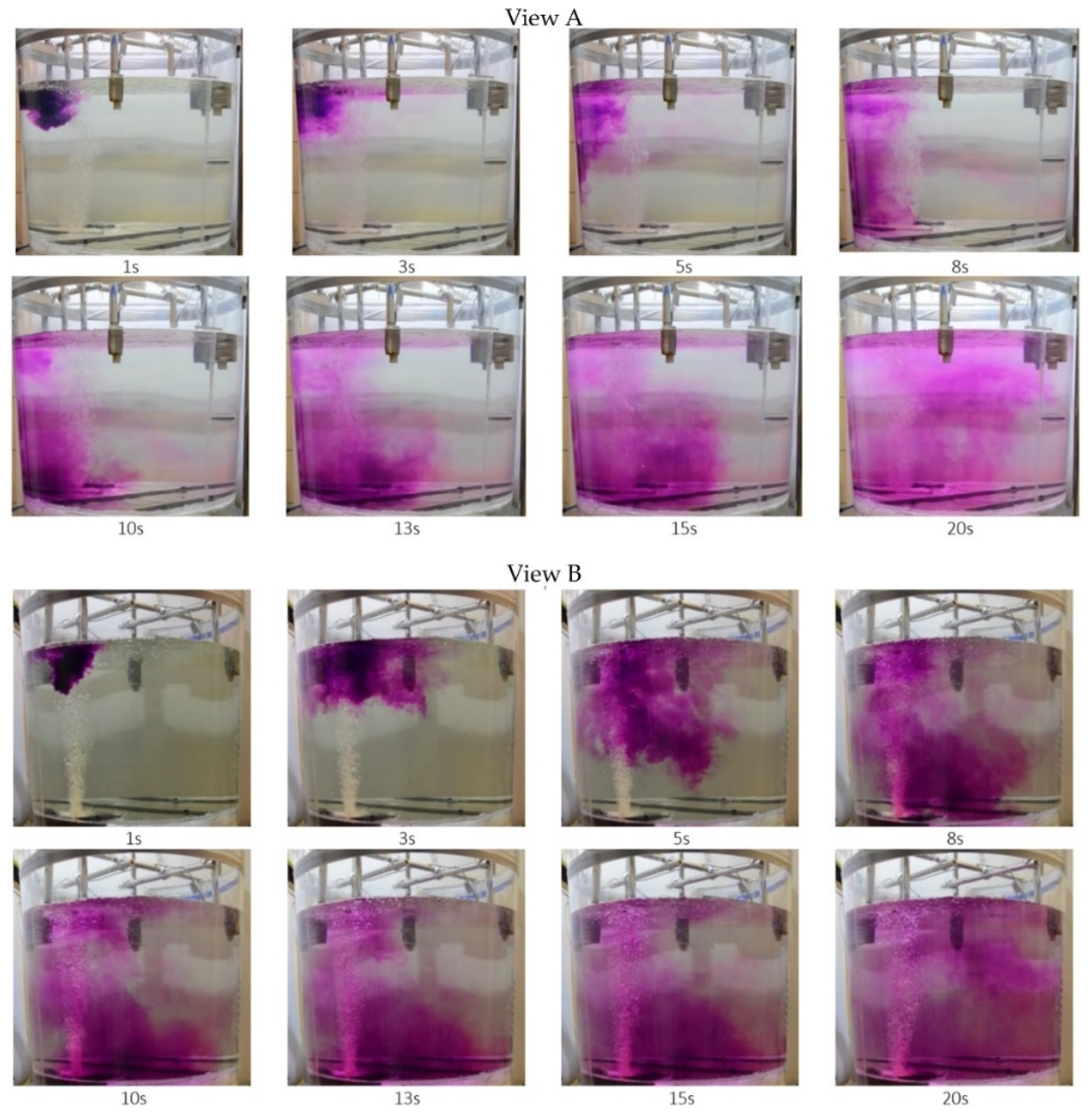
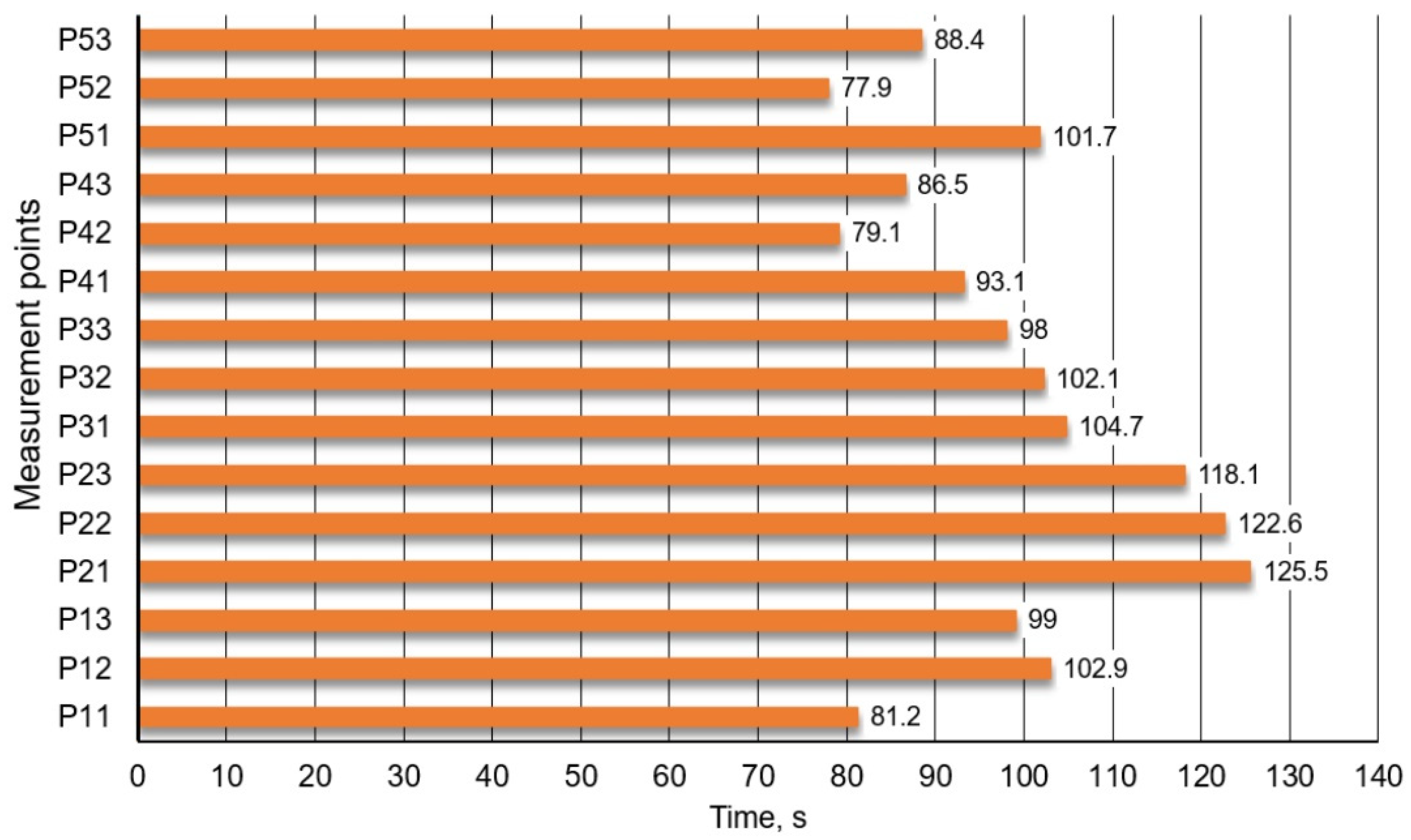
3.1. Water Model Results
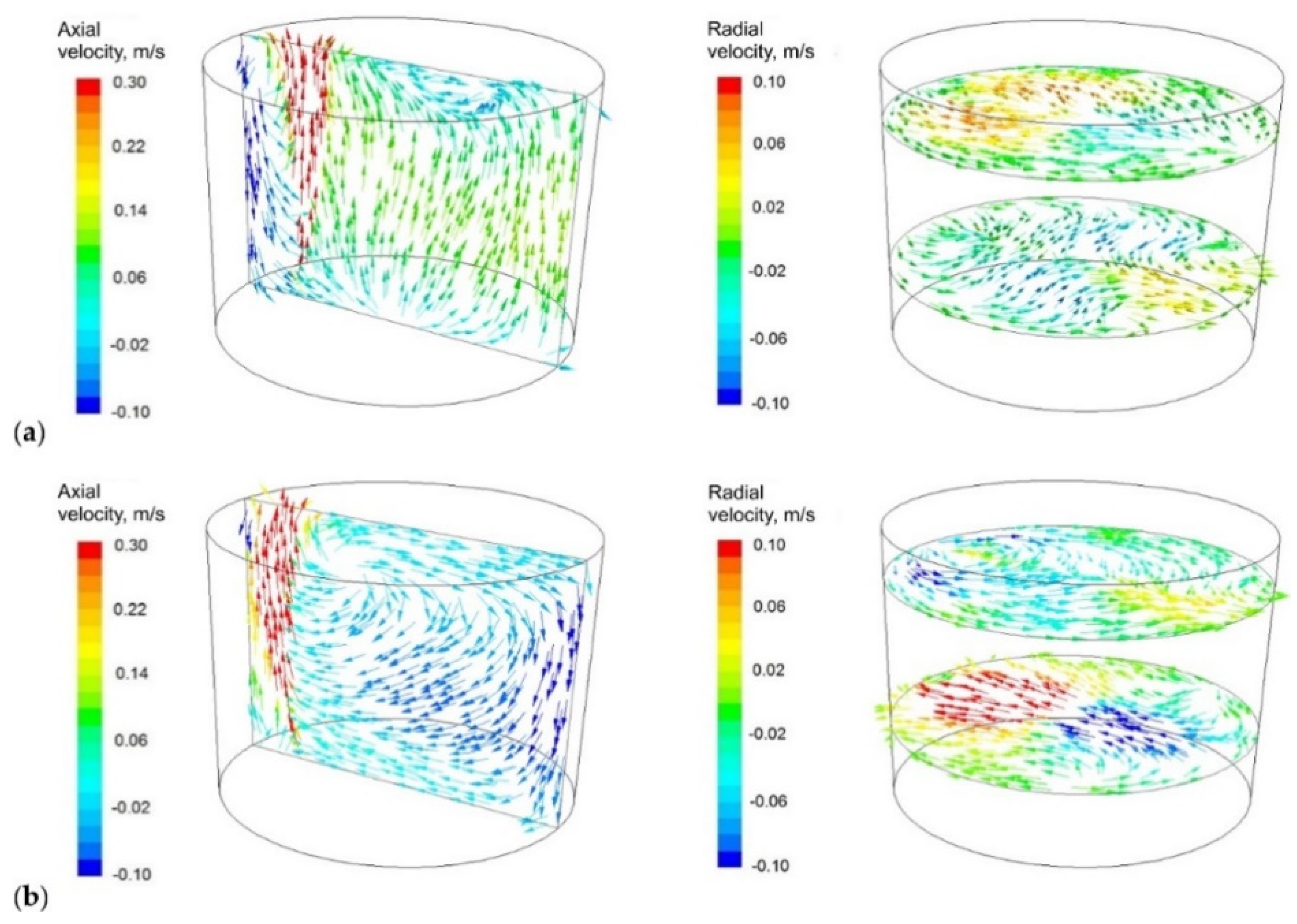
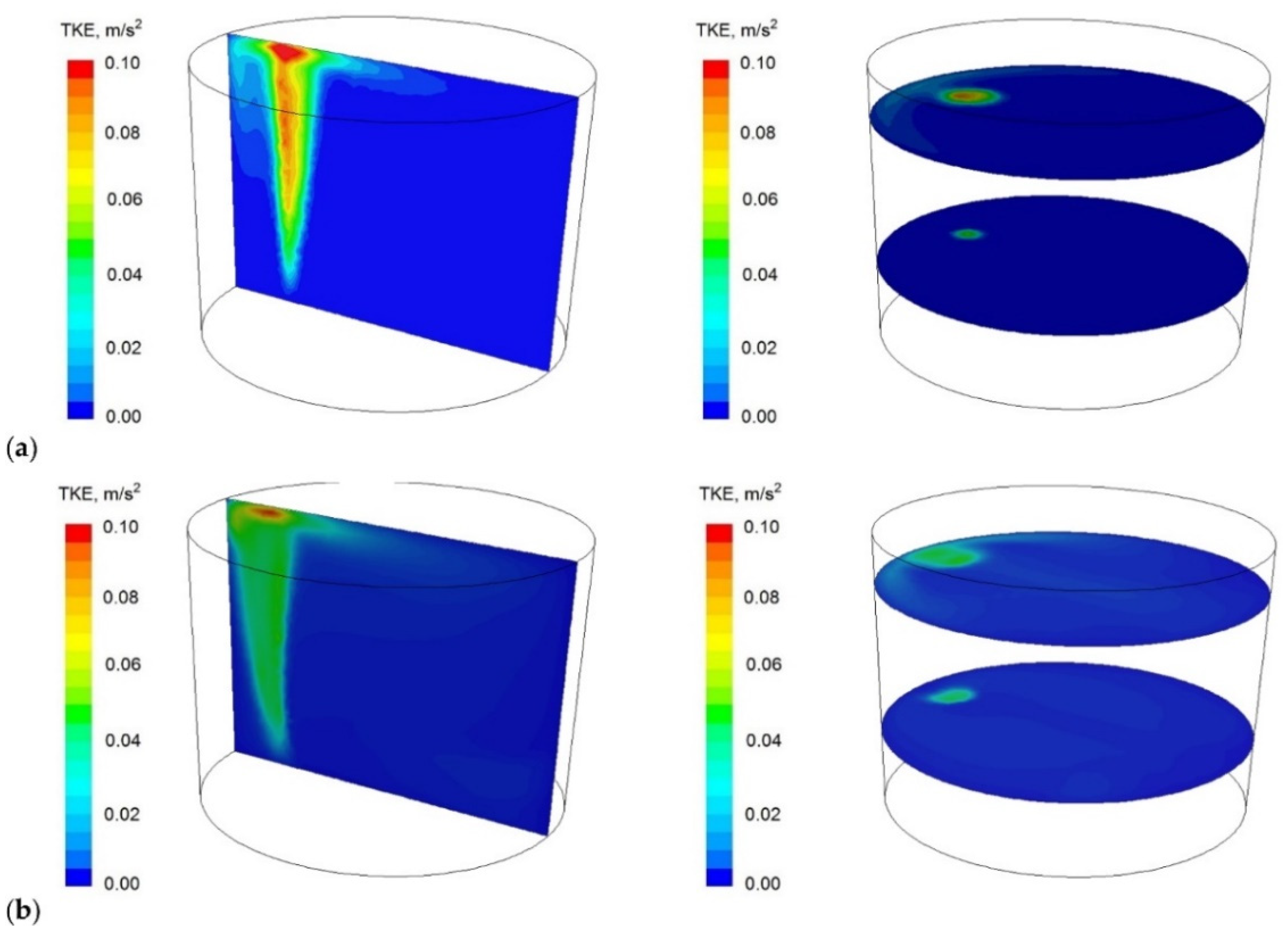
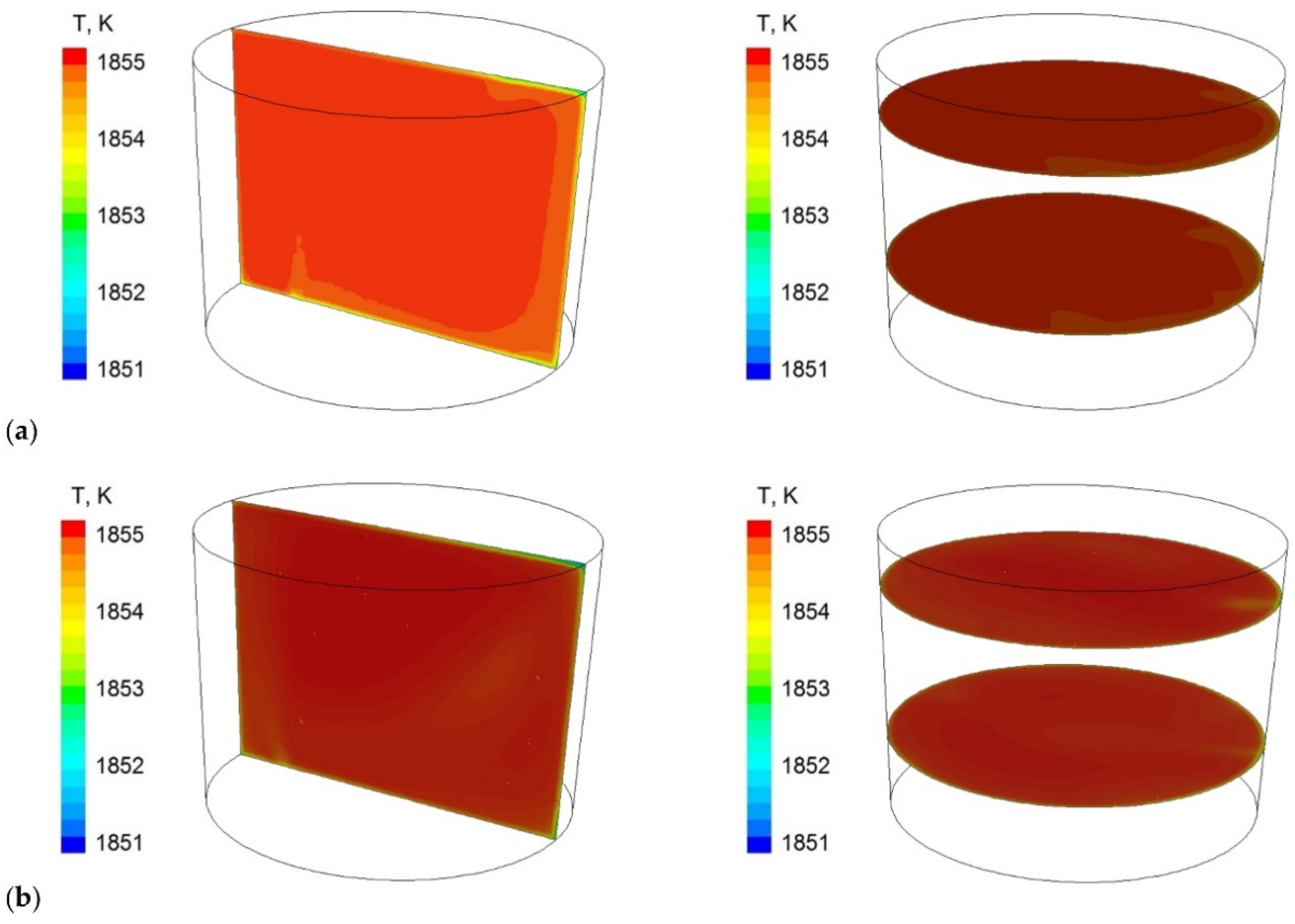
3.2. CFD Simulation Results
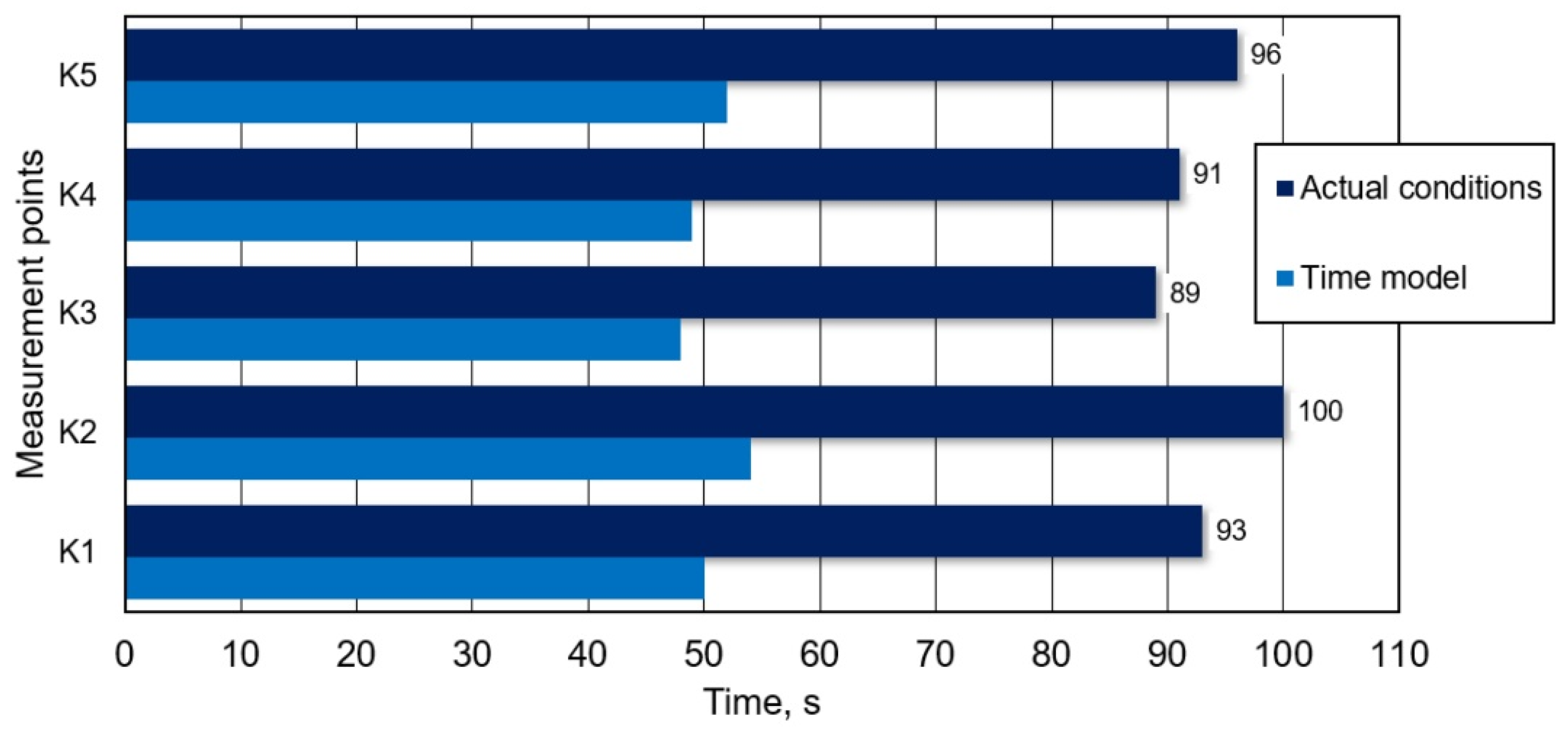
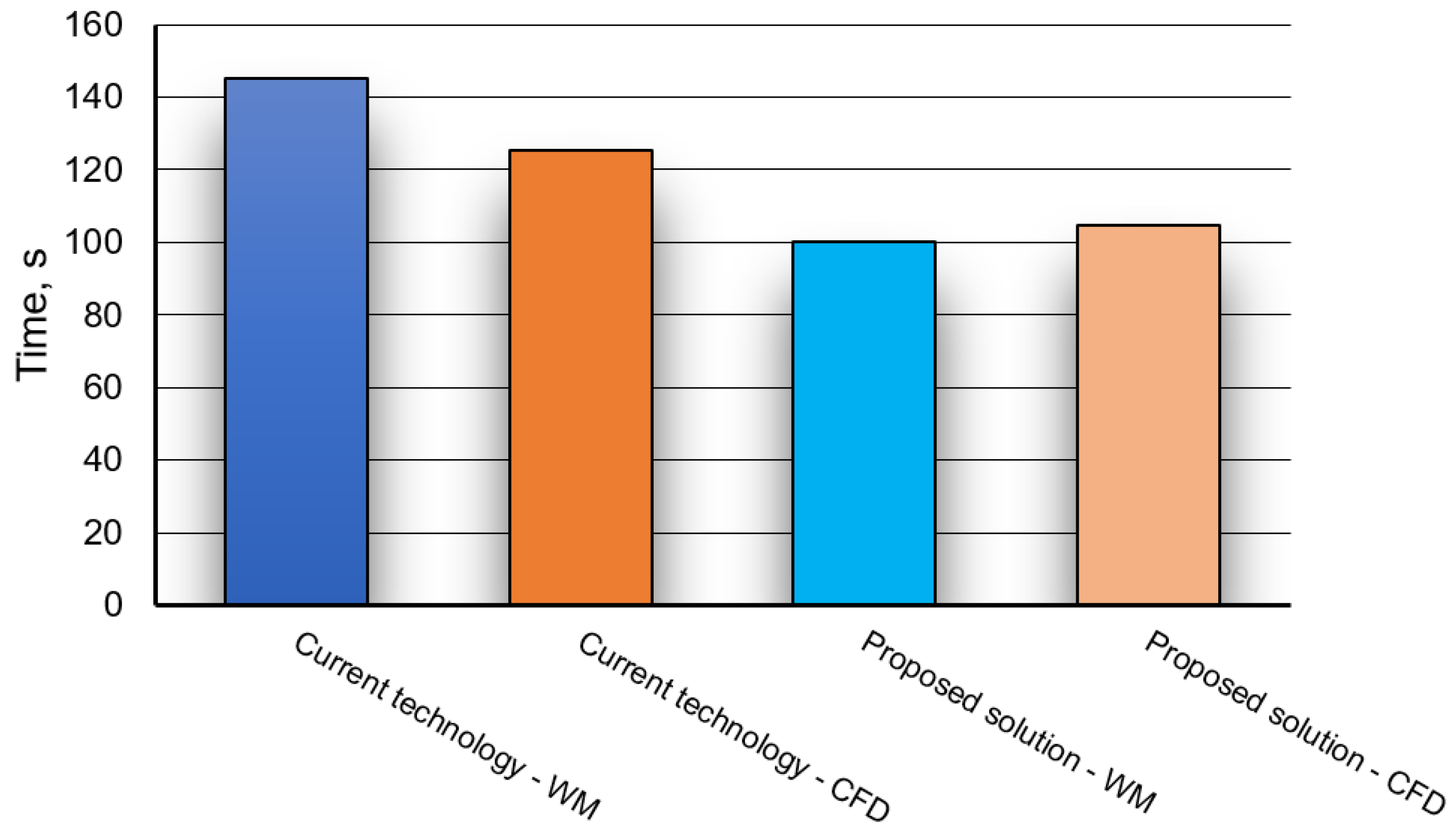
3.3. CFD Simulation and Physical Modelling Result Comparison to Verify Suitability of New Solution Proposed
- harder to catch starting moment in water model,
- precision of tracer insertion in water model,
- numerical idealisation of tracer introduction and/or simplifications used in the CFD model.
4. Conclusions
- The use of a newly proposed gas-permeable module changes the previously obtained structure of the gas-liquid column. The use of the module causes the formation of a large number of small gas bubbles, which helps to increase the refining capacity.
- Due to the strong fragmentation of the gas bubbles, the growth of the gas column at the metal surface is small, which has a beneficial effect on the free surface waving phenomenon.
- For the same reason, the interaction of the gas column with the refractory lining is also weakened. This limits the risk of secondary contamination of the metal bath.
- Increasing the active surface of the module has a beneficial effect on increasing the degree of gas dispersion in the metal bath and, consequently, improving the refining capacity.
- Verification (using the water model) of adopted assumptions and calculation procedures necessary for the description of liquid movement and mixing in the ladle tested, indicates data good quality compliance.
- Module using significantly changes the circulation pattern in the ladle workspace. There occur two distinct circulation areas (vortices) that dominate the flow. It also affects turbulent kinetic energy distribution in the ladle (it covers larger areas) and has a direct effect on the metal bath thermal homogenisation degree.
- The new gas-permeable module using causes the gas-liquid column to be more dispersed and homogenous along the entire height. This brings a positive effect on the liquid steel mixing process after alloy addition introduction.
- The liquid flow structure in the ladle caused by gas introduction through the module proposed results in much faster tracer (alloy additive) dispersion in object volume as compared with the process course with the standard tracer using. Thus, the gas-permeable module using has a clear effect on alloy additive mixing time reduction as compared with the plugs currently used.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mapelli, C. Non-Metallic Inclusions and Clean Steel. La Metall. Ital. 2008, 6, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcellos da Costa e Silva, A.L. Non-metallic inclusions in steels—Origin and control. J. Mater. Technol. 2018, 7, 283–299. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Thomas, B.G.; Wang, X.; Cai, K. Evaluation and Control of Steel Cleanliness—Review. In Proceedings of the 85th Steelmaking Conference Proceedings, ISS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, USA, 10–13 March 2002; Volume 85, pp. 431–452. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, F.; He, Z.; Jin, S.; Pan, L.; Li, Y.; Li, B. Physical Modeling Evaluation on Refining Effects of Ladle with Different Purging Plug Designs. Steel Res. Int. 2020, 91, 1900606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.S.; Jin, Z.; Li, Y. Structural optimization and design of purging plug for improving its service performance. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2022, 29, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardón-Pérez, L.E.; González-Rivera, C.; Ramirez-Argaez, M.A.; Dutta, A. Numerical Modeling of Equal and Dierentiated Gas Injection in Ladles: Eect on Mixing Time and Slag Eye. Processes 2020, 8, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, S.; Wang, D.; Qu, T.; Wu, G.; Zhang, P.; Quan, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z. Inclusion Removements in a Bottom-Stirring Ladle with Novel Slot-Porous Matched Dual Plugs. Metals 2022, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Zhang, L.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J. Effect of Side Blowing on Fluid Flow and Mixing Phenomenon in Gas-Stirred Ladle. Metals 2021, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakkum, S.; Kowitwarangkul, P. Numerical Investigations on the Effect of Gas Flow Rate in the Gas Stirred Ladle with Dual Plugs. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 526, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakkum, S.; Ninpetch, P.; Phophichit, N.; Kowitwarangkul, P. Numerical and Physical Investigations of the Mixing Process in Gas Stirred Lade System. Appl. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2021, 14, 447–459. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, T.; Kumar, S.; Sarkar, A.; Vishwanath, S. Optimization of bath mixing and steel cleanliness during steel refin-ing through physical and mathematical modeling. Sādhanā 2021, 46, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, P.; Haas, T.; Owusu, K.; Eickhoff, M.; Kowitwarangkul, P.; Pfeifer, H. Physical study of the impact of injector de-sign on mixing, convection and turbulence in ladle metallurgy. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2019, 22, 538–547. [Google Scholar]
- Ramasetti, E.; Visuri, V.; Sulasalmi, P.; Mattila, R.; Fabritius, T. Modeling of the Effect of the Gas Flow Rate on the Fluid Flow and Open-Eye Formation in a Water Model of a Steelmaking Ladle. Steel Res. Int. 2018, 90, 1800365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchuk, Y.; Shcherbak, M. Moduł do Dennego Przedmuchiwania Wytopu Gazami Szlachetnymi. PL Patent 229475, 31 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ANSYS. User’s Guide; ANSYS: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.L.; Ahokainen, T. Homogenization of temperature field in a steelmaking ladle with gas injection. Scand. J. Metall. 2003, 32, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, K. The Use of Physical Modeling and Numerical Optimization for Metallurgical Processes; VSB: Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, L. Application of Dimensional Analysis in Model Research; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Mazdumar, D.; Guthrie, R.I. The physical and mathematical modelling of gas stirred ladle systems. ISIJ Int. 1995, 35, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Panic, B. 3D Model studies on the effect of bed and powder type upon radial static pressure and powder distribution in met-allurgical furnaces. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2017, 62, 1449–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Michalek, K.; Gryc, K.; Moravka, J. Physical modelling of bath homogenization in argon stirred ladle. Metalurgija 2009, 48, 215–218. [Google Scholar]
- Merder, T.; Pieprzyca, J.; Warzecha, M.; Warzecha, P. Application of high flow rate gas in the process of argon blowing trough steel. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2017, 62, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowsa, J. Engineering of Ladle Processes in Metallurgy; Częstochowa University of Technology Publishing: Czestochowa, Poland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Szekely, J.; Carlsson, G.; Helle, L. Ladle Metallurgy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
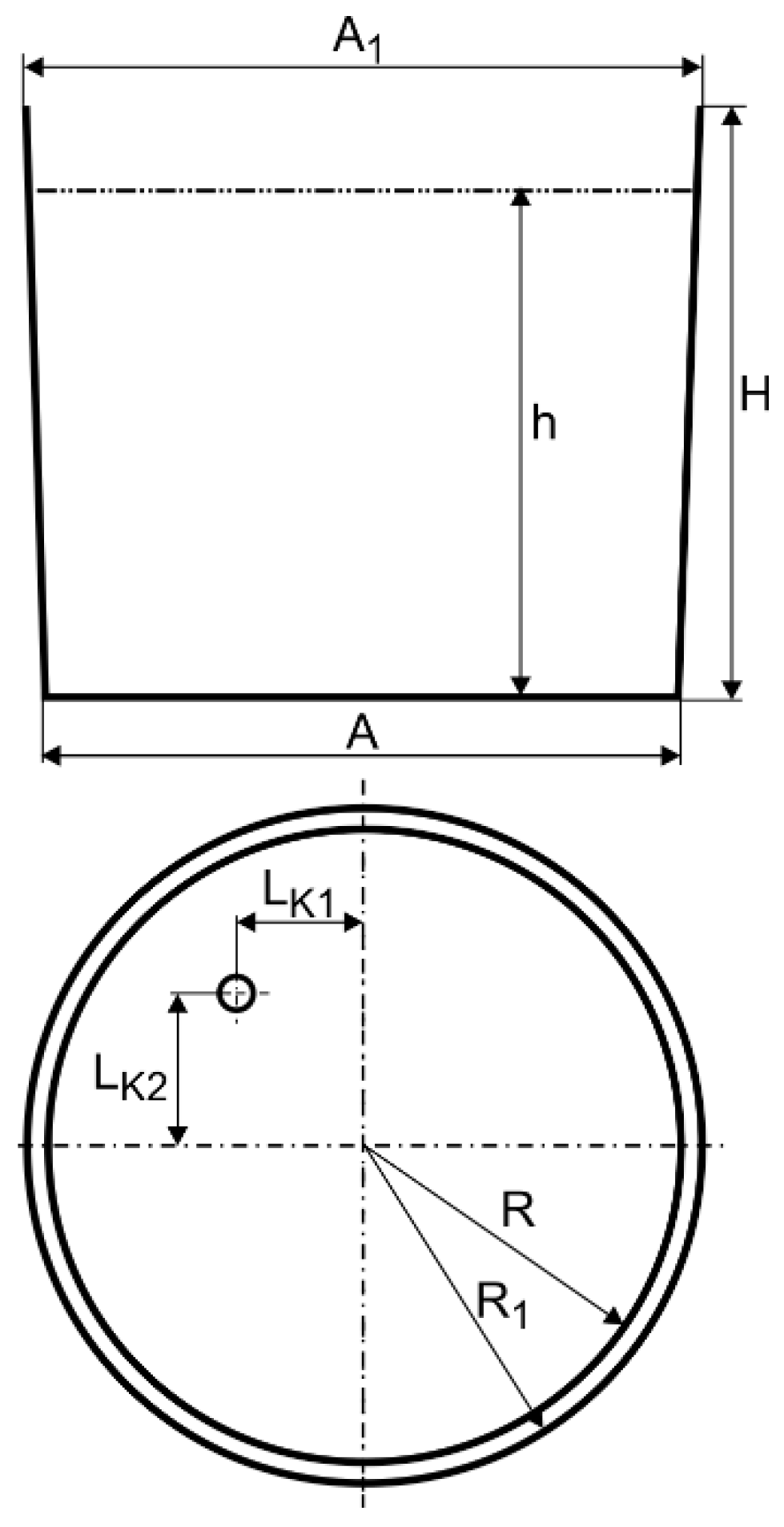


| Parameter | Symbol | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter | A | m | 2.456 |
| A1 | 2.616 | ||
| Radius | R | 1.228 | |
| R1 | 1.308 | ||
| Ladle height | H | 2.322 | |
| Ladle height (liquid steel level) | h | 1.840 | |
| Position of the fitting | LK1 | 0.500 | |
| LK2 | 0.600 |
| Fluid | Property | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid steel | Temperature | 1858 | K |
| Density | 7011 | kg·m−3 | |
| Viscosity | 6.7 | kg·m−1·s−1 | |
| Argon | Density | 1.634 | kg·m−3 |
| Steel Grade | Liquid Steel Temperature in Ladle, °C | Liquid Steel Density, kg·m−3 | Amounts of Alloy Addition, kg | Gas (Ar) Intensity, dm3·min−1 | Heat Flux Losses [16], kW·m−2 by | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | Walls and Bottom | |||||
| B500B | 1585 | 7011 | 100 | 200 | 12.5 | 5.0 |
| Gas (Ar) Intensity—Industry dm3·min−1 | Gas (O2) Intensity—Model dm3·min−1 | Water Density kg·m−3 | Tracer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantitative Research—Mixing Curves | Qualitative Research—Visualization | |||
| 200 | 3.7 | 997 | NaCl | KMnO4 |
| Variant | Error Value (%) |
|---|---|
| Current technology—porous plug (slotted type) | 13.4 |
| Solution proposed—innovative module | −4.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merder, T.; Warzecha, P.; Pieprzyca, J.; Warzecha, M.; Wende, R.; Hutny, A. Model Investigation of Argon Injection into Liquid Steel at Ladle Furnace Station with Using of Innovative Module. Materials 2023, 16, 7698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247698
Merder T, Warzecha P, Pieprzyca J, Warzecha M, Wende R, Hutny A. Model Investigation of Argon Injection into Liquid Steel at Ladle Furnace Station with Using of Innovative Module. Materials. 2023; 16(24):7698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247698
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerder, Tomasz, Piotr Warzecha, Jacek Pieprzyca, Marek Warzecha, Robert Wende, and Artur Hutny. 2023. "Model Investigation of Argon Injection into Liquid Steel at Ladle Furnace Station with Using of Innovative Module" Materials 16, no. 24: 7698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247698
APA StyleMerder, T., Warzecha, P., Pieprzyca, J., Warzecha, M., Wende, R., & Hutny, A. (2023). Model Investigation of Argon Injection into Liquid Steel at Ladle Furnace Station with Using of Innovative Module. Materials, 16(24), 7698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16247698







