Phase Field Study on the Spinodal Decomposition of β Phase in Zr–Nb-Ti Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Phase Field Model
2.1. Cahn–Hilliard Equation
2.2. Simulation Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
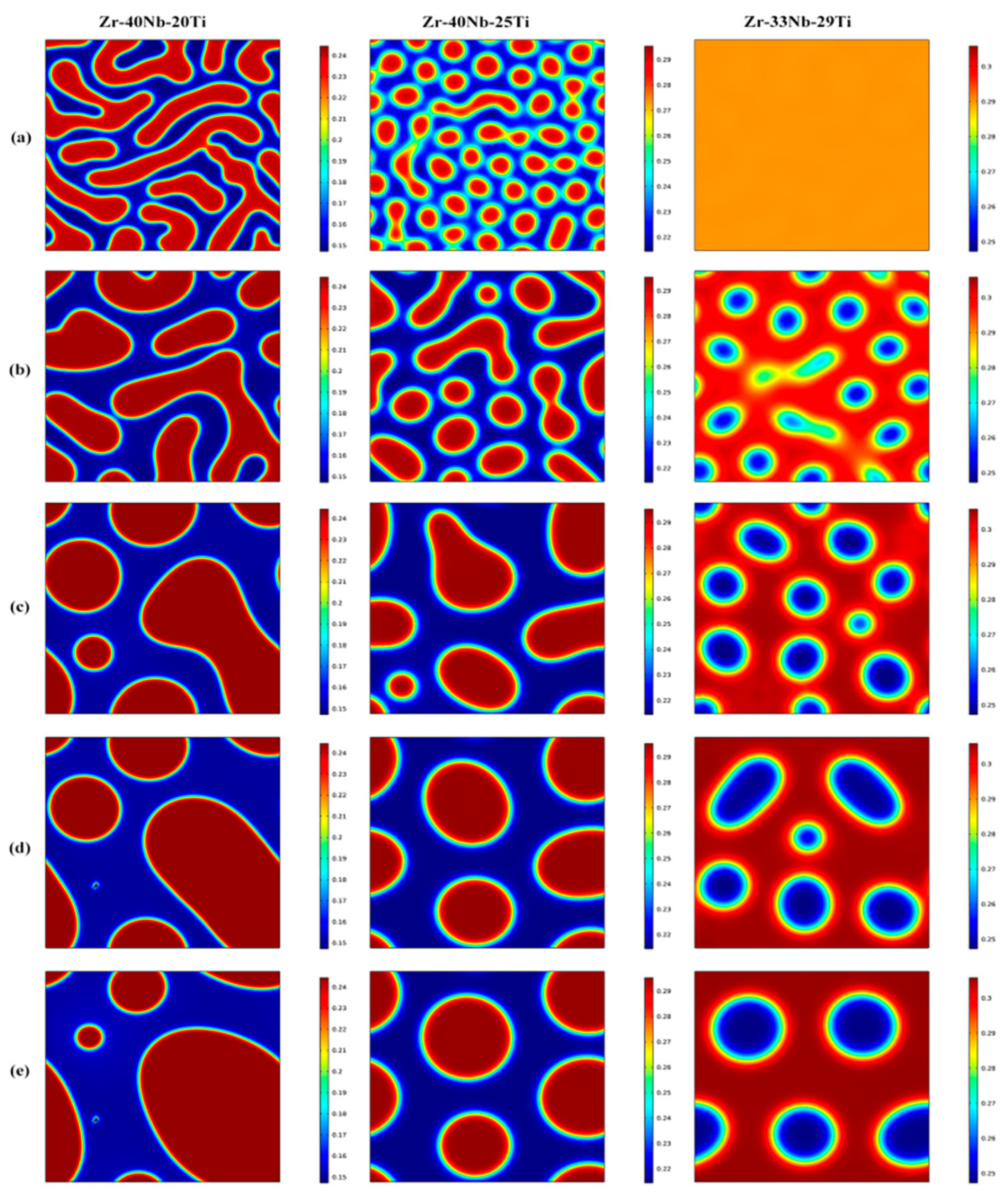
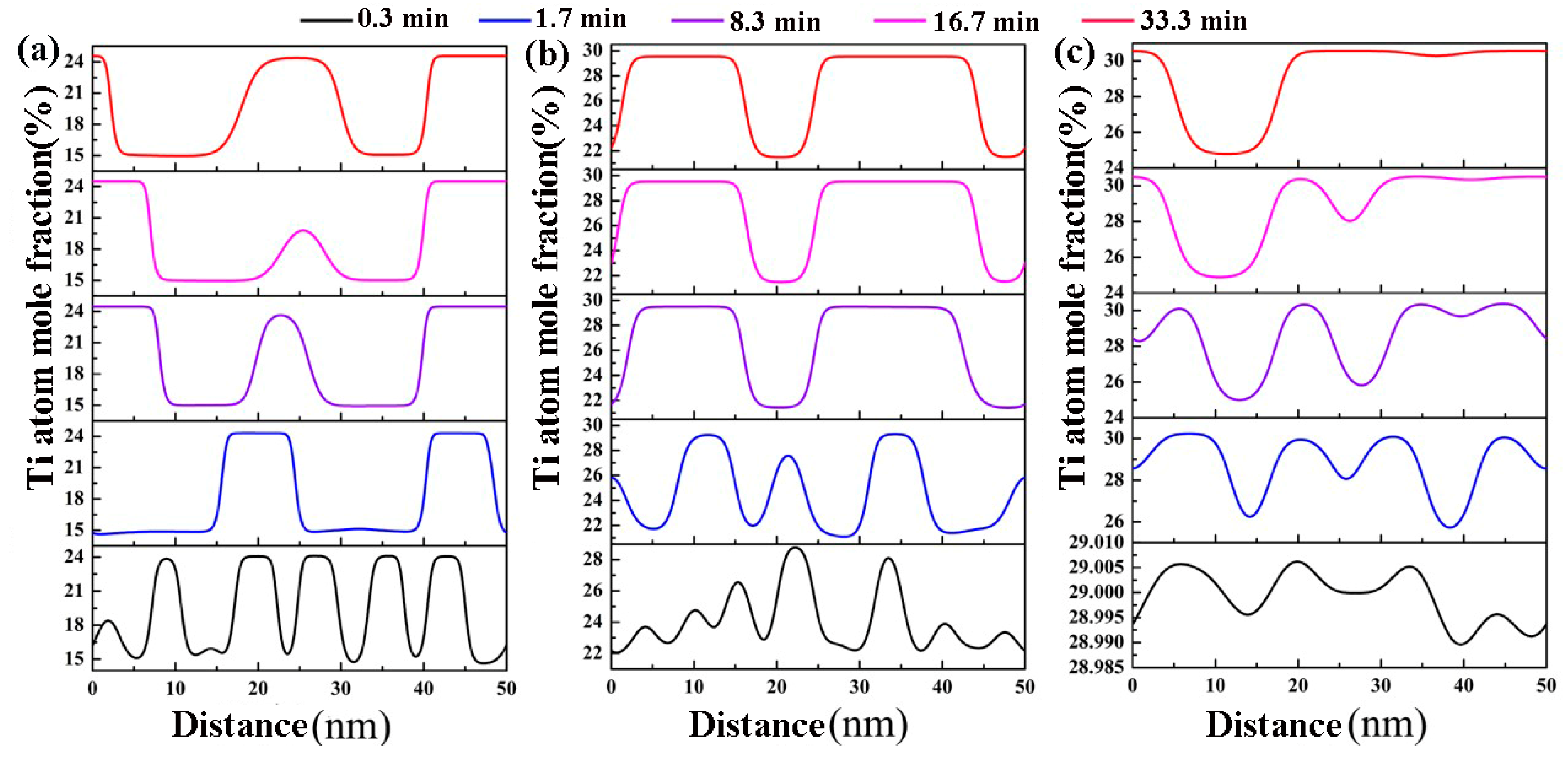
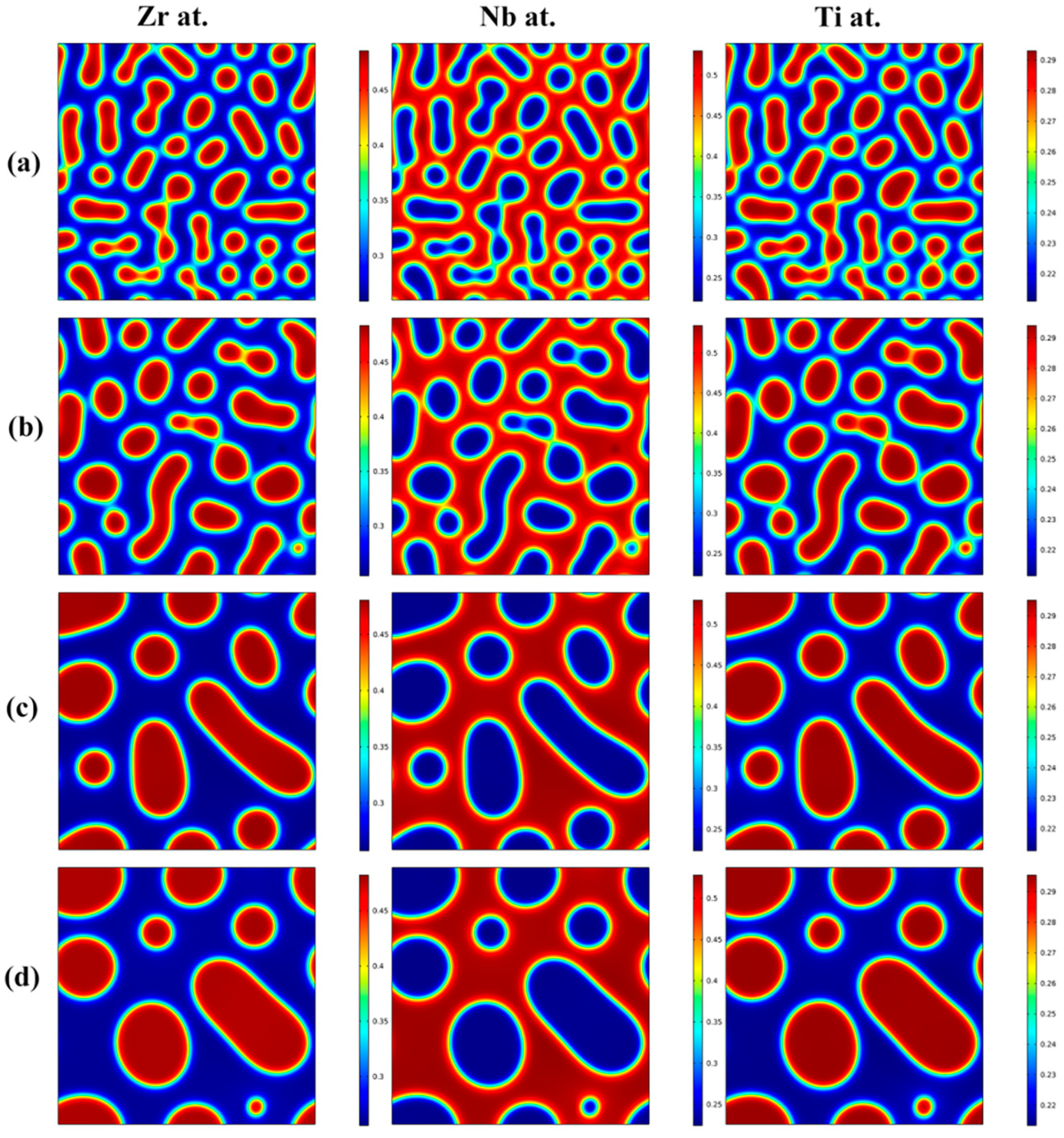
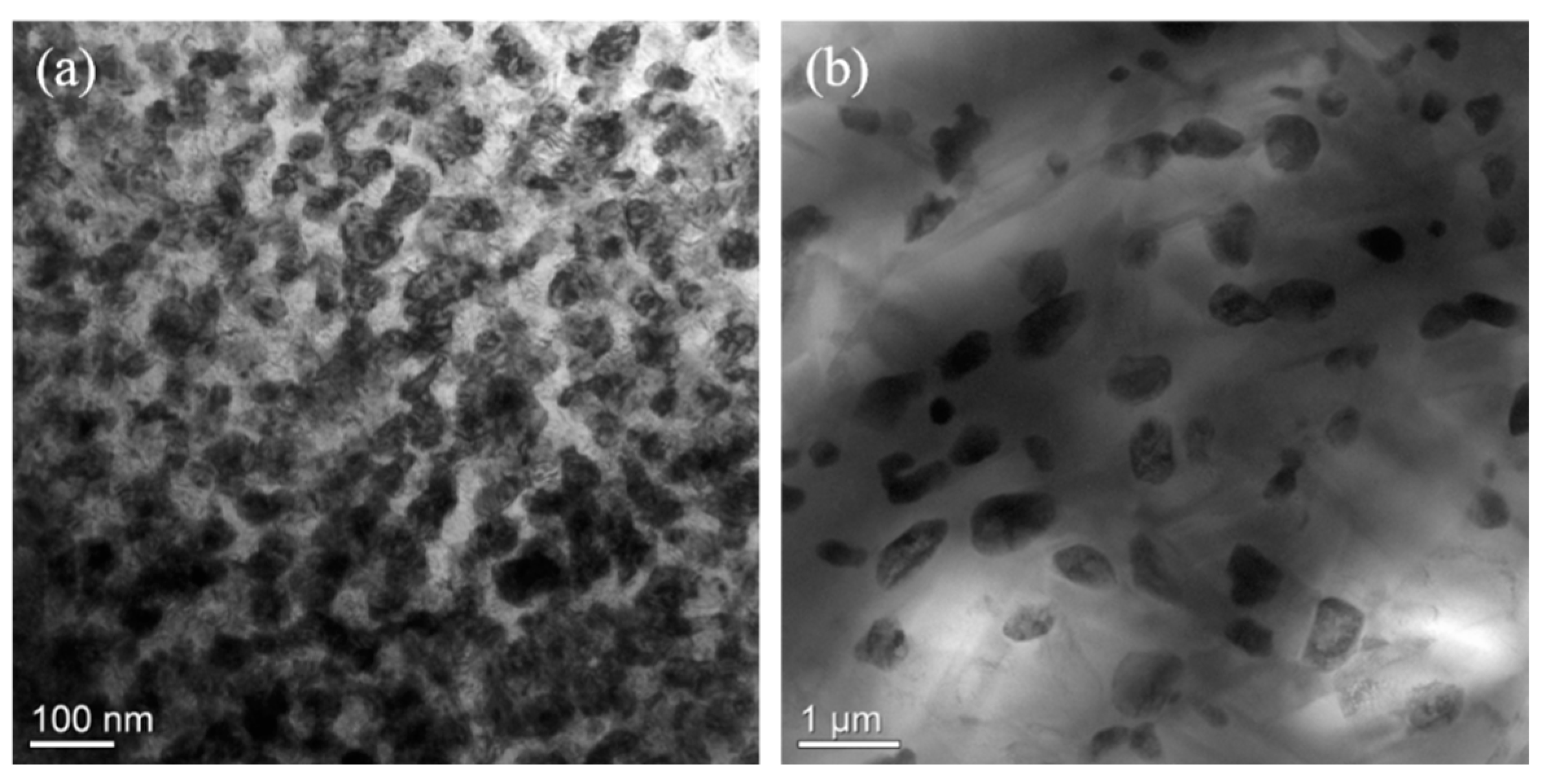
3.1. Effects of the Concentration of Ti on the Spinodal Decomposition of Zr-Nb-Ti Alloys
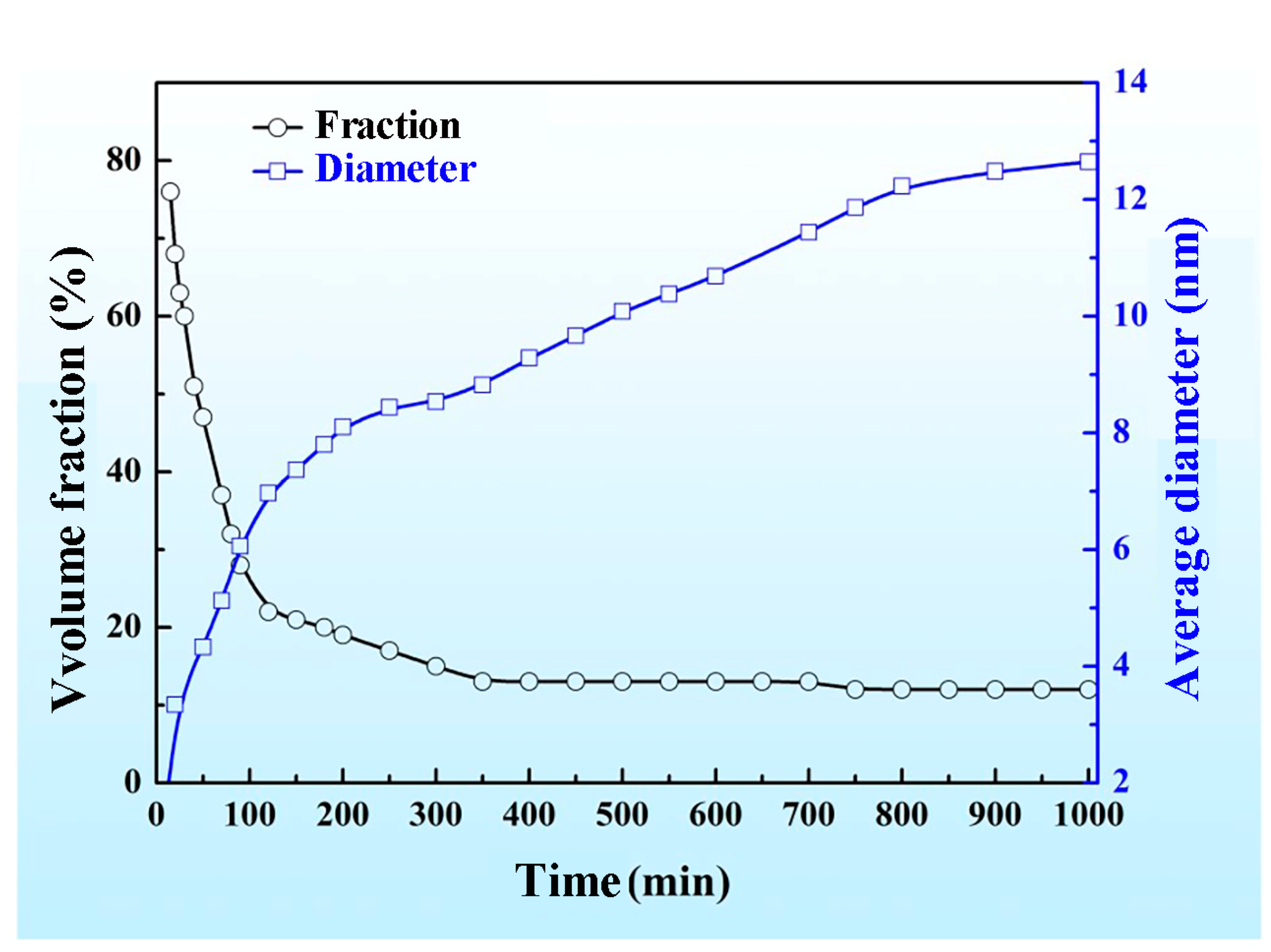
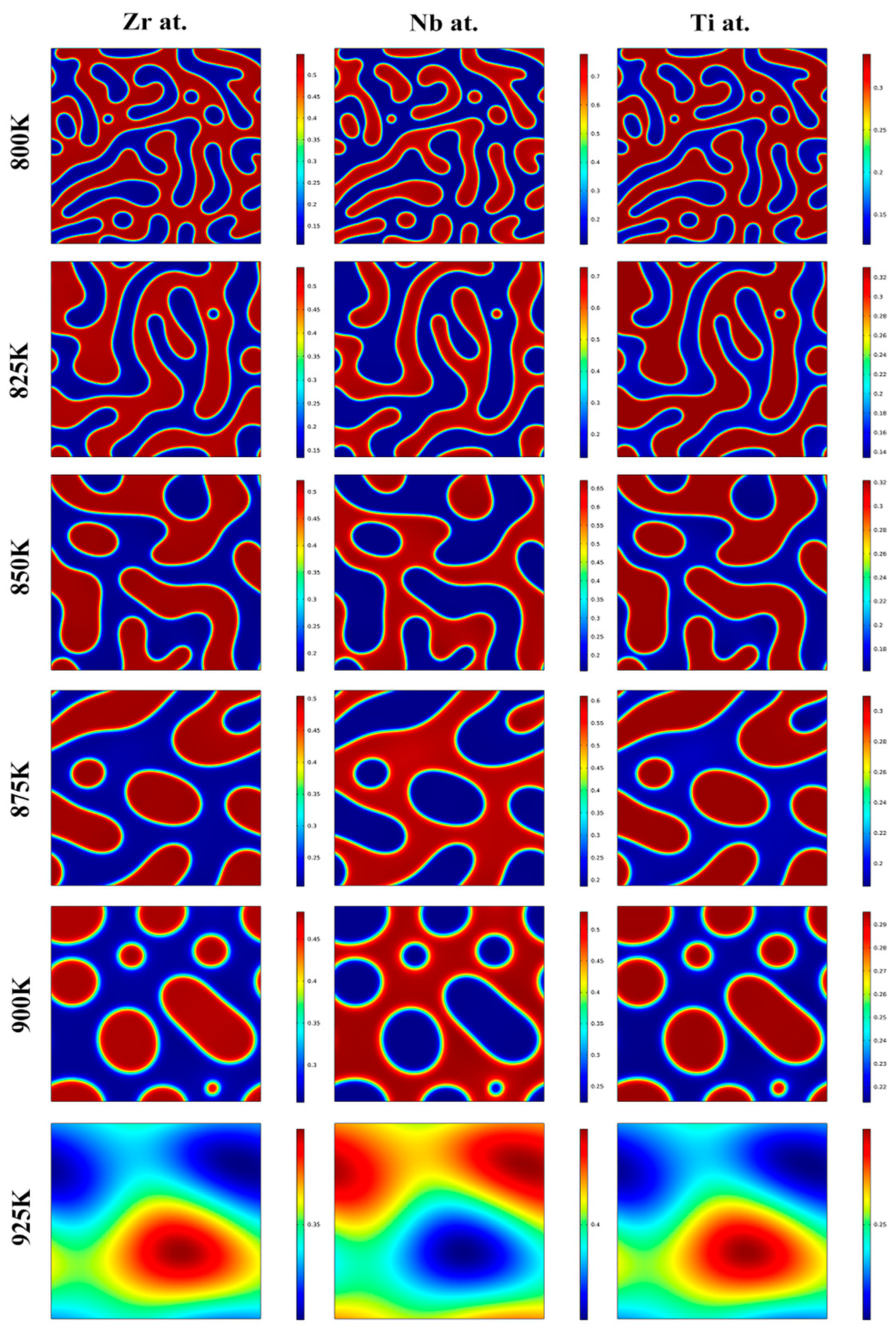
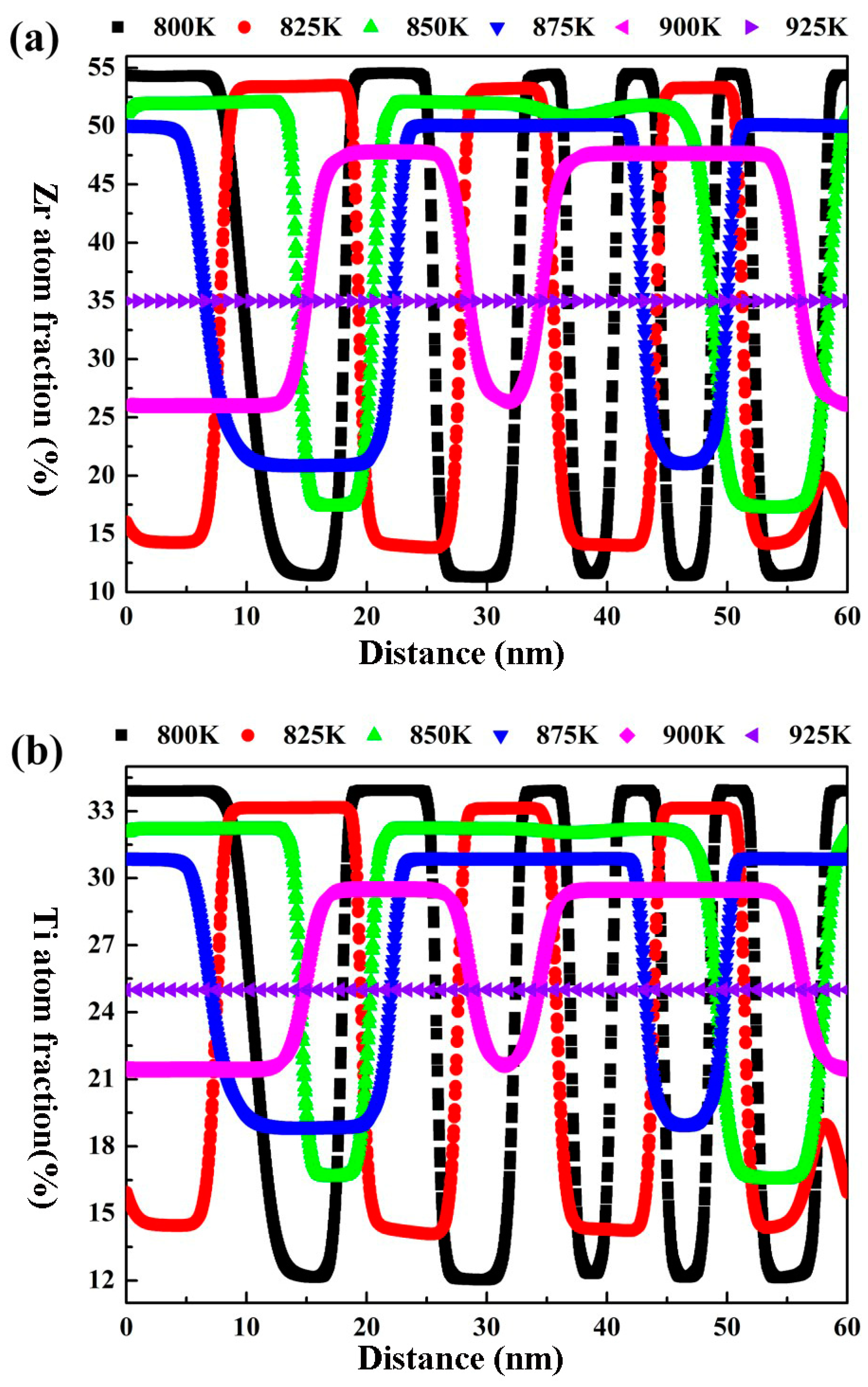
3.2. Effects of Aging Temperature and Time on the Spinodal Decomposition of Zr-Nb-Ti Alloys
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The spinodal decomposition occurred in the Zr-40Nb-20Ti, Zr-40Nb-25Ti and Zr-33Nb-29Ti alloys aged at 900 K with the formation of the Ti-rich phases and Ti-poor phases.
- (2)
- The Ti concentration has important effects on the morphology of the spinodal phases and the wavelength and the amplitude of the concentration modulation. The spinodal phases in the Zr-40Nb-20Ti, Zr-40Nb-25Ti and Zr-33Nb-29Ti alloys aged at 900 K were an interconnected non-oriented maze-like shape, a discrete droplet-like shape and a clustering sheet-like shape in the early aging period, respectively. Increasing the Ti concentration of the alloy increased the wavelength of the concentration modulation; decreasing the Ti concentration decreased the amplitude.
- (3)
- The aging temperature also has important effects on the morphology of the spinodal phases and on the wavelength and amplitude of the concentration modulation. For the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy, with the increase in the aging temperature, the shape of the Zr-rich phase changed from an interconnected non-oriented maze-like shape to a discrete droplet-like shape, and the wavelength of the concentration modulate increased quickly to a stable value, but the amplitude decreased in the alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madikizela, C.; Cornish, L.A.; Chown, L.H.; Möller, H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Zr-4Mo compared to Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 747, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, C.; Yu, Q.; Song, L.; Yang, G.; Zhang, J. New β-type Ti-Zr-V-Nb alloys used for laser-based direct energy deposition: Design, microstructure, and properties. Mater. Charact. 2022, 189, 111917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Yang, S.; Sun, Y.; Gu, Y.; Mercelis, B.; Zhong, S.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Politis, C. In-situ formation of Ti-Mo biomaterials by selective laser melting of Ti/Mo and Ti/Mo2C powder mixtures: A comparative study on microstructure, mechanical and wear performance, and thermal mechanisms. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 115, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Du, P.; Cai, Z.; Li, K.; Bao, W.; Yang, X.; Xie, G. Phase-tunable equiatomic and non-equiatomic Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta high-entropy alloys with ultrahigh strength for metallic biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 117, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Tian, Y.; Xu, G.; Yang, Z.; Liu, L.; Masset, P.J.; Zhang, L. Diffusivities and atomic mobilities in bcc Ti-Zr-Nb alloys. Calphad 2019, 64, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Maimaitijuma, T.; Yu, B.; Li, X.; Xi, G.; Liu, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, T. Ti-Zr-Nb based BCC solid solution alloy containing trace Cu and Ag with low modulus and excellent antibacterial properties. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, K.; Wang, Q.; Dai, P.; Fang, H.; Wu, F.; Guo, Q.; Liaw, P.K.; Hua, N. Novel Ti-Zr-Hf-Nb-Fe refractory high-entropy alloys for potential biomedical applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 906, 164383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lim, J.-H.; Rehman, I.U.; Lee, W.-T.; Kim, J.G.; Oh, J.S.; Lee, T.; Nam, T.-H. Tuning the texture characteristics and superelastic behaviors of Ti–Zr–Nb–Sn shape memory alloys by varying Nb content. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 845, 143243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-C.; Wong, K.-K.; Wu, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-X.; Ho, W.-F. Metastable dual-phase Ti–Nb–Sn–Zr and Ti–Nb–Sn–Fe alloys with high strength-to-modulus ratio. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 30, 103168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Song, K.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, F. Structural characterization and nanoscale strain field analysis of alpha/beta interface layer of a near alpha titanium alloy. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021, 10, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, J.W. On Spinodal Decomposition. Acta Metall. 1961, 9, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.A.; Easterling, K.E. Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys (Revised Reprint); CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Findik, F. Improvements in spinodal alloys from past to present. Mater. Des. 2012, 42, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahn, J.W. Hardening by spinodal decomposition. Acta Metall. 1963, 11, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Song, K.; Shao, H.; Lu, H.; Xu, J. Effect of Nb content on Ti-Mo-Nb alloy materials for neutron high pressure diffraction. Mater. Lett. 2022, 314, 131821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, N.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Ye, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Q.; Brechtl, J.; Liaw, P.K. Mechanical, corrosion, and wear properties of biomedical Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta-Mo high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 861, 157997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yi, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, K.; Liu, J.; Meng, X.; Gao, Z. Effect of thermo-mechanical treatment on Ti-Ta-Hf high temperature shape memory alloy. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2021, 31, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Sun, K.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Meng, X.; Gao, Z.; Cai, W. Tailoring the microstructure, martensitic transformation and strain recovery characteristics of Ti-Ta shape memory alloys by changing Hf content. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussiba, A.; Artzy, A.B.; Shtechman, A.; Ifergan, S.; Kupiec, M. Grain refinement of AZ31 and ZK60 Mg alloys—Towards superplasticity studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 302, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, T. Precipitation hardening in metals. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1999, 15, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, N.F.; Nabarro, F.R.N. An attempt to estimate the degree of precipitation hardening, with a simple model. Proc. Phys. Soc. 2002, 52, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cahn, J.W.; Hilliard, J.E. Spinodal decomposition: A reprise. Acta Metall. 1971, 19, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesiekierski, A.; Ping, D.; Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Munir, K.S.; Yamabe-Mitarai, Y.; Wen, C. Extraordinary high strength Ti-Zr-Ta alloys through nanoscaled, dual-cubic spinodal reinforcement. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozan, S.; Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Ipek, R.; Wen, C. Development of Ti-Nb-Zr alloys with high elastic admissible strain for temporary orthopedic devices. Acta Biomater. 2015, 20, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. Interdiffusion and atomic mobility in bcc Ti-rich Ti-Nb-Zr system. Calphad 2018, 60, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Vargas, O.; Avila-Davila, E.O.; Lopez-Hirata, V.M.; Cayetano-Castro, N.; Gonzalez-Velazquez, J.L. Effect of spinodal decomposition on the mechanical behavior of Fe–Cr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2910–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orthacker, A.; Haberfehlner, G.; Taendl, J.; Poletti, M.C.; Sonderegger, B.; Kothleitner, G. Diffusion-defining atomic-scale spinodal decomposition within nanoprecipitates. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, K.; Koyama, T.; Tsukada, Y. Phase-Field Simulation of Spinodal Decomposition on Metastable Hexagonal Close-Packed Phase in Magnesium-Yttrium-Zinc Alloy. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suwa, Y.; Saito, Y.; Ochi, K.; Aoki, T.; Goto, K.; Abe, K. Kinetics of Phase Separation in Fe-Cr-Mo Ternary Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Tao, X.; Liu, L. Study of low-modulus biomedical beta Ti-Nb-Zr alloys based on single-crystal elastic constants modeling. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 62, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari Kumar, K.C.; Wollants, P.; Delacy, L. Thermodynamic assessment of the Ti-Zr system and calculation of the Nb-Ti-Zr phase diagram. J. Alloys Compd. 1994, 206, 126–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| (K) | 850 875 900 |
| (J/mol) | −1272.064 + 134.71418 − 25.5768 ln − 0.663845 − 0.27880 + 7208 |
| (J/mol) | −8519.353 + 142.045475 − 26.4711 ln + 2.03475 − 3.5012 − 93,399 |
| (J/mol) | −525.539 + 124.9457 − 25.607406 ln − 3.40084 − 9.729 + 25,233 − 7.6143 |
| (J/mol) | 13,045.3 |
| (J/mol) | −9321 + 11.9 |
| (J/mol) | 15,911 + 3.35 |
| (J/mol) | −1000 |
| (J/mol) | −13,000 |
| (J/mol) | 16,800 |
| (m3/mol) | 1.2496 |
| (J/mol) | −171,237.75–115.83 |
| (J/mol) | −131,670.56–133.36 |
| (J/mol) | −135,119.44–148.59 |
| (J/mol) | −358,612.72–84.43 |
| (J/mol) | −104,624.81–163.15 |
| (J/mol) | −395,598.95–82.03 |
| (J/mol) | 14,510.81 |
| (J/mol) | 113,467.29–32.01 T |
| (J/mol) | 43,010.37 + 74.52 T |
| (J/mol) | 41,384.1106–12.57 T |
| (J/mol) | 12,851.76 |
| (J/mol) | 83,103.91 + 50.78 T |
| (nm) | 0.3315 0.357 0.331 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Dai, Y.; Lin, J. Phase Field Study on the Spinodal Decomposition of β Phase in Zr–Nb-Ti Alloys. Materials 2023, 16, 2969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16082969
Yang K, Wang Y, Tang J, Wang Z, Zhang D, Dai Y, Lin J. Phase Field Study on the Spinodal Decomposition of β Phase in Zr–Nb-Ti Alloys. Materials. 2023; 16(8):2969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16082969
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Kun, Yanghe Wang, Jingjing Tang, Zixuan Wang, Dechuang Zhang, Yilong Dai, and Jianguo Lin. 2023. "Phase Field Study on the Spinodal Decomposition of β Phase in Zr–Nb-Ti Alloys" Materials 16, no. 8: 2969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16082969
APA StyleYang, K., Wang, Y., Tang, J., Wang, Z., Zhang, D., Dai, Y., & Lin, J. (2023). Phase Field Study on the Spinodal Decomposition of β Phase in Zr–Nb-Ti Alloys. Materials, 16(8), 2969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16082969






