Ultra-High Sensitivity and Temperature-Insensitive Optical Fiber Strain Sensor Based on Dual Air Cavities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Device Fabrication
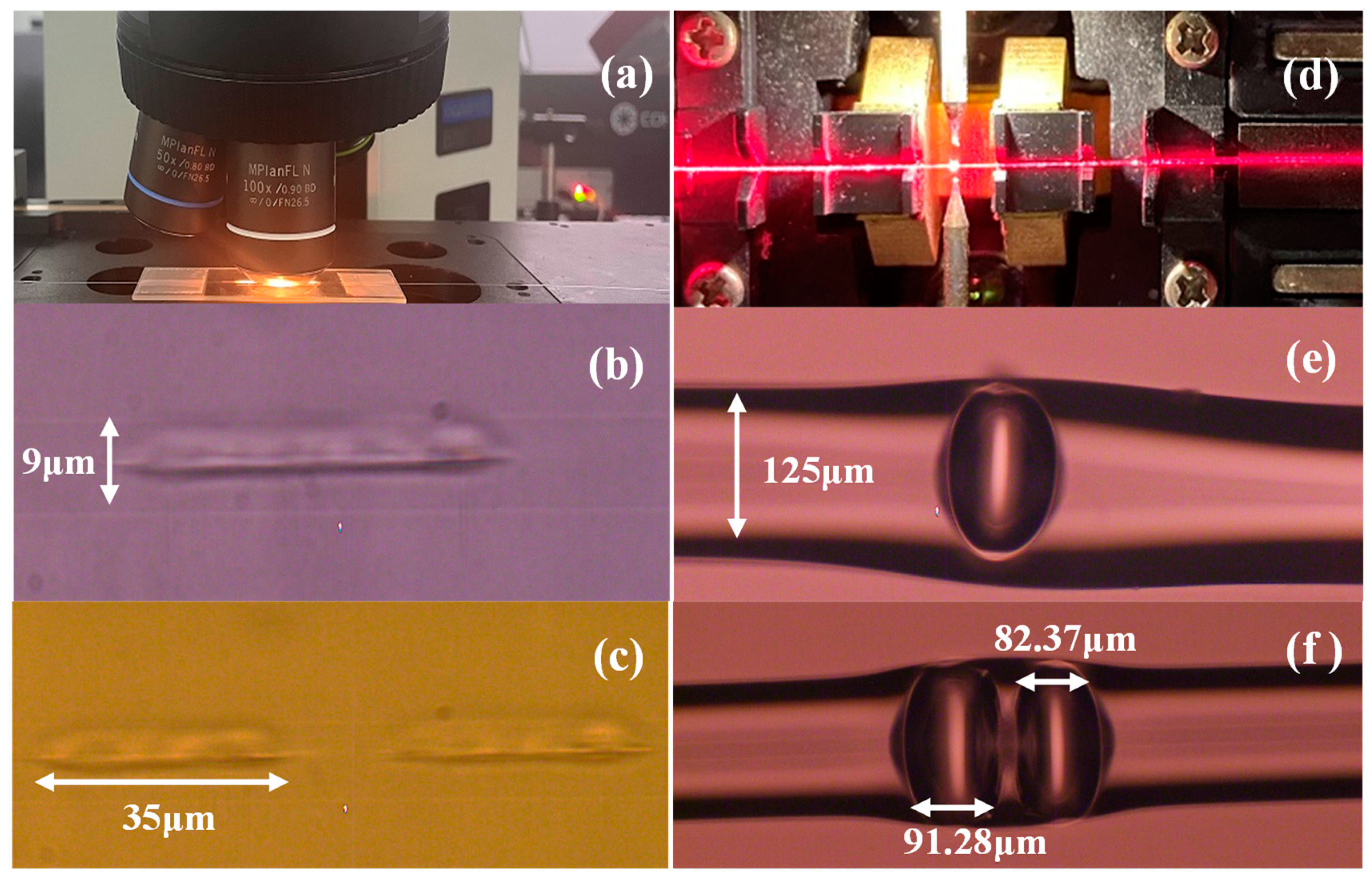
- As illustrated in Figure 1b, a 35 µm short-line structure is inscribed on the fiber core using a femtosecond laser pulse at a scanning speed of 10 µm/s. Each transverse short-line structure is written in just 3.5 s. The same procedure is used to inscribe two short-line structures on the fiber, each 35 µm long and 15 µm apart, as shown in Figure 1c. This process does not create a cavity; it merely modifies the fiber’s refractive index;
- The area where the refractive index has been altered by direct writing with the femtosecond laser is observed using a laser pass-through pen. When the laser travels through the laser-etched zone, it experiences a relatively high insertion loss, producing a bright spot when the laser passes through it, as shown in Figure 1d. The fiber with only one horizontal short structure is placed in a fusion splicer and discharged against the splicer’s center to form an air cavity 95.35 µm wide, as demonstrated in Figure 1e. The first fiber optic sensor containing a single bubble was fabricated. Subsequently, the second fiber sensor with a double bubble is created by discharging a fiber fusion machine in the gap between two short structures, resulting in two air cavities close to each other in a standard SMF with widths of 82.37 µm and 91.28 µm and a spacing of about 21 µm between them, as shown in Figure 1f. Next, we compare the performance of single-bubble and double-bubble fiber sensors.
3. Operation Principle of the Device
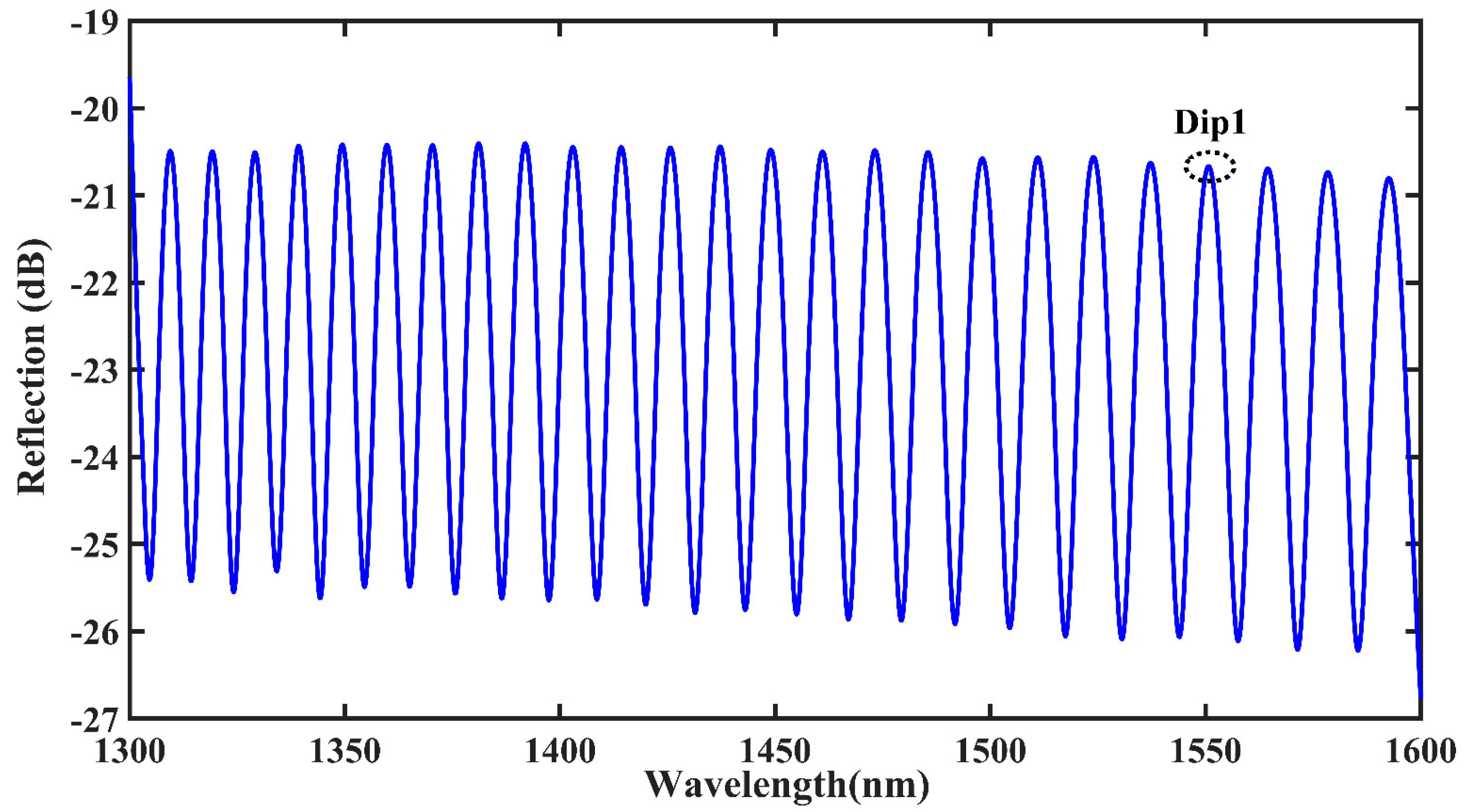
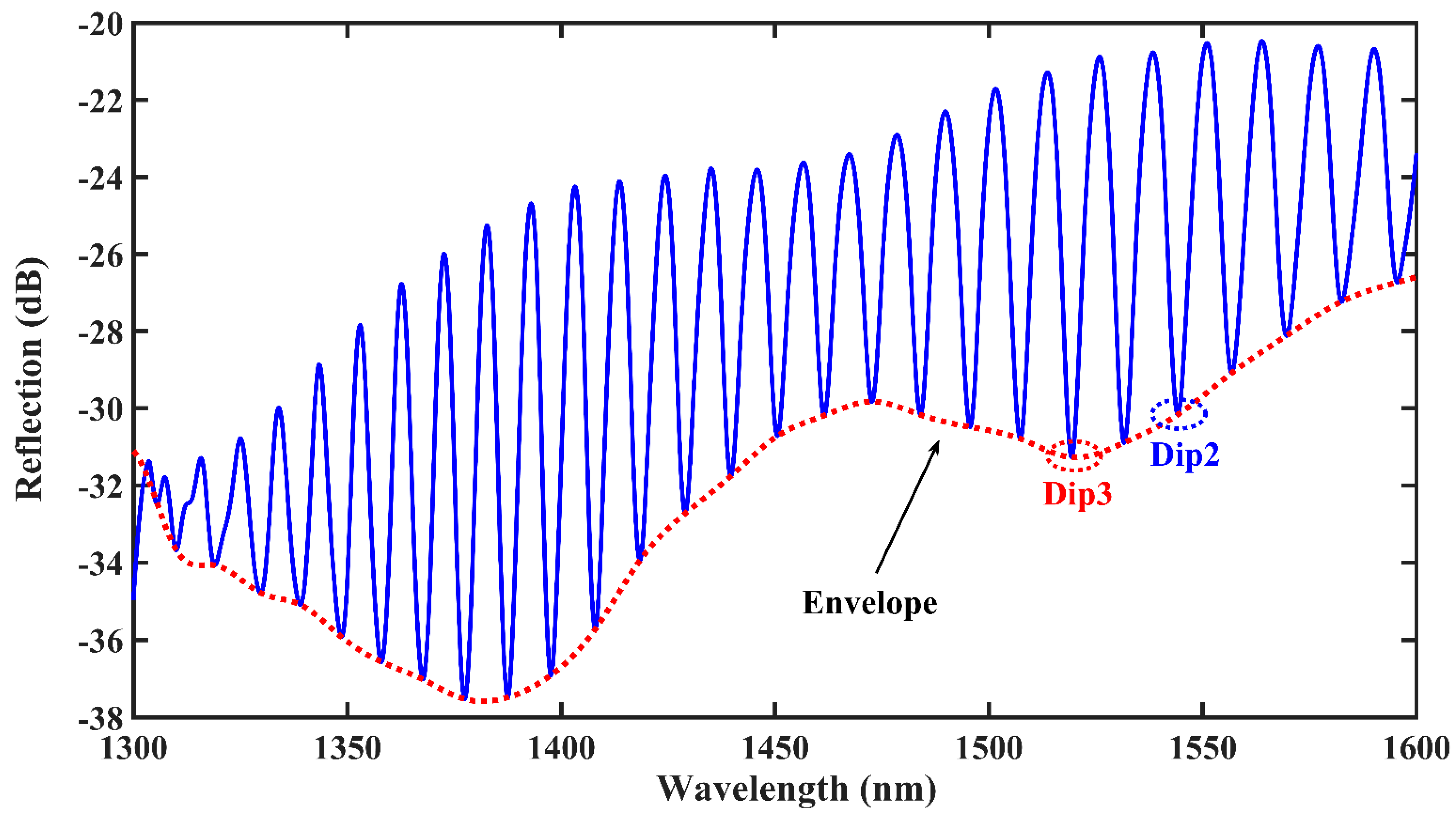
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
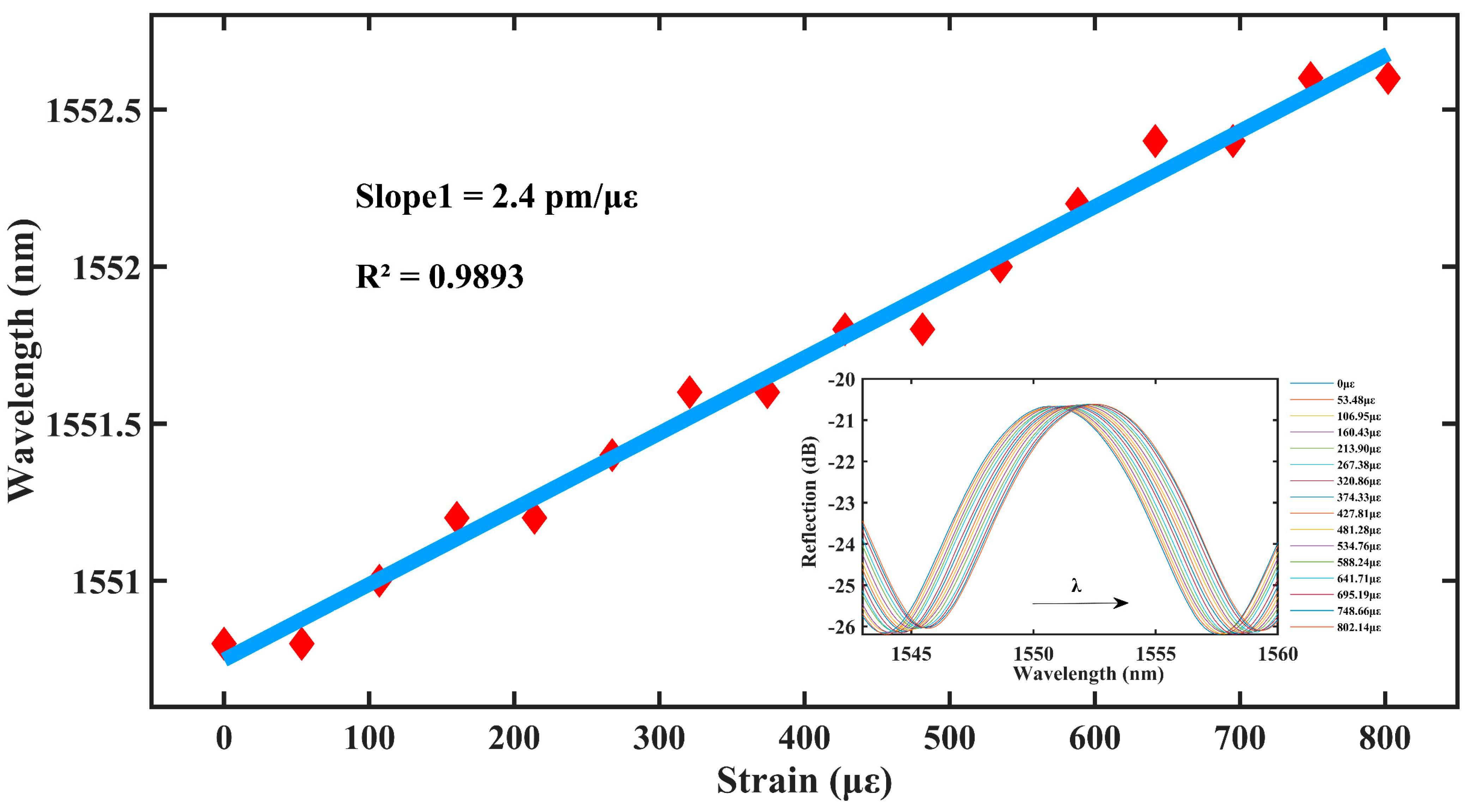
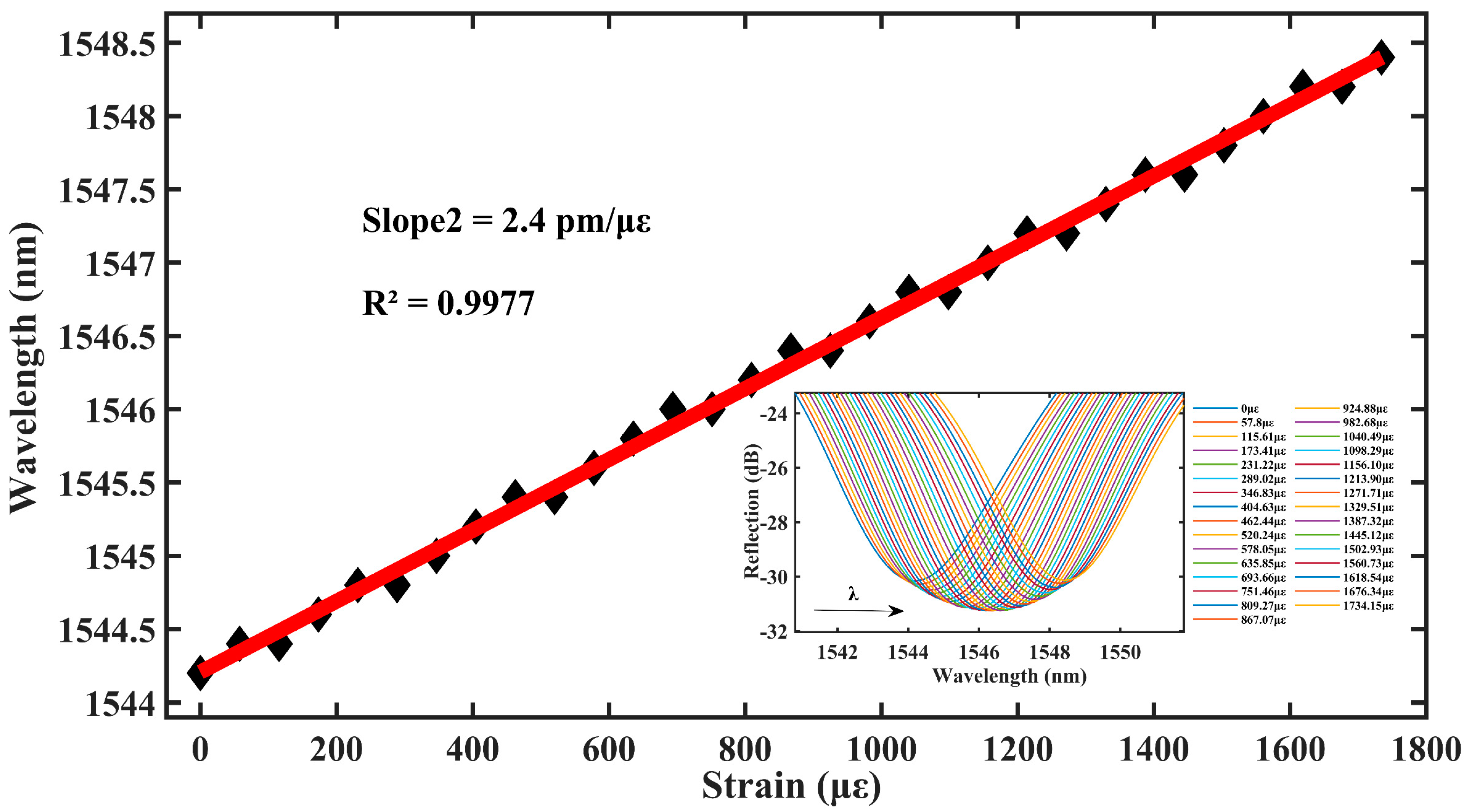
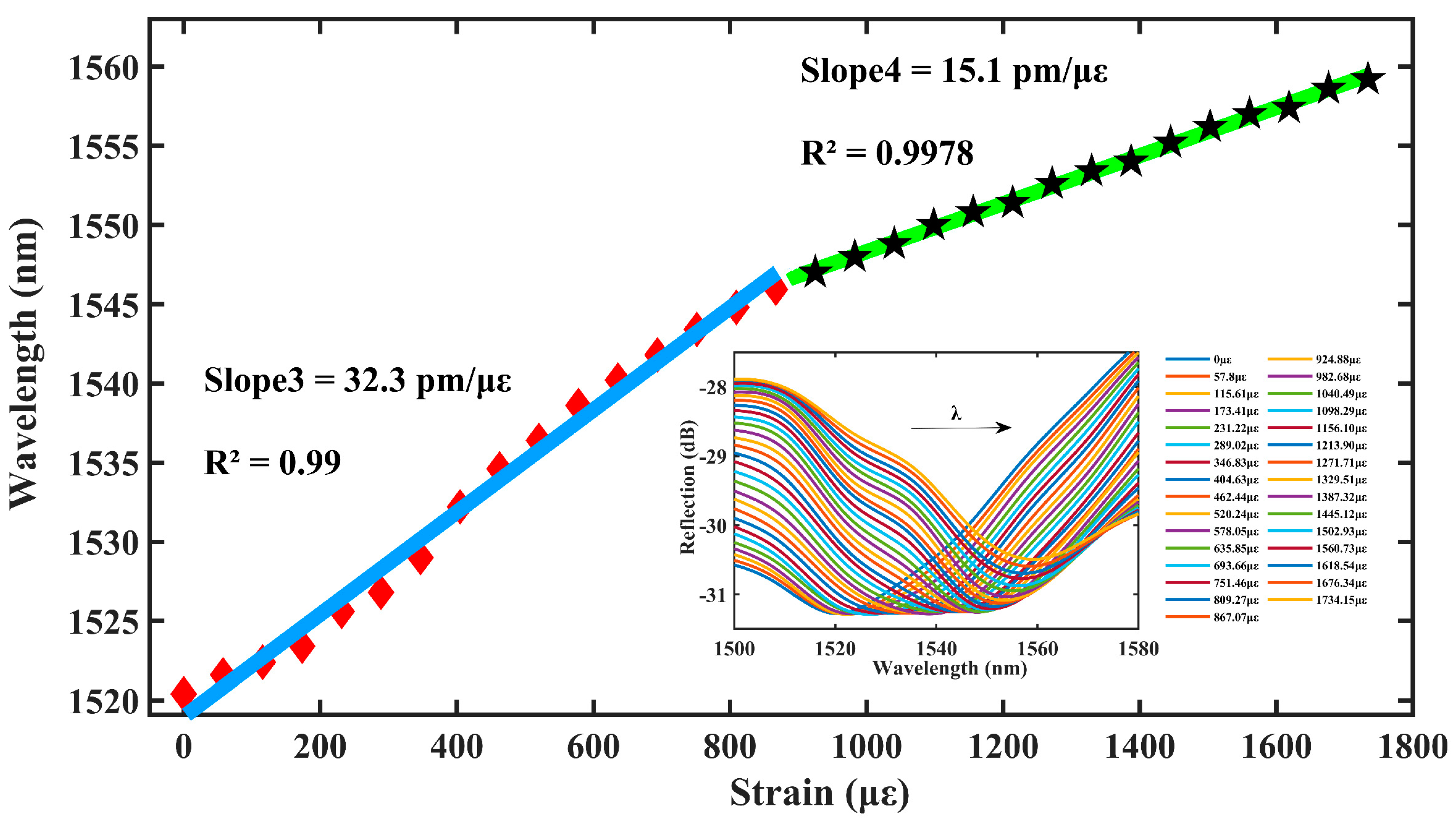
4.1. Axial Strain Experiment
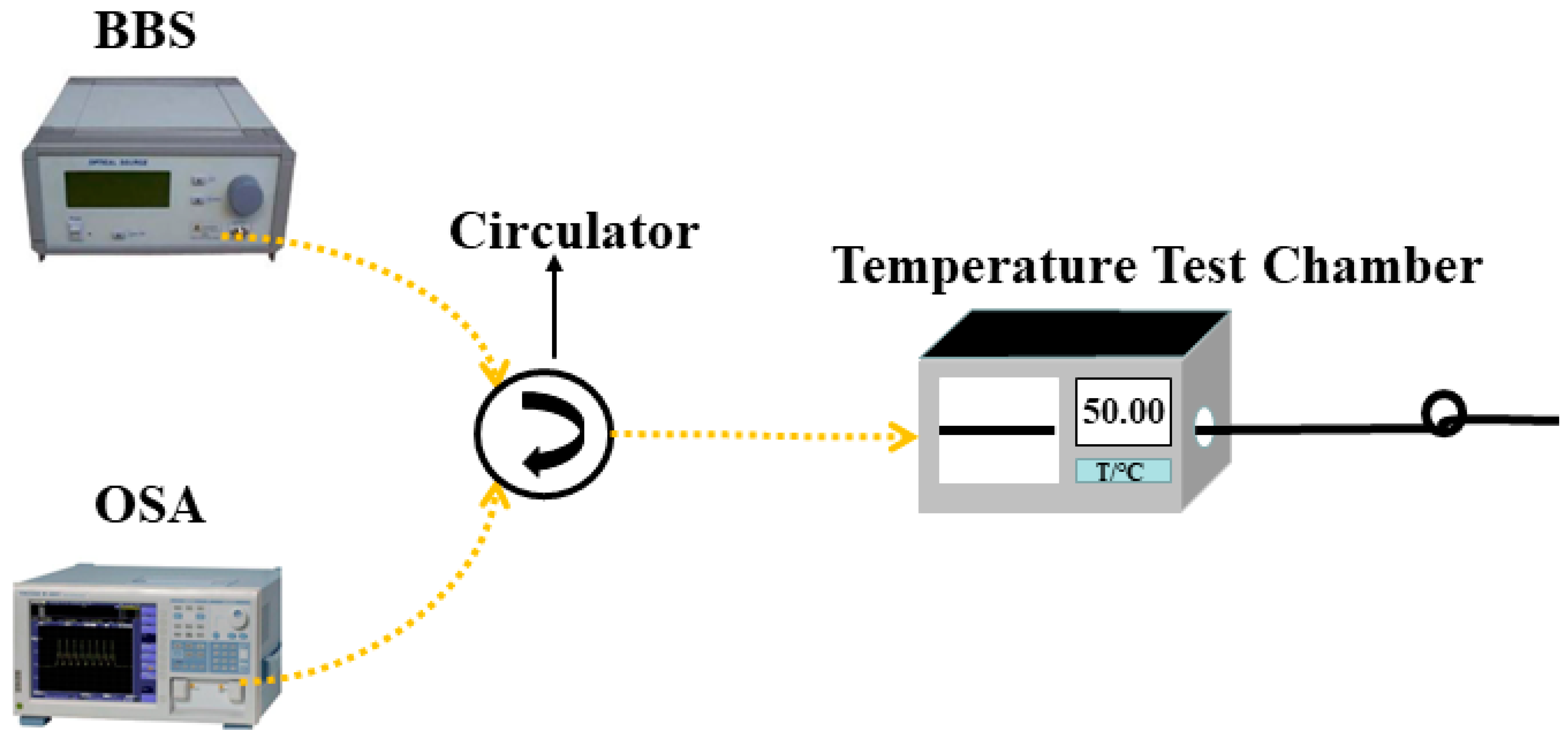
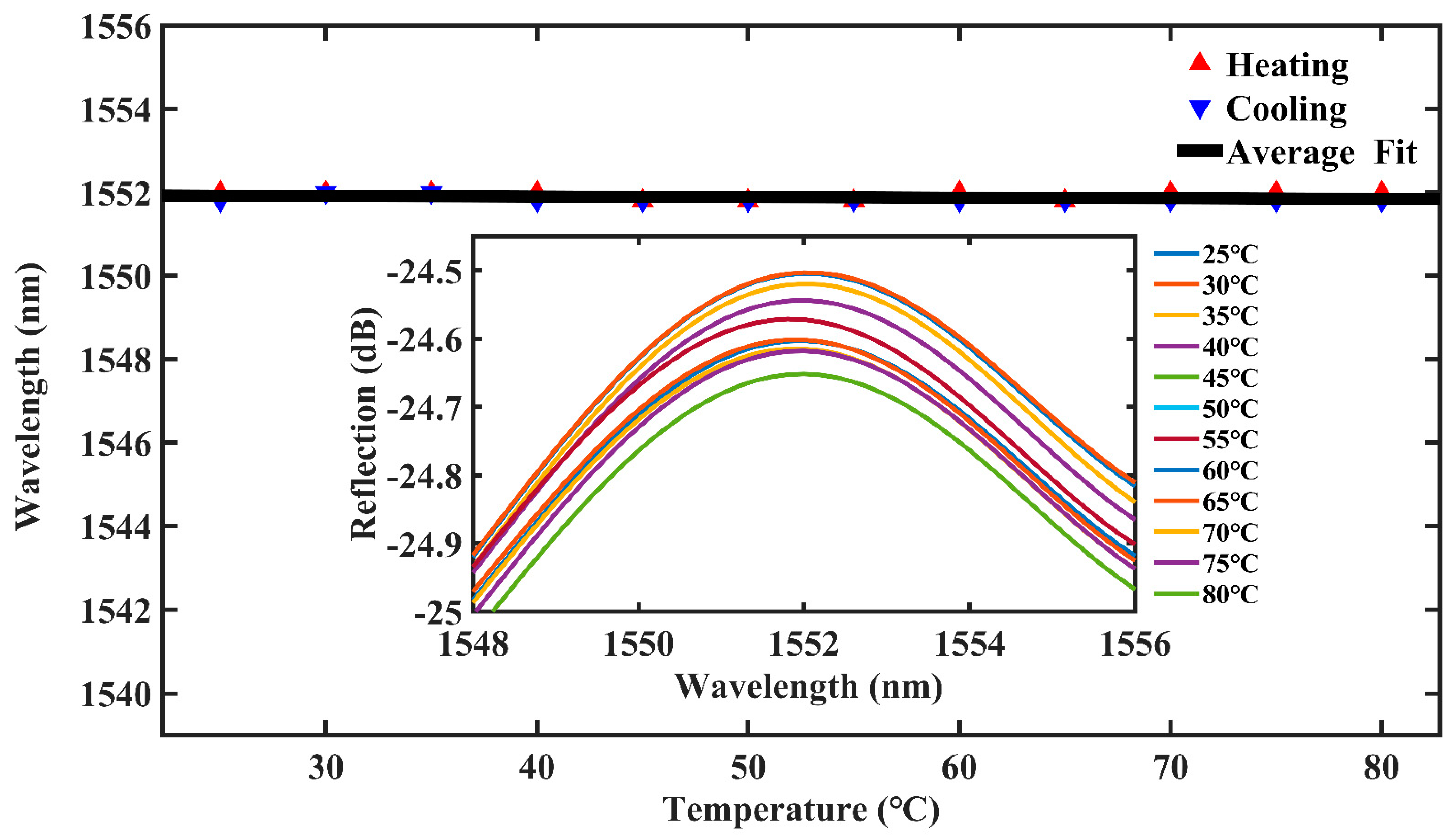
4.2. Temperature Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, H.; Liu, F.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, A. Cascaded fiber Mach–Zehnder interferometers for sensitivity-enhanced gas pressure measurement. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 19, 2581–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, Y.M.; Wang, D.N.; Jia, D.; Jiang, C. Optical fiber Fabry–Pérot interferometer based on an air cavity for gas pressure sensing. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.N.; Tao, W.Q.; Chen, C.; Liao, Y. Fabricating Air Pressure Sensors in Hollow-Core Fiber Using Femtosecond Laser Pulse. Micromachines 2023, 14, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneswaran, D.; Ayyanar, N.; Sharma, M.; Sumathi, M.; Rajan, M.; Porsezian, K. Salinity sensor using photonic crystal fiber. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 269, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Q.L.; Yang, Y. Review of salinity measurement technology based on optical fiber sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 260, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Luo, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, J.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, D. Vibration sensing using liquid-filled photonic crystal fiber with a central air-bore. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 4625–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Tian, T.; Qian, L.; Fan, D.; Liang, W.; Ou, Y. Doppler effect-based optical fiber vibration sensor using frequency-shifted interferometry demodulation. J. Light. Technol. 2017, 35, 3483–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Qian, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, B.; An, G.; Hong, Y.; Jia, P.; Xiong, J. An In-Line Fiber Optic Fabry-Perot Sensor for High-Temperature Vibration Measurement. Micromachines 2020, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Jia, Z.N.; Dai, M.L.; Zhao, C.Y.; Gandhi, M.S.A.; Sun, S.Q.; Li, Q.; Fu, H.Y. Cascaded fiber non-adiabatic taper and Sagnac loop for refractive index sensing. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 332, 113212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Dong, X.; Sun, T.; Grattan, K.T. Ultrasensitive Refractive Index Sensor Based on Mach–Zehnder Interferometer and a 40 μm Fiber. J. Light. Technol. 2021, 39, 5625–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, R.; Xin, X. Hollow-core fiber refractive index sensor with high sensitivity and large dynamic range based on a multiple mode transmission mechanism. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 19703–19714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Liu, C.N.; Lu, Z.Q.; Tao, W.Q.; Peng, M. Femtosecond laser processing for a high sensitivity fiber MZI microcavity. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 12397–12408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.N. Review of femtosecond laser fabricated optical fiber high temperature sensors. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2021, 19, 091204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.W.; Wu, S.; Cheng, H.H.; Yang, X.M.; Wang, S.; Lu, P.X. Sensitivity-enhanced temperature sensor based on encapsulated S-taper fiber Modal interferometer. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 139, 106933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, T.T.; Tong, R.X.; Bian, C. A novel strain sensor using a fiber taper cascaded with an air bubble based on Fabry–Pérot interferometer. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 4618–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Qi, B.; Su, B.; Xu, O.; Qin, Y. High Sensitivity Hollow-Core Fiber Strain Sensor Based on Signal Processing Assisted Vernier Effect. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2022, 34, 1050–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Yan, F.P.; Liu, S.; Wen, X.D. All fiber Fabry–Pérot interferometer for high-sensitive micro-displacement sensing. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2016, 48, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Jiang, M.S.; Sui, Q.M.; Geng, X.Y. Optical fiber Fabry–Perot relative humidity sensor based on HCPCF and chitosan film. J. Mod. Opt. 2016, 63, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.R.; Wang, D.N.; Wang, Y. Microfiber in-line Mach–Zehnder interferometer for strain sensing. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 757–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.R.; Du, H.F.; Sun, X.Y.; Luo, Z.; Duan, J.A. A novel strain sensor with large measurement range based on all fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Sensors 2018, 18, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazão, O.; Marques, L.M.; Santos, S.; Baptista, J.M.; Santos, J.L. Simultaneous measurement for strain and temperature based on a long-period grating combined with a high-birefringence fiber loop mirror. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2006, 18, 2407–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.P.; Guo, Q.; Wu, Y.D.; Liu, S.R.; Wang, B.; Yu, Y.S.; Sun, H.B. Femtosecond laser inscribed chirped fiber Bragg gratings. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 2059–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorathin, E.; Hafizi, Z.M.; Aizzuddin, A.M.; Lim, K.S. A natural rubber diaphragm-based transducer for simultaneous pressure and temperature measurement by using a single FBG. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2018, 45, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favero, F.C.; Araujo, L.; Bouwmans, G.; Finazzi, V.; Villatoro, J.; Pruneri, V. Spheroidal Fabry-Perot microcavities in optical fibers for high-sensitivity sensing. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 7112–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.R.; Luo, Z.; Du, H.F.; Sun, X.Y.; Yin, K.; Duan, J.A. Highly sensitive strain sensor based on a novel Mach–Zehnder mode interferometer with TCF-PCF-TCF structure. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2019, 116, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Jiao, Y.; Ji, S.; Dong, X.; Yao, Y. Cascaded-cavity Fabry–Perot interferometer for simultaneous measurement of temperature and strain with cross-sensitivity compensation. Opt. Commun. 2018, 412, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yuan, P. Temperature-insensitive fiber optic Fabry-Perot interferometer based on special air cavity for transverse load and strain measurements. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 9443–9448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Liao, C.; Wang, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Tang, J. High-sensitivity strain sensor based on in-fiber improved Fabry–Perot interferometer. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 2121–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ning, T.; Zheng, J.; Xu, J.; Gao, X.; Lin, H.; Pei, L. An optical fiber strain sensor by using of taper based TCF structure. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 120, 105687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Zhang, M.; Farrell, G.; Wang, R.; Lewis, E.; Wang, P. Highly sensitive strain sensor based on composite interference established within S-tapered multimode fiber structure. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 33982–33992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Flores, C.E.; Rodríguez-Quiroz, O.; Monzon-Hernandez, D.; Ascorbe, J.; Corres, J.M.; Arregui, F.J. Dual-Cavity Fiber Fabry-Perot Interferometer Coated with SnO2 for Relative Humidity and Temperature Sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 14195–14201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Ma, C.T.; Yeh, K.C.; Chen, Y.M. A Dual-Cavity Fiber Fabry–Pérot Interferometer for Simultaneous Measurement of Thermo-Optic and Thermal Expansion Coefficients of a Polymer. Polymers 2022, 14, 4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullteap, S.; Seat, H.C.; Bosch, T. Modified fringe-counting technique applied to a dual-cavity fiber Fabry-Pérot vibrometer. Opt. Eng. 2007, 46, 115603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, H.; Jia, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, S.; Hu, J. Simultaneous measurements of temperature and pressure with a dual-cavity Fabry–Perot sensor. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2018, 31, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, T.; Hu, J.; Jiang, L. A dual-cavity Fabry–Perot interferometric fiber-optic sensor for the simultaneous measurement of high-temperature and high-gas-pressure. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 80582–80587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, M.R.; Tian, J.J.; Yao, Y. Ultra-high sensitivity Fabry–Perot interferometer gas refractive index fiber sensor based on photonic crystal fiber and Vernier effect. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 4891–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, C.L.; Wang, D.N.; Yang, M.H. Optical cascaded Fabry–Perot interferometer hydrogen sensor based on vernier effect. Opt. Commun. 2018, 414, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, D.N. Ultra-sensitive strain sensor based on femtosecond laser inscribed in-fiber reflection mirrors and Vernier effect. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 4935–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.N.; Liao, C.R.; Hu, T.Y.; Guo, J.T.; Wei, H.F. Temperature-insensitive refractive index sensing by use of micro Fabry–Pérot cavity based on simplified hollow-core photonic crystal fiber. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ref. | Device Structure | Strain Sensitivity | Measurement Range of Strain | Temperature Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [22] | FBGs | 1.21 pm/µε | 0–3138 με | 14.91 pm/°C |
| [24] | Spheroidal FP cavities | 10.3 pm/με | 0–1100 με | 1 pm/°C |
| [25] | Hollow-core PCF | 1.89 pm/µε | 0–4000 με | 5.58 pm/°C |
| [26] | Cascaded FP cavities | 2.97 pm/με | 0–1000 με | 0.9 pm/°C |
| [27] | FPI with air cavity | 3.29 pm/με | 0–1100 με | 1.08 pm/°C |
| [28] | FPIs | 6.0 pm/με | 0–1000 με | 1 pm/°C |
| [29] | Tapered-based TCF | 6.11 pm/με | 0–841.5 με | 0.69 pm/°C |
| [30] | S-tapered with MMF | 103.8 pm/με | 0–170 με | 36.2 pm/°C |
| [38] | FPI based on Vernier effect | 28.11 pm/με | 0–1500 με | 278.48 pm/°C |
| This work | FPIs | 32.3 pm/με | 0–1734.15 με | 0.91 pm/°C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, C.; Ren, J.; Yang, L. Ultra-High Sensitivity and Temperature-Insensitive Optical Fiber Strain Sensor Based on Dual Air Cavities. Materials 2023, 16, 3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16083165
Lu Z, Liu C, Li C, Ren J, Yang L. Ultra-High Sensitivity and Temperature-Insensitive Optical Fiber Strain Sensor Based on Dual Air Cavities. Materials. 2023; 16(8):3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16083165
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Zhiqi, Changning Liu, Chi Li, Jie Ren, and Lun Yang. 2023. "Ultra-High Sensitivity and Temperature-Insensitive Optical Fiber Strain Sensor Based on Dual Air Cavities" Materials 16, no. 8: 3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16083165
APA StyleLu, Z., Liu, C., Li, C., Ren, J., & Yang, L. (2023). Ultra-High Sensitivity and Temperature-Insensitive Optical Fiber Strain Sensor Based on Dual Air Cavities. Materials, 16(8), 3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16083165






