Effect of Electrode Induction Melting Gas Atomization on Powder Quality: Satellite Formation Mechanism and Pressure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental and Simulation Methods
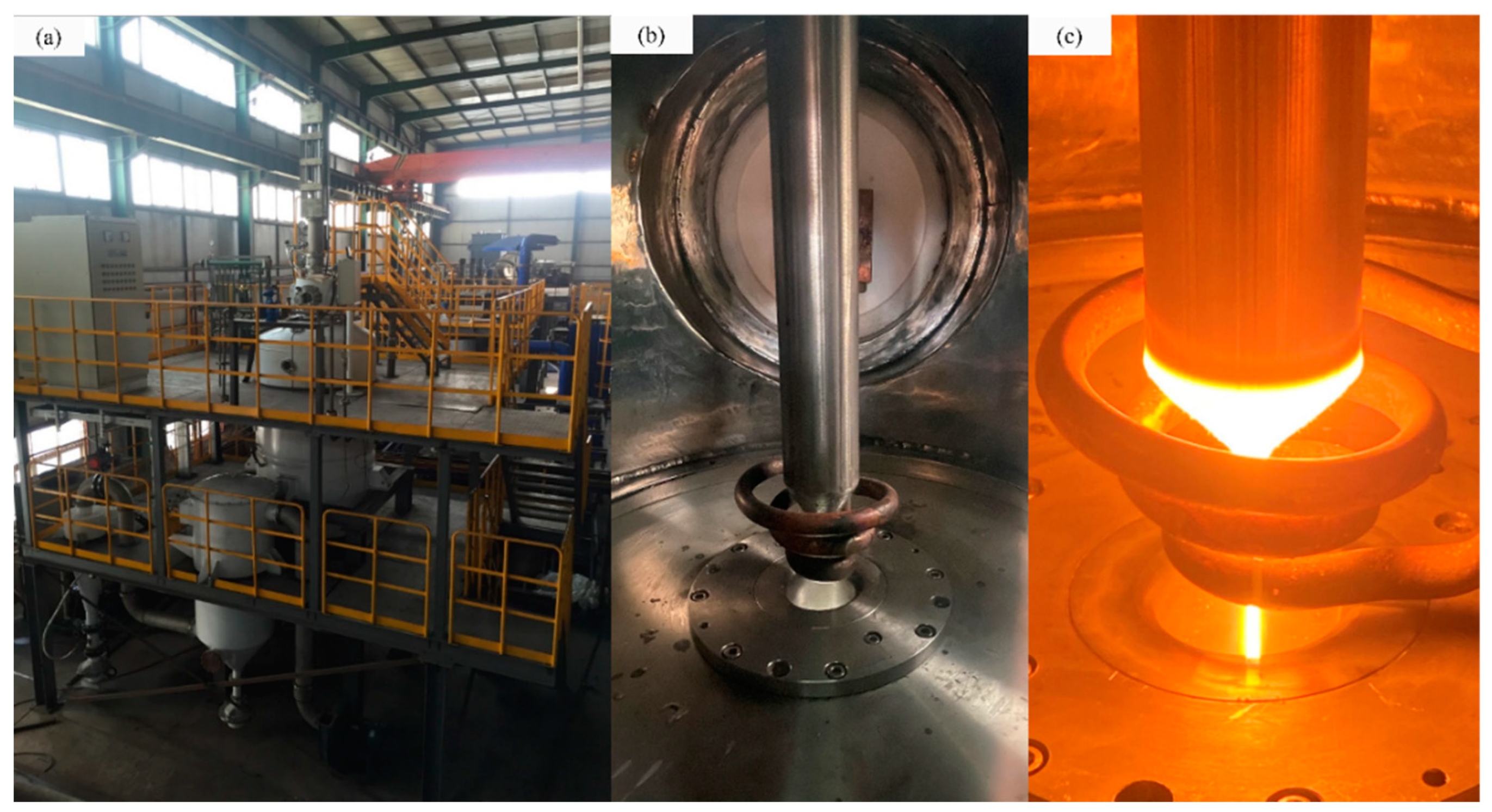
2.1. Experiments
2.2. Numerical Simulation Parameters
2.3. Theoretical Model
3. Results and Discussion
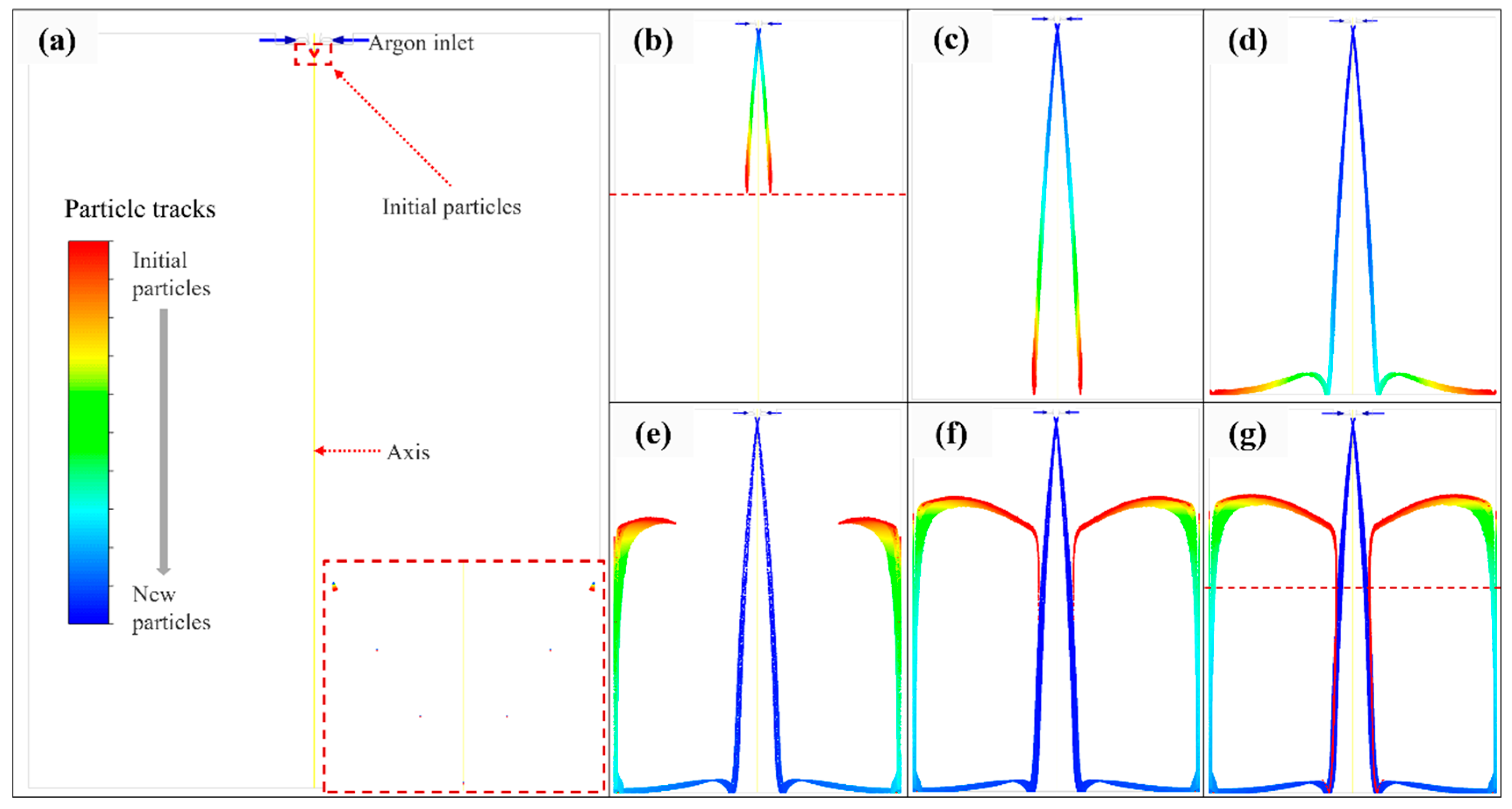
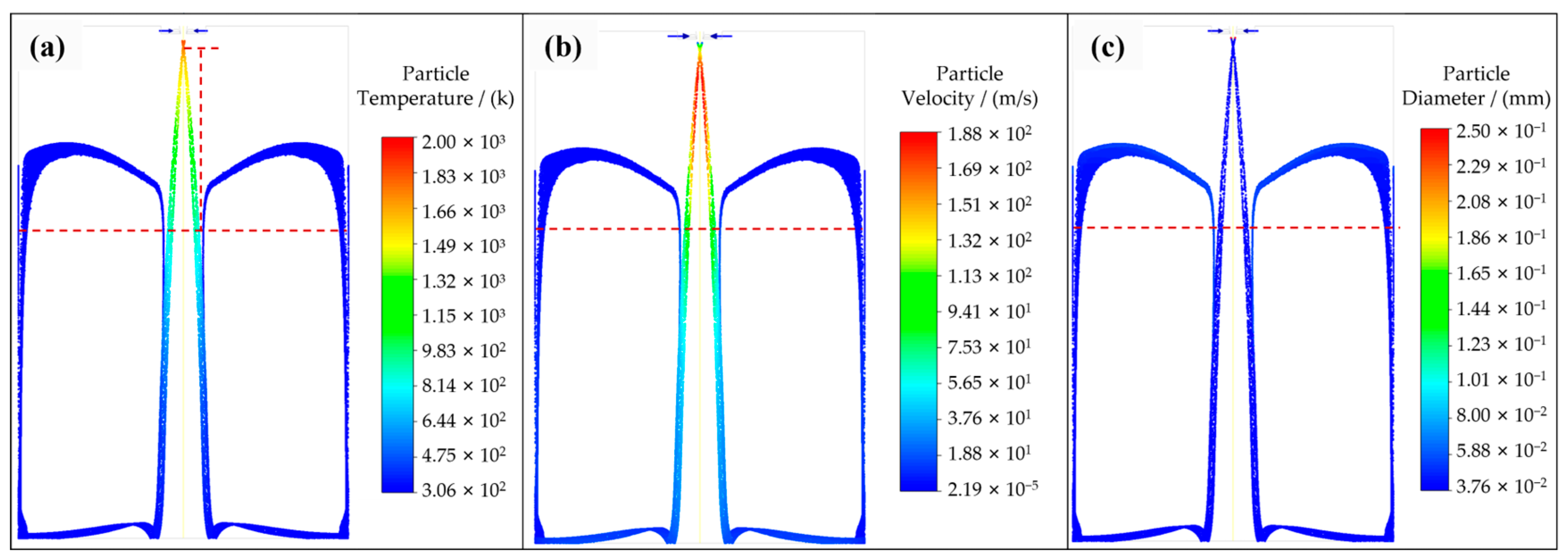
3.1. Satellite Formation
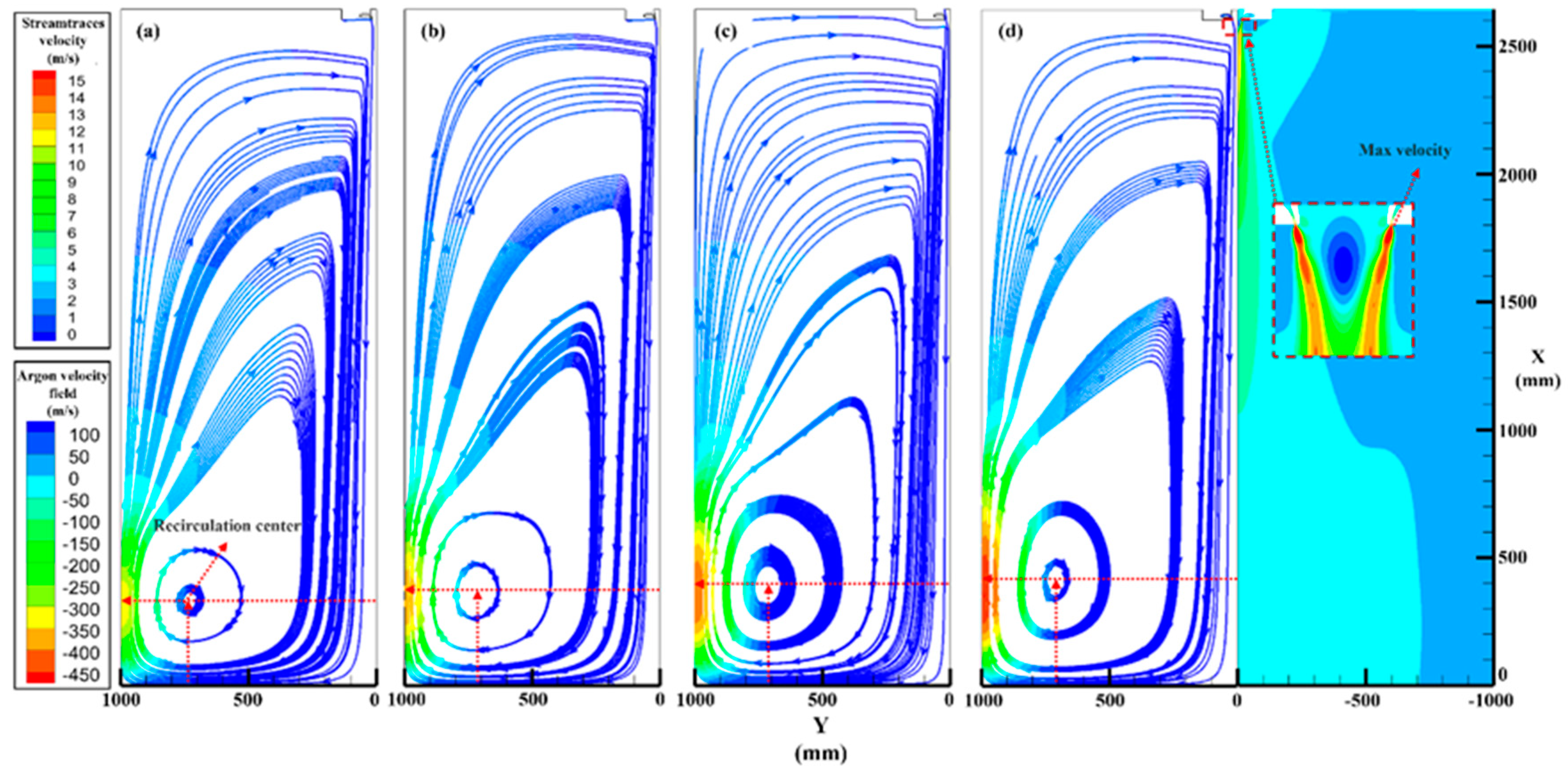
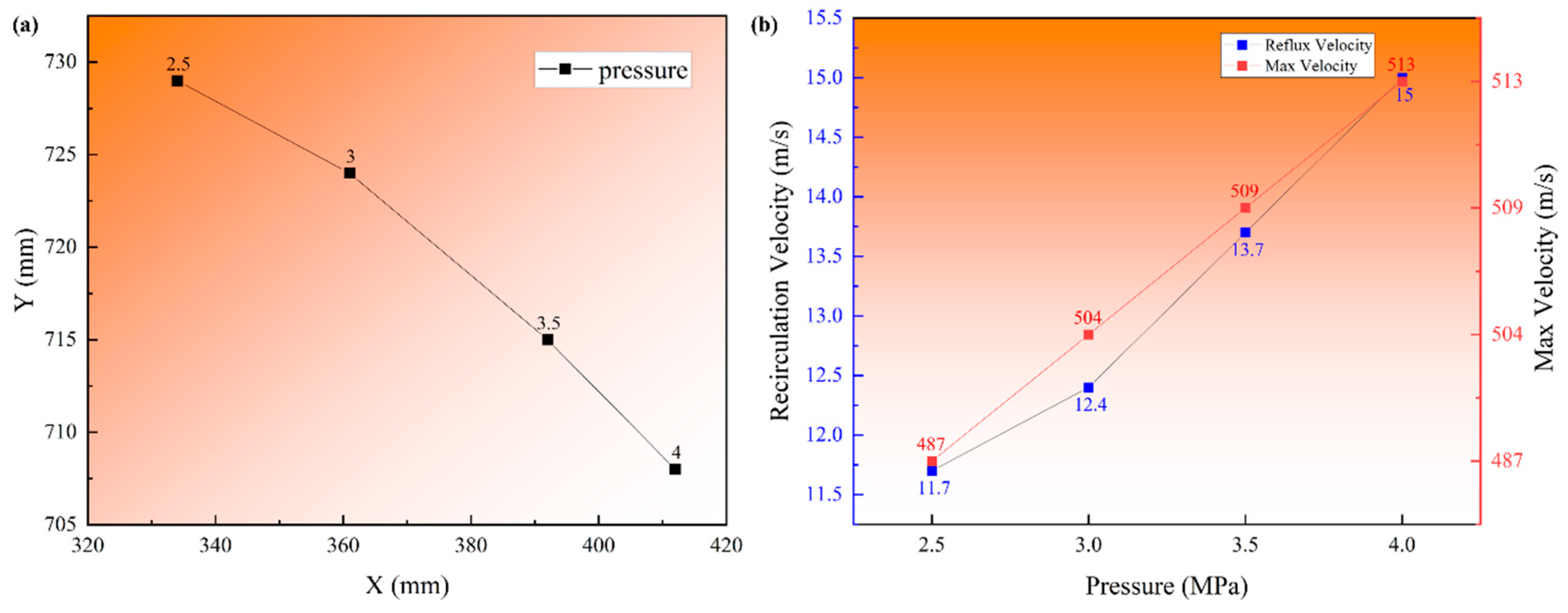
3.2. Argon Recirculation Velocity Field in Different Pressure
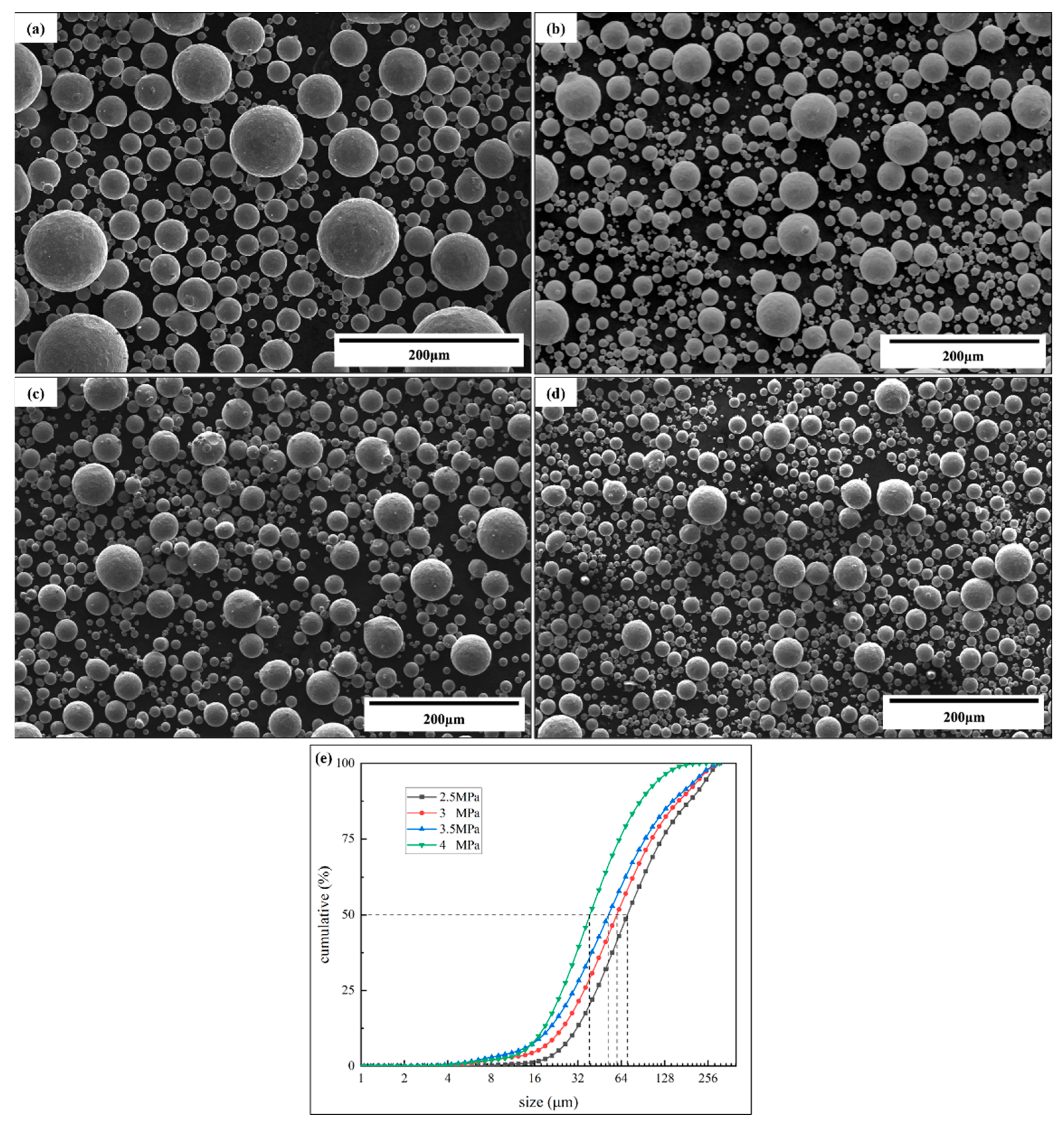
3.3. Atomized Powder Detection
4. Conclusions
- A numerical simulation of particle trajectory verified the formation of satellites, and the simulation results were consistent with the experimental photos. Moreover, the decreasing trend of particle temperature in the numerical simulation was verified by the particle cooling equation, and the accuracy of the simulation work was verified.
- A numerical simulation of the single-phase argon flow field verified the difference in the recirculation zone characteristics at different atomization pressures. The centric position gradually approached the primary atomization area (X from 334 to 412 mm and Y from 729 to 708 mm), and the recirculation velocities increased from 11.7 to 15 m/s, which provides a theoretical basis for the increase in satellite content in high-pressure atomization.
- The detection of atomized powder under different pressures proved the decrease in powder fluidity prepared under high pressure. The Carr compressibility and Hausner’s ratio increased from 11% to 18% and from 1.13 to 1.22, and the Hall flow rate increased from 13.3 to 16.8 s/(50 g), which indicates that the powder fluidity decreased with the pressure increase.
- Moreover, this work indicates that the selection of pressure should consider the adverse effects caused by the increase in satellite content and the decrease in powder quality under high pressure, and the appropriate atomization pressure should be selected comprehensively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Mass density (kg·m−3) | |
| Time (s) | |
| Velocity momentum (m·s−1) | |
| Axial coordinate | |
| Axial velocity (m·s−1) | |
| Radial coordinate | |
| Radial velocity (m·s−1) | |
| Static pressure (Pa) | |
| Viscous stress tensor | |
| Gravitational acceleration (m·s−2) | |
| Surface tension (N·m−1) | |
| Internal energy of the material (J) | |
| Enthalpy of species (J) | |
| Diffusive flux of species (kg·(m2·s)−1) | |
| The viscous dissipation term | |
| Gas density (kg·m−3) | |
| Relative velocity of gas and droplet (m·s−1) | |
| Particle diameter (m) | |
| Surface tension of the molten droplet (N·m−1) |
References
- Bojarevics, V.; Dughiero, F.; Roy, A.; Pericleous, K. Numerical model of electrode induction melting for gas atomization. COMPEL-Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2011, 30, 1455–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.F.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Zou, H.P.; Liu, Z.Q.; Chen, J.; Li, S.K.; Zhang, D.T. Characterization of spherical AlSi10Mg powder produced by double-nozzle gas atomization using different parameters. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Tong, H.; Yang, F.; Cheng, C. Plasma-assisted preparation and characterization of spherical stainless steel powders. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 252, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, C.-R.; Zhang, X.-J.; Wang, J.-B.; Li, Y.-J. Design and evaluation of a Laval-type supersonic atomizer for low-pressure gas atomization of molten metals. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2014, 21, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.W.; Chen, S.Y.; Sun, M.; Liang, J.; Liu, C.S.; Wang, M. Atomization simulation and preparation of 24CrNiMoY alloy steel powder using VIGA technology at high gas pressure. Powder Technol. 2020, 367, 724–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.L.; Attallah, M.M.; Wu, X.H.; Andrews, P. Influence of hot isostatic pressing temperature on microstructure and tensile properties of a nickel-based superalloy powder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 564, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, M.; Ludwig, N. Einrichtung zum Herstellen von Pulvern aus Metallen. DE 4102101C2, 18 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Q.; Xu, J.; Mao, W.; Lu, L.; He, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W. A novel crucible-less inert gas atomisation method of producing titanium powder for additive manufacturing. Powder Metall. 2018, 62, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerling, R.; Hohmann, M.; Schimansky, F.P. Gas atomization of high melting reactive metals by a crucible- and ceramic-free technique. Mater. Sci. Forum 2007, 539–543, 2693–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zheng, Z.; Chang, L.T.; Xu, L.; Cui, Y.Y.; Yang, R. Characterization of tial pre-alloyed powder and its densification microstructure. Acta Metall. Sin. 2011, 47, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, K.K.; Liu, C.S.; Chen, S.Y.; Dong, H.H.; Wang, S.Y. High pressure EIGA preparation and 3D printing capability of Ti-6Al-4V powder. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, G.M.; Li, Q.; Dong, X.F.; Xu, Q.D.; Hu, Y.; Li, P. Fabrication Techniques of Spherical-Shaped Metal Powders Suitable for Additive Manufacturing. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2017, 46, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.Y.; Yuan, L.; Wang, L.L.; Cheng, L.Y. Study on the Formability of 3D Printed TC4 Alloy Powder by EIGA. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Frontiers of Materials Synthesis and Processing, Sanya, China, 9 October 2019; Volume 493. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, C.; Gao, C.; Liu, R.; Chen, J.; Xiao, Z. characterization of ti6al4v powders produced by different methods for selective electron beam melting. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B-Metall. 2019, 55, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Y.; Tang, H.P.; Chen, G.; Yin, J.O.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Li, Z.F.; Tan, P. Preparation of TC4 Powder for 3D Printing and Characterization of Synchrotron Radiation CT. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2018, 47, 3853–3859. [Google Scholar]
- Özbilen, S. Satellite formation mechanism in gas atomised powders. Powder Metall. 1999, 42, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achelis, L.; Uhlenwinkel, V. Characterisation of metal powders generated by a pressure-gas-atomiser. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2008, 477, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xie, H.W.; Wang, L.; Luo, J.W.; Cai, Y.X. Production of Fe-Si-Al-Ni-Ti soft magnetic alloy powder by inert-gas atomization. Chin. Mater. Conf. 2012, 27, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Zou, H.P.; Li, S.K.; Li, A.H. Preparation and Characterization of Fine 316L Stainless Steel Powders Prepared by Gas Atomization. In Proceedings of the Chinese Materials Conference (CMC), Yinchuan, China, 6–12 July 2017; pp. 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zeoli, N.; Gu, S. Numerical modelling of droplet break-up for gas atomisation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2006, 38, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.H.; Ge, C.C. Computational fluid dynamic investigation of the primary and secondary atomization of the free-fall atomizer in electrode induction melting gas atomization process. Acta Phys. Sin. 2018, 67, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Lena, C.; Djambazov, G.; Pericleous, K. Tms, Modelling metal powder production by the gas atomisation process. Mater. Charact. Comput. Model. 2008, 2, 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Wang, H.Z.; Gao, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.W. Interaction between high-velocity gas and liquid in gas atomization revealed by a new coupled simulation model. Mater. Des. 2021, 212, 110264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Xia, M.; Ge, C.-C. Consecutive induction melting of nickel-based superalloy in electrode induction gas atomization. Chin. Phys. B 2017, 26, 60201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, J.; Connor, J.; Ridder, S. High-speed cinematography of gas-metal atomization. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 390, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.B.; Ren, X.N.; Xia, M.; Sun, H.T.; Lv, X.A.; Ge, C.C. Study on Powder Characteristics and Effect Factors of Droplets Size During Electrode Induction Melting Gas Atomization. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2020, 49, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Xia, M.; Guo, S.; Wang, J.; Ge, C. Effect of Electrode Induction Melting Gas Atomization Process on Fine Powder Yields: Diameter of Free-Fall Gas Atomizer. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launder, B.E.; Spalding, D.B. Lectures in Mathematical Model of Turbulence; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- ANSYS. ANSYS Fluent Users Guide; ANSYS: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 2181–2354. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.S.; Fan, B.; Gan, P.; Guo, R.F.; Ge, X.Y.; Wang, M.H. Close-coupled nozzle atomization integral simulation and powder preparation using vacuum induction gas atomization technology. Chin. Phys. B 2021, 30, 027502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-G.; Fritsching, U. Process modeling pressure-swirl-gas-atomization for metal powder production. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 239, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeoli, N.; Tabbara, H.; Gu, S. CFD modeling of primary breakup during metal powder atomization. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 6498–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.P.; Rawlinson-Malone, C.F.; Gamble, J.; Nicholson, S.; Tobyn, M. Chapter 10—Applications of Multivariate Analysis to Monitor and Predict Pharmaceutical Materials Properties. In Multivariate Analysis in the Pharmaceutical Industry; Ferreira, A.P., Menezes, J.C., Tobyn, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 235–267. [Google Scholar]

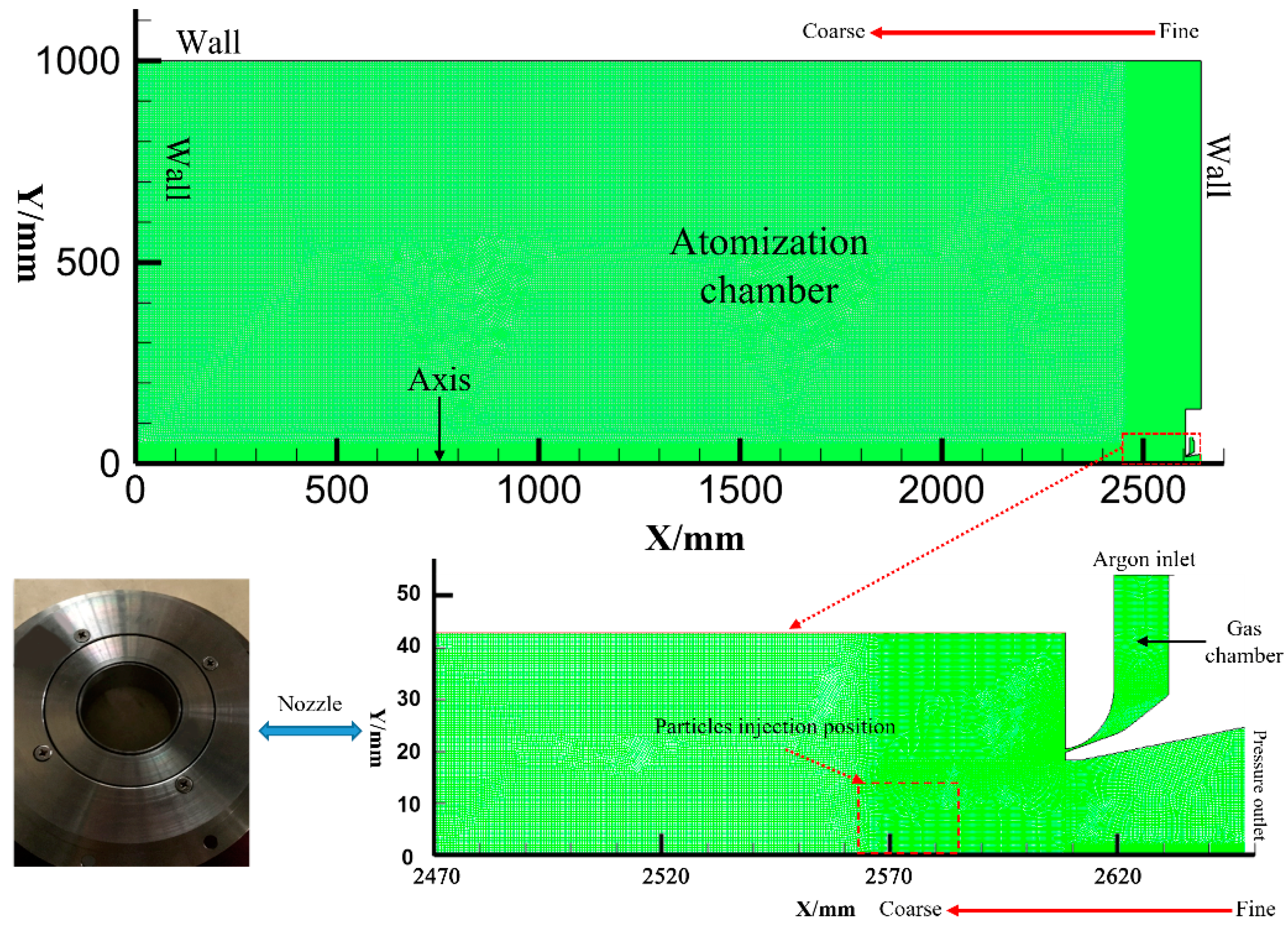
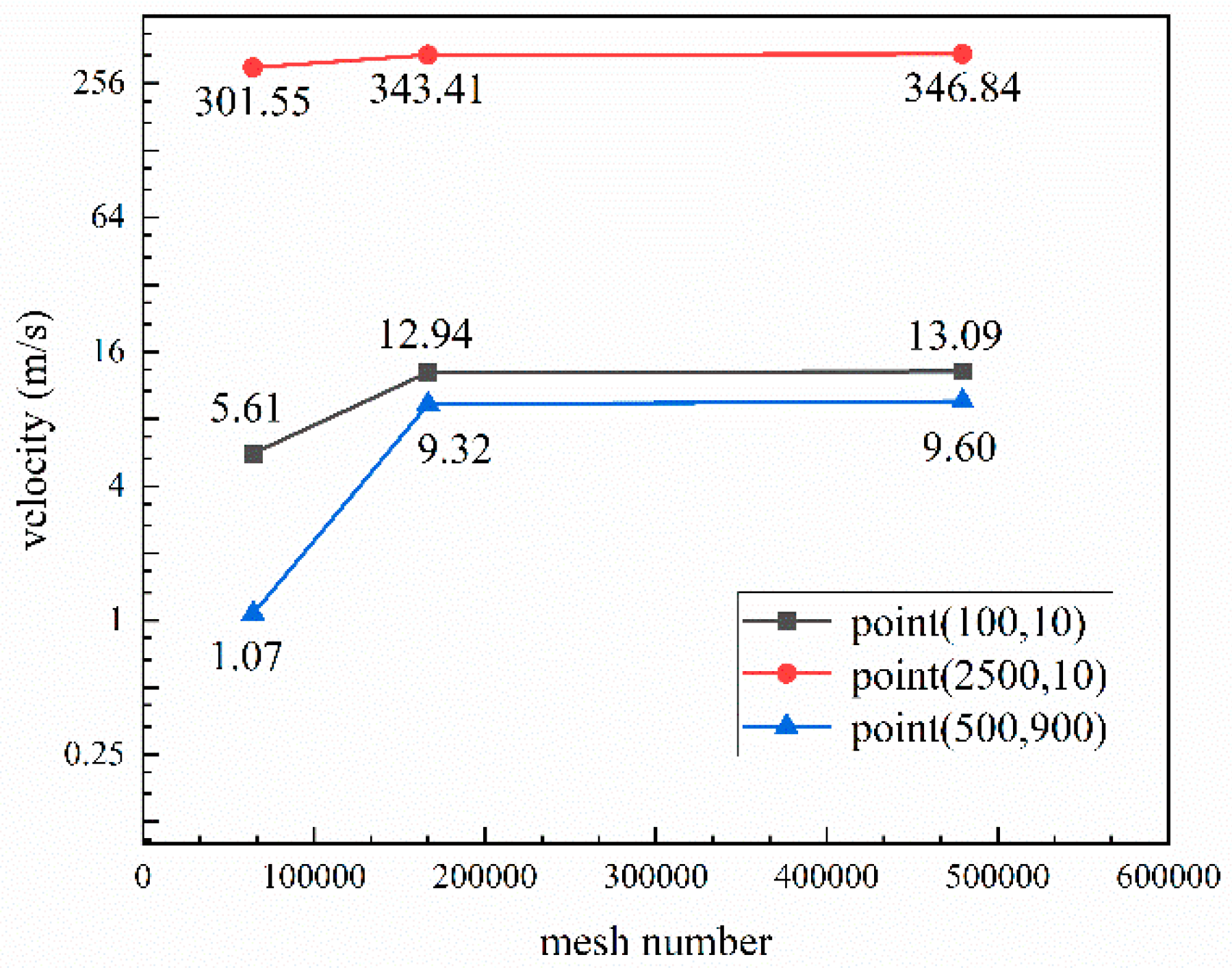
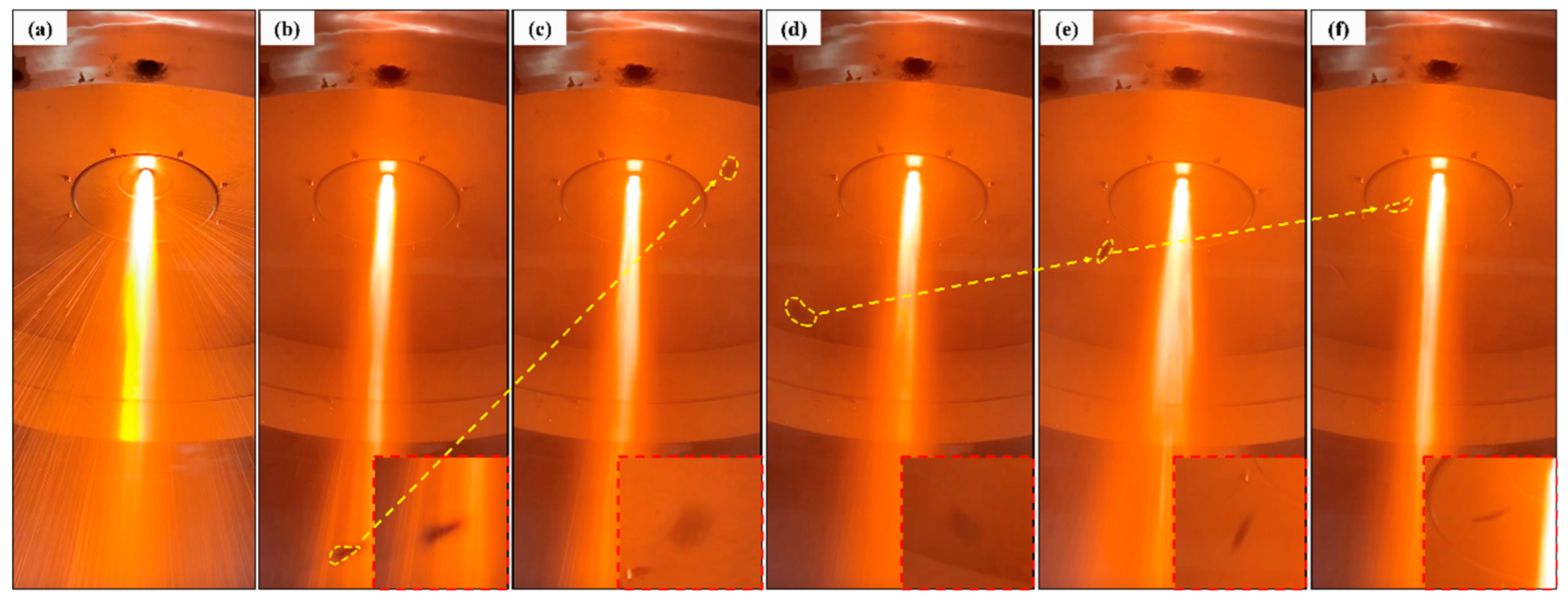
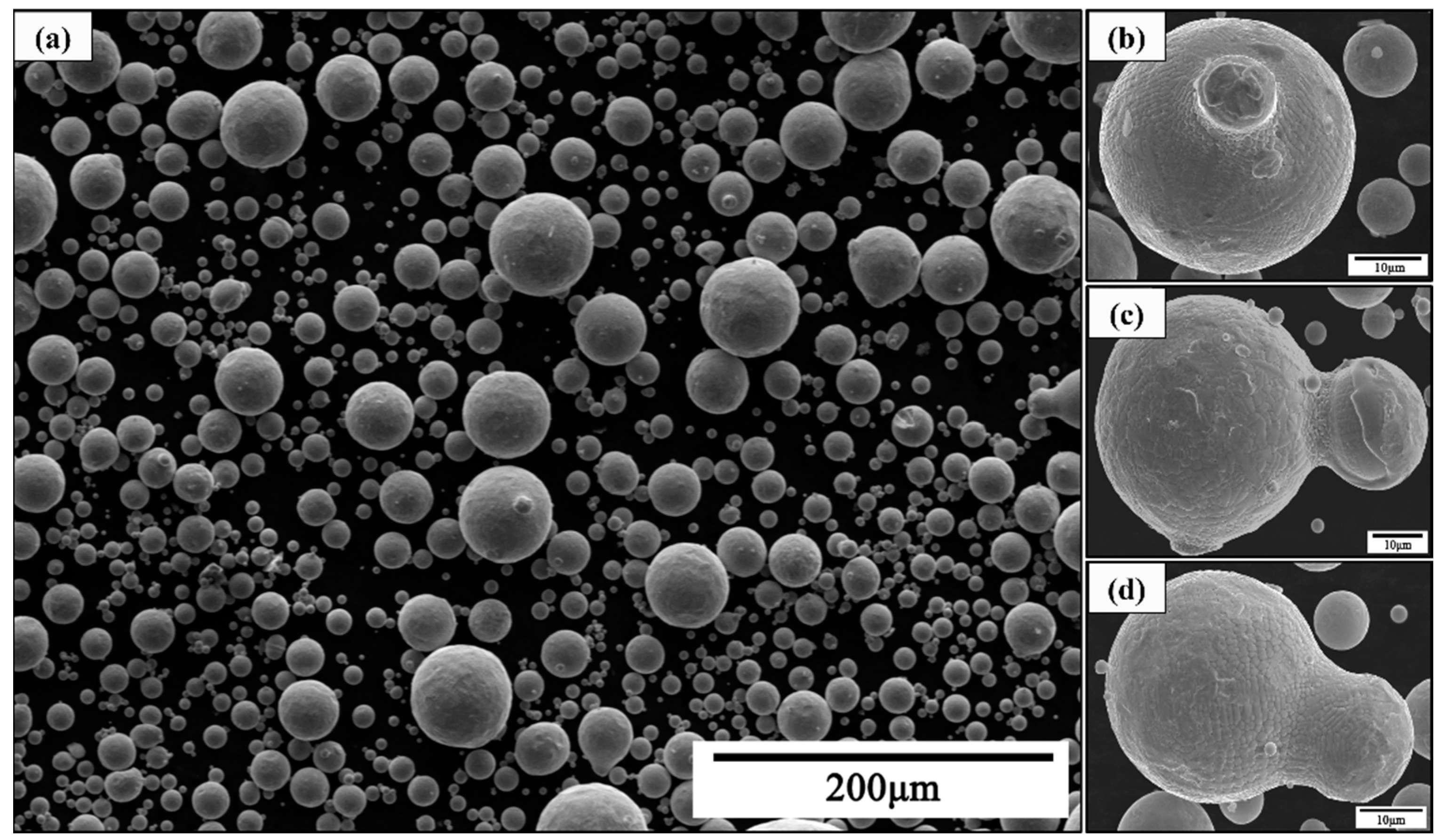
| Component | Ni | Co | Cr | W | Ti | Al | Mo | Ta | Nb | C | B | Zr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content/% | 46.1 | 21.7 | 13.4 | 4.73 | 3.58 | 3.49 | 2.67 | 1.59 | 1.70 | 0.046 | 0.025 | 0.063 |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.63 | kg·m−3 |
| Cp (specific heat) | 520 | j·kg−1·k−1 |
| Thermal conductivity | 1.58 × 10−2 | w·m−1·k−1 |
| Viscosity | 2.13 × 10−5 | kg·m−1·s−1 |
| Molecular weight | 39.9 | kg·kmol−1 |
| Temperature | 300 | K |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific heat | 720 | J·kg−1·K−1 |
| Thermal conductivity | 29.6 | W·m−1·K−1 |
| Viscosity | 0.05 | mPa·s |
| Surface tension | 1.84 | mN·m−1 |
| Density | 7056 | kg·m−3 |
| Melting point | 1683 | K |
| Solidification interval | 1683–1823 | K |
| No. | Argon Pressure/MPa | Powder Size/μm | Apparent Density/g·cm−3 | Tapped Density/g·cm−3 | Flow Index | Hall Flow Rate/s·(50 g)−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carr Compressibility | Hausner’s Ratio | ||||||
| 1 | 2.5 | D50 = 78.58 | 5.12 | 5.76 | 11% | 1.13 | 13.3 |
| 2 | 3.0 | D50 = 66.27 | 5.19 | 5.88 | 12% | 1.13 | 13.8 |
| 3 | 3.5 | D50 = 58.07 | 5.27 | 6.12 | 14% | 1.16 | 15.6 |
| 4 | 4.0 | D50 = 43.19 | 5.20 | 6.32 | 18% | 1.22 | 16.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Xia, M.; Wang, J.; Zhao, B.; Ge, C. Effect of Electrode Induction Melting Gas Atomization on Powder Quality: Satellite Formation Mechanism and Pressure. Materials 2023, 16, 2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062499
Wu J, Xia M, Wang J, Zhao B, Ge C. Effect of Electrode Induction Melting Gas Atomization on Powder Quality: Satellite Formation Mechanism and Pressure. Materials. 2023; 16(6):2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062499
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jialun, Min Xia, Junfeng Wang, Bo Zhao, and Changchun Ge. 2023. "Effect of Electrode Induction Melting Gas Atomization on Powder Quality: Satellite Formation Mechanism and Pressure" Materials 16, no. 6: 2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062499
APA StyleWu, J., Xia, M., Wang, J., Zhao, B., & Ge, C. (2023). Effect of Electrode Induction Melting Gas Atomization on Powder Quality: Satellite Formation Mechanism and Pressure. Materials, 16(6), 2499. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062499








