Recent Advances on PEO-PCL Block and Graft Copolymers as Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
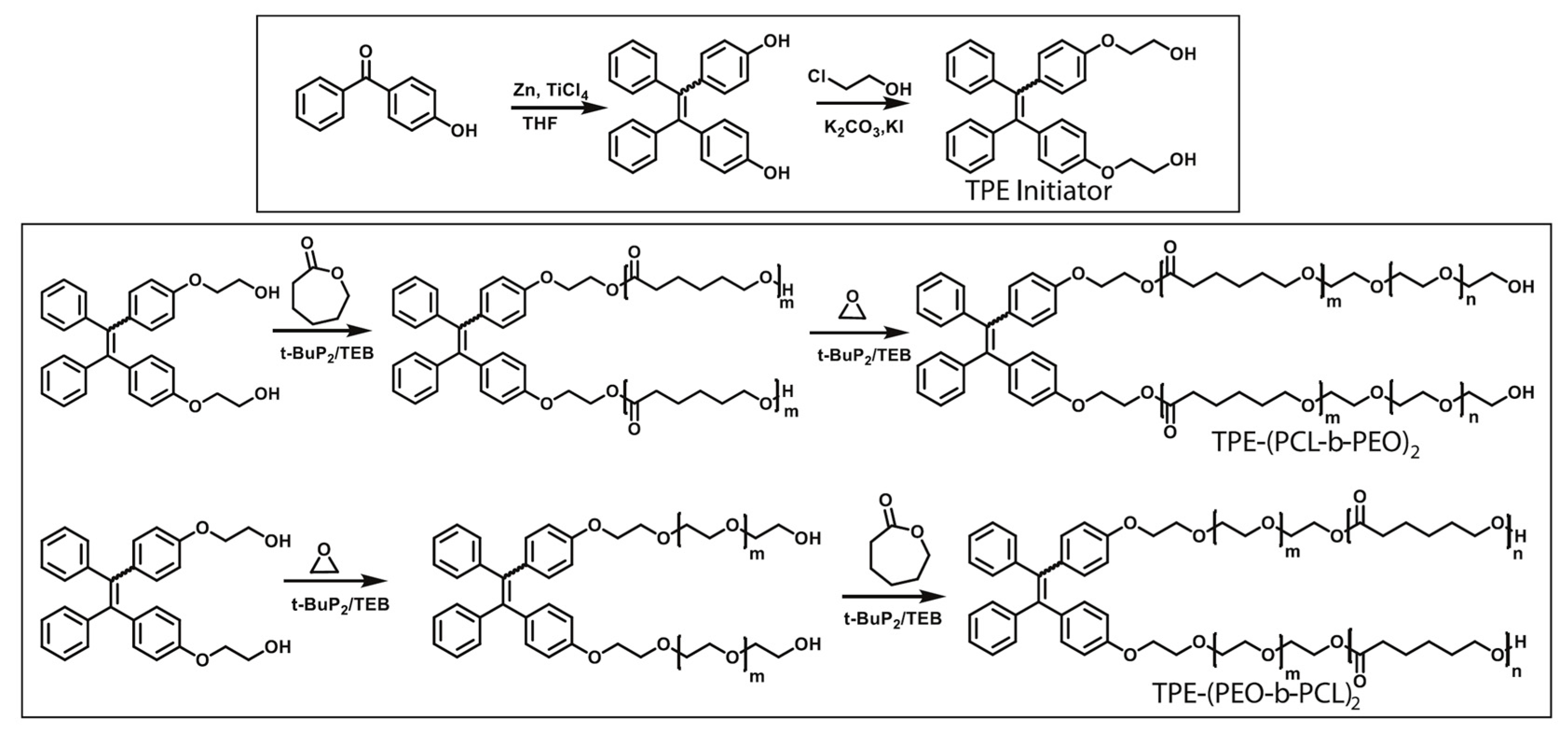
2. Synthesis and Characterization of PEO–PCL Block and Graft Copolymers
3. Drug Delivery Systems
3.1. Micelles
3.2. Polymeric Nanoparticles
3.3. Hybrid Polymer-Lipid Nanopartilces
4. Technology of PEO-PCL Based Nanosystems for Drug Delivery
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pippa, N.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, D. Polymer Self-assembled nanostructures as innovative drug nanocarrier platforms. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 2788–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, P.; Baumann, P.; Enea, R.; Onaca, O.; Palivan, C.; Meier, W. Polymeric vesicles: From drug carriers to nanoreactors and artificial organelles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiserman, A.; Koliada, A.; Zayachkivska, A.; Lushchak, O. Nanodelivery of natural antioxidants: An anti-aging perspective. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 7, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Holkar, A.; Srivastava, S. Protein-polyelectrolyte complexes and micellar assemblies. Polymers 2019, 22, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pippa, N.; Gazouli, M.; Pispas, S. Recent advances and future perspectives in polymer-based nanovaccines. Vaccines 2021, 9, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Gong, C.; Gou, M.; Fu, S.; Guo, Q.; Shi, S.; Luo, F.; Guo, G.; Qiu, L.; Qian, Z. Biodegradable poly (ɛ-caprolactone)–poly (Ethylene glycol) copolymers as drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 381, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondrinos, M.J.; Dembzynski, R.; Lu, L.; Byrapogu, V.K.; Wootton, D.M.; Lelkes, P.I.; Zhou, J. Porogen-based solid freeform fabrication of polycaprolactone–calcium phosphate scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4399–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.T.; Lee, Y.-K.; Han, J.K.; Byun, Y. Improved blood compatibility by sustained release of heparin–deoxycholic acid conjugates in a PCL–PEG multiblock copolymer matrix. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2002, 13, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elistratova, A.A.; Gubarev, A.S.; Lezov, A.A.; Vlasov, P.S.; Solomatina, A.I.; Liao, Y.C.; Chou, P.T.; Tunik, S.P.; Chelushkin, P.S.; Tsvetkov, N.V. Amphiphilic Diblock Copolymers Bearing Poly(Ethylene glycol) Block: Hydrodynamic Properties in Organic Solvents and Water Micellar Dispersions, Effect of Hydrophobic Block Chemistry on Dispersion Stability and Cytotoxicity. Polymers 2022, 14, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.; Zheng, X.; Men, K.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Luo, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Y.; et al. Poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/poly(ethylene glycol)/poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization, and application in doxorubicin delivery. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2009, 113, 12928–12933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.; Wei, X.; Men, K.; Wang, B.; Luo, F.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Y.; Qian, Z. PCL/PEG copolymeric nanoparticles: Potential nanoplatforms for anticancer agent delivery. Curr. Drug Targets. 2011, 12, 1131–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, T.K.; Konkimalla, V.B.J. Poly-є-caprolactone based formulations for drug delivery and tissue engineering: A review. J. Control. Release 2012, 158, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figarol, A.; Gibot, L.; Golzio, M.; Lonetti, B.; Mingotaud, A.-F.; Rols, M.-P. A journey from the endothelium to the tumor tissue: Distinct behavior between PEO-PCL micelles and polymersomes nanocarriers. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1766–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.K.; Cho, K.S.; Cho, J.H.; Choi, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Cheong, I.W. Synthesis and characterization of PEO–PCL–PEO triblock copolymers: Effects of the PCL chain length on the physical property of W1/O/W2 multiple emulsions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 65, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.K.; Lone, S.; Kim, D.D.; Choi, J.H.; Choi, S.W.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Cheong, I.W. Synthesis and characterization of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled PEO–PCL–PEO triblock copolymers for topical delivery. Polymer 2009, 50, 2357–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglio, G.; Nicodemi, F.; Conte, C.; Palumbo, R.; Tirino, P.; Panza, E.; Ianaro, A.; Ungaro, F.; Quaglia, F. Nanocapsules based on linear and Y-shaped 3-miktoarm star-block PEO-PCL copolymers as sustained delivery system for hydrophilic molecules. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 4221–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, S.; Kolev, I.; Miloshev, S.; Apostolova, M.D.; Mateva, R. Synthesis of amphiphilic [PEO (PCL) 2] triarm star-shaped block copolymers: A promising system for in cell delivery. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Huang, B.; Wang, G.; Huang, J. Synthesis of biocompatible tadpole-shaped copolymer with one poly (ethylene oxide)(PEO) ring and two poly (ɛ-caprolactone)(PCL) tails by combination of glaser coupling with ring-opening polymerization. Polymer 2012, 53, 2890–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Xie, D.; Yang, S.; Wang, T.; Feng, L.; Chu, C. Synthesis, characterization, and self-assembly of linear poly (ethylene oxide)-block–poly (propylene oxide)-block–poly (ε-caprolactone)(PEO–PPO–PCL) copolymers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 393, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Ghoroghchian, P.P.; Li, G.; Hammer, D.A.; Therien, M.J. Aqueous self-assembly of poly (ethylene oxide)-block-poly (ε-caprolactone)(PEO-b-PCL) copolymers: Disparate diblock copolymer compositions give rise to nano-and meso-scale bilayered vesicles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 10908–10915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naolou, T.; Meister, A.; Schöps, R.; Pietzsch, M.; Kressler, J. Synthesis and characterization of graft copolymers able to form polymersomes and worm-like aggregates. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 10364–10372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grancharov, G.; Gancheva, V.; Kyulavska, M.; Momekova, D.; Momekov, G.; Petrov, P. Functional multilayered polymeric nanocarriers for delivery of mitochondrial targeted anticancer drug curcumin. Polymer 2016, 84, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gan, Z. Hydrophilic Block Azidation of PCL-b-PEO Block Copolymers from Epichlorohydrin. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhayo, A.M.; Abdul-Karim, R.; Musharraf, S.G.; Malik, M.I. Synthesis and characterization of 4-arm star-shaped amphiphilic block copolymers consisting of poly (ethylene oxide) and poly (ε-caprolactone). RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 28569–28580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Lyu, R.; Yu, L.; Su, S.; Du, F.-S.; Li, Z.-C. Synthesis of a ROS-responsive analogue of poly (ε-caprolactone) by the living ring-opening polymerization of 1, 4-oxathiepan-7-one. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 4574–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Kareem, F.; Rahim, S.; Perveen, S.; Ahmed, S.; Shah, M.R.; Malik, M.I. Architecture based selectivity of Amphiphilic block copolymers of poly (ethylene oxide) and poly (ε-caprolactone) for drug delivery. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 150, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, B.; Qutub, S.; Ladelta, V.; Khashab, N.M.; Hadjichristidis, N. AIE-Based fluorescent triblock copolymer micelles for simultaneous drug delivery and intracellular imaging. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 5243–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefpour Marzbali, M.; Yari Khosroushahi, A. Polymeric micelles as mighty nanocarriers for cancer gene therapy: A review. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 79, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.; Ramsey, J.D.; Kabanov, A.V. Polymeric micelles for the delivery of poorly soluble drugs: From nanoformulation to clinical approval. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 156, 80–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Biswas, S. Polymeric micelles in cancer therapy: State of the art. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, H.; Nakanishi, M.; Kumagai, M.; Jang, W.-D.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. A photo-activated targeting chemotherapy using glutathione sensitive camptothecin-loaded polymeric micelles. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, J.; Wang, F.; Luan, Y. Co-delivery of docetaxel and chloroquine via PEO–PPO–PCL/TPGS micelles for overcoming multidrug resistance. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqr, A.; Vakili, M.R.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lai, R.; Lavasanifar, A. Development of traceable rituximab-modified PEO-polyester micelles by postinsertion of PEG-phospholipids for targeting of B-cell lymphoma. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 18867–18879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.M.; Paiva, I.M.; Vakili, M.R.; Soudy, R.; Agopsowicz, K.; Soleimani, A.H.; Hitt, M.; Kaur, K.; Lavasanifar, A. Traceable PEO-poly (ester) micelles for breast cancer targeting: The effect of core structure and targeting peptide on micellar tumor accumulation. Biomaterials 2017, 144, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglia, F.; Ostacolo, L.; Nese, G.; Canciello, M.; De Rosa, G.; Ungaro, F.; Palumbo, R.; La Rotonda, M.I.; Maglio, G. Micelles based on amphiphilic PCL-PEO triblock and star-shaped diblock copolymers: Potential in drug delivery applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2008, 87, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Liu, L.; Feng, X.; Wang, C.; Shuai, X.; Chen, Y. Molecular nanoworm with PCL core and PEO shell as a non-spherical carrier for drug delivery. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, H.M.; Mahmud, A.; Sharifabadi, A.D.; Lavasanifar, A. Micelles of methoxy poly (ethylene oxide)-b-poly (ɛ-caprolactone) as vehicles for the solubilization and controlled delivery of cyclosporine A. J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkhathlan, Z.; Ali, R.; Qamar, W.; Al-Lawati, H.; Lavasanifar, A. Pharmacokinetic and Tissue Distribution of Orally Administered Cyclosporine A-Loaded poly (ethylene oxide)-block-Poly (ε-caprolactone) Micelles versus Sandimmune® in Rats. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkhathlan, Z.; Ali, R.; Qamar, W.; Lavasanifar, A. Pharmacokinetics of Orally Administered Poly (Ethylene Oxide)-block-Poly (ε-Caprolactone) Micelles of Cyclosporine A in Rats: Comparison with Neoral®. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 21, 177s–191s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Haddadi, A.; Molavi, O.; Lavasanifar, A.; Lai, R.; Samuel, J. Micelles of poly (ethylene oxide)-b-poly (ε-caprolactone) as vehicles for the solubilization, stabilization, and controlled delivery of curcumin. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2008, 86, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, A.; Xiong, X.-B.; Lavasanifar, A. Development of novel polymeric micellar drug conjugates and nano-containers with hydrolyzable core structure for doxorubicin delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, X.; Bao, X.; Huang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Lu, H.; Lu, Z. Mechanisms of cytotoxicity of nickel ions based on gene expression profiles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, A.; Lavasanifar, A. The effect of block copolymer structure on the internalization of polymeric micelles by human breast cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2005, 45, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binkhathlan, Z.; Hamdy, D.A.; Brocks, D.R.; Lavasanifar, A. Development of a polymeric micellar formulation for valspodar and assessment of its pharmacokinetics in rat. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 75, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Meng, L.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, W.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, R. Targeted micelles with chemotherapeutics and gene drugs to inhibit the G1/S and G2/M mitotic cycle of prostate cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, G.; Gan, Z. c (RGDfK) decorated micellar drug delivery system for intravesical instilled chemotherapy of superficial bladder cancer. J. Control. Release 2013, 169, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.-B.; Ma, Z.; Lai, R.; Lavasanifar, A. The therapeutic response to multifunctional polymeric nano-conjugates in the targeted cellular and subcellular delivery of doxorubicin. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, M.L.; Yáñez, J.A.; Remsberg, C.M.; Ohgami, Y.; Kwon, G.S.; Davies, N.M. Paclitaxel prodrugs with sustained release and high solubility in poly (ethylene glycol)-b-poly (ε-caprolactone) micelle nanocarriers: Pharmacokinetic disposition, tolerability, and cytotoxicity. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostacolo, L.; Marra, M.; Ungaro, F.; Zappavigna, S.; Maglio, G.; Quaglia, F.; Abbruzzese, A.; Caraglia, M. In vitro anticancer activity of docetaxel-loaded micelles based on poly (ethylene oxide)-poly (epsilon-caprolactone) block copolymers: Do nanocarrier properties have a role? J. Control. Release 2010, 148, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisey, B.; Ragogna, P.J.; Gillies, E.R. Phosphonium-functionalized polymer micelles with intrinsic antibacterial activity. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavilar, N.; Choi, P. Molecular dynamics study of the diffusivity of a hydrophobic drug Cucurbitacin B in pseudo-poly (ethylene oxide-b-caprolactone) micelle environments. Langmuir 2014, 30, 7798–7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Lavasanifar, A.; Choi, P. Roles of nonpolar and polar intermolecular interactions in the improvement of the drug loading capacity of PEO-b-PCL with increasing PCL content for two hydrophobic cucurbitacin drugs. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2584–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Chang, Y.S.; Jeong, J.M.; Chung, J.K.; Lee, M.C.; Park, K.B.; Lee, S.J. Radioisotope carrying polyethylene oxide–polycaprolactone copolymer micelles for targetable bone imaging. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wulff, J.E.; Moffitt, M.G. Microfluidic processing approach to controlling drug delivery properties of curcumin-loaded block copolymer nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4517–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaghavami, P.S.; Khoei, S.; Khoee, S.; Shirvalilou, S. Folic acid-conjugated magnetic triblock copolymer nanoparticles for dual targeted delivery of 5-fluorouracil to colon cancer cells. Cancer Nano 2022, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Lu, W.; Gao, H.; Hu, K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.; Gao, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, C. Preparation and brain delivery property of biodegradable polymersomes conjugated with OX26. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.J.; Gou, M.L.; Qian, Z.Y.; Dai, M.; Li, X.Y.; Cao, M.; Wang, K.; Zhao, J.; Yang, J.L.; Lu, Y.; et al. One-step preparation of poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanoparticles for plasmid DNA delivery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2008, 86, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, R.T.; Qian, H.Q.; Yang, M.; Zhu, Z.S.; Wu, W.; Qian, X.P.; Yu, L.X.; Jiang, X.Q.; Liu, B.R. Gelatinase-stimuli strategy enhances the tumor delivery and therapeutic efficacy of docetaxel-loaded poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ɛ-caprolactone) nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossen, P.; Québatte, G.; Witzigmann, D.; Prescianotto-Baschong, C.; Dieu, L.-H.; Huwyler, J. Functionalized Solid-Sphere PEG-b-PCL Nanoparticles to Target Brain Capillary Endothelial Cells In Vitro. J. Nanomater. 2016, 7818501, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, T.; Dembele, F.; Beugnet, A.; Sengmanivong, L.; Trepout, S.; Marco, S.; de Marco, A.; Li, M.H. Nanobody-functionalized PEG-b-PCL polymersomes and their targeting study. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 214, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Xia, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, M.; Kang, T.; Miao, D.; Tu, Y.; Pang, Z.; Song, Q.; et al. PEG-co-PCL nanoparticles modified with MMP-2/9 activatable low molecular weight protamine for enhanced targeted glioblastoma therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, H.; Jiang, X.; Gu, J.; Sha, X.; Chen, L.; Law, K.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, X. Angiopep-conjugated poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles as dual-targeting drug delivery system for brain glioma. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4293–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.K.; Mishra, P.; Jain, S.; Mishra, P.; Mishra, A.K.; Agrawal, G.P. Preparation and characterization of HA-PEG-PCL intelligent core-corona nanoparticles for delivery of doxorubicin. J. Drug Target. 2008, 16, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, M.L.; Dai, M.; Li, X.Y.; Yang, L.; Huang, M.J.; Wang, Y.S.; Kan, B.; Lu, Y.; Wei, Y.Q.; Qian, Z.Y. Preparation of mannan modified anionic PCL–PEG–PCL nanoparticles at one-step for bFGF antigen delivery to improve humoral immunity. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 2008, 64, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, M.; Kang, T.; Miao, D.; Gu, G.; Song, Q.; Yao, L.; Hu, Q.; Tu, Y.; Pang, Z.; et al. Lactoferrin-modified PEG-co-PCL nanoparticles for enhanced brain delivery of NAP peptide following intranasal administration. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3870–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surnar, B.; Jayakannan, M. Stimuli-Responsive Poly(caprolactone) Vesicles for Dual Drug Delivery under the Gastrointestinal Tract. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 4377–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Uthaman, S.; Park, I.-K. Utilization of Polymer-Lipid Hybrid Nanoparticles for Targeted Anti-Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2020, 25, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippa, N.; Kaditi, E.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. PEO-b-PCL–DPPC chimeric nanocarriers: Self-assembly aspects in aqueous and biological media and drug incorporation. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 4073–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippa, N.; Naziris, N.; Stellas, D.; Massala, C.; Zouliati, K.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C.; Forys, A.; Marcinkowski, A.; Trzebicka, B. PEO-b-PCL grafted niosomes: The cooperativilty of amphiphilic components and their properties in vitro and in vivo. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 177, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, D.; Dong, X.; Sun, H.; Song, C.; Wang, C.; Kong, D. Folate-modified lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles for targeted paclitaxel delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 2101–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannopoulos, A.; Pippa, N.; Demetzos, C.; Pispas, S.; Radulescu, A. Formation of Uni-Lamellar Vesicles in Mixtures of DPPC with PEO-b-PCL Amphiphilic Diblock Copolymers. Polymers 2021, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gan, L.; Zhu, D.; Xiong, W.; Lv, Y.; Xu, Z.; Hao, Z.; Chen, L. Preparation, characterization and properties of liposome-loaded polycaprolactone microspheres as a drug delivery system. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 395, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibot, L.; Demazeau, M.; Pimienta, V.; Mingotaud, A.F.; Vicendo, P.; Collin, F.; Martins-Froment, N.; Dejean, S.; Nottelet, B.; Roux, C.; et al. Role of Polymer Micelles in the Delivery of Photodynamic Therapy Agent to Liposomes and Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, L.; Su, H.; Zhou, D.; Song, H.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X. Poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(ε-caprolactone)-and phospholipid-based stealth nanoparticles with enhanced therapeutic efficacy on murine breast cancer by improved intracellular drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1791–1804. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.K.; Ho, J.C.S.; Roy, S.; Liedberg, B.; Nallani, M. Facile Mixing of Phospholipids Promotes Self-Assembly of Low-Molecular-Weight Biodegradable Block Co-Polymers into Functional Vesicular Architectures. Polymers 2020, 12, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palominos, M.A.; Vilches, D.; Bossel, E.; Soto-Arriaza, M.A. Interaction between amphipathic triblock copolymers and L-α-dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine large unilamellar vesicles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 148, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chountoulesi, M.; Perinelli, D.R.; Forys, A.; Bonacucina, G.; Trzebicka, B.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. Liquid crystalline nanoparticles for drug delivery: The role of gradient and block copolymers on the morphology, internal organisation and release profile. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 158, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chountoulesi, M.; Perinelli, D.R.; Forys, A.; Chrysostomou, V.; Kaminari, A.; Bonacucina, G.; Trzebicka, B.; Pispas, S.; Demetzos, C. Development of stimuli-responsive lyotropic liquid crystalline nanoparticles targeting lysosomes: Physicochemical, morphological and drug release studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 630, 122440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Techniques/ Methods | Light Scattering (Dynamic, Static, Electrophoretic) |
| (micro-) Differetial Scanning Calorimetry | |
| Fluorescence Spectroscopy | |
| SANS | |
| SAXS | |
| AFM | |
| (cryo-)TEM | |
| % Encapuslation Efficiency | |
| Protein Binding/Interactions | |
| Drug Release studies |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chountoulesi, M.; Selianitis, D.; Pispas, S.; Pippa, N. Recent Advances on PEO-PCL Block and Graft Copolymers as Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery Applications. Materials 2023, 16, 2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062298
Chountoulesi M, Selianitis D, Pispas S, Pippa N. Recent Advances on PEO-PCL Block and Graft Copolymers as Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery Applications. Materials. 2023; 16(6):2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062298
Chicago/Turabian StyleChountoulesi, Maria, Dimitrios Selianitis, Stergios Pispas, and Natassa Pippa. 2023. "Recent Advances on PEO-PCL Block and Graft Copolymers as Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery Applications" Materials 16, no. 6: 2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062298
APA StyleChountoulesi, M., Selianitis, D., Pispas, S., & Pippa, N. (2023). Recent Advances on PEO-PCL Block and Graft Copolymers as Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery Applications. Materials, 16(6), 2298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062298








