Investigating Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Method for Evaluating High-Temperature Properties of Non-Sintered Hwangto-Mixed Concrete as a Cement Replacement Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Outline
2.2. Materials
2.3. Mix Proportions
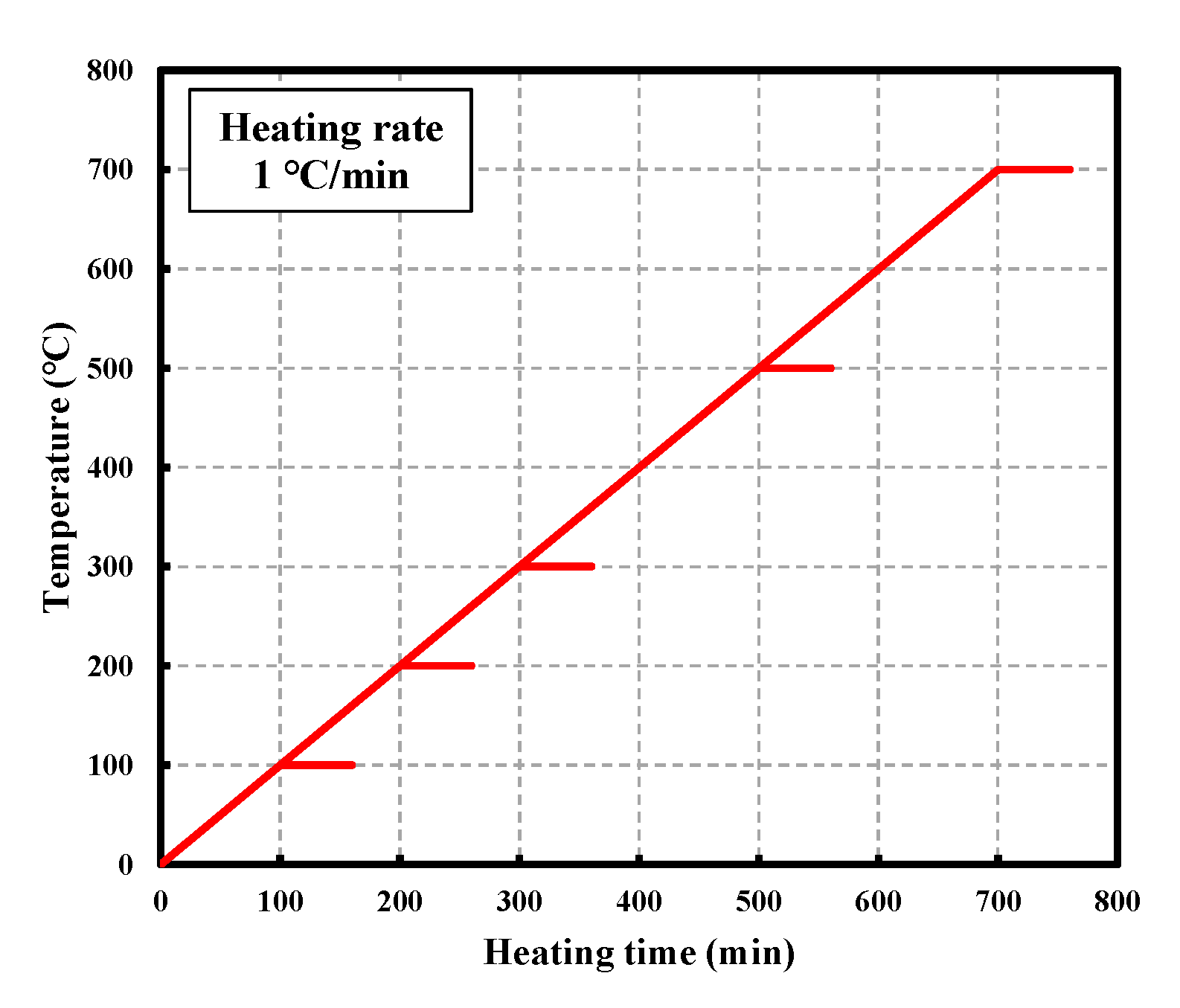
2.4. Heating and Test Methods
3. Results and Discussion
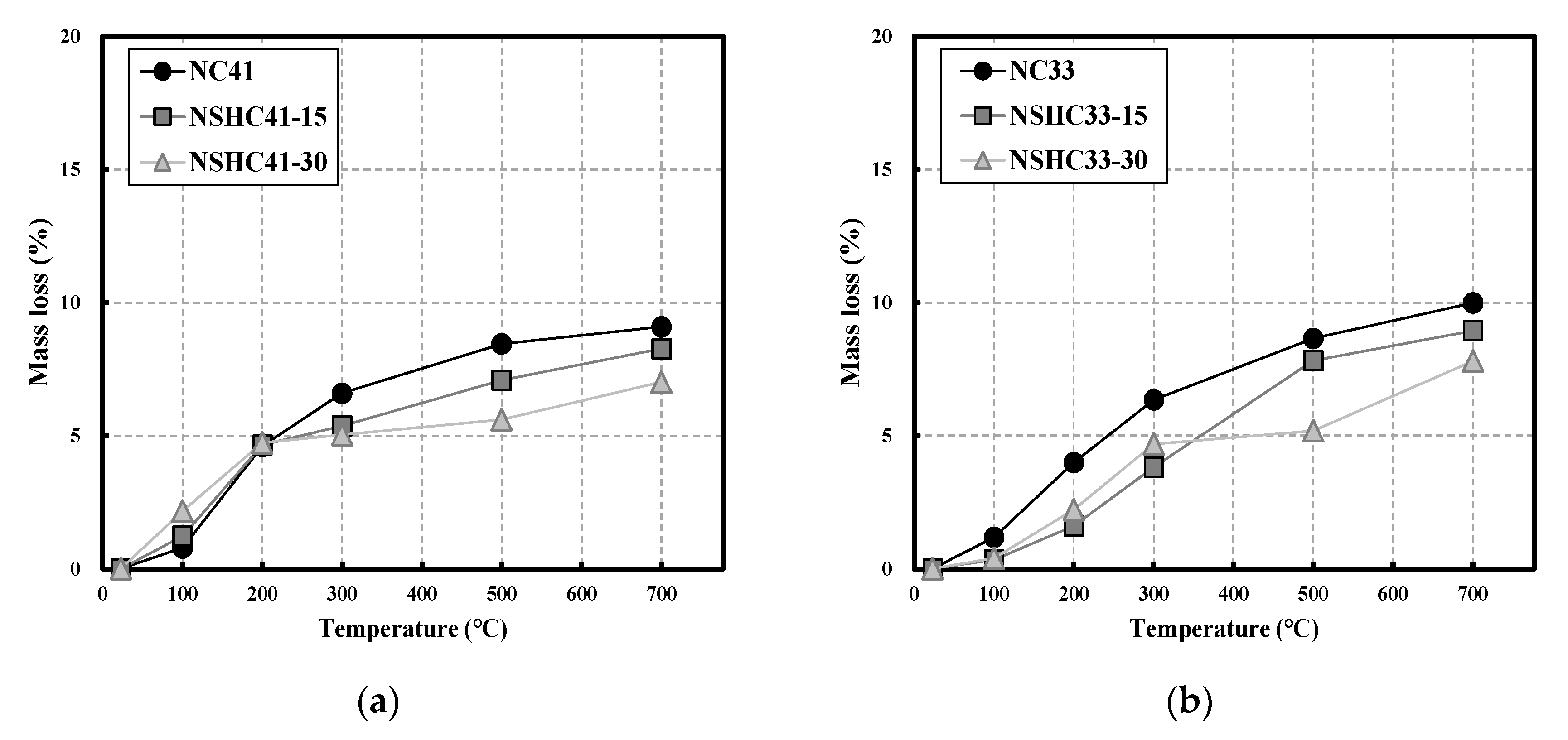
3.1. Mass Loss
3.2. Residual Compressive Strength
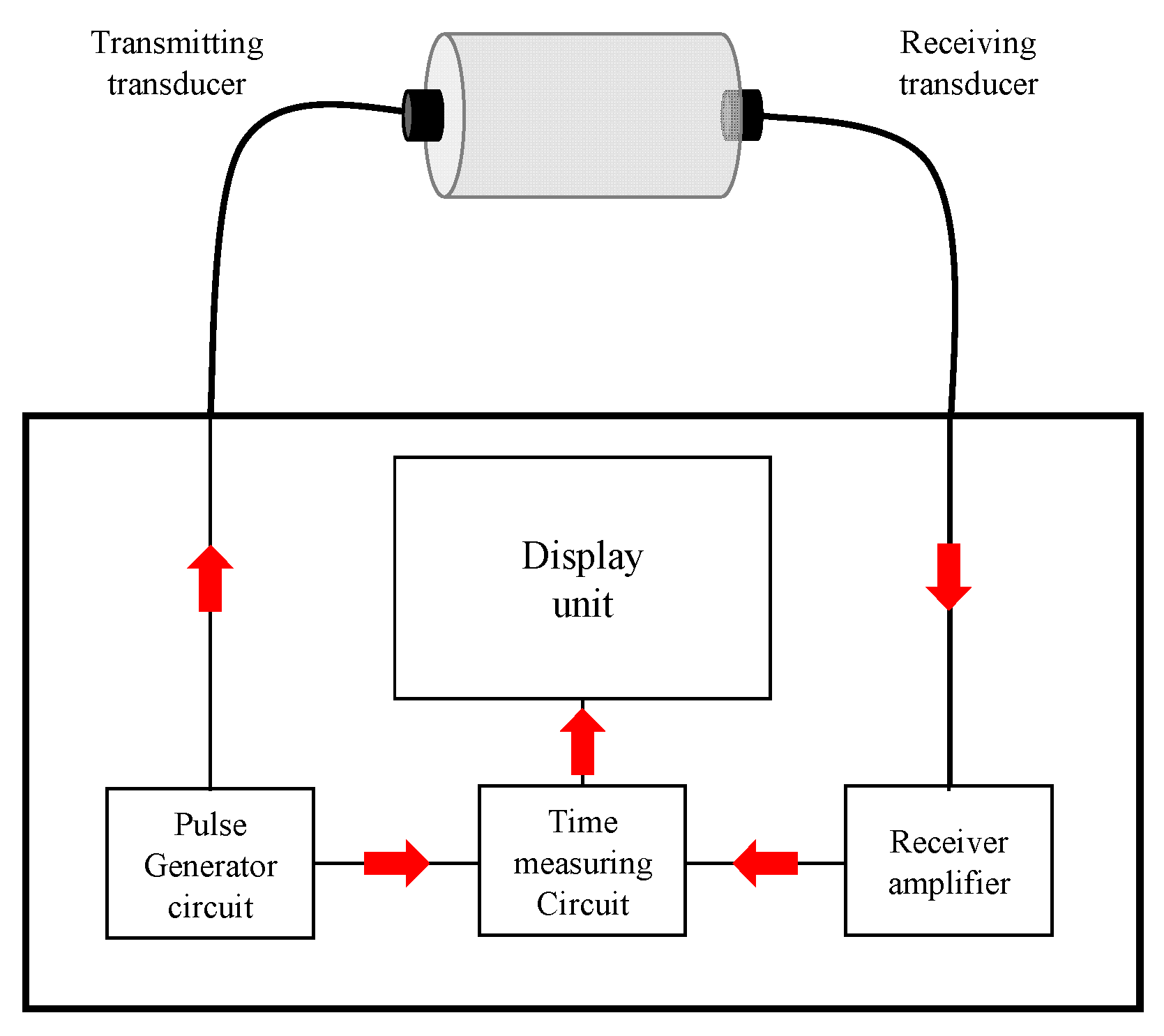
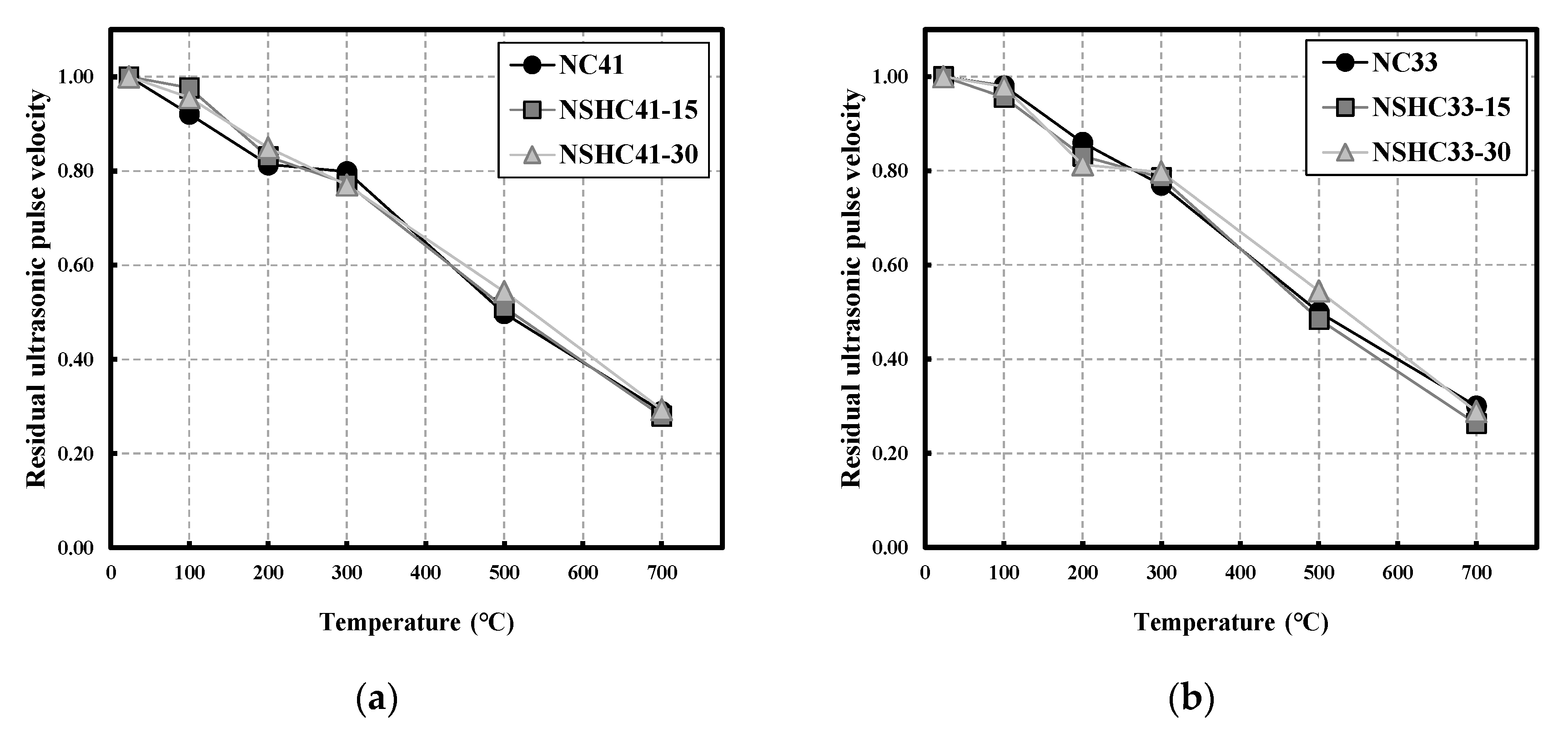
3.3. Residual Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity
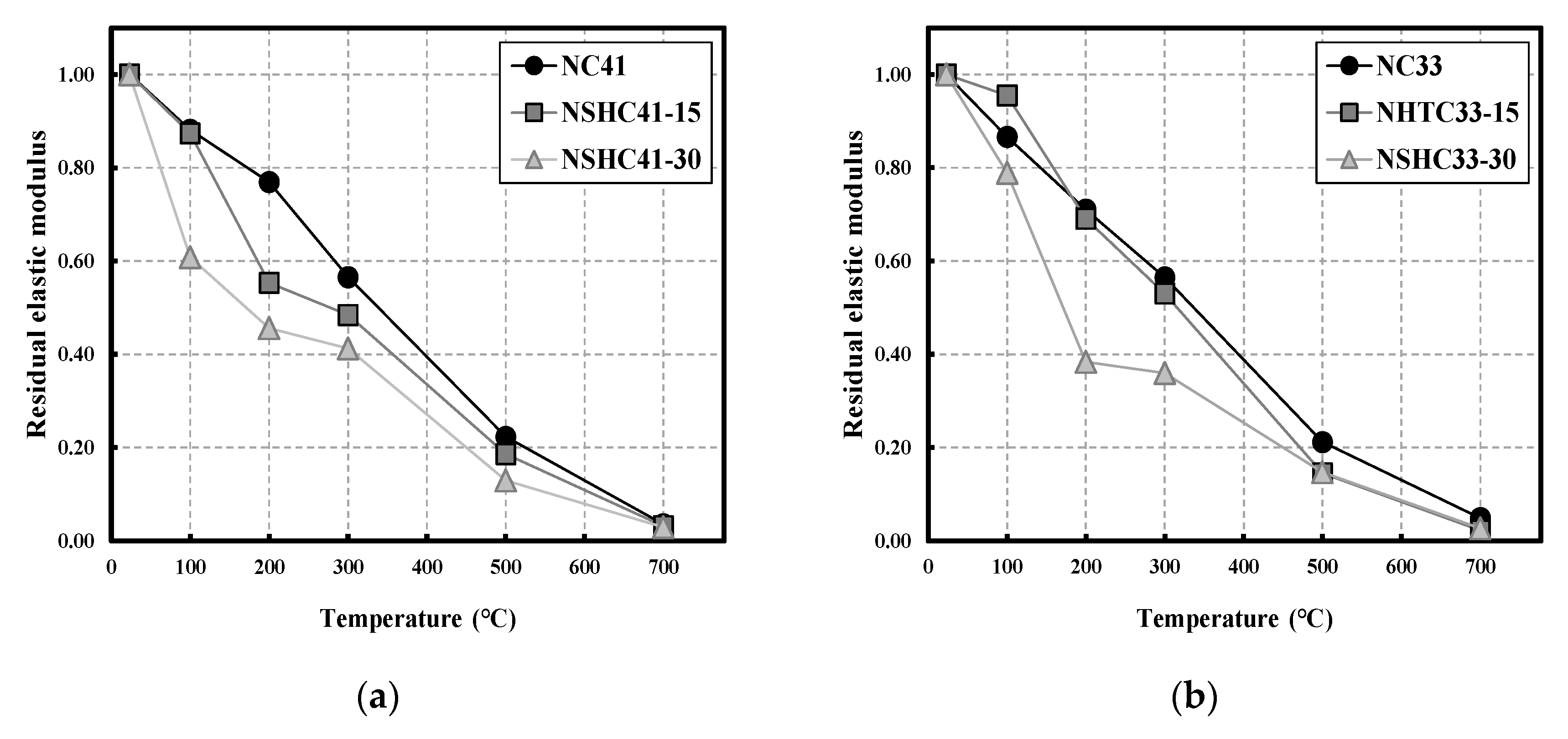
3.4. Residual Modulus of Elasticity
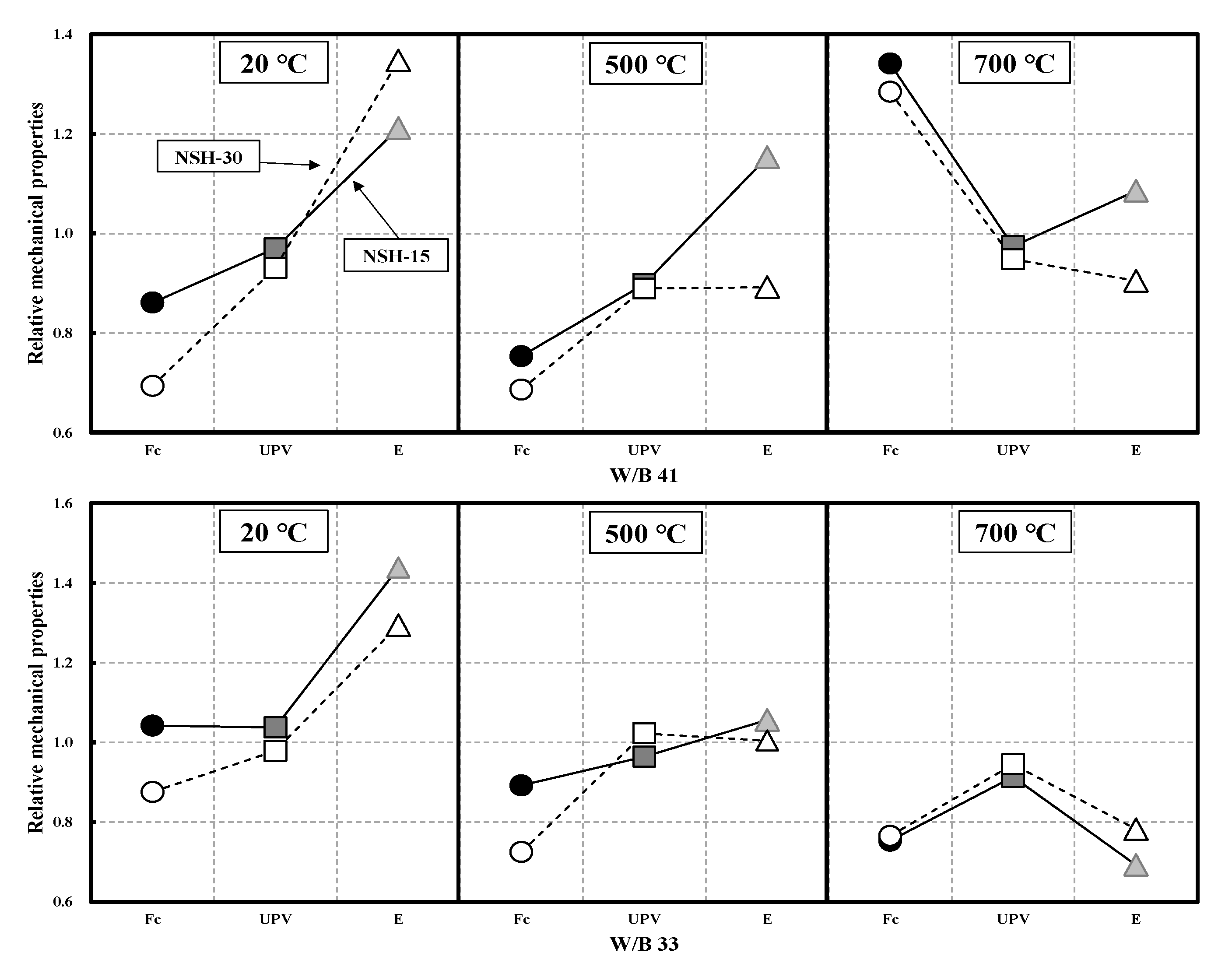
3.5. Relative Mechanical Properties
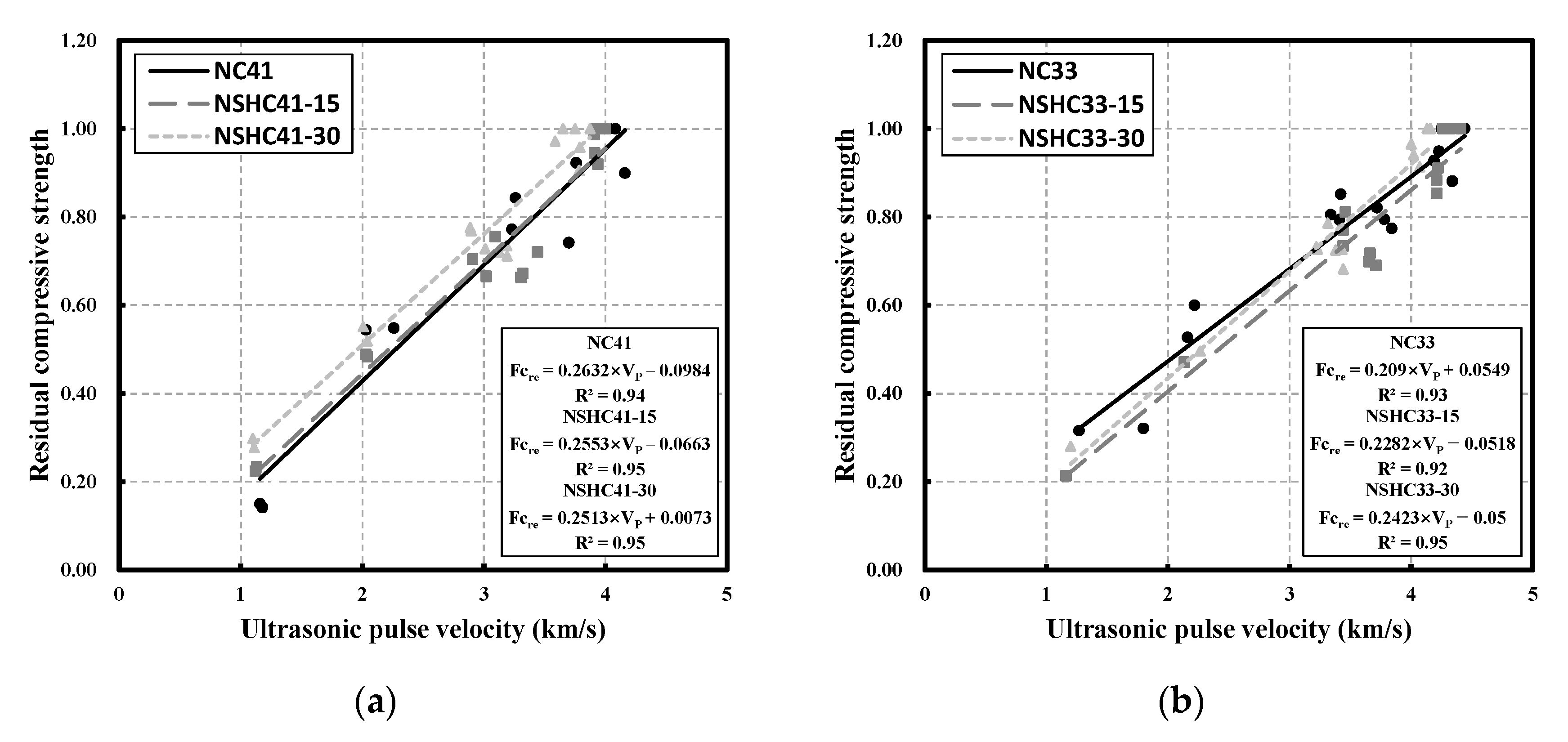
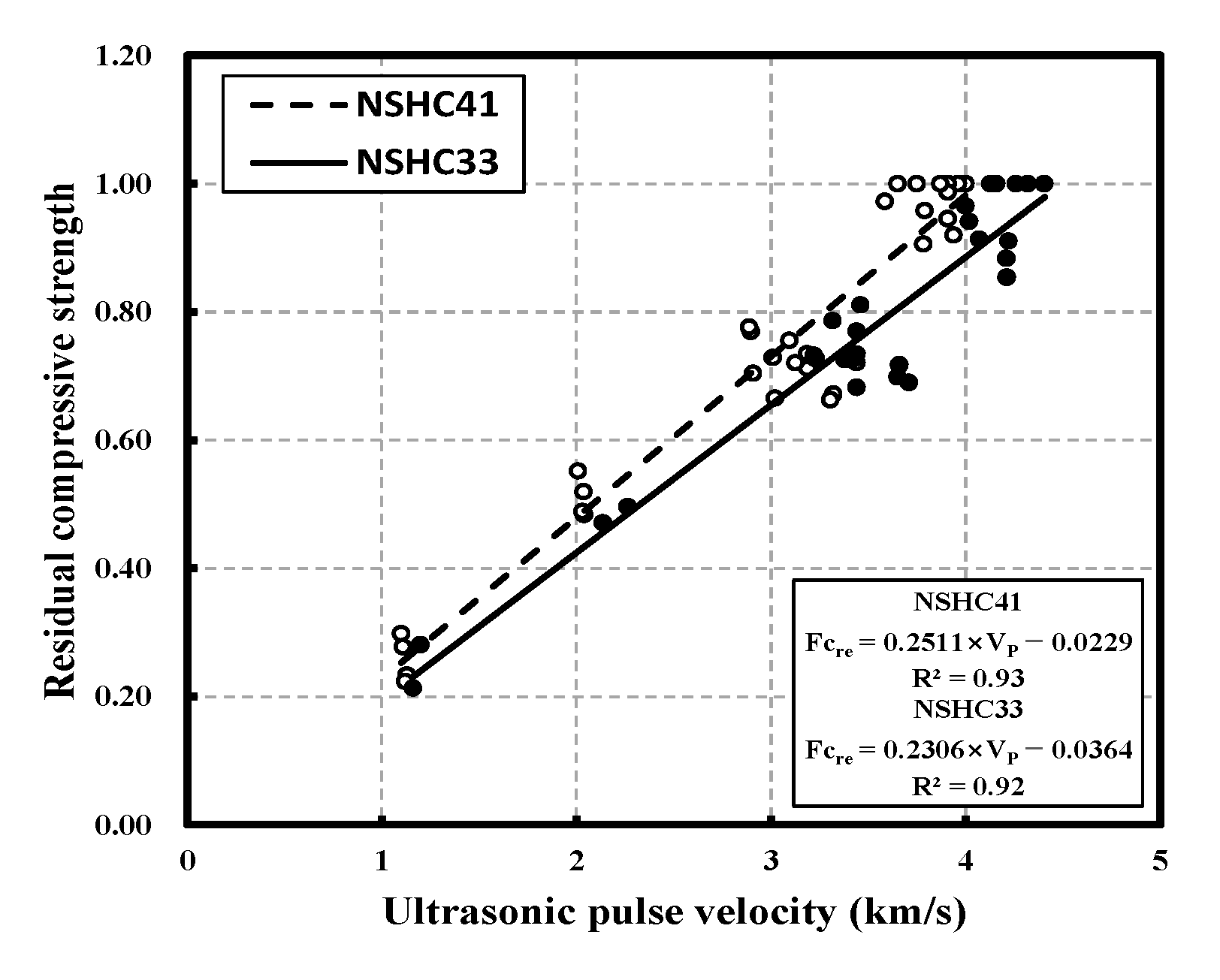
3.6. Correlation between Residual Compressive Strength and Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Mass loss decreased as temperature increased, whereas NSH replacement increased. Significant differences were observed at temperatures above 500 °C, with NSHC41-15 demonstrating a higher mass loss of approximately 26% compared to NSHC41-30, and NSHC33-15 demonstrated a higher mass loss of approximately 51% compared to NSHC33-30.
- (2)
- The residual compressive strength of NSHC41-15 and NSHC41-30 at 700 °C was 0.23 and 0.28, respectively, which is higher than that of NC41; all specimens with W/B 33 showed similar residual compressive strength. This is believed to be the effect of the formation of aggregated structures according to the increase in cohesion following the evaporation of water on the surface of the NSH and the slight sintering of clay minerals.
- (3)
- Regardless of NSH replacement, residual UPV showed a linearly decreasing trend with increasing temperature. This is because hwangto, which has a low density, may lower UPV, whereas NSH, which forms aggregates at high temperatures, has a positive effect on UPV.
- (4)
- The residual modulus of elasticity for NSHC41-30 at 100 °C was 0.61 and 0.38 for NSHC33-30 at 200 °C. Therefore, the modulus of elasticity showed a significant decrease with increasing NSH replacement, and with rising temperature, it also decreased with increasing NSH replacement.
- (5)
- The analysis of the correlation between residual compressive strength and UPV following high-temperature exposure revealed that for W/B 41, NC41 and NSHC41-15 showed a similar trend, but NSHC41-30 had an approximately 16% higher value than the other two specimens. In the case of W/B 33, as the temperature increased, NC33 showed values higher than those of NSHC33-15 and NSHC33-30 by approximately 21% and 12%, respectively. Finally, following high-temperature exposure of NSHC, an equation for predicting compressive strength was proposed by W/B using UPV analysis. For NSHC41 and NSHC33, the correlation between residual compressive strength and UPV was strong, with the following correlation coefficients (R2): 0.93 and 0.92, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, C.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Hyung, W.G. Properties of non-sintered cement mortar using non-activated Hwangto. J. Korea Soc. Waste Manag. 2019, 36, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.R.; Kim, S.H. An experimental study on the bond characteristic of GFRP bars in PVA fiber reinforced activated Hwangtoh concrete. J. Korea Inst. Struct. Maint. Insp. 2017, 21, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, H.S.; Yi, T.H. Behavior of HPC with fly ash after elevated temperature. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 478421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, M.; Yilmaz, K.; Ipek, M. Properties and behavior of self-compacting concrete produced with GBFS and FA additives subjected to high temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kancir, I.V.; Serdar, M. Construction to understanding of synergy between red mud and common supplementary cementitious materials. Materials 2022, 15, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balgourinejad, N.; Haghighifar, M.; Madandoust, R.; Charkhtab, S. Experimental study on mechanical properties, microstructural of lightweight concrete incorporating polypropylene fibers and metakaolin at high temperatures. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 5238–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermilova, E.; Kamalova, Z.; Ravil, R. Influence of clay mineral composition on properties of blended Portland cement with complex additives of clays and carbonates. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 890, 012087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.M.; Choi, M.Y.; Hwang, H.Z.; Hong, M.H.; Kim, M.H. The research on the general properties of red-clay. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual Meeting of the Architectural Institute of Korea, Ulsan, Republic of Korea, 25 October 1997; Volume 1251. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Choi, H.; Rye, H.M.; Yoon, K.B.; Lee, D.E. A study on the red clay binder stabilized with a polymer aqueous solution. Polymers 2020, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, H.; Lee, T.; Choi, H. Engineering properties and economic feasibility evaluation of eco-friendly rainwater detention system with red clay water-permeable block body. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Choi, H.; Yoon, K.B.; Lee, D.E. Performance evaluation of red clay binder with epoxy emulsion for autonomous rammed earth construction. Polymers 2020, 12, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaling, C.; Shusheng, J.; Qinghai, Z. Mechanical model of unsaturated loess-concrete interface due to freeze-thaw action. J. Eng. Geol. 2018, 26, 825–834. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, Y.; Liu, B. Experimental study on the performance of improved collapsible loess mixture with concrete crushed gravel. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 781, 022068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Hu, R. Energy performance of a new Yaodong dwelling in the loess plateau of China. Energy Build. 2014, 70, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yuan, P.; Liu, D.; Tan, D.; He, H.; Zhu, J. Effects of solid acidity of clay minerals on the thermal decomposition of 12-aminolauric acid. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 114, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Sun, Q.; Jia, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S. Effects of water content salinity on the porosity structure and resistivity of loess soil sintered at 100 °C. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mukhtar, M.; Lasledj, A.; Alcover, J.F. Lime consumption different clayey soils. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 95, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, V.; Cuisinier, O.; Masrouri, F.; Javadi, A.A. Chemo-mechanical modelling of lime treated soils. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 95, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, M.S.; Galal, A.F.; Abo-El-Enein, S.A. Effect of temperature on phase composition and microstructure of artificial pozzolana-cement pastes containing burnt kaolinite clay. Cem. Concr. Res. 1998, 28, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, G.W.; Maroney, D.M.; Udagawa, S. High-temperature reactions of clay minerals mixtures and their ceramic properteis: III. Shrinkage and porosity in relation to initial mineralogy. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1961, 44, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.E.; Piumper, O.; Putnis, C.V.; O’Neill, H.S.C.; Klemme, S.; Putnis, A. Mineral surface rearrangement at high temperature: Implications for extraterrestrial mineral grain reactivity. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2017, 1, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balek, V.; Pérez-Rodríguez, J.L.; Pérez-Maqueda, L.A.; Šubrt, J.; Poyato, J. Thermal behaviour of ground vermiculite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2007, 88, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, K.H.; Stuart, B.H.; Thomas, P.S.; Ray, A.S. Thermal characterization of the clay binder of heritage sydney sandstones. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2008, 92, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-Cuesta, V.; Shi, J.Y.; Skaf, M.; Ortega-López, V.; Manso, J.M. Non-destructive density-corrected estimation of the elastic modulus of slag-cement self-compacting concrete containing recycled aggregate. Dev. Built Environ. 2022, 12, 100097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, P.; Hrabová, K. Relationship of Time-Dependent Parameters from Destructive and Non-Destructive Tests of Structural Concrete. Mathematics 2022, 10, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariq, M.; Prasad, J.; Masood, A. Studies in ultrasonic pulse velocity of concrete containing GGBFS. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sua-iam, G.; Makul, N. Use of increasing amounts of bagasses ash waste to produce self-compacting concrete by adding limestone powder waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 57, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.K.; Sravana, P.; Rao, T.C. Experimental studies in ultrasonic pulse velocity of roller compacted concrete pavement containing fly ash and M-sand. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2016, 9, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.T.; Wang, W.C.; Wang, H.Y. Mechanical properties ultrasonic velocity of lightweight aggregate concrete containing mineral powder materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 119550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C39/C39M; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. American Society of Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–8.
- ASTM C469; Standard Test Method for Static Modulus of Elasticity and Poisson’s Ratio of Concrete in Compression. Annual Book of ASTM Standards: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011.
- ASTM C597-16; Standard Test Method for Pulse Velocity Through Concrete. American Society of Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–4.
- Bellotto, M. High temperature phase transitions in kaolinite: The influence of disorder and kinetics on the reaction path. Mater. Sci. Forum. 1994, 166–169, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.C. Porcellanite-CaCO3 high temperature reaction: Phases microstructure, microhardness. Ceram. Int. 2005, 31, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarıdemir, M.; Çelikten, S. Investigation of fire and chemical effects on the properties of alkali-activated lightweight concretes produced with basaltic pumice aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C642-13; Standard Test Method for Density, Absorption, and Voids in Hardened, Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- Dinakar, P.; Babu, K.G.; Santhanam, M. Durability properties of high volume fly ash self compacting concretes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhao, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H. Thermal effects on the electrical characteristics of Maln loess. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 15160–15172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Sun, Q.; Xing, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H. Experimental study on thermophysical properties of clay after high temperature. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 111, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Kong, R.; Peng, J. Effects of heating on compositional, structural, and physicochemical properties of loess under laboratory conditions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 228, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Jeong, K.; Lee, T.; Park, S. A study on correlation between ultrasonic pulse velocity method and coarse aggregate for estimating residual modulus of elasticity of concrete exposed to high temperatures. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y. Correlation analyses of effects of temperature on physical and mechanical properties of clay. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Sun, Q. Effects of high temperature treatment on physical-thermal properties of clay. Thermochim. Acta 2018, 666, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, Q.; Wang, N.; Luo, T.; Zhang, H. High-temperature response characteristics of loess porosity and strength. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufael, G.; Beaucour, A.L.; Eslami, J.; Hoxha, D.; Noumowé, A. Influence of lightweight aggregates on the physical and mechanical residual properties of concrete subjected to high temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torić, N.; Boko, I.; Juradin, S.; Baloević, G. Mechanical properties of lightweight concrete after fire exposure. Struct. Concr. 2016, 17, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andiç-Çakır, Ö.; Hızal, S. Influence of elevated temperatures on the mechanical properties and microstructure of self consolidating Lightweight aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 34, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; Hsiao, C.; Liu, J. Evaluating residual compressive strength of concrete at elevated temperatures using ultrasonic pulse velocity. Fire Saf. J. 2009, 44, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.V.S.; Ram, K.S.S. Performance of concrete at elevated temperatures made with crushed rock dust as filler material. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 18, 2270–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrmomtazi, A.; Gashti, S.H.; Tahmouresi, B. Residual strength and microstructure of fiber reinforced self-compacting concrete exposed to high temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 116969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.Z.; Sohel, K.M.A.; Al-Jabri, K.; Al Harthy, A.A. Properties of concrete with ferrochrome slag as a fine aggregate at elevated temperatures. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
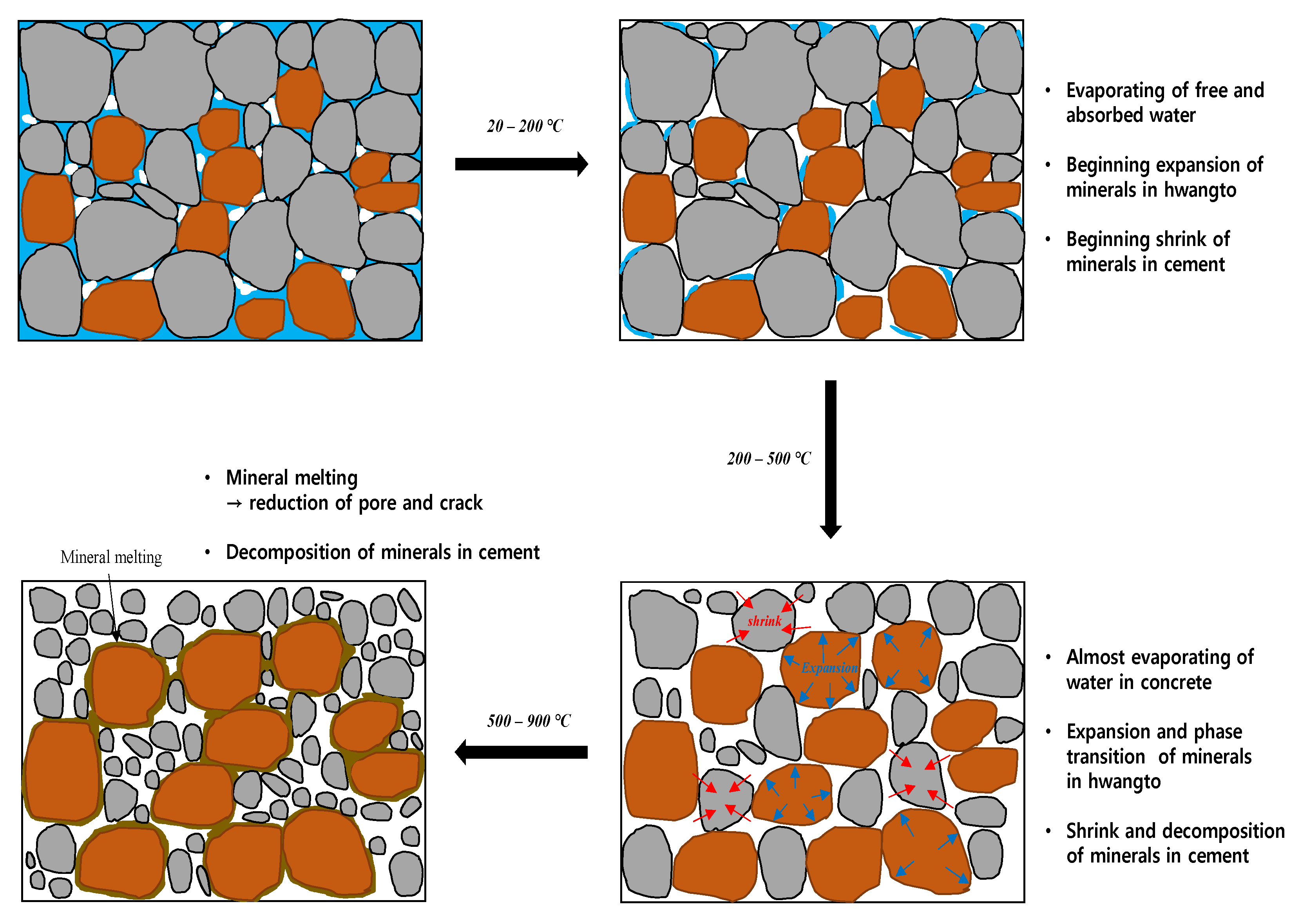
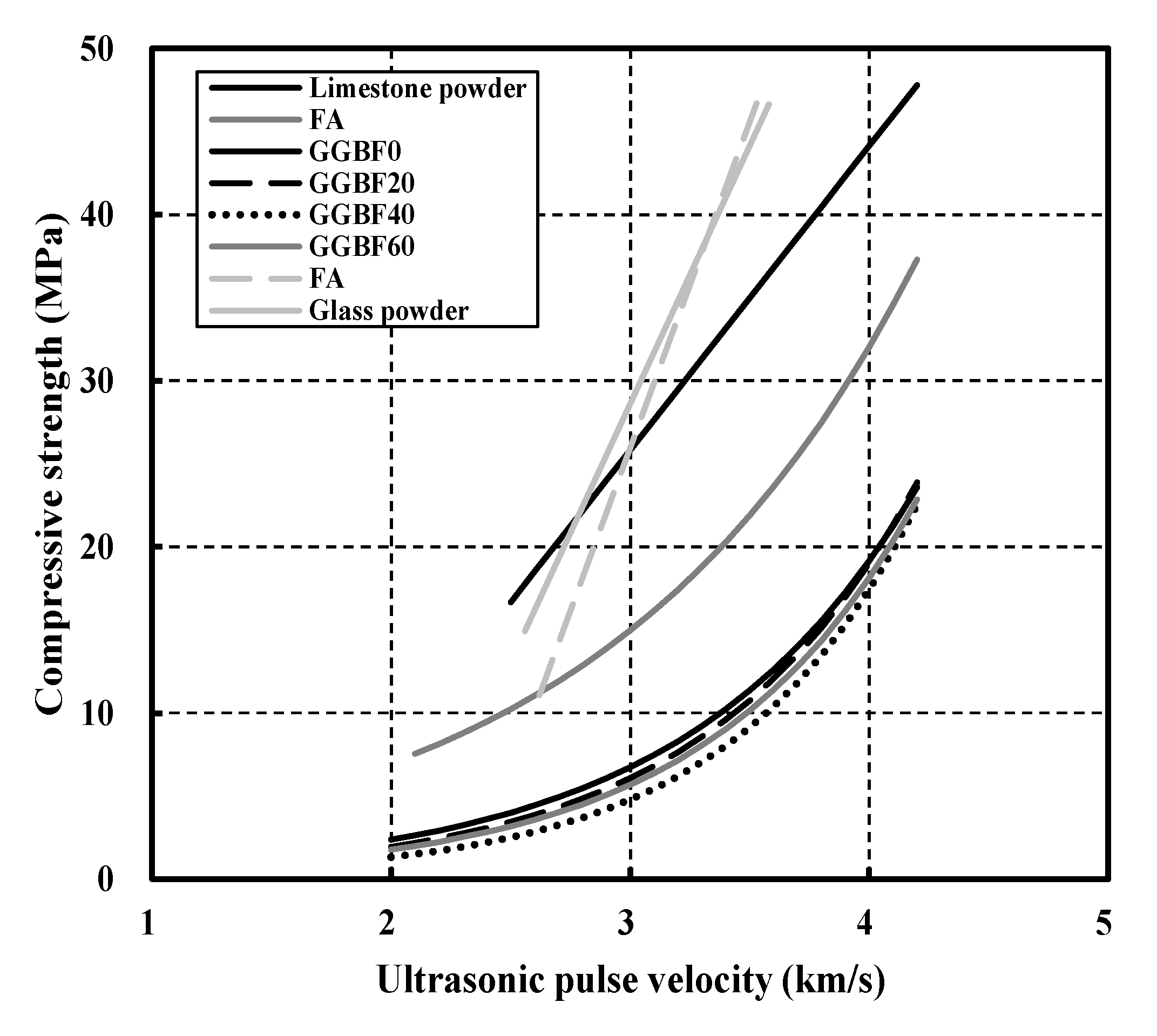


| Researcher | Admixture | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| G. Sua-iam | Limestone powder | |
| S. K. Rao | Fly ash | |
| M. Shariq | GGBF 0% | |
| GGBF 20% | ||
| GGBF 40% | ||
| GGBF 60% |
| ID | Replacement Rate of NSH (1) | W/B | Curing | Heat Method | Test Item |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 0% 15% 30% | 0.41 0.33 | Water curing Room temperature (20 ± 2 °C) Humidity (60 ± 5%) | 20, 100, 200, 300, 500, 700 °C (1 °C/min) | Compressive strength Ultrasonic pulse velocity Modulus of elasticity |
| NSHC |
| Property | Cement (Type I Ordinary Portland Cement) | Non-Sintered Hwangto | Coarse Aggregate (Crushed Granite) | Fine Aggregate (River Sand) | Super Plasticizer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (kg/m3) | 3150 | 2500 | 2680 | 2540 | Polycarboxylic-based acid |
| Fineness (m2/kg) | 320 | 330 | - | - | |
| Fineness modulus | - | - | 7.03 | 2.54 | |
| Absorption (%) | - | - | 0.68 | 1.6 | |
| Maximum size (mm) | - | - | 20 | - | |
| Chemical Composition (%) | |||||
| CaO | 60.34 | 0.39 | |||
| SiO2 | 19.82 | 40.0 | |||
| Al2O3 | 4.85 | 32.9 | |||
| Fe2O3 | 3.30 | 7.79 | |||
| MgO | 3.83 | 1.54 | |||
| SO3 | 2.88 | - | |||
| K2O | 1.08 | 0.76 | |||
| Others | 0.86 | 16.62 | |||
| L.O.I | 3.02 | 13.7 |
| Mix ID | NC41 | NSHC41-15 | NSHC41-30 | NC33 | NSHC33-15 | NSHC33-30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water/Binder | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| Sand/aggregate (%) | 46.0 | 46.0 | 46.0 | 43.0 | 43.0 | 43.0 |
| Water (kg/m3) | 165 | 165 | 165 | 165 | 165 | 165 |
| Cement (kg/m3) | 400 | 340 | 280 | 500 | 425 | 350 |
| Non-sintered hwangto (kg/m3) | - | 60 | 120 | 75 | 150 | |
| Fine aggregate (kg/m3) | 799 | 794 | 788 | 711 | 705 | 699 |
| Coarse aggregate (kg/m3) | 956 | 950 | 943 | 961 | 953 | 944 |
| Test Item | Test Method | Equation (1) | Equation (2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compressive strength | ASTM C39/C39M | ||
| Modulus of elasticity | ASTM C469 | ||
| Ultrasonic pulse velocity | ASTM C597 | : ultrasonic pulse velocity(m/s) : distance(m) : time(s) | : residual mechanical properties : mechanical properties at room temperature : mechanical properties at high temperature |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, W.; Choi, H.; Lee, T. Investigating Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Method for Evaluating High-Temperature Properties of Non-Sintered Hwangto-Mixed Concrete as a Cement Replacement Material. Materials 2023, 16, 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16031099
Kim W, Choi H, Lee T. Investigating Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Method for Evaluating High-Temperature Properties of Non-Sintered Hwangto-Mixed Concrete as a Cement Replacement Material. Materials. 2023; 16(3):1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16031099
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Wonchang, Hyeonggil Choi, and Taegyu Lee. 2023. "Investigating Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Method for Evaluating High-Temperature Properties of Non-Sintered Hwangto-Mixed Concrete as a Cement Replacement Material" Materials 16, no. 3: 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16031099
APA StyleKim, W., Choi, H., & Lee, T. (2023). Investigating Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Method for Evaluating High-Temperature Properties of Non-Sintered Hwangto-Mixed Concrete as a Cement Replacement Material. Materials, 16(3), 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16031099







