Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Super-Resolution Microscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Super-Resolution Techniques
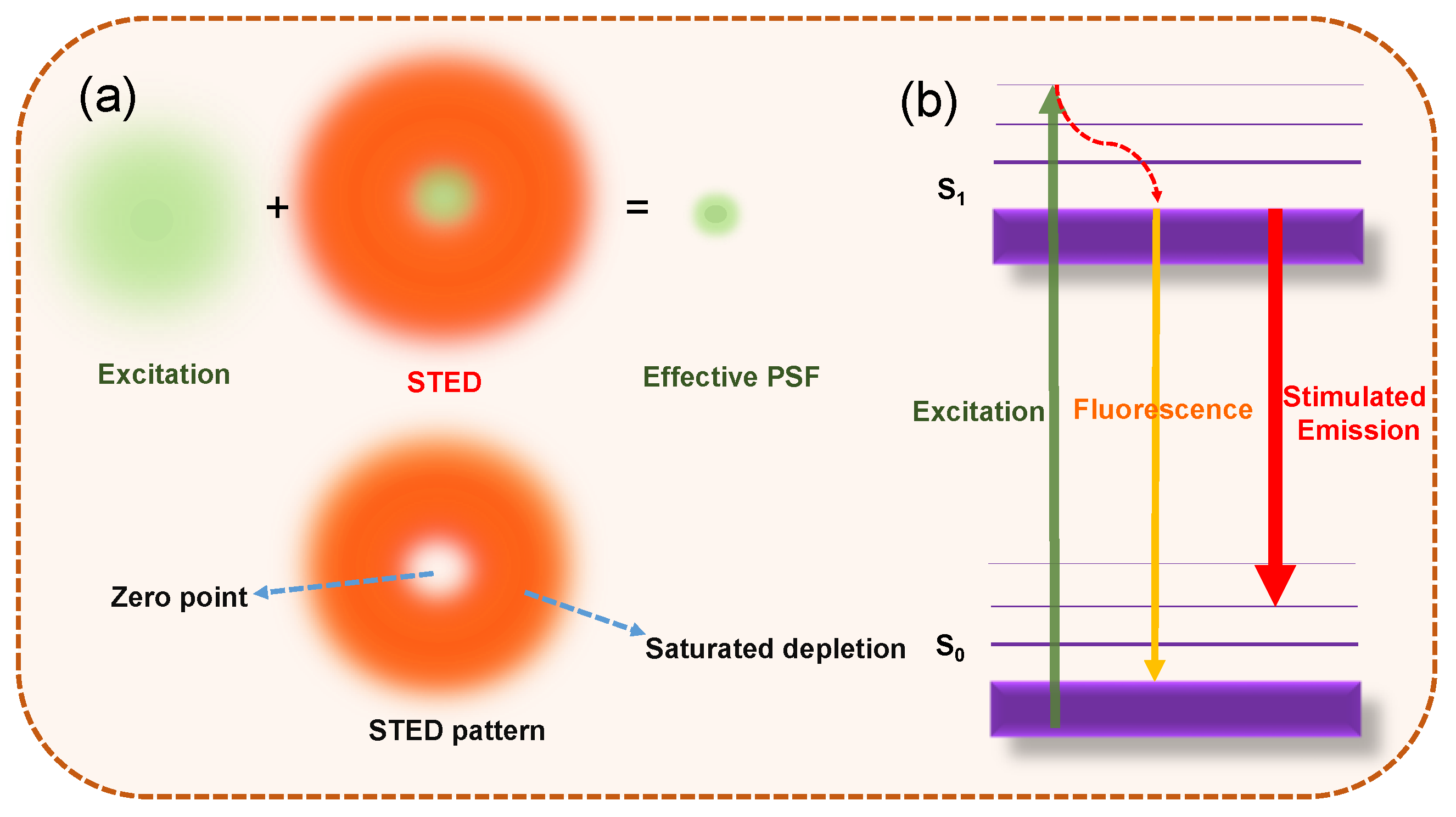
2.1. Spatially Patterned Excitation for Super-Resolution Imaging
2.2. Localization-Based Super-Resolution Imaging
3. Properties of Carbon Dots
3.1. Single-Particle Fluorescence Properties
3.2. Tuned Emission Colors
3.3. Specific Labeling Properties
3.4. Biocompatibility and Low Cytotoxicity
4. Super-Resolution Imaging Using CDs
4.1. Patterned Excitation-Based Super-Resolution Techniques
| Ref. | Emission, nm | Photostability | Excitation Laser, nm | Depletion Laser, nm | Imaged Bio-Systems | Labeling | Resolution, nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [41] 2014 | 490 | / | 405 | 592 | Fixed and live MCF7 cell | Non-covalent interactions | 30 |
| [49] 2016 | 580 | / | 552 | 660 | Gram-positive bacteria | Electrostatic interactions | ~130 |
| [48] 2017 | 532 | 1260 s at 100 µW UV excitation | 405 | 532 | / | / | / |
| [39] 2019 | 510 | ~10 h under UV illumination | 560 | 595 | DNA, RNA Chromosomes and nucleolus | Charge effect | 50 |
| [35] 2019, | 605 | 1 h after 552 nm laser irradiation | 552 | 660 | Cell nuclei, mice and zebrafish | Electrostatic interactions | 146 |
| [50] 2019 | 513 | 1000 scan cycles | 470 | 660, 775 | Nucleus cytoskeleton | Electrostatic interactions | ~20 75 |
| [43] 2021 | 515 | 200 frames under 448 nm irradiation | 465 | 592 | Nucleic acid, chromatin | Electrostatic interactions | 90 |
| [34] 2022 | 584 | 100 min continuous UV irradiation | 488 | 660 | ER structure and cell division | Non-covalent interactions | 100 |
4.2. Single-Molecule Localization-Based Super-Resolution Techniques
| Ref. | Emission, nm | Photon Counts | Duty Cycle | Excitation, nm | Imaging Targets | Labeling | Resolution, nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [33] 2016 | 639 | 2885 | / | 532 | E. coli and HeLa cells | Non-covalent interactions | ~35 |
| [25] 2017 | 590 | 7876 | 0.0032 | 532 | Peptide, microtubules, subcellular structures | EDC/NHS reactions | ~25 |
| [42] 2018 | 460 | ~8000 | 0.0053 | 542 | Epithelial gill cell | Non-covalent interactions | ~36 |
| [45] 2018 | 480 | ~3000 | ~0.003 | 532 | Endocytosis and trafficking drug carriers | EDC/NHS reactions | / |
| [51] 2018 | 612 | 1000 s of | / | 560 | Nucleolar RNA | Non-covalent interactions | ~400 |
| [52] 2018 | 570 | 2986 | 0.0036 | 532 | Actin filament | Non-covalent interactions | ~64 |
| [31] 2019 | 591 | ~8000 | 0.16 | 532 | Dynamic fusion from mitochondria in live cells | Electrostatic interactions | 130 |
| [44] 2019 | 612 | ~6879 | / | / | Actin filaments in HeLa cells | EDC coupling | ~35 |
| [47] 2019 | 450 | ~1200 | / | 639 | Bacteria | / | / |
| [53] 2019 | 450 | ~900 | / | 647 | HeLa cells and DNA fibers | Non-covalent interactions | ~60 |
| [57] 2019 | 701 | 4960 | 0.00013 | 532 | Cracking on the glass (non-bio) | Non-covalent interactions | ~80 |
| [38] 2021 | 440/600 | / | / | 560 | Mitochondria and lysosomes | Non-covalent interactions | / |
| [46] 2021 | 580 | 1583 | / | 488 | / | EDC/NHS reactions | / |
| [55] 2021 | 580 | 5171 | ~0.1 | 532 | Nucleolar ultrastructure | Non-covalent interactions | / |
| [56] 2021 | ~600 | 6100 | 0.0086 | 405 | Microtubules | Non-covalent interactions | ~50 |
| [54] 2022 | 535 | 3000 | 0.06 | 473 | Nucleolar RNA | Non-covalent interactions | ~100 |
4.3. Image-Correlation Techniques: Super-Resolution Optical Fluctuation Imaging (SOFI)
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Super-resolution microscopy | SRM |
| Stimulated emission depletion | STED |
| Reversible saturated optically linear fluorescence transition | RESOLFT |
| Saturated structured illumination microscopy | SSIM |
| Stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy | STORM |
| Photoactivated localization microscopy | PALM |
| Fluorescence photoactivated localization microscopy | FPALM |
| Super-resolution | SR |
| Quantum dots | QDs |
| Carbon Dots | CDs |
| Graphene quantum dots | GQDs |
| Point spread function | PSF |
| Near infrared | NIR |
| Nitrogen doped | N-CD |
| Boron and nitrogen co-doped carbon dots | BN-CD |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | ER |
| N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide | NHS |
| Folate receptor | FR |
| Full width at half-maximum | FWHM |
| Transmission electron microscopy | TEM |
| Carbonized polymer dots | CPDs |
| Poly vinyl alcohol | PVA |
| 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide | EDC |
| Graphene oxide nanosheets | GONS |
| Super-resolution imaging | SRI |
| Fluorescence resonance electron transfer | FRET |
| Single-molecule localization microscopy | SMLM |
| Atomic force microscopy | AFM |
| Super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging | SOFI |
| p-phenylendiamine | Pda |
| 4-carboxybutyltriphenylphosphonium | PPh3+ |
References
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Basabe-Desmonts, L.; Reinhoudt, D.N.; Crego-Calama, M. Design of Fluorescent Materials for Chemical Sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolfbeis, O.S. An Overview of Nanoparticles Commonly Used in Fluorescent Bioimaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4743–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.; Bates, M.; Zhuang, X. Super-Resolution Fluorescence Microscopy. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 993–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Sharma, A.; Qi, J.; Peng, X.; Lee, D.Y.; Hu, R.; Lin, D.; Qu, J.; Kim, J.S. Super-Resolution Fluorescent Materials: An Insight into Design and Bioimaging Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 4651–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Frei, M.S.; Salim, A.; Johnsson, K. Small-Molecule Fluorescent Probes for Live-Cell Super-Resolution Microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 2770–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Suárez, M.; Ting, A.Y. Fluorescent Probes for Super-Resolution Imaging in Living Cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 929–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozma, E.; Kele, P. Fluorogenic Probes for Super-Resolution Microscopy. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic Analysis and Purification of Fluorescent Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.L.; Liu, Z.X.; Yuan, Y.H. Carbon Dots: Materials, Synthesis, Properties and Approaches to Long-Wavelength and Multicolor Emission. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3794–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. The Photoluminescence Mechanism in Carbon Dots (Graphene Quantum Dots, Carbon Nanodots, and Polymer Dots): Current State and Future Perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon Quantum Dots and Their Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Lei, Y. Fluorescent Carbon Dots and Their Sensing Applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienhaus, K.; Ulrich Nienhaus, G. Fluorescent Proteins for Live-Cell Imaging with Super-Resolution. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1088–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Vaughan, J.C. Switchable Fluorophores for Single-Molecule Localization Microscopy. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 9412–9454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Juette, M.F.; Jockusch, S.; Wasserman, M.R.; Zhou, Z.; Altman, R.B.; Blanchard, S.C. Ultra-Stable Organic Fluorophores for Single-Molecule Research. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1044–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, D.; Xi, P.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Enderlein, J.; van Oijen, A.M. Nanoparticles for Super-Resolution Microscopy and Single-Molecule Tracking. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Kaminski Schierle, G.S.; Lei, B.; Liu, Y.; Kaminski, C.F. Fluorescent Nanoparticles for Super-Resolution Imaging. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 12495–12543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.C.; Yadav, A.; Rao, C.; Mishra, P.M.; Nandi, C.K. Emergence of Carbon Nanodots as a Probe for Super-Resolution Microscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 1637–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, G.T.; Vaughan, J.C.; Chen, K.H.; Bates, M.; Zhuang, X. Evaluation of Fluorophores for Optimal Performance in Localization-Based Super-Resolution Imaging. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, B.; Nie, H.; Liu, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, M.; Wu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.X.-A. Full-Colour Carbon Dots: Integration of Multiple Emission Centres into Single Particles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 13326–13333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Liu, Y.; Yeom, S.; Kim, D.Y.; Richards, C.I. Single-Particle Fluorescence Intensity Fluctuations of Carbon Nanodots. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.K.; Luk, C.M.; Martin, W.E.; Tang, L.; Kim, D.Y.; Lau, S.P.; Richards, C.I. Size and Dopant Dependent Single Particle Fluorescence Properties of Graphene Quantum Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 17988–17994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Chizhik, A.M.; Karedla, N.; Dekaliuk, M.O.; Gregor, I.; Schuhmann, H.; Seibt, M.; Bodensiek, K.; Schaap, I.A.T.; Schulz, O.; et al. Photoluminescence of Carbon Nanodots: Dipole Emission Centers and Electron–Phonon Coupling. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 5656–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Ren, H.; Ge, B.; Wang, S.; et al. High-Density Super-Resolution Localization Imaging with Blinking Carbon Dots. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11831–11838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Zhou, P.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Ma, M.; Chen, B.; Xiao, L. Fabrication of Bright and Small Size Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticles for Cellular Labelling and Single Particle Tracking. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11351–11358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Kang, B.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, G.T.; Kang, H.; Lee, B.R.; Kim, H.; Shim, S.-H.; Lee, G.; et al. Integrative Approach toward Uncovering the Origin of Photoluminescence in Dual Heteroatom-Doped Carbon Nanodots. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 6840–6847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.; Khan, S.; Verma, N.C.; Nandi, C.K. Labelling Proteins with Carbon Nanodots. ChemBioChem 2017, 18, 2385–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Verma, N.C.; Gupta, A.; Nandi, C.K. Reversible Photoswitching of Carbon Dots. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Li, W.; Karedla, N.; Thiart, J.; Gregor, I.; Chizhik, A.M.; Enderlein, J.; Nandi, C.K.; Chizhik, A.I. Charge-Driven Fluorescence Blinking in Carbon Nanodots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 5751–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Wei, L.; Geng, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Xiao, L. Mitochondrion-Specific Blinking Fluorescent Bioprobe for Nanoscopic Monitoring of Mitophagy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 11593–11602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; He, J.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X.; Dey, S.; Zhao, J.; Lei, Y. Microwave-Assisted Ultrafast and Facile Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles from a Single Precursor: Preparation, Characterization and Their Application for the Highly Selective Detection of Explosive Picric Acid. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 4161–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.C.; Khan, S.; Nandi, C.K. Single-Molecule Analysis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots towards Localization-Based Super-Resolution Microscopy. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2016, 4, 044006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, B.; Han, M.; Han, G.; Zhang, Z. One-Step Synthesized Amphiphilic Carbon Dots for the Super-Resolution Imaging of Endoplasmic Reticulum in Live Cells. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 19424–19430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.-W.; Bao, Y.-W.; Zeng, J.; Wu, F.-G. Nucleolus-Targeted Red Emissive Carbon Dots with Polarity-Sensitive and Excitation-Independent Fluorescence Emission: High-Resolution Cell Imaging and in Vivo Tracking. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 32647–32658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Tan, Z.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. Bright Multicolor Bandgap Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots for Electroluminescent Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Brückner, C.; Lei, Y. One-Pot and Ultrafast Synthesis of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Co-Doped Carbon Dots Possessing Bright Dual Wavelength Fluorescence Emission. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 17278–17282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, B.; Yao, X.; Wu, M.; Mensch, A.; Cui, Y.; Deng, J.; Duchimaza-Heredia, J.J.; Trerayapiwat, K.J.; Niehaus, T.; Nishimoto, Y.; et al. Multicolor Polymeric Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Separation and Polyamide-Supported Molecular Fluorescence. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 2441–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, R.; Tian, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, A.; Liu, R.; Liu, B.; Han, M.; Gao, X.; et al. Membrane-Penetrating Carbon Quantum Dots for Imaging Nucleic Acid Structures in Live Organisms. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7087–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yu, S.-B.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State-Controlled Luminescence Mechanism. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leménager, G.; De Luca, E.; Sun, Y.-P.; Pompa, P.P. Super-Resolution Fluorescence Imaging of Biocompatible Carbon Dots. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, B.; Cui, Y.; Wang, S.; Frank, B.P.; Williams, D.N.; Brown, R.P.; Melby, E.S.; Hamers, R.J.; Rosenzweig, Z.; Fairbrother, D.H.; et al. Malic Acid Carbon Dots: From Super-Resolution Live-Cell Imaging to Highly Efficient Separation. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5741–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Peng, X.; Yan, W.; Qu, J. Responsive Carbonized Polymer Dots for Optical Super-Resolution and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging of Nucleic Acids in Living Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 50733–50743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, N.C.; Rao, C.; Singh, A.; Garg, N.; Nandi, C.K. Dual Responsive Specifically Labelled Carbogenic Fluorescent Nanodots for Super Resolution and Electron Microscopy. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 6561–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Li, S.; Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Guo, A.; Ge, B.; Khan, N.U.; Huang, F. Quantitative Nanoscopy of Small Blinking Graphene Nanocarriers in Drug Delivery. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 3658–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Nau, W.M.; Huang, F. Carbon Dot Blinking Enables Accurate Molecular Counting at Nanoscale Resolution. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3968–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkahla, H.; Boudjemaa, R.; Caorsi, V.; Pineau, D.; Curcio, A.; Lomas, J.S.; Decorse, P.; Chevillot-Biraud, A.; Azaïs, T.; Wilhelm, C.; et al. Carbon Dots, a Powerful Non-Toxic Support for Bioimaging by Fluorescence Nanoscopy and Eradication of Bacteria by Photothermia. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G. Experimental Investigations on Fluorescence Excitation and Depletion of Carbon Dots. J. Fluoresc. 2017, 27, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.-H.; Gao, G.; Chen, X.; Jia, H.-R.; Li, Y.-H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, F.-G. Carbon Dot-Based Platform for Simultaneous Bacterial Distinguishment and Antibacterial Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32170–32181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ye, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Yan, W.; Song, J.; Qu, J. Biocompatible Carbon Dots with Low-Saturation-Intensity and High-Photobleaching-Resistance for STED Nanoscopy Imaging of the Nucleolus and Tunneling Nanotubes in Living Cells. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 3075–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Verma, N.C.; Chethana; Nandi, C.K. Carbon Dots for Single-Molecule Imaging of the Nucleolus. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.C.; Rao, C.; Nandi, C.K. Nitrogen-Doped Biocompatible Carbon Dot as a Fluorescent Probe for STORM Nanoscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 4704–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.; Luo, T.; Peng, H.; Li, L.; Long, D.; Peng, J.; Huang, J. One-Step Synthesis of N-Doped Carbon Dots, and Their Applications in Curcumin Sensing, Fluorescent Inks, and Super-Resolution Nanoscopy. Microchim. Acta. 2019, 186, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Geng, X.; Wang, X.; Wei, L.; Li, Z.; Lin, S.; Xiao, L. A Carbonized Fluorescent Nucleolus Probe Discloses RNA Reduction in the Process of Mitophagy. CCS Chem. 2022, 4, 2698–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Chen, X.; Feng, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Bi, S. Nanoscopic Imaging of Nucleolar Stress Enabled by Protein-Mimicking Carbon Dots. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 5689–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zong, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Cui, Y. Dual-Labeled Graphene Quantum Dot-Based Förster Resonance Energy Transfer Nanoprobes for Single-Molecule Localization Microscopy. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 8808–8815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Chen, Q.; Yao, X.; Gelléri, M.; Ritz, S.; Kumar, S.; Cremer, C.; Landfester, K.; Müllen, K.; et al. Nanographenes: Ultrastable, Switchable, and Bright Probes for Super-Resolution Microscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chizhik, A.M.; Stein, S.; Dekaliuk, M.O.; Battle, C.; Li, W.; Huss, A.; Platen, M.; Schaap, I.A.T.; Gregor, I.; Demchenko, A.P.; et al. Super-Resolution Optical Fluctuation Bio-Imaging with Dual-Color Carbon Nanodots. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butkevich, E.; Verma, N.C.; Oleksiievets, N.; Gregor, I.; Schmidt, C.F.; Enderlein, J.; Nandi, C.K.; Chizhik, A.I. Carbon Dots for Studying Muscle Architecture. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 7466–7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; Mosleh, N. Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Super-Resolution Microscopy. Materials 2023, 16, 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16030890
Sun X, Mosleh N. Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Super-Resolution Microscopy. Materials. 2023; 16(3):890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16030890
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xiangcheng, and Nazanin Mosleh. 2023. "Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Super-Resolution Microscopy" Materials 16, no. 3: 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16030890
APA StyleSun, X., & Mosleh, N. (2023). Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Super-Resolution Microscopy. Materials, 16(3), 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16030890





