The Tunable Rhenium Effect on the Creep Properties of a Nickel-Based Superalloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-Y. Alloying-element dependence of structural, elastic and electronic properties of nickel-based superalloys: Influence of γ’ volume fraction. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 838, 155141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Louat, N.; Sadananda, K. Dislocation network formation and coherency loss around gamma- prime precipitates in a nickel- base superalloy. Metall. Trans. A 1988, 19, 2965–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Li, S.; Chen, L.-Q.; Han, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Li, J. Re segregation at interfacial dislocation network in a nickel-based superalloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 154, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, R.; Pollockf, T.; Murphy, W. The Development of γ/γ’ Interfacial Dislocation Networks During Creep in N&Base Superalloys; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, C.-Y. Misfit dislocation networks in the γ/γ’ phase interface of a Ni-based single-crystal superalloy: Molecular dynamics simulations. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 75, 014111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, J.; Pei, Y.; Wang, H.; Gong, S.; Xu, H. Dislocation network with pair-coupling structure in {111} γ/γ′ interface of Ni-based single crystal superalloy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wang, C.; Yu, T. Construction and application of multi-element EAM potential (Ni–Al–Re) in γ/γ′ Ni-based single crystal superalloys. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2012, 21, 015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, E.; Yu, T.; Wang, C.; Du, J. Construction of Ni–Al–Ru EAM potential and application in misfit dislocation system. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2020, 30, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Luo, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, J. Distribution of rhenium in a single crystal nickel-based superalloy. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 969–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, J.; Li, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J. Coupling between Re segregation and γ/γ′ interfacial dislocations during high-temperature, low-stress creep of a nickel-based single-crystal superalloy. Acta Mater. 2014, 76, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhu, J. An overview of rhenium effect in single-crystal superalloys. Rare Metals 2016, 35, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, R.; Tang, M.; Li, X. Simulation study and experiment verification of the creep mechanism of a nickel-based single crystal superalloy obtained from microstructural evolution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 107748–107758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoei, A.; Eshlaghi, G.T.; Shahoveisi, S. Atomistic simulation of creep deformation mechanisms in nickel-based single crystal superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 809, 140977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoei, A.R.; Youzi, M.; Eshlaghi, G.T. Mechanical properties and γ/γ’ interfacial misfit network evolution: A study towards the creep behavior of Ni-based single crystal superalloys. Mech. Mater. 2022, 171, 104368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, B.; Shen, H.; Ding, Z. Molecular dynamics simulation of rhenium effects on creep behavior of Ni-based single crystal superalloys. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2022, 32, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pun, G.P.; Mishin, Y. Development of an interatomic potential for the Ni-Al system. Philos. Mag. 2009, 89, 3245–3267. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.P.; Liu, J.L.; Song, X.P.; Jin, T.; Sun, X.F.; Hu, Z.Q. Measurements of γ/γ′ Lattice Misfit and γ′ Volume Fraction for a Ru-containing Nickel-based Single Crystal Superalloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, H.; Branicio, P.S.; Rino, J.P. Structural characterization of deformed crystals by analysis of common atomic neighborhood. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2007, 177, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, E.-L.; Yu, T.; Wang, Y.-J.; Wang, C.-Y. Synergistic strengthening mechanisms of rhenium in nickel-based single crystal superalloys. Intermetallics 2021, 132, 107133. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.; He, Y.; Zheng, W.; Lou, L.; Zhang, J. Role of interfacial dislocation networks during secondary creep at elevated temperatures in a single crystal Ni-based superalloy. Scr. Mater. 2022, 217, 114769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Wu, R.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Lian, Y.; Wen, Z. Elastoplastic behavior of the γ-phase in Ni-based single crystal superalloys: A molecular dynamics study considering Re and temperature effect. Mech. Mater. 2021, 160, 103989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-P.; Ding, Z.-J.; Chen, B.; Shen, H.-F.; Li, Y.-L. Effect of rhenium on low cycle fatigue behaviors of Ni-based single crystal superalloys: A molecular dynamics simulation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 5144–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Lu, H.; Gu, J. Atomistic simulations of the nanoindentation-induced incipient plasticity in Ni3Al crystal. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2016, 115, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.P.; Aktulga, H.M.; Berger, R.; Bolintineanu, D.S.; Brown, W.M.; Crozier, P.S.; in’t Veld, P.J.; Kohlmeyer, A.; Moore, S.G.; Nguyen, T.D.; et al. LAMMPS—A flexible simulation tool for particle-based materials modeling at the atomic, meso, and continuum scales. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2022, 271, 108171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukowski, A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO—The Open Visualization Tool. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 18, 015012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukowski, A.; Bulatov, V.V.; Arsenlis, A. Automated identification and indexing of dislocations in crystal interfaces. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2012, 20, 085007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
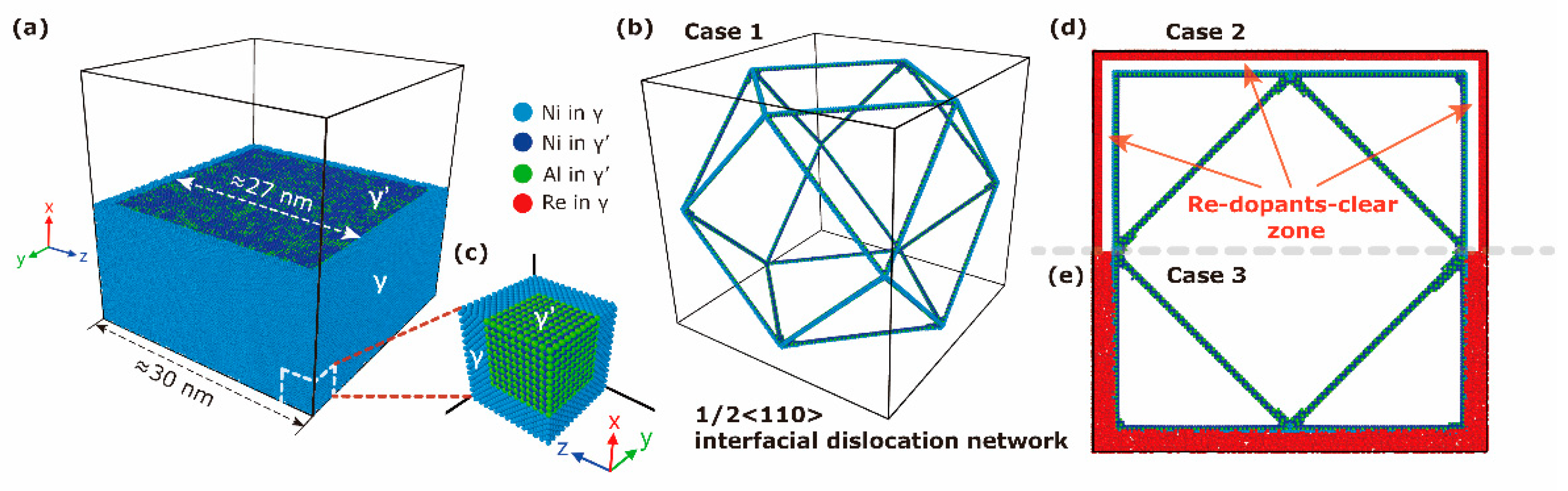

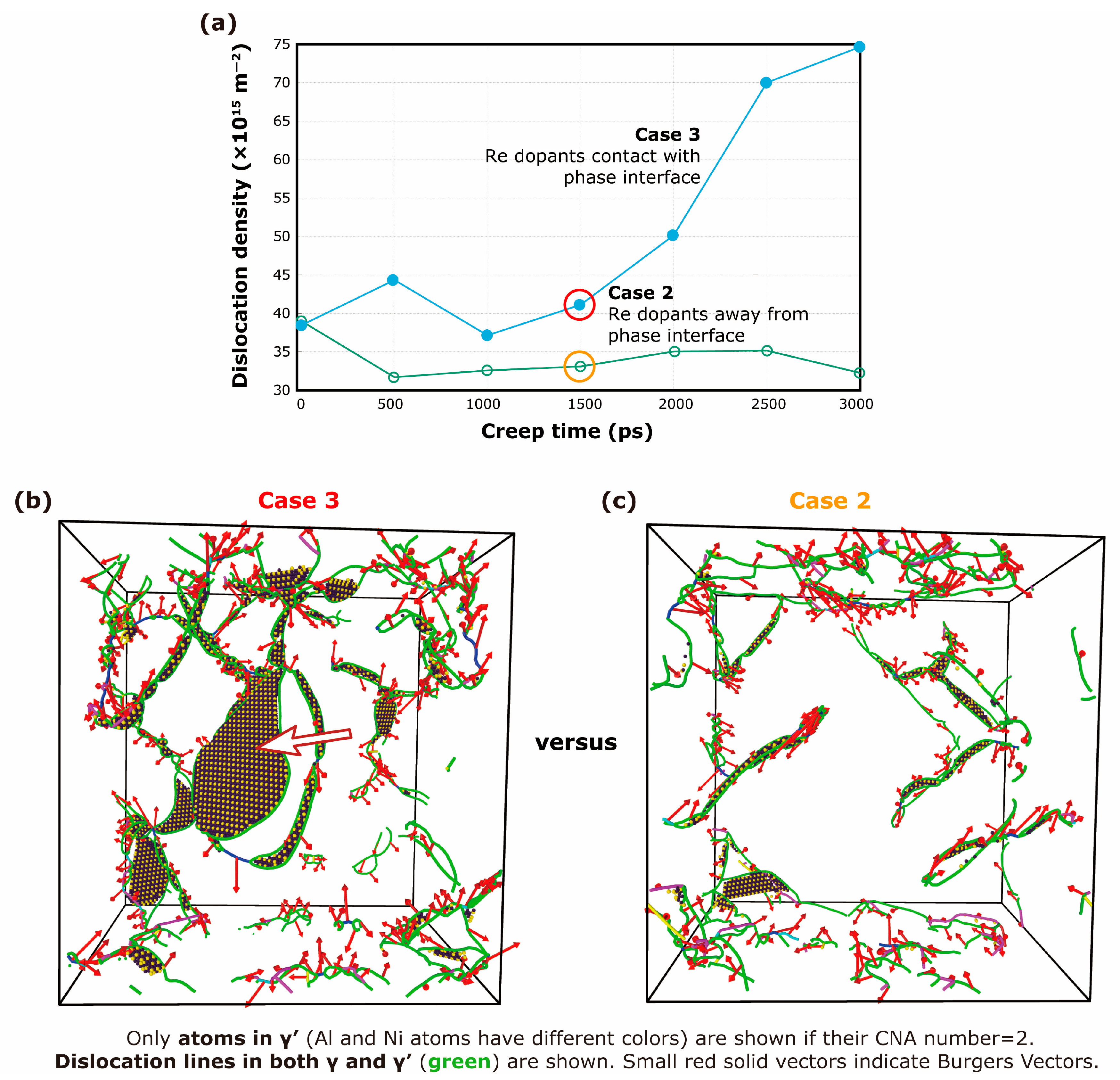
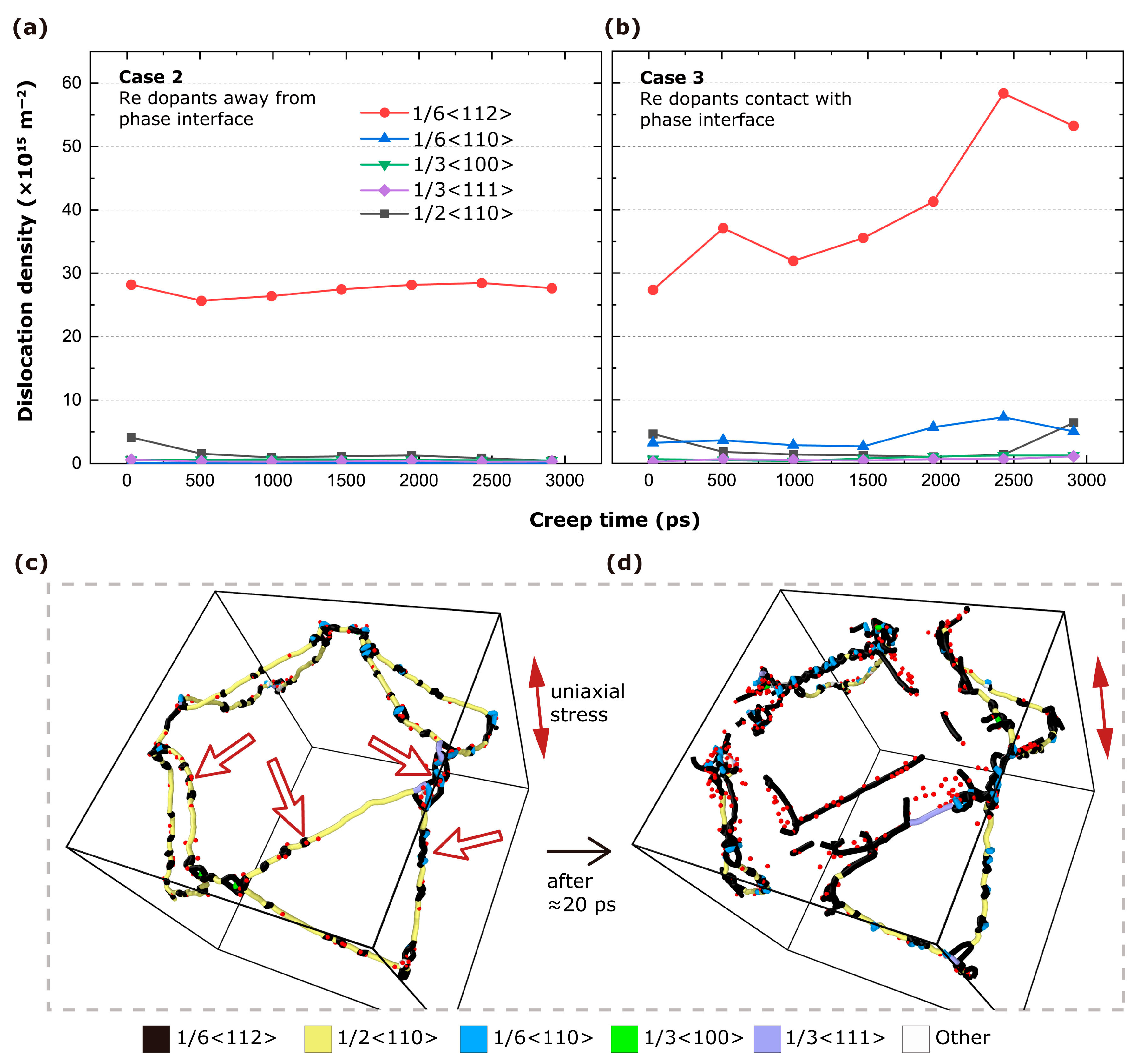
| Research | Correct Volume Fraction | Alloying Dopants | Dopant Distribution Effect | Temperature | Stress | Creep Time | Atomic Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. [12] | No | No | No | 1100 K to 1300 K | 0.3 GPa to 0.5 GPa | Up to 750 ps | Not mentioned |
| Ref. [13] | No | No | No | 1100 K to 1700 K | 0.5 GPa to 5 GPa | Up to 670 ps | 2009 Mishin [16] |
| Ref. [14] | No | Yes | No | 1400 K to 1700 K | 2.5 Gpa | Up to 750 ps | 2012 Du [7] |
| Ref. [15] | Yes | Yes | No | 1000 K | 0.5 GPa to 2 GPa | Up to 2 × 104 ps | 2012 Du [7] |
| Present study | Yes | Yes | Yes | 1300 K and 1500 K | 2 GPa | Up to 3 × 103 ps | 2012 Du [7] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.-Z.; Guo, Y.-F. The Tunable Rhenium Effect on the Creep Properties of a Nickel-Based Superalloy. Materials 2024, 17, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17010191
Tang X-Z, Guo Y-F. The Tunable Rhenium Effect on the Creep Properties of a Nickel-Based Superalloy. Materials. 2024; 17(1):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17010191
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xiao-Zhi, and Ya-Fang Guo. 2024. "The Tunable Rhenium Effect on the Creep Properties of a Nickel-Based Superalloy" Materials 17, no. 1: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17010191
APA StyleTang, X.-Z., & Guo, Y.-F. (2024). The Tunable Rhenium Effect on the Creep Properties of a Nickel-Based Superalloy. Materials, 17(1), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17010191







