Effect of Through-the-Thickness Delamination Position on the R-Curve Behavior of Plain-Woven ENF Specimens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Properties and Fabrication of Samples
Fracture Test and Data Reduction Method
3. Results and Discussion
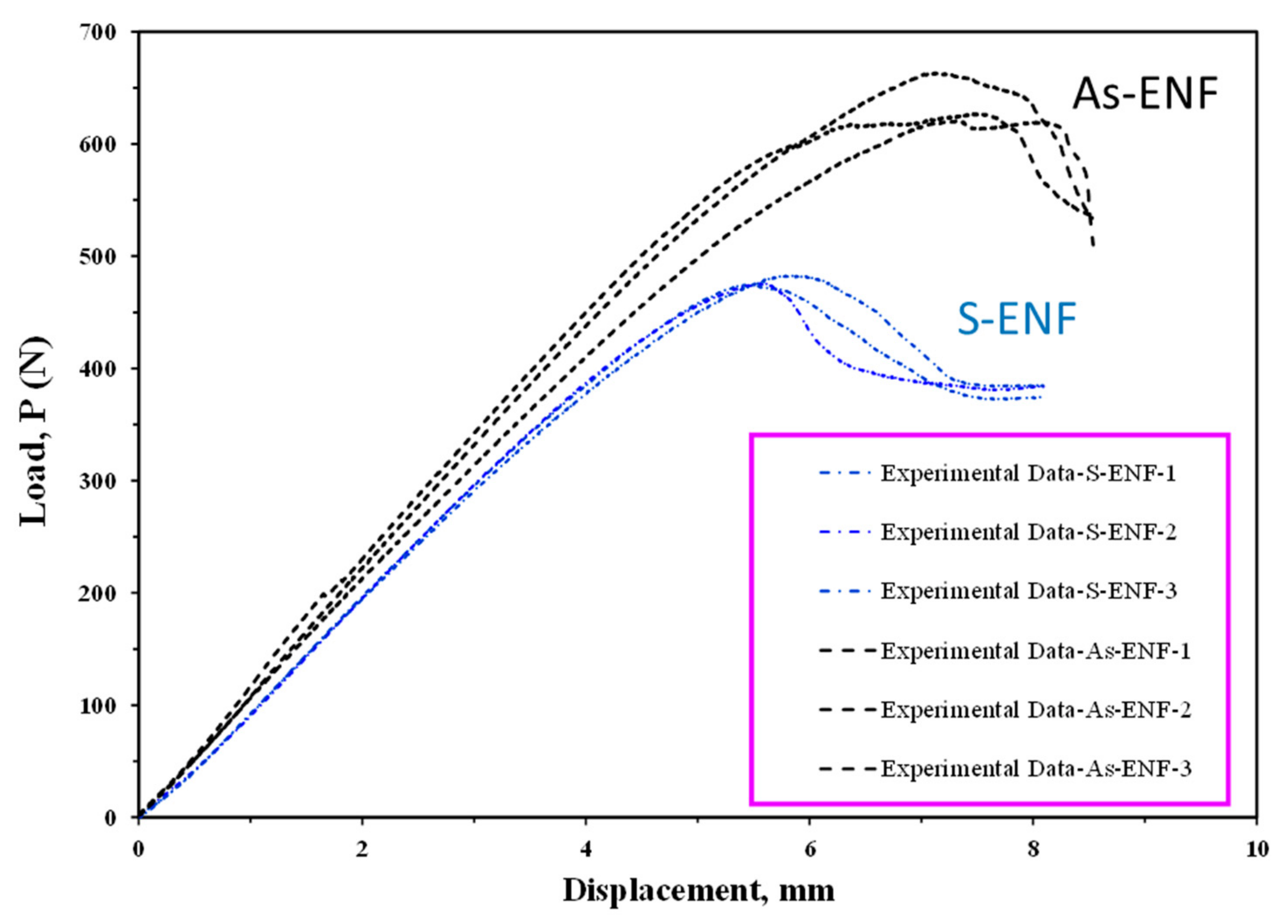
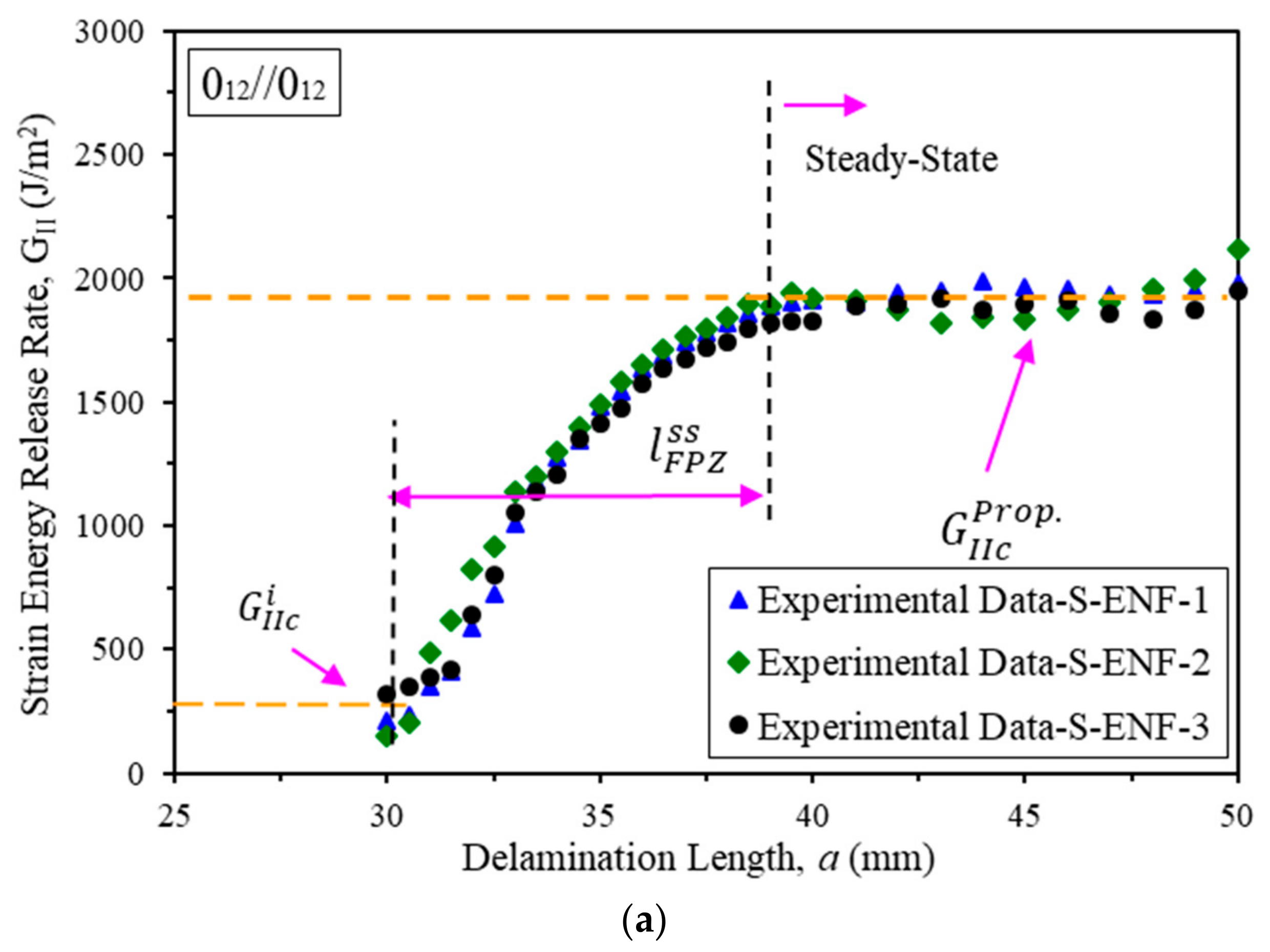
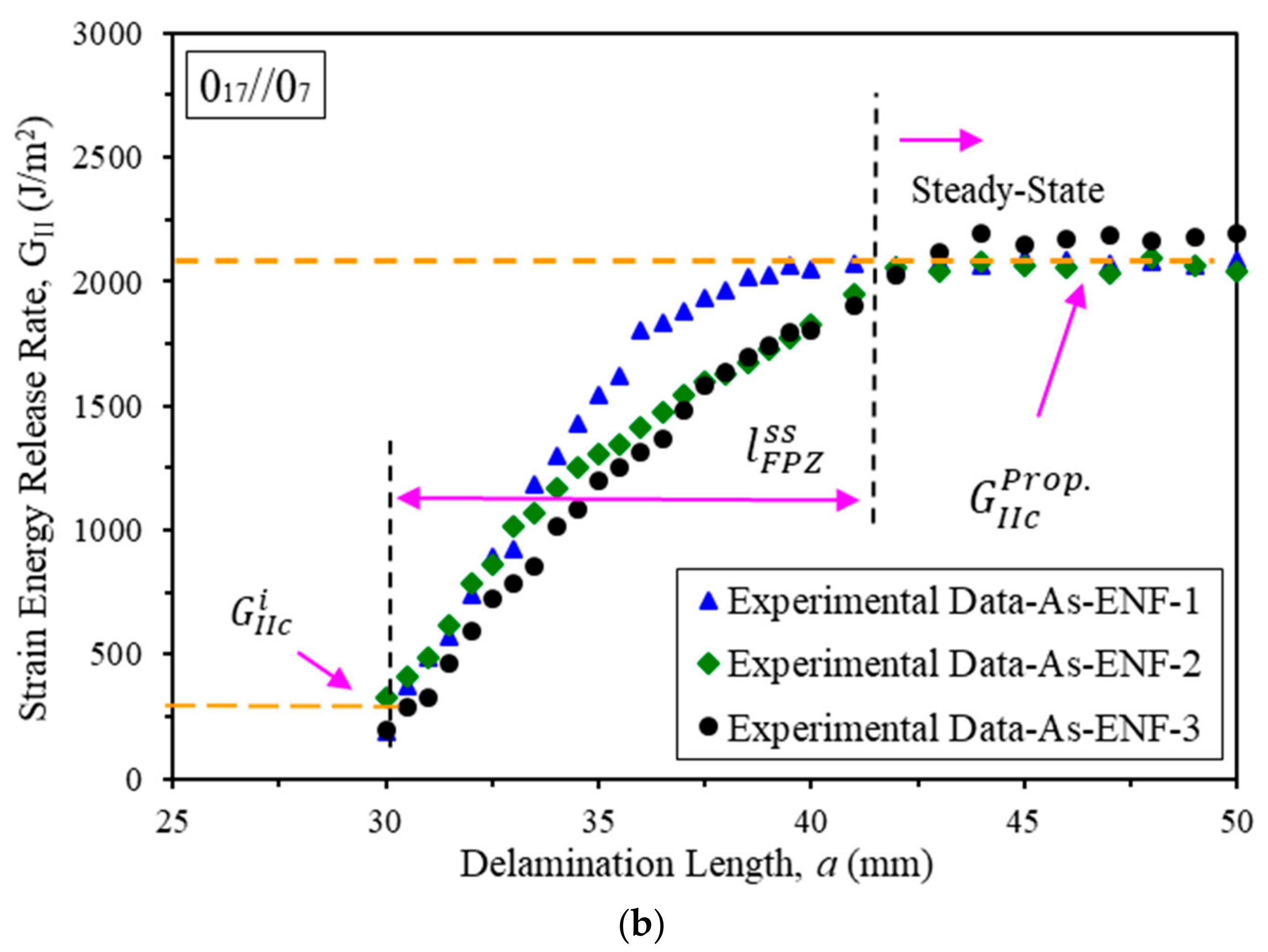
3.1. Fracture Toughness and R-Curve
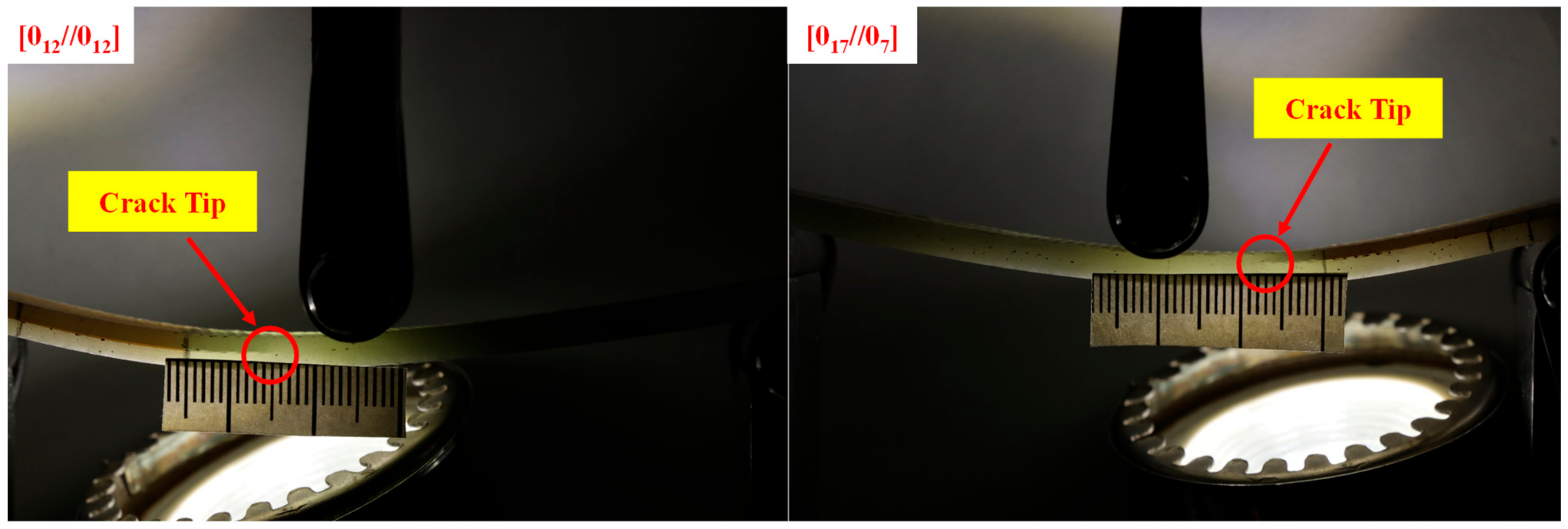
3.2. Morphology
4. Finite Element Simulation of the Delamination Growth
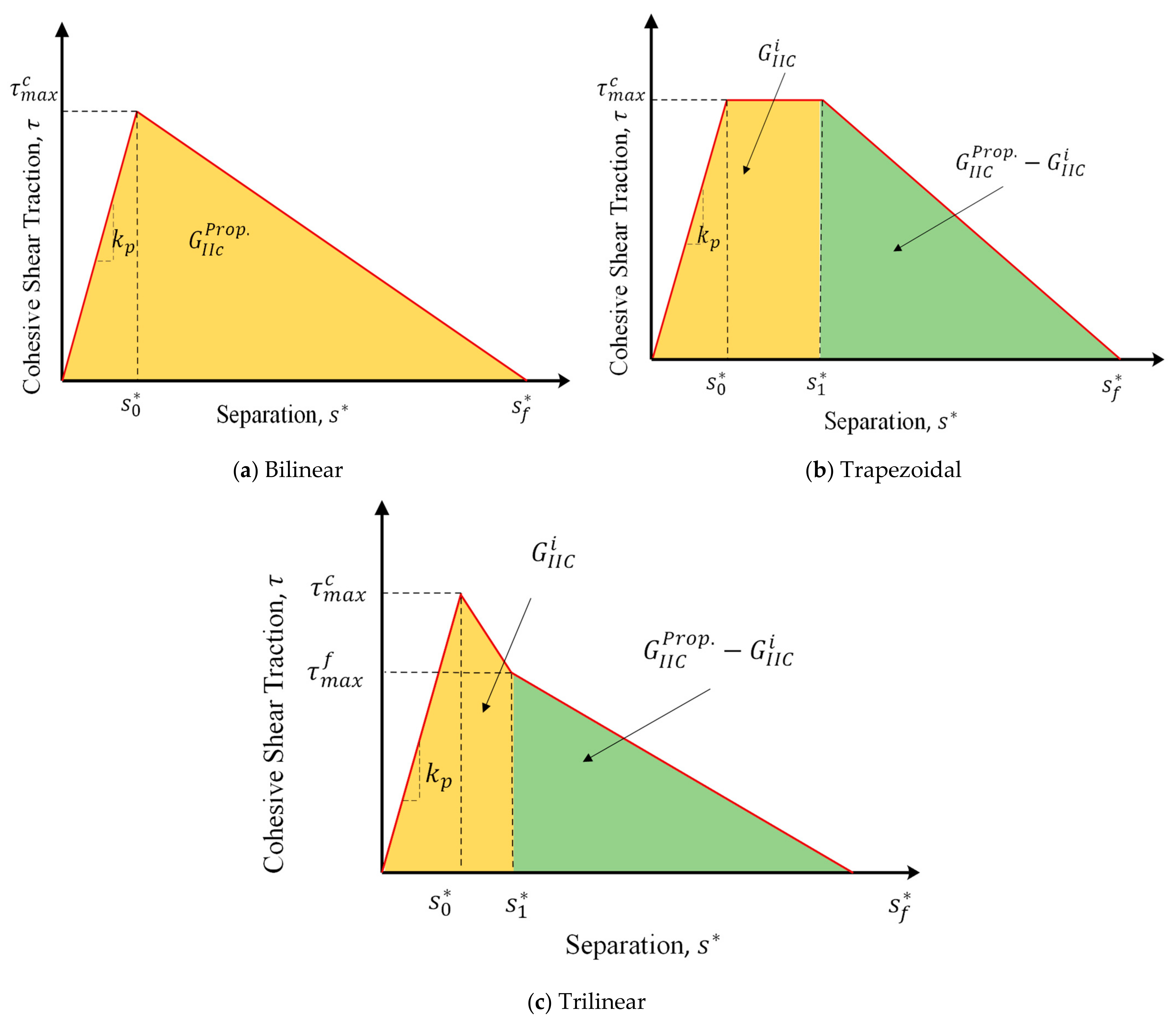
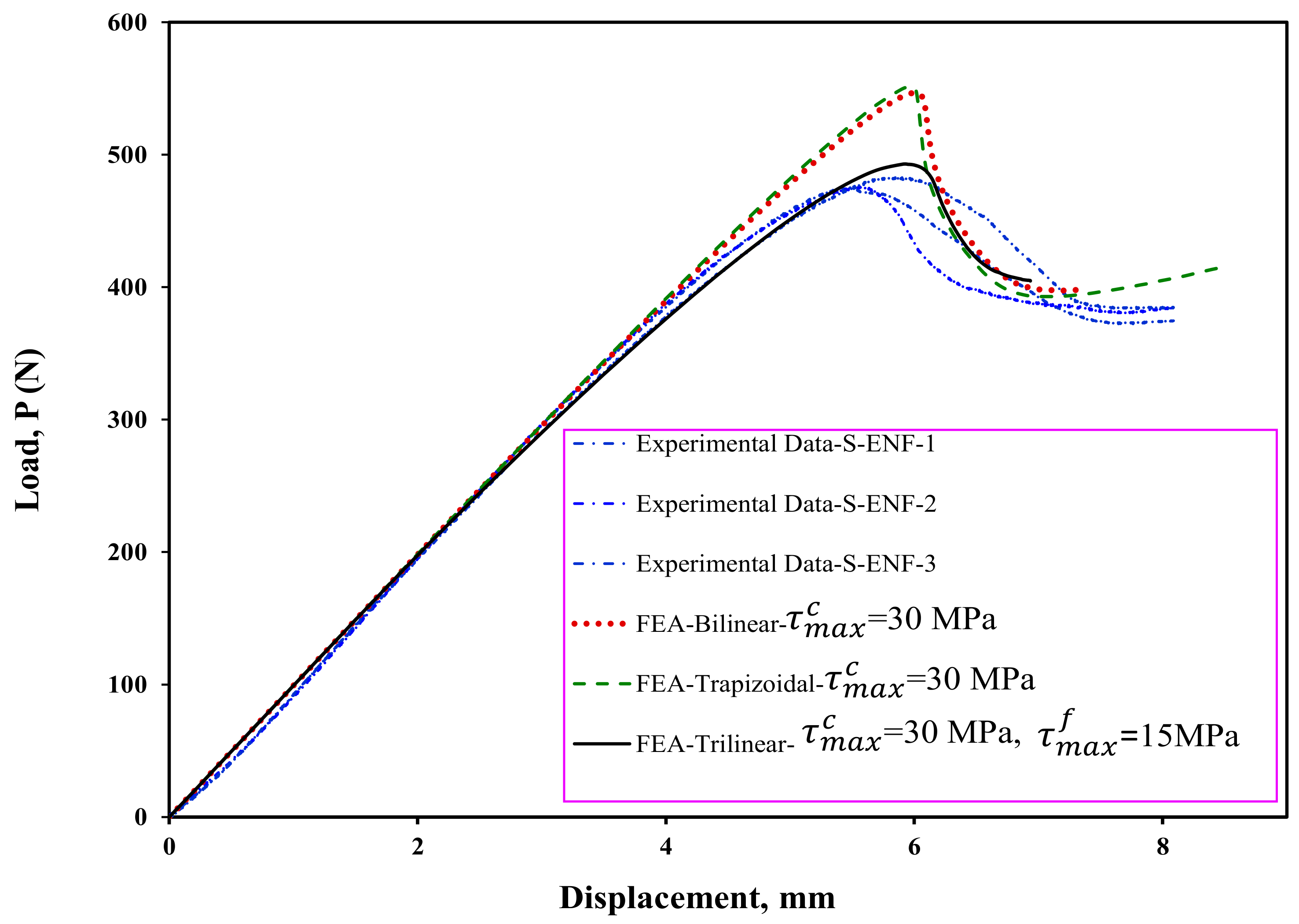
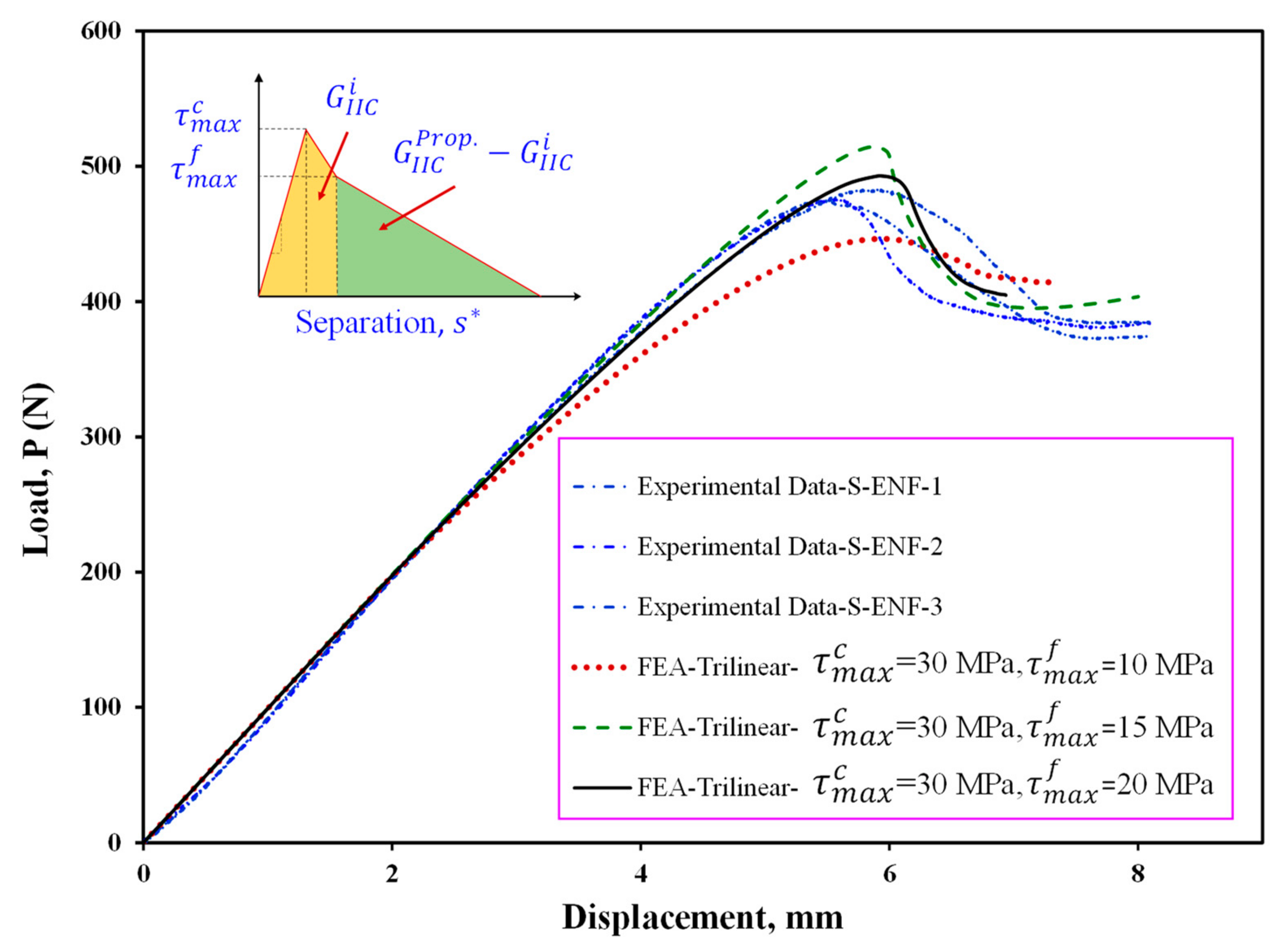
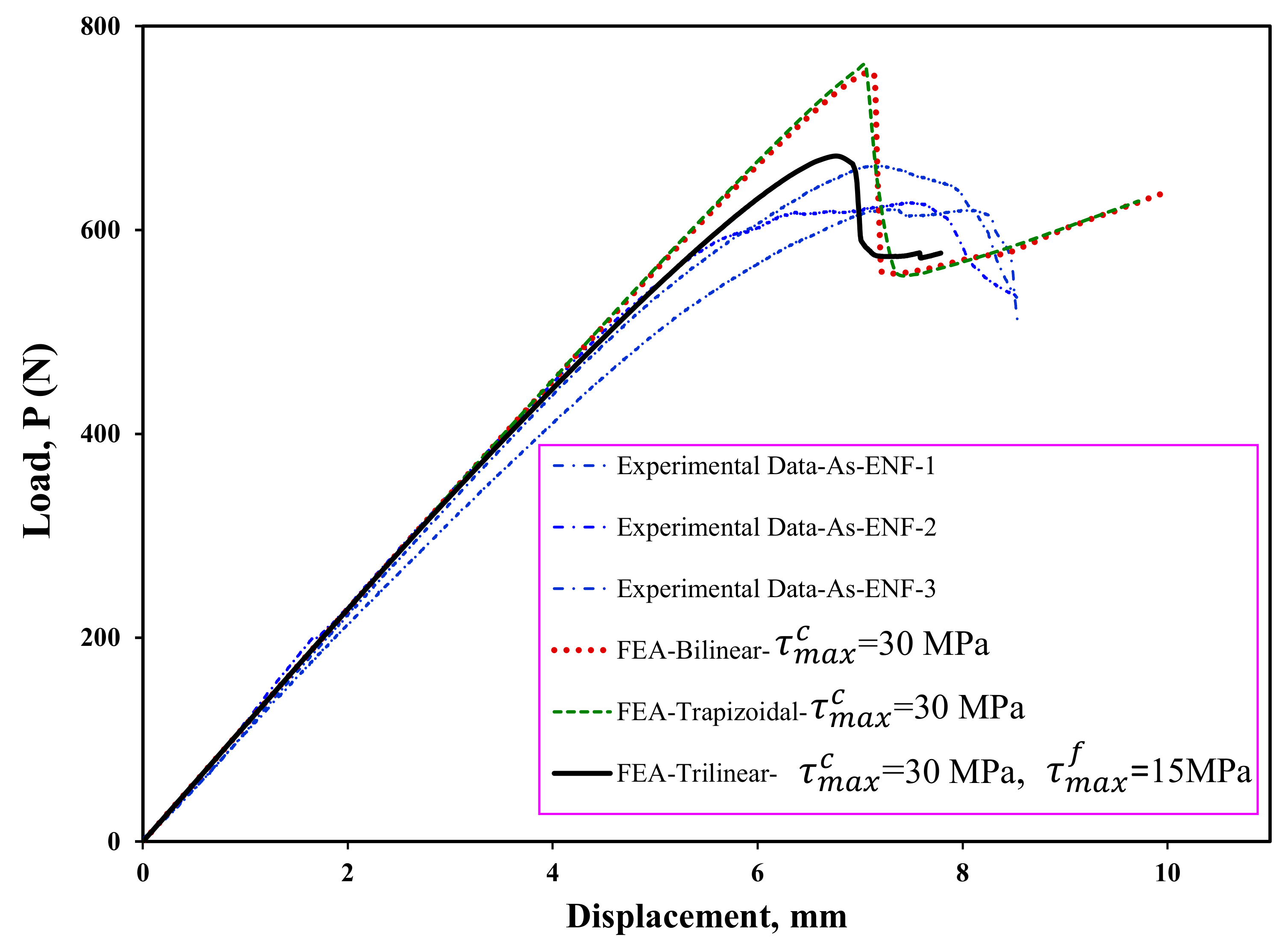
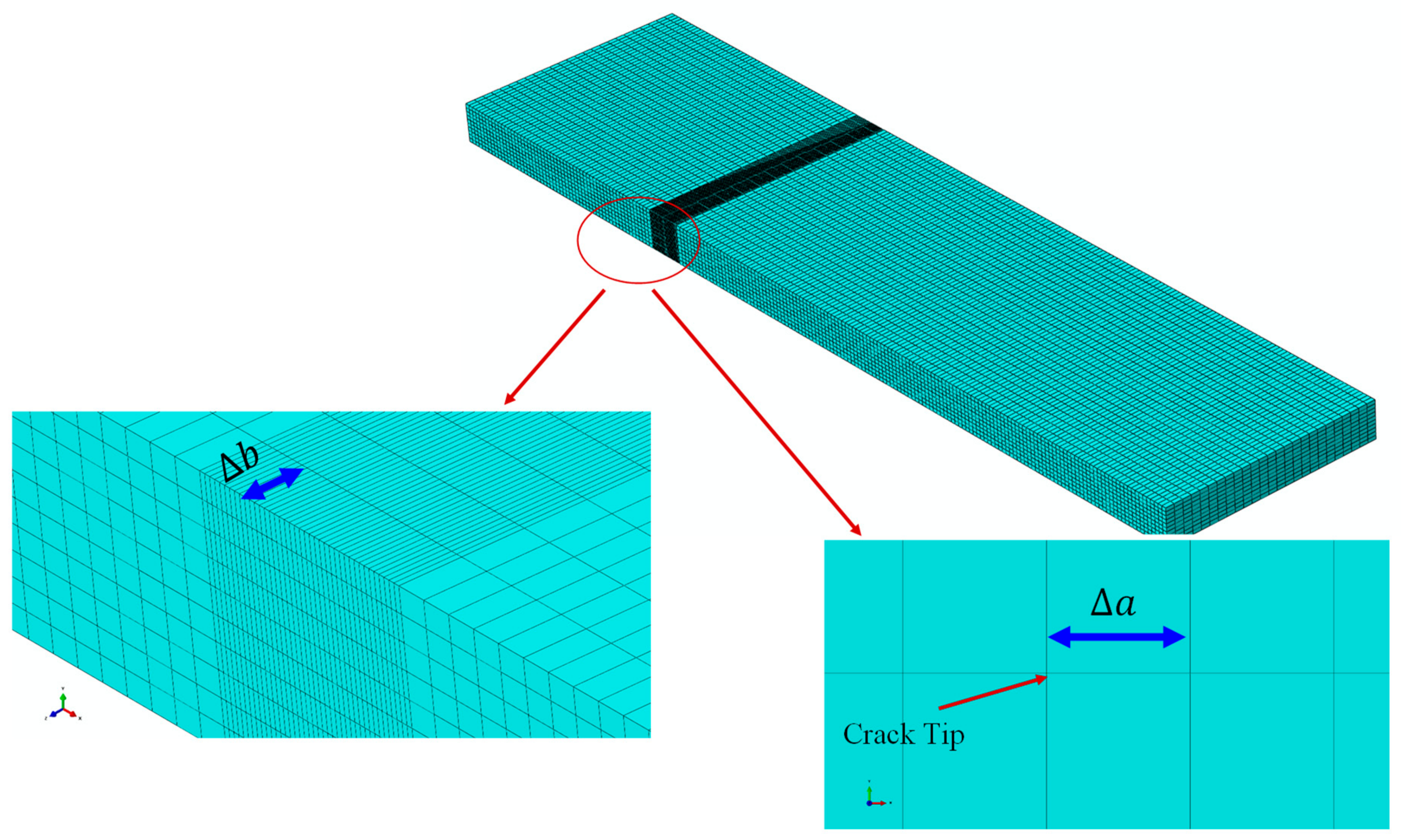
4.1. Simulation of the Delamination Using CZM
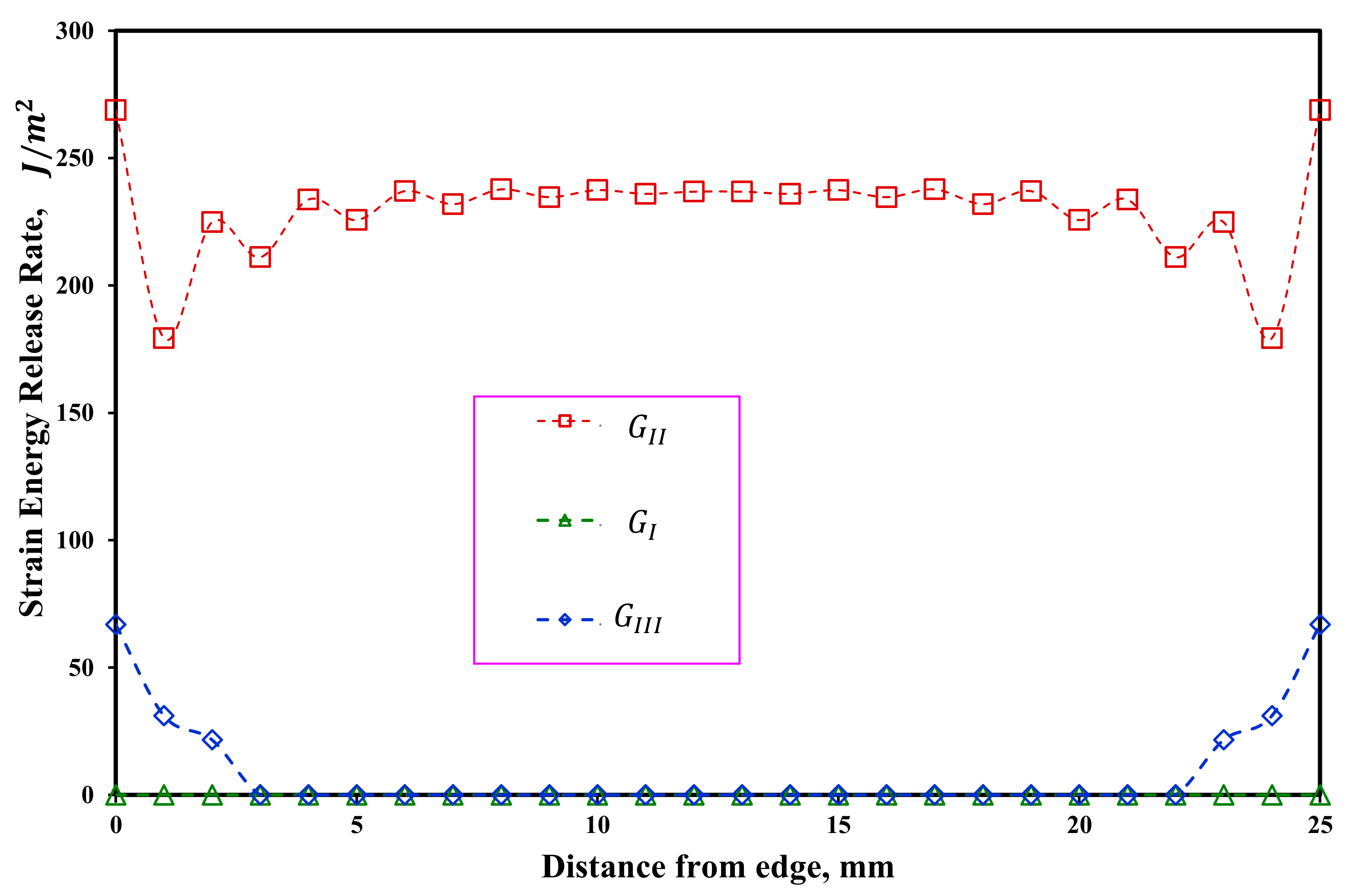
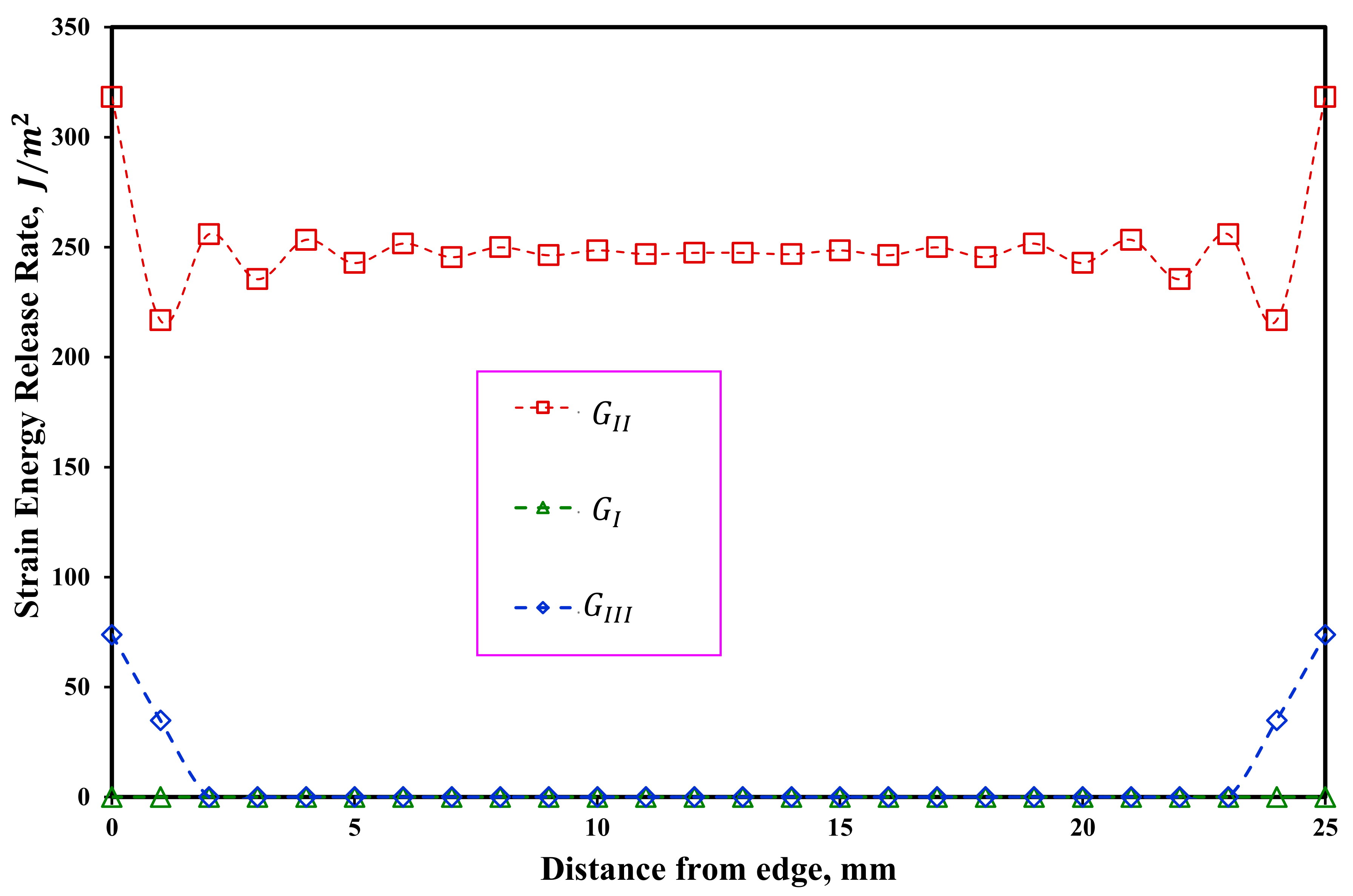
4.2. Effect Delamination Position and Mode Mixity on the Obtained Fracture Toughness
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moazzami, M.; Ayatollahi, M.; Akhavan-Safar, A.; De Freitas, S.T.; Poulis, J.; Da Silva, L. Effect of Cyclic Aging on Mode I Fracture Energy of Dissimilar Metal/Composite DCB Adhesive Joints. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 271, 108675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzami, M.; Ayatollahi, M.; Akhavan-Safar, A.; De Freitas, S.T.; Poulis, J.; Da Silva, L. Influence of Cyclic Aging on Adhesive Mode Mixity in Dissimilar Composite/Metal Double Cantilever Beam Joints. Proc. IME J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2022, 236, 1476–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan-Safar, A.; Eisaabadi Bozchaloei, G.; Jalali, S.; Beygi, R.; Ayatollahi, M.; Da Silva, L. Impact Fatigue Life of Adhesively Bonded Composite-Steel Joints Enhanced with the Bi-Adhesive Technique. Materials 2023, 16, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokrieh, M.; Heidari-Rarani, M.; Ayatollahi, M. Delamination R-curve as a Material Property of Unidirectional Glass/Epoxy Composites. Mater. Des. 2012, 34, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrieh, M.; Zeinedini, A.; Ghoreishi, S. On the Mixed Mode I/II Delamination R-curve of E-Glass/Epoxy Laminated Composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 171, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, L.; Zhao, J. An Experimental and Numerical Study of the Influence of Temperature on Mode II Fracture of a T800/Epoxy Unidirectional Laminate. Materials 2022, 15, 8108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, X.; Jiang, Z.; Luo, Q.; Li, Q.; Sun, G. Mechanical Characterization and Numerical Modeling on the Yield and Fracture Behaviors of Polymethacrylimide (PMI) Foam Materials. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 218, 107033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi-Moghadam, B.; Taheri, F. Influence of Graphene Nanoplatelets on Modes I, II and III Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2015, 143, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinolabedin Beygi, A.; Salamat-talab, M.; Farrokhabadi, F.; Moslemi Naeini, H. Experimental Investigation of the Effect of Natural Microfibers on the Mode I Fracture Toughness of Plain-Woven Laminated Composites. Modares Mech. Eng. 2022, 22, 271–279. Available online: https://mme.modares.ac.ir/article-15-53223-en.html (accessed on 30 November 2022). (In Persian).
- Almansour, F.; Dhakal, H.; Zhang, Z.Y. Investigation into Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness Characteristics of Flax/Basalt Reinforced Vinyl Ester Hybrid Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 154, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan-Safar, A.; Salamat-Talab, M.; Delzendehrooy, F.; Barbosa, A.; Da Silva, L. Mode II Fracture Energy of Laminated Composites Enhanced with Micro-Cork Particles. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2021, 43, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.C.; Lee, W.I.; Kim, H.S. Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Carbon Nanotubes/Epoxy Film-Interleaved Carbon Fiber Composites. Compos. Struct. 2020, 236, 111808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.K.; Gries, T.; Veit, D.; Quadflieg, T.; Mohr, B.; Kolloch, M. Effect of Nanomaterial on Mode I and Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Woven Carbon Fabric Reinforced Polymer Composites. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2017, 180, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekeoseye, W.S.; Kolasangiani, K.; Oguamanam, D.C.; Bougherara, H. Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Flax/Glass/Epoxy Hybrid Composite Materials: An Experimental and Numerical Study. J. Nat. Fibers 2020, 19, 4286–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, B.; Liu, Y.; Mo, S.; He, M.; Zhai, L.; Fan, L. Interlaminar Fracture Behavior of Carbon Fiber/Polyimide Composites Toughened by Interleaving Thermoplastic Polyimide Fiber Veils. Materials 2021, 14, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamat-talab, M.; Zeinolabedin Beygi, A.; Seyyednejad, M. Experimental Investigation of the Effect of Interface Fiber Angle on the Fracture Toughness of Woven Laminated Composites Under Mode II Loading. Modares Mech. Eng. 2021, 21, 225–233. Available online: http://mme.modares.ac.ir/article-15-45627-en.html (accessed on 25 March 2021). (In Persian).
- De Morais, A.; Pereira, A. Application of the Effective Crack Method to Mode I and Mode II Interlaminar Fracture of Carbon/Epoxy Unidirectional Laminates. Compos. Part A 2007, 38, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Nakata, M.; Takao, Y.; Matsubara, T. Experimental Investigation on Test Methods for Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Testing of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Composites. Compos. Part A 2009, 40, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersons, J.; König, M. Dependence of Fracture Toughness of Composite Laminates on Interface Ply Orientations and Delamination Growth Direction. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2004, 64, 2139–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashiro, S.; Agata, T.; Yoshimura, A. A New Approach for Evaluating Crack Growth Resistance Curve of Mode II Delamination by Doubly End-Notched Tension Tests. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2018, 27, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H. Interlaminar Shear Fracture of Laminated Composites. Int. J. Fract. 1990, 43, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.R.; Taheri-Behrooz, F.; Salamat-Talab, M. Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Woven E-Glass/Epoxy Composites in the Presence of Mat Interleaves. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 98, 102523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollón, V.; Bonhomme, J.; Argüelles, A.; Viña, J. Influence of the Crack Plane Asymmetry Over GII Results in Carbon Epoxy ENF Specimens. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; De Morais, A.; Marques, A.; De Castro, P. Mode II Interlaminar Fracture of Carbon/Epoxy Multidirectional Laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2004, 64, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan-Safar, A.; Salamat-Talab, M.; Delzendehrooy, F.; Zeinolabedin-Beygi, A.; Da Silva, L. Effects of Natural Date Palm Tree Fibers on Mode II Fracture Energy of E-Gass/Epoxy Plain-Woven Laminated Composites. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2022, 44, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan-Safar, A.; Marques, E.A.; Carbas, R.J.; Da Silva, F. Cohesive Zone Modelling-CZM. In Cohesive Zone Modelling for Fatigue Life Analysis of Adhesive Joints; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi-Rajoli, J.; Akhavan-Safar, A.; Hosseini-Toudeshky, H.; Da Silva, L. Progressive damage modeling of composite materials subjected to mixed mode cyclic loading using cohesive zone model. Mech. Mater. 2020, 143, 103322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliese, G.; Palazzetti, R.; Moroni, F.; Zucchelli, A.; Pirondi, A. Cohesive Zone Modelling of Delamination Response of a Composite Laminate with Interleaved Nylon 6, 6 Nanofibers. Compos. Part B 2015, 78, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghafi, H.; Ghaffarian, S.; Salimi-Majd, D.; Saghafi, H.A. Investigation of Interleaf Sequence Effects on Impact Delamination of Nano-Modified Woven Composite Laminates Using Cohesive Zone Model. Compos. Struct. 2017, 166, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, B.M.; Shyamsunder, L.; Holt, N.; Hoover, C.G.; Rajan, S.D.; Blankenhorn, G. Enhancing the Predictive Capabilities of a Composite Plasticity Model Using Cohesive Zone Modeling. Compos. Part A 2019, 121, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrese, A.; Insausti, N.; Mujika, F.; Perez-Galmés, M.; Renart, J. A Novel Experimental Procedure to Determine the Cohesive Law in ENF Tests. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 170, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Prusty, B.G.; Ooi, E.T.; Song, C.; Pearce, G.; Phillips, A.W. Application of Scaled Boundary Finite Element Method for Delamination Analysis of Composite Laminates Using Cohesive Zone Modelling. Compos. Struct. 2020, 253, 112773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioutis, I.; Tserpes, K. Development and Numerical Implementation of a Modified Mixed-Mode Traction–Separation Law for the Simulation of Interlaminar Fracture of Co-Consolidated Thermoplastic Laminates Considering the Effect of Fiber Bridging. Materials 2022, 15, 5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moura, M.; De Morais, A. Equivalent Crack Based Analyses of ENF and ELS Tests. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2008, 75, 2584–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, N.; Li, H.; Shet, C.; Ghonem, H. Some Issues in the Application of Cohesive Zone Models for Metal–Ceramic Interfaces. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2002, 39, 2827–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Hadavinia, H. Analytical Solutions for Cohesive Zone Models. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2002, 50, 809–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyfantis, K.N.; Tsouvalis, N.G. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Mode II Fracture in Fibrous Reinforced Composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2011, 30, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Li, G. Nonlinear Interface Shear Fracture of End Notched Flexure Specimens. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamat-Talab, M.; Shokrieh, M.; Mohaghegh, M. On the R-curve and Cohesive Law of Glass/Epoxy End-Notch Flexure Specimens with 0//θ Interface Fiber Angles. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 106992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari-Rarani, M.; Ghasemi, A. Appropriate Shape of Cohesive Zone Model for Delamination Propagation in ENF Specimens with R-Curve Effects. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2017, 90, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, N.; De Moura, M.; De Morais, A.; Pereira, A. Bilinear Approximations to the Mode II Delamination Cohesive Law Using an Inverse Method. Mech. Mater. 2012, 49, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3518; Standard Test Method for In-Plane Shear Response of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials by Tensile Test of a±45° Laminate. A. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001.
- ASTM D790; Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials. Annual book of ASTM Standards. S. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1997.
- ASTM D3039/DM; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. A. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008.
- ASTM D7905 D7905M; Standard Test Method for Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Undirectional Fiber-reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Carlsson, L.A.; Kardomateas, G.A. Structural and Failure Mechanics of Sandwich Composites; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, R. Virtual Crack Closure Technique: History, Approach, and Applications. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2004, 57, 109–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orifici, A.C.; Krueger, R. Benchmark Assessment of Automated Delamination Propagation Capabilities in Finite Element Codes for Static Loading. Finite. Elem. Anal. Des. 2012, 54, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, B.D.; Kruger, R.; König, M. Three Dimensional Analysis and Resulting Design Recommendations for Unidirectional and Multidirectional End-Notched Flexure Tests. J. Compos. Mater. 1995, 29, 2108–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
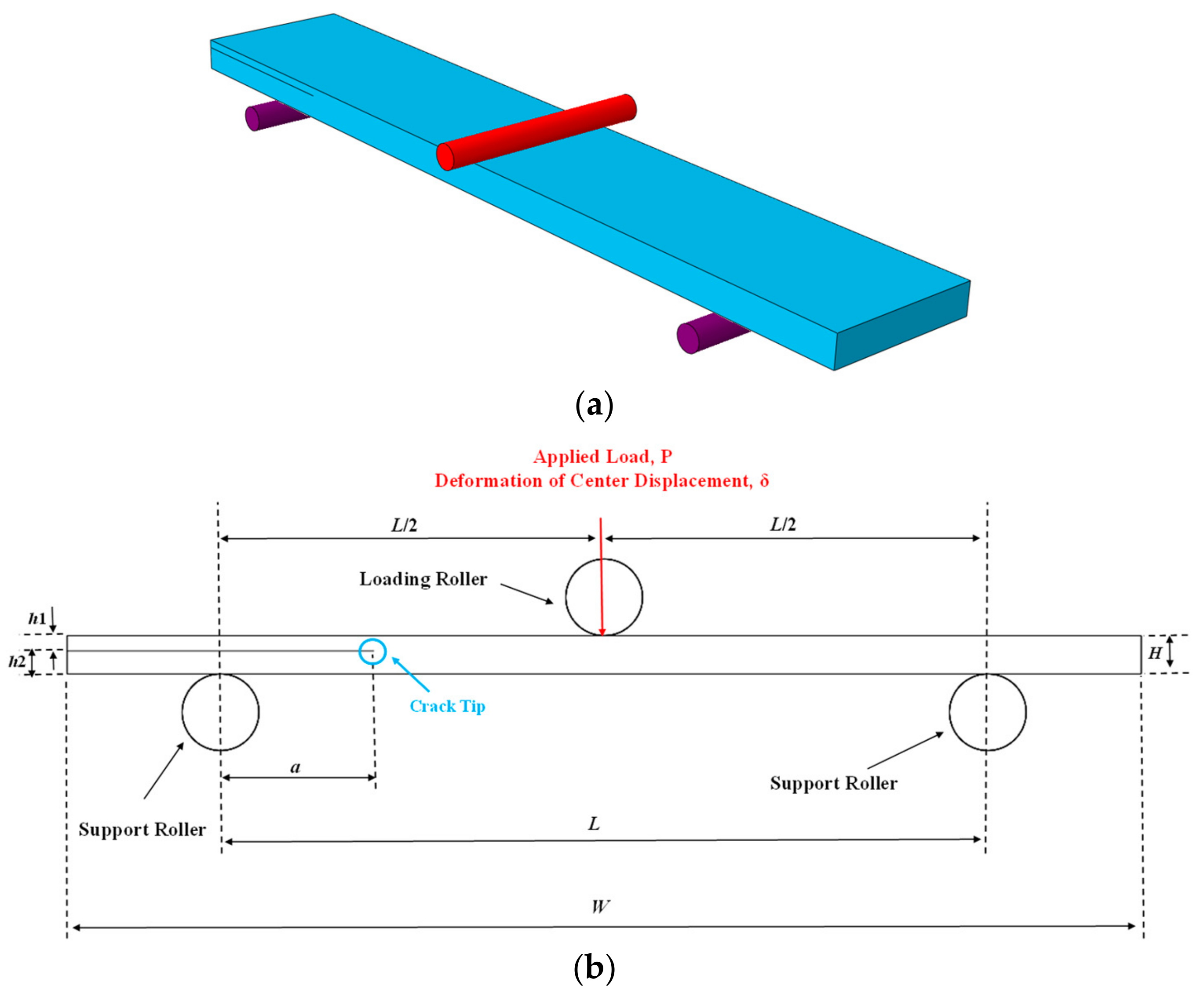



| Geometrical Parameters | ENF Specimen with Symmetrical Delamination Plane (S-ENF) [012//012] | ENF Specimen with Asymmetrical Delamination Plane (As-ENF) [017//07] |
|---|---|---|
| Total length of the beam, W (mm) | 140 | 140 |
| Span length, L (mm) | 100 | 100 |
| Beam width, b (mm) | 25 | 25 |
| Initial crack length, a (mm) | 30 | 30 |
| The thickness of arm-1, h1 (mm) | 2.06 | 1.22 |
| The thickness of arm-2, h2 (mm) | 2.06 | 2.94 |
| Total thickness of the beam, H (mm) | 4.12 | 4.16 |
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Longitudinal elastic modulus (E1) | 19.5 GPa |
| Transverse elastic modulus (E2) | 19.5 GPa |
| In-plane shear modulus (G12) | 3.1 GPa |
| Flexural modulus (Eb) | 18.1 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio (ν12) | 0.29 |
| Delamination Plane | Maximum Load, P (N) | Initial Fracture Toughness, (J/m2) | Propagation Fracture Toughness, (J/m2) | FPZ Length, (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [012//012] | 477.60 ± 4.48 | 226.82 ± 85.96 | 1905.85 ± 34.74 | 8.67 ± 0.29 |
| [017//07] | 636.87 ± 23.03 | 237.83 ± 77.50 | 2082.71 ± 63.96 | 11.50 ± 1.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salamat-Talab, M.; Akhavan-Safar, A.; Zeinolabedin-Beygi, A.; Carbas, R.J.C.; da Silva, L.F.M. Effect of Through-the-Thickness Delamination Position on the R-Curve Behavior of Plain-Woven ENF Specimens. Materials 2023, 16, 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051811
Salamat-Talab M, Akhavan-Safar A, Zeinolabedin-Beygi A, Carbas RJC, da Silva LFM. Effect of Through-the-Thickness Delamination Position on the R-Curve Behavior of Plain-Woven ENF Specimens. Materials. 2023; 16(5):1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051811
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalamat-Talab, Mazaher, Alireza Akhavan-Safar, Ali Zeinolabedin-Beygi, Ricardo J. C. Carbas, and Lucas F. M. da Silva. 2023. "Effect of Through-the-Thickness Delamination Position on the R-Curve Behavior of Plain-Woven ENF Specimens" Materials 16, no. 5: 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051811
APA StyleSalamat-Talab, M., Akhavan-Safar, A., Zeinolabedin-Beygi, A., Carbas, R. J. C., & da Silva, L. F. M. (2023). Effect of Through-the-Thickness Delamination Position on the R-Curve Behavior of Plain-Woven ENF Specimens. Materials, 16(5), 1811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051811









