Boosting the Dehydrogenation Properties of LiAlH4 by Addition of TiSiO4
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
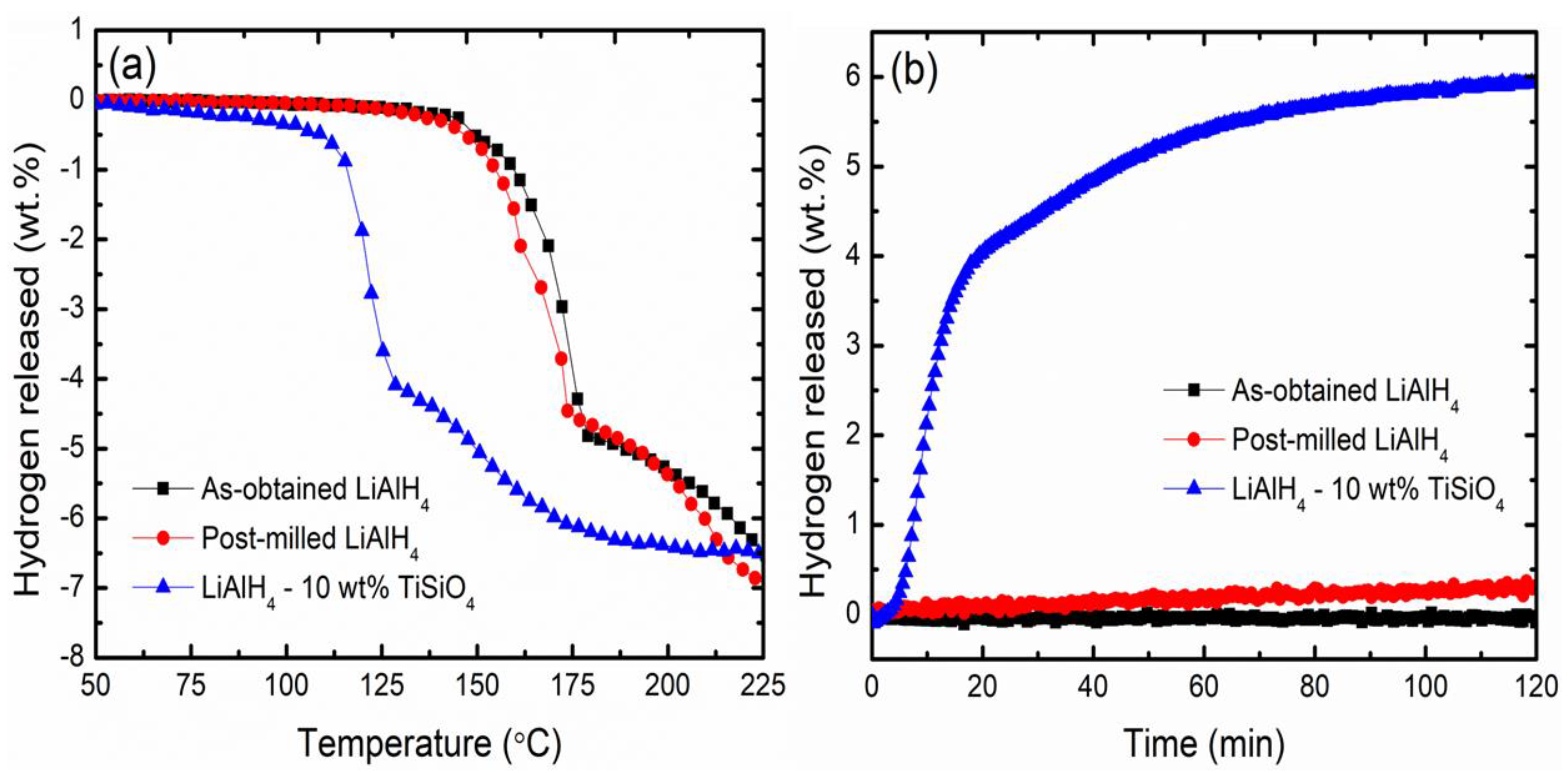
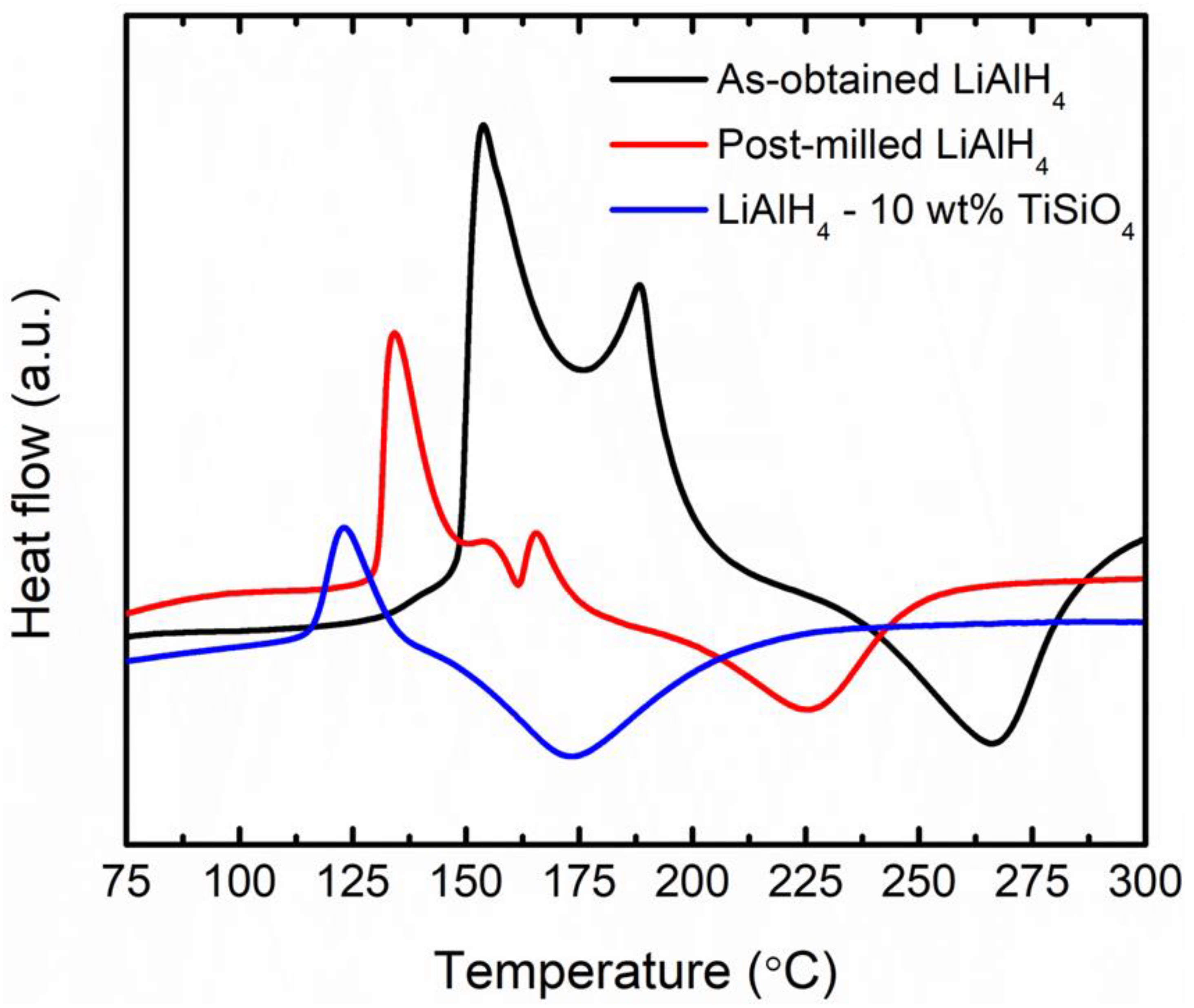
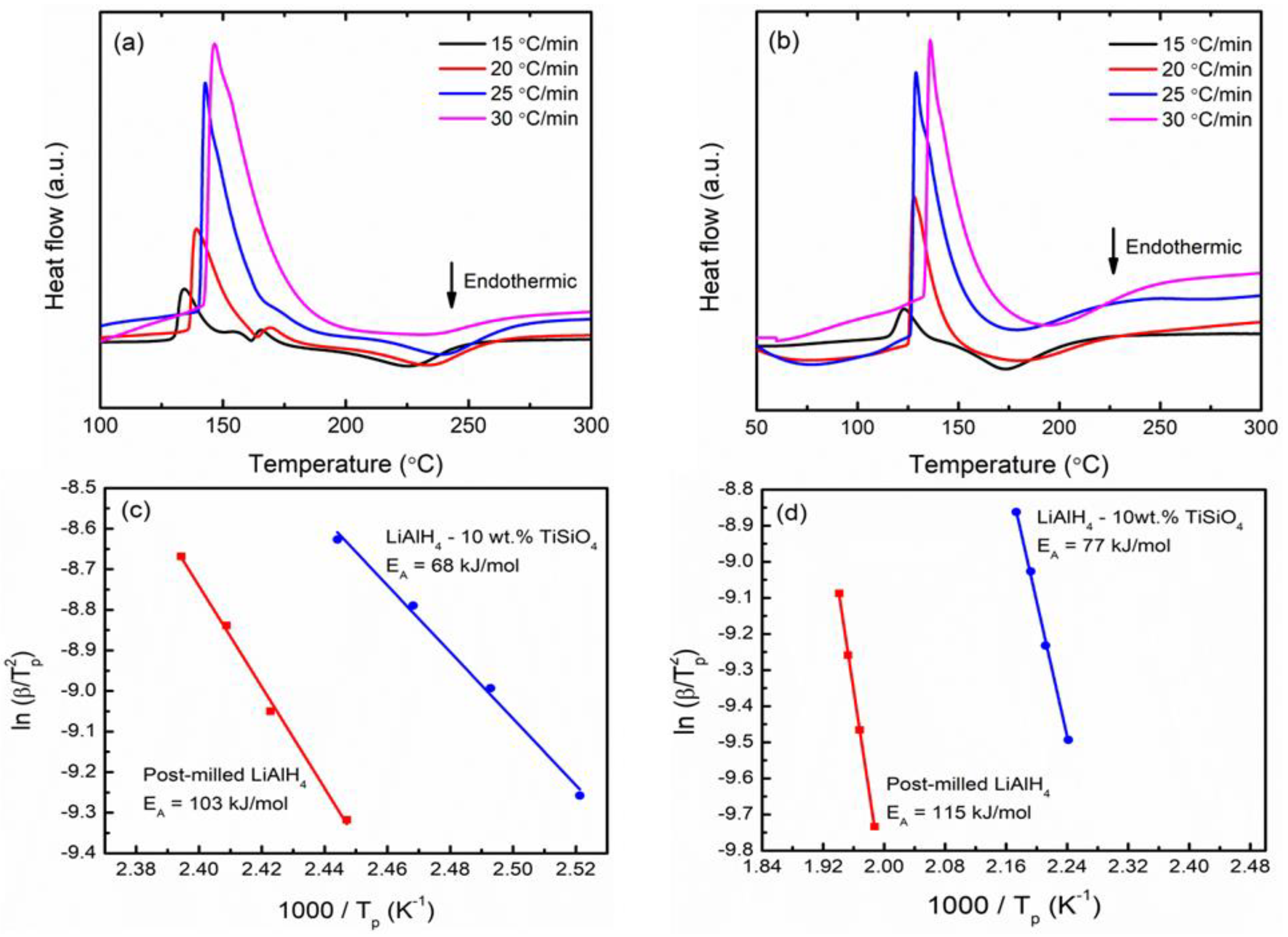
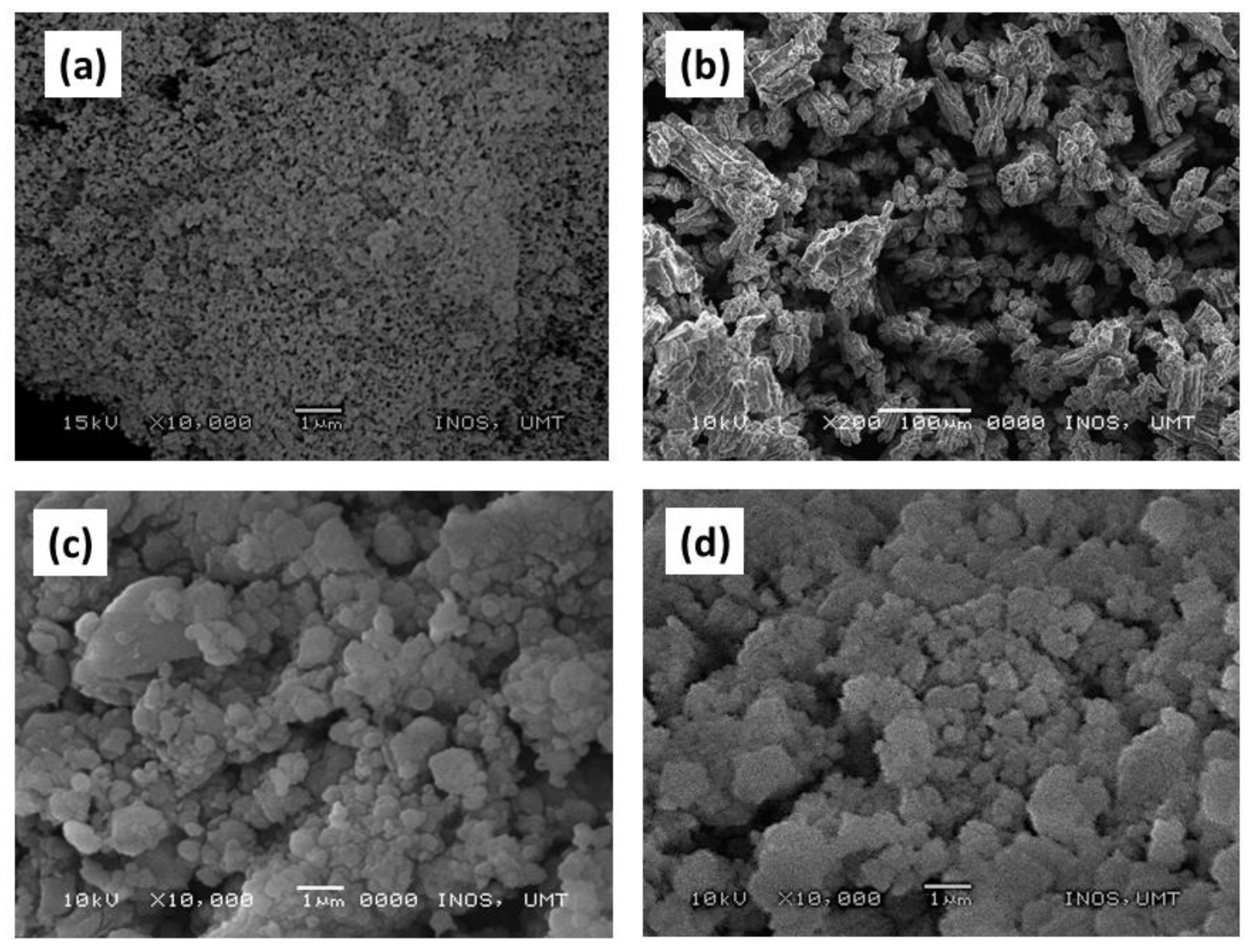
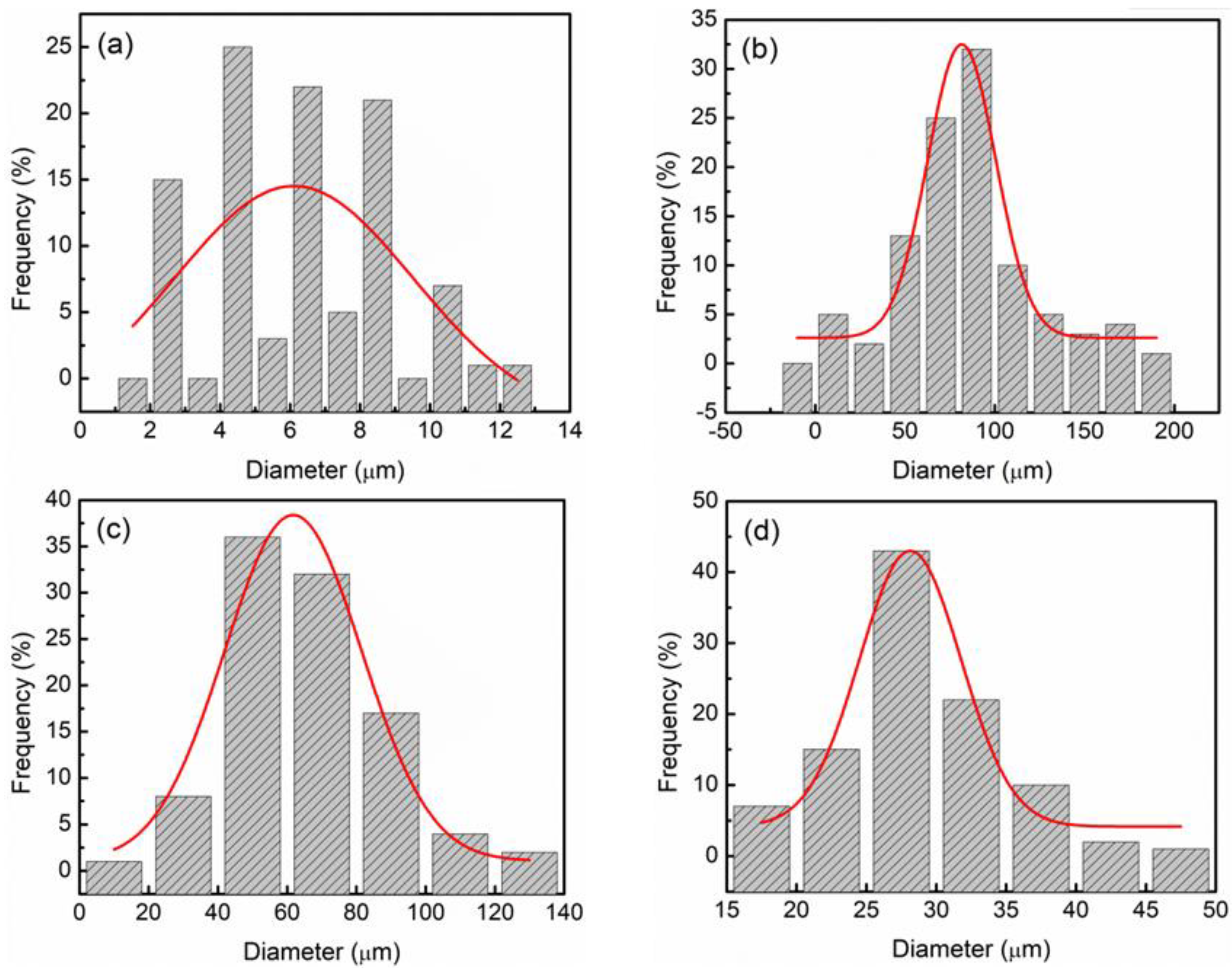
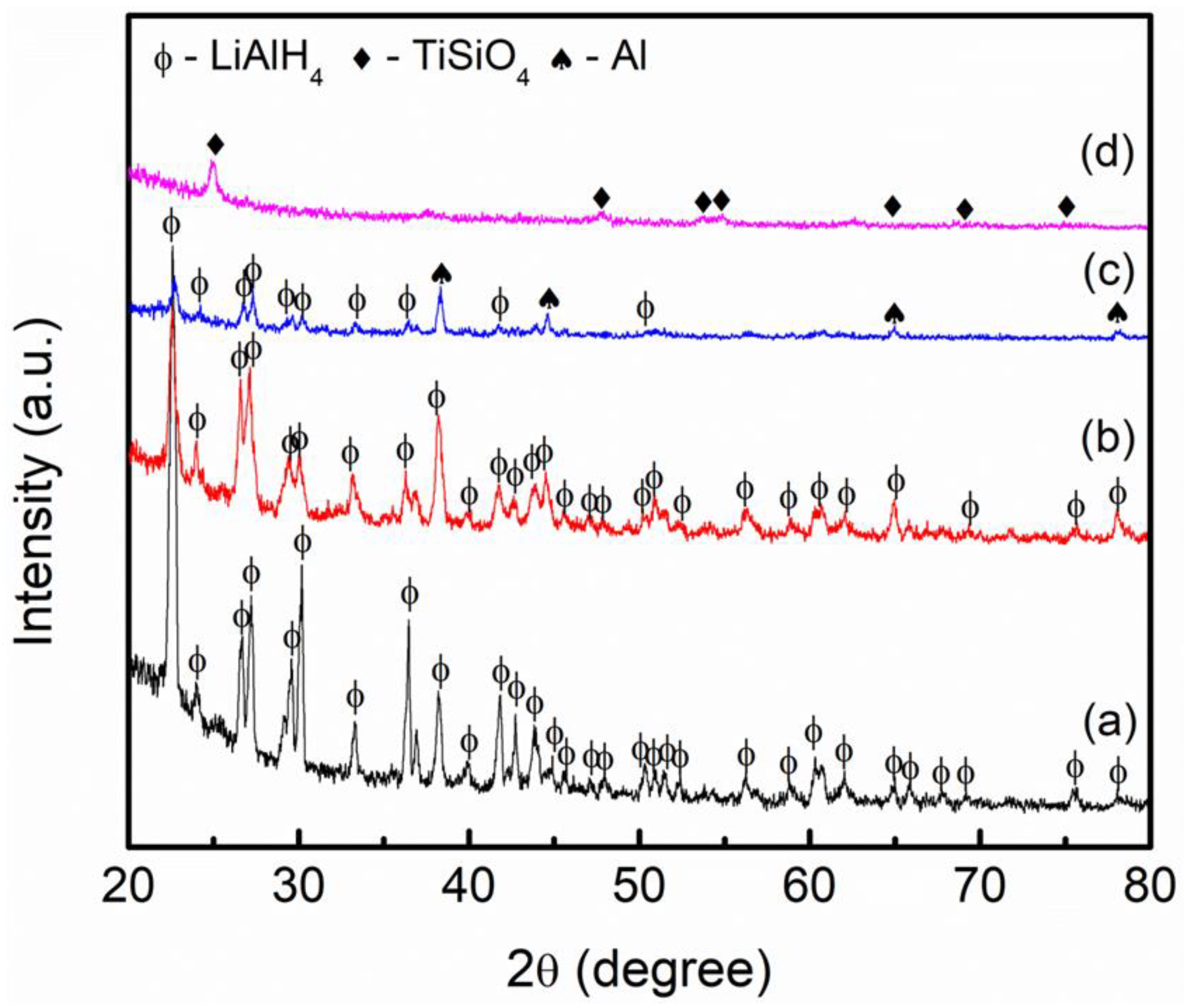
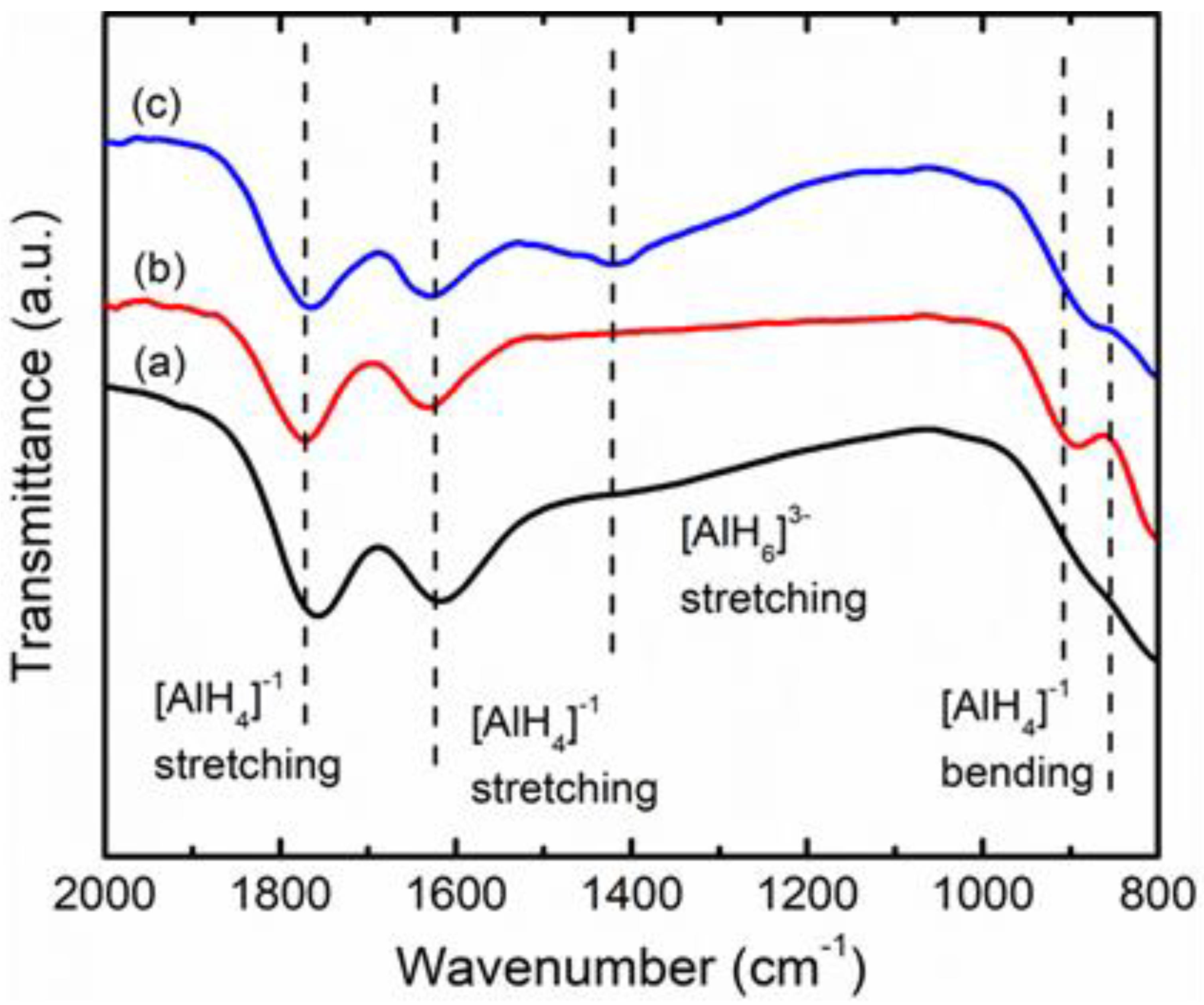
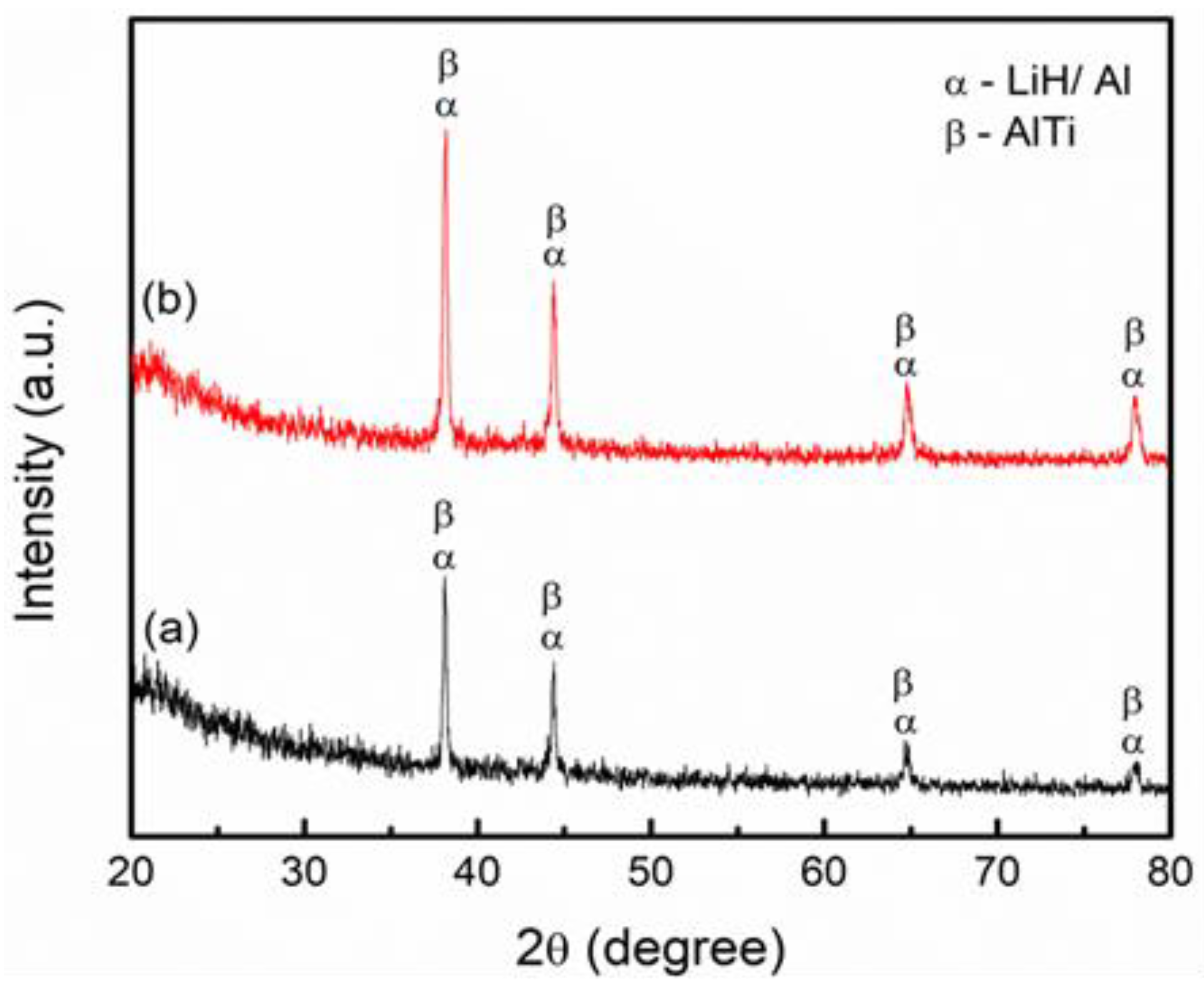
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, Y.; Lu, J.; Ding, J.; Wang, W.; Yan, J. Numerical simulation on the storage performance of a phase change materials based metal hydride hydrogen storage tank. Appl. Energy 2020, 278, 115682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J. A review of high density solid hydrogen storage materials by pyrolysis for promising mobile applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 2737–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivard, E.; Trudeau, M.; Zaghib, K. Hydrogen storage for mobility: A review. Materials 2019, 12, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, J.; Shabani, B. A critical study of stationary energy storage policies in Australia in an international context: The role of hydrogen and battery technologies. Energies 2016, 9, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, L.; Züttel, A. Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications. J. Nat. 2001, 414, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, N.S.; Yahya, M.S.; Itam Sulaiman, N.N.; Yap, F.A.H.; Ismail, M. Enhanced the hydrogen storage properties and reaction mechanisms of 4MgH2+ LiAlH4 composite system by addition with TiO2. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 21365–21374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehabadi, A.; Umar, M.F.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, M.I.; Ismail, N.; Rafatullah, M. Carbon-based nanocomposites in solid-state hydrogen storage technology: An overview. Int. J. Energy. Res. 2020, 44, 11044–11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeland-Eriksen, T.; Hajizadeh, A.; Sartori, S. Hydrogen-based systems for integration of renewable energy in power systems: Achievements and perspectives. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 31963–31983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DOE Technical Targets for Onboard Hydrogen Storage for Light-Duty Vehicles. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/doe-technical-targets-onboard-hydrogen-storage-light-duty-vehicles (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Aziz, M.; Wijayanta, A.T.; Nandiyanto, A.B.D. Ammonia as effective hydrogen storage: A review on production, storage and utilization. Energies 2020, 13, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Liu, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.-S.; Sun, L.; Zhu, M. Magnesium-based hydrogen storage compounds: A review. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 832, 154865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Chen, K.; Jiang, J.; Yang, X.-S.; Zhu, M. Hydrogen storage in light-metal based systems: A review. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 829, 154597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Ismail, M. Advanced hydrogen storage of the Mg–Na–Al system: A review. J. Magnes. Alloy 2021, 9, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Sazelee, N.A.; Ismail, M. An overview of reactive hydride composite (RHC) for solid-state hydrogen storage materials. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 31674–31698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazelee, N.A.; Yahya, M.S.; Idris, N.H.; Din, M.M.; Ismail, M. Desorption properties of LiAlH4 doped with LaFeO3 catalyst. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 11953–11960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Yahya, M.S.; Mustafa, N.S.; Sazelee, N.A.; Idris, N.H.; Ismail, M. Modifying the hydrogen storage performances of NaBH4 by catalyzing with MgFe2O4 synthesized via hydrothermal method. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 6720–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim Yap, F.A.; Ali, N.A.; Idris, N.H.; Ismail, M. Catalytic effect of MgFe2O4 on the hydrogen storage properties of Na3AlH6–LiBH4 composite system. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 20882–20891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juahir, N.; Mustafa, N.S.; Yap, F.A.H.; Ismail, M. Study on the hydrogen storage properties and reaction mechanism of NaAlH4–Mg(BH4)2 (2:1) with and without TiF3 additive. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 7628–7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazelee, N.A.; Yahya, M.S.; Ali, N.A.; Idris, N.H.; Ismail, M. Enhancement of dehydrogenation properties in LiAlH4 catalysed by BaFe12O19. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 835, 155183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Fang, F.; Zhou, G.; Chen, G.; Ouyang, L.; Zhu, M.; Sun, D. Hydrogen storage properties of space-confined NaAlH4 nanoparticles in ordered mesoporous silica. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3954–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigma-Aldrich. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/MY/en/campaigns/connected-lab-instrumentation (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Ahmad, M.A.N.; Sazelee, N.A.; Ali, N.A.; Ismail, M. Enhancing the dehydrogenation properties of LiAlH4 using K2NiF6 as additive. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 24843–24851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J. Advanced Doping Techniques and Dehydrogenation Properties of Transition Metal-Doped LiAlH4 for Fuel Cell Systems. Ph.D Thesis, Dresden University of Technology, Dresden, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Orimo, S.-I.; Nakamori, Y.; Eliseo, J.R.; Züttel, A.; Jensen, C.M. Complex hydrides for hydrogen storage. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 4111–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, C.; Zhou, H.; Gao, M.; Pan, H.; Wang, Q. A novel catalyst precursor K2TiF6 with remarkable synergetic effects of K, Ti and F together on reversible hydrogen storage of NaAlH4. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1740–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, A.; Vegge, T.; Pedersen, A.S. Dehydrogenation kinetics of as-received and ball-milled LiAlH4. J. Solid State Chem. 2005, 178, 3672–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-S.; Sun, L.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhang, J.; Chu, H.-L.; Fan, M.Q.; Zhang, T.; Song, X.Y.; Grolier, J.P. Effect of ball milling time on the hydrogen storage properties of TiF3-doped LiAlH4. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 8079–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; McGrady, G.S.; Langmi, H.W.; Jensen, C.M. Facile cycling of Ti-doped LiAlH4 for high performance hydrogen storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5032–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, P.; Wan, Q.; Zhai, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, K.; Wang, L.; Lü, S.; Zou, L.; Qu, X.; et al. Dehydrogenation improvement of LiAlH4 catalyzed by Fe2O3 and Co2O3 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 18343–18352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resan, M.; Hampton, M.D.; Lomness, J.K.; Slattery, D.K. Effects of various catalysts on hydrogen release and uptake characteristics of LiAlH4. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2005, 30, 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balema, V.P.; Wiench, J.W.; Dennis, K.W.; Pruski, M.; Pecharsky, V.K. Titanium catalyzed solid-state transformations in LiAlH4 during high-energy ball-milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 329, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shenglin, L.; Qiuhua, M.; Xueping, Z.; Xin, F.; Guo, X.; Jiaojiao, Z. Influences of Y2O3 doping on hydrogen release property of LiAlH4. Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 2014, 43, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.; Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, L. Catalytic effect of ScCl3 on the dehydrogenation properties of LiAlH4. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 762, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varin, R.A.; Zbroniec, L. Fast and slow dehydrogenation of ball milled lithium alanate (LiAlH4) catalyzed with manganese chloride (MnCl2) as compared to nanometric nickel catalyst. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, S736–S739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazelee, N.A.; Ismail, M. Recent advances in catalyst-enhanced LiAlH4 for solid-state hydrogen storage: A review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 9123–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, F.; Li, P.; Sun, A.; Wu, S.; Wan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Cui, L.; Qu, X. Significantly improved dehydrogenation of LiAlH4 destabilized by MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 11939–11945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X.; Nevirkovets, I.; Dou, S. Significantly improved dehydrogenation of LiAlH4 catalysed with TiO2 nanopowder. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 8327–8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuanhui, Q.; Ping, L.; Zhang, L.; Ahmad, M. Hydrogen sorption improvement of LiAlH4 catalyzed by Nb2O5 and Cr2O3 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 13088–13099. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.; Ali, N.A.; Sazelee, N.A.; Suwarno, S. Catalytic effect of Al2TiO5 on the dehydrogenation properties of LiAlH4. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 31903–31910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Sazelee, N.A.; Ali, N.A.; Suwarno, S. Catalytic effect of SrTiO3 on the dehydrogenation properties of LiAlH4. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 855, 157475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; An, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Qiu, F.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, L.; Yuan, H. Enhancement of the H2 desorption properties of LiAlH4 doping with NiCo2O4 nanorods. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 4414–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-S.; Li, Z.-B.; Jiao, C.-L.; Si, X.-L.; Yang, L.-N.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.Y.; Huang, F.L.; Gabelica, Z.; Schick, C.; et al. Improved reversible hydrogen storage of LiAlH4 by nano-sized TiH2. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 2770–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X.B.; Ranjbar, A.; Dou, S.X. Improved hydrogen desorption in lithium alanate by addition of SWCNT–metallic catalyst composite. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 3593–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X.B.; Dou, S.X. Effects of NbF5 addition on the hydrogen storage properties of LiAlH4. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 2361–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czujko, T.; Oleszek, E.E.; Szot, M. New aspects of MgH2 morphological and structural changes during high-energy ball milling. Materials 2020, 13, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Révész, Á.; Gajdics, M. Improved H-storage performance of novel Mg-based nanocomposites prepared by high-energy ball milling: A review. Energies 2021, 14, 6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varin, R.A.; Czujko, T.; Wronski, Z. Particle size, grain size and γ-MgH2 effects on the desorption properties of nanocrystalline commercial magnesium hydride processed by controlled mechanical milling. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zang, L.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Dehydrogenation characteristics of LiAlH4 improved by in-situ formed catalysts. J. Energy Chem. 2016, 25, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Ahmad, M.A.N.; Yahya, M.S.; Sazelee, N.; Ismail, M. Improved dehydrogenation properties of LiAlH4 by addition of nanosized CoTiO3. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devrim, Y.; Erkan, S.; Bac, N.; Eroglu, I. Improvement of PEMFC performance with Nafion/inorganic nanocomposite membrane electrode assembly prepared by ultrasonic coating technique. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 16748–16758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balema, V.P.; Pecharsky, V.K.; Dennis, K.W. Solid state phase transformations in LiAlH4 during high-energy ball-milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 313, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Sun, L.; Xu, F.; Sun, S.; Zhang, G.; Huang, P.; Du, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Dehybridization effect in improved dehydrogenation of LiAlH4 by doping with two-dimensional Ti3C2. Mater. Today Nano 2019, 8, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi ud, d.; Zhang, L.; Ping, L.; Xuanhui, Q. Catalytic effects of nano-sized TiC additions on the hydrogen storage properties of LiAlH4. J. Alloy. Compd. 2010, 508, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Cai, J.; Zhao, L.; Gao, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Improved hydrogen storage properties of LiAlH4 by mechanical milling with TiF3. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 647, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Yahya, M.S.; Sazelee, N.A.; Ali, N.A.; Yap, F.A.H.; Mustafa, N.S. The effect of K2SiF6 on the MgH2 hydrogen storage properties. J. Magnes. Alloy 2020, 8, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, A.; Guo, Z.; Yu, X.; Attard, D.; Calka, A.; Liu, H.-K. Effects of SiC nanoparticles with and without Ni on the hydrogen storage properties of MgH2. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 7263–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurko, S.; Rašković, Ž.; Novaković, N.; Mamula, B.P.; Jovanović, Z.; Baščarević, Z.; Novaković, J.G.; Matović, L. Hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 mechanically milled with α and β SiC. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yusnizam, N.Y.; Ali, N.A.; Sazelee, N.; Ismail, M. Boosting the Dehydrogenation Properties of LiAlH4 by Addition of TiSiO4. Materials 2023, 16, 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062178
Yusnizam NY, Ali NA, Sazelee N, Ismail M. Boosting the Dehydrogenation Properties of LiAlH4 by Addition of TiSiO4. Materials. 2023; 16(6):2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062178
Chicago/Turabian StyleYusnizam, Nurul Yasmeen, Nurul Amirah Ali, Noratiqah Sazelee, and Mohammad Ismail. 2023. "Boosting the Dehydrogenation Properties of LiAlH4 by Addition of TiSiO4" Materials 16, no. 6: 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062178
APA StyleYusnizam, N. Y., Ali, N. A., Sazelee, N., & Ismail, M. (2023). Boosting the Dehydrogenation Properties of LiAlH4 by Addition of TiSiO4. Materials, 16(6), 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062178










